Antenna (biology) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Antennae ( antenna), sometimes referred to as "feelers", are paired
Antennae ( antenna), sometimes referred to as "feelers", are paired


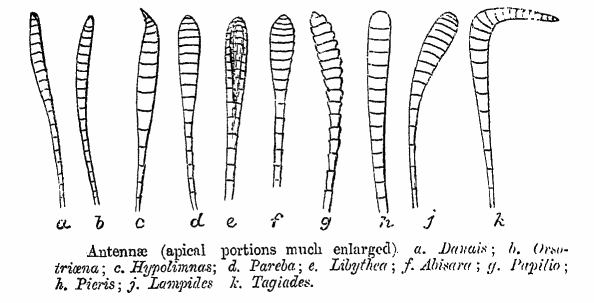 Insects evolved from prehistoric crustaceans, and they have secondary antennae like crustaceans, but not primary antennae. Antennae are the primary
Insects evolved from prehistoric crustaceans, and they have secondary antennae like crustaceans, but not primary antennae. Antennae are the primary
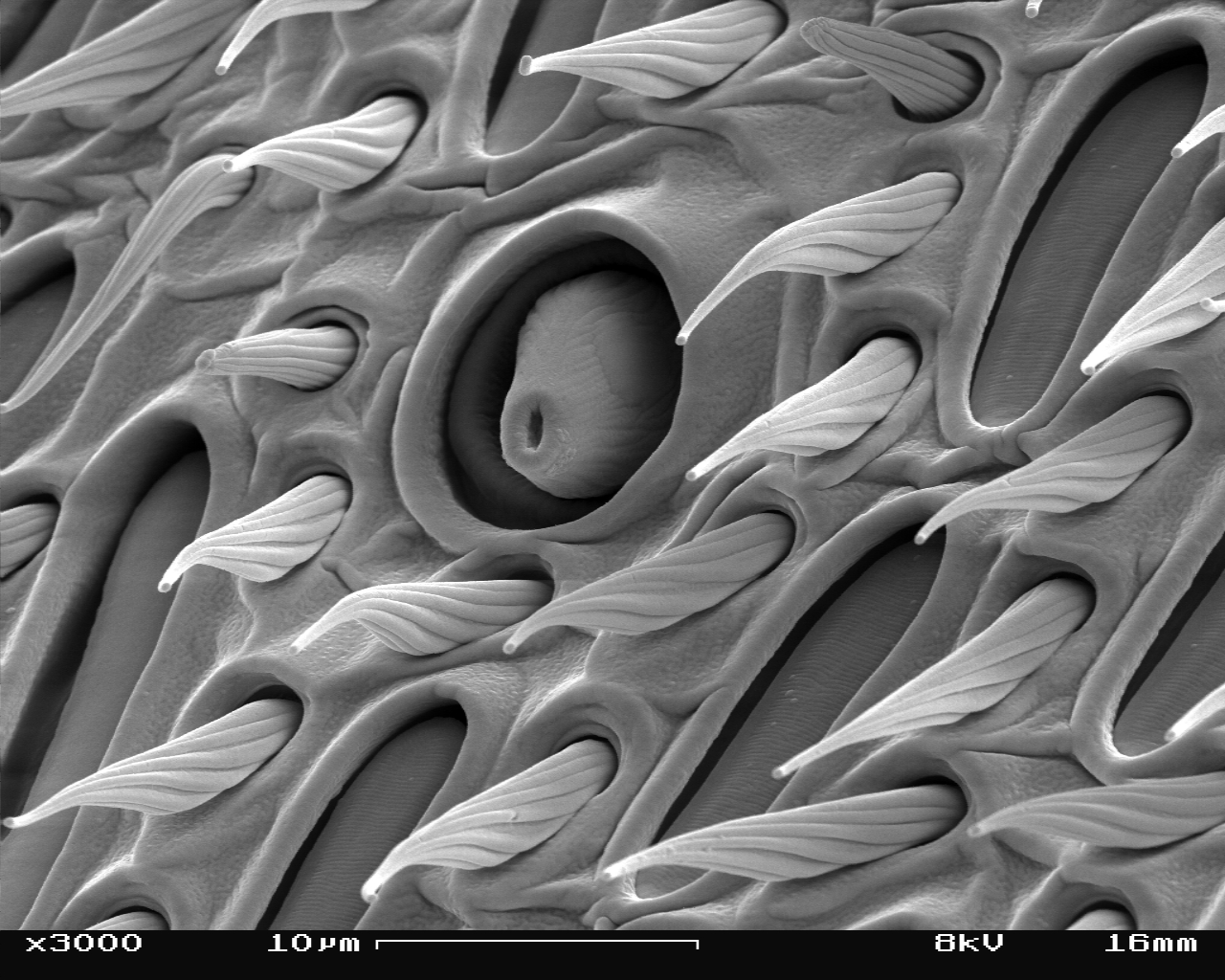 The three basic segments of the typical insect antenna are the scape or ''scapus'' (base), the pedicel or ''pedicellus'' (stem), and finally the flagellum, which often comprises many units known as flagellomeres. The pedicel (the second segment) contains the
The three basic segments of the typical insect antenna are the scape or ''scapus'' (base), the pedicel or ''pedicellus'' (stem), and finally the flagellum, which often comprises many units known as flagellomeres. The pedicel (the second segment) contains the

appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part, or natural prolongation, that protrudes from an organism's body.
In arthropods, an appendage refers to any of the homologous body parts that may extend from a body segment, including ante ...
s used for sensing in arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s.
Antennae are connected to the first one or two segments of the arthropod head. They vary widely in form but are always made of one or more jointed segments. While they are typically sensory organ
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system re ...
s, the exact nature of what they sense and how they sense it is not the same in all groups. Functions may variously include sensing touch
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch ( haptic perception), as well as temperature ( thermoception), body position (proprioception), and pain. It ...
, air motion, heat, vibration (sound), and especially smell or taste
The gustatory system or sense of taste is the sensory system that is partially responsible for the perception of taste (flavor). Taste is the perception produced or stimulated when a substance in the mouth reacts chemically with taste receptor ...
