Armoured train on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
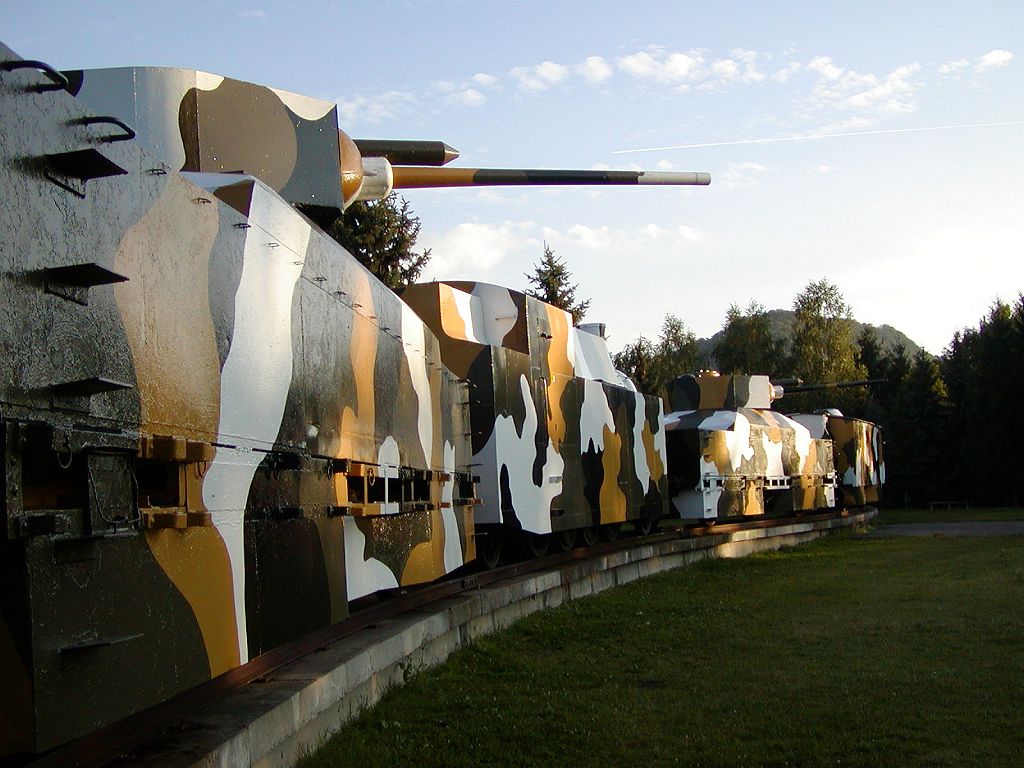 An armoured train is a railway
An armoured train is a railway
 The rail cars on an armoured train were designed for many tasks. Typical roles included:
*
The rail cars on an armoured train were designed for many tasks. Typical roles included:
*
 Two armoured trains were constructed at Crewe Works during 1915 for British coastal defense duties; one was based in
Two armoured trains were constructed at Crewe Works during 1915 for British coastal defense duties; one was based in
 The
The 
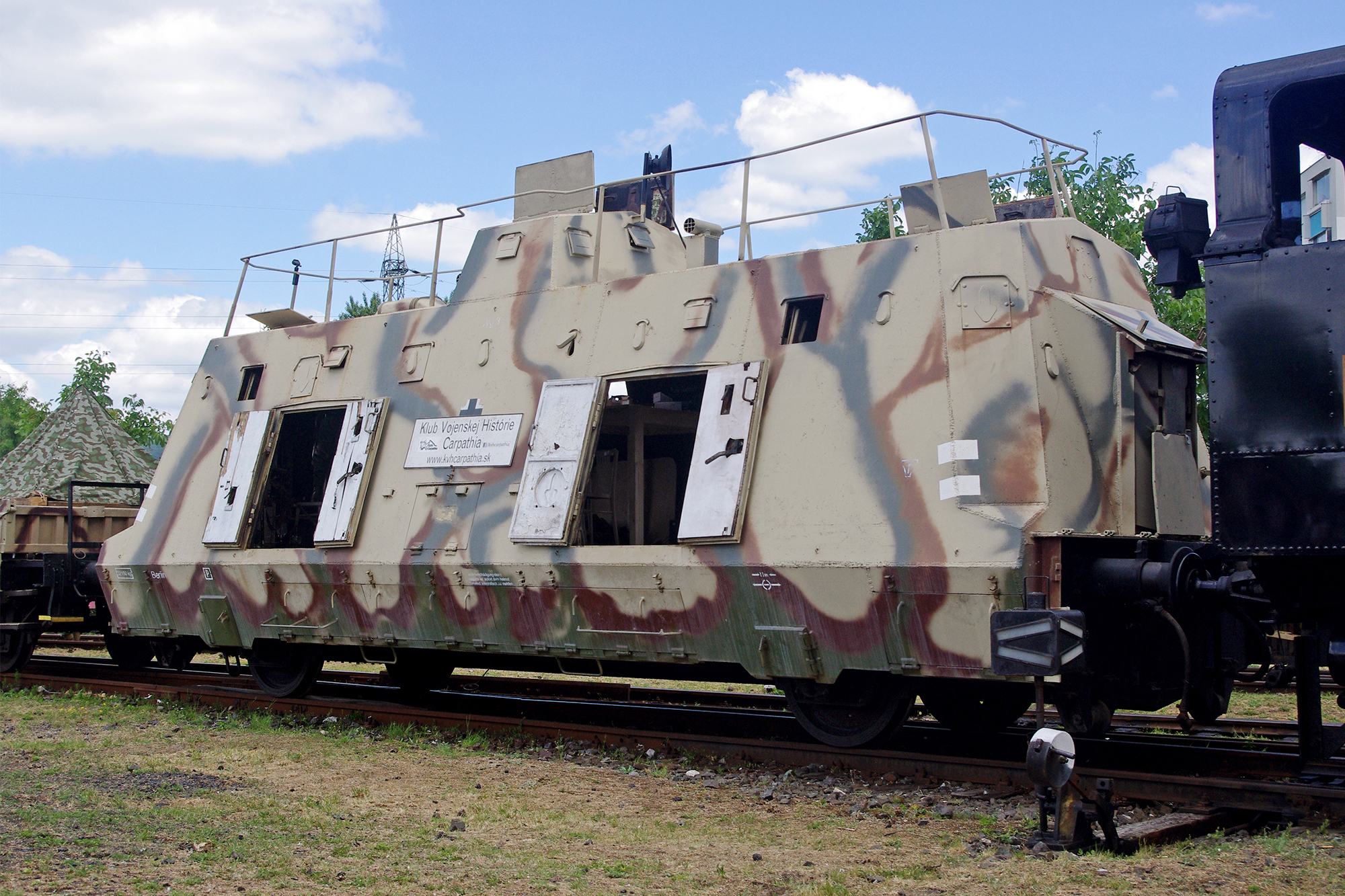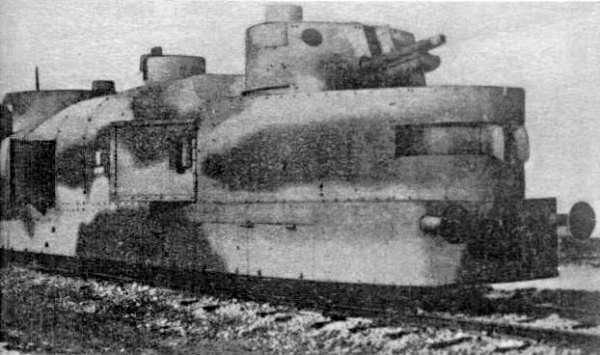
