Antinuclear antibody on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the
 Anti-Ro and anti-La antibodies, also known as SS-A and SS-B, respectively, are commonly found in primary Sjögren's syndrome, an autoimmune disorder that affects the
Anti-Ro and anti-La antibodies, also known as SS-A and SS-B, respectively, are commonly found in primary Sjögren's syndrome, an autoimmune disorder that affects the
 Anti-double stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibodies are highly associated with SLE. They are a very specific marker for the disease, with some studies quoting nearly 100%. Data on sensitivity ranges from 25 to 85%. Anti-dsDNA antibody levels, known as titres, correlate with disease activity in SLE; high levels indicate more active lupus. The presence of anti-dsDNA antibodies is also linked with lupus nephritis and there is evidence they are the cause. Some anti-dsDNA antibodies are cross reactive with other antigens found on the
Anti-double stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibodies are highly associated with SLE. They are a very specific marker for the disease, with some studies quoting nearly 100%. Data on sensitivity ranges from 25 to 85%. Anti-dsDNA antibody levels, known as titres, correlate with disease activity in SLE; high levels indicate more active lupus. The presence of anti-dsDNA antibodies is also linked with lupus nephritis and there is evidence they are the cause. Some anti-dsDNA antibodies are cross reactive with other antigens found on the
 Anti-centromere antibodies are associated with limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis, also known as CREST syndrome, primary biliary cirrhosis and proximal scleroderma. There are six known antigens, which are all associated with the
Anti-centromere antibodies are associated with limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis, also known as CREST syndrome, primary biliary cirrhosis and proximal scleroderma. There are six known antigens, which are all associated with the

 The presence of ANAs in blood can be confirmed by a screening test. Although there are many tests for the detection of ANAs, the most common tests used for screening are indirect immunofluorescence and
The presence of ANAs in blood can be confirmed by a screening test. Although there are many tests for the detection of ANAs, the most common tests used for screening are indirect immunofluorescence and
 Until around 1975, when HEp-2 cells were introduced, animal tissue was used as the standard substrate for immunofluorescence. HEp-2 cells are currently one of the most common substrates for ANA detection by immunofluorescence.
Originally started a laryngeal carcinoma strain, the cell line was contaminated and displaced by HeLa cells, and has now been identified as actually HeLa cells.
They are superior to the previously used animal tissues because of their large size and the high rate of
Until around 1975, when HEp-2 cells were introduced, animal tissue was used as the standard substrate for immunofluorescence. HEp-2 cells are currently one of the most common substrates for ANA detection by immunofluorescence.
Originally started a laryngeal carcinoma strain, the cell line was contaminated and displaced by HeLa cells, and has now been identified as actually HeLa cells.
They are superior to the previously used animal tissues because of their large size and the high rate of
 '' Crithidia luciliae'' are haemoflaggelate
'' Crithidia luciliae'' are haemoflaggelate
 The LE cell was discovered in bone marrow in 1948 by Hargraves ''et al.''Hargraves M, Richmond H, Morton R. ''Presentation of two bone marrow components, the tart cell and the LE cell.'' Mayo Clin Proc 1948;27:25–28. In 1957 Holborow et al. first demonstrated ANA using indirect immunofluorescence. This was the first indication that processes affecting the cell nucleus were responsible for SLE. In 1959 it was discovered that serum from individuals with SLE contained antibodies that precipitated with saline extracts of nuclei, known as extractable nuclear antigens (ENAs). This led to the characterisation of ENA antigens and their respective antibodies. Thus, anti-Sm and anti-RNP antibodies were discovered in 1966 and 1971, respectively. In the 1970s, the anti-Ro/anti-SS-A and anti-La/anti-SS-B antibodies were discovered. The Scl-70 antibody was known to be a specific antibody to scleroderma in 1979, however the antigen (topoisomerase-I) was not characterised until 1986. The Jo-1 antigen and antibody were characterised in 1980.
The LE cell was discovered in bone marrow in 1948 by Hargraves ''et al.''Hargraves M, Richmond H, Morton R. ''Presentation of two bone marrow components, the tart cell and the LE cell.'' Mayo Clin Proc 1948;27:25–28. In 1957 Holborow et al. first demonstrated ANA using indirect immunofluorescence. This was the first indication that processes affecting the cell nucleus were responsible for SLE. In 1959 it was discovered that serum from individuals with SLE contained antibodies that precipitated with saline extracts of nuclei, known as extractable nuclear antigens (ENAs). This led to the characterisation of ENA antigens and their respective antibodies. Thus, anti-Sm and anti-RNP antibodies were discovered in 1966 and 1971, respectively. In the 1970s, the anti-Ro/anti-SS-A and anti-La/anti-SS-B antibodies were discovered. The Scl-70 antibody was known to be a specific antibody to scleroderma in 1979, however the antigen (topoisomerase-I) was not characterised until 1986. The Jo-1 antigen and antibody were characterised in 1980.
Autoimmunityblog – HEp-2 ANA summary
* * {{Autoantibodies Chemical pathology Autoantibodies Antibodies Immunologic tests
 Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ...
. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respon ...
s) but not to human proteins (autoantigen
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". ...
s). In some cases, antibodies to human antigens are produced.
There are many subtypes of ANAs such as anti-Ro antibodies, anti-La antibodies, anti-Sm antibodies, anti-nRNP antibodies, anti-Scl-70 antibodies, anti-dsDNA antibodies, anti-histone antibodies, antibodies to nuclear pore complexes, anti-centromere antibodies and anti-sp100 antibodies
Anti-sp100 antibodies are found in association with primary biliary cirrhosis. The autoimmune target of anti-sp100 is the sp100 nuclear antigen which was identified by its association with primary biliary cirrhosis
Primary biliary cholangitis ( ...
. Each of these antibody subtypes binds to different proteins or protein complexes within the nucleus. They are found in many disorders including autoimmunity, cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
and infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
, with different prevalences of antibodies depending on the condition. This allows the use of ANAs in the diagnosis of some autoimmune disorders, including systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, scleroderma, mixed connective tissue disease
Mixed connective tissue disease, commonly abbreviated as MCTD, is an autoimmune disease characterized by the presence of elevated blood levels of a specific autoantibody, now called anti-U1 ribonucleoprotein (RNP) together with a mix of symptoms o ...
, polymyositis
Polymyositis (PM) is a type of chronic inflammation of the muscles (inflammatory myopathy) related to dermatomyositis and inclusion body myositis. Its name means "inflammation of many muscles" ('' poly-'' + '' myos-'' + '' -itis''). The inflam ...
, dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis (DM) is a long-term inflammatory disorder which affects skin and the muscles. Its symptoms are generally a skin rash and worsening muscle weakness over time. These may occur suddenly or develop over months. Other symptoms may inc ...
, autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis, formerly known as lupoid hepatitis, plasma cell hepatitis, or autoimmune chronic active hepatitis, is a chronic, autoimmune disease of the liver that occurs when the body's immune system attacks liver cells, causing the live ...
and drug induced lupus.
The ANA test detects the autoantibodies present in an individual's blood serum. The common tests used for detecting and quantifying ANAs are indirect immunofluorescence and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence ...
(ELISA). In immunofluorescence, the level of autoantibodies is reported as a titre. This is the highest dilution of the serum at which autoantibodies are still detectable. Positive autoantibody titres at a dilution equal to or greater than 1:160 are usually considered as clinically significant. Positive titres of less than 1:160 are present in up to 20% of the healthy population, especially the elderly. Although positive titres of 1:160 or higher are strongly associated with autoimmune disorders, they are also found in 5% of healthy individuals. Autoantibody screening is useful in the diagnosis of autoimmune disorders and monitoring levels helps to predict the progression of disease. A positive ANA test is seldom useful if other clinical or laboratory data supporting a diagnosis are not present.
Immunity and autoimmunity
The human body has many defense mechanisms againstpathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a g ...
s, one of which is humoral immunity. This defence mechanism produces antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of ...
(large glycoproteins) in response to an immune stimulus. Many cells of the immune system are required for this process, including lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic a ...
s ( T-cells and B-cells) and antigen presenting cell
An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a cell that displays antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize these complexes using ...
s. These cells coordinate an immune response upon the detection of foreign proteins (antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respon ...
s), producing antibodies that bind to these antigens. In normal physiology, lymphocytes that recognise human proteins (autoantigen
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". ...
s) either undergo programmed cell death (apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
) or become non-functional. This self-tolerance means that lymphocytes should not incite an immune response against human cellular antigens. Sometimes, however, this process malfunctions and antibodies are produced against human antigens, which may lead to autoimmune disease.
ANA subtypes
ANAs are found in many disorders, as well as some healthy individuals. These disorders include: systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE),rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are inv ...
, Sjögren syndrome, scleroderma, polymyositis
Polymyositis (PM) is a type of chronic inflammation of the muscles (inflammatory myopathy) related to dermatomyositis and inclusion body myositis. Its name means "inflammation of many muscles" ('' poly-'' + '' myos-'' + '' -itis''). The inflam ...
, dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis (DM) is a long-term inflammatory disorder which affects skin and the muscles. Its symptoms are generally a skin rash and worsening muscle weakness over time. These may occur suddenly or develop over months. Other symptoms may inc ...
, primary biliary cirrhosis
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), previously known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is an autoimmune disease of the liver. It results from a slow, progressive destruction of the small bile ducts of the liver, causing bile and other toxins to build ...
, drug induced lupus, autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis, formerly known as lupoid hepatitis, plasma cell hepatitis, or autoimmune chronic active hepatitis, is a chronic, autoimmune disease of the liver that occurs when the body's immune system attacks liver cells, causing the live ...
, multiple sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This ...
, discoid lupus, thyroid disease
Thyroid disease is a medical condition that affects the function of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located at the front of the neck and produces thyroid hormones that travel through the blood to help regulate many other organs, meaning ...
