Bangladesh War on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in
 Prior to the
Prior to the
 In 1947 the Bengali Muslims had identified themselves with Pakistan's Islamic project but by the 1970s the people of East Pakistan had given priority to their Bengali ethnicity over their religious identity, desiring a society in accordance with Western principles such as
In 1947 the Bengali Muslims had identified themselves with Pakistan's Islamic project but by the 1970s the people of East Pakistan had given priority to their Bengali ethnicity over their religious identity, desiring a society in accordance with Western principles such as
 Although East Pakistan accounted for a slight majority of the country's population, political power remained in the hands of West Pakistanis. Since a straightforward system of representation based on population would have concentrated political power in East Pakistan, the West Pakistani establishment came up with the "
Although East Pakistan accounted for a slight majority of the country's population, political power remained in the hands of West Pakistanis. Since a straightforward system of representation based on population would have concentrated political power in East Pakistan, the West Pakistani establishment came up with the "
 A planned military pacification carried out by the
A planned military pacification carried out by the

 Bangladesh forces command was set up on 11 July, with Col. M. A. G. Osmani as commander-in-chief (C-in-C) with the status of Cabinet Minister, Lt. Col., Abdur Rabb as chief of Staff (COS), Group Captain A K Khandker as Deputy Chief of Staff (DCOS) and Major A R Chowdhury as Assistant Chief of Staff (ACOS).
General Osmani had differences of opinion with the Indian leadership regarding the role of the Mukti Bahini in the conflict. Indian leadership initially envisioned a well trained force of 8,000 guerrillas, operating in small cells around Bangladesh to facilitate eventual conventional combat. With the Bangladesh government in exile, General Osmani favoured a different strategy:
* Bengali conventional forces would occupy lodgments inside Bangladesh and then the Bangladesh government would request international diplomatic recognition and intervention. Initially Mymensingh was picked for this operation, but Gen. Osmani later settled on Sylhet.
* Sending the maximum number of guerrillas into Bangladesh as soon as possible with the following objectives:
** Increasing Pakistani casualties through raids and ambush.
** Cripple economic activity by hitting power stations, railway lines, storage depots and communication networks.
** Destroy Pakistan army mobility by blowing up bridges/culverts, fuel depots, trains and river crafts.
** The strategic objective was to make the Pakistanis spread their forces inside the province, so attacks could be made on isolated Pakistani detachments.
Bangladesh was divided into List of sectors in the Bangladesh Liberation War, eleven sectors in July, each with a commander chosen from defected officers of the Pakistani army who joined the Mukti Bahini to lead guerrilla operations. The Mukti Bahini forces were given two to five weeks of training by the Indian army on guerilla warfare. Most of their training camps were situated near the border area and were operated with assistance from India. The 10th Sector was directly placed under the Commander in Chief (C-in-C) General M. A. G. Osmani and included the Naval Commandos and C-in-C's special force. Three brigades (11 Battalions) were raised for conventional warfare; a large guerrilla force (estimated at 100,000) was trained.
Five infantry battalions were reformed and positioned along the northern and eastern borders of Bangladesh. Three more battalions were raised, and artillery batteries were formed. During June and July, Mukti Bahini had regrouped across the border with Indian aid through
Bangladesh forces command was set up on 11 July, with Col. M. A. G. Osmani as commander-in-chief (C-in-C) with the status of Cabinet Minister, Lt. Col., Abdur Rabb as chief of Staff (COS), Group Captain A K Khandker as Deputy Chief of Staff (DCOS) and Major A R Chowdhury as Assistant Chief of Staff (ACOS).
General Osmani had differences of opinion with the Indian leadership regarding the role of the Mukti Bahini in the conflict. Indian leadership initially envisioned a well trained force of 8,000 guerrillas, operating in small cells around Bangladesh to facilitate eventual conventional combat. With the Bangladesh government in exile, General Osmani favoured a different strategy:
* Bengali conventional forces would occupy lodgments inside Bangladesh and then the Bangladesh government would request international diplomatic recognition and intervention. Initially Mymensingh was picked for this operation, but Gen. Osmani later settled on Sylhet.
* Sending the maximum number of guerrillas into Bangladesh as soon as possible with the following objectives:
** Increasing Pakistani casualties through raids and ambush.
** Cripple economic activity by hitting power stations, railway lines, storage depots and communication networks.
** Destroy Pakistan army mobility by blowing up bridges/culverts, fuel depots, trains and river crafts.
** The strategic objective was to make the Pakistanis spread their forces inside the province, so attacks could be made on isolated Pakistani detachments.
Bangladesh was divided into List of sectors in the Bangladesh Liberation War, eleven sectors in July, each with a commander chosen from defected officers of the Pakistani army who joined the Mukti Bahini to lead guerrilla operations. The Mukti Bahini forces were given two to five weeks of training by the Indian army on guerilla warfare. Most of their training camps were situated near the border area and were operated with assistance from India. The 10th Sector was directly placed under the Commander in Chief (C-in-C) General M. A. G. Osmani and included the Naval Commandos and C-in-C's special force. Three brigades (11 Battalions) were raised for conventional warfare; a large guerrilla force (estimated at 100,000) was trained.
Five infantry battalions were reformed and positioned along the northern and eastern borders of Bangladesh. Three more battalions were raised, and artillery batteries were formed. During June and July, Mukti Bahini had regrouped across the border with Indian aid through
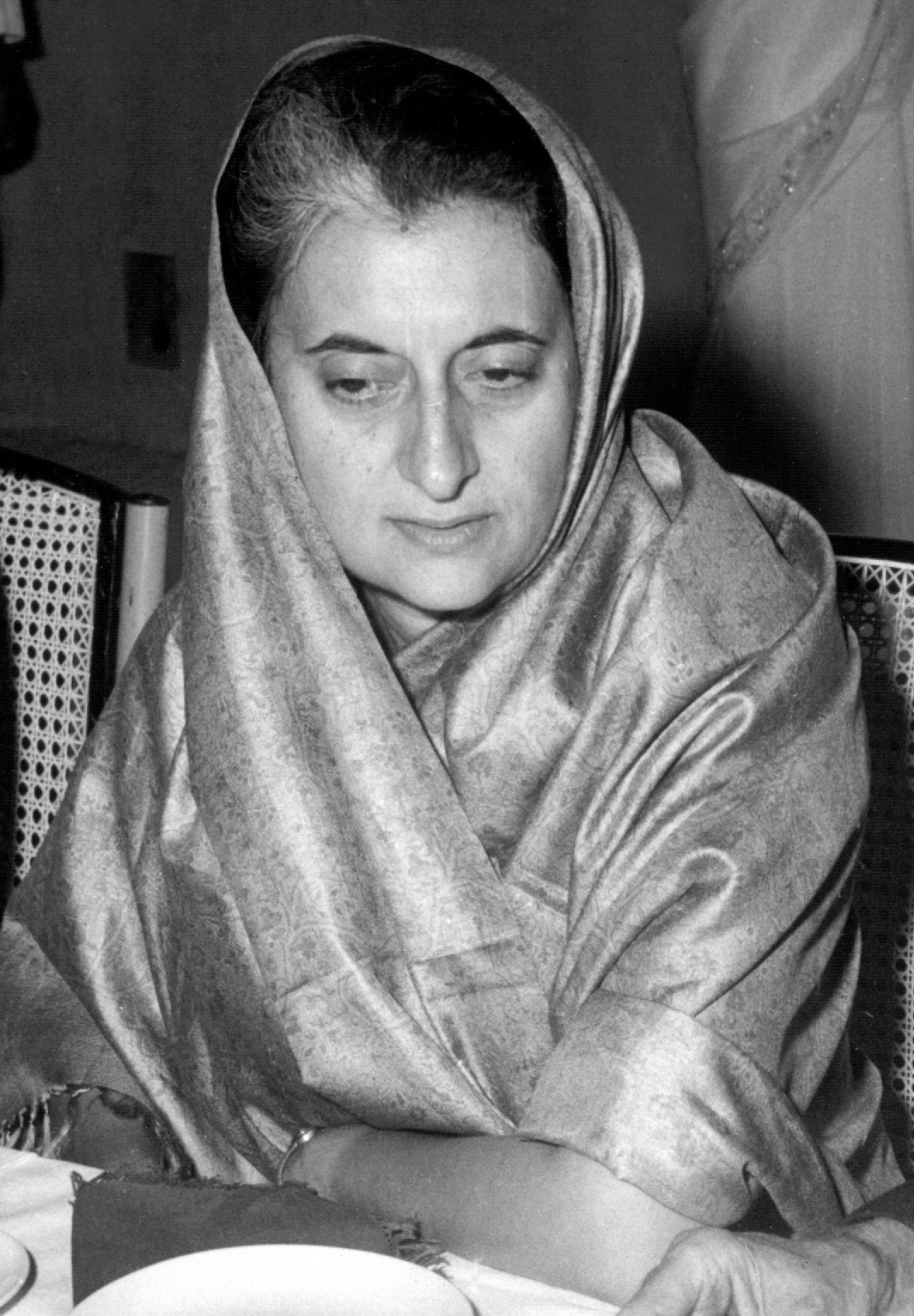
 Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi had concluded that instead of taking in millions of refugees, India would be economically better off going to war against Pakistan. As early as 28 April 1971, the Indian Cabinet had asked General Sam Manekshaw, Manekshaw (Chairman of the Chiefs of Staff Committee) to "Go into East Pakistan". Hostile relations in the past between India and Pakistan added to India's decision to intervene in Pakistan's civil war.
As a result, the Indian government decided to support the creation of a separate state for ethnic Bengalis by supporting the
Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi had concluded that instead of taking in millions of refugees, India would be economically better off going to war against Pakistan. As early as 28 April 1971, the Indian Cabinet had asked General Sam Manekshaw, Manekshaw (Chairman of the Chiefs of Staff Committee) to "Go into East Pakistan". Hostile relations in the past between India and Pakistan added to India's decision to intervene in Pakistan's civil war.
