Azerbaijani Language on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Azerbaijani () or Azeri (), also referred to as Azeri Turkic or Azeri Turkish, is a Turkic language from the Oghuz sub-branch spoken primarily by the Azerbaijani people, who live mainly in the Republic of Azerbaijan where the North Azerbaijani variety is spoken, and in the
 Azerbaijani evolved from the Eastern branch of Oghuz Turkic ("Western Turkic") which spread to the Caucasus, in
Azerbaijani evolved from the Eastern branch of Oghuz Turkic ("Western Turkic") which spread to the Caucasus, in
 The development of Azerbaijani literature is closely associated with Anatolian Turkish, written in
The development of Azerbaijani literature is closely associated with Anatolian Turkish, written in
p. 246.
/ref> During the 16th century, the poet, writer and thinker Fuzûlî wrote mainly in Azerbaijani but also translated his poems into
 Azerbaijani is one of the
Azerbaijani is one of the
 North Azerbaijani, or Northern Azerbaijani, is the
North Azerbaijani, or Northern Azerbaijani, is the
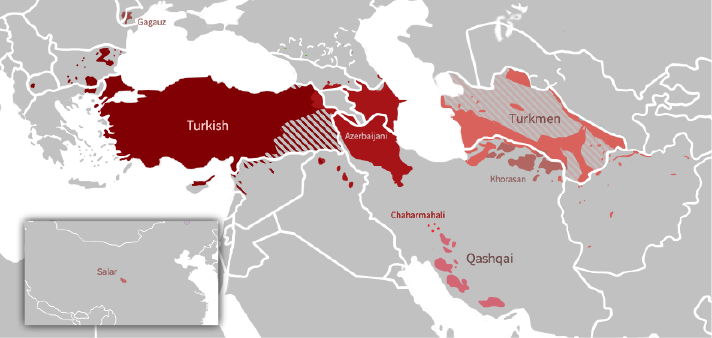 North and South Azerbaijani speakers and Turkish speakers can communicate with varying degrees of mutual intelligibility. Turkish soap operas are very popular with Azeris in both Iran and Azerbaijan. Reza Shah Pahlavi of
North and South Azerbaijani speakers and Turkish speakers can communicate with varying degrees of mutual intelligibility. Turkish soap operas are very popular with Azeris in both Iran and Azerbaijan. Reza Shah Pahlavi of
 The typical phonetic quality of South Azerbaijani vowels is as follows:
* are close to cardinal .
* The F1 and F2 formant frequencies overlap for and . Their acoustic quality is more or less close-mid central . The main role in the distinction of two vowels is played by the different F3 frequencies in audition, and rounding in articulation. Phonologically, however, they are more distinct: is phonologically a mid front rounded vowel, the front counterpart of and the rounded counterpart of . is phonologically a close back unrounded vowel, the back counterpart of and the unrounded counterpart of .
* The other mid vowels are closer to close-mid than open-mid .
* is phonetically near-open back .
The typical phonetic quality of South Azerbaijani vowels is as follows:
* are close to cardinal .
* The F1 and F2 formant frequencies overlap for and . Their acoustic quality is more or less close-mid central . The main role in the distinction of two vowels is played by the different F3 frequencies in audition, and rounding in articulation. Phonologically, however, they are more distinct: is phonologically a mid front rounded vowel, the front counterpart of and the rounded counterpart of . is phonologically a close back unrounded vowel, the back counterpart of and the unrounded counterpart of .
* The other mid vowels are closer to close-mid than open-mid .
* is phonetically near-open back .
A blog on Azerbaijani language resources and translations
*
A blog about the Azerbaijani language and lessons
azeri.org
Azerbaijani literature and English translations.
Online bidirectional Azerbaijani-English Dictionary
roken as of 2022
Learn Azerbaijani
at learn101.org.
by Ahmad Kasravi. * including sound file.
Azerbaijani<>Turkish dictionary
(Pamukkale University)
Azerbaijan Language with Audio
Azerbaijani thematic vocabulary
AzConvert
an open source Azerbaijani transliteration program.