 During the
During the
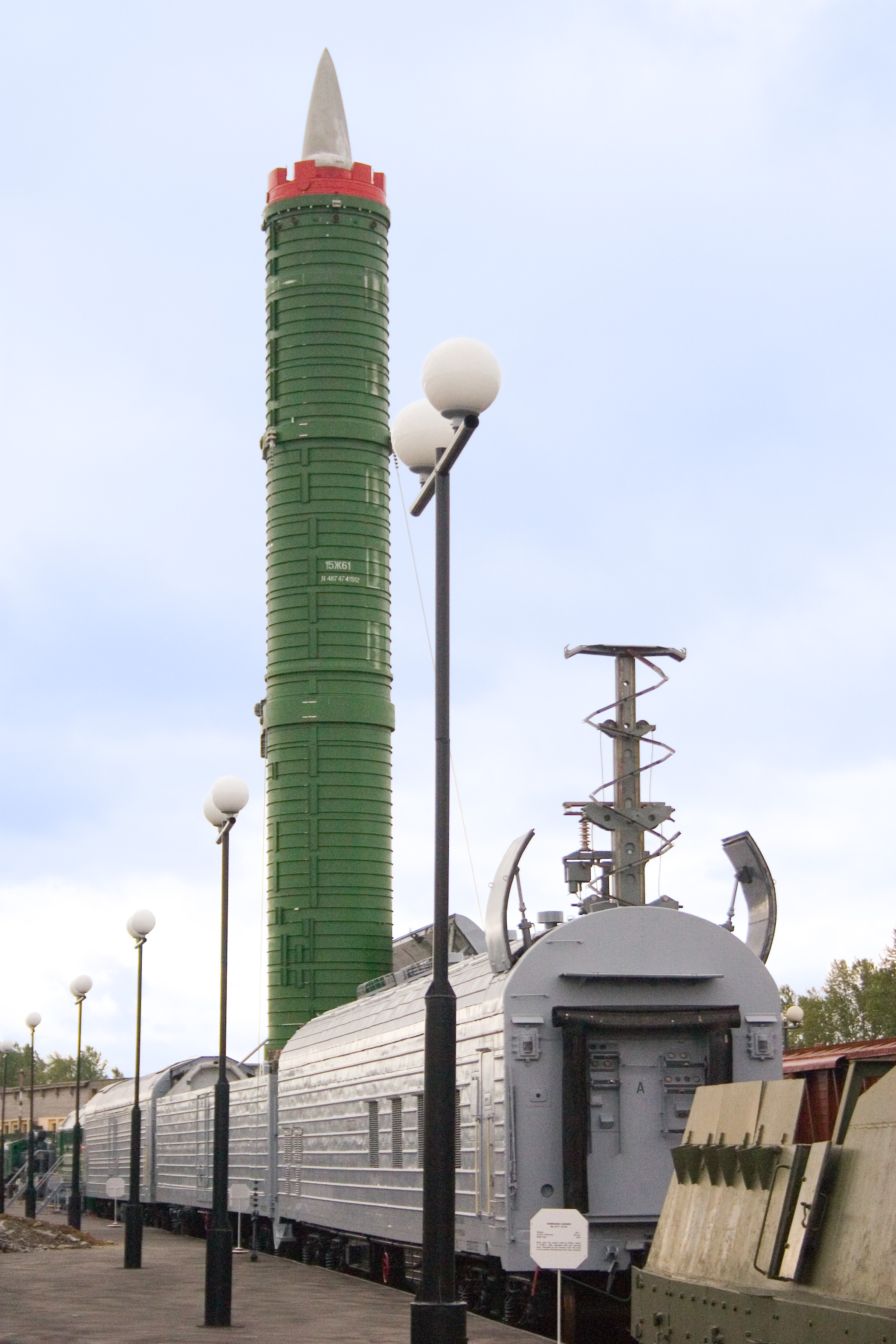 In the
In the
The Czech and Slovak Republics
' (excerpt from
Finnish armoured trains
{{DEFAULTSORT:Armoured Train Articles containing video clips
 An armoured train is a railway
An armoured train is a railway train
In rail transport, a train (from Old French , from Latin , "to pull, to draw") is a series of connected vehicles that run along a railway track and transport people or freight. Trains are typically pulled or pushed by locomotives (often ...
protected with armour
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or f ...