, antiphospholipid syndrome, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that occurs in people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic feature of psoriatic arthritis is swelling of entire fingers and toes with a sausage-like appearance. T ...
, juvenile dermatomyositis
Juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) is an idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IMM) of presumed autoimmune dysfunction resulting in muscle weakness among other complications. It manifests itself in children; it is the pediatric counterpart of dermatomyo ...
, idiopathic thrombocytopaenic purpura, infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
and cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
. These antibodies can be subdivided according to their specificity, and each subset has different propensities for specific disorders.
Extractable nuclear antigens
Extractable nuclear antigen Extractable nuclear antigens (ENAs) are over 100 different soluble cytoplasmic and nuclear antigens. They are known as "extractable" because they can be removed from cell nuclei using saline and represent six main proteins: Ro, La, Sm, RNP, Scl-70, ...
s (ENA) are a group of autoantigen
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". ...
s that were originally identified as antibody targets in people with autoimmune disorders. They are termed ENA because they can be extracted from the cell nucleus with saline. The ENAs consist of ribonucleoproteins and non-histone
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes in turn a ...
proteins, named by either the name of the donor who provided the prototype serum (Sm, Ro, La, Jo), or the name of the disease setting in which the antibodies were found (SS-A, SS-B, Scl-70).
Anti-Ro/SS-A and anti-La/SS-B
 Anti-Ro and anti-La antibodies, also known as SS-A and SS-B, respectively, are commonly found in primary Sjögren's syndrome, an autoimmune disorder that affects the
Anti-Ro and anti-La antibodies, also known as SS-A and SS-B, respectively, are commonly found in primary Sjögren's syndrome, an autoimmune disorder that affects the exocrine gland
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one ...
s. The presence of both antibodies is found in 30–60% of Sjögren's syndrome, anti-Ro antibodies alone are found in 50–70% of Sjögren's syndrome and 30% of SLE with cutaneous involvement, and anti-La antibodies are rarely found in isolation. Anti-La antibodies are also found in SLE; however, Sjögren's syndrome is normally also present. Anti-Ro antibodies are also found less frequently in other disorders including autoimmune liver diseases, coeliac disease, autoimmune rheumatic diseases, cardiac neonatal lupus erythematosus and polymyositis
Polymyositis (PM) is a type of chronic inflammation of the muscles (inflammatory myopathy) related to dermatomyositis and inclusion body myositis. Its name means "inflammation of many muscles" ('' poly-'' + '' myos-'' + '' -itis''). The inflam ...
. During pregnancy, anti-Ro antibodies can cross the placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate mate ...
and cause heart block and neonatal lupus in babies. In Sjögren's syndrome, anti-Ro and anti-La antibodies correlate with early onset, increased disease duration, parotid gland enlargement, disease outside the glands and infiltration of glands by lymphocytes. Anti-Ro antibodies are specific to components of the Ro-RNP complex, comprising 45kDa, 52kDa, 54kDa and 60kDa proteins and RNA. The 60kDa DNA/RNA binding protein and 52kDa T-cell regulatory protein are the best characterised antigens of anti-Ro antibodies. Collectively, these proteins are part of a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex that associate with the human Y RNA
Y RNAs are small non-coding RNAs. They are components of the Ro60 ribonucleoprotein particle which is a target of autoimmune antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. They are also reported to be necessary for DNA replication thro ...
s, hY1-hY5. The La antigen is a 48kDa transcription termination factor of RNA polymerase III, which associates with the Ro-RNP complex.
The mechanism of antibody production in Sjögren's syndrome is not fully understood, but apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
(programmed cell death) and molecular mimicry Molecular mimicry is defined as the theoretical possibility that sequence similarities between foreign and self-peptides are sufficient to result in the cross-activation of autoreactive T or B cells by pathogen-derived peptides. Despite the preval ...
may play a role. The Ro and La antigens are expressed on the surface of cells undergoing apoptosis and may cause the inflammation within the salivary gland by interaction with cells of the immune system. The antibodies may also be produced through molecular mimicry, where cross reactive antibodies bind to both virus and human proteins. This may occur with one of the antigens, Ro or La, and may subsequently produce antibodies to other proteins through a process known as epitope spreading. The retroviral gag protein shows similarity to the La protein and is proposed as a possible example for molecular mimicry in Sjögren's syndrome.
Anti-Sm
Anti-Smith (Anti-Sm) antibodies are a very specific marker for SLE. Approximately 99% of individuals without SLE lack anti-Sm antibodies, but only 20% of people with SLE have the antibodies. They are associated withcentral nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
involvement, kidney disease
Kidney disease, or renal disease, technically referred to as nephropathy, is damage to or disease of a kidney. Nephritis is an inflammatory kidney disease and has several types according to the location of the inflammation. Inflammation can ...
, lung fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory failu ...
and pericarditis in SLE, but they are not associated with disease activity. The antigens of the anti-Sm antibodies are the core units of the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs), termed A to G, and will bind to the U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 snRNPs. Most commonly, the antibodies are specific for the B, B' and D units. Molecular and epidemiological studies suggest that anti-Sm antibodies may be induced by molecular mimicry because the protein shows some similarity to Epstein-Barr virus proteins.
