Antoine Lavoisier on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( , ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794),
CNRS (

 At the age of 26, around the time he was elected to the Academy of Sciences, Lavoisier bought a share in the ''
At the age of 26, around the time he was elected to the Academy of Sciences, Lavoisier bought a share in the ''
 Lavoisier's researches on combustion were carried out in the midst of a very busy schedule of public and private duties, especially in connection with the ''Ferme Générale''. There were also innumerable reports for and committees of the Academy of Sciences to investigate specific problems on order of the royal government. Lavoisier, whose organizing skills were outstanding, frequently landed the task of writing up such official reports. In 1775 he was made one of four commissioners of gunpowder appointed to replace a private company, similar to the Ferme Générale, which had proved unsatisfactory in supplying France with its munitions requirements. As a result of his efforts, both the quantity and quality of French
Lavoisier's researches on combustion were carried out in the midst of a very busy schedule of public and private duties, especially in connection with the ''Ferme Générale''. There were also innumerable reports for and committees of the Academy of Sciences to investigate specific problems on order of the royal government. Lavoisier, whose organizing skills were outstanding, frequently landed the task of writing up such official reports. In 1775 he was made one of four commissioners of gunpowder appointed to replace a private company, similar to the Ferme Générale, which had proved unsatisfactory in supplying France with its munitions requirements. As a result of his efforts, both the quantity and quality of French
Who was the first to classify materials as "compounds"?
– Fred Senese
;His writings * *
Les Œuvres de Lavoisier
(The Complete Works of Lavoisier) edited by Pietro Corsi (Oxford University) and Patrice Bret (CNRS)
Oeuvres de Lavoisier
(Works of Lavoisier) at Gallica BnF in six volumes.
WorldCat author page
* Title page, woodcuts, and copperplate engravings by Madame Lavoisier from a 1789 first edition of
Traité élémentaire de chimie
' (all images freely available for download in a variety of formats from
digital.sciencehistory.org
{{DEFAULTSORT:Lavoisier, Antoine 1743 births 1794 deaths Scientists from Paris University of Paris alumni 18th-century French chemists 18th-century French writers 18th-century French male writers French biologists Members of the French Academy of Sciences Fellows of the Royal Society Discoverers of chemical elements Independent scientists Fermiers généraux People of the Industrial Revolution French Roman Catholics French people executed by guillotine during the French Revolution Executed scientists Burials at Picpus Cemetery Members of the American Philosophical Society
CNRS (
Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique
The French National Centre for Scientific Research (french: link=no, Centre national de la recherche scientifique, CNRS) is the French state research organisation and is the largest fundamental science
Basic research, also called pure research o ...
) also Antoine Lavoisier after the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
, was a French nobleman
The French nobility (french: la noblesse française) was a privileged social class in France from the Middle Ages until its abolition on June 23, 1790 during the French Revolution.
From 1808 to 1815 during the First Empire the Emperor Napolé ...
and chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties. Chemists carefully describe th ...
who was central to the 18th-century chemical revolution
The chemical revolution, also called the ''first chemical revolution'', was the early modern reformulation of chemistry that culminated in the law of conservation of mass and the oxygen theory of combustion.
During the 19th and 20th century, thi ...
and who had a large influence on both the history of chemistry and the history of biology
The history of biology traces the study of the living world from ancient to modern times. Although the concept of ''biology'' as a single coherent field arose in the 19th century, the biological sciences emerged from traditions of medicine a ...
.
It is generally accepted that Lavoisier's great accomplishments in chemistry stem largely from his changing the science from a qualitative to a quantitative
Quantitative may refer to:
* Quantitative research, scientific investigation of quantitative properties
* Quantitative analysis (disambiguation)
* Quantitative verse, a metrical system in poetry
* Statistics, also known as quantitative analysis ...
one. Lavoisier is most noted for his discovery of the role oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
plays in combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combusti ...
. He recognized and named oxygen (1778) and hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
(1783), and opposed phlogiston theory
The phlogiston theory is a superseded scientific theory that postulated the existence of a fire-like element called phlogiston () contained within combustible bodies and released during combustion. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''burni ...
. Lavoisier helped construct the metric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the Decimal, decimalised system based on the metre that had been introduced in French Revolution, France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the d ...
, wrote the first extensive list of elements, and helped to reform chemical nomenclature
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
The ...
. He predicted the existence of silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
(1787) and discovered that, although matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic partic ...
may change its form or shape, its mass always remains the same.
Lavoisier was a powerful member of a number of aristocratic
Aristocracy (, ) is a form of government that places strength in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocrats. The term derives from the el, αριστοκρατία (), meaning 'rule of the best'.
At the time of the word's ...
councils, and an administrator of the ''Ferme générale
The ''ferme générale'' (, "general farm") was, in ''ancien régime'' France, essentially an outsourced customs, excise and indirect tax operation. It collected duties on behalf of the King (plus hefty bonus fees for themselves), under renewable ...
''. The ''Ferme générale'' was one of the most hated components of the ''Ancien Régime
''Ancien'' may refer to
* the French word for "ancient, old"
** Société des anciens textes français
* the French for "former, senior"
** Virelai ancien
** Ancien Régime
** Ancien Régime in France
{{disambig ...
'' because of the profits it took at the expense of the state, the secrecy of the terms of its contracts, and the violence of its armed agents. All of these political and economic activities enabled him to fund his scientific research. At the height of the French Revolution, he was charged with tax fraud and selling adulterated tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, and was guillotine
A guillotine is an apparatus designed for efficiently carrying out executions by beheading. The device consists of a tall, upright frame with a weighted and angled blade suspended at the top. The condemned person is secured with stocks at th ...
d.
Biography

Early life and education
Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier was born to a wealthy family of the nobility inParis
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
on 26 August 1743. The son of an attorney at the Parlement of Paris
The Parliament of Paris (french: Parlement de Paris) was the oldest ''parlement'' in the Kingdom of France, formed in the 14th century. It was fixed in Paris by Philip IV of France in 1302. The Parliament of Paris would hold sessions inside the ...
, he inherited a large fortune at the age of five upon the death of his mother. Lavoisier began his schooling at the Collège des Quatre-Nations
The Collège des Quatre-Nations ("College of the Four Nations"), also known as the Collège Mazarin after its founder, was one of the colleges of the historic University of Paris. It was founded through a bequest by the Cardinal Mazarin. At his d ...
, University of Paris
, image_name = Coat of arms of the University of Paris.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of Arms
, latin_name = Universitas magistrorum et scholarium Parisiensis
, motto = ''Hic et ubique terrarum'' (Latin)
, mottoeng = Here and a ...
(also known as the Collège Mazarin) in Paris in 1754 at the age of 11. In his last two years (1760–1761) at the school, his scientific interests were aroused, and he studied chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions ...
, botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek w ...
, astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest ...
, and mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
. In the philosophy class he came under the tutelage of Abbé Nicolas Louis de Lacaille
Abbé Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille (; 15 March 171321 March 1762), formerly sometimes spelled de la Caille, was a French astronomer and geodesist who named 14 out of the 88 constellations. From 1750 to 1754, he studied the sky at the Cape of Goo ...
, a distinguished mathematician and observational astronomer who imbued the young Lavoisier with an interest in meteorological observation, an enthusiasm which never left him. Lavoisier entered the school of law, where he received a bachelor's degree in 1763 and a licentiate in 1764. Lavoisier received a law degree and was admitted to the bar
Bar or BAR may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bar (establishment), selling alcoholic beverages
* Candy bar
* Chocolate bar
Science and technology
* Bar (river morphology), a deposit of sediment
* Bar (tropical cyclone), a layer of cloud
* Bar (u ...
, but never practiced as a lawyer. However, he continued his scientific education in his spare time.
Early scientific work
Lavoisier's education was filled with the ideals of the French Enlightenment of the time, and he was fascinated byPierre Macquer
Pierre-Joseph Macquer (9 October 1718 – 15 February 1784) was an influential French chemist.
He is known for his ''Dictionnaire de chymie'' (1766). He was also involved in practical applications, to medicine and industry, such as the French dev ...
's dictionary of chemistry. He attended lectures in the natural sciences. Lavoisier's devotion and passion for chemistry were largely influenced by Étienne Condillac
Étienne, a French analog of Stephen or Steven, is a masculine given name. An archaic variant of the name, prevalent up to the mid-17th century, is Estienne.
Étienne, Etienne, Ettiene or Ettienne may refer to:
People
Scientists and inventors
...
, a prominent French scholar of the 18th century. His first chemical publication appeared in 1764. From 1763 to 1767, he studied geology under Jean-Étienne Guettard
Jean-Étienne Guettard (22 September 1715 – 7 January 1786), French naturalist and mineralogist, was born at Étampes, near Paris.
In boyhood, he gained a knowledge of plants from his grandfather, who was an apothecary, and later he qualif ...