As a result, the Indian government decided to support the creation of a separate state for ethnic Bengalis by supporting the
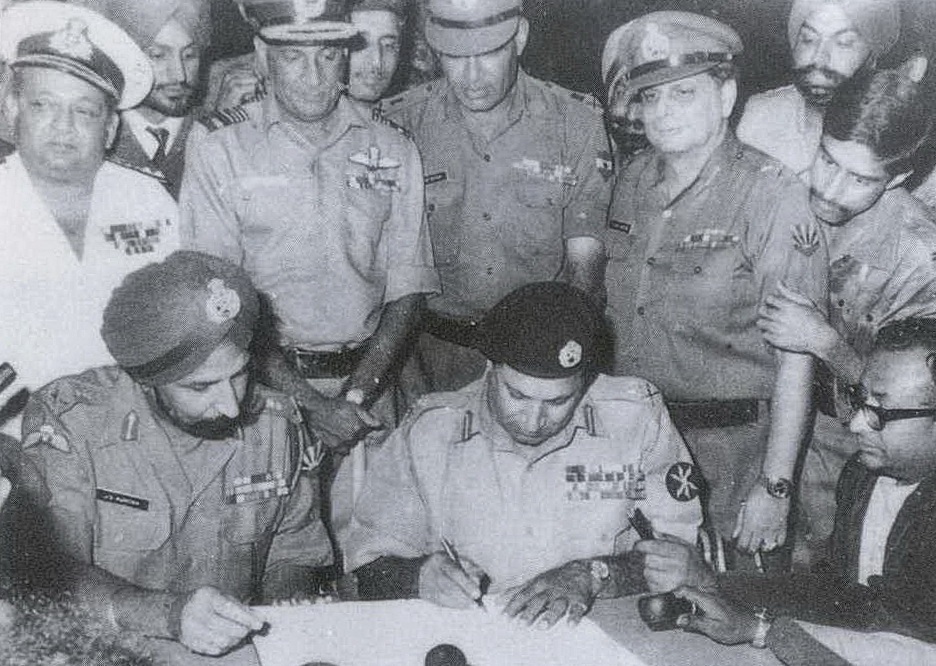
 On 16 December 1971, Lt. Gen Amir Abdullah Khan Niazi, Chief Martial Law Administrator of
On 16 December 1971, Lt. Gen Amir Abdullah Khan Niazi, Chief Martial Law Administrator of
Death Tolls for the Major Wars and Atrocities of the Twentieth Century
'' and raped between 200,000 and 400,000 Bangladeshis, Bangladeshi women in a systematic campaign of genocidal rape. Pakistan's religious leaders openly supported the crime by labelling Mukti Bahini, Bengali freedom fighters as "Hindus" and Bengali women as "the booty of war". But in reality, more than 80 percent of the Bengali people were Muslims at that time. A large section of the intellectual community of Bangladesh were murdered, mostly by the Al-Shams and Many mass graves have been discovered in Bangladesh. The first night of war on Bengalis, which is documented in telegrams from the American Consulate in Dacca to the United States State Department, saw indiscriminate killings of students of University of Dhaka, Dacca University and other civilians. Numerous women were tortured, raped and killed during the war; the exact numbers are not known and are a subject of debate. The widespread rape of Bangladeshi women led to birth of thousands of War children, war babies.
The Pakistan Army also kept numerous Bengali women as sex-slaves inside the Dacca Cantonment. Most of the girls were captured from Dacca University and private homes. There was significant sectarian violence not only perpetrated and encouraged by the Pakistani army,U.S. Consulate (Dacca) Cable, Sitrep
Many mass graves have been discovered in Bangladesh. The first night of war on Bengalis, which is documented in telegrams from the American Consulate in Dacca to the United States State Department, saw indiscriminate killings of students of University of Dhaka, Dacca University and other civilians. Numerous women were tortured, raped and killed during the war; the exact numbers are not known and are a subject of debate. The widespread rape of Bangladeshi women led to birth of thousands of War children, war babies.
The Pakistan Army also kept numerous Bengali women as sex-slaves inside the Dacca Cantonment. Most of the girls were captured from Dacca University and private homes. There was significant sectarian violence not only perpetrated and encouraged by the Pakistani army,U.S. Consulate (Dacca) Cable, Sitrep
Army Terror Campaign Continues in Dacca; Evidence Military Faces Some Difficulties Elsewhere
, 31 March 1971, Confidential, 3 pp but also by Bengali nationalists against non-Bengali minorities, especially Biharis. In June 1971, Bihari representatives stated that 500,000 Biharis were killed by Bengalis. R. J. Rummel gives a prudent estimate of 150,000 killed. On 16 December 2002, the George Washington University's National Security Archive published a collection of declassified documents, consisting mostly of communications between US embassy officials and United States Information Agency, United States Information Service centres in Dacca and India, and officials in Washington, D.C. These documents show that US officials working in diplomatic institutions within Bangladesh used the terms "selective genocide"U.S. Consulate in Dacca (27 March 1971),
Selective genocide
'', Cable (PDF) and "genocide" (see Archer Blood#The Blood telegram, The Blood Telegram) for information on events they had knowledge of at the time. ''Genocide'' is the term that is still used to describe the event in almost every major publication and newspaper in Bangladesh, although in Pakistan, the accusations against Pakistani forces continue to be disputed.
 Following Sheikh Mujibur Rahman's declaration of independence in March 1971, a worldwide campaign was undertaken by the Provisional Government of Bangladesh to drum up political support for the independence of East Pakistan as well as humanitarian support for the Bengali people.
Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi provided extensive diplomatic and political support to the Bangladesh movement. She toured many countries in a bid to create awareness of the Pakistani atrocities against Bengalis. This effort was to prove vital later during the war, in framing the world's context of the war and to justify military action by India. Also, following Pakistan's defeat, it ensured prompt recognition of the newly independent state of Bangladesh.
Following Sheikh Mujibur Rahman's declaration of independence in March 1971, a worldwide campaign was undertaken by the Provisional Government of Bangladesh to drum up political support for the independence of East Pakistan as well as humanitarian support for the Bengali people.
Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi provided extensive diplomatic and political support to the Bangladesh movement. She toured many countries in a bid to create awareness of the Pakistani atrocities against Bengalis. This effort was to prove vital later during the war, in framing the world's context of the war and to justify military action by India. Also, following Pakistan's defeat, it ensured prompt recognition of the newly independent state of Bangladesh.
 The US government stood by its old ally Pakistan in terms of diplomacy and military threats. US President Richard Nixon and his National Security Advisor Henry Kissinger feared Soviet expansion into South and Southeast Asia. Pakistan was a close ally of the People's Republic of China, with whom Nixon had been negotiating a ''China–United States relations#Rapprochement, rapprochement'' and which he intended to visit in February 1972. Nixon feared that an Indian invasion of
The US government stood by its old ally Pakistan in terms of diplomacy and military threats. US President Richard Nixon and his National Security Advisor Henry Kissinger feared Soviet expansion into South and Southeast Asia. Pakistan was a close ally of the People's Republic of China, with whom Nixon had been negotiating a ''China–United States relations#Rapprochement, rapprochement'' and which he intended to visit in February 1972. Nixon feared that an Indian invasion of
The Men Behind Yahya in the Indo-Pak War of 1971
To demonstrate to China the ''bona fides'' of the United States as an ally, and in direct violation of the US Congress-imposed sanctions on Pakistan, Nixon sent military supplies to Pakistan and routed them through Jordan and Iran, while also encouraging China to increase its arms supplies to Pakistan. The Nixon administration also ignored reports it received of the genocidal activities of the Pakistani Army in East Pakistan, most notably the Archer Blood#The Blood telegram, Blood telegram. Nixon denied getting involved in the situation, saying that it was an internal matter of Pakistan, but when Pakistan's defeat seemed certain, Nixon sent the aircraft carrier USS Enterprise (CVN-65), USS ''Enterprise'' to the
Nixon denied getting involved in the situation, saying that it was an internal matter of Pakistan, but when Pakistan's defeat seemed certain, Nixon sent the aircraft carrier USS Enterprise (CVN-65), USS ''Enterprise'' to the
The Tilt: the U.S. and the South Asian Crisis of 1971
* Quereshi, Major General Hakeem Arshad, ''The 1971 Indo-Pak War, A Soldiers Narrative'', Oxford University Press, 2002. * Raghavan, Srinath, ''1971: A Global History of the Creation of Bangladesh,'' Harvard Univ. Press, 2013. * Rummel, R. J., ''Death By Government'', Transaction Publishers, 1997. * Sisson, Richard & Rose, Leo, ''War and secession: Pakistan, India, and the creation of Bangladesh'', University of California Press (Berkeley), 1990. * Stephen, Pierre, and Payne, Robert, ''Massacre'', Macmillan, New York, (1973). * Totten, Samuel et al., eds., ''Century of Genocide: Eyewitness Accounts and Critical Views'', Garland Reference Library, 1997 * US Department of State Office of the Historian
''Foreign Relations of the United States, 1969–1976, Volume XI, South Asia Crisis, 1971''
* Zaheer, Hasan: ''The separation of East Pakistan: The rise and realisation of Bengali Muslim nationalism'', Oxford University Press, 1994. *
1971 Bangladesh Genocide Archive
Freedom In the Air
The Daily Star
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20030501230820/http://www.bangladeshmariners.com/HmdrRprt/71mass.html 1971 Massacre in Bangladesh and the Fallacy in the Hamoodur Rahman Commission Report, Dr. M.A. Hasan]
Women of Pakistan Apologize for War Crimes, 1996
Sheikh Mujib wanted a confederation: US papers, by Anwar Iqbal, Dawn, 7 July 2005
Bangladesh Liberation War Picture Gallery
Graphic images, viewer discretion advised
1971 War: How Russia sank Nixon's gunboat diplomacy
PM reiterated her vow to declare March 25 as Genocide Day
Call for international recognition and observance of genocide day
Genocide Day: As it was in March 1971
The case for UN recognition of Bangladesh genocide
{{Authority control Bangladesh Liberation War, Separatism in Pakistan Civil wars involving the states and peoples of Asia Civil wars post-1945 War crimes in Bangladesh Wars involving Bangladesh Military history of Bangladesh Wars involving Pakistan Bangladesh–Pakistan relations, War
Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
) was a revolution
In political science, a revolution (Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically due ...
and armed conflict
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regul ...
sparked by the rise of the Bengali nationalist and self-determination
The right of a people to self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law (commonly regarded as a '' jus cogens'' rule), binding, as such, on the United Nations as authoritative interpretation of the Charter's norms. It sta ...
movement in East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Myanmar, wit ...
, which resulted in the independence of Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
. The war began when the Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
i military junta
A military junta () is a government led by a committee of military leaders. The term ''junta'' means "meeting" or "committee" and originated in the national and local junta organized by the Spanish resistance to Napoleon's invasion of Spain in ...
based in West Pakistan
West Pakistan ( ur, , translit=Mag̱ẖribī Pākistān, ; bn, পশ্চিম পাকিস্তান, translit=Pôścim Pakistan) was one of the two Provincial exclaves created during the One Unit Scheme in 1955 in Pakistan. It was ...
—under the orders of Yahya Khan
General Agha Muhammad Yahya Khan , (Urdu: ; 4 February 1917 – 10 August 1980); commonly known as Yahya Khan, was a Pakistani military general who served as the third President of Pakistan and Chief Martial Law Administrator following his p ...
—launched Operation Searchlight
Operation Searchlight was the codename for a planned military operation carried out by the Pakistan Army in an effort to curb the Bengali nationalist movement in former East Pakistan in March 1971. Pakistan retrospectively justified the opera ...
against the people of East Pakistan on the night of 25 March 1971, initiating the Bangladesh genocide.