. Armoured trains usually include railway wagons armed with artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during si ...
, machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifles ...
s and autocannon
An autocannon, automatic cannon or machine cannon is a fully automatic gun that is capable of rapid-firing large-caliber ( or more) armour-piercing, explosive or incendiary shells, as opposed to the smaller-caliber kinetic projectiles (bul ...
s. Some also had slits used to fire small arms
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
from the inside of the train, a facility especially prevalent in earlier armoured trains. For the most part they were used during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, when they offered an innovative way to quickly move large amounts of firepower. Most countries discontinued their use – road vehicles became much more powerful and offered more flexibility, and train tracks proved too vulnerable to sabotage
Sabotage is a deliberate action aimed at weakening a polity, effort, or organization through subversion, obstruction, disruption, or destruction. One who engages in sabotage is a ''saboteur''. Saboteurs typically try to conceal their identitie ...
and attacks from the air. However, the Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
used improvised armoured trains in the Second Chechen War
The Second Chechen War (russian: Втора́я чече́нская война́, ) took place in Chechnya and the border regions of the North Caucasus between the Russian Federation and the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, from August 1999 ...
of 1999–2009 and the Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. An ...
in 2022.
Armoured trains were usually fighting systems, equipped with heavy weapons such as artillery. An exception was the US " White Train", the Department of Energy Nuclear Weapons Transport Train, armoured and escorted by personnel armed with personal weapons.
Design and equipment
 The rail cars on an armoured train were designed for many tasks. Typical roles included:
*
The rail cars on an armoured train were designed for many tasks. Typical roles included:
* Artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during si ...
– fielding a mixture of guns, machine guns and rocket launchers. See also railway guns.
* Infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and mar ...
– designed to carry infantry units, may also mount machine guns.
* Machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifles ...
– dedicated to machine guns.
* Anti-aircraft
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based ...
– equipped with anti-aircraft weapons.
* Command
Command may refer to:
Computing
* Command (computing), a statement in a computer language
* COMMAND.COM, the default operating system shell and command-line interpreter for DOS
* Command key, a modifier key on Apple Macintosh computer keyboards
* ...
– similar to infantry wagons, but designed to be a train command centre
* Anti-tank
Anti-tank warfare originated from the need to develop technology and tactics to destroy tanks during World War I. Since the Triple Entente deployed the first tanks in 1916, the German Empire developed the first anti-tank weapons. The first dev ...
– equipped with anti-tank guns, usually in a tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful ...
gun turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanis ...
* Platform – unarmoured, used for any purpose from the transport of ammunition
Ammunition (informally ammo) is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. Ammunition is both expendable weapons (e.g., bombs, missiles, grenades, land mines) and the component parts of other we ...
or vehicles, through track repair or derailing protection to railroad ploughs for track destruction.
* Troop sleepers
* The German Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
would sometimes use a flatbed car to carry a ''Fremdgerät'' light tank, such as a captured French Somua S-35 or Czech PzKpfw 38(t), or a Panzer II
The Panzer II is the common name used for a family of German tanks used in World War II. The official German designation was ''Panzerkampfwagen'' II (abbreviated PzKpfw II).
Although the vehicle had originally been designed as a stopgap while l ...
, which could quickly drive down a ramp and pursue enemy partisans away from the railway line
* Missile
In military terminology, a missile is a guided airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight usually by a jet engine or rocket motor. Missiles are thus also called guided missiles or guided rockets (when a previously unguided rocket ...
transport – the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nati ...
had railway-based RT-23 Molodets ICBMs by the late 1980s (to reduce the chances of a first strike succeeding in destroying the launchers for a retaliatory strike). The US at one time proposed having a railway-based system for the MX Missile program, but this never got past the planning stage. The US also used an armoured Department of Energy Nuclear Weapons Transport Train, not for fighting but for transport within the country
Different types of armour were used to protect from attack by tanks. In addition to various metal plates, concrete and sandbags were used in some cases for improvised armoured trains.
Armoured trains were sometimes escorted by a kind of rail-tank called a draisine
A draisine () is a light auxiliary rail vehicle, driven by service personnel, equipped to transport crew and material necessary for the maintenance of railway infrastructure.
The eponymous term is derived from the German inventor Baron Karl ...
. One such example was the 'Littorina' armoured trolley which had a cab in the front and rear, each with a control set so it could be driven down the tracks in either direction. Littorina mounted two dual 7.92 mm MG13
The MG 13 (shortened from German Maschinengewehr 13) is a German light machine gun developed by converting the Dreyse Model 1918 heavy water-cooled machine gun into an air-cooled version.
History
Dreyse Model 1918 Machinegun: In 1907 Louis Schmeis ...
machine gun turrets from Panzer I
The Panzer I was a light tank produced in Nazi Germany in the 1930s. Its name is short for (German for "armored fighting vehicle mark I"), abbreviated as . The tank's official German ordnance inventory designation was '' Sd.Kfz. 101' ...
light tanks.
History
Origins
Armoured and armed trains saw use during the 19th century in theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
(1861–1865), the Franco-Prussian War (1870–1871), the First and Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the So ...
s (1880–1881 and 1899–1902). During the Second Boer War Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
, then a war correspondent, was travelling on an armoured train which was ambushed by a Boer
Boers ( ; af, Boere ()) are the descendants of the Dutch-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled this are ...
commando led by General Louis Botha
Louis Botha (; 27 September 1862 – 27 August 1919) was a South African politician who was the first prime minister of the Union of South Africa – the forerunner of the modern South African state. A Boer war hero during the Second Boer Wa ...
on 15 November 1899; the Boers captured Churchill and many of the train's contingent.