Azerbaijani Alphabet and Language in Transition
the entire issue of ''Azerbaijan International'', Spring 2000 (8.1) at azer.com. *
*
** ttp://azer.com/aiweb/categories/magazine/81_folder/81_articles/81_alphabet_sequence1.html Chart: Changes in the Four Azerbaijan Alphabet Sequence in the 20th century*
Baku’s Institute of Manuscripts: Early Alphabets in Azerbaijan
{{Authority control Agglutinative languages Languages of Azerbaijan Languages of Georgia (country) Languages of Iran Languages of Iraq Languages of Russia Languages of Turkey Subject–object–verb languages Turkic languages
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
region of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, where the South Azerbaijani variety is spoken. Although there is a very high degree of mutual intelligibility
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. It is sometimes used as ...
between both forms of Azerbaijani, there are significant differences in phonology
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a ...
, lexicon
A lexicon is the vocabulary of a language or branch of knowledge (such as nautical or medical). In linguistics, a lexicon is a language's inventory of lexemes. The word ''lexicon'' derives from Greek word (), neuter of () meaning 'of or fo ...
, morphology, syntax
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituenc ...
, and sources of loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because ...
s.
North Azerbaijani has official status in the Republic of Azerbaijan and Dagestan (a federal subject of Russia), but South Azerbaijani does not have official status in Iran, where the majority of Azerbaijani people live. It is also spoken to lesser varying degrees in Azerbaijani communities of Georgia and Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
and by diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews after ...
communities, primarily in Europe and North America.
Both Azerbaijani varieties are members of the Oghuz branch of the Turkic languages. The standardized form of North Azerbaijani (spoken in the Republic of Azerbaijan and Russia) is based on the Shirvani dialect, while South Azerbaijani uses the Tabrizi dialect as its prestige variety. Since the Republic of Azerbaijan's independence from the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
in 1991, Northern Azerbaijani uses the Latin script. South Azerbaijani, on the other hand, has always used and continues to use the Perso-Arabic script
The Persian alphabet ( fa, الفبای فارسی, Alefbâye Fârsi) is a writing system that is a version of the Arabic script used for the Persian language spoken in Iran ( Western Persian) and Afghanistan ( Dari Persian) since the 7th ce ...
. Azerbaijani language is closely related to Gagauz, Qashqai, Crimean Tatar, Turkish, and Turkmen, sharing varying degrees of mutual intelligibility with each of those languages.
Etymology and background
Historically the language was referred by its native speakers as or meaning either "Turkish" or "Turkic". After the establishment of the Azerbaijan SSR, on the order of Soviet leaderJoseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet Union, Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as Ge ...
, the "name of the formal language" of the Azerbaijan SSR was changed from "Turkish" to "Azerbaijani".
History and evolution
 Azerbaijani evolved from the Eastern branch of Oghuz Turkic ("Western Turkic") which spread to the Caucasus, in
Azerbaijani evolved from the Eastern branch of Oghuz Turkic ("Western Turkic") which spread to the Caucasus, in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
, and northern Iran, in Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes A ...
, during the medieval Turkic migrations. Persian and Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
influenced the language, but Arabic words were mainly transmitted through the intermediary of literary Persian. Azerbaijani is, perhaps after Uzbek, the Turkic language upon which Persian and other Iranian languages
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are groupe ...
have exerted the strongest impact—mainly in phonology, syntax, and vocabulary, less in morphology.
The Turkic language of Azerbaijan gradually supplanted the Iranian languages in what is now northwestern Iran, and a variety of languages of the Caucasus and Iranian languages
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are groupe ...
spoken in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
, particularly Udi Udi may refer to:
Places
* Udi, Enugu, a local government areas and city in Nigeria
* Udi, a place in the Etawah district of Uttar Pradesh, India
People
* Udi Gal (born 1979), Israeli Olympic sailor
* Udi Vaks (born 1979), Israeli Olympic judoka ...
and Old Azeri
Old Azeri (also spelled Adhari, Azeri or Azari) is the extinct Iranian language that was once spoken in the northwestern Iranian historic region of Azerbaijan (Iranian Azerbaijan) before the Turkification of the region. Some linguists believe t ...
. By the beginning of the 16th century, it had become the dominant language of the region. It was a spoken language in the court of the Safavids, Afsharids and Qajars.