In response to the violence, members of the Mukti Bahini
The Mukti Bahini ( bn, মুক্তিবাহিনী, translates as 'freedom fighters', or liberation army), also known as the Bangladesh Forces, was the guerrilla resistance movement consisting of the Bangladeshi military, paramilitary ...
—a guerrilla resistance movement
A resistance movement is an organized effort by some portion of the civil population of a country to withstand the legally established government or an occupying power and to disrupt civil order and stability. It may seek to achieve its objectives ...
formed by Bengali military, paramilitary and civilians—launched a mass guerrilla war
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run tactics ...
against the Pakistani military, liberating numerous towns and cities in the initial months of the conflict. At first, the Pakistan Army regained momentum during the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
, but Bengali guerrillas counterattacked by carrying out widespread sabotage, including through Operation Jackpot
The Operation Jackpot was a codename for three operations undertaken by Bengali ''Mukti Bahini'' in former East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) against the Federation of Pakistan during the climax of the Bangladesh Liberation War.''Surrender at Dac ...
against the Pakistan Navy, while the nascent Bangladesh Air Force
The Bangladesh Air Force (BAF) ( bn, বাংলাদেশ বিমান বাহিনী, Bangladesh Biman Bahini) is the aerial warfare branch of the Bangladesh Armed Forces. The Air Force is primarily responsible for air defence of ...
flew sortie
A sortie (from the French word meaning ''exit'' or from Latin root ''surgere'' meaning to "rise up") is a deployment or dispatch of one military unit, be it an aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining supp ...
s against Pakistani military bases. India joined the war on 3 December 1971, after which Pakistan launched preemptive air strikes on northern India. The subsequent Indo-Pakistani War witnessed engagements on two warfronts; with air supremacy
Aerial supremacy (also air superiority) is the degree to which a side in a conflict holds control of air power over opposing forces. There are levels of control of the air in aerial warfare. Control of the air is the aerial equivalent of comm ...
achieved in the eastern theatre, and the rapid advance of the Allied Forces of Mukti Bahini and the Indian military, Pakistan surrendered
Surrender, in military terms, is the relinquishment of control over territory, combatants, fortifications, ships or armament to another power. A surrender may be accomplished peacefully or it may be the result of defeat in battle. A sove ...
in Dhaka on 16 December 1971, in what remains to date the largest surrender of armed personnel since the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
.
Rural and urban areas across East Pakistan saw extensive military operations and air strikes to suppress the tide of civil disobedience
Civil disobedience is the active, professed refusal of a citizen to obey certain laws, demands, orders or commands of a government (or any other authority). By some definitions, civil disobedience has to be nonviolent to be called "civil". H ...
that formed following the 1970 election stalemate. The Pakistan Army
The Pakistan Army (, ) is the land service branch of the Pakistan Armed Forces. The roots of its modern existence trace back to the British Indian Army that ceased to exist following the Partition of British India, which occurred as a result ...
, which had the backing of Islamists, created radical religious militias—the Razakars Razakar (رضا کار) is etymologically an Arabic word which literally means volunteer. The word is also common in Urdu language as a loanword. On the other hand, in Bangladesh, razakar is a pejorative word meaning a traitor or Judas.
In Pakis ...
, Al-Badr
Al Badr is a village in Mecca Province, in western Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it ...
and Al-Shams—to assist it during raids on the local populace. Members of the Pakistani military and supporting militias engaged in mass murder, deportation and genocidal rape
Genocidal rape, a form of wartime sexual violence, is the action of a group which has carried out acts of mass rape and gang rapes, against its enemy during wartime as part of a genocidal campaign. During the Armenian Genocide, the second Sin ...
, pursuing a systematic campaign of annihilation against nationalist Bengali civilians, students, intelligentsia
The intelligentsia is a status class composed of the university-educated people of a society who engage in the complex mental labours by which they critique, shape, and lead in the politics, policies, and culture of their society; as such, the i ...
, religious minorities and armed personnel. The capital, Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), List of renamed places in Bangladesh, formerly known as Dacca, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Bangladesh, largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest ...
, was the scene of numerous massacres, including the Dhaka University massacre. Sectarian violence
Sectarian violence and/or sectarian strife is a form of communal violence which is inspired by sectarianism, that is, discrimination, hatred or prejudice between different sects of a particular mode of an ideology or different sects of a religion ...
also broke out between Bengalis and Urdu-speaking Biharis. An estimated 10 million Bengali refugees
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution.
fled to neighbouring India, while 30 million were internally displaced.
The war changed the geopolitical landscape of South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
, with the emergence of Bangladesh as the seventh-most populous country in the world. Due to complex regional alliances, the war was a major episode in Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
tensions involving the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
and the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
. The majority of member states in the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
recognised Bangladesh as a sovereign nation in 1972.
Background
 Prior to the
Prior to the Partition of British India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: India and Pakistan. T ...
, the Lahore Resolution
The Lahore Resolution ( ur, , ''Qarardad-e-Lahore''; Bengali: লাহোর প্রস্তাব, ''Lahor Prostab''), also called Pakistan resolution, was written and prepared by Muhammad Zafarullah Khan and was presented by A. K. Fazlul ...
initially envisaged separate Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
-majority states in the eastern and northwestern zones of British India. A proposal for an independent United Bengal
United Bengal was a proposal to transform Bengal Province into an undivided, sovereign state at the time of the Partition of India in 1947. It sought to prevent the division of Bengal on religious grounds. The proposed state was to be called t ...
was mooted by Prime Minister Huseyn Shaheed Suhrawardy
Huseyn Shaheed Suhrawardy ( bn, হোসেন শহীদ সোহ্রাওয়ার্দী; ur, ; 8 September 18925 December 1963) was a Bengali barrister and politician. He served as the Prime Minister of Pakistan from 1956 ...
in 1946, but was opposed by the colonial authorities. The East Pakistan Renaissance Society
The East Pakistan Renaissance Society was a political organisation formed to articulate and promote culturally and intellectually the idea for a separate Muslim state for Indian Muslims and specifically for the Muslims of Bengal. The organisati ...
advocated the creation of a sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defined ter ...
in eastern British India.
Political negotiations led, in August 1947, to the official birth of two states, Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, giving presumably permanent homes for Muslims and Hindus respectively following the departure of the British. The Dominion of Pakistan
Between 14 August 1947 and 23 March 1956, Pakistan was an independent federal dominion in the Commonwealth of Nations, created by the passing of the Indian Independence Act 1947 by the British parliament, which also created the Dominion of ...
comprised two geographically and culturally separate areas to the east and the west with India in between.
The western zone was popularly (and for a period, also officially) termed West Pakistan and the eastern zone (modern-day Bangladesh) was initially termed East Bengal
ur,
, common_name = East Bengal
, status = Province of the Dominion of Pakistan
, p1 = Bengal Presidency
, flag_p1 = Flag of British Bengal.svg
, s1 = Ea ...
and later, East Pakistan. Although the population of the two zones was close to equal, political power was concentrated in West Pakistan and it was widely perceived that East Pakistan was being exploited economically, leading to many grievances. Administration of two discontinuous territories was also seen as a challenge.
On 25 March 1971, after an election won by an East Pakistani political party (the Awami League In Urdu language, Awami is the adjectival form for '' Awam'', the Urdu language word for common people.
The adjective appears in the following proper names:
*Awami Colony, a neighbourhood of Landhi Town in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
*Awami Front, wa ...
) was ignored by the ruling (West Pakistani) establishment, rising political discontent and cultural nationalism
Cultural nationalism is nationalism in which the nation is defined by a shared culture and a common language, rather than on the concepts of common ancestry or race.
Cultural nationalism does not tend to manifest itself in independent movements, ...
in East Pakistan was met by brutal and suppressive force from the ruling elite of the West Pakistan establishment, in what came to be termed as Operation Searchlight
Operation Searchlight was the codename for a planned military operation carried out by the Pakistan Army in an effort to curb the Bengali nationalist movement in former East Pakistan in March 1971. Pakistan retrospectively justified the opera ...
. The violent crackdown by the Pakistan Army led to Awami League leader Sheikh Mujibur Rahman
Sheikh Mujibur Rahman ( bn, শেখ মুজিবুর রহমান; 17 March 1920 – 15 August 1975), often shortened as Sheikh Mujib or Mujib and widely known as Bangabandhu (meaning ''Friend of Bengal''), was a Bengali politi ...
declaring East Pakistan's independence as the state of Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
on 26 March 1971. Most Bengalis supported this move although Islamists
Islamism (also often called political Islam or Islamic fundamentalism) is a political ideology which posits that modern states and regions should be reconstituted in constitutional, economic and judicial terms, in accordance with what is c ...
and Biharis opposed this and sided with the Pakistan Army instead.
Pakistani President Agha Muhammad Yahya Khan ordered the Pakistani military to restore the Pakistani government's authority, beginning the civil war. The war led to a substantial number of refugees (estimated at the time to be about 10 million) flooding into the eastern provinces of India.''Crisis in South Asia – A report'' by Senator Edward Kennedy to the Subcommittee investigating the Problem of Refugees and Their Settlement, Submitted to U.S. Senate Judiciary Committee, 1 November 1971, U.S. Govt. Press.pp6-7 Facing a mounting humanitarian and economic crisis, India started actively aiding and organising the Bangladeshi resistance army known as the Mukti Bahini
The Mukti Bahini ( bn, মুক্তিবাহিনী, translates as 'freedom fighters', or liberation army), also known as the Bangladesh Forces, was the guerrilla resistance movement consisting of the Bangladeshi military, paramilitary ...
.
Language controversy
In 1948,Governor-General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
Muhammad Ali Jinnah
Muhammad Ali Jinnah (, ; born Mahomedali Jinnahbhai; 25 December 1876 – 11 September 1948) was a barrister, politician, and the founder of Pakistan. Jinnah served as the leader of the All-India Muslim League from 1913 until the ...
declared that "Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
'' subcontinent A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
; whereas in East Bengal, the native language was '' subcontinent A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
, one of the two most easterly branches of the Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, D ...
. The Bengali-speaking people of Pakistan constituted over 56% of the country's population.
The government stand was widely viewed as an attempt to suppress the culture of the eastern wing. The people of East Bengal demanded that their language be given federal status alongside Urdu and English. The Language Movement began in 1948, as civil society protested the removal of the Bengali script
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
from currency and stamps, which were in place since the British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was him ...
.
The movement reached its climax in 1952, when on 21 February, the police fired on protesting students and civilians, causing several deaths. The day is revered in Bangladesh as the Language Movement Day
(''Bhasha Andolôn Dibôs'')
, nickname = bn, শহীদ দিবস (''Shôhid Dibôs'')
, duration = 1 day
, frequency = Annual
, observedby = Bangladesh and Bengali speakers in India and elsewhere
, date = 21 Feb ...
. Later, in memory of the deaths in 1952, UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
declared 21 February as International Mother Language Day
International Mother Language Day is a worldwide annual observance held on 21 February to promote awareness of linguistic and cultural diversity and to promote multilingualism. First announced by UNESCO on 17 November 1999, it was formal ...
in November 1999.