. Antennae are sometimes modified for other purposes, such as mating, brooding, swimming, and even anchoring the arthropod to a substrate. Larval arthropods have antennae that differ from those of the adult. Many crustaceans, for example, have free-swimming larvae
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
T ...
that use their antennae for swimming. Antennae can also locate other group members if the insect lives in a group, like the ant
Ants are eusocial insects of the family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cretaceous period. More than 13,800 of an estimated total of ...
.
The common ancestor of all arthropods likely had one pair of uniramous (unbranched) antenna-like structures, followed by one or more pairs of biramous The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, plu ...
(having two major branches) leg-like structures, as seen in some modern crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapoda, decapods, ostracoda, seed shrimp, branchiopoda, branchiopods, argulidae, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopoda, isopods, barnacles, copepods, ...
s and fossil trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the ...
s. Except for the chelicerates and proturans, which have none, all non-crustacean arthropods have a single pair of antennae.
Crustaceans
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapoda, decapods, ostracoda, seed shrimp, branchiopoda, branchiopods, argulidae, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopoda, isopods, barnacles, copepods, ...
s bear two pairs of antennae. The pair attached to the first segment of the head are called primary antennae or antennules. This pair is generally uniramous, but is biramous in crabs and lobsters and remipedes
Remipedia is a class of blind crustaceans found in coastal aquifers which contain saline groundwater, with populations identified in almost every ocean basin so far explored, including in Australia, the Caribbean Sea, and the Atlantic Ocean. The ...
. The pair attached to the second segment are called secondary antennae or simply antennae. The second antennae are plesiomorphic
In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy ("near form") and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all members of a clade, which does not distinguish the clade from other clades.
