Back Pain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Back pain is
Diagnosis and treatment of back pain
. ''Radiologic Technology''&nbs
serial online
November 2007;79(2):126–204. Available from: CINAHL Plus with Full Text, Ipswich, MA. Accessed December 12, 2017. An episode of back pain may be
"Diagnosis and Management of Acute Low Back Pain"
American Academy of Family Physicians. Retrieved March 12, 2007
Alternate Link
/ref> Some estimate that as many of 95% of people will experience back pain at some point in their lifetime. It is the most common cause of chronic pain and is a major contributor to missed work and disability. For most individuals, back pain is self-limiting. Most people with back pain do not experience chronic severe pain but rather persistent or intermittent pain that is mild or moderate. In most cases of
"2010 Global Burden of Disease Study"ArchivedAlternate Link
 Severe spinal-cord compression is considered a surgical emergency and requires decompression to preserve motor and sensory function.
Severe spinal-cord compression is considered a surgical emergency and requires decompression to preserve motor and sensory function.
 Inflammatory arthritides such as
Inflammatory arthritides such as
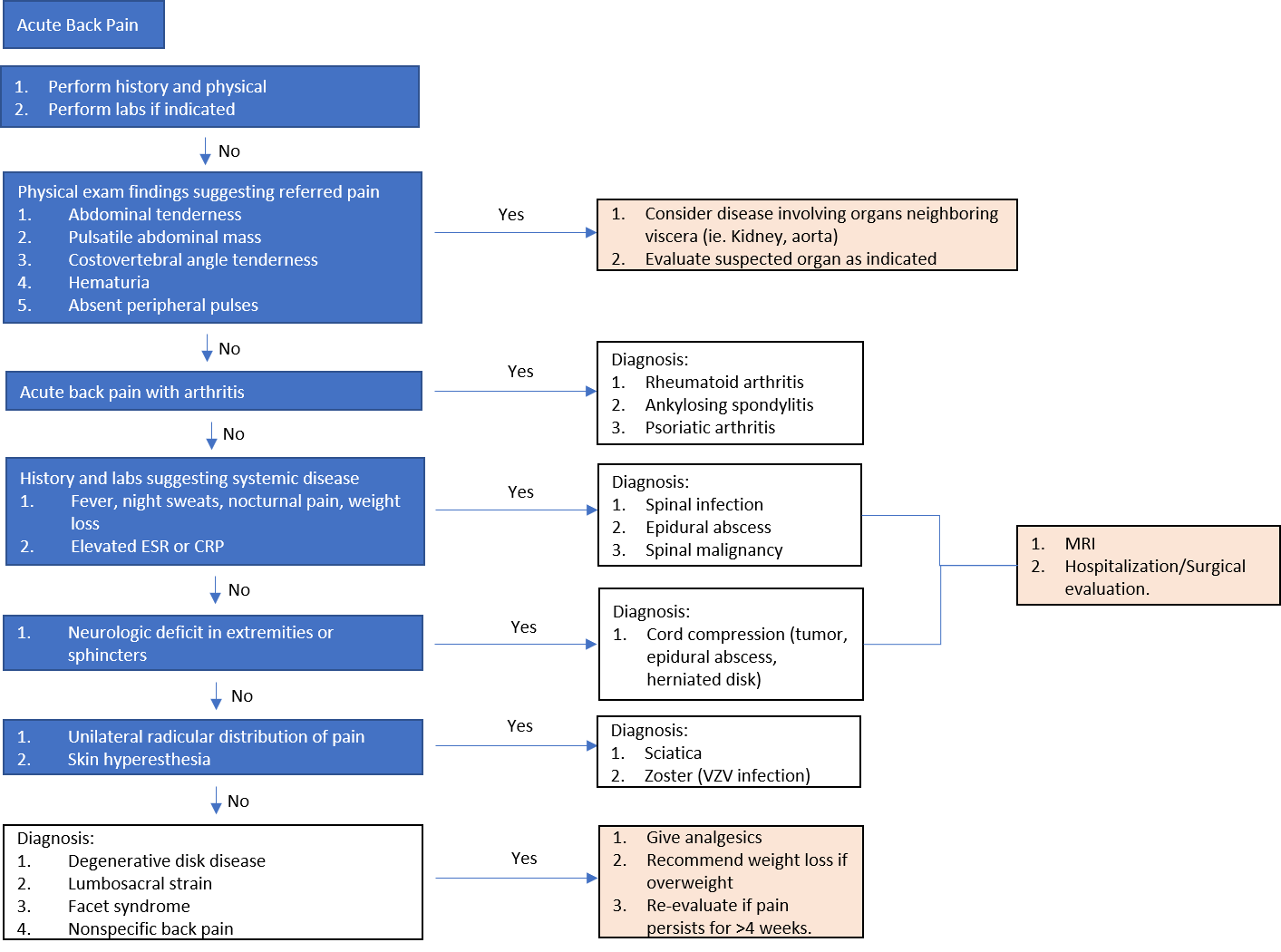 Initial assessment of back pain consists of a history and physical examination. Important characterizing features of back pain include location, duration, severity, history of prior back pain and possible trauma. Other important components of the patient history include age, physical trauma, prior history of cancer, fever, weight loss, urinary incontinence, progressive weakness or expanding sensory changes, which can indicate a medically urgent condition.