Disparities
Although East Pakistan had a larger population, West Pakistan dominated the divided country politically and received more money from the common budget. East Pakistan was already economically disadvantaged at the time of Pakistan's creation yet this economic disparity only increased under Pakistani rule. Factors included not only the deliberate state discrimination in developmental policies but also the fact that the presence of the country's capital and more immigrant businessmen in the Western wing directed greater government allocations there. Due to low numbers of native businessmen in East Pakistan, substantial labour unrest and a tense political environment, there were also much lower foreign investments in the eastern wing. The Pakistani state's economic outlook was geared towards urban industry, which was not compatible with East Pakistan's mainly agrarian economy. Bengalis were under-represented in the Pakistan military. Officers of Bengali origin in the different wings of the armed forces made up just 5% of overall force by 1965; of these, only a few were in command positions, with the majority in technical or administrative posts. West Pakistanis believed that Bengalis were not "martially inclined" unlikePashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
and Punjabis
The Punjabis (Punjabi: ; ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ; romanised as Panjābīs), are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group associated with the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of eastern Pakistan and northwestern India. ...
; the "martial race
Martial race was a designation which was created by army officials in British India after the Indian Rebellion of 1857, in which they classified each caste as belonging to one of two categories, the 'martial' caste and the 'non-martial' caste. ...
s" notion was dismissed as ridiculous and humiliating by Bengalis.
Moreover, despite huge defence spending, East Pakistan received none of the benefits, such as contracts, purchasing and military support jobs. The Indo-Pakistani War of 1965
The Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 or the Second Kashmir War was a culmination of skirmishes that took place between April 1965 and September 1965 between Pakistan and India. The conflict began following Pakistan's Operation Gibraltar, which was d ...
over Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
also highlighted the sense of military insecurity among Bengalis, as only an under-strength infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and mar ...
division and 15 combat aircraft without tank support were in East Pakistan to thwart any Indian retaliations during the conflict.
Ideological and cultural differences
 In 1947 the Bengali Muslims had identified themselves with Pakistan's Islamic project but by the 1970s the people of East Pakistan had given priority to their Bengali ethnicity over their religious identity, desiring a society in accordance with Western principles such as
In 1947 the Bengali Muslims had identified themselves with Pakistan's Islamic project but by the 1970s the people of East Pakistan had given priority to their Bengali ethnicity over their religious identity, desiring a society in accordance with Western principles such as secularism
Secularism is the principle of seeking to conduct human affairs based on secular, naturalistic considerations.
Secularism is most commonly defined as the separation of religion from civil affairs and the state, and may be broadened to a si ...
, democracy and socialism. Many Bengali Muslims strongly objected to the Islamist paradigm imposed by the Pakistani state.
Most members of West Pakistan's ruling elite shared a vision of a liberal society, but nevertheless viewed a common faith as an essential mobilising factor behind Pakistan's creation and the subsuming of Pakistan's multiple regional identities into one national identity. West Pakistanis were substantially more supportive than East Pakistanis of an Islamic state, a tendency that persisted after 1971.
Cultural and linguistic differences between the two wings gradually outweighed any sense of religious unity. The Bengalis took great pride in their culture and language which, with its Bengali script
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
and vocabulary
A vocabulary is a set of familiar words within a person's language. A vocabulary, usually developed with age, serves as a useful and fundamental tool for communication and acquiring knowledge. Acquiring an extensive vocabulary is one of the ...
, was unacceptable to the West Pakistani elite, who believed that it had assimilated considerable Hindu cultural influences. West Pakistanis, in an attempt to "Islamise" the East, wanted the Bengalis to adopt Urdu. The activities of the language movement nurtured a sentiment among Bengalis in favour of discarding Pakistan's communalism in favour of secular politics. The Awami League began propagating its secular message through its newspaper to the Bengali readership.
The Awami League's emphasis on secularism differentiated it from the Muslim League. In 1971, the Bangladeshi liberation struggle against Pakistan was led by secular leaders and secularists hailed the Bangladeshi victory as the triumph of secular Bengali nationalism over religion-centred Pakistani nationalism. While Pakistan's government strives for an Islamic state, Bangladesh was established secular. After the liberation victory, the Awami League attempted to build a secular order and the pro-Pakistan Islamist parties were barred from political participation. The majority of East Pakistani ulama
In Islam, the ''ulama'' (; ar, علماء ', singular ', "scholar", literally "the learned ones", also spelled ''ulema''; feminine: ''alimah'' ingularand ''aalimath'' lural are the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious ...
had either remained neutral or supported the Pakistani state, since they felt that the break-up of Pakistan would be detrimental for Islam.
Political differences
 Although East Pakistan accounted for a slight majority of the country's population, political power remained in the hands of West Pakistanis. Since a straightforward system of representation based on population would have concentrated political power in East Pakistan, the West Pakistani establishment came up with the "
Although East Pakistan accounted for a slight majority of the country's population, political power remained in the hands of West Pakistanis. Since a straightforward system of representation based on population would have concentrated political power in East Pakistan, the West Pakistani establishment came up with the "One Unit
The One Unit Scheme ( ur, ; bn, এক ইউনিট ব্যবস্থা) was a geopolitical programme launched by the Government of Pakistan led by Prime Minister Muhammad Ali Bogra on 22 November 1954 and passed on 30 September 1955 ...
" scheme, where all of West Pakistan was considered one province. This was solely to counterbalance the East wing's votes.
After the assassination of Liaquat Ali Khan
Liaquat Ali Khan ( ur, ; 1 October 1895 – 16 October 1951), also referred to in Pakistan as ''Quaid-e-Millat'' () or ''Shaheed-e-Millat'' ( ur, lit=Martyr of the Nation, label=none, ), was a Pakistani statesman, lawyer, political theoris ...
, Pakistan's first prime minister, in 1951, political power began to devolve to the new President of Pakistan
The president of Pakistan ( ur, , translit=s̤adr-i Pākiṣṭān), officially the President of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is the ceremonial head of state of Pakistan and the commander-in-chief of the Pakistan Armed Forces.Governor General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy ...
when Pakistan became a republic, and, eventually, the military. The nominal elected chief executive, the Prime Minister, was frequently sacked by the establishment, acting through the President.
The East Pakistanis observed that the West Pakistani establishment would swiftly depose any East Pakistanis elected Prime Minister of Pakistan, such as Khawaja Nazimuddin
Sir Khawaja Nazimuddin ( bn, খাজা নাজিমুদ্দীন; ur, ; 19 July 1894 – 22 October 1964) was a Pakistani politician and one of the leading founding fathers of Pakistan. He is noted as being the first Bengali to ha ...
, Mohammad Ali Bogra
Sahibzada Syed Mohammad Ali Chowdhury ( bn, সৈয়দ মোহাম্মদ আলী চৌধুরী; Urdu: سید محمد علی چوہدری), more commonly known as Mohammad Ali Bogra ( bn, মোহাম্মদ আলী ...
, or Huseyn Shaheed Suhrawardy
Huseyn Shaheed Suhrawardy ( bn, হোসেন শহীদ সোহ্রাওয়ার্দী; ur, ; 8 September 18925 December 1963) was a Bengali barrister and politician. He served as the Prime Minister of Pakistan from 1956 ...
. Their suspicions were further aggravated by the military dictatorships of Ayub Khan
Ayub Khan is a compound masculine name; Ayub is the Arabic version of the name of the Biblical figure Job, while Khan or Khaan is taken from the title used first by the Mongol rulers and then, in particular, their Islamic and Persian-influenced s ...
(27 October 1958 – 25 March 1969) and Yahya Khan
General Agha Muhammad Yahya Khan , (Urdu: ; 4 February 1917 – 10 August 1980); commonly known as Yahya Khan, was a Pakistani military general who served as the third President of Pakistan and Chief Martial Law Administrator following his p ...
(25 March 1969 – 20 December 1971), both West Pakistanis. The situation reached a climax in 1970, when the Bangladesh Awami League
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
, the largest East Pakistani political party, led by Sheikh Mujibur Rahman
Sheikh Mujibur Rahman ( bn, শেখ মুজিবুর রহমান; 17 March 1920 – 15 August 1975), often shortened as Sheikh Mujib or Mujib and widely known as Bangabandhu (meaning ''Friend of Bengal''), was a Bengali politi ...
, won a landslide victory in the national elections. The party won 167 of the 169 seats allotted to East Pakistan, and thus a majority of the 313 seats in the National Assembly. This gave the Awami League the constitutional right to form a government. However, Zulfikar Ali Bhutto
Zulfikar (or Zulfiqar) Ali Bhutto ( ur, , sd, ذوالفقار علي ڀٽو; 5 January 1928 – 4 April 1979), also known as Quaid-e-Awam ("the People's Leader"), was a Pakistani barrister, politician and statesman who served as the fourt ...
(a former Foreign Minister), the leader of the Pakistan People's Party
The Pakistan People's Party ( ur, , ; PPP) is a centre-left, social-democratic political party in Pakistan. It is currently the third largest party in the National Assembly and second largest in the Senate of Pakistan. The party was founded i ...
, refused to allow Rahman to become the Prime Minister of Pakistan.
Instead, he proposed the idea of having two Prime Ministers, one for each wing. The proposal elicited outrage in the east wing, already chafing under the other constitutional innovation, the "One Unit scheme". Bhutto also refused to accept Rahman's Six Points. On 3 March 1971, the two leaders of the two wings along with the President General Yahya Khan met in Dacca
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest Bengali-speaking city. It is the eighth largest and sixth most densely populated city i ...
to decide the fate of the country.
After their discussions yielded no satisfactory results, Sheikh Mujibur Rahman called for a nationwide strike. Bhutto feared a civil war, therefore, he sent his trusted companion, Mubashir Hassan
Mubashir Hassan ( ur, ; 22 January 1922 – 14 March 2020), was a Pakistani politician, humanist, political adviser, and an engineer who served in the capacity of Finance Minister in Bhutto administration from 1971 until 1974.
In 1967, Hass ...
. A message was conveyed, and Rahman decided to meet Bhutto. Upon his arrival, Rahman met with Bhutto and both agreed to form a coalition government with Rahman as premier and Bhutto as president; however, Sheikh Mujib later ruled out such possibility. Meanwhile, the military was unaware of these developments, and Bhutto increased his pressure on Rahman to reach a decision.
On 7 March 1971, Sheikh Mujibur Rahman (soon to be the prime minister) delivered a speech at the Racecourse Ground (now called the Suhrawardy Udyan
Suhrawardy Udyan ( bn, সোহরাওয়ার্দী উদ্যান) formerly known as Ramna Race Course ground is a national memorial located in Dhaka, Bangladesh. It is named after Huseyn Shaheed Suhrawardy. Originally it serve ...
