Barrancoid People on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
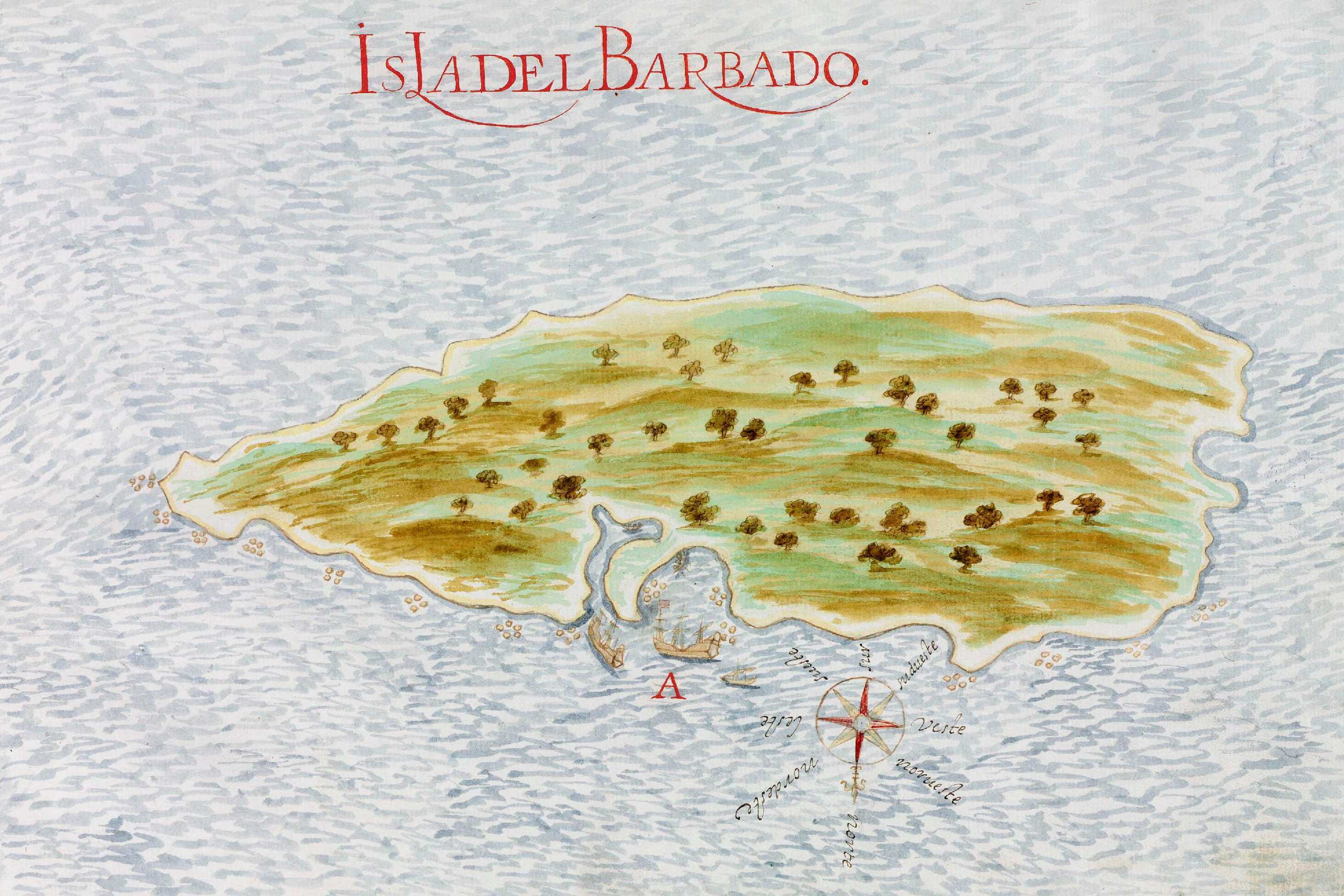 The Portuguese were the first Europeans to discover the island. Portuguese navigator Pedro A. Campos named it ''Os Barbados'' (meaning "bearded ones").
Frequent slave-raiding missions by the
The Portuguese were the first Europeans to discover the island. Portuguese navigator Pedro A. Campos named it ''Os Barbados'' (meaning "bearded ones").
Frequent slave-raiding missions by the
The Civil War in Barbados
History in-depth, BBC, 5 November 2009. Willoughby rounded up and deported many Roundheads from Barbados, confiscating their property. To try to bring the recalcitrant colony to heel, the Commonwealth Parliament passed an act on 3 October 1650 prohibiting trade between England and Barbados, and because the island also traded with the



 The British abolished the
The British abolished the
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
is an island country in the southeastern Caribbean Sea, situated about 100 miles (160 km) east of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. Roughly triangular in shape, the island measures some 21 miles (32 km) from northwest to southeast and about 14 miles (25 km) from east to west at its widest point. The capital and largest town is Bridgetown, which is also the main seaport.
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
was inhabited by its indigenous peoples – Arawak
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Great ...
s and Caribs
“Carib” may refer to:
People and languages
*Kalina people, or Caribs, an indigenous people of South America
**Carib language, also known as Kalina, the language of the South American Caribs
*Kalinago people, or Island Caribs, an indigenous pe ...
– prior to the European colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale European colonization of the Americas took place between about 1492 and 1800. Although the Norse had explored and colonized areas of the North Atlantic, colonizing Greenland and creating a short t ...
in the 16th century. Barbados was briefly claimed by the Spanish who saw the trees with the beard like feature (hence the name barbados), and then by Portugal from 1532 to 1620. The island was English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
and later a British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
colony from 1625 until 1966. From 1966 to 2021, it was a constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
and parliamentary democracy
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the ...
, modelled on the Westminster system, with Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during ...
, Queen of Barbados
The monarchy of Barbados was a system of government in which a hereditary monarch was the sovereign and head of state of Barbados from 1966 to 2021. Barbados shared the Sovereign with the other Commonwealth realms, with the country's monarchy be ...
, as head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
. Barbados became a republic on November 30, 2021.