Anti-nRNP/anti-U1-RNP
Anti-nuclear ribonucleoprotein (anti-nRNP) antibodies, also known as anti-U1-RNP antibodies, are found in 30–40% of SLE. They are often found with anti-Sm antibodies, but they may be associated with different clinical associations. In addition to SLE, these antibodies are highly associated withmixed connective tissue disease
Mixed connective tissue disease, commonly abbreviated as MCTD, is an autoimmune disease characterized by the presence of elevated blood levels of a specific autoantibody, now called anti-U1 ribonucleoprotein (RNP) together with a mix of symptoms o ...
. Anti-nRNP antibodies recognise the A and C core units of the snRNPs and because of this they primarily bind to the U1-snRNP. The immune response to RNP may be caused by the presentation of the nuclear components on the cell membrane in apoptotic blebs. Molecular mimicry has also been suggested as a possible mechanism for the production of antibodies to these proteins because of similarity between U1-RNP polypeptides and Epstein-Barr virus polypeptides.
Anti-Scl-70/anti-topoisomerase I
Anti-Scl-70 antibodies are linked to scleroderma. The sensitivity of the antibodies for scleroderma is approximately 34%, but is higher for cases with diffuse cutaneous involvement (40%), and lower for limited cutaneous involvement (10%). The specificity of the antibodies is 98% and 99.6% in other rheumatic diseases and normal individuals, respectively. In addition to scleroderma, these antibodies are found in approximately 5% of individuals with SLE. The antigenic target of anti-Scl-70 antibodies is topoisomerase I.Anti-Jo-1
Although anti-Jo-1 antibodies are often included with ANAs, they are actually antibodies to the cytoplasmic protein, Histidyl-tRNA synthetase - an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase essential for the synthesis of histidine loaded tRNA. They are highly associated withpolymyositis
Polymyositis (PM) is a type of chronic inflammation of the muscles (inflammatory myopathy) related to dermatomyositis and inclusion body myositis. Its name means "inflammation of many muscles" ('' poly-'' + '' myos-'' + '' -itis''). The inflam ...
and dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis (DM) is a long-term inflammatory disorder which affects skin and the muscles. Its symptoms are generally a skin rash and worsening muscle weakness over time. These may occur suddenly or develop over months. Other symptoms may inc ...
, and are rarely found in other connective tissue diseases. Around 20–40% of polymyositis is positive for Jo-1 antibodies and most will have interstitial lung disease, HLA-DR3 and HLA-DRw52 human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for the regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of th ...
(HLA) markers; collectively known as Jo-1 syndrome.
Anti-dsDNA
 Anti-double stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibodies are highly associated with SLE. They are a very specific marker for the disease, with some studies quoting nearly 100%. Data on sensitivity ranges from 25 to 85%. Anti-dsDNA antibody levels, known as titres, correlate with disease activity in SLE; high levels indicate more active lupus. The presence of anti-dsDNA antibodies is also linked with lupus nephritis and there is evidence they are the cause. Some anti-dsDNA antibodies are cross reactive with other antigens found on the
Anti-double stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibodies are highly associated with SLE. They are a very specific marker for the disease, with some studies quoting nearly 100%. Data on sensitivity ranges from 25 to 85%. Anti-dsDNA antibody levels, known as titres, correlate with disease activity in SLE; high levels indicate more active lupus. The presence of anti-dsDNA antibodies is also linked with lupus nephritis and there is evidence they are the cause. Some anti-dsDNA antibodies are cross reactive with other antigens found on the glomerular basement membrane
The glomerular basement membrane of the kidney is the basal lamina layer of the glomerulus. The glomerular endothelial cells, the glomerular basement membrane, and the filtration slits between the podocytes perform the filtration function of ...
(GBM) of the kidney, such as heparan sulphate, collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whol ...
IV, fibronectin
Fibronectin is a high- molecular weight (~500-~600 kDa) glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that binds to membrane-spanning receptor proteins called integrins. Fibronectin also binds to other extracellular matrix proteins such as coll ...
and laminin. Binding to these antigens within the kidney could cause inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
and complement fixation, resulting in kidney damage. Presence of high DNA-binding and low C3 levels have been shown to have extremely high predictive value (94%) for the diagnosis of SLE. It is also possible that the anti-dsDNA antibodies are internalised by cells when they bind membrane antigens and then are displayed on the cell surface. This could promote inflammatory responses by T-cells within the kidney. It is important to note that not all anti-dsDNA antibodies are associated with lupus nephritis and that other factors can cause this symptom in their absence. The antigen of anti-dsDNA antibodies is double stranded DNA.
Anti-histone antibodies
Anti-histone antibodies are found in the serum of up to 75–95% of people with drug induced lupus and 75% of idiopathic SLE. Unlike anti-dsDNA antibodies in SLE, these antibodies do not fix complement. Although they are most commonly found in drug induced lupus, they are also found in some cases of SLE, scleroderma,rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are inv ...
and undifferentiated connective tissue disease
Undifferentiated connective tissue disease (UCTD) is a disease in which the body mistakenly attacks its own tissues. It is diagnosed when there is evidence of an existing autoimmune condition which does not meet the criteria for any specific auto ...