The historical development of Azerbaijani can be divided into two major periods: early (c. 14th to 18th century) and modern (18th century to present). Early Azerbaijani differs from its descendant in that it contained a much larger number of Persian and Arabic loanwords, phrases and syntactic elements. Early writings in Azerbaijani also demonstrate linguistic interchangeability between Oghuz and Kypchak elements in many aspects (such as pronouns, case endings, participles, etc.). As Azerbaijani gradually moved from being merely a language of epic and lyric poetry
Modern lyric poetry is a formal type of poetry which expresses personal emotions or feelings, typically spoken in the first person.
It is not equivalent to song lyrics, though song lyrics are often in the lyric mode, and it is also ''not'' equi ...
to being also a language of journalism
Journalism is the production and distribution of reports on the interaction of events, facts, ideas, and people that are the " news of the day" and that informs society to at least some degree. The word, a noun, applies to the occupation (p ...
and scientific research
Research is "creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness ...
, its literary version has become more or less unified and simplified with the loss of many archaic Turkic elements, stilted Iranisms and Ottomanisms, and other words, expressions, and rules that failed to gain popularity among the Azerbaijani masses.
The Russian annexation of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
's territories in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
through the Russo-Iranian wars
The Russo-Persian Wars or Russo-Iranian Wars were a series of conflicts between 1651 and 1828, concerning Persia (Iran) and the Russian Empire. Russia and Persia fought these wars over disputed governance of territories and countries in the Cau ...
of 1804–1813 and 1826-1828 split the language community across two states. Afterwards, the Tsarist administration encouraged the spread of Azerbaijani in eastern Transcaucasia as a replacement for Persian spoken by the upper classes, and as a measure against Persian influence in the region.
Between c. 1900 and 1930, there were several competing approaches to the unification of the national language in what is now the Azerbaijan Republic, popularized by scholars such as Hasan bey Zardabi
Hasan bey Zardabi ( az, Həsən bəy Zərdabi ), born Hasan bey Salim bey oghlu Malikov ( az, Həsən bəy Səlim bəy oğlu Məlikov, links=no ; 28 June 1842 — 15 November 1907), was an Azerbaijani journalist and intellectual, founder of the ...
and Mammad agha Shahtakhtinski
Mammad agha Shahtakhtinski ( az, Məhəmməd ağa Məhəmmədtağı sultan oğlu Şahtaxtılı; 1846 in Erivan – 1931 in Baku) was an Azerbaijani journalist, scholar, and political writer.
Life and education
Shahtakhtinski was born into an Azeri ...
. Despite major differences, they all aimed primarily at making it easy for semi-literate masses to read and understand literature. They all criticized the overuse of Persian, Arabic, and European elements in both colloquial and literary language and called for a simpler and more popular style.
The Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
promoted the development of the language but set it back considerably with two successive script changes – from the Persian to Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
and then to the Cyrillic script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking c ...
– while Iranian Azerbaijanis continued to use the Persian script as they always had. Despite the wide use of Azerbaijani in the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic, it became the official language of Azerbaijan only in 1956. After independence, the Republic of Azerbaijan decided to switch back to a modified Latin script.
Azerbaijani literature
 The development of Azerbaijani literature is closely associated with Anatolian Turkish, written in
The development of Azerbaijani literature is closely associated with Anatolian Turkish, written in Perso-Arabic script
The Persian alphabet ( fa, الفبای فارسی, Alefbâye Fârsi) is a writing system that is a version of the Arabic script used for the Persian language spoken in Iran ( Western Persian) and Afghanistan ( Dari Persian) since the 7th ce ...
. Examples of its detachment date to the 14th century or earlier. Kadi Burhan al-Din, Hesenoghlu, and Imadaddin Nasimi
Alī Imādud-Dīn Nasīmī ( az, Seyid Əli İmadəddin Nəsimi سئید علی عمادالدّین نسیمی, fa, عمادالدین نسیمی), often known as Nesimi, was a 14th-century Azerbaijani Ḥurūfī poet. Known mostly by his ...
helped to establish Azerbaiijani as a literary language in the 14th century through poetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek '' poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meani ...
and other works. The ruler of the Qara Qoyunlu state, Jahanshah, wrote poems in Azerbaijani language with the nickname "Haqiqi". Sultan Yaqub, the ruler of the Aq Qoyunlu state, wrote poems in the Azerbaijani language. The ruler and poet Ismail I wrote under the pen name ''Khatā'ī'' (which means "sinner" in Persian) during the fifteenth century.G. Doerfer, "Azeri Turkish", Encyclopaedia Iranica
An encyclopedia (American English) or encyclopædia (British English) is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge either general or special to a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into article ...