History before colonization
Some evidence suggests that Barbados may have been settled in the second millennium BC, but this is limited to fragments of conch lipadzes
An adze (; alternative spelling: adz) is an ancient and versatile cutting tool similar to an axe but with the cutting edge perpendicular to the handle rather than parallel. Adzes have been used since the Stone Age. They are used for smoothing o ...
found in association with shells that have been radiocarbon-dated to about 1630 BC.
Fully documented Amerindian
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the A ...
settlement dates to between about 350 and 650 AD, when the Troumassoid people arrived. The arrivals were a group known as the Saladoid
The Saladoid culture is a pre-Columbian indigenous culture of territory in present-day Venezuela and the Caribbean that flourished from 500 BCE to 545 CE. The Saladoid were an Arawak people. Concentrated along the lowlands of the Orinoco River, th ...
-Barrancoid from the mainland of South America.
The second wave of settlers appeared around 800 AD (the Spanish referred to these as " Arawaks") and a third in the mid-13th century. However, the Amerindian settlement surprisingly came to an end in the early 16th century. There's no evidence that the Kalinago
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated langua ...
(called "Caribs
“Carib” may refer to:
People and languages
*Kalina people, or Caribs, an indigenous people of South America
**Carib language, also known as Kalina, the language of the South American Caribs
*Kalinago people, or Island Caribs, an indigenous pe ...
" by the Spanish) ever established a permanent settlement in Barbados, though they often visited the island in their canoes.
Colonial history
Early colonial history
 The Portuguese were the first Europeans to discover the island. Portuguese navigator Pedro A. Campos named it ''Os Barbados'' (meaning "bearded ones").
Frequent slave-raiding missions by the
The Portuguese were the first Europeans to discover the island. Portuguese navigator Pedro A. Campos named it ''Os Barbados'' (meaning "bearded ones").
Frequent slave-raiding missions by the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
in the early 16th century led to a massive decline in the Amerindian population so that by 1541 a Spanish writer claimed they were uninhabited. The Amerindians were either captured for use as slaves by the Spanish or fled to other, more easily defensible mountainous islands nearby.
From about 1600 the English, French, and Dutch began to found colonies in the North American mainland and the smaller islands of the West Indies. Although Spanish and Portuguese sailors had visited Barbados, the first English ship touched the island on 14 May 1625, and England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
was the first European nation to establish a lasting settlement there from 1627, when the ''William and John'' arrived with more than 60 white settlers and six African slaves.
England is commonly said to have made its initial claim to Barbados in 1625, although reportedly an earlier claim may have been made in 1620. Nonetheless, Barbados was claimed from 1625 in the name of King James I of England
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until ...
. There were earlier English settlements in The Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
(1607: Jamestown, 1609: Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
, and 1620: Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes Plimouth) was, from 1620 to 1691, the first permanent English colony in New England and the second permanent English colony in North America, after the Jamestown Colony. It was first settled by the passengers on the ...
), and several islands in the Leeward Islands were claimed by the English at about the same time as Barbados (1623: St Kitts
Saint Kitts, officially the Saint Christopher Island, is an island in the West Indies. The west side of the island borders the Caribbean Sea, and the eastern coast faces the Atlantic Ocean. Saint Kitts and the neighbouring island of Nevis cons ...
, 1628: Nevis
Nevis is a small island in the Caribbean Sea that forms part of the inner arc of the Leeward Islands chain of the West Indies. Nevis and the neighbouring island of Saint Kitts constitute one country: the Federation of Saint Kitts and ...
, 1632: Montserrat, 1632: Antigua). Nevertheless, the Colony of Barbados quickly grew to become the third major English settlement in the Americas due to its prime eastern location.
Early English settlement
The settlement was established as aproprietary colony
A proprietary colony was a type of English colony mostly in North America and in the Caribbean in the 17th century. In the British Empire, all land belonged to the monarch, and it was his/her prerogative to divide. Therefore, all colonial proper ...
and funded by Sir William Courten
Sir William Courten or Curteen (1572–1636) was a wealthy 17th century merchant, operating from London. He financed the colonisation of Barbados, but lost his investment and interest in the islands to the Earl of Carlisle.
Birth and upbringing ...
, a City of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London f ...
merchant who acquired the title to Barbados and several other islands. So the first colonists were actually tenants and much of the profits of their labor returned to Courten and his company.
The first English ship, which had arrived on 14 May 1625, was captained by John Powell. The first settlement began on 17 February 1627, near what is now Holetown (formerly Jamestown), by a group led by John Powell's younger brother, Henry, consisting of 80 settlers and 10 English laborers. The latter were young indentured labor
Indentured servitude is a form of labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract, called an " indenture", may be entered "voluntarily" for purported eventual compensation or debt repayment ...
ers who according to some sources had been abducted, effectively making them slaves. About 40 Taino slaves were brought in from Guyana to help plant crops on the west coast of the island.Karl Watson, "A brief history of Barbados", ''Barbados'' (Hansib), Arif Ali (ed.), p. 44.
Courten's title was transferred to James Hay, 1st Earl of Carlisle
James Hay, 1st Earl of Carlisle KB (c. 1580March 1636) was a British noble.
Life
A Scot, he was the son of Sir James Hay of Fingask, second son of Peter Hay of Megginch (a branch member of Hay of Leys, a younger branch of the Erroll family) a ...
, in what was called the "Great Barbados Robbery." Carlisle established a separate settlement at what he called Carlisle Bay, which later became known as Bridgetown.
Carlisle then chose as governor Henry Hawley
Henry Hawley (12 January 1685 – 24 March 1759) was a British army officer who served in the wars of the first half of the 18th century. He fought in a number of significant battles, including the Capture of Vigo in 1719, Dettingen, Fo ...
, who established the House of Assembly
House of Assembly is a name given to the legislature or lower house of a bicameral parliament. In some countries this may be at a subnational level.
Historically, in British Crown colonies as the colony gained more internal responsible gove ...
in 1639, in an effort to appease the planters, who might otherwise have opposed his controversial appointment. That year, 12 years after the settlement was established, the white adult population stood at an estimated 8,700.
In the period 1640–1660, the West Indies attracted over two-thirds of the total number of English emigrants to the Americas. By 1650, there were 44,000 settlers in the West Indies, as compared to 12,000 on the Chesapeake and 23,000 in New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
.