Early in the 20th century, Russia used armoured trains during the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
. Armoured trains were also used during the Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution ( es, Revolución Mexicana) was an extended sequence of armed regional conflicts in Mexico from approximately 1910 to 1920. It has been called "the defining event of modern Mexican history". It resulted in the destruction ...
(1910–1920) and World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
(1914–1918). The most intensive use of armoured trains was during the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
(1918–1920). The Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlism, Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebeli ...
saw a little use of armoured trains, though World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
(1939–1945) saw more. The French used them during the First Indochina War
The First Indochina War (generally known as the Indochina War in France, and as the Anti-French Resistance War in Vietnam) began in French Indochina from 19 December 1946 to 20 July 1954 between France and Việt Minh (Democratic Republic of Vi ...
(1946–1954), a number of countries had armoured trains during the Cold War, and they were used during the Yugoslav wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related Naimark (2003), p. xvii. ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and insurgencies that took place in the SFR Yugoslavia from 1991 to 2001. The conflicts both led up to and resulted from ...
of the 1990s and the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.
American Civil War
The most successful armed train was a single armoured wagon built to defend thePhiladelphia, Wilmington and Baltimore Railroad
The Philadelphia, Wilmington and Baltimore Railroad (PW&B) was an American railroad that operated independently from 1836 to 1881.
It was formed in 1836 by the merger of four state-chartered railroads in three Middle Atlantic states to create a ...
. The railroad had been attacked by southern forces to prevent transport of Union soldiers to the front, and snipers were discouraging men attempting to repair the damage. Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railroad locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, in the early 20th century. The company was for decades ...
modified a baggage wagon in late April 1861. A 24-pounder howitzer
A howitzer () is a long- ranged weapon, falling between a cannon (also known as an artillery gun in the United States), which fires shells at flat trajectories, and a mortar, which fires at high angles of ascent and descent. Howitzers, like ot ...
was placed on a swivel mount at the opposite end of the wagon from the pushing locomotive. The sides of the wagon were sheathed with oak planks covered with boiler plate. The end of the wagon around the howitzer was fitted with hinged panels which could be temporarily lifted to aim and fire the howitzer and then lowered to protect the crew of six men loading the howitzer with canister shot
Canister shot is a kind of anti-personnel artillery ammunition. Canister shot has been used since the advent of gunpowder-firing artillery in Western armies. However, canister shot saw particularly frequent use on land and at sea in the various ...
or grapeshot. The remainder of the wagon contained fifty ports for riflemen. The wagon was effective for its original purpose, but vulnerability to artillery rendered such wagons of comparatively little use during later stages of the war. In August 1864, a Confederate raiding party disabled a Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States, with its first section opening in 1830. Merchants from Baltimore, which had benefited to some extent from the construction of ...
locomotive pushing an armoured wagon, and then piled ties around the armoured wagon and set them afire.
Volunteers
In 1884 Charles Gervaise Boxall (1852–1914), aBrighton
Brighton () is a seaside resort and one of the two main areas of the City of Brighton and Hove in the county of East Sussex, England. It is located south of London.
Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze A ...
-born solicitor and officer in the 1st Sussex Artillery Volunteers, published ''The Armoured Train for Coast Defence in Great Britain'', outlining a new way to employ heavy artillery. In 1894, when he had become commanding officer of the 1st Sussex AV, railway workers among the volunteers of No 6 Garrison Company manned an armoured train constructed in the workshops of the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway
The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR; known also as the Brighton line, the Brighton Railway or the Brighton) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1846 to 1922. Its territory formed a rough triangle, with London at its ...
(of which the unit's Honorary Colonel, Sir Julian Goldsmid, was a director).
Second Boer War
TheBritish Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkha ...
employed armoured trains during the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the So ...
, most famously a train that was extemporised in the railway workshops at Ladysmith Ladysmith may refer to:
* Ladysmith, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa
* Ladysmith, British Columbia, Canada
* Ladysmith, Wisconsin, United States
* Ladysmith, New South Wales, Australia
* Ladysmith, Virginia, United States
* Ladysmith Island, Queenslan ...
just before the siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteriz ...
was closed round the town. On 15 November 1899 it left the town on reconnaissance manned by a company of the Royal Dublin Fusiliers
The Royal Dublin Fusiliers was an Irish infantry Regiment of the British Army created in 1881, one of eight Irish regiments raised and garrisoned in Ireland, with its home depot in Naas. The Regiment was created by the amalgamation of two Brit ...
under the command of Captain Aylmer Haldane, a company of volunteers of the Durban Light Infantry
The Durban Light Infantry is a Motorised Infantry regiment of the South African Army. It lost its status as a Mechanised infantry regiment in 2010 in line with the rationalisation of resources. As a reserve unit, it has a status roughly equival ...
, and a 7-pounder mountain gun manned by sailors from HMS ''Tartar''. Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
accompanied the mission as a war correspondent. The train was ambushed and part-derailed, and Haldane, Churchill and some 70 of the troops were captured after a fire-fight, although the locomotive got away with the wounded. Recalling his experience in My Early Life
''My Early Life'', also known in the USA as ''A Roving Commission: My Early Life'', is a 1930 book by Winston Churchill. It is an autobiography from his birth in 1874 to around 1902. The book closes with mention of his marriage in 1908, stating t ...
, Churchill wrote "Nothing looks more formidable and impressive than an armoured train; but nothing is in fact more vulnerable and helpless. It was only necessary to blow up a bridge of culvert to leave the monster stranded, far from home and help, at the mercy of the enemy".
World War I
During World War I Russia used a mix of light and heavy armoured trains. The heavy trains mounted 4.2 inch or 6 inch guns; the light trains were equipped with 7.62 mm guns.Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
also fielded armoured trains against the Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
in World War I.
A Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
armoured train from Britain, armed with four QF 6 inch naval guns and one QF 4 inch naval gun, was used in support of the British Expeditionary Force in the opening phase of the First Battle of Ypres
The First Battle of Ypres (french: Première Bataille des Flandres; german: Erste Flandernschlacht – was a battle of the First World War, fought on the Western Front around Ypres, in West Flanders, Belgium. The battle was part of the Firs ...
in October 1914.
 Two armoured trains were constructed at Crewe Works during 1915 for British coastal defense duties; one was based in
Two armoured trains were constructed at Crewe Works during 1915 for British coastal defense duties; one was based in Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
and one in Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
to patrol rail routes on stretches of coast considered vulnerable to amphibious assault. The trains comprised two gun trucks, one at each end, mounted with a 12-pounder quick firing gun and a machine gun; an armoured cabin behind the artillery piece contained the magazine
A magazine is a periodical publication, generally published on a regular schedule (often weekly or monthly), containing a variety of content. They are generally financed by advertising, purchase price, prepaid subscriptions, or by a combinatio ...
. Inboard of each gun truck was a truck for infantry quarters. This was also armoured, with observation ports and loops for rifle fire. The armoured locomotive, with the cab and motion
In physics, motion is the phenomenon in which an object changes its position with respect to time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed and frame of reference to an observer and m ...
protected, was marshalled into the centre of the train. The driver took up a position at whichever end of the train was leading, with the regulator controlled by a mechanical connection. The intention was that the infantry, with artillery support from the train's guns, was to hold off a hostile landing force until reinforcements could be deployed.
Italy fitted twelve armed trains (under the control of the Regia Marina
The ''Regia Marina'' (; ) was the navy of the Kingdom of Italy (''Regno d'Italia'') from 1861 to 1946. In 1946, with the birth of the Italian Republic (''Repubblica Italiana''), the ''Regia Marina'' changed its name to ''Marina Militare'' ("M ...
) to protect its Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the ...
coast from raids on part of the k.u.k Kriegsmarine; each train was supplemented by a support one. Each armed train was formed by a FS Class 290
The Ferrovie dello Stato Italiane (FS; Italian State Railways) Class 290 (Italian: ''Gruppo 290''), formerly the Rete Adriatica Class 350 bis, is a 0-6-0 steam locomotive.
Design and construction
The Class 290 was a development of the earlier FS ...
locomotive, three to five gun cars, two to four ammo cars and a command car; there were three types of armed train, one with 152 mm guns, another with 120 mm guns and the last with 76 mm AA guns. These trains were considered overall a success, and blunted attempted Austro-Hungarian raids on the Italian coast.
Two armoured trains were produced in the railway workshop located at Ajmer
Ajmer is one of the major and oldest cities in the Indian state of Rajasthan and the centre of the eponymous Ajmer District. It is located at the centre of Rajasthan. It is also known as heart of Rajasthan. The city was established as "' ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
. One sent to Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
(now Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
) by sea route for the Mesopotamian Campaign
The Mesopotamian campaign was a campaign in the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I fought between the Allies represented by the British Empire, troops from Britain, Australia and the vast majority from British India, against the Central Po ...
. Each train consists six wagons, Two wagons of each trains were ceiling less, each train consists 12-pounder guns, two Maxim heavy machine guns, two mine-exploding wagons, search light truck and a dynamo telegraph accommodation truck.
Interwar years
 The
The Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
forces in the Russian Civil War used a wide range of armoured trains, including Trotsky's one. Many were improvised by locals, others were constructed by naval engineers at the Putilov and Izhorskiy factories. As a result, the trains ranged from little more than sandbagged flatbeds to the heavily armed and armoured trains produced by the naval engineers. An attempt to standardise the design from October 1919 only had limited success. By the end of the war the Bolshevik forces had 103 armoured trains of all types.
The Czechoslovak Legion
The Czechoslovak Legion (Czech language, Czech: ''Československé legie''; Slovak language, Slovak: ''Československé légie'') were volunteer armed forces composed predominantly of Czechs and Slovaks fighting on the side of the Allies of World ...
used heavily armed and armoured trains to control large lengths of the Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway (TSR; , , ) connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the ea ...
(and of Russia itself) during the Russian Civil War at the end of World War I.''First World War'' - Willmott, H.P.; Dorling Kindersley
Dorling Kindersley Limited (branded as DK) is a British multinational publishing company specialising in illustrated reference books for adults and children in 63 languages.
It is part of Penguin Random House, a subsidiary of German media c ...
, 2003, Page 251
Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, an ...
built a total of 13 armoured trains during the Estonian War of Independence
The Estonian War of Independence ( et, Vabadussõda, literally "Freedom War"), also known as the Estonian Liberation War, was a defensive campaign of the Estonian Army and its allies, most notably the United Kingdom, against the Bolshevik westw ...
: six on broad-gauge
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways.
Broad gauge of , commonly known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union ( ...
and seven on narrow-gauge railways. The first three armoured trains with fully volunteer crews formed the backbone of the front in critical early stages of conflict. Carriages were former goods carriages and at first armor was limited to wood and sand, but later steel plating, machine guns, and cannons were added.

Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
had three armoured trains, named after the Grand Dukes of Lithuania: ''Gediminas'', ''Kęstutis'' and ''Algirdas''. The armoured trains were used from 1920 to 1935. The first of them, ''Gediminas'', was used in the Polish–Lithuanian War
The Polish–Lithuanian War (in Polish historiography, Polish–Lithuanian Conflict) was an undeclared war between newly-independent Lithuania and Poland following World War I, which happened mainly, but not only, in the Vilnius and Suwałki ...
.
After the First World War the use of armoured trains declined. They were used in China in the twenties and early thirties during the Chinese Civil War, most notably by the warlord
A warlord is a person who exercises military, economic, and political control over a region in a country without a strong national government; largely because of coercive control over the armed forces. Warlords have existed throughout much of h ...
Zhang Zongchang, who employed refugee Russians to man them.
World War II

Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
used armoured trains extensively during the invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week af ...