). In this speech he mentioned a further four-point condition to consider at the National Assembly Meeting on 25 March:
* The immediate lifting of martial law
Martial law is the imposition of direct military control of normal civil functions or suspension of civil law by a government, especially in response to an emergency where civil forces are overwhelmed, or in an occupied territory.
Use
Martia ...
.
* Immediate withdrawal of all military personnel to their barracks.
* An inquiry into the loss of life.
* Immediate transfer of power to the elected representative of the people before the assembly meeting 25 March.
He urged his people to turn every house into a fort of resistance. He closed his speech saying, "Our struggle is for our freedom. Our struggle is for our independence." This speech is considered the main event that inspired the nation to fight for its independence. General Tikka Khan
General Tikka Khan ( ur, ٹکا خان; 10 February 1915 – 28 March 2002) was a Pakistan Army general who was the first chief of army staff from 3 March 1972 until retiring on 1 March 1976. Along with Yahya Khan, he is considered a chief a ...
was flown into Dacca to become Governor of East Bengal. East-Pakistani judges, including Justice Siddique, refused to swear him in.
Between 10 and 13 March, Pakistan International Airlines
Pakistan International Airlines ( ur, ; abbreviated PIA, ur, ) is an international airline that serves as the national flag carrier of Pakistan under the administrative control of the Aviation Secretary of Pakistan, Secretary to the Governme ...
cancelled all their international routes to urgently fly "government passengers" to Dacca. These "government passengers" were almost all Pakistani soldiers in civilian dress. MV ''Swat'', a ship of the Pakistan Navy carrying ammunition and soldiers, was harboured in Chittagong
Chittagong ( /ˈtʃɪt əˌɡɒŋ/ ''chit-uh-gong''; ctg, চিটাং; bn, চিটাগং), officially Chattogram ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম), is the second-largest city in Bangladesh after Dhaka and third largest city in ...
Port, but the Bengali workers and sailors at the port refused to unload the ship. A unit of East Pakistan Rifles
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
refused to obey commands to fire on the Bengali demonstrators, beginning a mutiny among the Bengali soldiers.
Response to the 1970 cyclone
The 1970 Bhola cyclone madelandfall
Landfall is the event of a storm moving over land after being over water. More broadly, and in relation to human travel, it refers to 'the first land that is reached or seen at the end of a journey across the sea or through the air, or the fact ...
on the East Pakistan coastline during the evening of 12 November, around the same time as a local high tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables c ...
, killing an estimated 300,000 people. A 2017 World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
The WMO originated from the Inter ...
panel considers it the deadliest tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Dep ...
since at least 1873. A week after the landfall, President Khan conceded that his government had made "slips" and "mistakes" in its handling of the relief efforts due to a lack of understanding of the magnitude of the disaster.
A statement released by eleven political leaders in East Pakistan ten days after the cyclone hit charged the government with "gross neglect, callous and utter indifference". They also accused the president of playing down the magnitude of the problem in news coverage. On 19 November, students held a march in Dacca protesting the slowness of the government's response. Abdul Hamid Khan Bhashani
Abdul Hamid Khan Bhashani (12 December 1880 – 17 November 1976), often shortened as Maulana Bhashani, was a Bengali politician. His political tenure spanned the British colonial India, Pakistan and Bangladesh periods.
Maulana Bhashani was po ...
addressed a rally of 50,000 people on 24 November, where he accused the president of inefficiency and demanded his resignation.
As the conflict between East and West Pakistan developed in March, the Dacca offices of the two government organisations directly involved in relief efforts were closed for at least two weeks, first by a general strike
A general strike refers to a strike action in which participants cease all economic activity, such as working, to strengthen the bargaining position of a trade union or achieve a common social or political goal. They are organised by large coa ...
and then by a ban on government work in East Pakistan by the Awami League In Urdu language, Awami is the adjectival form for '' Awam'', the Urdu language word for common people.
The adjective appears in the following proper names:
*Awami Colony, a neighbourhood of Landhi Town in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
*Awami Front, wa ...
. With this increase in tension, foreign personnel were evacuated over fears of violence. Relief work continued in the field, but long-term planning was curtailed. This conflict widened into the Bangladesh Liberation War in December and concluded with the creation of Bangladesh. This was one of the first times that a natural event helped trigger a civil war.
Operation Searchlight
Pakistan Army
The Pakistan Army (, ) is the land service branch of the Pakistan Armed Forces. The roots of its modern existence trace back to the British Indian Army that ceased to exist following the Partition of British India, which occurred as a result ...
—codenamed ''Operation Searchlight''—started on 25 March 1971 to curb the Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
independence movement by taking control of the major cities on 26 March, and then eliminating all opposition, political or military, within one month. The Pakistani state used anti-Bihari violence by Bengalis in early March to justify launching Operation Searchlight.
Before the beginning of the operation, all foreign journalists were systematically deported from East Pakistan.
The main phase of Operation Searchlight ended with the fall of the last major town in Bengali hands in mid-May. The operation also began the 1971 Bangladesh genocide
The genocide in Bangladesh began on 25 March 1971 with the launch of Operation Searchlight, as the government of Pakistan, dominated by West Pakistan, began a military crackdown on East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) to suppress Bengali call ...
. These systematic killings served only to enrage the Bengalis, which ultimately resulted in the secession of East Pakistan later in the same year. Bangladeshi media and reference books in English have published casualty figures which vary greatly, from 5,000 to 35,000 in Dacca, and 200,000 to 3,000,000 for Bangladesh as a whole, although independent researchers, including the British Medical Journal
''The BMJ'' is a weekly peer-reviewed medical trade journal, published by the trade union the British Medical Association (BMA). ''The BMJ'' has editorial freedom from the BMA. It is one of the world's oldest general medical journals. Origi ...
, have put forward the figure ranging from between 125,000 and 505,000. American political scientist
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and power, and the analysis of political activities, political thought, political behavior, and associated constitutions and la ...
Rudolph Rummel
Rudolph Joseph Rummel (October 21, 1932 – March 2, 2014) was an American political scientist and professor at the Indiana University, Yale University, and University of Hawaiʻi. He spent his career studying data on collective violence and war w ...
puts total deaths at 1.5 million. The atrocities have been referred to as acts of genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the ...
.
According to the ''Asia Times'',
Although the violence focused on the provincial capital, Dacca, it also affected all parts of East Pakistan. Residential halls of the University of Dacca
The University of Dhaka (also known as Dhaka University, or DU) is a public research university located in Dhaka, Bangladesh. It is the oldest university in Bangladesh. The university opened its doors to students on July 1st 1921. Currently it ...
were particularly targeted. The only Hindu residential hall—Jagannath Hall
Jagannath Hall of Dhaka University is a residence hall for minority students, Hindu, Buddhist, Christian, and others. It is one of the three original residence halls that date from when the University was founded in 1921, and like them is modelled ...
—was destroyed by the Pakistani armed forces, and an estimated 600 to 700 of its residents were murdered. The Pakistani army denied any cold blooded killings at the university, though the Hamoodur Rahman Commission
The Hamoodur Rahman Commission (otherwise known as War Enquiry Commission), was a judicial inquiry commission that assessed Pakistan's political–military involvement in East-Pakistan from 1947 to 1971. The commission was set up on 26 Decem ...
in Pakistan concluded that overwhelming force was used at the university. This fact, and the massacre at Jagannath Hall and nearby student dormitories of Dacca University, are corroborated by a videotape secretly filmed by Professor Nurul Ula of the East Pakistan University of Engineering and Technology
Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, commonly known by the acronym BUET, is a public technological research university in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Founded in 1876 as the Dacca Survey School, it is the oldest institution for the stud ...
, whose residence was directly opposite the student dormitories.
The scale of the atrocities was first made clear in the West when Anthony Mascarenhas
Neville Anthony Mascarenhas (10 July 1928 – 3 December 1986) was a Pakistani journalist and author. His works include exposés on the brutality of Pakistan's military during the 1971 independence movement of Bangladesh, ''The Rape of Bangla ...
, a Pakistani journalist who had been sent to the province by the military authorities to write a story favourable to Pakistan's actions, instead fled to the United Kingdom and, on 13 June 1971, published an article in ''The Sunday Times
''The Sunday Times'' is a British newspaper whose circulation makes it the largest in Britain's quality press market category. It was founded in 1821 as ''The New Observer''. It is published by Times Newspapers Ltd, a subsidiary of News UK, whi ...
'' describing the systematic killings by the military. The BBC wrote: "There is little doubt that Mascarenhas' reportage played its part in ending the war. It helped turn world opinion against Pakistan and encouraged India to play a decisive role", with Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (; ''née'' Nehru; 19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was an Indian politician and a central figure of the Indian National Congress. She was elected as third prime minister of India in 1966 and was al ...
herself stating that Mascarenhas' article has led her "to prepare the ground for India's armed intervention".
Sheikh Mujibur Rahman was arrested by the Pakistani Army. Yahya Khan appointed Brigadier (later General) Rahimuddin Khan
Rahimuddin Khan (21 July 1926 – 22 August 2022) was a general of the Pakistan Army who served as the 4th Chairman Joint Chiefs of Staff Committee from 1984 to 1987, after serving as the 7th governor of Balochistan from 1978 to 1984. He also ...
to preside over a special tribunal prosecuting Rahman with multiple charges. The tribunal's sentence was never made public, but Yahya caused the verdict to be held in abeyance in any case. Other Awami League leaders were arrested as well, while a few fled Dacca to avoid arrest. The Awami League was banned by General Yahya Khan.
Declaration of independence
The violence unleashed by the Pakistani forces on 25 March 1971 proved the last straw to the efforts to negotiate a settlement. Following these incidents, Sheikh Mujibur Rahman signed an official declaration that read: Sheikh Mujib also called upon the people to resist the occupation forces through a radio message. Rahman was arrested on the night of 25–26 March 1971 at about 1:30 am (as per Radio Pakistan's news on 29 March 1971). A telegram containing the text of Sheikh Mujibur Rahman's declaration reached some students inChittagong
Chittagong ( /ˈtʃɪt əˌɡɒŋ/ ''chit-uh-gong''; ctg, চিটাং; bn, চিটাগং), officially Chattogram ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম), is the second-largest city in Bangladesh after Dhaka and third largest city in ...
. The message was translated to Bengali by Dr. Manjula Anwar. The students failed to secure permission from higher authorities to broadcast the message from the nearby Agrabad Station of Pakistan Broadcasting Corporation
Radio Pakistan serves as the national public broadcaster for radio in Pakistan. Although some local stations predate Radio Pakistan's founding, it is the oldest existing broadcasting network in Pakistan. The network was established on 14 August ...
. However, the message was read several times by the independent Swadhin Bangla Betar Kendro Radio established by some rebel Bangali Radio workers in Kalurghat. Major Ziaur Rahman was requested to provide security of the station and he also read the Declaration on 27 March 1971. Major Ziaur Rahman
Lt. General Ziaur Rahman (19 January 1936 – 30 May 1981), was a Bangladeshi military officer and politician who served as the President of Bangladesh from 1977 to 1981. He was assassinated on 30 May 1981 in Chittagong in an army coup ...
broadcast announcement of the declaration of independence on behalf of Sheikh Mujibur Rahman.
The Kalurghat
Kalurghat ( bn, কালুরঘাট) is located several miles north of the port city of Chittagong, Bangladesh, and is mostly famous for several heavy industries located there. A bridge near Kalurghat on the Karnaphuli River connects Chittag ...
Radio Station's transmission capability was limited, but the message was picked up by a Japanese ship in the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line bet ...
. It was then re-transmitted by Radio Australia
ABC Radio Australia, also known as Radio Australia, is the international broadcasting and online service operated by the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC), Australia's public broadcaster. Most programming is in English, with some in T ...
and later by the BBC.
M. A. Hannan
M. A. Hannan (February 10, 1930 – June 12, 1974) was a politician of Bangladesh.
Early life
M. A. Hannan born in Tehat, West Bengal on 10 February 1930. His father was Maulana Muhammad Muhibur Rahman, who was a Congress politician who later ...
, an Awami League leader from Chittagong, is said to have made the first announcement of the declaration of independence over the radio on 26 March 1971.
26 March 1971 is considered the official Independence Day of Bangladesh, and the name Bangladesh was in effect henceforth. In July 1971, Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (; ''née'' Nehru; 19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was an Indian politician and a central figure of the Indian National Congress. She was elected as third prime minister of India in 1966 and was al ...
openly referred to the former East Pakistan as Bangladesh. Some Pakistani and Indian officials continued to use the name "East Pakistan" until 16 December 1971.
Liberation war
March–June
At first, resistance was spontaneous and disorganised, and was not expected to be prolonged. However, when the Pakistani Army cracked down upon the population, resistance grew. TheMukti Bahini
The Mukti Bahini ( bn, মুক্তিবাহিনী, translates as 'freedom fighters', or liberation army), also known as the Bangladesh Forces, was the guerrilla resistance movement consisting of the Bangladeshi military, paramilitary ...
became increasingly active. The Pakistani military sought to quell them, but increasing numbers of Bengali soldiers defected to this underground "Bangladesh army". These Bengali units slowly merged into the Mukti Bahini and bolstered their weaponry with supplies from India. Pakistan responded by airlifting in two infantry divisions and reorganising their forces. They also raised paramilitary forces of Razakars Razakar (رضا کار) is etymologically an Arabic word which literally means volunteer. The word is also common in Urdu language as a loanword. On the other hand, in Bangladesh, razakar is a pejorative word meaning a traitor or Judas.
In Pakis ...
, Al-Badrs and Al-Shams (who were mostly members of the Muslim League and other Islamist groups), as well as other Bengalis who opposed independence, and Bihari Muslims who had settled during the time of Partition of India, partition.
On 17 April 1971, a Provisional Government of Bangladesh, provisional government was formed in Meherpur District in western Bangladesh bordering India with Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, who was in prison in Pakistan, as president, Syed Nazrul Islam as acting president, Tajuddin Ahmad as prime minister, and General M. A. G. Osmani, Muhammad Ataul Ghani Osmani as Commander-in-Chief, Bangladesh Forces. As fighting grew between the occupation army and the Bengali Mukti Bahini, an estimated 10 million Bengalis sought refuge in the Indian states of Assam and West Bengal.
June–September
 Bangladesh forces command was set up on 11 July, with Col. M. A. G. Osmani as commander-in-chief (C-in-C) with the status of Cabinet Minister, Lt. Col., Abdur Rabb as chief of Staff (COS), Group Captain A K Khandker as Deputy Chief of Staff (DCOS) and Major A R Chowdhury as Assistant Chief of Staff (ACOS).
General Osmani had differences of opinion with the Indian leadership regarding the role of the Mukti Bahini in the conflict. Indian leadership initially envisioned a well trained force of 8,000 guerrillas, operating in small cells around Bangladesh to facilitate eventual conventional combat. With the Bangladesh government in exile, General Osmani favoured a different strategy:
* Bengali conventional forces would occupy lodgments inside Bangladesh and then the Bangladesh government would request international diplomatic recognition and intervention. Initially Mymensingh was picked for this operation, but Gen. Osmani later settled on Sylhet.
* Sending the maximum number of guerrillas into Bangladesh as soon as possible with the following objectives:
** Increasing Pakistani casualties through raids and ambush.
** Cripple economic activity by hitting power stations, railway lines, storage depots and communication networks.
** Destroy Pakistan army mobility by blowing up bridges/culverts, fuel depots, trains and river crafts.
** The strategic objective was to make the Pakistanis spread their forces inside the province, so attacks could be made on isolated Pakistani detachments.
Bangladesh was divided into List of sectors in the Bangladesh Liberation War, eleven sectors in July, each with a commander chosen from defected officers of the Pakistani army who joined the Mukti Bahini to lead guerrilla operations. The Mukti Bahini forces were given two to five weeks of training by the Indian army on guerilla warfare. Most of their training camps were situated near the border area and were operated with assistance from India. The 10th Sector was directly placed under the Commander in Chief (C-in-C) General M. A. G. Osmani and included the Naval Commandos and C-in-C's special force. Three brigades (11 Battalions) were raised for conventional warfare; a large guerrilla force (estimated at 100,000) was trained.
Five infantry battalions were reformed and positioned along the northern and eastern borders of Bangladesh. Three more battalions were raised, and artillery batteries were formed. During June and July, Mukti Bahini had regrouped across the border with Indian aid through
Bangladesh forces command was set up on 11 July, with Col. M. A. G. Osmani as commander-in-chief (C-in-C) with the status of Cabinet Minister, Lt. Col., Abdur Rabb as chief of Staff (COS), Group Captain A K Khandker as Deputy Chief of Staff (DCOS) and Major A R Chowdhury as Assistant Chief of Staff (ACOS).
General Osmani had differences of opinion with the Indian leadership regarding the role of the Mukti Bahini in the conflict. Indian leadership initially envisioned a well trained force of 8,000 guerrillas, operating in small cells around Bangladesh to facilitate eventual conventional combat. With the Bangladesh government in exile, General Osmani favoured a different strategy:
* Bengali conventional forces would occupy lodgments inside Bangladesh and then the Bangladesh government would request international diplomatic recognition and intervention. Initially Mymensingh was picked for this operation, but Gen. Osmani later settled on Sylhet.
* Sending the maximum number of guerrillas into Bangladesh as soon as possible with the following objectives:
** Increasing Pakistani casualties through raids and ambush.
** Cripple economic activity by hitting power stations, railway lines, storage depots and communication networks.
** Destroy Pakistan army mobility by blowing up bridges/culverts, fuel depots, trains and river crafts.
** The strategic objective was to make the Pakistanis spread their forces inside the province, so attacks could be made on isolated Pakistani detachments.
Bangladesh was divided into List of sectors in the Bangladesh Liberation War, eleven sectors in July, each with a commander chosen from defected officers of the Pakistani army who joined the Mukti Bahini to lead guerrilla operations. The Mukti Bahini forces were given two to five weeks of training by the Indian army on guerilla warfare. Most of their training camps were situated near the border area and were operated with assistance from India. The 10th Sector was directly placed under the Commander in Chief (C-in-C) General M. A. G. Osmani and included the Naval Commandos and C-in-C's special force. Three brigades (11 Battalions) were raised for conventional warfare; a large guerrilla force (estimated at 100,000) was trained.
Five infantry battalions were reformed and positioned along the northern and eastern borders of Bangladesh. Three more battalions were raised, and artillery batteries were formed. During June and July, Mukti Bahini had regrouped across the border with Indian aid through Operation Jackpot
The Operation Jackpot was a codename for three operations undertaken by Bengali ''Mukti Bahini'' in former East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) against the Federation of Pakistan during the climax of the Bangladesh Liberation War.''Surrender at Dac ...
and began sending 2000–5000 guerrillas across the border, the so-called Monsoon Offensive, which for various reasons (lack of proper training, supply shortage, lack of a proper support network inside Bangladesh) failed to achieve its objectives. Bengali regular forces also attacked border outposts in Mymensingh, Comilla and Sylhet, but the results were mixed. Pakistani authorities concluded that they had successfully contained the Monsoon Offensive, which proved a near-accurate observation.
Guerrilla operations, which slackened during the training phase, picked up after August. Economic and military targets in Dacca were attacked. The major success story was Operation Jackpot, in which naval commandos mined and blew up berthed ships in Chittagong, Port of Mongla, Mongla, Narayanganj and Chandpur District, Chandpur on 15 August 1971.
October–December
Bangladeshi conventional forces attacked border outposts. Kamalpur, Belonia and the Battle of Boyra are a few examples. 90 out of 370 border outposts fell to Bengali forces. Guerrilla attacks intensified, as did Pakistani and Razakar reprisals on civilian populations. Pakistani forces were reinforced by eight battalions from West Pakistan. The Bangladeshi independence fighters even managed to temporarily capture Aerodrome#Airstrip, airstrips at Lalmonirhat District, Lalmonirhat and Shalutikar. Both of these were used for flying in supplies and arms from India. Pakistan sent another five battalions from West Pakistan as reinforcements.Indian involvement

 Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi had concluded that instead of taking in millions of refugees, India would be economically better off going to war against Pakistan. As early as 28 April 1971, the Indian Cabinet had asked General Sam Manekshaw, Manekshaw (Chairman of the Chiefs of Staff Committee) to "Go into East Pakistan". Hostile relations in the past between India and Pakistan added to India's decision to intervene in Pakistan's civil war.
As a result, the Indian government decided to support the creation of a separate state for ethnic Bengalis by supporting the
Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi had concluded that instead of taking in millions of refugees, India would be economically better off going to war against Pakistan. As early as 28 April 1971, the Indian Cabinet had asked General Sam Manekshaw, Manekshaw (Chairman of the Chiefs of Staff Committee) to "Go into East Pakistan". Hostile relations in the past between India and Pakistan added to India's decision to intervene in Pakistan's civil war.
As a result, the Indian government decided to support the creation of a separate state for ethnic Bengalis by supporting the Mukti Bahini
The Mukti Bahini ( bn, মুক্তিবাহিনী, translates as 'freedom fighters', or liberation army), also known as the Bangladesh Forces, was the guerrilla resistance movement consisting of the Bangladeshi military, paramilitary ...
. Research and Analysis Wing, RAW helped to organise, train and arm these insurgents. Consequently, the Mukti Bahini succeeded in harassing Pakistani military in East Pakistan, thus creating conditions conducive for a full-scale Indian military intervention in early December.
The Pakistan Air Force (PAF) launched Operation Chengiz Khan, a pre-emptive strike on Indian Air Force bases on 3 December 1971. The attack was modelled on the Israeli Air Force's Operation Focus during the Six-Day War, and intended to neutralise the Indian Air Force planes on the ground. The strike was seen by India as an open act of unprovoked aggression, which marked the official start of the Indo-Pakistani War. As a response to the attack, both India and Pakistan formally acknowledged the "existence of a state of war between the two countries" even though neither government had formally issued a declaration of war.
Three Indian corps were involved in the liberation of East Pakistan. They were supported by nearly three brigades of Mukti Bahini fighting alongside them, and many more who were fighting irregularly. That was far superior to the Pakistani army of three division (military), divisions. The Indians quickly overran the country, selectively engaging or bypassing heavily defended strongholds. Pakistani forces were unable to effectively counter the Indian attack, as they had been deployed in small units around the border to counter the guerrilla attacks by the Mukti Bahini. Unable to defend Dacca, the Pakistanis surrendered on 16 December 1971.
Air and naval war
The Indian Air Force carried out several sorties against Pakistan, and within a week, IAF aircraft dominated the skies of East Pakistan. It East Pakistan Air Operations, 1971, achieved near-totalair supremacy
Aerial supremacy (also air superiority) is the degree to which a side in a conflict holds control of air power over opposing forces. There are levels of control of the air in aerial warfare. Control of the air is the aerial equivalent of comm ...
by the end of the first week, as the entire Pakistani air contingent in the east, PAF No.14 Squadron, was grounded because of Indian and Bangladesh airstrikes at Tejgaon, Kurmitolla, Lalmonirhat and Shamsher Nagar. Hawker Sea Hawk, Sea Hawks from the carrier also struck Chittagong, Barisal and Cox's Bazar, destroying the eastern wing of the Pakistan Navy and effectively blockading the East Pakistan ports, thereby cutting off any escape routes for the stranded Pakistani soldiers. The nascent Bangladesh Navy (comprising officers and sailors who defected from the Pakistani Navy) aided the Indians in the marine warfare, carrying out attacks, most notably Operation Jackpot
The Operation Jackpot was a codename for three operations undertaken by Bengali ''Mukti Bahini'' in former East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) against the Federation of Pakistan during the climax of the Bangladesh Liberation War.''Surrender at Dac ...
.
Surrender and aftermath

 On 16 December 1971, Lt. Gen Amir Abdullah Khan Niazi, Chief Martial Law Administrator of
On 16 December 1971, Lt. Gen Amir Abdullah Khan Niazi, Chief Martial Law Administrator of East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Myanmar, wit ...
and Commander of Pakistan Army forces located in East Pakistan signed the Pakistani Instrument of Surrender, Instrument of Surrender. At the time of surrender only a few countries had provided International recognition of Bangladesh, diplomatic recognition to the new nation. Over 93,000 Pakistani troops surrendered to the Indian forces and Bangladesh Liberation forces, making it the largest surrender since World War II.
Bangladesh sought admission to the UN with most voting in its favour. China vetoed this as Pakistan was its key ally. The United States, also a key ally of Pakistan, was one of the last nations to accord Bangladesh recognition. To ensure a smooth transition, in 1972 the Simla Agreement was signed between India and Pakistan. The treaty ensured that Pakistan recognised the independence of Bangladesh in exchange for the return of the Pakistani Prisoner of war, PoWs.
India treated all the PoWs in strict accordance with the Geneva Convention, rule 1925. It released more than 93,000 Pakistani PoWs in five months. Further, as a gesture of goodwill, nearly 200 soldiers who were sought for war crimes by Bengalis were also pardoned by India. The accord also gave back of land that Indian troops had seized in West Pakistan during the war, though India retained a few strategic areas; most notably Kargil district, Kargil (which would in turn again be the focal point for Kargil War, a war between the two nations in 1999). This was done as a measure of promoting "lasting peace" and was acknowledged by many observers as a sign of maturity by India. However, some in India felt that the treaty had been too lenient to Bhutto, who had pleaded for leniency, arguing that the fragile democracy in Pakistan would crumble if the accord was perceived as being overly harsh by Pakistanis.
Reaction in West Pakistan to the war
Reaction to the defeat and dismemberment of half the nation was a shocking loss to top military and civilians alike. Few had expected that they would lose the formal war in under a fortnight, and there was also unsettlement over what was perceived as a meek surrender of the army in East Pakistan.Yahya Khan
General Agha Muhammad Yahya Khan , (Urdu: ; 4 February 1917 – 10 August 1980); commonly known as Yahya Khan, was a Pakistani military general who served as the third President of Pakistan and Chief Martial Law Administrator following his p ...
's dictatorship collapsed and gave way to Bhutto, who took the opportunity to rise to power.
Amir Abdullah Khan Niazi, General Niazi, who surrendered along with 93,000 troops, was viewed with suspicion and contempt upon his return to Pakistan. He was shunned and branded a Treason, traitor. The war also exposed the shortcomings of Pakistan's declared strategic doctrine that the "defence of East Pakistan lay in West Pakistan".
Atrocities
During the war there were widespread killings and other atrocities—including the displacement of civilians in Bangladesh (East Pakistan at the time) and widespread violations of human rights began with the start ofOperation Searchlight
Operation Searchlight was the codename for a planned military operation carried out by the Pakistan Army in an effort to curb the Bengali nationalist movement in former East Pakistan in March 1971. Pakistan retrospectively justified the opera ...
on 25 March 1971. Members of the Pakistan Armed Forces, Pakistani military and supporting paramilitary forces killed an estimated 300,000 to 3,000,000 peopleWhite, Matthew, Death Tolls for the Major Wars and Atrocities of the Twentieth Century
'' and raped between 200,000 and 400,000 Bangladeshis, Bangladeshi women in a systematic campaign of genocidal rape. Pakistan's religious leaders openly supported the crime by labelling Mukti Bahini, Bengali freedom fighters as "Hindus" and Bengali women as "the booty of war". But in reality, more than 80 percent of the Bengali people were Muslims at that time. A large section of the intellectual community of Bangladesh were murdered, mostly by the Al-Shams and
Al-Badr
Al Badr is a village in Mecca Province, in western Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it ...
forces, at the instruction of the Pakistani Army. Just two days before the surrender, on 14 December 1971, Pakistan Army and Razakar militia (local collaborators) picked up at least 100 physicians, professors, writers and engineers in Dacca, and murdered them, leaving the dead bodies in a mass grave.
 Many mass graves have been discovered in Bangladesh. The first night of war on Bengalis, which is documented in telegrams from the American Consulate in Dacca to the United States State Department, saw indiscriminate killings of students of University of Dhaka, Dacca University and other civilians. Numerous women were tortured, raped and killed during the war; the exact numbers are not known and are a subject of debate. The widespread rape of Bangladeshi women led to birth of thousands of War children, war babies.
The Pakistan Army also kept numerous Bengali women as sex-slaves inside the Dacca Cantonment. Most of the girls were captured from Dacca University and private homes. There was significant sectarian violence not only perpetrated and encouraged by the Pakistani army,U.S. Consulate (Dacca) Cable, Sitrep
Many mass graves have been discovered in Bangladesh. The first night of war on Bengalis, which is documented in telegrams from the American Consulate in Dacca to the United States State Department, saw indiscriminate killings of students of University of Dhaka, Dacca University and other civilians. Numerous women were tortured, raped and killed during the war; the exact numbers are not known and are a subject of debate. The widespread rape of Bangladeshi women led to birth of thousands of War children, war babies.
The Pakistan Army also kept numerous Bengali women as sex-slaves inside the Dacca Cantonment. Most of the girls were captured from Dacca University and private homes. There was significant sectarian violence not only perpetrated and encouraged by the Pakistani army,U.S. Consulate (Dacca) Cable, SitrepArmy Terror Campaign Continues in Dacca; Evidence Military Faces Some Difficulties Elsewhere
, 31 March 1971, Confidential, 3 pp but also by Bengali nationalists against non-Bengali minorities, especially Biharis. In June 1971, Bihari representatives stated that 500,000 Biharis were killed by Bengalis. R. J. Rummel gives a prudent estimate of 150,000 killed. On 16 December 2002, the George Washington University's National Security Archive published a collection of declassified documents, consisting mostly of communications between US embassy officials and United States Information Agency, United States Information Service centres in Dacca and India, and officials in Washington, D.C. These documents show that US officials working in diplomatic institutions within Bangladesh used the terms "selective genocide"U.S. Consulate in Dacca (27 March 1971),
Selective genocide
'', Cable (PDF) and "genocide" (see Archer Blood#The Blood telegram, The Blood Telegram) for information on events they had knowledge of at the time. ''Genocide'' is the term that is still used to describe the event in almost every major publication and newspaper in Bangladesh, although in Pakistan, the accusations against Pakistani forces continue to be disputed.
International reactions
 Following Sheikh Mujibur Rahman's declaration of independence in March 1971, a worldwide campaign was undertaken by the Provisional Government of Bangladesh to drum up political support for the independence of East Pakistan as well as humanitarian support for the Bengali people.
Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi provided extensive diplomatic and political support to the Bangladesh movement. She toured many countries in a bid to create awareness of the Pakistani atrocities against Bengalis. This effort was to prove vital later during the war, in framing the world's context of the war and to justify military action by India. Also, following Pakistan's defeat, it ensured prompt recognition of the newly independent state of Bangladesh.
Following Sheikh Mujibur Rahman's declaration of independence in March 1971, a worldwide campaign was undertaken by the Provisional Government of Bangladesh to drum up political support for the independence of East Pakistan as well as humanitarian support for the Bengali people.
Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi provided extensive diplomatic and political support to the Bangladesh movement. She toured many countries in a bid to create awareness of the Pakistani atrocities against Bengalis. This effort was to prove vital later during the war, in framing the world's context of the war and to justify military action by India. Also, following Pakistan's defeat, it ensured prompt recognition of the newly independent state of Bangladesh.
United Nations
Though the United Nations condemned the human rights violations during and following Operation Searchlight, it failed to defuse the situation politically before the start of the war. Following India's entry into the war, Pakistan, fearing certain defeat, made urgent appeals to the United Nations to intervene and force India to agree to a ceasefire. The United Nations Security Council, UN Security Council assembled on 4 December 1971 to discuss the hostilities in South Asia. After lengthy discussions on 7 December, the United States made a resolution for "immediate cease-fire and withdrawal of troops". While supported by the majority, the USSR vetoed the resolution twice. In light of the Pakistani atrocities against Bengalis, the United Kingdom and France abstained on the resolution. On 12 December, with Pakistan facing imminent defeat, the United States requested that the Security Council be reconvened. Pakistan's Deputy Prime Minister and Foreign Minister, Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, was rushed to New York City to make the case for a resolution on the cease fire. The council continued deliberations for four days. By the time proposals were finalised, Pakistan's forces in the East had surrendered and the war had ended, making the measures merely academic. Bhutto, frustrated by the failure of the resolution and the inaction of the United Nations, ripped up his speech and left the council. Most UN member nations were quick to recognise Bangladesh within months of its independence.Bhutan
As the Bangladesh Liberation War approached the defeat of the Pakistan Army, the Himalayan kingdom of Bhutan became the first state in the world to recognise the newly independent country on 6 December 1971.Sheikh Mujibur Rahman
Sheikh Mujibur Rahman ( bn, শেখ মুজিবুর রহমান; 17 March 1920 – 15 August 1975), often shortened as Sheikh Mujib or Mujib and widely known as Bangabandhu (meaning ''Friend of Bengal''), was a Bengali politi ...