Physical examination of the back should assess for posture and deformities. Pain elicited by palpating certain structures may be helpful in localizing the affected area. A neurologic exam is needed to assess for changes in gait, sensation and motor function.
Determining if there are radicular symptoms, such as pain, numbness or weakness that radiate down limbs, is important for differentiating between central and peripheral causes of back pain. The straight leg test is a maneuver used to determine the presence of lumbosacral
Initial assessment of back pain consists of a history and physical examination. Important characterizing features of back pain include location, duration, severity, history of prior back pain and possible trauma. Other important components of the patient history include age, physical trauma, prior history of cancer, fever, weight loss, urinary incontinence, progressive weakness or expanding sensory changes, which can indicate a medically urgent condition.
Physical examination of the back should assess for posture and deformities. Pain elicited by palpating certain structures may be helpful in localizing the affected area. A neurologic exam is needed to assess for changes in gait, sensation and motor function.
Determining if there are radicular symptoms, such as pain, numbness or weakness that radiate down limbs, is important for differentiating between central and peripheral causes of back pain. The straight leg test is a maneuver used to determine the presence of lumbosacral

Chapter 9: The Surgical Treatment
/ref> If infection, such as a spinal epidural abscess, is the source of the back pain, surgery may be indicated when a trial of antibiotics is ineffective. Surgical evacuation of spinal hematoma can also be attempted, if the blood products fail to break down on their own.
Handout on Health: Back Pain
at
Non-specific Back Pain Guidelines 2017 – Kaiser Foundation Health Plan of WashingtonArchived
{{DEFAULTSORT:Back Pain Pain Bones of the vertebral column Human back
pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
felt in the back
The human back, also called the dorsum, is the large posterior area of the human body, rising from the top of the buttocks to the back of the neck. It is the surface of the body opposite from the chest and the abdomen. The vertebral column runs ...
. It may be classified as neck pain
Neck pain, also known as cervicalgia, is a common problem, with two-thirds of the population having neck pain at some point in their lives.
Neck pain, although felt in the neck, can be caused by numerous other spinal problems. Neck pain may arise ...
(cervical), middle back pain
Middle back pain, also known as thoracic back pain, is back pain that is felt in the region of the thoracic vertebrae, which are between the bottom of the neck and top of the lumbar spine. It has a number of potential causes, ranging from muscle s ...
(thoracic), lower back pain
Low back pain (LBP) or lumbago is a common disorder involving the muscles, nerves, and bones of the back, in between the lower edge of the ribs and the lower fold of the buttocks. Pain can vary from a dull constant ache to a sudden sharp feel ...
(lumbar) or coccydynia
Coccydynia is a medical term meaning pain in the coccyx or tailbone area, often brought on by a fall onto the coccyx or by persistent irritation usually from sitting.
Synonyms
Coccydynia is also known as coccygodynia, coccygeal pain, coccyx pain, ...
(tailbone or sacral pain) based on the segment affected. The lumbar area is the most common area affected.Church E, Odle TDiagnosis and treatment of back pain
. ''Radiologic Technology''&nbs
serial online
November 2007;79(2):126–204. Available from: CINAHL Plus with Full Text, Ipswich, MA. Accessed December 12, 2017. An episode of back pain may be
acute
Acute may refer to:
Science and technology
* Acute angle
** Acute triangle
** Acute, a leaf shape in the glossary of leaf morphology
* Acute (medicine), a disease that it is of short duration and of recent onset.
** Acute toxicity, the adverse eff ...
, subacute or chronic depending on the duration. The pain may be characterized as a dull ache, shooting or piercing pain or a burning sensation. Discomfort can radiate to the arm
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between th ...
s and hand
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each "h ...
s as well as the leg
A leg is a weight-bearing and locomotive anatomical structure, usually having a columnar shape. During locomotion, legs function as "extensible struts". The combination of movements at all joints can be modeled as a single, linear element ca ...
s or feet
The foot ( : feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made ...
, and may include numbness
Hypoesthesia or numbness is a common side effect of various medical conditions that manifests as a reduced sense of touch or sensation, or a partial loss of sensitivity to sensory stimuli. In everyday speech this is generally referred to as num ...
or weakness in the legs and arms.
The majority of back pain is nonspecific and idiopathic
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparent wikt:spontaneous, spontaneous origin. From Ancient Greek, Greek ἴδιος ''idios'' "one's own" and πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", ''idiopathy'' means approxi ...
. Common underlying mechanisms include degenerative or traumatic changes to the discs and facet joints
Facets () are flat faces on geometric shapes. The organization of naturally occurring facets was key to early developments in crystallography, since they reflect the underlying symmetry of the crystal structure. Gemstones commonly have facets cut ...
, which can then cause secondary pain in the muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
s and nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system.
A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the e ...
s and referred pain
Referred pain, also called reflective pain, is pain perceived at a location other than the site of the painful stimulus. An example is the case of angina pectoris brought on by a myocardial infarction (heart attack), where pain is often felt in ...
to the bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
s, joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw ...
s and extremities. Diseases and inflammation of the gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although ...
, pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an end ...
, aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes ...
and kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ...
s may also cause referred pain in the back. Tumors of the vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic ...
e, neural tissues and adjacent structures can also manifest as back pain.
Back pain is common; approximately nine of ten adults experiencing it at some point in their lives, and five of ten working adults experience back pain each year.A.T. Patel, A.A. Ogle"Diagnosis and Management of Acute Low Back Pain"
American Academy of Family Physicians. Retrieved March 12, 2007
Alternate Link
/ref> Some estimate that as many of 95% of people will experience back pain at some point in their lifetime. It is the most common cause of chronic pain and is a major contributor to missed work and disability. For most individuals, back pain is self-limiting. Most people with back pain do not experience chronic severe pain but rather persistent or intermittent pain that is mild or moderate. In most cases of
herniated disk
Spinal disc herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physic ...
s and stenosis, rest, injections or surgery have similar general pain-resolution outcomes on average after one year. In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, acute low back pain is the fifth most common reason for physician visits and causes 40% of missed work days. It is the single leading cause of disability worldwide.Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation"2010 Global Burden of Disease Study"
Classification
Back pain is classified in terms of duration of symptoms. # Acute back pain lasts <6 weeks # Subacute back pain lasts between 6 and 12 weeks. # Chronic back pain lasts for greater than 12 weeks.Causes
There are many causes of back pain, including blood vessels,internal organs
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a ...
, infections
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
, mechanical and autoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". ...
causes. Approximately 90 percent of people with back pain are diagnosed with nonspecific, idiopathic acute pain with no identifiable underlying pathology. In approximately 10 percent of people, a cause can be identified through diagnostic imaging. Fewer than two percent of cases are attributed to secondary factors, with metastatic cancer
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, the ...
s and serious infections, such as spinal osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the ...
and epidural abscesses, accounting for approximately one percent.
Nonspecific
In as many as 90 percent of cases, no physiological causes or abnormalities on diagnostic tests can be found. Nonspecific back pain can result from back strain or sprains, which can cause peripheral injury to muscle or ligaments. Many patients cannot identify the events or activities that may have caused the strain. The pain can present acutely but in some cases can persist, leading to chronic pain. Chronic back pain in people with otherwise normal scans can result fromcentral sensitization
Nociplastic pain or central sensitisation is a type of pain which is mechanically different from the normal nociceptive pain caused by inflammation and tissue damage or the neuropathic pain which results from nerve damage. It may occur in com ...
, in which an initial injury causes a longer-lasting state of heightened sensitivity to pain. This persistent state maintains pain even after the initial injury has healed. Treatment of sensitization may involve low doses of antidepressants
Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common side-effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, hea ...
and directed rehabilitation such as physical therapy.
Spinal disc disease
Spinal disc disease occurs when thenucleus pulposus
An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold t ...
, a gel-like material in the inner core of the vertebral disc, ruptures. Rupturing of the nucleus pulposus can lead to compression of nerve roots. Symptoms may be unilateral or bilateral, and correlate to the region of the spine affected. The most common region for spinal disk disease is at L4–L5 or L5–S1. The risk for lumbar disc disease is increased in overweight individuals because of the increased compressive force on the nucleus pulposus, and is twice as likely to occur in men. A 2002 study found that lifestyle factors such as night-shift work and lack of physical activity can also increase the risk of lumbar disc disease.  Severe spinal-cord compression is considered a surgical emergency and requires decompression to preserve motor and sensory function.