. Many drugs are known to cause drug induced lupus and they produce various antigenic targets within the nucleosome that are often cross reactive with several histone proteins and DNA. Procainamide causes a form of drug-induced lupus that produces antibodies to the histone H2A and H2B complex.
Anti-gp210 and anti-p62
Both anti-glycoprotein-210 (anti-gp210) and anti-nucleoporin 62 (anti-p62) antibodies are antibodies to components of the nuclear membrane and are found inprimary biliary cirrhosis
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), previously known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is an autoimmune disease of the liver. It results from a slow, progressive destruction of the small bile ducts of the liver, causing bile and other toxins to build ...
(PBC). Each antibody is present in approximately 25–30% of PBC. The antigens of both antibodies are constituents of the nuclear membrane. gp210 is a 200kDa protein involved in anchoring components of the nuclear pore
A nuclear pore is a part of a large complex of proteins, known as a nuclear pore complex that spans the nuclear envelope, which is the double membrane surrounding the eukaryotic cell nucleus. There are approximately 1,000 nuclear pore comple ...
to the nuclear membrane. The p62 antigen is a 60kDa nuclear pore complex.
Anti-centromere antibodies
 Anti-centromere antibodies are associated with limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis, also known as CREST syndrome, primary biliary cirrhosis and proximal scleroderma. There are six known antigens, which are all associated with the
Anti-centromere antibodies are associated with limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis, also known as CREST syndrome, primary biliary cirrhosis and proximal scleroderma. There are six known antigens, which are all associated with the centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers ...
; CENP-A to CENP-F. CENP-A is a 17kDa histone H3
Histone H3 is one of the five main histones involved in the structure of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. Featuring a main globular domain and a long N-terminal tail, H3 is involved with the structure of the nucleosomes of the 'beads on a st ...
-like protein. CENP-B is an 80kDa DNA binding protein involved in the folding of heterochromatin
Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of DNA or '' condensed DNA'', which comes in multiple varieties. These varieties lie on a continue between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Both play a rol ...
. CENP-C is a 140kDa protein involved in kinetochore assembly. CENP-D is a 50kDa protein of unknown function, but may be homologous to another protein involved in chromatin condensation, RCC1. CENP-E is a 312kDa protein from the kinesin motor protein family. CENP-F is a 367kDa protein from the nuclear matrix that associates with the kinetochore in late G2 phase
G2 phase, Gap 2 phase, or Growth 2 phase, is the third subphase of interphase in the cell cycle directly preceding mitosis. It follows the successful completion of S phase, during which the cell’s DNA is replicated. G2 phase ends with th ...
during mitosis. CENP-A, B and C antibodies are most commonly found (16–42% of systemic sclerosis) and are associated with Raynaud's phenomenon, telangiectasia
Telangiectasias, also known as spider veins, are small dilated blood vessels that can occur near the surface of the skin or mucous membranes, measuring between 0.5 and 1 millimeter in diameter. These dilated blood vessels can develop anywhere on ...
s, lung involvement and early onset in systemic sclerosis.
Anti-sp100
Anti-sp100 antibodies
Anti-sp100 antibodies are found in association with primary biliary cirrhosis. The autoimmune target of anti-sp100 is the sp100 nuclear antigen which was identified by its association with primary biliary cirrhosis
Primary biliary cholangitis ( ...
are found in approximately 20–30% of primary biliary cirrhosis
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), previously known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is an autoimmune disease of the liver. It results from a slow, progressive destruction of the small bile ducts of the liver, causing bile and other toxins to build ...
(PBC). They are found in few individuals without PBC, and therefore are a very specific marker of the disease. The sp100 antigen is found within nuclear bodies; large protein complexes in the nucleus that may have a role in cell growth and differentiation.
Anti-PM-Scl
Anti-PM-Scl antibodies are found in up to 50% of polymyositis/systemic sclerosis (PM/SSc) overlap syndrome. Around 80% of individuals with antibodies present in their blood serum will have the disorder. The presence of the antibodies is linked to limited cutaneous involvement of PM/SSc overlap syndrome. The antigenic targets of the antibodies are components of the RNA-processingexosome complex
The exosome complex (or PM/Scl complex, often just called the exosome) is a multi- protein intracellular complex capable of degrading various types of RNA (ribonucleic acid) molecules. Exosome complexes are found in both eukaryotic cells and ...
in the nucleolus
The nucleolus (, plural: nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis, which is the synthesis of ribosomes. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of sign ...
. There are ten proteins in this complex and antibodies to eight of them are found at varying frequencies; PM/Scl-100 (70–80%), PM/Scl-75 (46–80%), hRrp4 (50%), hRrp42 (21%), hRrp46 (18%), hCs14 (14%), hRrp41 (10%) and hRrp40 (7%).
