Average Variance Extracted on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 In
In statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
(classical test theory
Classical test theory (CTT) is a body of related psychometric theory that predicts outcomes of psychological Test (assessment), testing such as the difficulty of items or the ability of test-takers. It is a theory of testing based on the idea that ...
), average variance extracted (AVE) is a measure of the amount of variance that is captured by a construct in relation to the amount of variance due to measurement error.
History
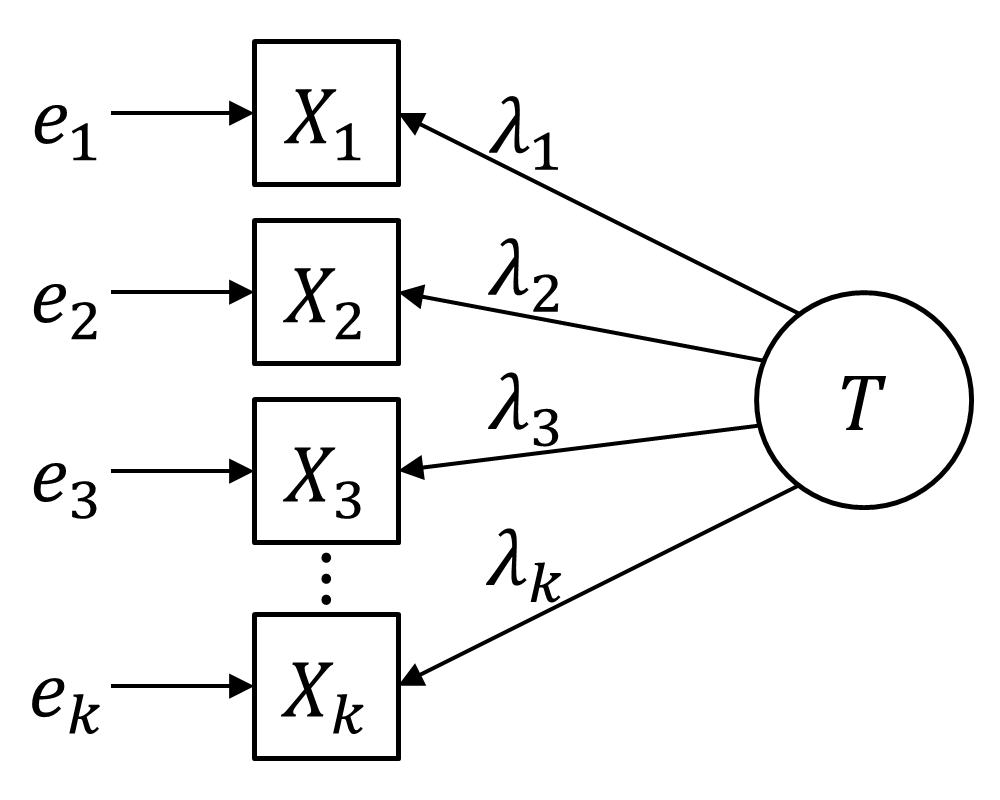
The average variance extracted was first proposed by Fornell & Larcker (1981).Calculation
The average variance extracted can be calculated as follows: : Here, is the number of items, the factor loading of item and thevariance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean of a random variable. The standard deviation (SD) is obtained as the square root of the variance. Variance is a measure of dispersion ...
of the error of item .
Role for assessing discriminant validity
The average variance extracted has often been used to assess discriminant validity based on the following "rule of thumb": the positive square root of the AVE for each of the latent variables should be higher than the highest correlation with any other latent variable. If that is the case, discriminant validity is established at the construct level. This rule is known as Fornell–Larcker criterion. However, in simulation models this criterion did not prove reliable for composite-based structural equation models (e.g., PLS-PM),Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., Sarstedt, M., 2014. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 43 (1), 115–135. but indeed proved to be reliable for factor-based structural equation models (e.g., Amos, PLSF-SEM).Kock, N. (2019). From composites to factors: Bridging the gap between PLS and covariance-based structural equation modeling. Information Systems Journal, 29(3), 674-706.Voorhees, C. M., Brady, M. K., Calantone, R., Ramirez, E., 2015. Discriminant validity testing in marketing: an analysis, causes for concern, and proposed remedies. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 1–16.Related coefficients
Related coefficients are tau-equivalent reliability (; traditionally known as "Cronbach's ") and congeneric reliability (; also known as composite reliability) which can be used to evaluate the reliability of tau-equivalent and congeneric measurement models, respectively.References