Severe spinal-cord compression is considered a surgical emergency and requires decompression to preserve motor and sensory function. Cauda equina syndrome
Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a condition that occurs when the bundle of nerves below the end of the spinal cord known as the cauda equina is damaged. Signs and symptoms include low back pain, pain that radiates down the leg, numbness around ...
involves severe compression of the cauda equina
The cauda equina () is a bundle of spinal nerves and spinal nerve rootlets, consisting of the second through fifth lumbar nerve pairs, the first through fifth sacral nerve pairs, and the coccygeal nerve, all of which arise from the lumbar enlarg ...
and presents initially with pain followed by motor and sensory. Bladder incontinence is seen in later stages of cauda equina syndrome.
Degenerative disease
Spondylosis
Spondylosis is the degeneration of the vertebral column from any cause. In the more narrow sense it refers to spinal osteoarthritis, the age-related wear and tear of the spinal column, which is the most common cause of spondylosis. The degenera ...
, or degenerative arthritis of the spine, occurs when the intervertebral disc undergoes degenerative changes, causing the disc to fail at cushioning the vertebrae. There is an association between intervertebral disc space narrowing and lumbar spine pain. The space between the vertebrae becomes more narrow, resulting in compression and irritation of the nerves.
Spondylolithesis is the anterior shift of one vertebra compared to the neighboring vertebra. It is associated with age-related degenerative changes as well as trauma and congenital anomalies.
Spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen that results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs. Symptoms are typically gradual i ...
can occur in cases of severe spondylosis, spondylotheisis and age-associated thickening of the ligamentum flavum. Spinal stenosis involves narrowing of the spinal canal and typically presents in patients greater than 60 years of age. Neurogenic claudication
Neurogenic claudication (NC), also known as pseudoclaudication, is the most common symptom of lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) and describes intermittent leg pain from impingement of the nerves emanating from the spinal cord. ''Neurogenic'' means that ...
can occur in cases of severe lumbar spinal stenosis and presents with symptoms of pain in the lower back, buttock or leg that is worsened by standing and relieved by sitting.
Vertebral compression fracture
A compression fracture is a collapse of a vertebra. It may be due to trauma or due to a weakening of the vertebra (compare with burst fracture). This weakening is seen in patients with osteoporosis or osteogenesis imperfecta, lytic lesions from ...
s occur in four percent of patients presenting with lower back pain. Risk factors include age, female gender, history of osteoporosis, and chronic glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebr ...
use. Fractures can occur as a result of trauma but in many cases can be asymptomatic.
Infection
Common infectious causes of back pain includeosteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the ...
, septic discitis, paraspinal abscess and epidural abscess. Infectious causes that lead to back pain involve various structures surrounding the spine.
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the ...
is the bacterial infection of the bone. Vertebral osteomyelitis
Vertebral osteomyelitis is a type of osteomyelitis (infection and inflammation of the bone and bone marrow) that affects the vertebrae. It is a rare bone infection concentrated in the vertebral column. Cases of vertebral osteomyelitis are so rare ...
is most commonly caused by staphylococci
''Staphylococcus'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical ( cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultati ...
. Risk factors include skin infection, urinary tract infection, IV catheter use, IV drug use, previous endocarditis and lung disease.
Spinal epidural abscess
An epidural abscess refers to a collection of pus and infectious material located in the epidural space superficial to the dura mater which surrounds the central nervous system. Due to its location adjacent to brain or spinal cord, epidural abscess ...
is commonly caused by severe infection with bacteremia
Bloodstream infections (BSIs), which include bacteremias when the infections are bacterial and fungemias when the infections are fungal, are infections present in the blood. Blood is normally a sterile environment, so the detection of microb ...
. Risk factors include recent administration of epidurals, IV drug use or recent infection.
Cancer
Spread of cancer to the bone or spinal cord can lead to back pain. Bone is one of the most common sites of metastatic lesions. Patients typically have a history of malignancy. Common types of cancer that present with back pain include multiple myeloma, lymphoma, leukemia, spinal cord tumors, primary vertebral tumors and prostate cancer. Back pain is present in 29% of patients with systemic cancer. Unlike other causes of back pain that commonly affect the lumbar spine, the thoracic spine is most commonly affected. The pain can be associated with systemic symptoms such as weight loss, chills, fever, nausea and vomiting. Unlike other causes of back pain, neoplasm-associated back pain is constant, dull, poorly localized and worsens with rest. Metastasis to the bone also increases the risk of spinal-cord compression or vertebral fractures that require emergency surgical treatment.Autoimmune
 Inflammatory arthritides such as
Inflammatory arthritides such as ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine typically where the spine joins the pelvis. Occasionally areas affected may include other joints such as the shoulders or hip ...
, psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that occurs in people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic feature of psoriatic arthritis is swelling of entire fingers and toes with a sausage-like appearance. Th ...
, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involv ...
and systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Comm ...
can all cause varying levels of joint destruction. Among the inflammatory arthritides, ankylosing spondylitis is most closely associated with back pain because of the inflammatory destruction of the bony components of the spine. Ankylosing spondylitis is common in young men and presents with a range of possible symptoms such as uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and in ...
, psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete ...
and inflammatory bowel disease.
Referred pain
Back pain can also be referred from another source. Referred pain occurs when pain is felt at a location different than the source of the pain. Disease processes that can present with back pain includepancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large organ behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and a number of hormones. There are two main types: acute pancreatitis, and chronic pancr ...
, kidney stones
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine s ...
, severe urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney ...
s and abdominal aortic aneurysm
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a localized enlargement of the abdominal aorta such that the diameter is greater than 3 cm or more than 50% larger than normal. They usually cause no symptoms, except during rupture. Occasionally, abdominal, ...
s.
Risk factors
Heavy lifting, obesity, sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise can increase the risk of back pain. Cigarette smokers are more likely to experience back pain than are nonsmokers. Poor posture and weight gain in pregnancy are also risk factors for back pain. In general, fatigue can worsen pain. A few studies suggest thatpsychosocial
The psychosocial approach looks at individuals in the context of the combined influence that psychological factors and the surrounding social environment have on their physical and mental wellness and their ability to function. This approach is ...
factors such as work-related stress and dysfunctional family relationships may correlate more closely with back pain than do structural abnormalities revealed in X-rays and other medical imaging scans.
While back pain physical effects can range from muscle aching to a shooting, burning, or stabbing sensation. It can radiate pain down the legs and have pain increased by bending, twisting, lifting, standing, or walking. While the physical effects of back pain are always at the forefront back pain also has other psychological effects. Back pain has been linked to depression, anxiety, stress, and avoidance behaviors due to mentally not being able to cope with the physical pain. “Both acute and chronic back pain can be associated with psychological distress in the form of anxiety (worries, stress) or depression (sadness, discouragement). Psychological distress is a common reaction to the suffering aspects of acute back pain, even when symptoms are short-term and not medically serious 5��( (IASP, 2021)
Diagnosis
 Initial assessment of back pain consists of a history and physical examination. Important characterizing features of back pain include location, duration, severity, history of prior back pain and possible trauma. Other important components of the patient history include age, physical trauma, prior history of cancer, fever, weight loss, urinary incontinence, progressive weakness or expanding sensory changes, which can indicate a medically urgent condition.
Physical examination of the back should assess for posture and deformities. Pain elicited by palpating certain structures may be helpful in localizing the affected area. A neurologic exam is needed to assess for changes in gait, sensation and motor function.
Determining if there are radicular symptoms, such as pain, numbness or weakness that radiate down limbs, is important for differentiating between central and peripheral causes of back pain. The straight leg test is a maneuver used to determine the presence of lumbosacral
Initial assessment of back pain consists of a history and physical examination. Important characterizing features of back pain include location, duration, severity, history of prior back pain and possible trauma. Other important components of the patient history include age, physical trauma, prior history of cancer, fever, weight loss, urinary incontinence, progressive weakness or expanding sensory changes, which can indicate a medically urgent condition.
Physical examination of the back should assess for posture and deformities. Pain elicited by palpating certain structures may be helpful in localizing the affected area. A neurologic exam is needed to assess for changes in gait, sensation and motor function.
Determining if there are radicular symptoms, such as pain, numbness or weakness that radiate down limbs, is important for differentiating between central and peripheral causes of back pain. The straight leg test is a maneuver used to determine the presence of lumbosacral radiculopathy
Radiculopathy, also commonly referred to as pinched nerve, refers to a set of conditions in which one or more nerves are affected and do not work properly (a neuropathy). Radiculopathy can result in pain (radicular pain), weakness, altered sens ...
, which occurs when there is irritation in the nerve root that causes neurologic symptoms such as numbness and tingling. Non-radicular back pain is most commonly caused by injury to the spinal muscles or ligaments, degenerative spinal disease or a herniated disc
Spinal disc herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical ...
. Disc herniation and foraminal stenosis are the most common causes of radiculopathy.
