Automobile Transmission on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A transmission (also called a gearbox) is a mechanical device which uses

 Many transmissions - especially for transportation applications - have multiple gear ratios that can be switched between while the machine is operating. The multiple ratios are used to match the range of input speeds (e.g. engine rpm) with the output speed (e.g. the speed of a car) required for a given situation.
Many transmissions - especially for transportation applications - have multiple gear ratios that can be switched between while the machine is operating. The multiple ratios are used to match the range of input speeds (e.g. engine rpm) with the output speed (e.g. the speed of a car) required for a given situation.
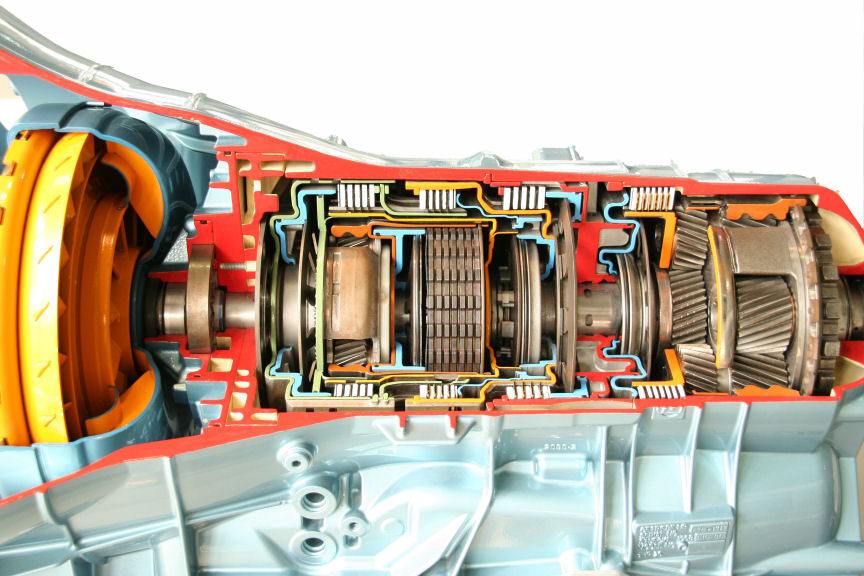
File:Cambio H.jpg , Transmission internals for a 2009
 An
An
gears
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic p ...
to change the speed or direction of rotation in a mechanical device
A machine is a physical system using power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolecul ...
. Many transmissions have multiple gear ratio
A gear train is a mechanical system formed by mounting gears on a frame so the teeth of the gears engage.
Gear teeth are designed to ensure the Pitch circle diameter (gears), pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, pr ...
s, however there are also transmissions that use a single fixed gear ratio.
Most currently-produced passenger cars with petrol or diesel engines use transmissions with 5-8 forward gear ratios and one reverse gear ratio. Electric vehicles typically use a single-speed or two-speed transmission.
Fixed-ratio transmissions
The simplest transmissions used a fixed ratio to provide either a gear reduction or increase in speed, sometimes in conjunction with a change in the orientation of the output shaft. Examples of such transmissions are used inhelicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes ...
s, wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each yea ...
s and power take-offs (PTOs) for tractors. In the case of a wind turbine, the first stage of the gearbox is usually a planetary gear, to minimize the size while withstanding the high torque inputs from the turbine.
Multi-ratio transmissions

 Many transmissions - especially for transportation applications - have multiple gear ratios that can be switched between while the machine is operating. The multiple ratios are used to match the range of input speeds (e.g. engine rpm) with the output speed (e.g. the speed of a car) required for a given situation.
Many transmissions - especially for transportation applications - have multiple gear ratios that can be switched between while the machine is operating. The multiple ratios are used to match the range of input speeds (e.g. engine rpm) with the output speed (e.g. the speed of a car) required for a given situation.
Manual
A manual transmission requires the driver to manually select the gears by operating agear stick
A gear stick (rarely spelled ''gearstick''), gear lever (both UK English), gearshift or shifter (both U.S. English), more formally known as a transmission lever, is a metal lever attached to the transmission of an automobile. The term ''gear st ...
and clutch (which is usually a foot pedal for cars or a hand lever for motorcycles).
Most transmissions in modern cars use synchromesh to synchronise the speeds of the input and output shafts. However, prior to the 1950s, most cars used non-synchronous transmissions.
Volkswagen Golf
The Volkswagen Golf () is a compact car/small family car (C-segment) produced by the German automotive manufacturer Volkswagen since 1974, marketed worldwide across eight generations, in various body configurations and under various nameplates ...
File:John Deere 3350 tractor cut transmission.JPG , 16-speed tractor transmission (plus 8 reverse gears)
Sequential manual
A sequential manual transmission is a type of non-synchronous transmission used mostly for motorcycles and racing cars. It produces faster shift times than synchronized manual transmissions, through the use ofdog clutch
A dog clutch (also known as a positive clutch or dog gears) is a type of clutch that couples two rotating shafts or other rotating components by engagement of interlocking teeth or dogs rather than by friction. The two parts of the clutch are de ...
es rather than synchromesh. Sequential manual transmissions also restricts the driver to selecting either the next or previous gear, in a successive order.
Automatic and semi-automatic
automatic transmission
An automatic transmission (sometimes abbreviated to auto or AT) is a multi-speed transmission used in internal combustion engine-based motor vehicles that does not require any input from the driver to change forward gears under normal driving ...
does not require any input from the driver to change forward gears under normal driving conditions. A semi-automatic transmission
A semi-automatic transmission is a "theoretical" multiple-speed transmission where part of its operation is automated (typically the actuation of the clutch), but the driver's input would be required to launch the vehicle from a standstill and t ...
is where some of the operation is automated (often the actuation of the clutch), but the driver's input is required to move off from a standstill or to change gears.
Hydraulic automatic
The most common design of automatic transmissions is the hydraulic automatic, which typically uses planetary gearsets that are operated usinghydraulics
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counte ...
. The transmission is connected to the engine via a torque converter
A torque converter is a type of fluid coupling that transfers rotating power from a prime mover, like an internal combustion engine, to a rotating driven load. In a vehicle with an automatic transmission, the torque converter connects the power ...
(or a fluid coupling
A fluid coupling or hydraulic coupling is a hydrodynamic or 'hydrokinetic' device used to transmit rotating mechanical power.
prior to the 1960s), instead of the friction clutch used by most manual transmissions and dual-clutch transmissions.
Dual-clutch (DCT)
A dual-clutch transmission (DCT) uses two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets. The design is often similar to two separatemanual transmission
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission system, where gear change ...
s with their respective clutches contained within one housing, and working as one unit. In car and truck applications, the DCT functions as an automatic transmission, requiring no driver input to change gears.
Continuously variable (CVT)
A continuously variable transmission (CVT) can change seamlessly through a continuous range ofgear ratio
A gear train is a mechanical system formed by mounting gears on a frame so the teeth of the gears engage.
Gear teeth are designed to ensure the Pitch circle diameter (gears), pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, pr ...
s. This contrasts with other transmissions that provide a limited number of gear ratios in fixed steps. The flexibility of a CVT with suitable control may allow the engine to operate at a constant RPM
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionl ...
while the vehicle moves at varying speeds.
CVTs are used in cars, tractors, side-by-sides, motor scooters, snowmobile
A snowmobile, also known as a Ski-Doo, snowmachine, sled, motor sled, motor sledge, skimobile, or snow scooter, is a motorized vehicle designed for winter travel and recreation on snow. It is designed to be operated on snow and ice and does not ...
s, bicycles, and earthmoving equipment.
The most common type of CVT uses two pulleys connected by a belt
Belt may refer to:
Apparel
* Belt (clothing), a leather or fabric band worn around the waist
* Championship belt, a type of trophy used primarily in combat sports
* Colored belts, such as a black belt or red belt, worn by martial arts practit ...
or chain; however, several other designs have also been used at times.
Automated manual / clutchless manual
An automated manual transmission (AMT) is essentially a conventional manual transmission that uses automatic actuation to operate the clutch and/or shift between gears. Many early versions of these transmissions were semi-automatic in operation, such as ''Autostick
The name Autostick has been used for a Volkswagen semi-automatic transmission, which is a vacuum-operated automatic clutch system, coupled with a conventional 3-speed manual transmission. The "AutoStick" system designed by Chrysler allows for ma ...
'', which automatically control only the clutch, but still require the driver's input to initiate gear changes. Some of these systems are also referred to as ''clutchless manual'' systems. Modern versions of these systems that are fully automatic in operation, such as ''Selespeed
Selespeed is the name of an automated manual transmission used in Alfa Romeo cars, developed by Italian company Magneti Marelli and made by Graziano Trasmissioni.
The Selespeed is an automated manual gearbox with an electronic clutch. In its curre ...
'' and ''Easytronic
Easytronic is the Opel tradename for a type of transaxle-based automated manual transmission or gearbox, as used in some Opel/Vauxhall cars.
Easytronic is not a tiptronic gearbox design; it does not have a torque converter. It is fundamental ...
'', can control both the clutch operation and the gear shifts automatically, without any input from the driver.
Applications
Early uses
Early transmissions included the right-angle drives and other gearing inwindmill
A windmill is a structure that converts wind power into rotational energy using vanes called sails or blades, specifically to mill grain (gristmills), but the term is also extended to windpumps, wind turbines, and other applications, in some ...
s, horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million yea ...
-powered devices, and steam-powered devices. Applications of these devices included pumps, mills
Mills is the plural form of mill, but may also refer to:
As a name
* Mills (surname), a common family name of English or Gaelic origin
* Mills (given name)
*Mills, a fictional British secret agent in a trilogy by writer Manning O'Brine
Places Uni ...
and hoists.
Automobiles
The need for multiple gear ratios inICE
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaqu ...
-powered motor vehicles is because the engines typically operate over a range of approximately 600-7000 rpm
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionl ...
, while the road speed of the vehicle typically equates to a rotational speed
Rotational frequency (also known as rotational speed or rate of rotation) of an object rotating around an axis is the frequency of rotation of the object. Its unit is revolution per minute (rpm), cycle per second (cps), etc.
The symbol fo ...
of the wheels in the range of 0-1800 rpm. In addition, the engine's characteristics result in different optimal rpm ranges for the power band
The power band of an internal combustion engine or electric motor is the range of operating speeds under which the engine or motor is able to output the most power, that is, the maximum energy per unit of time. This usually means that maximum a ...
and achieving highest fuel efficiency.
Motorcycles
See also
* Bicycle gearing *Direct-drive mechanism
A direct-drive mechanism is a mechanism design where the force or torque from a prime mover is transmitted directly to the effector device (such as the drive wheels of a vehicle) without involving any intermediate couplings such as a gear train ...
*Transfer case
A transfer case is a part of the drivetrain of four-wheel-drive, all-wheel-drive, and other multiple powered axle vehicles. The transfer case transfers power from the transmission to the front and rear axles by means of drive shafts. It also syn ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Transmission (Mechanics) Mechanisms (engineering)