. In collaboration with Guettard, Lavoisier worked on a geological survey of Alsace-Lorraine in June 1767. In 1764 he read his first paper to the French Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific me ...
, France's most elite scientific society, on the chemical and physical properties of gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywall. ...
(hydrated calcium sulfate
Calcium sulfate (or calcium sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the formula CaSO4 and related hydrates. In the form of γ-anhydrite (the anhydrous form), it is used as a desiccant. One particular hydrate is better known as plaster of Pari ...
), and in 1766 he was awarded a gold medal by the King for an essay on the problems of urban street lighting
A street light, light pole, lamp pole, lamppost, street lamp, light standard, or lamp standard is a raised source of light on the edge of a road or path. Similar lights may be found on a railway platform. When urban electric power distribution ...
. In 1768 Lavoisier received a provisional appointment to the Academy of Sciences. In 1769, he worked on the first geological map of France.
Lavoisier as a social reformer

Research benefitting the public good
While Lavoisier is commonly known for his contributions to the sciences, he also dedicated a significant portion of his fortune and work toward benefitting the public. Lavoisier was a humanitarian—he cared deeply about the people in his country and often concerned himself with improving the livelihood of the population by agriculture, industry, and the sciences. The first instance of this occurred in 1765, when he submitted an essay on improving urban street lighting to the French Academy of Sciences. Three years later in 1768, he focused on a new project to design an aqueduct. The goal was to bring water from the river Yvette into Paris so that the citizens could have clean drinking water. But, since the construction never commenced, he instead turned his focus to purifying the water from the Seine. This was the project that interested Lavoisier in the chemistry of water and public sanitation duties. Additionally, he was interested in air quality and spent some time studying the health risks associated with gunpowder's effect on the air. In 1772, he performed a study on how to reconstruct the Hôtel-Dieu hospital, after it had been damaged by fire, in a way that would allow proper ventilation and clean air throughout. At the time, the prisons in Paris were known to be largely unlivable and the prisoners' treatment inhumane. Lavoisier took part in investigations in 1780 (and again in 1791) on the hygiene in prisons and had made suggestions to improve living conditions, suggestions which were largely ignored. Once a part of the Academy, Lavoisier also held his own competitions to push the direction of research towards bettering the public and his own work. One such project he proposed in 1793 was to better public health on the "insalubrious arts".Sponsorship of the sciences
Lavoisier had a vision of public education having roots in "scientific sociability" and philanthropy. Lavoisier gained a vast majority of his income through buying stock in the General Farm, which allowed him to work on science full-time, live comfortably, and allowed him to contribute financially to better the community. (It would also contribute to his demise during theReign of Terror
The Reign of Terror (french: link=no, la Terreur) was a period of the French Revolution when, following the creation of the First Republic, a series of massacres and numerous public executions took place in response to revolutionary fervour, ...
many years later.)
It was very difficult to secure public funding for the sciences at the time, and additionally not very financially profitable for the average scientist, so Lavoisier used his wealth to open a very expensive and sophisticated laboratory in France so that aspiring scientists could study without the barriers of securing funding for their research.
He also pushed for public education in the sciences. He founded two organizations, and Musée des Arts et Métiers
The Musée des Arts et Métiers () (French for Museum of Arts and Crafts) is an industrial design museum in Paris that houses the collection of the Conservatoire national des arts et métiers, which was founded in 1794 as a repository for the pr ...
, which were created to serve as educational tools for the public. Funded by the wealthy and noble, the Lycée regularly taught courses to the public beginning in 1793.
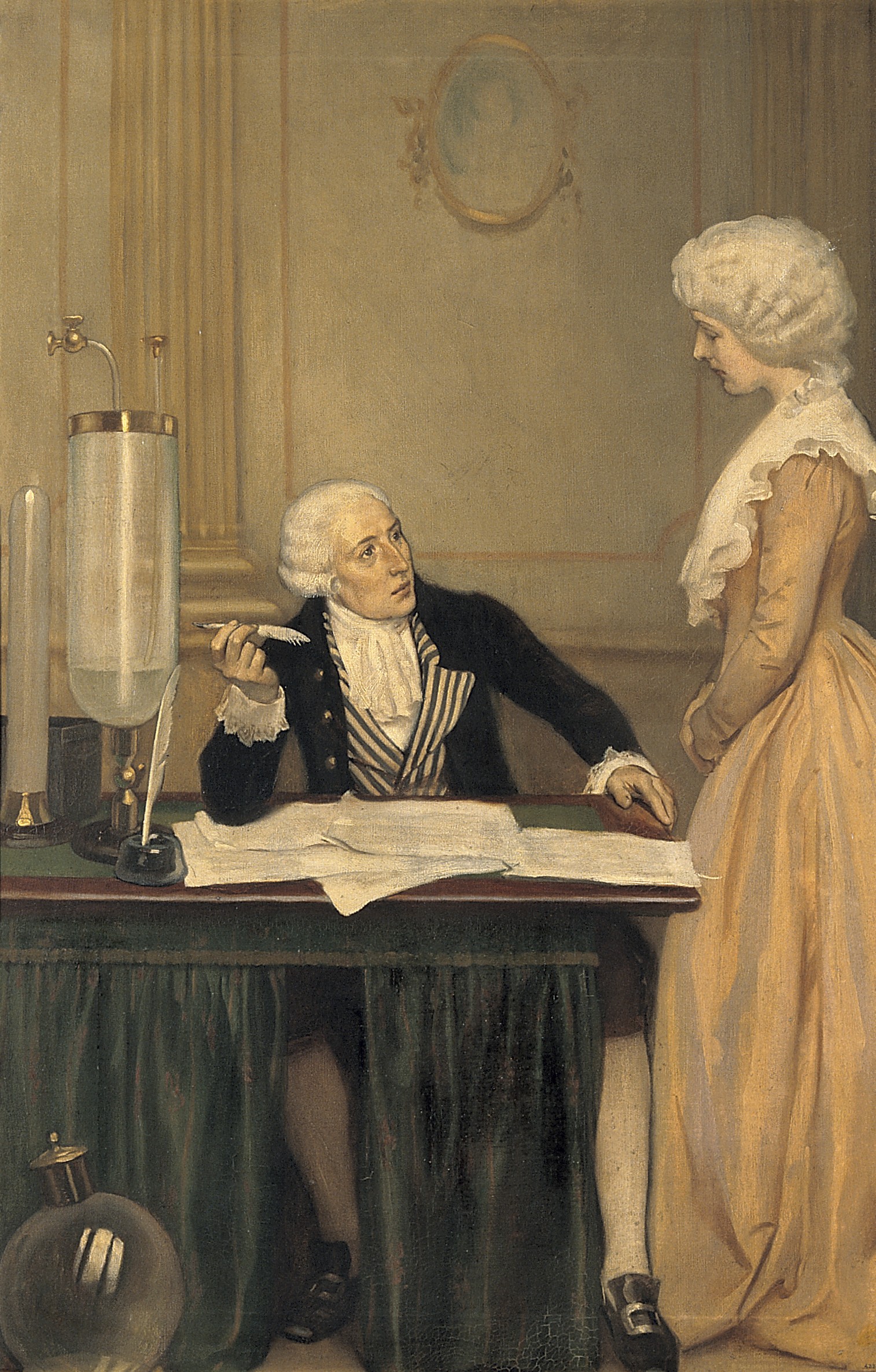
Ferme générale and marriage
 At the age of 26, around the time he was elected to the Academy of Sciences, Lavoisier bought a share in the ''
At the age of 26, around the time he was elected to the Academy of Sciences, Lavoisier bought a share in the ''Ferme générale
The ''ferme générale'' (, "general farm") was, in ''ancien régime'' France, essentially an outsourced customs, excise and indirect tax operation. It collected duties on behalf of the King (plus hefty bonus fees for themselves), under renewable ...
'', a tax farming
Farming or tax-farming is a technique of financial management in which the management of a variable revenue stream is assigned by legal contract to a third party and the holder of the revenue stream receives fixed periodic rents from the contrac ...
financial company which advanced the estimated tax revenue to the royal government in return for the right to collect the taxes. On behalf of the Ferme générale Lavoisier commissioned the building of a wall
A wall is a structure and a surface that defines an area; carries a load; provides security, shelter, or soundproofing; or, is decorative. There are many kinds of walls, including:
* Walls in buildings that form a fundamental part of the supe ...
around Paris so that customs duties could be collected from those transporting goods into and out of the city. His participation in the collection of its taxes did not help his reputation when the Reign of Terror
The Reign of Terror (french: link=no, la Terreur) was a period of the French Revolution when, following the creation of the First Republic, a series of massacres and numerous public executions took place in response to revolutionary fervour, ...
began in France, as taxes and poor government reform were the primary motivators during the French Revolution.