, viii, Online Editionp. 246.
/ref> During the 16th century, the poet, writer and thinker Fuzûlî wrote mainly in Azerbaijani but also translated his poems into
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
and Persian.
Starting in the 1830s, several newspapers were published in Iran during the reign of the Azerbaijani speaking Qajar dynasty but it is unknown whether any of these newspapers were written in Azerbaijani. In 1875, ''Akinchi
''Akinchi'' ( az, Əkinçi, ), also transliterated as ''Ekinchi'' ("The Cultivator"), was the first Azerbaijani-language newspaper, published in Baku (then part of the Russian Empire, now the capital of the Republic of Azerbaijan) between 1875 an ...
'' (' / ) ("The Ploughman") became the first Azerbaijani newspaper to be published in the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
. It was started by Hasan bey Zardabi
Hasan bey Zardabi ( az, Həsən bəy Zərdabi ), born Hasan bey Salim bey oghlu Malikov ( az, Həsən bəy Səlim bəy oğlu Məlikov, links=no ; 28 June 1842 — 15 November 1907), was an Azerbaijani journalist and intellectual, founder of the ...
, a journalist
A journalist is an individual that collects/gathers information in form of text, audio, or pictures, processes them into a news-worthy form, and disseminates it to the public. The act or process mainly done by the journalist is called journalis ...
and education advocate.
Following the rule of the Qajar dynasty, Iran was ruled by Reza Shah who banned the publication of texts in Azerbaijani. Modern literature in the Republic of Azerbaijan is based on the Shirvani dialect mainly, while in Iranian Azerbaijan, it is based on the Tabrizi dialect.
Mohammad-Hossein Shahriar is an important figure in Azerbaijani poetry. His most important work is '' Heydar Babaya Salam'' and it is considered to be a pinnacle of Azerbaijani literature
Azerbaijani literature ( az, Azərbaycan ədəbiyyatı) is written in Azerbaijani, a Turkic language, which is the official state language of the Republic of Azerbaijan, where the North Azerbaijani variety is spoken. It is also natively spoken ...
and gained popularity in the Turkic-speaking world. It was translated into more than 30 languages.
In the mid-19th century, Azerbaijani literature was taught at schools in Baku, Ganja
Ganja (, ; ) is one of the oldest and most commonly used synonyms for marijuana. Its usage in English dates to before 1689.
Etymology
''Ganja'' is borrowed from Hindi/Urdu ( hi, गांजा, links=no, ur, , links=no, IPA: �aːɲd͡ ...
, Shaki, Tbilisi
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the capital and the largest city of Georgia, lying on the banks of the Kura River with a population of approximately 1.5 million pe ...
, and Yerevan. Since 1845, it has also been taught in the Saint Petersburg State University in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
. In 2018, Azerbaijani language and literature programs are offered in the United States at several universities, including Indiana University
Indiana University (IU) is a system of public universities in the U.S. state of Indiana.
Campuses
Indiana University has two core campuses, five regional campuses, and two regional centers under the administration of IUPUI.
*Indiana Universi ...
, UCLA, and University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 ...
. The vast majority, if not all Azerbaijani language courses teach North Azerbaijani written in the Latin script and not South Azerbaijani written in the Perso-Arabic script.
Modern literature in the Republic of Azerbaijan is primarily based on the Shirvani dialect, while in the Iranian Azerbaijan region (historic Azerbaijan) it is based on the Tabrizi one.
Lingua franca
Azerbaijani served as a '' lingua franca'' throughout most parts ofTranscaucasia
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
except the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
coast, in southern Dagestan, the Eastern Anatolia Region and all over Iran from the 16th to the early 20th centuries, alongside cultural, administrative, court literature, and most importantly official language (along with Azerbaijani) of all these regions, namely Persian. From the early 16th century up to the course of the 19th century, these regions and territories were all ruled by the Safavids, Afsharids and Qajars until the cession of Transcaucasia proper and Dagestan by Qajar Iran to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
per the 1813 Treaty of Gulistan and the 1828 Treaty of Turkmenchay. Per the 1829 Caucasus School Statute, Azerbaijani was to be taught in all district schools of Ganja
Ganja (, ; ) is one of the oldest and most commonly used synonyms for marijuana. Its usage in English dates to before 1689.