Plesiomorphy, symplesiomorphy, apomorphy, and ...
ally biramous, but many species later evolved uniramous pairs. The second antennae may be significantly reduced (e.g. remipedes) or apparently absent (e.g. barnacles
A barnacle is a type of arthropod constituting the subclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacea, and is hence related to crabs and lobsters. Barnacles are exclusively marine, and tend to live in shallow and tidal waters, typically in erosiv ...
).
The subdivisions of crustacean antennae have many names, including flagellomeres (a shared term with insects), annuli, articles, and segments. The terminal ends of crustacean antennae have two major categorizations: segmented and flagellate. An antenna is considered segmented if each of the annuli is separate from those around it and has individual muscle attachments. Flagellate antennae, on the other hand, have muscle attachments only around the base, acting as a hinge for the flagellum—a flexible string of annuli with no muscle attachment.
There are several notable non-sensory uses of antennae in crustaceans. Many crustaceans have a mobile larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
l stage called a nauplius, which is characterized by its use of antennae for swimming. Barnacles
A barnacle is a type of arthropod constituting the subclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacea, and is hence related to crabs and lobsters. Barnacles are exclusively marine, and tend to live in shallow and tidal waters, typically in erosiv ...
, a highly modified crustacean, use their antennae to attach to rocks and other surfaces.
Insects
 Insects evolved from prehistoric crustaceans, and they have secondary antennae like crustaceans, but not primary antennae. Antennae are the primary
Insects evolved from prehistoric crustaceans, and they have secondary antennae like crustaceans, but not primary antennae. Antennae are the primary olfactory
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, ...
sensors of insects and are accordingly well-equipped with a wide variety of sensilla
A sensillum (plural ''sensilla'') is an arthropod sensory organ protruding from the cuticle of exoskeleton, or sometimes lying within or beneath it. Sensilla appear as small hairs or pegs over an individual's body. Inside each sensillum there are ...
(singular: ''sensillum''). Paired, mobile, and segmented, they are located between the eyes on the forehead. Embryologically, they represent the appendages of the second head segment.
All insects have antennae, however they may be greatly reduced in the larval forms. Amongst the non-insect classes of the Hexapoda
The subphylum Hexapoda (from Greek for 'six legs') comprises most species of arthropods and includes the insects as well as three much smaller groups of wingless arthropods: Collembola, Protura, and Diplura (all of these were once considere ...
, both Collembola
Springtails (Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered insects (the other two are the Protura and Diplura). Although the three orders are sometimes grouped together in a class called ...
and Diplura have antenna, but Protura do not.
Antennal fibrillae play an important role in ''Culex pipiens
''Culex pipiens'', commonly referred to as the common house mosquito, is a species of mosquito. House mosquitoes are some of the most common mosquitoes in the United States. More specifically, ''Culex pipiens'' is considered as the northern hous ...
'' mating practices. The erection of these fibrillae is considered to be the first stage in reproduction. These fibrillae serve different functions across the sexes. As antennal fibrillae are used by female ''C. pipiens'' to locate hosts to feed on, male ''C. pipiens'' utilize them to locate female mates.
Structure
 The three basic segments of the typical insect antenna are the scape or ''scapus'' (base), the pedicel or ''pedicellus'' (stem), and finally the flagellum, which often comprises many units known as flagellomeres. The pedicel (the second segment) contains the
The three basic segments of the typical insect antenna are the scape or ''scapus'' (base), the pedicel or ''pedicellus'' (stem), and finally the flagellum, which often comprises many units known as flagellomeres. The pedicel (the second segment) contains the Johnston's organ Johnston's organ is a collection of sensory cells found in the pedicel (the second segment) of the antennae in the class Insecta. Johnston's organ detects motion in the flagellum (third and typically final antennal segment). It consists of scol ...
which is a collection of sensory cells.