. One observer noted that "Poland had only few armoured trains, but their officers and soldiers were fighting well. Again and again they were emerging from a cover in thick forests, disturbing German lines". One under-appreciated aspect of so many Polish armoured trains being deployed during the Polish Defensive War in 1939 is that when German planes attacked the railroads, it was usually the tracks themselves. As late as 17 September, three fresh divisions in the east were moved westward by train. On 18 September, three more divisions followed.
This in turn prompted Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
to reintroduce armoured trains into its own armies. Germany then used them to a small degree during World War II. They introduced significant designs of a versatile and well-equipped nature, including railcars which housed anti-aircraft gun turrets, or designed to load and unload tanks and railcars which had complete armour protection with a large concealed gun/howitzer. Germany also had fully armoured locomotives which were used on such trains.
 During the
During the Slovak National Uprising
The Slovak National Uprising ( sk, Slovenské národné povstanie, abbreviated SNP) was a military uprising organized by the Slovak resistance movement during World War II. This resistance movement was represented mainly by the members of the ...
, the Slovak resistance used three armoured trains. They were named ''Hurban'', ''Štefánik'' and ''Masaryk''. They were built in the Zvolen
Zvolen (; hu, Zólyom; german: Altsohl) is a town in central Slovakia, situated on the confluence of Hron and Slatina rivers, close to Banská Bystrica. It is surrounded by Poľana mountain from the East, by Kremnické vrchy from the West ...
railway factory in very short time – Štefánik was built just in 14 days, Hurban in 11 days. Boiler plates were used as the armor. In case of tank cars, whole tanks were used – tanks LT-35 were placed at the platform wagon and armored construction was built around the hull. Trains saw combat near Stará Kremnička, Čremošné, around Brezno. Later they were abandoned near Harmanec. Some of train cars were later used by Germans for training and for patrolling. Two original cars from the Štefánik train are preserved – the tank car (with original LT-35 tank inside) and machine gun car, and they are exhibited in the Museum of Slovak National Uprising in Banská Bystrica
Banská Bystrica (, also known by other alternative names) is a middle-sized town in central Slovakia, located on the Hron River in a long and wide valley encircled by the mountain chains of the Low Tatras, the Veľká Fatra, and the Kremnica ...
. Another train is exhibited in Zvolen
Zvolen (; hu, Zólyom; german: Altsohl) is a town in central Slovakia, situated on the confluence of Hron and Slatina rivers, close to Banská Bystrica. It is surrounded by Poľana mountain from the East, by Kremnické vrchy from the West ...
– it's a replica of armoured train Hurban, which was built for the movie ''Deň, ktorý neumrie''. Difference of this replica in comparison with original trains are bigger turrets from tank T-34/85, instead of turrets from LT-35.
The Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
had a large number of armoured trains at the start of World War II but many were lost in 1941. Trains built later in the war tended to be fitted with T-34
The T-34 is a Soviet medium tank introduced in 1940. When introduced its 76.2 mm (3 in) tank gun was less powerful than its contemporaries while its 60-degree sloped armour provided good protection against anti-tank weapons. The C ...
or KV series tank turrets. Others were fitted as specialist anti-aircraft batteries. A few were fitted as heavy artillery batteries often using guns taken from ships.
Canada used an armoured train to patrol the Canadian National Railway
The Canadian National Railway Company (french: Compagnie des chemins de fer nationaux du Canada) is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States.
CN i ...
along the Skeena River
The Skeena River is the second-longest river entirely within British Columbia, Canada (after the Fraser River). Since ancient times, the Skeena has been an important transportation artery, particularly for the Tsimshian and the Gitxsan—whose n ...
from Prince Rupert, British Columbia
Prince Rupert is a port city in the province of British Columbia, Canada. Its location is on Kaien Island near the Alaskan panhandle. It is the land, air, and water transportation hub of British Columbia's North Coast, and has a population of 1 ...
to the Pacific coast, against a possible Japanese seaborne raid. The train was equipped with a 75 mm gun, two Bofors 40 mm gun Bofors 40 mm gun is a name or designation given to two models of 40 mm calibre anti-aircraft guns designed and developed by the Swedish company Bofors:
*Bofors 40 mm L/60 gun - developed in the 1930s, widely used in World War II and into the 1990s
...
s, and could accommodate a full infantry company. The No 1 Armoured Train entered service in June 1942, was put into reserve in September 1943, and dismantled the following year.
Twelve armoured trains were formed in Britain in 1940 as part of the preparations to face a German invasion; these were initially armed with QF 6 pounder 6 cwt Hotchkiss guns and six Bren Guns. They were operated by Royal Engineer crews and manned by Royal Armoured Corps
The Royal Armoured Corps is the component of the British Army, that together with the Household Cavalry provides its armour capability, with vehicles such as the Challenger 2 Tank and the Scimitar Reconnaissance Vehicle. It includes most of the ...
troops. In late 1940 preparations began to hand the trains over to the Polish Army in the West, who operated them until 1942. They continued in use in Scotland and were operated by the Home Guard until the last one was withdrawn in November 1944. A 6-pounder wagon from one of these trains is preserved at the Tank Museum
The Tank Museum (previously The Bovington Tank Museum) is a collection of armoured fighting vehicles at Bovington Camp in Dorset, South West England. It is about north of the village of Wool and west of the major port of Poole. The collection ...
. A miniature armoured train ran on the 15-inch gauge Romney Hythe and Dymchurch Railway
The Romney, Hythe and Dymchurch Railway (RH&DR) is a gauge light railway in Kent, England, operating steam and internal combustion locomotives. The line runs from the Cinque Port of Hythe via Dymchurch, St. Mary's Bay, New Romney and Romne ...
.
The Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emper ...
also utilized armored trains. First in the 1920s, to guard the rail lines in Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
and later when they engaged Chinese NRA
The National Rifle Association of America (NRA) is a gun rights advocacy group based in the United States. Founded in 1871 to advance rifle marksmanship, the modern NRA has become a prominent gun rights lobbying organization while contin ...
and CPC troops in Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific T ...