Lavoisier consolidated his social and economic position when, in 1771 at age 28, he married Marie-Anne Pierrette Paulze
Marie-Anne Pierrette Paulze Lavoisier (20 January 1758 in Montbrison, Loire, France – 10 February 1836) was a French chemist and noblewoman. Madame Lavoisier was the wife of the chemist and nobleman Antoine Lavoisier, and acted as his laborator ...
, the 13-year-old daughter of a senior member of the ''Ferme générale''. She was to play an important part in Lavoisier's scientific career—notably, she translated English documents for him, including Richard Kirwan
Richard Kirwan, LL.D, FRS, FRSE MRIA (1 August 1733 – 22 June 1812) was an Irish geologist and chemist. He was one of the last supporters of the theory of phlogiston.
Kirwan was active in the fields of chemistry, meteorology, and geol ...
's ''Essay on Phlogiston'' and Joseph Priestley
Joseph Priestley (; 24 March 1733 – 6 February 1804) was an English chemist, natural philosopher, separatist theologian, grammarian, multi-subject educator, and liberal political theorist. He published over 150 works, and conducted exp ...
's research. In addition, she assisted him in the laboratory and created many sketches and carved engravings of the laboratory instruments used by Lavoisier and his colleagues for their scientific works. Madame Lavoisier edited and published Antoine's memoirs (whether any English translations of those memoirs have survived is unknown as of today) and hosted parties at which eminent scientists discussed ideas and problems related to chemistry.
A portrait of Antoine and Marie-Anne Lavoisier was painted by the famed artist Jacques-Louis David
Jacques-Louis David (; 30 August 1748 – 29 December 1825) was a French painter in the Neoclassicism, Neoclassical style, considered to be the preeminent painter of the era. In the 1780s, his cerebral brand of history painting marked a change in ...
. Completed in 1788 on the eve of the Revolution, the painting was denied a customary public display at the Paris Salon
The Salon (french: Salon), or rarely Paris Salon (French: ''Salon de Paris'' ), beginning in 1667 was the official art exhibition of the Académie des Beaux-Arts in Paris. Between 1748 and 1890 it was arguably the greatest annual or biennial art ...
for fear that it might inflame anti-aristocratic passions.
For three years following his entry into the ''Ferme générale'', Lavoisier's scientific activity diminished somewhat, for much of his time was taken up with official ''Ferme générale'' business. He did, however, present one important memoir to the Academy of Sciences during this period, on the supposed conversion of water into earth by evaporation. By a very precise quantitative experiment, Lavoisier showed that the "earthy" sediment produced after long-continued reflux heating of water in a glass vessel was not due to a conversion of the water into earth but rather to the gradual disintegration of the inside of the glass vessel produced by the boiling water. He also attempted to introduce reforms in the French monetary
Money is any item or verifiable record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts, such as taxes, in a particular country or socio-economic context. The primary functions which distinguish money are as ...
and taxation system to help the peasants.
Adulteration of tobacco
The Farmers General held a monopoly of the production, import and sale of tobacco in France, and the taxes they levied on tobacco brought revenues of 30 millionlivres
The (; ; abbreviation: ₶.) was one of numerous currencies used in medieval France, and a unit of account (i.e., a monetary unit used in accounting) used in Early Modern France.
The 1262 monetary reform established the as 20 , or 80.88 gr ...
a year. This revenue began to fall because of a growing black market in tobacco that was smuggled and adulterated, most commonly with ash and water. Lavoisier devised a method of checking whether ash had been mixed in with tobacco: "When a spirit of vitriol
Vitriol is the general chemical name encompassing a class of chemical compound comprising sulfates of certain metalsoriginally, iron or copper. Those mineral substances were distinguished by their color, such as green vitriol for hydrated iron( ...
, ''aqua fortis'' or some other acid solution is poured on ash, there is an immediate very intense effervescent reaction, accompanied by an easily detected noise." Lavoisier also noticed that the addition of a small amount of ash improved the flavour of tobacco. Of one vendor selling adulterated goods, he wrote "His tobacco enjoys a very good reputation in the province... the very small proportion of ash that is added gives it a particularly pungent flavour that consumers look for. Perhaps the Farm could gain some advantage by adding a bit of this liquid mixture when the tobacco is fabricated." Lavoisier also found that while adding a lot of water to bulk the tobacco up would cause it to ferment and smell bad, the addition of a very small amount improved the product. Thereafter the factories of the Farmers General added, as he recommended, a consistent 6.3% of water by volume to the tobacco they processed. To allow for this addition, the Farmers General delivered to retailers seventeen ounces of tobacco while only charging for sixteen. To ensure that only these authorised amounts were added, and to exclude the black market, Lavoisier saw to it that a watertight system of checks, accounts, supervision and testing made it very difficult for retailers to source contraband tobacco or to improve their profits by bulking it up. He was energetic and rigorous in implementing this, and the systems he introduced were deeply unpopular with the tobacco retailers across the country. This unpopularity was to have consequences for him during the French Revolution.
Royal Commission on Agriculture
Lavoisier urged the establishment of a Royal Commission on Agriculture. He then served as its Secretary and spent considerable sums of his own money in order to improve the agricultural yields in theSologne
Sologne (; ) is a natural region in Centre-Val de Loire, France, extending over portions of the departements of Loiret, Loir-et-Cher and Cher. Its area is about . To its north is the river Loire, to its south the river Cher, while the districts ...
, an area where farmland was of poor quality. The humidity of the region often led to a blight of the rye harvest, causing outbreaks of ergotism among the population. In 1788 Lavoisier presented a report to the Commission detailing ten years of efforts on his experimental farm to introduce new crops and types of livestock. His conclusion was that despite the possibilities of agricultural reforms, the tax system left tenant farmers with so little that it was unrealistic to expect them to change their traditional practices.
Gunpowder Commission
 Lavoisier's researches on combustion were carried out in the midst of a very busy schedule of public and private duties, especially in connection with the ''Ferme Générale''. There were also innumerable reports for and committees of the Academy of Sciences to investigate specific problems on order of the royal government. Lavoisier, whose organizing skills were outstanding, frequently landed the task of writing up such official reports. In 1775 he was made one of four commissioners of gunpowder appointed to replace a private company, similar to the Ferme Générale, which had proved unsatisfactory in supplying France with its munitions requirements. As a result of his efforts, both the quantity and quality of French
Lavoisier's researches on combustion were carried out in the midst of a very busy schedule of public and private duties, especially in connection with the ''Ferme Générale''. There were also innumerable reports for and committees of the Academy of Sciences to investigate specific problems on order of the royal government. Lavoisier, whose organizing skills were outstanding, frequently landed the task of writing up such official reports. In 1775 he was made one of four commissioners of gunpowder appointed to replace a private company, similar to the Ferme Générale, which had proved unsatisfactory in supplying France with its munitions requirements. As a result of his efforts, both the quantity and quality of French gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). ...
greatly improved, and it became a source of revenue for the government. His appointment to the Gunpowder Commission brought one great benefit to Lavoisier's scientific career as well. As a commissioner, he enjoyed both a house and a laboratory in the Royal Arsenal. Here he lived and worked between 1775 and 1792.
Lavoisier was a formative influence in the formation of the Du Pont gunpowder business because he trained Éleuthère Irénée du Pont
Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours (; ; 24 June 1771 – 31 October 1834) was a French-American chemist and industrialist who founded the gunpowder manufacturer E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company. His descendants, the du Pont family, hav ...
, its founder, on gunpowder-making in France; the latter said that the Du Pont gunpowder mills "would never have been started but for his kindness to me."
During the Revolution
In June 1791, Lavoisier made a loan of 71,000 livres to Pierre Samuel du Pont de Nemours to buy a printing works so that du Pont could publish a newspaper, ''La Correspondance Patriotique''. The plan was for this to include both reports of debates in the National Constituent Assembly as well as papers from the Academy of Sciences. The revolution quickly disrupted the elder du Pont's first newspaper, but his son E.I. du Pont soon launched ''Le Republicain'' and published Lavoisier's latest chemistry texts. Lavoisier also chaired the commission set up to establish a uniform system of weights and measures''A Cultural History of the French Revolution'', Emmet Kennedy, Yale University Press 1989, p. 193 which in March 1791 recommended the adoption of themetric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the Decimal, decimalised system based on the metre that had been introduced in French Revolution, France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the d ...
. The new system of weights and measures was adopted by the Convention on 1 August 1793.''Chronicle of the French Revolution'', Jacques Legrand, Longman 1989, p. 356 Lavoisier himself was removed from the commission on weights and measures on 23 December 1793, together with mathematician Pierre-Simon Laplace
Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace (; ; 23 March 1749 – 5 March 1827) was a French scholar and polymath whose work was important to the development of engineering, mathematics, statistics, physics, astronomy, and philosophy. He summarized ...
and several other members, for political reasons.