Etymology
''Ganja'' is borrowed from Hindi/Urdu ( hi, गांजा, links=no, ur, , links=no, IPA: �aːɲd͡ ...
, Shusha, Nukha (present-day Shaki), Shamakhi
Shamakhi ( az, Şamaxı, ) is a city in Azerbaijan and the administrative centre of the Shamakhi District. The city's estimated population was 31,704. It is famous for its traditional dancers, the Shamakhi Dancers, and also for perhaps giving it ...
, Quba, Baku, Derbent
Derbent (russian: Дербе́нт; lez, Кьвевар, Цал; az, Дәрбәнд, italic=no, Dərbənd; av, Дербенд; fa, دربند), formerly romanized as Derbend, is a city in Dagestan, Russia, located on the Caspian Sea. It ...
, Yerevan, Nakhchivan, Akhaltsikhe
Akhaltsikhe ( ka, ახალციხე ), formerly known as Lomsia ( ka, ლომსია), is a small city in Georgia's southwestern region ('' mkhare'') of Samtskhe–Javakheti. It is situated on both banks of a small river Potskhovi (a l ...
, and Lankaran
Lankaran ( az, Lənkəran, ) is a city in Azerbaijan, on the coast of the Caspian Sea, near the southern border with Iran. As of 2021, the city had a population of 89,300. It is next to, but independent of, Lankaran District. The city forms a di ...
. Beginning in 1834, it was introduced as a language of study in Kutaisi instead of Armenian. In 1853, Azerbaijani became a compulsory language for students of all backgrounds in all of Transcaucasia with the exception of the Tiflis Governorate.
Dialects of Azerbaijani
 Azerbaijani is one of the
Azerbaijani is one of the Oghuz languages
The Oghuz languages are a sub-branch of the Turkic language family, spoken by approximately 108 million people. The three languages with the largest number of speakers are Turkish, Azerbaijani and Turkmen, which, combined, account for more t ...
within the Turkic language family. '' Ethnologue'' classifies North Azerbaijani (spoken mainly in the Republic of Azerbaijan and Russia) and South Azerbaijani (spoken in Iran, Iraq, and Syria) as separate languages with "significant differences in phonology, lexicon, morphology, syntax, and loanwords." The International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in A ...
(ISO) also considers Northern and Southern Azerbaijani to be distinct languages.
Svante Cornell wrote in his 2001 book ''Small Nations and Great Powers'' that "it is certain that Russian and Iranian words (sic), respectively, have entered the vocabulary on either side of the Araxes river, but this has not occurred to an extent that it could pose difficulties for communication".A study of Study of Ethnopolitical Conflict in the Caucasus, author Svante E.Cornell, 2001, page 22 () There are numerous dialects, with 21 North Azerbaijani dialects and 11 South Azerbaijani dialects identified by Ethnologue.
Four varieties have been accorded ISO 639-3
ISO 639-3:2007, ''Codes for the representation of names of languages – Part 3: Alpha-3 code for comprehensive coverage of languages'', is an international standard for language codes in the ISO 639 series. It defines three-letter codes for ...
language codes: North Azerbaijani, South Azerbaijani, Salchuq, and Qashqai. The '' Glottolog'' 4.1 database classifies North Azerbaijani, with 20 dialects, and South Azerbaijani, with 13 dialects, under the Modern Azeric family, a branch of Central Oghuz.
In the northern dialects of the Azerbaijani language, linguists find traces of the influence of the Khazar language.
According to the Linguasphere Observatory, all Oghuz languages form part of a single "outer language" of which North and South Azerbaijani are "inner languages".
North Azerbaijani
 North Azerbaijani, or Northern Azerbaijani, is the
North Azerbaijani, or Northern Azerbaijani, is the official language
An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ...
of the Republic of Azerbaijan. It is closely related to modern-day Istanbul Turkish, the official language of Turkey. It is also spoken in southern Dagestan, along the Caspian coast in the southern Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains,
: pronounced
* hy, Կովկասյան լեռներ,
: pronounced
* az, Qafqaz dağları, pronounced
* rus, Кавка́зские го́ры, Kavkázskiye góry, kɐfˈkasːkʲɪje ˈɡorɨ
* tr, Kafkas Dağla ...
and in scattered regions throughout Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
. As of 2011, there are some 9.23 million speakers of North Azerbaijani including 4 million monolingual speakers (many North Azerbaijani speakers also speak Russian, as is common throughout former USSR countries).