(1937–1945).
In 1940 Italy had twelve armed trains ready for use (again under Regia Marina
The ''Regia Marina'' (; ) was the navy of the Kingdom of Italy (''Regno d'Italia'') from 1861 to 1946. In 1946, with the birth of the Italian Republic (''Repubblica Italiana''), the ''Regia Marina'' changed its name to ''Marina Militare'' ("M ...
control), nine for anti-ship duties and three for AA duties; six were assigned to La Spezia
La Spezia (, or , ; in the local Spezzino dialect) is the capital city of the province of La Spezia and is located at the head of the Gulf of La Spezia in the southern part of the Liguria region of Italy.
La Spezia is the second largest cit ...
, and the other six to Taranto
Taranto (, also ; ; nap, label=Tarantino, Tarde; Latin: Tarentum; Old Italian: ''Tarento''; Ancient Greek: Τάρᾱς) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Taranto, serving as an important comme ...
. One of them was heavily involved in the Battle of the Alps, shelling French forts in support of an Italian attack towards Menton
Menton (; , written ''Menton'' in classical norm or ''Mentan'' in Mistralian norm; it, Mentone ) is a commune in the Alpes-Maritimes department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region on the French Riviera, close to the Italian border.
Me ...
, and suffering heavy damage by return fire. By 1943, eight trains had been deployed to Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
; Allied air superiority did not allow them to have any meaningful role, and eventually they were all abandoned and destroyed by their crews.
Post-World War II
 In the
In the First Indochina War
The First Indochina War (generally known as the Indochina War in France, and as the Anti-French Resistance War in Vietnam) began in French Indochina from 19 December 1946 to 20 July 1954 between France and Việt Minh (Democratic Republic of Vi ...
, the French Union
The French Union () was a political entity created by the French Fourth Republic to replace the old French colonial empire system, colloquially known as the " French Empire" (). It was the formal end of the "indigenous" () status of French subj ...
used the armoured and armed train La Rafale as both a cargo-carrier and a mobile surveillance unit. In February 1951 the first Rafale was in service on the Saigon
, population_density_km2 = 4,292
, population_density_metro_km2 = 697.2
, population_demonym = Saigonese
, blank_name = GRP (Nominal)
, blank_info = 2019
, blank1_name = – Total
, blank1_ ...
- Nha Trang line, Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
while from 1947 to May 1952 the second one which was escorted by onboard Cambodian troops of the BSPP (''Brigade de Surveillance de Phnom Penh'') was used on the Phnom Penh
Phnom Penh (; km, ភ្នំពេញ, ) is the capital and most populous city of Cambodia. It has been the national capital since the French protectorate of Cambodia and has grown to become the nation's primate city and its economic, indus ...
-Battambang
Battambang ( km, បាត់ដំបង, UNGEGN: ) is the capital of Battambang Province and the third largest city in Cambodia.
Founded in the 11th century by the Khmer Empire, Battambang is the leading rice-producing province of the cou ...
line, Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailand ...
. In 1953 both trains were attacked by the Viet-Minh guerrillas who destroyed or mined stone bridges when passing by.
Fulgencio Batista
Fulgencio Batista y Zaldívar (; ; born Rubén Zaldívar, January 16, 1901 – August 6, 1973) was a Cuban military officer and politician who served as the elected president of Cuba from 1940 to 1944 and as its U.S.-backed military dictator ...
's army operated an armoured train during the Cuban Revolution
The Cuban Revolution ( es, Revolución Cubana) was carried out after the 1952 Cuban coup d'état which placed Fulgencio Batista as head of state and the failed mass strike in opposition that followed. After failing to contest Batista in co ...
; it was derailed and destroyed during the Battle of Santa Clara
The Battle of Santa Clara was a series of events in late December 1958 that led to the capture of the Cuban city of Santa Clara by revolutionaries under the command of Che Guevara.
The battle was a decisive victory for the rebels fighting ag ...
, and is commemorated by the ''Tren Blindado
The ''Tren Blindado'' (Spanish for armoured train) is a national monument, memorial park, and museum of the Cuban Revolution, located in the city of Santa Clara, Cuba. It was created by the Cuban sculptor José Delarra on the site of and in memo ...
'' (armoured train) memorial.
An improvised armoured train named the " Krajina express" (''Krajina ekspres'') was used during the Croatian War of Independence
The Croatian War of Independence was fought from 1991 to 1995 between Croat forces loyal to the Government of Croatia—which had declared independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY)—and the Serb-controlled Yug ...
of the early 1990s by the army of the Republic of Serbian Krajina
The Republic of Serbian Krajina or Serb Republic of Krajina ( sh, Република Српска Крајина, italics=no / or РСК / ''RSK'', ), known as the Serbian Krajina ( / ) or simply Krajina, was a self-proclaimed Serb proto-state, ...
. Composed of three fighting cars and three freight cars hooked to the front to protect it from mine blasts,"Krajina Express" enhances Serb Firepower near BihacDeseret News
The ''Deseret News'' () is the oldest continuously operating publication in the American west. Its multi-platform products feature journalism and commentary across the fields of politics, culture, family life, faith, sports, and entertainment. Th ...
, 4 December 1994 the train carried a M18 Hellcat with a 76 mm cannon, a 40 mm Bofors, a 20 mm cannon, twin 57 mm rocket launchers and a 120 mm mortar, plus several machine guns of between 12.7 and 7.62 mm. During the Siege of Bihać in 1994, it was attacked on a few occasions with antitank rocket-propelled grenades and 76 mm guns and hit by a 9K11 Malyutka
The 9M14 Malyutka (russian: Малютка, links=no; "Little one", NATO reporting name: AT-3 Sagger) is a manual command to line of sight (MCLOS) wire-guided anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) system developed in the Soviet Union. It was the first ...
missile, but the damage was minor, as most of the train was covered with thick sheets of rubber which caused the missile's warhead to explode too early to do any real damage. The train was eventually destroyed by its own crew lest it fall into enemy hands during Operation Storm, Croatia's successful effort to reclaim the territories under occupation by Serbs. The Army of Republika Srpska operated a similar train that was ambushed and destroyed in October 1992 at the entrance to the town of Gradačac by Bosnian Muslim forces that included a T-55 tank. The wreckage was later converted into a museum. The Croatian Army
The Croatian Army ( hr, Hrvatska kopnena vojska or HKoV) is the largest and most significant component of the Croatian Armed Forces (CAF).
Role and deployment
The fundamental role and purpose of the Croatian Army is to protect vital national i ...
deployed a two-wagon armoured train built in Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, entertai ...
with a shield composed of two plates, one 8 mm and the other 6 mm thick, with a 30–50 mm gap filled with sand between them. The vehicle was armed with 12.7 mm machine guns.
One armoured train that remains in regular use is that of Kim Il-sung
Kim Il-sung (; , ; born Kim Song-ju, ; 15 April 1912 – 8 July 1994) was a North Korean politician and the founder of North Korea, which he ruled from the country's establishment in 1948 until his death in 1994. He held the posts of ...
and Kim Jong-il
Kim Jong-il (; ; ; born Yuri Irsenovich Kim;, 16 February 1941 – 17 December 2011) was a North Korean politician who was the second supreme leader of North Korea from 1994 to 2011. He led North Korea from the 1994 death of his father Ki ...
, which the former received as a gift from the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
and the latter used heavily for state visits to China and Russia as he had a fear of flying.
Soviet Union
Facing the threat of Chinese cross-border raids during theSino-Soviet split
The Sino-Soviet split was the breaking of political relations between the China, People's Republic of China and the Soviet Union caused by Doctrine, doctrinal divergences that arose from their different interpretations and practical applications ...
, the USSR developed armoured trains in the early 1970s to protect the Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway (TSR; , , ) connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the ea ...
. According to different accounts, four or five trains were built. Every train included ten main battle tank
A main battle tank (MBT), also known as a battle tank or universal tank, is a tank that fills the role of armor-protected direct fire and maneuver in many modern armies. Cold War-era development of more powerful engines, better suspension sys ...
s, two light amphibious tanks, several AA guns, as well as several armoured personnel carrier
An armoured personnel carrier (APC) is a broad type of armoured military vehicle designed to transport personnel and equipment in combat zones. Since World War I, APCs have become a very common piece of military equipment around the world.
Acc ...
s, supply vehicles and equipment for railway repairs. They were all mounted on open platforms or in special rail cars. Different parts of the train were protected with 5–20 mm thick armour. These trains were used by the Soviet Army
uk, Радянська армія
, image = File:Communist star with golden border and red rims.svg
, alt =
, caption = Emblem of the Soviet Army
, start_date ...
to intimidate nationalist paramilitary units in 1990 during the early stages of the First Nagorno-Karabakh War
The First Nagorno-Karabakh War, referred to in Armenia as the Artsakh Liberation War ( hy, Արցախյան ազատամարտ, Artsakhyan azatamart) was an ethnic conflict, ethnic and territorial conflict that took place from February 1988 t ...
.
Towards the end of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
, both superpowers began to develop railway-based ICBM
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons ...
s mounted on armoured trains; the Soviets deployed the SS-24
The RT-23 Molodets (russian: РТ-23 УТТХ «Мо́лодец», lit. "brave man" or "fine fellow"; NATO reporting name: SS-24 Scalpel) was a cold-launched, three-stage, solid-fueled intercontinental ballistic missile developed and produced b ...
missile in 1987, but budget costs and the changing international situation led to the cancellation of the programme, with all remaining railway-based missiles finally being deactivated in 2005.
Russia
Regular armoured trains have continued to be used by the post-Soviet Russian military. Two were deployed during theSecond Chechen War
The Second Chechen War (russian: Втора́я чече́нская война́, ) took place in Chechnya and the border regions of the North Caucasus between the Russian Federation and the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, from August 1999 ...
, assisting in the Battle of Grozny (1999–2000)
The 1999–2000 battle of Grozny was the siege and assault of the Chechen capital Grozny by Russian forces, lasting from late 1999 to early 2000. The siege and fighting left the capital devastated. In 2003, the United Nations called Grozny the ...
; one was sent to the 2008 Russo-Georgian War. Outside of the formal Russian military hierarchy, Russian-backed militants in the Donbass region of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
were pictured operating a homemade armoured train in late 2015.
An armoured train made up of two diesel locomotives powering eight various railcars, which carried anti-aircraft weaponry and unknown cargo supported the southern flank of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. A ...
. A Russian armoured train named ''Yenisei'' used in Ukraine was later reported in more detail; it was made up of two locomotives and eight cars. Ukrainian sources accused Russia of stealing Ukrainian Railways
Ukrainian Railways ( uk, Укрзалізниця, Ukrzaliznytsia, abbreviated as UZ) is a state-owned joint-stock company of rail transport in Ukraine, a monopoly that controls the vast majority of the railroad transportation in the country. ...
assets to build Yenisei. Russia released video of another armoured train in June 2022.
Armoured tram
Armouredtram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport ...
s were also used, although apparently not purpose-built. The just-formed Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
used at least one armoured tram during the fighting for Moscow in the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mom ...
in 1917. The Slovak National Uprising, better known for its armoured trains described above, also used at least one makeshift example.The Czech and Slovak Republics
' (excerpt from
Google Books
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical ...
) - Humphreys, Rob, Rough Guide, 2002, , Page 482
See also
* List of armoured trains * Battle of Mokra * Railway gunReferences
Further reading
*External links
Finnish armoured trains
{{DEFAULTSORT:Armoured Train Articles containing video clips