One of his last major works was a proposal to the National Convention
The National Convention (french: link=no, Convention nationale) was the parliament of the Kingdom of France for one day and the French First Republic for the rest of its existence during the French Revolution, following the two-year National ...
for the reform of French education. He also intervened on behalf of a number of foreign-born scientists including mathematician Joseph Louis Lagrange
Joseph-Louis Lagrange (born Giuseppe Luigi Lagrangia
As the
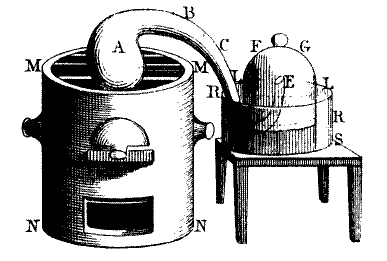 During late 1772 Lavoisier turned his attention to the phenomenon of
During late 1772 Lavoisier turned his attention to the phenomenon of

 In the spring of 1774, Lavoisier carried out experiments on the calcination of tin and lead in sealed vessels, the results of which conclusively confirmed that the increase in weight of metals in combustion was due to combination with air. But the question remained about whether it was in combination with common atmospheric air or with only a part of atmospheric air. In October the English chemist Joseph Priestley visited Paris, where he met Lavoisier and told him of the air which he had produced by heating the red calx of mercury with a burning glass and which had supported combustion with extreme vigor. Priestley at this time was unsure of the nature of this gas, but he felt that it was an especially pure form of common air. Lavoisier carried out his own research on this peculiar substance. The result was his memoir ''On the Nature of the Principle Which Combines with Metals during Their Calcination and Increases Their Weight'', read to the Academy on 26 April 1775 (commonly referred to as the Easter Memoir). In the original memoir, Lavoisier showed that the mercury calx was a true metallic calx in that it could be reduced with
In the spring of 1774, Lavoisier carried out experiments on the calcination of tin and lead in sealed vessels, the results of which conclusively confirmed that the increase in weight of metals in combustion was due to combination with air. But the question remained about whether it was in combination with common atmospheric air or with only a part of atmospheric air. In October the English chemist Joseph Priestley visited Paris, where he met Lavoisier and told him of the air which he had produced by heating the red calx of mercury with a burning glass and which had supported combustion with extreme vigor. Priestley at this time was unsure of the nature of this gas, but he felt that it was an especially pure form of common air. Lavoisier carried out his own research on this peculiar substance. The result was his memoir ''On the Nature of the Principle Which Combines with Metals during Their Calcination and Increases Their Weight'', read to the Academy on 26 April 1775 (commonly referred to as the Easter Memoir). In the original memoir, Lavoisier showed that the mercury calx was a true metallic calx in that it could be reduced with
"Mémoire sur la combustion en général"
("On Combustion in General"). ''Mémoires de l’Académie des sciences''.
/ref> When reduced without charcoal, it gave off an air which supported respiration and combustion in an enhanced way. He concluded that this was just a pure form of common air and that it was the air itself "undivided, without alteration, without decomposition" which combined with metals on calcination. After returning from Paris, Priestley took up once again his investigation of the air from mercury calx. His results now showed that this air was not just an especially pure form of common air but was "five or six times better than common air, for the purpose of respiration, inflammation, and ... every other use of common air". He called the air dephlogisticated air, as he thought it was common air deprived of its
 Lavoisier, together with
Lavoisier, together with

 Lavoisier's fundamental contributions to chemistry were a result of a conscious effort to fit all experiments into the framework of a single theory. He established the consistent use of the chemical balance, used oxygen to overthrow the phlogiston theory, and developed a new system of chemical nomenclature which held that oxygen was an essential constituent of all acids (which later turned out to be erroneous).
Lavoisier also did early research in physical chemistry and thermodynamics in joint experiments with Laplace. They used a calorimeter to estimate the heat evolved per unit of carbon dioxide produced, eventually finding the same ratio for a flame and animals, indicating that animals produced energy by a type of combustion reaction.
Lavoisier also contributed to early ideas on composition and chemical changes by stating the radical theory, believing that radicals, which function as a single group in a chemical process, combine with oxygen in reactions. He also introduced the possibility of
Lavoisier's fundamental contributions to chemistry were a result of a conscious effort to fit all experiments into the framework of a single theory. He established the consistent use of the chemical balance, used oxygen to overthrow the phlogiston theory, and developed a new system of chemical nomenclature which held that oxygen was an essential constituent of all acids (which later turned out to be erroneous).
Lavoisier also did early research in physical chemistry and thermodynamics in joint experiments with Laplace. They used a calorimeter to estimate the heat evolved per unit of carbon dioxide produced, eventually finding the same ratio for a flame and animals, indicating that animals produced energy by a type of combustion reaction.
Lavoisier also contributed to early ideas on composition and chemical changes by stating the radical theory, believing that radicals, which function as a single group in a chemical process, combine with oxygen in reactions. He also introduced the possibility of
 A number of
A number of
 * '' Opuscules physiques et chimiques'' (Paris: Chez Durand, Didot, Esprit, 1774).
* '' Opuscules physiques et chimiques'' (Paris: Chez Durand, Didot, Esprit, 1774).
Second edition, 1801
* ''L'art de fabriquer le salin et la potasse, publié par ordre du Roi, par les régisseurs-généraux des Poudres & Salpêtres'' (Paris, 1779). * ''Instruction sur les moyens de suppléer à la disette des fourrages, et d'augmenter la subsistence des bestiaux, Supplément à l'instruction sur les moyens de pourvoir à la disette des fourrages, publiée par ordre du Roi le 31 mai 1785'' (Instruction on the means of compensating for the food shortage with fodder, and of increasing the subsistence of cattle, Supplement to the instruction on the means of providing for the food shortage with fodder, published by order of King on 31 May 1785). * (with Guyton de Morveau, Claude-Louis Berthollet, Antoine Fourcroy)
Méthode de nomenclature chimique
' (Paris: Chez Cuchet, 1787) * (with Fourcroy, Morveau, Cadet, Baumé, d'Arcet, and Sage)
Nomenclature chimique, ou synonymie ancienne et moderne, pour servir à l'intelligence des auteurs.
' (Paris: Chez Cuchet, 1789) *
' (Paris: Chez Cuchet, 1789; Bruxelles: Cultures et Civilisations, 1965) (lit. Elementary Treatise on Chemistry, presented in a new order and alongside modern discoveries) als
* (with Pierre-Simon Laplace)
Mémoire sur la chaleur
" ''Mémoires de l'Académie des sciences'' (1780), pp. 355–408. *
Mémoire contenant les expériences faites sur la chaleur, pendant l'hiver de 1783 à 1784, par P.S. de Laplace & A. K. Lavoisier
' (1792) * ''Mémoires de Physique et de Chimie, de la Société d'Arcueil'' (1805: posthumous)
Essays Physical and Chemical
' (London: for Joseph Johnson, 1776; London: Frank Cass and Company Ltd., 1970) translation by Thomas Henry of ''Opuscules physiques et chimiques'' * ''The Art of Manufacturing Alkaline Salts and Potashes, Published by Order of His Most Christian Majesty, and approved by the Royal Academy of Sciences'' (1784) trans. by Charles WilliamosSee Denis I. Duveen and Herbert S. Klickstein,
The "American" Edition of Lavoisier's ''L'art de fabriquer le salin et la potasse''
" ''The William and Mary Quarterly, Third Series'' 13:4 (October 1956), 493–498. of ''L'art de fabriquer le salin et la potasse'' * (with Pierre-Simon Laplace) ''Memoir on Heat: Read to the Royal Academy of Sciences, 28 June 1783, by Messrs. Lavoisier & De La Place of the same Academy.'' (New York: Neale Watson Academic Publications, 1982) trans. by Henry Guerlac of ''Mémoire sur la chaleur'' *
Essays, on the Effects Produced by Various Processes On Atmospheric Air; With A Particular View To An Investigation Of The Constitution Of Acids
', trans. Thomas Henry (London: Warrington, 1783) collects these essays: # "Experiments on the Respiration of Animals, and on the Changes effected on the Air in passing through their Lungs." (Read to the Académie des Sciences, 3 May 1777) # "On the Combustion of Candles in Atmospheric Air and in Dephlogistated Air." (Communicated to the Académie des Sciences, 1777) # "On the Combustion of Kunckel's Phosphorus." # "On the Existence of Air in the Nitrous Acid, and on the Means of decomposing and recomposing that Acid." # "On the Solution of Mercury in Vitriolic Acid." # "Experiments on the Combustion of Alum with Phlogistic Substances, and on the Changes effected on Air in which the Pyrophorus was burned." # "On the Vitriolisation of Martial Pyrites." # "General Considerations on the Nature of Acids, and on the Principles of which they are composed." # "On the Combination of the Matter of Fire with Evaporable Fluids; and on the Formation of Elastic Aëriform Fluids." * “Reflections on Phlogiston”, translation by Nicholas W. Best of “Réflexions sur le phlogistique, pour servir de suite à la théorie de la combustion et de la calcination” (read to the Académie Royale des Sciences over two nights, 28 June and 13 July 1783). Published in two parts: # # * ''Method of chymical nomenclature: proposed by Messrs. De Moreau, Lavoisier, Bertholet, and De Fourcroy'' (1788
* ''Elements of Chemistry, in a New Systematic Order, Containing All the Modern Discoveries'' (Edinburgh: William Creech, 1790; New York: Dover, 1965) translation by Robert Kerr of ''Traité élémentaire de chimie''. (Dover). *
1799 edition
** 1802 edition
volume 1volume 2
*
Some illustrations
from 1793 edition *
Some more illustrations
from the
More illustrations
(from Collected Works) from the
File:Lavoisier-1.jpg, 1790 copy of "Elements of Chemistry in a Systematic Order Containing All the Modern Discoveries"
File:Lavoisier-2.jpg, Title page to "Elements of Chemistry in a Systematic Order Containing All the Modern Discoveries" (1790)
File:Lavoisier-3.jpg, Preface to "Elements of Chemistry in a Systematic Order Containing All the Modern Discoveries" (1790)
File:Lavoisier-4.jpg, First page of "Elements of Chemistry in a Systematic Order Containing All the Modern Discoveries" (1790)
Fonds Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier
Le Comité Lavoisier,
Panopticon Lavoisier
a virtual museum of Antoine Lavoisier
Bibliography
at Panopticon Lavoisier
Les Œuvres de Lavoisier
;About his work
Location of Lavoisier's laboratory in Paris
Radio 4 program on the discovery of oxygen
by the
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
gained momentum, attacks mounted on the deeply unpopular ''Ferme générale
The ''ferme générale'' (, "general farm") was, in ''ancien régime'' France, essentially an outsourced customs, excise and indirect tax operation. It collected duties on behalf of the King (plus hefty bonus fees for themselves), under renewable ...
'', and it was eventually abolished in March 1791. In 1792 Lavoisier was forced to resign from his post on the Gunpowder Commission and to move from his house and laboratory at the Royal Arsenal. On 8 August 1793, all the learned societies, including the Academy of Sciences, were suppressed at the request of Abbé Grégoire
''Abbé'' (from Latin ''abbas'', in turn from Greek , ''abbas'', from Aramaic ''abba'', a title of honour, literally meaning "the father, my father", emphatic state of ''abh'', "father") is the French word for an abbot. It is the title for lowe ...
.
On 24 November 1793, the arrest of all the former tax farmers was ordered. Lavoisier and the other Farmers General faced nine accusations of defrauding the state of money owed to it, and of adding water to tobacco before selling it. Lavoisier drafted their defense, refuting the financial accusations, reminding the court of how they had maintained a consistently high quality of tobacco. The court was however inclined to believe that by condemning them and seizing their goods, it would recover huge sums for the state. Lavoisier was convicted and guillotined on 8 May 1794 in Paris, at the age of 50, along with his 27 co-defendants.
According to popular legend, the appeal to spare his life so that he could continue his experiments was cut short by the judge, Coffinhal: ''"La République n'a pas besoin de savants ni de chimistes; le cours de la justice ne peut être suspendu."'' ("The Republic needs neither scholars nor chemists; the course of justice cannot be delayed.") The judge Coffinhal himself would be executed less than three months later, in the wake of the Thermidorian reaction
The Thermidorian Reaction (french: Réaction thermidorienne or ''Convention thermidorienne'', "Thermidorian Convention") is the common term, in the historiography of the French Revolution, for the period between the ousting of Maximilien Robespie ...
.
Lavoisier's importance to science was expressed by Lagrange who lamented the beheading by saying: ''"Il ne leur a fallu qu'un moment pour faire tomber cette tête, et cent années peut-être ne suffiront pas pour en reproduire une semblable."'' ("It took them only an instant to cut off this head, and one hundred years might not suffice to reproduce its like.")
Post-mortem
A year and a half after his execution, Lavoisier was completely exonerated by the French government. During theWhite Terror
White Terror is the name of several episodes of mass violence in history, carried out against anarchists, communists, socialists, liberals, revolutionaries, or other opponents by conservative or nationalist groups. It is sometimes contrasted wit ...
, his belongings were delivered to his widow. A brief note was included, reading "To the widow of Lavoisier, who was falsely convicted".
Contributions to chemistry
Oxygen theory of combustion
 During late 1772 Lavoisier turned his attention to the phenomenon of
During late 1772 Lavoisier turned his attention to the phenomenon of combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combusti ...
, the topic on which he was to make his most significant contribution to science. He reported the results of his first experiments on combustion in a note to the Academy on 20 October, in which he reported that when phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
burned, it combined with a large quantity of air to produce acid spirit of phosphorus, and that the phosphorus increased in weight on burning. In a second sealed note deposited with the Academy a few weeks later (1 November) Lavoisier extended his observations and conclusions to the burning of sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
and went on to add that "what is observed in the combustion of sulfur and phosphorus may well take place in the case of all substances that gain in weight by combustion and calcination: and I am persuaded that the increase in weight of metallic calces is due to the same cause."
Joseph Black's "fixed air"
During 1773 Lavoisier determined to review thoroughly the literature on air, particularly "fixed air," and to repeat many of the experiments of other workers in the field. He published an account of this review in 1774 in a book entitled ''Opuscules physiques et chimiques'' (Physical and Chemical Essays). In the course of this review, he made his first full study of the work ofJoseph Black
Joseph Black (16 April 1728 – 6 December 1799) was a Scottish physicist and chemist, known for his discoveries of magnesium, latent heat, specific heat, and carbon dioxide. He was Professor of Anatomy and Chemistry at the University of Glas ...
, the Scottish chemist who had carried out a series of classic quantitative experiments on the mild and caustic alkalies. Black had shown that the difference between a mild alkali, for example, chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Chalk ...
( CaCO3), and the caustic form, for example, quicklime
Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term "''lime''" connotes calcium-containing inorganic ma ...
(CaO Cao or CAO may refer to:
Mythology
*Cao (bull), a legendary bull in Meitei mythology
Companies or organizations
* Air China Cargo, ICAO airline designator CAO
*CA Oradea, Romanian football club
*CA Osasuna, Spanish football club
*Canadian Assoc ...
), lay in the fact that the former contained "fixed air," not common air fixed in the chalk, but a distinct chemical species, now understood to be carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
(CO2), which was a constituent of the atmosphere. Lavoisier recognized that Black's fixed air was identical with the air evolved when metal calces were reduced with charcoal and even suggested that the air which combined with metals on calcination and increased the weight might be Black's fixed air, that is, CO2.
Joseph Priestley

 In the spring of 1774, Lavoisier carried out experiments on the calcination of tin and lead in sealed vessels, the results of which conclusively confirmed that the increase in weight of metals in combustion was due to combination with air. But the question remained about whether it was in combination with common atmospheric air or with only a part of atmospheric air. In October the English chemist Joseph Priestley visited Paris, where he met Lavoisier and told him of the air which he had produced by heating the red calx of mercury with a burning glass and which had supported combustion with extreme vigor. Priestley at this time was unsure of the nature of this gas, but he felt that it was an especially pure form of common air. Lavoisier carried out his own research on this peculiar substance. The result was his memoir ''On the Nature of the Principle Which Combines with Metals during Their Calcination and Increases Their Weight'', read to the Academy on 26 April 1775 (commonly referred to as the Easter Memoir). In the original memoir, Lavoisier showed that the mercury calx was a true metallic calx in that it could be reduced with
In the spring of 1774, Lavoisier carried out experiments on the calcination of tin and lead in sealed vessels, the results of which conclusively confirmed that the increase in weight of metals in combustion was due to combination with air. But the question remained about whether it was in combination with common atmospheric air or with only a part of atmospheric air. In October the English chemist Joseph Priestley visited Paris, where he met Lavoisier and told him of the air which he had produced by heating the red calx of mercury with a burning glass and which had supported combustion with extreme vigor. Priestley at this time was unsure of the nature of this gas, but he felt that it was an especially pure form of common air. Lavoisier carried out his own research on this peculiar substance. The result was his memoir ''On the Nature of the Principle Which Combines with Metals during Their Calcination and Increases Their Weight'', read to the Academy on 26 April 1775 (commonly referred to as the Easter Memoir). In the original memoir, Lavoisier showed that the mercury calx was a true metallic calx in that it could be reduced with charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, cal ...
, giving off Black's fixed air in the process.Lavoisier, Antoine (1777"Mémoire sur la combustion en général"
("On Combustion in General"). ''Mémoires de l’Académie des sciences''.
/ref> When reduced without charcoal, it gave off an air which supported respiration and combustion in an enhanced way. He concluded that this was just a pure form of common air and that it was the air itself "undivided, without alteration, without decomposition" which combined with metals on calcination. After returning from Paris, Priestley took up once again his investigation of the air from mercury calx. His results now showed that this air was not just an especially pure form of common air but was "five or six times better than common air, for the purpose of respiration, inflammation, and ... every other use of common air". He called the air dephlogisticated air, as he thought it was common air deprived of its
phlogiston
The phlogiston theory is a superseded scientific theory that postulated the existence of a fire-like element called phlogiston () contained within combustible bodies and released during combustion. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''burni ...