The Shirvan dialect as spoken in Baku is the basis of standard Azerbaijani. Since 1992, it has been officially written with a Latin script in the Republic of Azerbaijan, but the older Cyrillic script was still widely used in the late 1990s.
''Ethnologue'' lists 21 North Azerbaijani dialects: Quba, Derbend, Baku, Shamakhi, Salyan, Lankaran, Qazakh, Airym, Borcala, Terekeme, Qyzylbash, Nukha, Zaqatala (Mugaly), Qabala, Yerevan, Nakhchivan, Ordubad, Ganja, Shusha (Karabakh), Karapapak.
South Azerbaijani
South Azerbaijani, or Iranian Azerbaijani, is widely spoken in Iranian Azerbaijan and, to a lesser extent, in neighboring regions ofTurkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
and Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, with smaller communities in Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
. In Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, the Persian word for Azerbaijani is borrowed as ' "Turkic". In Iran, it is spoken mainly in East Azerbaijan, West Azerbaijan, Ardabil and Zanjan. It is also widely spoken in Tehran
Tehran (; fa, تهران ) is the largest city in Tehran Province and the capital of Iran. With a population of around 9 million in the city and around 16 million in the larger metropolitan area of Greater Tehran, Tehran is the most popul ...
and across Tehran Province, as Azerbaijanis form by far the largest minority in the city and the wider province, comprising about of its total population. The CIA World Factbook reports that in 2010, the percentage of Iranian Azerbaijani speakers at around 16 percent of the Iranian population, or approximately 13 million people worldwide, and ethnic Azeris form by far the second largest ethnic group of Iran, thus making the language also the second most spoken language in the nation. Ethnologue reports 10.9 million Iranian Azerbaijani in Iran in 2016 and 13,823,350 worldwide.
Dialects of South Azerbaijani include: Aynallu (Inallu, Inanlu), Qarapapaq, Tabrizi, Qashqai, Afshari (Afsar, Afshar), Shahsavani (Shahseven), Muqaddam, Baharlu (Kamesh), Nafar, Qaragözlü, Pishaqchi (Bıçaqçı), Bayatlu, Qajar, Marandli.
Comparison with other Turkic languages
Azerbaijani and Turkish
 North and South Azerbaijani speakers and Turkish speakers can communicate with varying degrees of mutual intelligibility. Turkish soap operas are very popular with Azeris in both Iran and Azerbaijan. Reza Shah Pahlavi of
North and South Azerbaijani speakers and Turkish speakers can communicate with varying degrees of mutual intelligibility. Turkish soap operas are very popular with Azeris in both Iran and Azerbaijan. Reza Shah Pahlavi of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
(who spoke South Azerbaijani) met with Mustafa Kemal Atatürk of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
(who spoke Turkish) in 1934; the two were filmed speaking their respective language to each other and communicated effectively., p. 33, p. 57
Speakers of Turkish and Azerbaijani can, to an extent, communicate with each other as both languages have substantial variation and are to a degree mutually intelligible, though it is easier for a speaker of Azerbaijani to understand Turkish than the other way around.
In a 2011 study, 30 Turkish participants were tested to determine how well they understood written and spoken Azerbaijani. It was found that even though Turkish and Azerbaijani are typologically similar languages, on the part of Turkish speakers the intelligibility is not as high as is estimated. In a 2017 study, Iranian Azerbaijanis scored in average 56% of receptive intelligibility in spoken language of Turkish.
Azerbaijani exhibits a similar stress pattern to Turkish but simpler in some respects. Azerbaijani is a strongly stressed and partially stress-timed language, unlike Turkish which is weakly stressed and syllable-timed.