Most English arrivals were indentured. After five years of labour, they were given "freedom dues" of about £10, usually in goods. Before the mid-1630s, they also received 5–10 acres of land, but after that time the island filled and there was no more free land. Around the time of Cromwell a number of rebels and criminals were also transported there.
Timothy Meads of Warwickshire was one of the rebels sent to Barbados at that time, before he received compensation for servitude of 1000 acres of land in North Carolina in 1666. Parish registers from the 1650s show, for the white population, four times as many deaths as marriages. The death rate was very high.
Before this, the mainstay of the infant colony's economy was the growing export of tobacco, but tobacco prices eventually fell in the 1630s, as Chesapeake production expanded.
England's civil war
Around the same time, fighting during theWar of the Three Kingdoms
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms were a series of related conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland, then separate entities united in a personal union under Charles I. They include the 1639 to 1640 B ...
and the Interregnum spilled over into Barbados and Barbadian territorial waters. The island was not involved in the war until after the execution of Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
, when the island's government fell under the control of Royalists (ironically the Governor, Philip Bell, remained loyal to Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
while the Barbadian House of Assembly of Barbados
The House of Assembly of Barbados is the lower house of the bicameral Parliament of Barbados. It has 30 Members of Parliament (MPs), who are directly elected in single member constituencies using the simple-majority (or first-past-the-post) sys ...
, under the influence of Humphrey Walrond, supported Charles II). On 7 May 1650, the General Assembly of Barbados voted to receive Lord Willoughby as governor, a move which confirmed the Cavaliers as the government of Barbados.Hilary Beckles, "The 'Hub of Empire': The Caribbean and Britain in the Seventeenth Century", ''The Oxford History of the British Empire: Volume 1 The Origins of Empire'', ed. by Nicholas Canny (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2001), p. 238.Karl WatsonThe Civil War in Barbados
History in-depth, BBC, 5 November 2009. Willoughby rounded up and deported many Roundheads from Barbados, confiscating their property. To try to bring the recalcitrant colony to heel, the Commonwealth Parliament passed an act on 3 October 1650 prohibiting trade between England and Barbados, and because the island also traded with the
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, further navigation acts
The Navigation Acts, or more broadly the Acts of Trade and Navigation, were a long series of English laws that developed, promoted, and regulated English ships, shipping, trade, and commerce between other countries and with its own colonies. The ...
were passed prohibiting any but English vessels trading with Dutch colonies. These acts were a precursor to the First Anglo-Dutch War
The First Anglo-Dutch War, or simply the First Dutch War, ( nl, Eerste Engelse (zee-)oorlog, "First English (Sea) War"; 1652–1654) was a conflict fought entirely at sea between the navies of the Commonwealth of England and the United Province ...
.
The Commonwealth of England
The Commonwealth was the political structure during the period from 1649 to 1660 when England and Wales, later along with Ireland and Scotland, were governed as a republic after the end of the Second English Civil War and the trial and execu ...
sent an invasion force under the command of Sir George Ayscue, which arrived in October 1651, and blockaded the island. After some skirmishing, the Royalists in the House of Assembly, feeling the pressures of commercial isolation, led by Lord Willoughby surrendered. The conditions of the surrender were incorporated into the Charter of Barbados (Treaty of Oistins), which was signed at the Mermaid's Inn, Oistins
Oistins (Pronounced /'ȯis-tins/ -- UN/LOCODE: BB OST), is a coastal area located in the country of Barbados. It is situated centrally along the coastline of the parish of Christ Church. The area includes a fishing village as well as a tourist are ...
, on 17 January 1652.
Sugar cane and slavery

Sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalk ...
cultivation in Barbados began in the 1640s, after its introduction in 1637 by Pieter Blower. Initially, rum was produced but by 1642, sugar was the focus of the industry. As it developed into the main commercial enterprise, Barbados was divided into large plantation estates which replaced the small holdings of the early English settlers as the wealthy planters pushed out the poorer. Some of the displaced farmers relocated to the English colonies in North America, most notably South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
. To work the plantations, black Africans – primarily from West Africa – were imported as slaves in such numbers that there were three for every one planter. Increasingly after 1750 the plantations were owned by absentee landlords living in Britain and operated by hired managers. Persecuted Catholics from Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
also worked the plantations. Life expectancy of slaves was short and replacements were purchased annually.
The introduction of sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalk ...
from Dutch Brazil
Dutch Brazil ( nl, Nederlands-Brazilië), also known as New Holland ( nl, Nieuw-Holland), was a colony of the Dutch Republic in the northeastern portion of modern-day Brazil, controlled from 1630 to 1654 during Dutch colonization of the America ...
in 1640 completely transformed society and the economy. Barbados eventually had one of the world's biggest sugar industries. One group instrumental in ensuring the early success of the industry were the Sephardic Jews
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefa ...
, who had originally been expelled from the Iberian peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
, to end up in Dutch Brazil
Dutch Brazil ( nl, Nederlands-Brazilië), also known as New Holland ( nl, Nieuw-Holland), was a colony of the Dutch Republic in the northeastern portion of modern-day Brazil, controlled from 1630 to 1654 during Dutch colonization of the America ...
. As the effects of the new crop increased, so did the shift in the ethnic composition of Barbados and surrounding islands. The workable sugar plantation required a large investment and a great deal of heavy labour. At first, Dutch traders supplied the equipment, financing, and African slaves, in addition to transporting most of the sugar to Europe. Barbados replaced Hispaniola as the main sugar producer in the Caribbean.
In 1655, the population of Barbados was estimated at 43,000, of which about 20,000 were of African descent, with the remainder mainly of English descent. These English smallholders were eventually bought out and the island filled up with large African slave-worked sugar plantations. By 1660, there was near parity with 27,000 blacks and 26,000 whites. By 1666, at least 12,000 white smallholders had been bought out, died, or left the island. Many of the remaining whites were increasingly poor. By 1673, black slaves (33,184) outnumbered white settlers (21,309). By 1680, there were 17 slaves for every indentured servant. By 1684, the disparity grew even further to 19,568 white settlers and 46,502 black slaves. By 1696, there was an estimated 42,000 enslaved blacks, and the white population declined further to 16,888 by 1715.