Imaging of the spine and laboratory tests is not recommended during the acute phase. This assumes that there is no reason to expect that the patient has an underlying problem.*
*
*
*
*
* In most cases, the pain subsides naturally after several weeks. People who seek diagnosis through imaging are typically less likely to receive a better outcome than are those who wait for the condition to resolve.
Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(MRI) is the preferred modality for the evaluation of back pain and visualization of bone, soft tissue, nerves and ligaments. X-rays are a less costly initial option offered to patients with a low clinical suspicion of infection or malignancy, and they are combined with laboratory studies for interpretation.
Imaging is not needed for the majority of patients with back pain. In cases of acute back pain, MRI is recommended for those with major risk factors or clinical suspicion of cancer, spinal infection or severe progressive neurological deficits. For patients with subacute to chronic back pain, MRI is recommended if minor risk factors exist for cancer, ankylosing spondylitis or vertebral compression fracture, or if significant trauma or symptomatic spinal stenosis is present.
Early imaging studies during the acute phase do not improve care or prognosis. Imaging findings are not correlated with severity or outcome.
Laboratory studies
Laboratory studies are employed when there are suspicions of autoimmune causes, infection or malignancy. Laboratory testing may include white blood cell (WBC) count,erythrocyte sedimentation rate
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR or sed rate) is the rate at which red blood cells in anticoagulated whole blood descend in a standardized tube over a period of one hour. It is a common hematology test, and is a non-specific measure of ...
(ESR), and C-reactive protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin- ...
(CRP).
* Elevated ESR could indicate infection, malignancy, chronic disease, inflammation, trauma or tissue ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems wi ...
.
* Elevated CRP levels are associated with infection.

Red flags
Imaging is not typically needed in the initial diagnosis or treatment of back pain. However, if there are certain "red flag" symptoms present, plain radiographs (X-ray), CT scan or magnetic resonance imaging may be recommended. These red flags include: * History of cancer * Unexplained weight loss * Immunosuppression * Urinary infection * Intravenous drug use * Prolonged use of corticosteroids * Back pain not improved with conservative management * History of significant trauma * Minor fall or heavy lift in a potentially osteoporotic or elderly individual * Acute onset of urinary retention, overflow incontinence, loss of anal sphincter tone, or fecal incontinence *Saddle anesthesia
Saddle anesthesia is a loss of sensation (anesthesia) restricted to the area of the buttocks, perineum and inner surfaces of the thighs.
Asymmetric saddle anesthesia is frequently associated with the spine-related injury cauda equina syndrome. It ...
* Global or progressive motor weakness in the lower limbs
Prevention
Moderate-quality evidence exists that suggests that the combination of education and exercise may reduce an individual's risk of developing an episode of low back pain. Lesser-quality evidence points to exercise alone as a possible deterrent to the risk of the condition.Management
Nonspecific pain
Patients with uncomplicated back pain should be encouraged to remain active and to return to normal activities. The management goals when treating back pain are to achieve maximal reduction in pain intensity as rapidly as possible, to restore the individual's ability to function in everyday activities, to help the patient cope with residual pain, to assess for side effects of therapy and to facilitate the patient's passage through the legal and socioeconomic impediments to recovery. For many, the goal is to keep the pain at a manageable level to progress with rehabilitation, which then can lead to long-term pain relief. Also, for some people the goal is to use nonsurgical therapies to manage the pain and avoid major surgery, while for others surgery may represent the quickest path to pain relief. Not all treatments work for all conditions or for all individuals with the same condition, and many must try several treatment options to determine what works best for them. The present stage of the condition (acute or chronic) is also a determining factor in the choice of treatment. Only a minority of people with back pain (most estimates are 1–10%) require surgery.Nonmedical
Back pain is generally first treated with nonpharmacological therapy, as it typically resolves without the use of medication. Superficial heat and massage, acupuncture and spinal manipulation therapy may be recommended. *Heat therapy
Heat therapy, also called thermotherapy, is the use of heat in therapy, such as for pain relief and health. It can take the form of a hot cloth, hot water bottle, ultrasound, heating pad, hydrocollator packs, whirlpool baths, cordless FIR h ...
is useful for back spasm
A spasm is a sudden involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ such as the bladder.
A spasmodic muscle contraction may be caused by many medical conditions, including dystonia. Most commonly, it is a muscle c ...
s or other conditions. A review concluded that heat therapy can reduce symptoms of acute and subacute low-back pain.