Below are some words with different pronunciations in Azerbaijani and Turkish but have the same meaning in both languages:
Azerbaijani and Turkmen
The 1st person personal pronoun is ''mən'' in Azerbaijani just as ''men'' in Turkmen, whereas it is ''ben'' in Turkish. The same is true for demonstrative pronouns ''bu'', where sound ''b'' is replaced with sound ''m''. For example: ''bunun''>''munun''/''mının'', ''muna''/''mına'', ''munu''/''munı'', ''munda''/''mında'', ''mundan''/''mından''. This is observed in the Turkmen literary language as well, where the demonstrative pronoun ''bu'' undergoes some changes just as in: ''munuñ'', ''munı'', ''muña'', ''munda'', ''mundan'', ''munça''. ''b''>''m'' replacement is encountered in many dialects of the Turkmen language and may be observed in such words as: ''boyun''>''moyın'' in Yomut - Gunbatar dialect, ''büdüremek''>''müdüremek'' in Ersari and Stavropol Turkmens' dialects, ''bol''>''mol'' in Karakalpak Turkmens' dialects, ''buzav''>''mizov'' in Kirac dialects. Here are some words from the Swadesh list to compare Azerbaijani with Turkmen:Oghuric
Azerbaijani dialects
Azerbaijani dialects reflect relatively minor language differences and are mutually intelligible. The Azerbaijani language has two distinct sublanguages: Northern and Southern.
Southern Azerbaijani contains many Arabic and Persian words that are n ...
share paradigms of verbs in some tenses with the Chuvash language
Chuvash ( , ; , , ) is a Turkic language spoken in European Russia, primarily in the Chuvash Republic and adjacent areas. It is the only surviving member of the Oghur branch of Turkic languages, one of the two principal branches of the Tur ...
, on which linguists also rely in the study and reconstruction of the Khazar language.
Phonology
Phonotactics
Azerbaijani phonotactics is similar to that of other Oghuz Turkic languages, except: * Trimoraic syllables with long vowels are permissible. * There is an ongoing metathesis of neighboring consonants in a word. Speakers tend to reorder consonants in the order of decreasing sonority and back-to-front (for example, iləri becomes irəli, köprü becomes körpü, topraq becomes torpaq). Some of the metatheses are so common in the educated speech that they are reflected in orthography (all the above examples are like that). This phenomenon is more common in rural dialects but observed even in educated young urban speakers, but noticeably absent from some Southern dialects. * Intramorpheme becomes .Consonants
# The sound is used only in loanwords; the historical unpalatalized became voiced to . # and are realised as and respectively in the areas around Tabriz and to the west, south and southwest of Tabriz (including Kirkuk in Iraq); in the Nakhchivan and Ayrum dialects, inCəbrayil
Jabrayil ( az, Cəbrayıl, ) is a ghost city in Azerbaijan, nominally the administrative capital of Azerbaijan's Jabrayil District.
A town with Azerbaijani majority and Armenian plurality at various times during the Russian imperial era, and Az ...
and some Caspian coastal dialects;.
# Sounds and may also be recognized as separate phonemic sounds in the Tabrizi and southern dialects.
# In most dialects of Azerbaijani, is realized as when it is found in the syllabic coda or is preceded by a voiceless consonant (as in ' – "bread"; ' – "eighty").
# exists in the Kirkuk dialect as an allophone
In phonology, an allophone (; from the Greek , , 'other' and , , 'voice, sound') is a set of multiple possible spoken soundsor ''phones''or signs used to pronounce a single phoneme in a particular language. For example, in English, (as in '' ...
of in Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because ...
s.
# In the Baku subdialect, may be realised as , and and as , e.g. → , → , → , as well as with surnames ending in or (borrowed from Russian).
# In colloquial speech, is usually pronounced as
Dialect consonants
* Dz dz— * Ć ć— * Ŋ ŋ— * Q̇ q̇— * Ð ð— * W w— Examples: * —dzan * —ćay * —ataŋın * —q̇ar * —əðəli * —dowşan * —töwləVowels
The vowels of the Azerbaijani are, in alphabetical order, ' , ' , ' , ' , ' , ' , ' , ' , ' . There are no diphthongs in standard Azerbaijani when two vowels come together; when that occurs in some Arabic loanwords, diphthong is removed by either syllable separation at V.V boundary or fixing the pair as VC/CV pair, depending on the word.Writing systems
Before 1929, Azerbaijani was written only in the Perso-Arabic alphabet, an impure abjad that does not represent all vowels (without diacritical marks). In Iran, Azerbaijani is still written in a modified form of the Persian alphabet that the newspaper (started in 1979 by Javad Heyat) set the standard for.Azeri Arabic Turk standard of writing; authored by Dr. Javad Heyat; 2001 http://www.azeri.org/Azeri/az_arabic/azturk_standard.pdf () wrote in a reformed Perso-Arabic alphabet that represents all vowels with the exception of "''Ə''" as elucidated further by the newspaper's editor in a language guide written for Iranian Azerbaijanis titled "" published in 2001. Varlıq's standard of writing is today canonized by the official Persian–Azeri Turkish dictionary in Iran titled "". In 1929–1938 a Latin alphabet was in use for North Azerbaijani (although it was different from the one used now), from 1938 to 1991 theCyrillic script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking c ...
was used, and in 1991 the current Latin alphabet was introduced, although the transition to it has been rather slow. For instance, until an Aliyev Aliyev (sometimes spelled Aliev; az, Əliyev, kk, Áliyev, russian: Алиев), Aliyeva for females, is a surname originating from the Caucasus and Central Asia. The surname is derived from the Arabic male given name Ali and literally means ''A ...
decree on the matter in 2001, newspapers would routinely write headlines in the Latin script, leaving the stories in Cyrillic. The transition has also resulted in some misrendering of İ as ''Ì''. In Dagestan, Azerbaijani is still written in Cyrillic script.
The Azerbaijani Latin alphabet is based on the Turkish Latin alphabet, which in turn was based on former Azerbaijani Latin alphabet because of their linguistic connections and mutual intelligibility. The letters , , and are available only in Azerbaijani for sounds which do not exist as separate phonemes in Turkish.
Northern Azerbaijani, unlike Turkish, respells foreign names to conform with Latin Azerbaijani spelling, e.g. Bush is spelled and Schröder becomes . Hyphenation across lines directly corresponds to spoken syllables, except for geminated consonants which are hyphenated as two separate consonants as morphonology considers them two separate consonants back to back but enunciated in the onset of the latter syllable as a single long consonant, as in other Turkic languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia ( Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turki ...
.
Vocabulary
Interjections
Some samples include: Secular: * ' ("Ugh!") * ' ("Be quick!") * ' ("Be quick girls, to school!", a slogan for an education campaign in Azerbaijan) Invoking deity: * implicitly: ** ' ("Mercy") ** ' ("Much thanks") * explicitly: ** ' (pronounced as ') ("Goodness gracious") ** '; ' "By God swear it. ** ' ("Much thanks my god")Formal and informal
Azerbaijani has informal and formal ways of saying things. This is because there is a strong tu-vous distinction in Turkic languages like Azerbaijani and Turkish (as well as in many other languages). The informal "you" is used when talking to close friends, relatives, animals or children. The formal "you" is used when talking to someone who is older than you or someone for whom you would like to show respect (a professor, for example). As in many Turkic languages, personal pronouns can be omitted, and they are only added for emphasis. Since 1992 North Azerbaijani has used a phonetic writing system, so pronunciation is easy: most words are pronounced exactly as they are spelled.Numbers
For numbers 11–19, the numbers literally mean "10 one, 10 two" and so on. Greater numbers are constructed by combining in tens and thousands larger to smaller in the same way, without using a conjunction in between.Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * *External links
A blog on Azerbaijani language resources and translations
*
A blog about the Azerbaijani language and lessons
azeri.org
Azerbaijani literature and English translations.
Online bidirectional Azerbaijani-English Dictionary
roken as of 2022
Learn Azerbaijani
at learn101.org.
by Ahmad Kasravi. * including sound file.
Azerbaijani<>Turkish dictionary
(Pamukkale University)
Azerbaijan Language with Audio
Azerbaijani thematic vocabulary
AzConvert
an open source Azerbaijani transliteration program.
Azerbaijani Alphabet and Language in Transition
the entire issue of ''Azerbaijan International'', Spring 2000 (8.1) at azer.com. *
*
** ttp://azer.com/aiweb/categories/magazine/81_folder/81_articles/81_alphabet_sequence1.html Chart: Changes in the Four Azerbaijan Alphabet Sequence in the 20th century*
Baku’s Institute of Manuscripts: Early Alphabets in Azerbaijan
{{Authority control Agglutinative languages Languages of Azerbaijan Languages of Georgia (country) Languages of Iran Languages of Iraq Languages of Russia Languages of Turkey Subject–object–verb languages Turkic languages