The scape is mounted in a socket in a more or less ring-shaped sclerotised
Sclerotin is a component of the cuticle of various Arthropoda, most familiarly insects. It is formed by cross-linking members of particular classes of protein molecules, a biochemical process called sclerotization, a form of tanning in which qu ...
region called the torulus, often a raised portion of the insect's head capsule. The socket is closed off by the membrane into which the base of the scape is set. However, the antenna does not hang free on the membrane, but pivots on a rigidly sprung projection from the rim of the torulus. That projection on which the antenna pivots is called the antennifer. The whole structure enables the insect to move the antenna as a whole by applying internal muscles connected to the scape. The pedicel is flexibly connected to the distal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
end of the scape and its movements in turn can be controlled by muscular connections between the scape and pedicel. The number of flagellomeres can vary greatly between insect species, and often is of diagnostic importance.
True flagellomeres are connected by membranous linkage that permits movement, though the flagellum of "true" insects does not have any intrinsic
In science and engineering, an intrinsic property is a property of a specified subject that exists itself or within the subject. An extrinsic property is not essential or inherent to the subject that is being characterized. For example, mass ...
muscles. Some other Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
a do however have intrinsic muscles throughout the flagellum. Such groups include the Symphyla
Symphylans, also known as garden centipedes or pseudocentipedes, are soil-dwelling arthropods of the class Symphyla in the subphylum Myriapoda. Symphylans resemble centipedes, but are very small, non-venomous, and only distantly related to both ...
, Collembola
Springtails (Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered insects (the other two are the Protura and Diplura). Although the three orders are sometimes grouped together in a class called ...
and Diplura. In many true insects, especially the more primitive groups such as Thysanura
Thysanura is the now deprecated name of what was, for over a century, recognised as an order in the class Insecta. The two constituent groups within the former order, the Archaeognatha (jumping bristletails) and the Zygentoma (silverfish and fireb ...
and Blattodea
Blattodea is an order of insects that contains cockroaches and termites. Formerly, termites were considered a separate order, Isoptera, but genetic and molecular evidence suggests they evolved from within the cockroach lineage, cladistically mak ...
, the flagellum partly or entirely consists of a flexibly connected string of small ring-shaped annuli. The annuli are not true flagellomeres, and in a given insect species the number of annuli generally is not as consistent as the number of flagellomeres in most species.
In many beetle
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 describ ...
s and in the chalcidoid wasps, the apical flagellomeres form a club shape, and the collective term for the segments between the club and the antennal base is the funicle; traditionally in describing beetle anatomy, the term "funicle" refers to the segments between the club and the scape. However, traditionally in working on wasps the funicle is taken to comprise the segments between the club and the pedicel.
Quite commonly the funicle beyond the pedicel is quite complex in Endopterygota
Endopterygota (from Ancient Greek ''endon'' 'inner' + ''pterón'' 'wing' + New Latin ''-ota'' 'having'), also known as Holometabola, is a superorder of insects within the infraclass Neoptera that go through distinctive larval, pupal, and a ...
such as beetles, moths and Hymenoptera
Hymenoptera is a large order of insects, comprising the sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants. Over 150,000 living species of Hymenoptera have been described, in addition to over 2,000 extinct ones. Many of the species are parasitic.
Females typic ...
, and one common adaptation is the ability to fold the antenna in the middle, at the joint between the pedicel and the flagellum. This gives an effect like a "knee bend", and such an antenna is said to be geniculate. Geniculate antennae are common in the Coleoptera
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 describe ...
and Hymenoptera. They are important for insects like ants that follow scent trails, for bees and wasps that need to "sniff" the flowers that they visit, and for beetles such as Scarabaeidae
The family Scarabaeidae, as currently defined, consists of over 30,000 species of beetles worldwide; they are often called scarabs or scarab beetles. The classification of this family has undergone significant change in recent years. Several sub ...
and Curculionidae
The Curculionidae are a family of weevils, commonly called snout beetles or true weevils. They are one of the largest animal families, with 6,800 genera and 83,000 species described worldwide. They are the sister group to the family Brentidae.
...
that need to fold their antennae away when they self-protectively fold up all their limbs in defensive attitudes.