Anti-DFS70 antibodies
Anti-DFS70 antibodies generate a dense fine speckled pattern in indirect immunofluorescence and are found in normals and in various conditions, but are not associated with a systemic autoimmune pathology. Therefore, they can be used to help to rule out such conditions in ANA positive individuals. A significant number of patients are diagnosed as systemic lupus erythematosus or undifferentiated connective tissue disease largely based on a positive ANA. In case no defined autoantibody can be detected (e.g. anti-ENA antibodies), the testing of anti-DFS70 antibodies is recommended to verify the diagnosis. Anti-DFS70 antibody tests are available as CE-marked tests. Until now, no FDA cleared assay is available.ANA test

 The presence of ANAs in blood can be confirmed by a screening test. Although there are many tests for the detection of ANAs, the most common tests used for screening are indirect immunofluorescence and
The presence of ANAs in blood can be confirmed by a screening test. Although there are many tests for the detection of ANAs, the most common tests used for screening are indirect immunofluorescence and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence ...
(ELISA). Following detection of ANAs, various subtypes are determined.
Indirect immunofluorescence
Indirect immunofluorescence is one of the most commonly used tests for ANAs. Typically, HEp-2 cells are used as a substrate to detect the antibodies in human serum. Microscope slides are coated with HEp-2 cells and the serum is incubated with the cells. If the said and targeted antibodies are present then they will bind to theantigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respon ...
s on the cells; in the case of ANAs, the antibodies will bind to the nucleus. These can be visualised by adding a fluorescent tagged (usually FITC or rhodopsin B) anti-human antibody that binds to the antibodies. The molecule will fluoresce when a specific wavelength of light shines on it, which can be seen under the microscope. Depending on the antibody present in the human serum and the localisation of the antigen in the cell, distinct patterns of fluorescence will be seen on the HEp-2 cells. Levels of antibodies are analysed by performing dilutions on blood serum. An ANA test is considered positive if fluorescence is seen at a titre of 1:40/1:80. Higher titres are more clinically significant as low positives (≤1:160) are found in up to 20% of healthy individuals, especially the elderly. Only around 5% of the healthy population have ANA titres of 1:160 or higher.
HEp-2
 Until around 1975, when HEp-2 cells were introduced, animal tissue was used as the standard substrate for immunofluorescence. HEp-2 cells are currently one of the most common substrates for ANA detection by immunofluorescence.
Originally started a laryngeal carcinoma strain, the cell line was contaminated and displaced by HeLa cells, and has now been identified as actually HeLa cells.
They are superior to the previously used animal tissues because of their large size and the high rate of
Until around 1975, when HEp-2 cells were introduced, animal tissue was used as the standard substrate for immunofluorescence. HEp-2 cells are currently one of the most common substrates for ANA detection by immunofluorescence.
Originally started a laryngeal carcinoma strain, the cell line was contaminated and displaced by HeLa cells, and has now been identified as actually HeLa cells.
They are superior to the previously used animal tissues because of their large size and the high rate of mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintai ...