Due to the increased implementation of slave codes
The slave codes were laws relating to slavery and enslaved people, specifically regarding the Atlantic slave trade and chattel slavery in the Americas.
Most slave codes were concerned with the rights and duties of free people in regards to ensla ...
, which emphasized differential treatment between Africans, and the white workers and ruling planter class, the island became increasingly unattractive to poor whites. Black or slave codes were implemented in 1661, 1676, 1682, and 1688. In response to these codes, several slave rebellions were attempted or planned during this time, but none succeeded. Nevertheless, poor whites who had or acquired the means to emigrate often did so. Planters expanded their importation of African slaves to cultivate sugar cane. One early advocate of slave rights in Barbados was the visiting Quaker preacher Alice Curwen in 1677: "For I am persuaded, that if they whom thou call'st thy Slaves, be Upright-hearted to God, the Lord God Almighty will set them Free in a way that thou knowest not; for there is none set free but in Christ Jesus, for all other Freedom will prove but a Bondage."
By 1660, Barbados generated more trade than all the other English colonies combined. This remained so until it was eventually surpassed by geographically larger islands like Jamaica in 1713. But even so, the estimated value of the Colony of Barbados in 1730–1731 was as much as £5,500,000. Bridgetown, the capital, was one of the three largest cities in English America (the other two being Boston, Massachusetts and Port Royal, Jamaica
Port Royal is a village located at the end of the Palisadoes, at the mouth of Kingston Harbour, in southeastern Jamaica. Founded in 1494 by the Spanish, it was once the largest city in the Caribbean, functioning as the centre of shipping and c ...
.) By 1700, the English West Indies produced 25,000 tons of sugar, compared to 20,000 for Brazil, 10,000 for the French islands and 4,000 for the Dutch islands. This quickly replaced tobacco, which had been the island's main export.
As the sugar industry developed into its main commercial enterprise, Barbados was divided into large plantation estates that replaced the smallholdings of the early English settlers. In 1680, over half the arable land was held by 175 large planters, each of whom used at least 60 slaves. The great plantation ownershad connections with the English aristocracy and great influence on Parliament. (In 1668, the West Indian sugar crop sold for £180,000 after customs of £18,000. Chesapeake tobacco earned £50,000 after customs of £75,000).
So much land was devoted to sugar that most foods had to be imported from New England. The poorer whites who were moved off the island went to the English Leeward Islands, or especially to Jamaica. In 1670, the Province of South Carolina
Province of South Carolina, originally known as Clarendon Province, was a province of Great Britain that existed in North America from 1712 to 1776. It was one of the five Southern colonies and one of the thirteen American colonies. The monar ...
was founded, when some of the surplus population again left Barbados. Other nations receiving large numbers of Barbadians included British Guiana and Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
.
Roberts (2006) shows that enslaved persons did not spend the majority of time in restricted roles cultivating, harvesting and processing sugar cane, the island's most important cash crop. Rather, the enslaved were involved in various activities and in multiple roles: raising livestock, fertilizing soil, growing provisional crops, maintaining plantation infrastructure, caregiving and other tasks. One notable soil management
Soil management is the application of operations, practices, and treatments to protect soil and enhance its performance (such as soil fertility or soil mechanics). It includes soil conservation, soil amendment, and optimal soil health. In agricu ...
technique was intercropping, planting subsistence crops between the rows of cash crops, which demanded of the enslaved skilled and experienced observations of growing conditions for efficient land use.
"Slaveholders often counted as "married" only the enslaved with mates on the estate. For example, the manager of Newton estate... recorded 20 women with co-resident husbands and 35 with mates elsewhere. Members of the latter group were labelled single, members of extended units, or mother-child units."
By 1750, there were about 18,000 white settlers, compared to approximately 65,000 African slaves.
The slave trade ceased in 1807 and slaves were emancipated in 1834.
Bussa's rebellion

 The British abolished the
The British abolished the slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
in 1807, but not the institution itself. The abolition of slavery itself would only be enacted in 1833 in most parts of the British Empire.
In 1816, enslaved persons rose up in what was the first of three rebellions in the British West Indies to occur in the interval between the end of the slave trade and emancipation, and the largest slave uprising in the island's history. Around 20,000 enslaved persons from over 70 plantations are thought to have been involved. The rebellion was partly fuelled by information about the growing abolitionist movement in England, and the opposition against such by local whites.
The rebellion largely surprised planters, who felt that their slaves were content because they were allowed weekly dances, participated in social and economic activity across the island and were generally fed and looked after. However, they had refused to reform the Barbados Slave Code
The Barbados Slave Code of 1661, officially titled as An Act for the better ordering and governing of Negroes, was a law passed by the Parliament of Barbados to provide a legal basis for slavery in the English colony of Barbados. It is the first co ...
since its inception, a code that denied slaves human rights and prescribed inhumane torture, mutilation or death as a means of control. This contributed to what was later termed "Bussa's Rebellion", named after the slave ranger Bussa, and the result of a growing sentiment that the treatment of slaves in Barbados was "intolerable", and who believed the political climate in Britain made the time ripe to peacefully negotiate with planters for freedom. Bussa became the most famous of the rebellion's organizers, many of whom were either enslaved persons of some higher position or literate freedmen. One woman, Nanny Grigg, is also named as a principal organizer.
However, the rebellion eventually failed. The uprising was triggered prematurely, but the slaves were already greatly outmatched. Barbados' flat terrain gave the horses of the better-armed militia the clear advantage over the rebels, with no mountains or forest for concealment. Slaves had also thought they would be supported by freed men of colour, but these instead joined efforts to quell the rebellion. Although they drove whites off the plantations, widespread killings did not take place. By the end, 120 slaves died in combat or were immediately executed and another 144 brought to trial and executed. The remaining rebels were shipped off the island.
Towards the abolition of slavery
In 1826, the Barbados legislature passed the Consolidated Slave Law, which simultaneously granted concessions to the slaves while providing reassurances to the slave owners. Slavery was finally abolished in the British Empire eight years later, in 1834. In Barbados and the rest of the British West Indian colonies, full emancipation from slavery was preceded by a contentious apprenticeship period that lasted four years. In 1884, the Barbados Agricultural Society sent a letter to Sir Francis Hincks requesting his private and public views on whether the Dominion of Canada would favourably entertain having the then Colony of Barbados admitted as a member of theCanadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation (french: Confédération canadienne, link=no) was the process by which three British North American provinces, the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick, were united into one federation called the Dominion ...
. Asked from Canada were the terms of the Canadian side to initiate discussions, and whether or not the island of Barbados could depend on the full influence of Canada in getting the change agreed to by the British Parliament at Westminster.
Towards decolonisation
In 1952, the ''Barbados Advocate
The ''Advocate'' ("Barbados Advocate") is the second most dominant daily newspaper in the country of Barbados. First established in 1895, the Advocate is the longest continually published newspaper in the country. Printed in colour, the Advocat ...
'' newspaper polled several prominent Barbadian politicians, lawyers, businessmen, the Speaker of the House of Assembly
House of Assembly is a name given to the legislature or lower house of a bicameral parliament. In some countries this may be at a subnational level.
Historically, in British Crown colonies as the colony gained more internal responsible gove ...
and later as first President of the Senate, Sir Theodore Branker, Q.C.and found them to be in favour of immediate federation of Barbados along with the rest of the British Caribbean with complete Dominion Status within five years from the date of inauguration of the West Indies Federation
The West Indies Federation, also known as the West Indies, the Federation of the West Indies or the West Indian Federation, was a short-lived political union that existed from 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962. Various islands in the Caribbean that ...
with Canada.
However, plantation owners and merchants of British descent still dominated local politics, owing to the high income qualification required for voting. More than 70 per cent of the population, many of them disenfranchised women, were excluded from the democratic process. It was not until the 1930s that the descendants of emancipated slaves began a movement for political rights. One of the leaders of this, Sir Grantley Adams, founded the Barbados Progressive League in 1938, which later became known as the Barbados Labour Party
The Barbados Labour Party (BLP), colloquially known as the "Bees", is a social democratic political party in Barbados established in 1938. Led by Prime Minister Mia Amor Mottley, it is the governing party of Barbados and the sole ruling party ...
(BLP).
Adams and his party demanded more rights for the poor and for the people, and staunchly supported the monarchy. Progress toward a more democratic government in Barbados was made in 1942, when the exclusive income qualification was lowered and women were given the right to vote. By 1949, governmental control was wrested from the planters, and in 1953 Adams became Premier of Barbados.
From 1958 to 1962, Barbados was one of the ten members of the West Indies Federation
The West Indies Federation, also known as the West Indies, the Federation of the West Indies or the West Indian Federation, was a short-lived political union that existed from 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962. Various islands in the Caribbean that ...
, a federalist organisation doomed by nationalist attitudes and the fact that its members, as British colonies, held limited legislative power. Grantley Adams
Sir Grantley Herbert Adams, CMG, QC (28 April 1898 – 28 November 1971) was a Barbadian politician. He served as the inaugural premier of Barbados from 1953 to 1958 and then became the first and only prime minister of the West Indies Federa ...
served as its first and only "Premier", but his leadership failed in attempts to form similar unions, and his continued defence of the monarchy was used by his opponents as evidence that he was no longer in touch with the needs of his country. Errol Walton Barrow, a fervent reformer, became the people's new advocate. Barrow had left the BLP and formed the Democratic Labour Party (DLP) as a liberal alternative to Adams' conservative government. Barrow instituted many progressive social programmes, such as free education for all Barbadians and a school meals system. By 1961, Barrow had replaced Adams as Premier and the DLP controlled the government.
With the Federation dissolved, Barbados reverted to its former status, that of a self-governing colony
In the British Empire, a self-governing colony was a colony with an elected government in which elected rulers were able to make most decisions without referring to the colonial power with nominal control of the colony. This was in contrast to ...
. The island negotiated its own independence at a constitutional conference with Britain in June 1966. After years of peaceful and democratic progress, Barbados finally became an independent state on 30 November 1966, with Errol Barrow its first Prime Minister, although Queen Elizabeth II remained the monarch. Upon independence Barbados maintained historical linkages with Britain by becoming a member of the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the ...
. A year later, Barbados' international linkages were expanded by obtaining membership of both the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
and the Organization of American States.
Political history
Carrington (1982) examines politics during the American Revolution, revealing that Barbadian political leaders shared many of the grievances and goals of the American revolutionaries, but that they were unwilling to go to war over them. Nevertheless, the repeated conflicts between the island assembly and the royal governors brought important constitutional reforms which confirmed the legislature's control over most local matters and its power over the executive. From 1800 until 1885, Barbados then served as the main seat of Government for the formerBritish
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
colonies of the Windward Islands
french: Îles du Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Windward Islands. Clockwise: Dominica, Martinique, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Grenada.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean Sea No ...
. During that period of around 85 years, the resident Governor of Barbados
This article contains a list of viceroys in Barbados from its initial colonisation in 1627 by England until it achieved independence in 1966. From 1833 to 1885, Barbados was part of the colony of the Windward Islands, and the governor of Barbad ...
also served as the Colonial head of the Windward Islands. After the Government of Barbados officially exited from the Windward Island union in 1885, the seat was moved from Bridgetown to St. George's on the neighbouring island of Grenada, where it remained until the territory of the Windward Islands was dissolved.
Soon after Barbados' withdrawal from the Windward Islands, Barbados became aware that Tobago
Tobago () is an List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, island and Regions and municipalities of Trinidad and Tobago, ward within the Trinidad and Tobago, Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located northeast of the larger island of Trini ...
was going to be amalgamated with another territory as part of a single state. In response, Barbados made an official bid to the British Government to have neighbouring Island Tobago joined with Barbados in a political union. The British government however decided that Trinidad would be a better fit and Tobago instead was made a Ward of Trinidad.
African slaves worked on plantations owned by merchants of English and Scottish descent. It was these merchants who continued to dominate Barbados politics, even after emancipation, due to a high income restriction on voting. Only the upper 30 per cent had any voice in the democratic process. It was not until the 1930s that a movement for political rights was begun by the descendants of emancipated slaves, who started trade unions
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits ( ...
. Charles Duncan O’Neal
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was " ...