* Regular activity and gentle stretching exercises is encouraged in uncomplicated back pain and is associated with better long-term outcomes. Physical therapy to strengthen the muscles in the abdomen and around the spine may also be recommended. These exercises are associated with better patient satisfaction, although they have not been shown to provide functional improvement. However, one review found that exercise is effective for chronic back pain but not for acute pain. Exercise should be performed under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
* Massage therapy
Massage is the manipulation of the body's soft tissues. Massage techniques are commonly applied with hands, fingers, elbows, knees, forearms, feet or a device. The purpose of massage is generally for the treatment of body stress or pain. In Eu ...
may provide short-term pain relief, but not functional improvement, for those with acute lower back pain. It may also offer short-term pain relief and functional improvement for those with long-term (chronic) and subacute lower pack pain, but this benefit does not appear to be sustained after six months of treatment. There do not appear to be any serious adverse effects associated with massage.
* Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientif ...
may provide some relief for back pain. However, further research with stronger evidence is needed.
* Spinal manipulation appears similar to other recommended treatments.
* "Back school" is an intervention that consists of both education and physical exercises. There is no strong evidence supporting the use of back school for treating acute, subacute, or chronic non-specific back pain.
* Insoles
A removable shoe insert, otherwise known as a foot orthosis, insole or inner sole accomplishes many purposes, including daily wear comfort, height enhancement, plantar fasciitis treatment, arch support, foot and joint pain relief from arthritis ...
appear to be an ineffective treatment intervention.
* While traction for back pain is often used in combination with other approaches, there appears to be little or no impact on pain intensity, functional status, global improvement or return to work.
Medication
If nonpharmacological measures are ineffective, medication may be administered. * Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are typically attempted first. NSAIDs have been proven more effective than placebo, and are usually more effective than paracetamol (acetaminophen). * Long-term use ofopioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid us ...
s has not been tested to determine whether it is effective or safe for treating chronic lower back pain. For severe back pain not relieved by NSAIDs or acetaminophen, opioids may be used. Opioids may not be better than NSAIDs or antidepressants for chronic back pain with regard to pain relief and gain of function.
* Skeletal muscle relaxers may also be used. Their short-term use has been proven effective in the relief of acute back pain. However, the evidence of this effect has been disputed, and these medications do have negative side effects.
* For patients with nerve root pain and acute radiculopathy, there is evidence that a single dose of steroids, such as dexamethasone, may provide pain relief.
* Epidural corticosteroid injection (ESI) is a procedure in which steroid medications are injected into the epidural space
In anatomy, the epidural space is the potential space between the dura mater and vertebrae (spine).
The anatomy term "epidural space" has its origin in the Ancient Greek language; , "on, upon" + dura mater also known as "epidural cavity", "e ...
. The steroid medications reduce inflammation and thus decrease pain and improve function. ESI has long been used to both diagnose and treat back pain, although recent studies have shown a lack of efficacy in treating low back pain.
Surgery
Surgery for back pain is typically used as a last resort, when serious neurological deficit is evident. A 2009 systematic review of back surgery studies found that, for certain diagnoses, surgery is moderately better than other common treatments, but the benefits of surgery often decline in the long term. Surgery may sometimes be appropriate for people with severemyelopathy
Myelopathy describes any neurologic deficit related to the spinal cord. The most common form of myelopathy in humans, ''Spinal cord compression, cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM)'', also called ''degenerative cervical myelopathy'', results fro ...
or cauda equina syndrome
Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a condition that occurs when the bundle of nerves below the end of the spinal cord known as the cauda equina is damaged. Signs and symptoms include low back pain, pain that radiates down the leg, numbness around ...
. Causes of neurological deficits can include spinal disc herniation
Spinal disc herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical ...
, spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen that results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs. Symptoms are typically gradual i ...
, degenerative disc disease
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a medical condition typically brought on by the normal aging process in which there are anatomic changes and possibly a loss of function of one or more intervertebral discs of the spine. DDD can take place with ...
, tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
, infection, and spinal hematomas, all of which can impinge on the nerve roots around the spinal cord. There are multiple surgical options to treat back pain, and these options vary depending on the cause of the pain.
When a herniated disc is compressing the nerve roots, hemi- or partial- laminectomy
A laminectomy is a surgical procedure that removes a portion of a vertebra called the lamina, which is the roof of the spinal canal. It is a major spine operation with residual scar tissue and may result in postlaminectomy syndrome. Depending ...
or discectomy
A discectomy (also called open discectomy, if done through a 1/2 inch or larger skin opening) is the surgical removal of abnormal disc material that presses on a nerve root or the spinal cord. The procedure involves removing a portion of an int ...
may be performed, in which the material compressing on the nerve is removed. A mutli-level laminectomy can be done to widen the spinal canal in the case of spinal stenosis. A foraminotomy
Foraminotomy is a medical operation used to relieve pressure on nerves that are being compressed by the intervertebral foramina, the passages through the bones of the vertebrae of the spine that pass nerve bundles to the body from the spinal cord. ...
or foraminectomy may also be necessary, if the vertebrae are causing significant nerve root compression. A discectomy is performed when the intervertebral disc has herniated or torn. It involves removing the protruding disc, either a portion of it or all of it, that is placing pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and e ...
on the nerve root A nerve root (Latin: ''radix nervi'') is the initial segment of a nerve leaving the central nervous system. Nerve roots can be classified as:
*cranial nerves, Cranial nerve roots: the initial or proximal segment of one of the twelve pairs of crania ...
. Total disc replacement can also be performed, in which the source of the pain (the damaged disc) is removed and replaced, while maintaining spinal mobility. When an entire disc is removed (as in discectomy), or when the vertebrae are unstable, spinal fusion surgery may be performed. Spinal fusion
Spinal fusion, also called spondylodesis or spondylosyndesis, is a neurosurgical or orthopedic surgical technique that joins two or more vertebrae. This procedure can be performed at any level in the spine (cervical, thoracic, or lumbar) and pre ...
is a procedure in which bone grafts
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone in order to repair bone fractures that are extremely complex, pose a significant health risk to the patient, or fail to heal properly. Some small or acute fractures can be cured wit ...
and metal hardware is used to fix together two or more vertebrae, thus preventing the bones of the spinal column from compressing on the spinal cord or nerve roots.Burke, G.L., "Backache from Occiput to CoccyxChapter 9: The Surgical Treatment
/ref> If infection, such as a spinal epidural abscess, is the source of the back pain, surgery may be indicated when a trial of antibiotics is ineffective. Surgical evacuation of spinal hematoma can also be attempted, if the blood products fail to break down on their own.
Pregnancy
About 50% of women experience low back pain during pregnancy. Some studies have suggested that women who have experienced back pain before pregnancy are at a higher risk of experiencing back pain during pregnancy. It may be severe enough to cause significant pain and disability in as many as one third of pregnant women. Back pain typically begins at approximately 18 weeks of gestation and peaks between 24 and 36 weeks. Approximately 16% of women who experience back pain during pregnancy report continued back pain years after pregnancy, indicating that those with significant back pain are at greater risk of back pain following pregnancy. Biomechanical factors of pregnancy shown to be associated with back pain include increased curvature of the lower back, orlumbar lordosis
Lordosis is historically defined as an ''abnormal'' inward curvature of the lumbar spine. However, the terms ''lordosis'' and ''lordotic'' are also used to refer to the normal inward curvature of the lumbar and cervical regions of the human spin ...
, to support the added weight on the abdomen. Also, the hormone relaxin
Relaxin is a protein hormone of about 6000 Da first described in 1926 by Frederick Hisaw.
The relaxin family peptide hormones belong to the insulin superfamily and consists of seven peptides of high structural but low sequence similarity; rela ...
is released during pregnancy, which softens the structural tissues in the pelvis and lower back to prepare for vaginal delivery. This softening and increased flexibility of the ligaments and joints in the lower back can result in pain. Back pain in pregnancy is often accompanied by radicular symptoms, suggested to be caused by the baby pressing on the sacral plexus
In human anatomy, the sacral plexus is a nerve plexus which provides motor and sensory nerves for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis. It is part of the lumbosacral plexus and emerges from the lumbar verte ...
and lumbar plexus in the pelvis.
Typical factors aggravating the back pain of pregnancy include standing, sitting, forward bending, lifting and walking. Back pain in pregnancy may also be characterized by pain radiating into the thigh and buttocks, nighttime pain severe enough to wake the patient, pain that is increased at night or pain that is increased during the daytime.
Local heat, acetaminophen (paracetamol) and massage can be used to help relieve pain. Avoiding standing for prolonged periods of time is also suggested.
Economics
Although back pain does not typically cause permanent disability, it is a significant contributor to physician visits and missed work days in the United States, and is the single leading cause of disability worldwide. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons report approximately 12 million visits to doctor's offices each year are due to back pain. Missed work and disability related to low back pain costs over $50 billion each year in the United States. In the United Kingdom in 1998, approximately £1.6 billion per year was spent on expenses related to disability from back pain.References
External links
*Handout on Health: Back Pain
at
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
The National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS) is one of the institutes and centers that make up the National Institutes of Health, an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
...
*
Non-specific Back Pain Guidelines 2017 – Kaiser Foundation Health Plan of Washington
{{DEFAULTSORT:Back Pain Pain Bones of the vertebral column Human back