(cell division) in the cell line. This allows the detection of antibodies to mitosis-specific antigens, such as centromere antibodies. They also allow identification of anti-Ro antibodies, because acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone), is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour.
Acetone is miscibl ...
is used for fixation of the cells (other fixatives can wash the antigen away).
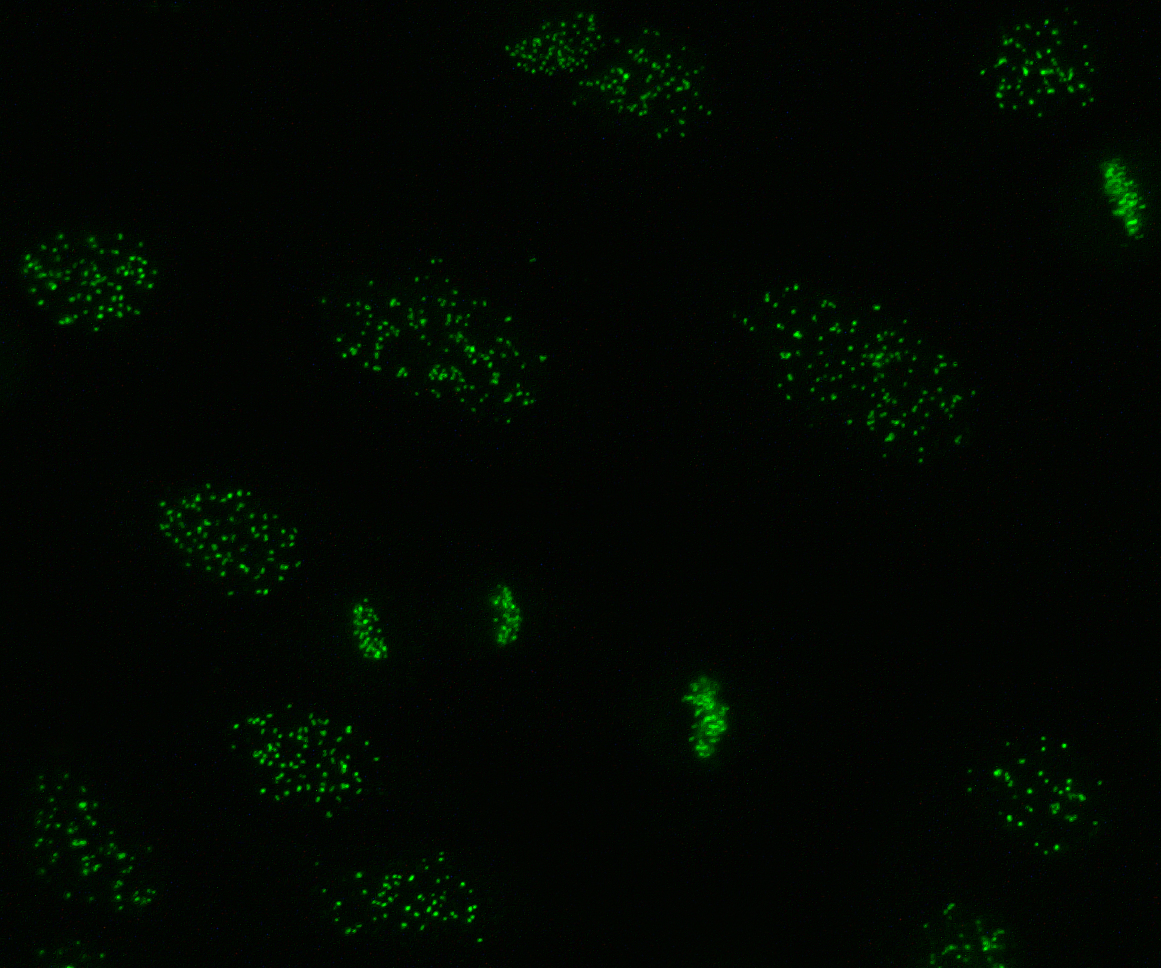
There are many nuclear staining patterns seen on HEp-2 cells: homogeneous, speckled, nucleolar, nuclear membranous, centromeric, nuclear dot and pleomorphic. The homogeneous pattern is seen when the condensed chromosomes
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
and interphase chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important ...
stain. This pattern is associated with anti-dsDNA antibodies, antibodies to nucleosomal components, and anti-histone antibodies. There are two speckled patterns: fine and coarse. The fine speckled pattern has fine nuclear staining with unstained metaphase
Metaphase ( and ) is a stage of mitosis in the eukaryotic cell cycle in which chromosomes are at their second-most condensed and coiled stage (they are at their most condensed in anaphase). These chromosomes, carrying genetic information, a ...
chromatin, which is associated with anti-Ro and anti-La antibodies. The coarse staining pattern has coarse granular nuclear staining, caused by anti-U1-RNP and anti-Sm antibodies. The nucleolar staining pattern is associated with many antibodies including anti-Scl-70, anti-PM-Scl, anti-fibrillarin and anti-Th/To. Nuclear membrane staining appears as a fluorescent ring around the cell nucleus and are produced by anti-gp210 and anti-p62 antibodies. The centromere pattern shows multiple nuclear dots in interphase and mitotic cells, corresponding to the number of chromosomes in the cell. Nuclear dot patterns show between 13 and 25 nuclear dots in interphase cells and are produced by anti- sp100 antibodies. Pleomorphic pattern is caused by antibodies to the proliferating cell nuclear antigen
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is a DNA clamp that acts as a processivity factor for DNA polymerase δ in eukaryotic cells and is essential for replication. PCNA is a homotrimer and achieves its processivity by encircling the DNA, wher ...
. Indirect immunofluorescence has been shown to be slightly superior compared to ELISA in detection of ANA from HEp-2 cells.
''Crithidia luciliae''
 '' Crithidia luciliae'' are haemoflaggelate
'' Crithidia luciliae'' are haemoflaggelate single celled
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and ...
protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the e ...
s. They are used as a substrate in immunofluorescence for the detection of anti-dsDNA antibodies. They possess an organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' th ...
known as the kinetoplast
A kinetoplast is a network of circular DNA (called kDNA) inside a large mitochondrion that contains many copies of the mitochondrial genome. The most common kinetoplast structure is a disk, but they have been observed in other arrangements. Kineto ...
which is a large mitochondrion
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is use ...
with a network of interlocking circular dsDNA molecules. After incubation with serum containing anti-dsDNA antibodies and fluorescent-labelled anti-human antibodies, the kinetoplast will fluoresce. The lack of other nuclear antigens in this organelle means that using ''C. luciliae'' as a substrate allows for the specific detection of anti-dsDNA antibodies.
ELISA
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence ...
