Alter Hof on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Alter Hof (''Old Court'') in the center of Munich is the former imperial residence of
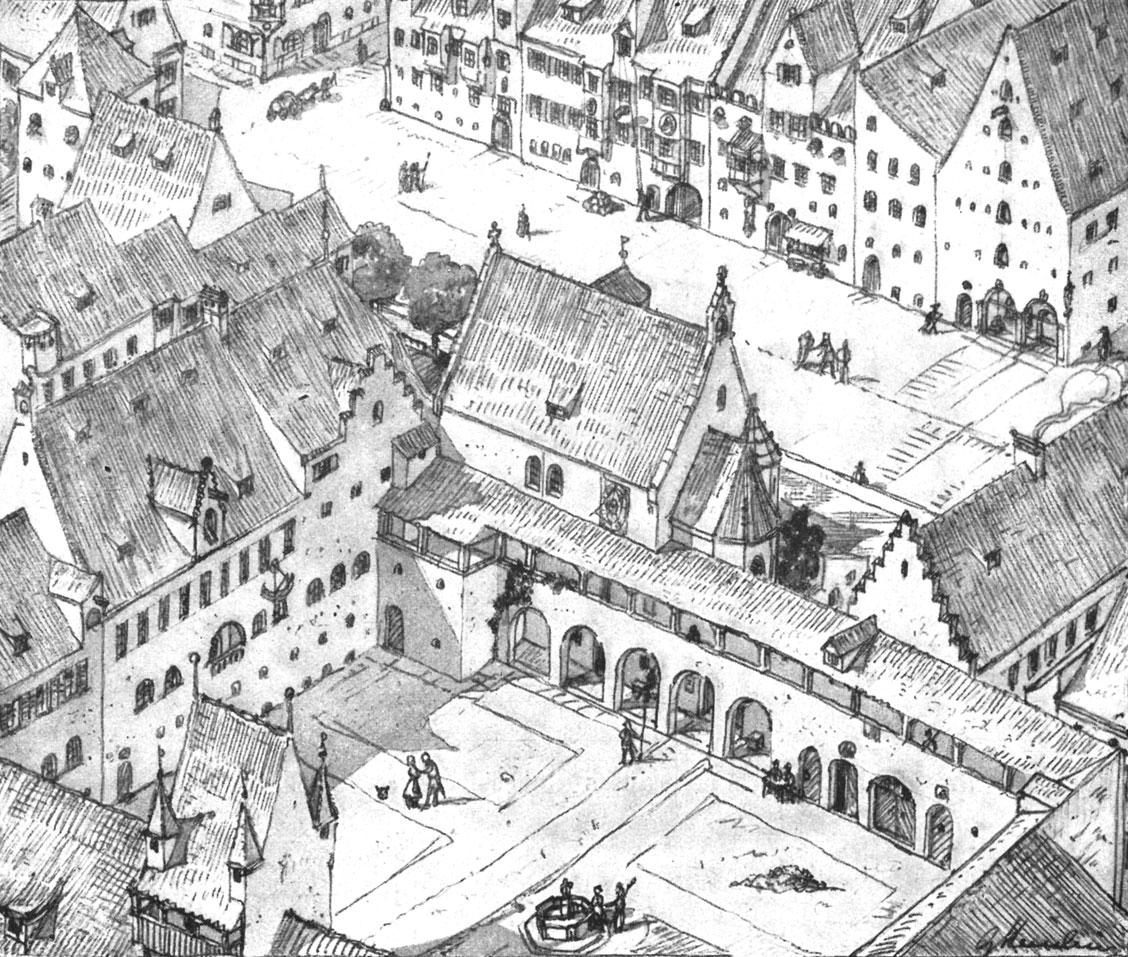 The late
The late
Infopoint Museen & Schlösser in Bayern
a central information point for the 1300 museums and palaces throughout Bavaria. The exhibition Münchner Kaiserburg (''The Imperial Castle in Munich'') can be found in the basement floor of the Infopoint. It is located in the old vaulted cellar dating back to around 1300. A short film (german/english) illustrates the history of the Old Court, the city of Munich and the life and rule of its well-known resident
Alter Hof, MunichAlter Hof, Munich
{{coord, 48, 08, 17, N, 11, 34, 41, E, region:DE-BY_type:landmark, display=title Buildings and structures in Munich Gothic architecture in Munich Palaces in Bavaria Castles in Bavaria Royal residences in Bavaria Tourist attractions in Munich Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Louis IV (german: Ludwig; 1 April 1282 – 11 October 1347), called the Bavarian, of the house of Wittelsbach, was King of the Romans from 1314, King of Italy from 1327, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1328.
Louis' election as king of Germany in ...
and consists of five wings: Burgstock, Zwingerstock, Lorenzistock, Pfisterstock and Brunnenstock. Like most of the old town, it was rebuilt after being destroyed in World War II. Hitler had once made a painting of it.
History
Archeological excavations have shown that a castle already existed there in the 12th century. After the first partition ofBavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
in 1255, the ''Alte Hof'' became the residence of Louis II, Duke of Bavaria in the then very northeastern part of the city. The castle was the first permanent imperial residence in the Holy Roman Empire under his son Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Louis IV (german: Ludwig; 1 April 1282 – 11 October 1347), called the Bavarian, of the house of Wittelsbach, was King of the Romans from 1314, King of Italy from 1327, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1328.
Louis' election as king of Germany in ...