. Since it was therefore in a state to absorb a much greater quantity of phlogiston given off by burning bodies and respiring animals, the greatly enhanced combustion of substances and the greater ease of breathing in this air were explained.
Pioneer of stoichiometry
Lavoisier's researches included some of the first truly quantitative chemical experiments. He carefully weighed the reactants and products of a chemical reaction in a sealed glass vessel so that nogas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
es could escape, which was a crucial step in the advancement of chemistry. In 1774, he showed that, although matter can change its state in a chemical reaction, the total mass of matter is the same at the end as at the beginning of every chemical change. Thus, for instance, if a piece of wood is burned to ashes, the total mass remains unchanged if gaseous reactants and products are included. Lavoisier's experiments supported the law of conservation of mass
In physics and chemistry, the law of conservation of mass or principle of mass conservation states that for any system closed to all transfers of matter and energy, the mass of the system must remain constant over time, as the system's mass can ...
. In France it is taught as Lavoisier's Law and is paraphrased from a statement in his ''Traité Élémentaire de Chimie
''Traité élémentaire de chimie'' (''Elementary Treatise on Chemistry'') is a textbook written by Antoine Lavoisier published in 1789 and translated into English by Robert Kerr in 1790 under the title ''Elements of Chemistry in a New Systemati ...
'': "Nothing is lost, nothing is created, everything is transformed." Mikhail Lomonosov
Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov (; russian: Михаил (Михайло) Васильевич Ломоносов, p=mʲɪxɐˈil vɐˈsʲilʲjɪvʲɪtɕ , a=Ru-Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov.ogg; – ) was a Russian Empire, Russian polymath, s ...
(1711–1765) had previously expressed similar ideas in 1748 and proved them in experiments; others whose ideas pre-date the work of Lavoisier include Jean Rey (1583–1645), Joseph Black
Joseph Black (16 April 1728 – 6 December 1799) was a Scottish physicist and chemist, known for his discoveries of magnesium, latent heat, specific heat, and carbon dioxide. He was Professor of Anatomy and Chemistry at the University of Glas ...
(1728–1799), and Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish ( ; 10 October 1731 – 24 February 1810) was an English natural philosopher and scientist who was an important experimental and theoretical chemist and physicist. He is noted for his discovery of hydrogen, which he termed "infl ...
(1731–1810).
Chemical nomenclature
 Lavoisier, together with
Lavoisier, together with Louis-Bernard Guyton de Morveau
Louis-Bernard Guyton, Baron de Morveau (also Louis-Bernard Guyton-Morveau after the French Revolution; 4 January 1737 – 2 January 1816) was a French chemist, politician, and aeronaut. He is credited with producing the first systematic method o ...
, Claude-Louis Berthollet
Claude Louis Berthollet (, 9 December 1748 – 6 November 1822) was a Duchy of Savoy, Savoyard-French chemist who became vice president of the French Senate in 1804. He is known for his scientific contributions to theory of chemical equilibr ...
, and Antoine François de Fourcroy, submitted a new program for the reforms of chemical nomenclature
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
The ...
to the Academy in 1787, for there was virtually no rational system of chemical nomenclature at this time. This work, titled ''Méthode de nomenclature chimique'' (''Method of Chemical Nomenclature'', 1787), introduced a new system which was tied inextricably to Lavoisier's new oxygen theory of chemistry.
The classical elements
Classical elements typically refer to earth, water, air, fire, and (later) aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler substances. Ancient cultures in Greece, Tibet, and India had simil ...
of earth, air, fire, and water were discarded, and instead some 55 substances which could not be decomposed into simpler substances by any known chemical means were provisionally listed as elements. The elements included light; caloric (matter of heat); the principles of oxygen, hydrogen, and azote (nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
); carbon; sulfur; phosphorus; the yet unknown "radicals" of muriatic acid (hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
), boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolves ...
, and "fluoric" acid; 17 metals; 5 earths (mainly oxides of yet unknown metals such as magnesia, baria, and strontia); three alkalies (potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water-soluble form.
, soda
Soda or SODA may refer to:
Chemistry
* Some chemical compounds containing sodium
** Sodium carbonate, washing soda or soda ash
** Sodium bicarbonate, baking soda
** Sodium hydroxide, caustic soda
** Sodium oxide, an alkali metal oxide
* Sod ...
, and ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
); and the "radicals" of 19 organic acids.
The acids, regarded in the new system as compounds of various elements with oxygen, were given names which indicated the element involved together with the degree of oxygenation of that element, for example sulfuric and sulfurous acids, phosphoric and phosphorous acids, nitric and nitrous acids, the "ic" termination indicating acids with a higher proportion of oxygen than those with the "ous" ending.
Similarly, salts of the "ic" acids were given the terminal letters "ate," as in copper sulfate, whereas the salts of the "ous" acids terminated with the suffix "ite," as in copper sulfite.
The total effect of the new nomenclature can be gauged by comparing the new name "copper sulfate Copper sulfate may refer to:
* Copper(II) sulfate, CuSO4, a common compound used as a fungicide and herbicide
* Copper(I) sulfate
Copper(I) sulfate, also known as cuprous sulfate, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Cu2 SO4. It ...
" with the old term "vitriol of Venus." Lavoisier's new nomenclature spread throughout Europe and to the United States and became common use in the field of chemistry. This marked the beginning of the anti-phlogistic approach to the field.
Chemical revolution and opposition
Lavoisier is commonly cited as a central contributor to thechemical revolution
The chemical revolution, also called the ''first chemical revolution'', was the early modern reformulation of chemistry that culminated in the law of conservation of mass and the oxygen theory of combustion.
During the 19th and 20th century, thi ...
. His precise measurements and meticulous keeping of balance sheets throughout his experiment were vital to the widespread acceptance of the law of conservation of mass. His introduction of new terminology, a binomial system modeled after that of Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
, also helps to mark the dramatic changes in the field which are referred to generally as the chemical revolution. Lavoisier encountered much opposition in trying to change the field, especially from British phlogistic scientists. Joseph Priestley, Richard Kirwan
Richard Kirwan, LL.D, FRS, FRSE MRIA (1 August 1733 – 22 June 1812) was an Irish geologist and chemist. He was one of the last supporters of the theory of phlogiston.
Kirwan was active in the fields of chemistry, meteorology, and geol ...
, James Keir
James Keir FRS (20 September 1735 – 11 October 1820) was a Scottish chemist, geologist, industrialist, and inventor, and an important member of the Lunar Society of Birmingham.
Life and work
Keir was born in Stirlingshire, Scotland, in 1 ...
, and William Nicholson, among others, argued that quantification of substances did not imply conservation of mass. Rather than reporting factual evidence, opposition claimed Lavoisier was misinterpreting the implications of his research. One of Lavoisier's allies, Jean Baptiste Biot
Jean-Baptiste Biot (; ; 21 April 1774 – 3 February 1862) was a French physicist, astronomer, and mathematician who co-discovered the Biot–Savart law of magnetostatics with Félix Savart, established the reality of meteorites, made an early b ...
, wrote of Lavoisier's methodology, "one felt the necessity of linking accuracy in experiments to rigor of reasoning." His opposition argued that precision in experimentation did not imply precision in inferences and reasoning. Despite opposition, Lavoisier continued to use precise instrumentation to convince other chemists of his conclusions, often results to five to eight decimal places. Nicholson, who estimated that only three of these decimal places were meaningful, stated:
Notable works

Easter memoir
The "official" version of Lavoisier's Easter Memoir appeared in 1778. In the intervening period, Lavoisier had ample time to repeat some of Priestley's latest experiments and perform some new ones of his own. In addition to studying Priestley's dephlogisticated air, he studied more thoroughly the residual air after metals had been calcined. He showed that this residual air supported neither combustion nor respiration and that approximately five volumes of this air added to one volume of the dephlogisticated air gave common atmospheric air. Common air was then a mixture of two distinct chemical species with quite different properties. Thus when the revised version of the Easter Memoir was published in 1778, Lavoisier no longer stated that the principle which combined with metals on calcination was just common air but "nothing else than the healthiest and purest part of the air" or the "eminently respirable part of the air". The same year he coined the name oxygen for this constituent of the air, from the Greek words meaning "acid former". He was struck by the fact that the combustion products of such nonmetals as sulfur, phosphorus, charcoal, and nitrogen were acidic. He held that all acids contained oxygen and that oxygen was therefore the acidifying principle.Dismantling phlogiston theory
Lavoisier's chemical research between 1772 and 1778 was largely concerned with developing his own new theory of combustion. In 1783 he read to the academy his paper entitled ''Réflexions sur le phlogistique'' (Reflections on Phlogiston), a full-scale attack on the current phlogiston theory of combustion. That year Lavoisier also began a series of experiments on the composition of water which were to prove an important capstone to his combustion theory and win many converts to it. Many investigators had been experimenting with the combination of Henry Cavendish's inflammable air, which Lavoisier termedhydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
(Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
for "water-former"), with "dephlogisticated air" (air in the process of combustion, now known to be oxygen) by electrically sparking mixtures of the gases. All of the researchers noted Cavendish's production of pure water by burning hydrogen in oxygen, but they interpreted the reaction in varying ways within the framework of phlogiston theory. Lavoisier learned of Cavendish's experiment in June 1783 via Charles Blagden (before the results were published in 1784), and immediately recognized water as the oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the E ...
of a hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
gas.
