Apocrine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
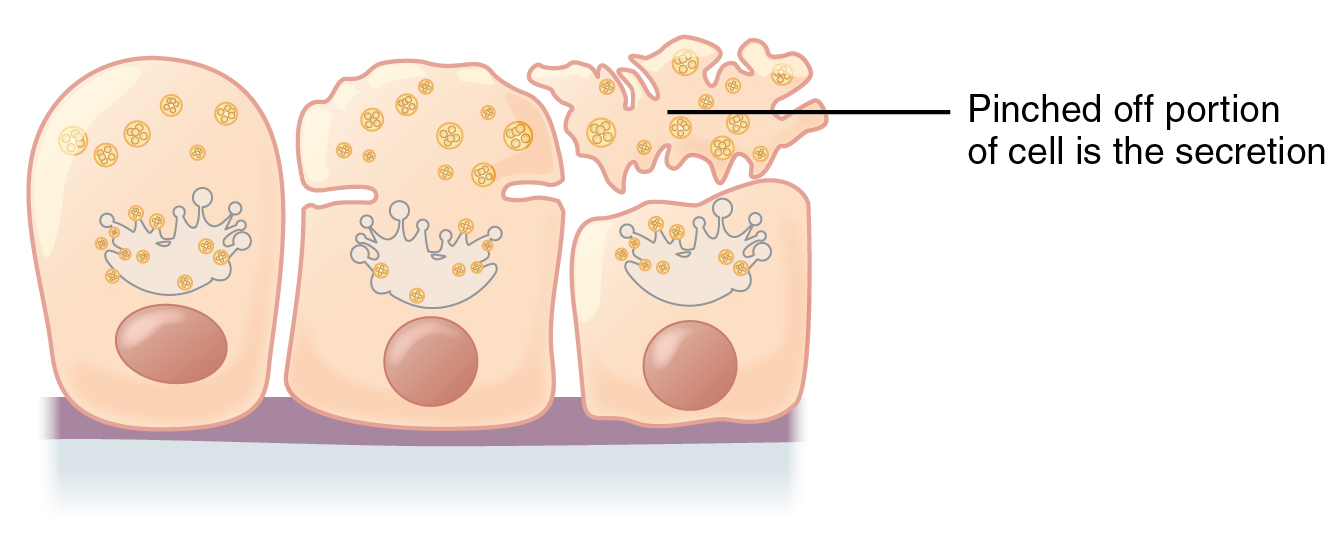 Apocrine () glands are a type of
Apocrine () glands are a type of
Diagram at uwa.edu.au
{{Glands Exocrine system
 Apocrine () glands are a type of
Apocrine () glands are a type of exocrine gland
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two ...
, which are themselves a type of gland
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland).
Structure
De ...
, i.e. a group of cells specialized for the release of secretion 440px
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical ...
s. Exocrine glands secrete by one of three means: holocrine
Holocrine (from Ancient Greek ὅλος; ''hólos'', “whole, entire” + κρῑ́νω; ''krī́nō'', “to separate”) is a term used to classify the mode of secretion in exocrine glands in the study of histology. Holocrine secretions are p ...
, merocrine
Merocrine (or eccrine) is a term used to classify exocrine glands and their secretions in the study of histology. A cell is classified as merocrine if the secretions of that cell are excreted via exocytosis from secretory cells into an epithelia ...
and apocrine. In apocrine secretion, secretory cells accumulate material at their apical
Apical means "pertaining to an apex". It may refer to:
*Apical ancestor, refers to the last common ancestor of an entire group, such as a species (biology) or a clan (anthropology)
*Apical (anatomy), an anatomical term of location for features loc ...
ends, and this material then buds off from the cells, forming extracellular vesicle
Vesicle may refer to:
; In cellular biology or chemistry
* Vesicle (biology and chemistry), a supramolecular assembly of lipid molecules, like a cell membrane
* Synaptic vesicle
; In human embryology
* Vesicle (embryology), bulge-like features o ...
s. The secretory cells therefore lose part of their cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
in the process of secretion.
An example of true apocrine glands is the mammary gland
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland in humans and other mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primat ...
s, responsible for secreting breast milk. Apocrine glands are also found in the anogenital region and axilla
The axilla (also, armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superior ...
e.
Apocrine secretion is less damaging to the gland than holocrine secretion (which destroys a cell) but more damaging than merocrine secretion (exocytosis
Exocytosis () is a form of active transport and bulk transport in which a cell transports molecules (e.g., neurotransmitters and proteins) out of the cell ('' exo-'' + ''cytosis''). As an active transport mechanism, exocytosis requires the use o ...
).
Apocrine metaplasia
Apocrine metaplasia is a reversible transformation of cells to an apocrinephenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological proper ...
. It is common in the breast in the context of fibrocystic change. It is seen in women mostly over the age of 50 years. Metaplasia happens when there is an irritation to the breast (breast cyst). Apocrine-like cells form in a lining of developing microcysts, due to the pressure buildup within the lumen. The pressure build up is caused by secretions. This type of metaplasia represents an exception to the common rule of metaplasia increasing the risk for developing cancer in that apocrine metaplasia doesn't increase the possibility of developing breast cancer.
Apocrine ductal carcinoma ''in situ''
Apocrine ductal carcinoma ''in situ'' (ACDIS) is a very rare breast carcinoma which is regarded as a variant of theductal carcinoma in situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma, is a pre-cancerous or non-invasive cancerous lesion of the breast. DCIS is classified as Stage 0. It rarely produces symptoms or a breast lump one can feel, typically being d ...
breast tumors. ACDIS tumors have microscopic histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Spe ...
features that are similar to pure apocrine carcinoma of the breast
Pure apocrine carcinoma of the breast (PACB) is a rare carcinoma derived from the epithelium, epithelial cells in the lactiferous ducts of the mammary gland. The mammary gland is an apocrine gland. Its lactiferous ducts have two layers of epitheli ...
tumors but differ from them in that they are completely localized, i.e. have not invaded nearby tissues or metastasized to distant tissues.
Apocrine carcinoma
''Apocrinecarcinoma
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesodermal ...
'' is a very rare form of female breast cancer. The rate of incidence varies from 0.5 to 4%. Cytologically, the cells of apocrine carcinoma are relatively large, granular, and it has a prominent eosinophilic
Eosinophilic (Greek suffix -phil-, meaning ''loves eosin'') is the staining of tissues, cells, or organelles after they have been washed with eosin, a dye.
Eosin is an acidic dye for staining cell cytoplasm, collagen, and muscle fibers. ''Eosi ...
cytoplasm. When apocrine carcinoma is tested as a “triple negative", it means that the cells of the patient cannot express the estrogen receptor
Estrogen receptors (ERs) are a group of proteins found inside cells. They are receptors that are activated by the hormone estrogen ( 17β-estradiol). Two classes of ER exist: nuclear estrogen receptors (ERα and ERβ), which are members of the ...
, progesterone receptor
The progesterone receptor (PR), also known as NR3C3 or nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 3, is a protein found inside cells. It is activated by the steroid hormone progesterone.
In humans, PR is encoded by a single ''PGR'' gene resid ...
, or HER2
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ERBB2'' gene. ERBB is abbreviated from erythroblastic oncogene B, a gene originally isolated from the avian genome. The human protein is also frequently refer ...
receptor.
References
External links
Diagram at uwa.edu.au
{{Glands Exocrine system