, Clennell Wickham and the members of the Democratic League were some of the leaders of this movement. This was initially opposed by Sir Grantley Adams
Sir Grantley Herbert Adams, CMG, QC (28 April 1898 – 28 November 1971) was a Barbadian politician. He served as the inaugural premier of Barbados from 1953 to 1958 and then became the first and only prime minister of the West Indies Federa ...
, who played an instrumental role in the bankruptcy and shutdown of ''The Herald'' newspapers, one of the movement's foremost voices. Adams would later found the Barbados Progressive League (now the Barbados Labour Party
The Barbados Labour Party (BLP), colloquially known as the "Bees", is a social democratic political party in Barbados established in 1938. Led by Prime Minister Mia Amor Mottley, it is the governing party of Barbados and the sole ruling party ...
) in 1938, during the Great Depression. The Depression caused mass unemployment and strikes, and the standard of living on the island fell drastically. With the death of O’Neal and the demise of the League, Adams cemented his power, but he used this to advocate for causes that had once been his rivals, including more help for the people especially the poor.
Finally, in 1942, the income qualification was lowered. This was followed by the introduction of universal adult suffrage in 1951, and Adams was elected as Premier of Barbados in 1958. For his action and leadership, Adams would later become a National Hero
The title of Hero is presented by various governments in recognition of acts of self-sacrifice to the state, and great achievements in combat or labor. It is originally a Soviet-type honor, and is continued by several nations including Belarus, Ru ...
.
From 1958 to 1962, Barbados was one of the ten members of the West Indies Federation
The West Indies Federation, also known as the West Indies, the Federation of the West Indies or the West Indian Federation, was a short-lived political union that existed from 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962. Various islands in the Caribbean that ...
, an organisation doomed to failure by a number of factors, including what were often petty nationalistic prejudices and limited legislative power. Indeed, Adams's position as "Prime Minister" was a misnomer, as all of the Federation members were still colonies of Britain. Adams, once a political visionary and now a man whose policies seemed to some blind to the needs of his country, not only held fast to his notion of defending the monarchy
A monarchy is a government#Forms, form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The legitimacy (political)#monarchy, political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restric ...
but also made additional attempts to form other Federation-like entities after that union's demise. When the Federation was terminated, Barbados reverted to its former status as a self-governing colony
In the British Empire, a self-governing colony was a colony with an elected government in which elected rulers were able to make most decisions without referring to the colonial power with nominal control of the colony. This was in contrast to ...
, but efforts were made by Adams to form another federation composed of Barbados and the Leeward and Windward Islands.
Errol Walton Barrow was to replace Grantley Adams as the advocate of populism, and it was he who would eventually lead the island into Independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the statu ...
in 1966. Barrow, a fervent reformer and once a member of the Barbados Labour Party
The Barbados Labour Party (BLP), colloquially known as the "Bees", is a social democratic political party in Barbados established in 1938. Led by Prime Minister Mia Amor Mottley, it is the governing party of Barbados and the sole ruling party ...
, had left the party to form his own Democratic Labour Party, as the liberal alternative to the conservative BLP government under Adams. He remains a National Hero
The title of Hero is presented by various governments in recognition of acts of self-sacrifice to the state, and great achievements in combat or labor. It is originally a Soviet-type honor, and is continued by several nations including Belarus, Ru ...
for his work in social reformation, including the institution of free education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty ...
for all Barbadians. In 1961, Barrow supplanted Adams as Premier as the DLP took control of the government.
Independence
Due to several years of growing autonomy, Barbados, with Barrow at the helm, was able successfully to negotiate its independence at a constitutional conference with the United Kingdom in June 1966. After years of peaceful and democratic progress, Barbados finally became an independent state and formally joined theCommonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the ...
on 30 November 1966, Errol Barrow serving as its first Prime Minister.
The Barrow government sought to diversify the economy away from agriculture, seeking to boost industry and the tourism sector. Barbados was also at the forefront of regional integration efforts, spearheading the creation of CARIFTA
The Caribbean Free Trade Association (CARIFTA) was organised on 1 May 1968, to provide a continued economic linkage between the English-speaking countries of the Caribbean. The agreements establishing it came following the dissolution of the ...
and CARICOM. The DLP lost the 1976 Barbadian general election to the BLP under Tom Adams. Adams adopted a more conservative and strongly pro-Western stance, allowing the Americans to use Barbados as the launchpad for their invasion of Grenada in 1983. Adams died in office in 1985 and was replaced by Harold Bernard St. John
Sir Harold Bernard St. John, KA (16 August 1931 – 29 February 2004) was a Barbadian politician who served as the third prime minister of Barbados from 1985 to 1986. To date, he is the shortest serving Barbadian prime minister. He was leader o ...
; however, St. John lost the 1986 Barbadian general election
General elections were held in Barbados on 28 May 1986. Dieter Nohlen (2005) ''Elections in the Americas: A data handbook, Volume I'', p90 The result was a landslide victory for the Democratic Labour Party, which won 24 of the 27 seats. Among ...
, which saw the return of the DLP under Errol Barrow, who had been highly critical of the US intervention in Grenada. Barrow, too, died in office, and was replaced by Lloyd Erskine Sandiford, who remained Prime Minister until 1994.
Owen Arthur
Owen Seymour Arthur, PC (17 October 194927 July 2020) was a Barbadian politician who served as the fifth prime minister of Barbados from 6 September 1994 to 15 January 2008. He is the longest-serving Barbadian prime minister to date. He also ...
of the BLP won the 1994 Barbadian general election
Early general elections were held in Barbados on 6 September 1994. Dieter Nohlen (2005) ''Elections in the Americas: A data handbook, Volume I'', p90 The result was a victory for the opposition Barbados Labour Party, which won 19 of the 28 seats ...