In cooperation with Laplace, Lavoisier synthesized water by burning jets of hydrogen and oxygen in a bell jar over mercury. The quantitative results were good enough to support the contention that water was not an element, as had been thought for over 2,000 years, but a compound of two gases, hydrogen and oxygen. The interpretation of water as a compound explained the inflammable air generated from dissolving metals in acids (hydrogen produced when water decomposes) and the reduction of calces by inflammable air (a combination of gas from calx with oxygen to form water).
Despite these experiments, Lavoisier's antiphlogistic approach remained unaccepted by many other chemists. Lavoisier labored to provide definitive proof of the composition of water, attempting to use this in support of his theory. Working with Jean-Baptiste Meusnier, Lavoisier passed water through a red-hot iron gun barrel, allowing the oxygen to form an oxide with the iron and the hydrogen to emerge from the end of the pipe. He submitted his findings of the composition of water to the Académie des Sciences in April 1784, reporting his figures to eight decimal places. Opposition responded to this further experimentation by stating that Lavoisier continued to draw the incorrect conclusions and that his experiment demonstrated the displacement of phlogiston from iron by the combination of water with the metal. Lavoisier developed a new apparatus which used a pneumatic trough, a set of balances, a thermometer, and a barometer, all calibrated carefully. Thirty savants were invited to witness the decomposition and synthesis of water using this apparatus, convincing many who attended of the correctness of Lavoisier's theories. This demonstration established water as a compound of oxygen and hydrogen with great certainty for those who viewed it. The dissemination of the experiment, however, proved subpar, as it lacked the details to properly display the amount of precision taken in the measurements. The paper ended with a hasty statement that the experiment was "more than sufficient to lay hold of the certainty of the proposition" of the composition of water and stated that the methods used in the experiment would unite chemistry with the other physical sciences and advance discoveries.
''Elementary Treatise of Chemistry''
Lavoisier employed the new nomenclature in his '' Traité élémentaire de chimie'' (''Elementary Treatise on Chemistry''), published in 1789. This work represents the synthesis of Lavoisier's contribution to chemistry and can be considered the first moderntextbook
A textbook is a book containing a comprehensive compilation of content in a branch of study with the intention of explaining it. Textbooks are produced to meet the needs of educators, usually at educational institutions. Schoolbooks are textboo ...
on the subject. The core of the work was the oxygen theory, and the work became a most effective vehicle for the transmission of the new doctrines. It presented a unified view of new theories of chemistry, contained a clear statement of the law of conservation of mass, and denied the existence of phlogiston. This text clarified the concept of an element as a substance that could not be broken down by any known method of chemical analysis and presented Lavoisier's theory of the formation of chemical compounds from elements. It remains a classic in the history of science. While many leading chemists of the time refused to accept Lavoisier's new ideas, demand for ''Traité élémentaire'' as a textbook in Edinburgh was sufficient to merit translation into English within about a year of its French publication. In any event, the ''Traité élémentaire'' was sufficiently sound to convince the next generation.
Physiological work
The relationship between combustion and respiration had long been recognized from the essential role which air played in both processes. Lavoisier was almost obliged, therefore, to extend his new theory of combustion to include the area of respiration physiology. His first memoirs on this topic were read to the Academy of Sciences in 1777, but his most significant contribution to this field was made in the winter of 1782–1783 in association with Laplace. The result of this work was published in a memoir, "On Heat." Lavoisier and Laplace designed an icecalorimeter
A calorimeter is an object used for calorimetry, or the process of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity. Differential scanning calorimeters, isothermal micro calorimeters, titration calorimete ...
apparatus for measuring the amount of heat given off during combustion or respiration. The outer shell of the calorimeter was packed with snow, which melted to maintain a constant temperature of around an inner shell filled with ice. By measuring the quantity of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
and heat produced by confining a live guinea pig in this apparatus, and by comparing the amount of heat produced when sufficient carbon was burned in the ice calorimeter to produce the same amount of carbon dioxide as that which the guinea pig exhaled, they concluded that respiration was, in fact, a slow combustion process. Lavoisier stated, ''"la respiration est donc une combustion,"'' that is, respiratory gas exchange is a combustion, like that of a candle burning.
This continuous slow combustion, which they supposed took place in the lungs, enabled the living animal to maintain its body temperature above that of its surroundings, thus accounting for the puzzling phenomenon of animal heat. Lavoisier continued these respiration experiments in 1789–1790 in cooperation with Armand Seguin
Armand refer to:
People
* Armand (name), list of people with this name
*Armand (photographer) (1901–1963), Armenian photographer
*Armand (singer) (1946–2015), Dutch protest singer
*Sean Armand (born 1991), American basketball player
*Armand, ...
. They designed an ambitious set of experiments to study the whole process of body metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
and respiration using Seguin as a human guinea pig in the experiments. Their work was only partially completed and published because of the Revolution's disruption, but Lavoisier's pioneering work in this field inspired similar research on physiological processes for generations.
Legacy
allotropy
Allotropy or allotropism () is the property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms, in the same physical state, known as allotropes of the elements. Allotropes are different structural modifications of an element: the ...
in chemical elements when he discovered that diamond is a crystalline form of carbon.
He was also responsible for the construction of the gasometer, an expensive instrument he used at his demonstrations. While he used his gasometer exclusively for these, he also created smaller, cheaper, more practical gasometers that worked with a sufficient degree of precision that more chemists could recreate.
Overall, his contributions are considered the most important in advancing chemistry to the level reached in physics and mathematics during the 18th century.
Mount Lavoisier in New Zealand's Paparoa Range
The Paparoa Range is a mountain range in the West Coast region of New Zealand's South Island. It was the first New Zealand land seen by a European – Abel Tasman in 1642. Part of the range has the country's highest protection as a national par ...
was named after him in 1970 by the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, abbreviated DSIR was the name of several British Empire organisations founded after the 1923 Imperial Conference to foster intra-Empire trade and development.
* Department of Scientific and Industria ...
.
Awards and honours
During his lifetime, Lavoisier was awarded a gold medal by the King of France for his work on urbanstreet lighting
A street light, light pole, lamp pole, lamppost, street lamp, light standard, or lamp standard is a raised source of light on the edge of a road or path. Similar lights may be found on a railway platform. When urban electric power distribution ...
(1766), and was appointed to the French Academy of Sciences (1768). He was elected as a member of the American Philosophical Society
The American Philosophical Society (APS), founded in 1743 in Philadelphia, is a scholarly organization that promotes knowledge in the sciences and humanities through research, professional meetings, publications, library resources, and communit ...
in 1775.
Lavoisier's work was recognized as an International Historic Chemical Landmark by the American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 155,000 members at all d ...
, Académie des sciences de L'institut de France and the Société Chimique de France
Lactalis is a French multinational dairy products corporation, owned by the Besnier family and based in Laval, Mayenne, France. The company's former name was Besnier SA.
Lactalis is the largest dairy products group in the world, and is the se ...
in 1999. Antoine Laurent Lavoisier's Louis 1788 publication entitled ''Méthode de Nomenclature Chimique'', published with colleagues Louis-Bernard Guyton de Morveau
Louis-Bernard Guyton, Baron de Morveau (also Louis-Bernard Guyton-Morveau after the French Revolution; 4 January 1737 – 2 January 1816) was a French chemist, politician, and aeronaut. He is credited with producing the first systematic method o ...
, Claude Louis Berthollet
Claude Louis Berthollet (, 9 December 1748 – 6 November 1822) was a Savoyard-French chemist who became vice president of the French Senate in 1804. He is known for his scientific contributions to theory of chemical equilibria via the mecha ...
, and Antoine François, comte de Fourcroy
Antoine is a French given name (from the Latin ''Antonius'' meaning 'highly praise-worthy') that is a variant of Danton, Titouan, D'Anton and Antonin.
The name is used in France, Switzerland, Belgium, Canada, West Greenland, Haiti, French Guiana ...
, was honored by a Citation for Chemical Breakthrough Award from the Division of History of Chemistry of the American Chemical Society, presented at the Académie des Sciences (Paris) in 2015.