(ELISA) uses antigen-coated microtitre plate
A microplate, also known as a microtiter plate (''Microtiter'' is a registered trademark in the United States, therefore it should not be used generically without attribution), microwell plate or multiwell, is a flat plate with multiple "wells" ...
s for the detection of ANAs. Each well of a microtitre plate is coated with either a single antigen or multiple antigens to detect specific antibodies or to screen for ANAs, respectively. The antigens are either from cell extracts or recombinant. Blood serum is incubated in the wells of the plate and is washed out. If antibodies that bind to antigen are present then they will remain after washing. A secondary anti-human antibody conjugated to an enzyme such as horseradish peroxidase
The enzyme horseradish peroxidase (HRP), found in the roots of horseradish, is used extensively in biochemistry applications. It is a metalloenzyme with many isoforms, of which the most studied type is C. It catalyzes the oxidation of various o ...
is added. The enzyme reaction will produce a change in colour of the solution that is proportional to the amount of antibody bound to the antigen. There are significant differences in the detection of ANA by immunofluorescence and different ELISA kits and there is only a marginal agreement between these. A clinician must be familiar with the differences in order to evaluate the outcomes of the various assays.
Sensitivity
The following table lists the sensitivity of different types of ANAs for different diseases. Some ANAs appear in several types of disease, resulting in lower specificity of the test. For example, IgM-rheumatoid factor
Rheumatoid factor (RF) is the autoantibody that was first found in rheumatoid arthritis. It is defined as an antibody against the Fc portion of IgG and different RFs can recognize different parts of the IgG-Fc. RF and IgG join to form immune com ...
(IgM-RF) have been shown to cross-react with ANA giving falsely positive immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on microbiological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to spe ...
. Positive ANA as well as anti-DNA antibodies have been reported in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease. ANA can have a positive test result in up to 45% of people with autoimmune thyroid conditions or rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are inv ...
and up to 15% of people with HIV or hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, ...
. As per Lupus Foundation of America, "about 5% of the general population will have a positive ANA. However, at least 95% of the people who have a positive ANA do not have lupus. A positive ANA test can sometimes run in families, even if family members have no evidence of lupus." On the other hand, they say, although 95% of the patients who actually have lupus test positive for ANA, "Only a small percentage have a negative ANA, and many of those have other antibodies (such as anti-phospholipid antibodies, anti-Ro, anti-SSA) or their ANA converted from positive to negative from steroids
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
, cytotoxic medications, or uremia
Uremia is the term for high levels of urea in the blood. Urea is one of the primary components of urine. It can be defined as an excess of amino acid and protein metabolism end products, such as urea and creatinine, in the blood that would be no ...
(kidney failure)."
History
 The LE cell was discovered in bone marrow in 1948 by Hargraves ''et al.''Hargraves M, Richmond H, Morton R. ''Presentation of two bone marrow components, the tart cell and the LE cell.'' Mayo Clin Proc 1948;27:25–28. In 1957 Holborow et al. first demonstrated ANA using indirect immunofluorescence. This was the first indication that processes affecting the cell nucleus were responsible for SLE. In 1959 it was discovered that serum from individuals with SLE contained antibodies that precipitated with saline extracts of nuclei, known as extractable nuclear antigens (ENAs). This led to the characterisation of ENA antigens and their respective antibodies. Thus, anti-Sm and anti-RNP antibodies were discovered in 1966 and 1971, respectively. In the 1970s, the anti-Ro/anti-SS-A and anti-La/anti-SS-B antibodies were discovered. The Scl-70 antibody was known to be a specific antibody to scleroderma in 1979, however the antigen (topoisomerase-I) was not characterised until 1986. The Jo-1 antigen and antibody were characterised in 1980.
The LE cell was discovered in bone marrow in 1948 by Hargraves ''et al.''Hargraves M, Richmond H, Morton R. ''Presentation of two bone marrow components, the tart cell and the LE cell.'' Mayo Clin Proc 1948;27:25–28. In 1957 Holborow et al. first demonstrated ANA using indirect immunofluorescence. This was the first indication that processes affecting the cell nucleus were responsible for SLE. In 1959 it was discovered that serum from individuals with SLE contained antibodies that precipitated with saline extracts of nuclei, known as extractable nuclear antigens (ENAs). This led to the characterisation of ENA antigens and their respective antibodies. Thus, anti-Sm and anti-RNP antibodies were discovered in 1966 and 1971, respectively. In the 1970s, the anti-Ro/anti-SS-A and anti-La/anti-SS-B antibodies were discovered. The Scl-70 antibody was known to be a specific antibody to scleroderma in 1979, however the antigen (topoisomerase-I) was not characterised until 1986. The Jo-1 antigen and antibody were characterised in 1980.
See also
*Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody
Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs) are a group of autoantibodies, mainly of the IgG type, against antigens in the cytoplasm of neutrophils (the most common type of white blood cell) and monocytes. They are detected as a blood ...
(ANCA)
* Rheumatoid factor
Rheumatoid factor (RF) is the autoantibody that was first found in rheumatoid arthritis. It is defined as an antibody against the Fc portion of IgG and different RFs can recognize different parts of the IgG-Fc. RF and IgG join to form immune com ...
References
External links
Autoimmunityblog – HEp-2 ANA summary
* * {{Autoantibodies Chemical pathology Autoantibodies Antibodies Immunologic tests