, remaining Prime Minister until 2008. Dieter Nohlen (2005) ''Elections in the Americas: A data handbook, Volume I'', p90 Arthur was a strong advocate of republicanism, though a planned referendum to replace Queen Elizabeth as Head of State in 2008 never took place. The DLP won the 2008 Barbadian general election
General elections were held in Barbados on 15 January 2008.David Thompson died in 2010 and was replaced by
in JSTOR
* Blackman, Francis W., ''National Heroine of Barbados: Sarah Ann Gill'' (Barbados: Methodist Church, 1998, 27 pp.) *Blackman, Francis W., ''Methodism, 200 years in Barbados'' (Barbados: Caribbean Contact, 1988, 160 pp.) *Butler, Kathleen Mary. ''The Economics of Emancipation: Jamaica & Barbados, 1823–1843'' (1995)
online edition
*Dunn, Richard S., "The Barbados Census of 1680: Profile of the Richest Colony in English America", ''William and Mary Quarterly,'' vol. 26, no. 1 (January 1969), pp. 3–30
in JSTOR.
*Harlow, V. T. ''A History of Barbados'' (1926). *Michener, James, A. 1989. ''Caribbean''. Secker & Warburg. London. . Especially see Chapter V., "Big Storms in Little England", pp. 140–172; popular writer *Kurlansky, Mark. 1992. ''A Continent of Islands: Searching for the Caribbean Destiny''. Addison-Wesley Publishing. . *Howe, Glenford D., and Don D. Marshall, eds. ''The Empowering Impulse: The Nationalist Tradition of Barbados'' (Canoe Press, 2001
online edition
*Molen, Patricia A. "Population and Social Patterns in Barbados in the Early Eighteenth Century," ''William and Mary Quarterly,'' Vol. 28, No. 2 (April 1971), pp. 287–30
in JSTOR
* * * *Richardson; Bonham C. ''Economy and Environment in the Caribbean: Barbados and the Windwards in the Late 1800s'' (The University of the West Indies Press, 1997
online edition
*Ragatz, Lowell Joseph. "Absentee Landlordism in the British Caribbean, 1750–1833", ''Agricultural History,'' Vol. 5, No. 1 (January 1931), pp. 7–2
in JSTOR
* * *Sheridan; Richard B. ''Sugar and Slavery: An Economic History of the British West Indies, 1623–1775'' (University of the West Indies Press, 1994
online edition
*Starkey, Otis P. ''The Economic Geography of Barbados'' (1939). *Thomas, Robert Paul. "The Sugar Colonies of the Old Empire: Profit or Loss for Great Britain?" ''Economic History Review'', Vol. 21, No. 1 (April 1968), pp. 30–4
in JSTOR
– Government of Barbados
Barbados Museum & Historical Society
Government Information Services, Government of Barbados
List of rulers for Barbados *Watson, Karl
The Civil War in Barbados
BBC History, 2001-04-01.
* ttp://www.brown.edu/Research/Slavery_Justice/documents/SlaveryAndJustice.pdf Report of the Brown University Steering Committee on Slavery and Justice {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Barbados Barbados, History
Freundel Stuart
Freundel Jerome Stuart, OR, PC, SC (born 27 April 1951) is a Barbadian politician who served as seventh Prime Minister of Barbados and the leader of the Democratic Labour Party (DLP) from 23 October 2010 to 21 February 2013; and from 21 Febr ...
. The BLP returned to power in 2018 under Mia Mottley
Mia Amor Mottley, (born 1 October 1965) is a Barbadian politician and attorney who has served as the eighth prime minister of Barbados since 2018 and as Leader of the Barbados Labour Party (BLP) since 2008. Mottley is the first woman to hold ...
, who became Barbados's first female Prime Minister.
Transition to republic
The Government of Barbados announced on 15 September 2020 that it intended to become a republic by 30 November 2021, the 55th anniversary of its independence resulting in the replacement of the hereditary monarch of Barbados with an elected president. Barbados would then cease to be a Commonwealth realm, but could maintain membership in theCommonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the ...
, like Guyana and Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
.
On 20 September 2021, just over a full year after the announcement for the transition was made, the Constitution (Amendment) (No. 2) Bill, 2021 was introduced to the Parliament of Barbados. Passed on 6 October, the Bill made amendments to the Constitution of Barbados, introducing the office of the President of Barbados
The president of Barbados is the head of state of Barbados and the commander-in-chief of the Barbados Defence Force. The office was established when the country became a parliamentary republic on 30 November 2021. Before, the head of state was ...
to replace the role of Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during ...
, Queen of Barbados. The following week, on 12 October 2021, incumbent Governor-General of Barbados
The governor-general of Barbados was the representative of the Barbadian monarch from independence in 1966 until the establishment of a republic in 2021. Under the government's Table of Precedence for Barbados, the governor-general of Barbados ...
Sandra Mason was jointly nominated by the Prime Minister and Leader of the Opposition as candidate to be the first President of Barbados
The president of Barbados is the head of state of Barbados and the commander-in-chief of the Barbados Defence Force. The office was established when the country became a parliamentary republic on 30 November 2021. Before, the head of state was ...
, and was subsequently elected Elected may refer to:
* "Elected" (song), by Alice Cooper, 1973
* ''Elected'' (EP), by Ayreon, 2008
*The Elected, an American indie rock band
See also
*Election
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population ...
on 20 October. Mason took office on 30 November 2021. Prince Charles, who was heir apparent to the Barbadian Crown, attended the swearing-in ceremony in Bridgetown at the invitation of the Government of Barbados.
Queen Elizabeth II sent a message of congratulations to President Mason and the people of Barbados, saying: "As you celebrate this momentous day, I send you and all Barbadians my warmest good wishes for your happiness, peace and prosperity in the future."
A survey was taken between October 23, 2021, and November 10, 2021, by the University of the West Indies that showed 34% of respondents being in favour of transitioning to a republic, while 30% were indifferent. Notably, no overall majority was found in the survey; with 24% not indicating a preference, and the remaining 12% being opposed to the removal of Queen Elizabeth.
In January 2022, Barbados Prime Minister Mia Mottley’s Labor Party got a landslide victory, winning all 30 legislative seats, in the first general election
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has opera ...
since Barbados became a republic.
Confederations and union proposals
A number of proposals have been mooted in the past to integrate Barbados into neighbouring countries or even theCanadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation (french: Confédération canadienne, link=no) was the process by which three British North American provinces, the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick, were united into one federation called the Dominion ...