 A number of
A number of Lavoisier Medal A Lavoisier Medal is an award named and given in honor of Antoine Lavoisier, considered by some to be a father of modern chemistry.
s have been named and given in Lavoisier's honour, by organizations including the Société chimique de France
Lactalis is a French multinational dairy products corporation, owned by the Besnier family and based in Laval, Mayenne, France. The company's former name was Besnier SA.
Lactalis is the largest dairy products group in the world, and is the se ...
, the International Society for Biological Calorimetry, and the DuPont
DuPont de Nemours, Inc., commonly shortened to DuPont, is an American multinational chemical company first formed in 1802 by French-American chemist and industrialist Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours. The company played a major role in ...
company He is also commemorated by the Franklin-Lavoisier Prize, marking the friendship of Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier and Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading inte ...
. The prize, which includes a medal, is given jointly by the Fondation de la Maison de la Chimie in Paris, France and the Science History Institute
The Science History Institute is an institution that preserves and promotes understanding of the history of science. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it includes a library, museum, archive, research center and conference center.
It was fo ...
in Philadelphia, PA, USA.
Selected writings
 * '' Opuscules physiques et chimiques'' (Paris: Chez Durand, Didot, Esprit, 1774).
* '' Opuscules physiques et chimiques'' (Paris: Chez Durand, Didot, Esprit, 1774).Second edition, 1801
* ''L'art de fabriquer le salin et la potasse, publié par ordre du Roi, par les régisseurs-généraux des Poudres & Salpêtres'' (Paris, 1779). * ''Instruction sur les moyens de suppléer à la disette des fourrages, et d'augmenter la subsistence des bestiaux, Supplément à l'instruction sur les moyens de pourvoir à la disette des fourrages, publiée par ordre du Roi le 31 mai 1785'' (Instruction on the means of compensating for the food shortage with fodder, and of increasing the subsistence of cattle, Supplement to the instruction on the means of providing for the food shortage with fodder, published by order of King on 31 May 1785). * (with Guyton de Morveau, Claude-Louis Berthollet, Antoine Fourcroy)
Méthode de nomenclature chimique
' (Paris: Chez Cuchet, 1787) * (with Fourcroy, Morveau, Cadet, Baumé, d'Arcet, and Sage)
Nomenclature chimique, ou synonymie ancienne et moderne, pour servir à l'intelligence des auteurs.
' (Paris: Chez Cuchet, 1789) *
' (Paris: Chez Cuchet, 1789; Bruxelles: Cultures et Civilisations, 1965) (lit. Elementary Treatise on Chemistry, presented in a new order and alongside modern discoveries) als
* (with Pierre-Simon Laplace)
Mémoire sur la chaleur
" ''Mémoires de l'Académie des sciences'' (1780), pp. 355–408. *
Mémoire contenant les expériences faites sur la chaleur, pendant l'hiver de 1783 à 1784, par P.S. de Laplace & A. K. Lavoisier
' (1792) * ''Mémoires de Physique et de Chimie, de la Société d'Arcueil'' (1805: posthumous)
In translation
*Essays Physical and Chemical
' (London: for Joseph Johnson, 1776; London: Frank Cass and Company Ltd., 1970) translation by Thomas Henry of ''Opuscules physiques et chimiques'' * ''The Art of Manufacturing Alkaline Salts and Potashes, Published by Order of His Most Christian Majesty, and approved by the Royal Academy of Sciences'' (1784) trans. by Charles WilliamosSee Denis I. Duveen and Herbert S. Klickstein,
The "American" Edition of Lavoisier's ''L'art de fabriquer le salin et la potasse''
" ''The William and Mary Quarterly, Third Series'' 13:4 (October 1956), 493–498. of ''L'art de fabriquer le salin et la potasse'' * (with Pierre-Simon Laplace) ''Memoir on Heat: Read to the Royal Academy of Sciences, 28 June 1783, by Messrs. Lavoisier & De La Place of the same Academy.'' (New York: Neale Watson Academic Publications, 1982) trans. by Henry Guerlac of ''Mémoire sur la chaleur'' *
Essays, on the Effects Produced by Various Processes On Atmospheric Air; With A Particular View To An Investigation Of The Constitution Of Acids
', trans. Thomas Henry (London: Warrington, 1783) collects these essays: # "Experiments on the Respiration of Animals, and on the Changes effected on the Air in passing through their Lungs." (Read to the Académie des Sciences, 3 May 1777) # "On the Combustion of Candles in Atmospheric Air and in Dephlogistated Air." (Communicated to the Académie des Sciences, 1777) # "On the Combustion of Kunckel's Phosphorus." # "On the Existence of Air in the Nitrous Acid, and on the Means of decomposing and recomposing that Acid." # "On the Solution of Mercury in Vitriolic Acid." # "Experiments on the Combustion of Alum with Phlogistic Substances, and on the Changes effected on Air in which the Pyrophorus was burned." # "On the Vitriolisation of Martial Pyrites." # "General Considerations on the Nature of Acids, and on the Principles of which they are composed." # "On the Combination of the Matter of Fire with Evaporable Fluids; and on the Formation of Elastic Aëriform Fluids." * “Reflections on Phlogiston”, translation by Nicholas W. Best of “Réflexions sur le phlogistique, pour servir de suite à la théorie de la combustion et de la calcination” (read to the Académie Royale des Sciences over two nights, 28 June and 13 July 1783). Published in two parts: # # * ''Method of chymical nomenclature: proposed by Messrs. De Moreau, Lavoisier, Bertholet, and De Fourcroy'' (1788
* ''Elements of Chemistry, in a New Systematic Order, Containing All the Modern Discoveries'' (Edinburgh: William Creech, 1790; New York: Dover, 1965) translation by Robert Kerr of ''Traité élémentaire de chimie''. (Dover). *
1799 edition
** 1802 edition
volume 1
*
Some illustrations
from 1793 edition *
Some more illustrations
from the
Science History Institute
The Science History Institute is an institution that preserves and promotes understanding of the history of science. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it includes a library, museum, archive, research center and conference center.
It was fo ...
*More illustrations
(from Collected Works) from the
Science History Institute
The Science History Institute is an institution that preserves and promotes understanding of the history of science. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it includes a library, museum, archive, research center and conference center.
It was fo ...
See also
*Royal Commission on Animal Magnetism
The Royal Commission on Animal Magnetism involved two entirely separate and independent French Royal Commissions, each appointed by Louis XVI in 1784, that were conducted simultaneously by a committee composed of four physicians from the Paris ...
Notes
Further reading
* * Bailly, J.-S., "Secret Report on Mesmerism or Animal Magnetism", ''International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis'', Vol. 50, No. 4, (October 2002), pp. 364–368. * * ''Catalogue of Printed Works by and Memorabilia of Antoine Laurent Lavoisier, 1743–1794... Exhibited at the Grolier Club'' (New York, 1952). * * * Duveen, D.I. and H.S. Klickstein, ''A Bibliography of the Works of Antoine Laurent Lavoisier, 1743–1794'' (London, 1954) * Franklin, B., Majault, M.J., Le Roy, J.B., Sallin, C.L., Bailly, J.-S., d'Arcet, J., de Bory, G., Guillotin, J.-I. & Lavoisier, A., "Report of The Commissioners charged by the King with the Examination of Animal Magnetism", ''International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis'', Vol.50, No.4, (October 2002), pp. 332–363. * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* ArchivesFonds Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier
Le Comité Lavoisier,
Académie des sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French scientific research. It was at the ...
Panopticon Lavoisier
a virtual museum of Antoine Lavoisier
Bibliography
at Panopticon Lavoisier
Les Œuvres de Lavoisier
;About his work
Location of Lavoisier's laboratory in Paris
Radio 4 program on the discovery of oxygen
by the
BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...Who was the first to classify materials as "compounds"?
– Fred Senese
;His writings * *
Les Œuvres de Lavoisier
(The Complete Works of Lavoisier) edited by Pietro Corsi (Oxford University) and Patrice Bret (CNRS)
Oeuvres de Lavoisier
(Works of Lavoisier) at Gallica BnF in six volumes.
WorldCat author page
* Title page, woodcuts, and copperplate engravings by Madame Lavoisier from a 1789 first edition of
Traité élémentaire de chimie
' (all images freely available for download in a variety of formats from
Science History Institute
The Science History Institute is an institution that preserves and promotes understanding of the history of science. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it includes a library, museum, archive, research center and conference center.
It was fo ...
Digital Collections adigital.sciencehistory.org
{{DEFAULTSORT:Lavoisier, Antoine 1743 births 1794 deaths Scientists from Paris University of Paris alumni 18th-century French chemists 18th-century French writers 18th-century French male writers French biologists Members of the French Academy of Sciences Fellows of the Royal Society Discoverers of chemical elements Independent scientists Fermiers généraux People of the Industrial Revolution French Roman Catholics French people executed by guillotine during the French Revolution Executed scientists Burials at Picpus Cemetery Members of the American Philosophical Society