Because the funicle is without intrinsic muscles, it generally must move as a unit, in spite of being articulated. However, some funicles are complex and very mobile. For example, the Scarabaeidae have lamellate antennae that can be folded tightly for safety or spread openly for detecting odours or pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavio ...
s. The insect manages such actions by changes in blood pressure, by which it exploits elasticity in walls and membranes in the funicles, which are in effect erectile.Pass, Guenther. The Anatomy and Ultrastructure of the Antennal Circulatory Organs in the Cockchafer Beetle Melolontha melolontha L. (Coleoptera, Scarabaeidae) Zoomorphology 01/1980; 96(1):77-89.
In the groups with more uniform antennae (for example: millipede
Millipedes are a group of arthropods that are characterised by having two pairs of jointed legs on most body segments; they are known scientifically as the class Diplopoda, the name derived from this feature. Each double-legged segment is a resu ...
s), all segments are called ''antennomeres''. Some groups have a simple or variously modified apical or subapical bristle called an arista (this may be especially well-developed in various Diptera
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced ...
).
Functions

Olfactory receptor
Olfactory receptors (ORs), also known as odorant receptors, are chemoreceptors expressed in the cell membranes of olfactory receptor neurons and are responsible for the detection of odorants (for example, compounds that have an odor) which give r ...
s on the antennae bind to free-floating molecules, such as water vapour
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous pha ...
, and odour
An odor (American English) or odour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds that are generally found in low concentrations that humans and animals can perceive via their sens ...
s including pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavio ...
s. The neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa ...
s that possess these receptors signal this binding by sending action potential
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells ...
s down their axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action p ...
s to the antennal lobe The antennal lobe is the primary (first order) olfactory brain area in insects. The antennal lobe is a sphere-shaped deutocerebral neuropil in the brain that receives input from the olfactory sensory neurons in the antennae and mouthparts. Functi ...
in the brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
. From there, neurons in the antennal lobes connect to mushroom bodies that identify the odour. The sum of the electrical potentials of the antennae to a given odour can be measured using an electroantennogram.
In the monarch butterfly
The monarch butterfly or simply monarch (''Danaus plexippus'') is a milkweed butterfly (subfamily Danainae) in the family Nymphalidae. Other common names, depending on region, include milkweed, common tiger, wanderer, and black-veined brown. ...
, antennae are necessary for proper time-compensated solar compass
Burt's solar compass or astronomical compass is a surveying instrument that makes use of the Sun's direction instead of magnetism. William Austin Burt invented his solar compass in 1835. The solar compass works on the principle that the directi ...
orientation during migration. Antennal clocks exist in monarchs, and they are likely to provide the primary timing mechanism for sun compass orientation.
In the African cotton leafworm, antennae have an important function in signaling courtship. Specifically, antennae are required for males to answer the female mating call. Although females do not require antennae for mating, a mating that resulted from a female without antennae was abnormal.
In the diamondback moth, antennae serve to gather information about a host plant's taste and odor. After the desired taste and odor has been identified, the female moth will deposit her eggs onto the plant. Giant swallowtail butterflies also rely on antenna sensitivity to volatile compounds to identify host plants. It was found that females are actually more responsive with their antenna sensing, most likely because they are responsible for oviposition on the correct plant.
In the crepuscular hawk moth ('' Manduca sexta''), antennae aid in flight stabilization. Similar to halteres
''Halteres'' (; singular ''halter'' or ''haltere'') (from grc, ἁλτῆρες, weights held in the hands to give an impetus in leaping) are a pair of small club-shaped organs on the body of two orders of flying insects that provide infor ...
in Dipteran insects, the antennae transmit coriolis force
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
s through the Johnston's organ that can then be used for corrective behavior. A series of low-light, flight stability studies in which moths with flagellae amputated near the pedicel showed significantly decreased flight stability over those with intact antennae. To determine whether there may be other antennal sensory inputs, a second group of moths had their antennae amputated and then re-attached, before being tested in the same stability study. These moths showed slightly decreased performance from intact moths, indicating there are possibly other sensory inputs used in flight stabilization. Re-amputation of the antennae caused a drastic decrease in flight stability to match that of the first amputated group.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Antenna (Biology) Arthropod anatomy