, the first President of Bangladesh visited Bhutan to attend the coronation of Jigme Singye Wangchuck, the fourth King of Bhutan in June 1974.
US and USSR
 The US government stood by its old ally Pakistan in terms of diplomacy and military threats. US President Richard Nixon and his National Security Advisor Henry Kissinger feared Soviet expansion into South and Southeast Asia. Pakistan was a close ally of the People's Republic of China, with whom Nixon had been negotiating a ''China–United States relations#Rapprochement, rapprochement'' and which he intended to visit in February 1972. Nixon feared that an Indian invasion of
The US government stood by its old ally Pakistan in terms of diplomacy and military threats. US President Richard Nixon and his National Security Advisor Henry Kissinger feared Soviet expansion into South and Southeast Asia. Pakistan was a close ally of the People's Republic of China, with whom Nixon had been negotiating a ''China–United States relations#Rapprochement, rapprochement'' and which he intended to visit in February 1972. Nixon feared that an Indian invasion of West Pakistan
West Pakistan ( ur, , translit=Mag̱ẖribī Pākistān, ; bn, পশ্চিম পাকিস্তান, translit=Pôścim Pakistan) was one of the two Provincial exclaves created during the One Unit Scheme in 1955 in Pakistan. It was ...
would mean total Soviet domination of the region, and that it would seriously undermine the global position of the United States and the regional position of America's new tacit ally, China.Shalom, Stephen R.The Men Behind Yahya in the Indo-Pak War of 1971
To demonstrate to China the ''bona fides'' of the United States as an ally, and in direct violation of the US Congress-imposed sanctions on Pakistan, Nixon sent military supplies to Pakistan and routed them through Jordan and Iran, while also encouraging China to increase its arms supplies to Pakistan. The Nixon administration also ignored reports it received of the genocidal activities of the Pakistani Army in East Pakistan, most notably the Archer Blood#The Blood telegram, Blood telegram.
 Nixon denied getting involved in the situation, saying that it was an internal matter of Pakistan, but when Pakistan's defeat seemed certain, Nixon sent the aircraft carrier USS Enterprise (CVN-65), USS ''Enterprise'' to the
Nixon denied getting involved in the situation, saying that it was an internal matter of Pakistan, but when Pakistan's defeat seemed certain, Nixon sent the aircraft carrier USS Enterprise (CVN-65), USS ''Enterprise'' to the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line bet ...
, a move deemed by the Indians as a nuclear threat. ''Enterprise'' arrived on station on 11 December 1971. On 6 and 13 December, the Soviet Navy dispatched two groups of ships, armed with nuclear missiles, from Vladivostok; they trailed US Task Force 74 in the Indian Ocean from 18 December until 7 January 1972.
The Soviet Union supported Bangladesh and Indian armies, as well as the Mukti Bahini
The Mukti Bahini ( bn, মুক্তিবাহিনী, translates as 'freedom fighters', or liberation army), also known as the Bangladesh Forces, was the guerrilla resistance movement consisting of the Bangladeshi military, paramilitary ...
during the war, recognising that the independence of Bangladesh would weaken the position of its rivals—the United States and the People's Republic of China. It gave assurances to India that if a confrontation with the United States or China developed, the USSR would take countermeasures. This was enshrined in the Indo-Soviet Treaty of Friendship and Cooperation, Indo-Soviet friendship treaty signed in August 1971. The Soviets also sent a nuclear submarine to ward off the threat posed by USS ''Enterprise'' in the Indian Ocean.
At the end of the war, the Warsaw Pact countries were among the first to recognise Bangladesh. The Soviet Union accorded recognition to Bangladesh on 25 January 1972. The United States delayed recognition for some months, before according it on 8 April 1972.
China
As a long-standing ally of Pakistan, the People's Republic of China reacted with alarm to the evolving situation in East Pakistan and the prospect of India invading West Pakistan and Pakistani-controlledKashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
. On 10 December 1971, US President Nixon instructed Henry Kissinger to ask the Chinese to move some forces toward the frontier with India. Nixon said, "Threaten to move forces or move them, Henry, that's what they must do now." Kissinger met with Huang Hua, China's Permanent Representative to the United Nations, later that evening.
The Chinese did not, however, respond to this encouragement, because unlike the Sino-Indian War, 1962 Sino-Indian War when India was caught entirely unaware, this time the Indian Army was prepared and had deployed eight mountain divisions to the Sino-Indian border to guard against such an eventuality. China instead threw its weight behind demands for an immediate ceasefire.
When Bangladesh applied for membership to the United Nations in 1972, China vetoed their application because two United Nations resolutions regarding the repatriation of Pakistani prisoners of war and civilians had not yet been implemented. China was also among the last countries to recognise independent Bangladesh, refusing to do so until 31 August 1975.
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka saw the partition of Pakistan as an example for themselves and feared India might use its enhanced power against them in the future. Despite the left wing government of Sirimavo Bandaranaike following a neutral non-aligned foreign policy, Sri Lanka decided to help Pakistan in the war. As Pakistani aircraft could not fly over Indian territory, they would have to take a longer route around India and so they stopped at Bandaranaike Airport in Sri Lanka where they were refuelled before flying toEast Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Myanmar, wit ...
.
Arab world
As many Arab countries were allied with both theUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
, it was easy for Kissinger to encourage them to participate. He sent letters to both, the Hussein of Jordan, King of Jordan and the Shah Faisal, King of Saudi Arabia. President Nixon gave permission for Jordan to send ten F-104s and promised to provide replacements. According to author Martin Bowman, "Libyan Northrop F-5, F-5s were reportedly deployed to Sargodha Airbase, Sargodha AFB, perhaps as a potential training unit to prepare Pakistani pilots for an influx of more F-5s from Saudi Arabia."
History of Libya under Muammar Gaddafi#Libyan Arab Republic (1969–1977), Libyan dictator Gaddafi also personally directed a strongly worded letter to Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (; ''née'' Nehru; 19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was an Indian politician and a central figure of the Indian National Congress. She was elected as third prime minister of India in 1966 and was al ...
accusing her of aggression against Pakistan, which endeared him to all Pakistanis. In addition to these three countries, an unidentified Middle Eastern ally also supplied Pakistan with Mirage IIIs. However, other countries such as Syria and Tunisia were against interfering describing it as an internal matter of Pakistan.
In popular culture
See also
* Awards and decorations of the Bangladesh Liberation War * Liberation War Museum * Movement demanding trial of war criminals (Bangladesh) * NAP-Communist Party-Students Union Special Guerrilla ForcesNotes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Ayoob, Mohammed and K. Subrahmanyam, Subrahmanyam, K., ''The Liberation War'', S. Chand and Co. pvt Ltd. New Delhi, 1972. * Bass, Gary J. ''The Blood Telegram: Nixon, Kissinger, and a Forgotten Genocide.'' Vintage, 2014. * Bhargava, G.S., ''Crush India or Pakistan's Death Wish'', ISSD, New Delhi, 1972. * Bhattacharyya, S. K., ''Genocide in East Pakistan/Bangladesh: A Horror Story'', A. Ghosh Publishers, 1988. * Blood, A. K. (2005). The cruel birth of Bangladesh: Memoirs of an American diplomat. Dhaka: University Press. * Susan Brownmiller, Brownmiller, Susan: ''Against Our Will: Men, Women, and Rape'', Ballantine Books, 1993. * * * Govt. of Bangladesh, ''Documents of the war of Independence'', Vol 01–16, Ministry of Information. * Hitchens, Christopher, ''The Trials of Henry Kissinger'', Verso (2001). * Kanjilal, Kalidas, ''The Perishing Humanity'', Sahitya Loke, Calcutta, 1976 * Johnson, Rob, 'A Region in Turmoil' (New York and London, 2005) * Malik, Amita, ''The Year of the Vulture'', Orient Longmans, New Delhi, 1972. * Matinuddin, General Kamal, ''Tragedy of Errors: East Pakistan Crisis, 1968–1971'', Wajidalis, Lahore, Pakistan, 1994. * Mookherjee, Nayanika, ''A Lot of History: Sexual Violence, Public Memories and the Bangladesh Liberation War of 1971'', D.Phil. thesis in Social Anthropology, SOAS, University of London, 2002. * National Security ArchiveThe Tilt: the U.S. and the South Asian Crisis of 1971
* Quereshi, Major General Hakeem Arshad, ''The 1971 Indo-Pak War, A Soldiers Narrative'', Oxford University Press, 2002. * Raghavan, Srinath, ''1971: A Global History of the Creation of Bangladesh,'' Harvard Univ. Press, 2013. * Rummel, R. J., ''Death By Government'', Transaction Publishers, 1997. * Sisson, Richard & Rose, Leo, ''War and secession: Pakistan, India, and the creation of Bangladesh'', University of California Press (Berkeley), 1990. * Stephen, Pierre, and Payne, Robert, ''Massacre'', Macmillan, New York, (1973). * Totten, Samuel et al., eds., ''Century of Genocide: Eyewitness Accounts and Critical Views'', Garland Reference Library, 1997 * US Department of State Office of the Historian
''Foreign Relations of the United States, 1969–1976, Volume XI, South Asia Crisis, 1971''
* Zaheer, Hasan: ''The separation of East Pakistan: The rise and realisation of Bengali Muslim nationalism'', Oxford University Press, 1994. *
External links
*1971 Bangladesh Genocide Archive
Freedom In the Air
The Daily Star
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20030501230820/http://www.bangladeshmariners.com/HmdrRprt/71mass.html 1971 Massacre in Bangladesh and the Fallacy in the Hamoodur Rahman Commission Report, Dr. M.A. Hasan]
Women of Pakistan Apologize for War Crimes, 1996
Sheikh Mujib wanted a confederation: US papers, by Anwar Iqbal, Dawn, 7 July 2005
Bangladesh Liberation War Picture Gallery
Graphic images, viewer discretion advised
1971 War: How Russia sank Nixon's gunboat diplomacy
PM reiterated her vow to declare March 25 as Genocide Day
Call for international recognition and observance of genocide day
Genocide Day: As it was in March 1971
The case for UN recognition of Bangladesh genocide
{{Authority control Bangladesh Liberation War, Separatism in Pakistan Civil wars involving the states and peoples of Asia Civil wars post-1945 War crimes in Bangladesh Wars involving Bangladesh Military history of Bangladesh Wars involving Pakistan Bangladesh–Pakistan relations, War