. To date all have failed, and one proposal led to deadly riots in 1876, when Governor John Pope Hennessy
Sir John Pope Hennessy (; 8 August 1834 – 7 October 1891), was an Irish and British politician and colonial administrator who served as the eighth Governor of Hong Kong and the fifteenth Governor of Mauritius.
Early life
John Pope Henness ...
tried to pressure Barbadian politicians to integrate more firmly into the Windward Islands
french: Îles du Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Windward Islands. Clockwise: Dominica, Martinique, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Grenada.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean Sea No ...
. Governor Hennessy was quickly transferred from Barbados by the British Crown. In 1884, attempts were then made by the influential Barbados Agricultural Society to have Barbados form a political association with the Canadian Confederation. From 1958 to 1962 Barbados became one of the ten states of the West Indies Federation. Lastly in the 1990s, a plan was devised by the leaders of Guyana, Barbados, and Trinidad and Tobago to form a political association between those three governments. Again this deal was never completed, following the loss of Sir Lloyd Erskine Sandiford in the Barbadian general elections.
See also
* Military history of Barbados * British colonization of the Americas *French colonization of the Americas
France began colonizing the Americas in the 16th century and continued into the following centuries as it established a colonial empire in the Western Hemisphere. France established colonies in much of eastern North America, on several Caribbe ...
*History of the Americas
The prehistory of the Americas (North, South, and Central America, and the Caribbean) begins with people migrating to these areas from Asia during the height of an ice age. These groups are generally believed to have been isolated from the peopl ...
*History of North America
History of North America encompasses the past developments of people populating the continent of North America. While it was widely believed that continent first became a human habitat when people migrated across the Bering Sea 40,000 to 17,0 ...
* History of the British West Indies
*List of prime ministers of Barbados
This is a list of prime ministers of Barbados.
Premiers of Barbados (1953–1966)
Queen Elizabeth II in right of the United Kingdom (1953–66)
Prime Ministers of Barbados (1966–Present) Queen Elizabeth II in right of Barbados (1966–20 ...
*List of governors of Barbados
This article contains a list of viceroys in Barbados from its initial colonisation in 1627 by England until it achieved independence in 1966. From 1833 to 1885, Barbados was part of the colony of the Windward Islands, and the governor of Barbad ...
*Longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lette ...
*Piracy in the Caribbean
]The era of piracy in the Caribbean began in the 1500s and phased out in the 1830s after the navies of the nations of Western Europe and North America with colonies in the Caribbean began combating pirates. The period during which pirates were ...
*Politics of Barbados
The politics of Barbados function within a framework of a parliamentary republic with strong democratic traditions; constitutional safeguards for nationals of Barbados include: freedom of speech, press, worship, movement, and association.
Execut ...
* Spanish colonization of the Americas
* Timeline of Barbadian history
*West Indies Federation
The West Indies Federation, also known as the West Indies, the Federation of the West Indies or the West Indian Federation, was a short-lived political union that existed from 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962. Various islands in the Caribbean that ...
Notes
Citations
References
* * *Hoyes, F. A. 1963. ''The Rise of West Indian Democracy: The Life and Times of Sir Grantley Adams''. Advocate Press. *Williams, Eric. 1964. ''British Historians and the West Indies''. P.N.M. Publishing Company, Port-of-Spain. *Scott, Caroline. 1999. ''Insight Guide Barbados''. Discovery Channel and Insight Guides; fourth edition, Singapore.Further reading
* Beckles, Hilary McD., and Andrew Downes. "The Economics of Transition to the Black Labor System in Barbados, 1630–1680," ''Journal of Interdisciplinary History,'' Vol. 18, No. 2 (Autumn 1987), pp. 225–247in JSTOR
* Blackman, Francis W., ''National Heroine of Barbados: Sarah Ann Gill'' (Barbados: Methodist Church, 1998, 27 pp.) *Blackman, Francis W., ''Methodism, 200 years in Barbados'' (Barbados: Caribbean Contact, 1988, 160 pp.) *Butler, Kathleen Mary. ''The Economics of Emancipation: Jamaica & Barbados, 1823–1843'' (1995)
online edition
*Dunn, Richard S., "The Barbados Census of 1680: Profile of the Richest Colony in English America", ''William and Mary Quarterly,'' vol. 26, no. 1 (January 1969), pp. 3–30
in JSTOR.
*Harlow, V. T. ''A History of Barbados'' (1926). *Michener, James, A. 1989. ''Caribbean''. Secker & Warburg. London. . Especially see Chapter V., "Big Storms in Little England", pp. 140–172; popular writer *Kurlansky, Mark. 1992. ''A Continent of Islands: Searching for the Caribbean Destiny''. Addison-Wesley Publishing. . *Howe, Glenford D., and Don D. Marshall, eds. ''The Empowering Impulse: The Nationalist Tradition of Barbados'' (Canoe Press, 2001
online edition
*Molen, Patricia A. "Population and Social Patterns in Barbados in the Early Eighteenth Century," ''William and Mary Quarterly,'' Vol. 28, No. 2 (April 1971), pp. 287–30
in JSTOR
* * * *Richardson; Bonham C. ''Economy and Environment in the Caribbean: Barbados and the Windwards in the Late 1800s'' (The University of the West Indies Press, 1997
online edition
*Ragatz, Lowell Joseph. "Absentee Landlordism in the British Caribbean, 1750–1833", ''Agricultural History,'' Vol. 5, No. 1 (January 1931), pp. 7–2
in JSTOR
* * *Sheridan; Richard B. ''Sugar and Slavery: An Economic History of the British West Indies, 1623–1775'' (University of the West Indies Press, 1994
online edition
*Starkey, Otis P. ''The Economic Geography of Barbados'' (1939). *Thomas, Robert Paul. "The Sugar Colonies of the Old Empire: Profit or Loss for Great Britain?" ''Economic History Review'', Vol. 21, No. 1 (April 1968), pp. 30–4
in JSTOR
External links
– Government of Barbados
Government Information Services, Government of Barbados
List of rulers for Barbados *Watson, Karl
The Civil War in Barbados
BBC History, 2001-04-01.
* ttp://www.brown.edu/Research/Slavery_Justice/documents/SlaveryAndJustice.pdf Report of the Brown University Steering Committee on Slavery and Justice {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Barbados Barbados, History
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...