. The St. Lorenz Chapel at the north side, which was demolished later in the 19th century, once housed the regalia of the House of Wittelsbach.
After some uprisings the castle became too unsafe, and in the course of an extension of the town, together with the construction of a new double-ring of town walls, the Wittelsbach dukes once again chose the very northeastern corner as the construction site for a replacement ducal residence. Consequently, as it was newly erected, the castle was called "Neuveste", new fortress. Over the course of centuries, the Neuveste would eventually develop into what is nowadays the Munich Residenz. When Duke Sigismund Sigismund (variants: Sigmund, Siegmund) is a German proper name, meaning "protection through victory", from Old High German ''sigu'' "victory" + ''munt'' "hand, protection". Tacitus latinises it '' Segimundus''. There appears to be an older form of ...
lived in the Alter Hof at the end of the fifteenth century and made further structural alterations to it, including painting in the courtyard with lozenge-shaped decoration, the actual residence was already the Neuveste. In the first half of the 16th century, Duke William IV
William IV (William Henry; 21 August 1765 – 20 June 1837) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from 26 June 1830 until his death in 1837. The third son of George III, William succeeded ...
finally transferred the residence permanently to the Neuveste. Thus from the 16th century onwards, the Alter Hof was only seat of several governmental departments including the stewardship.
In 1591–92, the Pfisterstock was built with decorative gables typical of the Renaissance; it was attributed to Wilhelm Egkl. In the first half of the 17th century, a building for the brewhouse and the brewhouse office, which had been known as the Brunnenstock since the end of the 18th century, was built. This was then replaced by Georg Friedrich Ziebland in 1831/32 by a new building on the old foundations for the Steering Commission. At the beginning of the 19th century, St.Lorenz chapel was broken off. The tower was also removed but later rebuilt. Instead of the church, the neoclassical Lorenzistock was built along the Hofgraben street in 1816–1819.
Restoration and tourism
 The late
The late Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
westwings (the Burgstock with its tower and its decorated oriel window and the Zwingerstock), which were altered under Duke Sigismund have been preserved. After destructions in World War II the castle was reconstructed. Portions of it (Lorenzistock, Pfisterstock and Brunnenstock) were redeveloped in post modernist style to serve as offices and luxury apartments in 2005/2006, very much to public dismay.
The Old Court also houses thInfopoint Museen & Schlösser in Bayern
a central information point for the 1300 museums and palaces throughout Bavaria. The exhibition Münchner Kaiserburg (''The Imperial Castle in Munich'') can be found in the basement floor of the Infopoint. It is located in the old vaulted cellar dating back to around 1300. A short film (german/english) illustrates the history of the Old Court, the city of Munich and the life and rule of its well-known resident
Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Louis IV (german: Ludwig; 1 April 1282 – 11 October 1347), called the Bavarian, of the house of Wittelsbach, was King of the Romans from 1314, King of Italy from 1327, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1328.
Louis' election as king of Germany in ...
. The exhibition also tells the legend of the oriel window
An oriel window is a form of bay window which protrudes from the main wall of a building but does not reach to the ground. Supported by corbels, brackets, or similar cantilevers, an oriel window is most commonly found projecting from an upper fl ...
on the westwing, which by locals is called "Affentürmchen" (''Monkey Tower'').
Into the Bavarian National Museum
The Bavarian National Museum (german: Bayerisches Nationalmuseum, links=no) in Munich is one of the most important museums of decorative arts in Europe and one of the list of largest art museums in the world , largest art museums in Germany. S ...
were moved the donation plate from 1324, a relief depicting the Emperor Louis and his second wife Margaret of Holland
Margaret II of Avesnes (1311 – 23 June 1356) was Countess of Hainaut and Countess of Holland (as Margaret I) from 1345 to 1356. She was Holy Roman Empress and Queen of Germany by marriage to Holy Roman Emperor Louis IV the Bavarian.
L ...
, with the enthroned Mother of God with the child in the center, which was formerly on the north side of the nave, as well as a fresco for an ancestral hall, dating back to 1460, depicting the ancestors of the Wittelsbach dukes with their coat of arms.
The mint yard (
Alte Münze The Alte Münze (Old Mint Yard) is a renaissance building in Munich which originally served for the ducal stables and the art collections of Albert V, Duke of Bavaria
Albert V (German: ''Albrecht V.'') (29 February 1528 – 24 October 1579) was ...
)
An arch in the north connects the Alter Hof with a Renaissance style building which originally served for the ducal stables and the art collections of Albert V, Duke of Bavaria
Albert V (German: ''Albrecht V.'') (29 February 1528 – 24 October 1579) was Duke of Bavaria from 1550 until his death. He was born in Munich to William IV and Maria Jacobäa of Baden.
Early life
Albert was educated at Ingolstadt by Catholic ...
. It was constructed by court architect Wilhelm Egkl in 1563. Later it served as mint. The inner courtyard has kept its renaissance arcades while the west facade was redesigned in neoclassical style in 1809. Finally the north facade facing got its neogothic decoration when the Maximilianstrasse was built to fit it with the concept of this royal avenue.
External links
Alter Hof, Munich
{{coord, 48, 08, 17, N, 11, 34, 41, E, region:DE-BY_type:landmark, display=title Buildings and structures in Munich Gothic architecture in Munich Palaces in Bavaria Castles in Bavaria Royal residences in Bavaria Tourist attractions in Munich Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor