Absolute Zero on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Absolute zero is the lowest limit of the
Absolute zero is the lowest limit of the
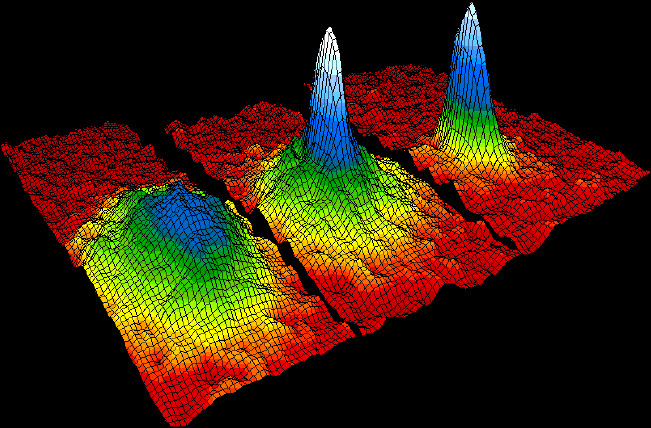 A
A
 One of the first to discuss the possibility of an absolute minimal temperature was
One of the first to discuss the possibility of an absolute minimal temperature was
thermodynamic temperature
Thermodynamic temperature is a quantity defined in thermodynamics as distinct from kinetic theory or statistical mechanics.
Historically, thermodynamic temperature was defined by Kelvin in terms of a macroscopic relation between thermodynamic ...
scale, a state at which the enthalpy
Enthalpy , a property of a thermodynamic system, is the sum of the system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant ...
and entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynam ...
of a cooled ideal gas
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles that are not subject to interparticle interactions. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is a ...
reach their minimum value, taken as zero kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and phy ...
. The fundamental particles of nature have minimum vibrational motion, retaining only quantum mechanical, zero-point energy
Zero-point energy (ZPE) is the lowest possible energy that a quantum mechanical system may have. Unlike in classical mechanics, quantum systems constantly fluctuate in their lowest energy state as described by the Heisenberg uncertainty pri ...
-induced particle motion. The theoretical temperature is determined by extrapolating the ideal gas law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stat ...
; by international agreement, absolute zero is taken as −273.15 degrees on the Celsius scale ( International System of Units), Note: The triple point of water is 0.01 °C, not 0 °C; thus 0 K is −2890.15 °C, not −273.16 °C. which equals −459.67 degrees on the Fahrenheit
The Fahrenheit scale () is a temperature scale based on one proposed in 1724 by the physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit (1686–1736). It uses the degree Fahrenheit (symbol: °F) as the unit. Several accounts of how he originally defined hi ...
scale ( United States customary units or Imperial units
The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units (also known as British Imperial or Exchequer Standards of 1826) is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed th ...
). The corresponding Kelvin and Rankine temperature scales set their zero points at absolute zero by definition.
It is commonly thought of as the lowest temperature possible, but it is not the lowest ''enthalpy'' state possible, because all real substances begin to depart from the ideal gas when cooled as they approach the change of state to liquid, and then to solid; and the sum of the enthalpy of vaporization
The enthalpy of vaporization (symbol ), also known as the (latent) heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance to transform a quantity of that substance into a gas. T ...
(gas to liquid) and enthalpy of fusion
In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of fusion of a substance, also known as (latent) heat of fusion, is the change in its enthalpy resulting from providing energy, typically heat, to a specific quantity of the substance to change its state from a s ...
(liquid to solid) exceeds the ideal gas's change in enthalpy to absolute zero. In the quantum-mechanical description, matter (solid) at absolute zero is in its ground state, the point of lowest internal energy.
The laws of thermodynamics
The laws of thermodynamics are a set of scientific laws which define a group of physical quantities, such as temperature, energy, and entropy, that characterize thermodynamic systems in thermodynamic equilibrium. The laws also use various paramet ...
indicate that absolute zero cannot be reached using only thermodynamic means, because the temperature of the substance being cooled approaches the temperature of the cooling agent asymptotically. Even a system at absolute zero, if it could somehow be achieved, would still possess quantum mechanical
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, qua ...
zero-point energy, the energy of its ground state at absolute zero; the kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acc ...
of the ground state cannot be removed.
Scientists and technologists routinely achieve temperatures close to absolute zero, where matter exhibits quantum effects such as Bose–Einstein condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero (−273.15 °C or −459.6 ...
, superconductivity and superfluidity
Superfluidity is the characteristic property of a fluid with zero viscosity which therefore flows without any loss of kinetic energy. When stirred, a superfluid forms vortices that continue to rotate indefinitely. Superfluidity occurs in two ...
.
Thermodynamics near absolute zero
At temperatures near , nearly all molecular motion ceases and Δ''S'' = 0 for anyadiabatic process
In thermodynamics, an adiabatic process (Greek: ''adiábatos'', "impassable") is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat or mass between the thermodynamic system and its environment. Unlike an isothermal proces ...
, where ''S'' is the entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynam ...
. In such a circumstance, pure substances can (ideally) form perfect crystals with no structural imperfections as ''T'' → 0. Max Planck
Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck (, ; 23 April 1858 – 4 October 1947) was a German theoretical physicist whose discovery of energy quanta won him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918.
Planck made many substantial contributions to theoretical p ...
's strong form of the third law of thermodynamics
The third law of thermodynamics states, regarding the properties of closed systems in thermodynamic equilibrium: This constant value cannot depend on any other parameters characterizing the closed system, such as pressure or applied magnetic fiel ...
states the entropy of a perfect crystal vanishes at absolute zero. The original Nernst
Walther Hermann Nernst (; 25 June 1864 – 18 November 1941) was a German chemist known for his work in thermodynamics, physical chemistry, electrochemistry, and solid state physics. His formulation of the Nernst heat theorem helped pave the w ...
'' heat theorem'' makes the weaker and less controversial claim that the entropy change for any isothermal process approaches zero as ''T'' → 0:
:
The implication is that the entropy of a perfect crystal approaches a constant value. An adiabat is a state with constant entropy, typically represented on a graph as a curve in a manner similar to isotherms and isobars.
The Nernst postulate identifies the isotherm T = 0 as coincident with the adiabat S = 0, although other isotherms and adiabats are distinct. As no two adiabats intersect, no other adiabat can intersect the T = 0 isotherm. Consequently no adiabatic process initiated at nonzero temperature can lead to zero temperature. (≈ Callen, pp. 189–190)A perfect crystal is one in which the internal
lattice
Lattice may refer to:
Arts and design
* Latticework, an ornamental criss-crossed framework, an arrangement of crossing laths or other thin strips of material
* Lattice (music), an organized grid model of pitch ratios
* Lattice (pastry), an orna ...
structure extends uninterrupted in all directions. The perfect order can be represented by translational symmetry along three (not usually orthogonal) axes
Axes, plural of '' axe'' and of '' axis'', may refer to
* ''Axes'' (album), a 2005 rock album by the British band Electrelane
* a possibly still empty plot (graphics)
See also
* Axess (disambiguation)
*Axxess (disambiguation) Axxess may refer to ...
. Every lattice element of the structure is in its proper place, whether it is a single atom or a molecular grouping. For substances that exist in two (or more) stable crystalline forms, such as diamond and graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on lar ...
for carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
, there is a kind of ''chemical degeneracy''. The question remains whether both can have zero entropy at ''T'' = 0 even though each is perfectly ordered.
Perfect crystals never occur in practice; imperfections, and even entire amorphous material inclusions, can and do get "frozen in" at low temperatures, so transitions to more stable states do not occur.
Using the Debye model
In thermodynamics and solid-state physics, the Debye model is a method developed by Peter Debye in 1912 for estimating the phonon contribution to the specific heat (Heat capacity) in a solid. It treats the vibrations of the atomic lattice (hea ...
, the specific heat
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol ) of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample, also sometimes referred to as massic heat capacity. Informally, it is the amount of heat t ...
and entropy of a pure crystal are proportional to ''T'' 3, while the enthalpy
Enthalpy , a property of a thermodynamic system, is the sum of the system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant ...
and chemical potential
In thermodynamics, the chemical potential of a species is the energy that can be absorbed or released due to a change of the particle number of the given species, e.g. in a chemical reaction or phase transition. The chemical potential of a species ...
are proportional to ''T'' 4. (Guggenheim, p. 111) These quantities drop toward their ''T'' = 0 limiting values and approach with ''zero'' slopes. For the specific heats at least, the limiting value itself is definitely zero, as borne out by experiments to below 10 K. Even the less detailed Einstein model shows this curious drop in specific heats. In fact, all specific heats vanish at absolute zero, not just those of crystals. Likewise for the coefficient of thermal expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions.
Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic ...
. Maxwell's relations show that various other quantities also vanish. These phenomena were unanticipated.
Since the relation between changes in Gibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy (or Gibbs energy; symbol G) is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum amount of work that may be performed by a thermodynamically closed system at constant temperature and ...
(''G''), the enthalpy (''H'') and the entropy is
:
thus, as ''T'' decreases, Δ''G'' and Δ''H'' approach each other (so long as Δ''S'' is bounded). Experimentally, it is found that all spontaneous processes (including chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the pos ...
s) result in a decrease in ''G'' as they proceed toward equilibrium. If Δ''S'' and/or ''T'' are small, the condition Δ''G'' < 0 may imply that Δ''H'' < 0, which would indicate an exothermic reaction. However, this is not required; endothermic
In thermochemistry, an endothermic process () is any thermodynamic process with an increase in the enthalpy (or internal energy ) of the system.Oxtoby, D. W; Gillis, H.P., Butler, L. J. (2015).''Principle of Modern Chemistry'', Brooks Cole. ...
reactions can proceed spontaneously if the ''T''Δ''S'' term is large enough.
Moreover, the slopes of the derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. ...
s of Δ''G'' and Δ''H'' converge and are equal to zero at ''T'' = 0. This ensures that Δ''G'' and Δ''H'' are nearly the same over a considerable range of temperatures and justifies the approximate empirical Principle of Thomsen and Berthelot, which states that ''the equilibrium state to which a system proceeds is the one that evolves the greatest amount of heat'', i.e., an actual process is the ''most exothermic one''. (Callen, pp. 186–187)
One model that estimates the properties of an electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
gas at absolute zero in metals is the Fermi gas
An ideal Fermi gas is a state of matter which is an ensemble of many non-interacting fermions. Fermions are particles that obey Fermi–Dirac statistics, like electrons, protons, and neutrons, and, in general, particles with half-integer sp ...
. The electrons, being fermions, must be in different quantum states, which leads the electrons to get very high typical velocities, even at absolute zero. The maximum energy that electrons can have at absolute zero is called the Fermi energy
The Fermi energy is a concept in quantum mechanics usually referring to the energy difference between the highest and lowest occupied single-particle states in a quantum system of non-interacting fermions at absolute zero temperature.
In a Fermi ga ...
. The Fermi temperature is defined as this maximum energy divided by the Boltzmann constant, and is on the order of 80,000 K for typical electron densities found in metals. For temperatures significantly below the Fermi temperature, the electrons behave in almost the same way as at absolute zero. This explains the failure of the classical equipartition theorem
In classical statistical mechanics, the equipartition theorem relates the temperature of a system to its average energies. The equipartition theorem is also known as the law of equipartition, equipartition of energy, or simply equipartition. T ...
for metals that eluded classical physicists in the late 19th century.
Relation with Bose–Einstein condensate
 A
A Bose–Einstein condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero (−273.15 °C or −459.6 ...
(BEC) is a state of matter
In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many intermediate states are known to exist, such as liquid crystal, ...
of a dilute gas of weakly interacting boson
In particle physics, a boson ( ) is a subatomic particle whose spin quantum number has an integer value (0,1,2 ...). Bosons form one of the two fundamental classes of subatomic particle, the other being fermions, which have odd half-integer spi ...
s confined in an external potential and cooled to temperatures very near absolute zero. Under such conditions, a large fraction of the bosons occupy the lowest quantum state
In quantum physics, a quantum state is a mathematical entity that provides a probability distribution for the outcomes of each possible measurement on a system. Knowledge of the quantum state together with the rules for the system's evolution i ...
of the external potential, at which point quantum effects become apparent on a macroscopic scale
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments. It is the opposite of microscopic.
Overview
When applied to physical phenomena a ...
.
This state of matter was first predicted by Satyendra Nath Bose
Satyendra Nath Bose (; 1 January 1894 – 4 February 1974) was a Bengali mathematician and physicist specializing in theoretical physics. He is best known for his work on quantum mechanics in the early 1920s, in developing the foundation for ...
and Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory ...
in 1924–25. Bose first sent a paper to Einstein on the quantum statistics of light quanta (now called photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they a ...
s). Einstein was impressed, translated the paper from English to German and submitted it for Bose to the '' Zeitschrift für Physik'', which published it. Einstein then extended Bose's ideas to material particles (or matter) in two other papers.
Seventy years later, in 1995, the first gaseous condensate
Condensate may refer to:
* The liquid phase produced by the condensation of steam or any other gas
* The product of a chemical condensation reaction, other than water
* Natural-gas condensate, in the natural gas industry
* ''Condensate'' (album) ...
was produced by Eric Cornell and Carl Wieman at the University of Colorado at Boulder
The University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder, CU, or Colorado) is a public research university in Boulder, Colorado. Founded in 1876, five months before Colorado became a state, it is the flagship university of the University of Colorado sy ...
NIST-JILA
JILA, formerly known as the Joint Institute for Laboratory Astrophysics, is a physical science research institute in the United States. JILA is located on the University of Colorado Boulder campus. JILA was founded in 1962 as a joint institute ...
lab, using a gas of rubidium atoms cooled to 170 nanokelvin
List of orders of magnitude for temperature
Detailed list for 100 K to 1000 K
Most ordinary human activity takes place at temperatures of this order of magnitude. Circumstances where water naturally occurs in liquid form are shown in light gre ...
(nK) ().
A record cold temperature of 450 ± 80 picokelvin (pK) () in a BEC of sodium atoms was achieved in 2003 by researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the ...
(MIT). The associated black-body
A black body or blackbody is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence. The name "black body" is given because it absorbs all colors of light. A black body ...
(peak emittance) wavelength of 6,400 kilometers is roughly the radius of Earth.
Absolute temperature scales
Absolute, orthermodynamic
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of the ...
, temperature is conventionally measured in kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and phy ...
( Celsius-scaled increments) and in the Rankine scale (Fahrenheit
The Fahrenheit scale () is a temperature scale based on one proposed in 1724 by the physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit (1686–1736). It uses the degree Fahrenheit (symbol: °F) as the unit. Several accounts of how he originally defined hi ...
-scaled increments) with increasing rarity. Absolute temperature measurement is uniquely determined by a multiplicative constant which specifies the size of the ''degree'', so the ''ratios'' of two absolute temperatures, ''T''2/''T''1, are the same in all scales. The most transparent definition of this standard comes from the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution. It can also be found in Fermi–Dirac statistics (for particles of half-integer spin) and Bose–Einstein statistics
In quantum statistics, Bose–Einstein statistics (B–E statistics) describes one of two possible ways in which a collection of non-interacting, indistinguishable particles may occupy a set of available discrete energy states at thermodynamic ...
(for particles of integer spin). All of these define the relative numbers of particles in a system as decreasing exponential function
The exponential function is a mathematical function denoted by f(x)=\exp(x) or e^x (where the argument is written as an exponent). Unless otherwise specified, the term generally refers to the positive-valued function of a real variable, ...
s of energy (at the particle level) over ''kT'', with ''k'' representing the Boltzmann constant
The Boltzmann constant ( or ) is the proportionality factor that relates the average relative kinetic energy of particles in a gas with the thermodynamic temperature of the gas. It occurs in the definitions of the kelvin and the gas constant, ...
and ''T'' representing the temperature observed at the macroscopic
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments. It is the opposite of microscopic.
Overview
When applied to physical phenomena a ...
level.
Negative temperatures
Temperatures that are expressed as negative numbers on the familiar Celsius or Fahrenheit scales are simply colder than the zero points of those scales. Certain systems can achieve truly negative temperatures; that is, theirthermodynamic temperature
Thermodynamic temperature is a quantity defined in thermodynamics as distinct from kinetic theory or statistical mechanics.
Historically, thermodynamic temperature was defined by Kelvin in terms of a macroscopic relation between thermodynamic ...
(expressed in kelvins) can be of a negative quantity. A system with a truly negative temperature is not colder than absolute zero. Rather, a system with a negative temperature is hotter than ''any'' system with a positive temperature, in the sense that if a negative-temperature system and a positive-temperature system come in contact, heat flows from the negative to the positive-temperature system.
Most familiar systems cannot achieve negative temperatures because adding energy always increases their entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynam ...
. However, some systems have a maximum amount of energy that they can hold, and as they approach that maximum energy their entropy actually begins to decrease. Because temperature is defined by the relationship between energy and entropy, such a system's temperature becomes negative, even though energy is being added. As a result, the Boltzmann factor for states of systems at negative temperature increases rather than decreases with increasing state energy. Therefore, no complete system, i.e. including the electromagnetic modes, can have negative temperatures, since there is no highest energy state, so that the sum of the probabilities of the states would diverge for negative temperatures. However, for quasi-equilibrium systems (e.g. spins out of equilibrium with the electromagnetic field) this argument does not apply, and negative effective temperatures are attainable.
On 3 January 2013, physicists announced that for the first time they had created a quantum gas made up of potassium atoms with a negative temperature in motional degrees of freedom.
History
 One of the first to discuss the possibility of an absolute minimal temperature was
One of the first to discuss the possibility of an absolute minimal temperature was Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle (; 25 January 1627 – 31 December 1691) was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of ...
. His 1665 ''New Experiments and Observations touching Cold'', articulated the dispute known as the ''primum frigidum''. The concept was well known among naturalists of the time. Some contended an absolute minimum temperature occurred within earth (as one of the four classical elements), others within water, others air, and some more recently within nitre
Niter or nitre is the mineral form of potassium nitrate, KNO3. It is a soft, white, highly soluble mineral found primarily in arid climates or cave deposits.
Historically, the term ''niter'' was not well differentiated from natron, both of w ...
. But all of them seemed to agree that, "There is some body or other that is of its own nature supremely cold and by participation of which all other bodies obtain that quality."
Limit to the "degree of cold"
The question whether there is a limit to the degree of coldness possible, and, if so, where the zero must be placed, was first addressed by the French physicistGuillaume Amontons
Guillaume Amontons (31 August 1663 – 11 October 1705) was a French scientific instrument inventor and physicist. He was one of the pioneers in studying the problem of friction, which is the resistance to motion when bodies make contact. He is ...
in 1702, in connection with his improvements in the air thermometer. His instrument indicated temperatures by the height at which a certain mass of air sustained a column of mercury—the volume, or "spring" of the air varying with temperature. Amontons therefore argued that the zero of his thermometer would be that temperature at which the spring of the air was reduced to nothing. He used a scale that marked the boiling point of water at +73 and the melting point of ice at +, so that the zero was equivalent to about −240 on the Celsius scale. Amontons held that the absolute zero cannot be reached, so never attempted to compute it explicitly.
The value of −240 °C, or "431 divisions n Fahrenheit's thermometerbelow the cold of freezing water" was published by George Martine in 1740.
This close approximation to the modern value of −273.15 °C for the zero of the air thermometer was further improved upon in 1779 by Johann Heinrich Lambert
Johann Heinrich Lambert (, ''Jean-Henri Lambert'' in French; 26 or 28 August 1728 – 25 September 1777) was a polymath from the Republic of Mulhouse, generally referred to as either Swiss or French, who made important contributions to the subject ...
, who observed that might be regarded as absolute cold.
Values of this order for the absolute zero were not, however, universally accepted about this period. Pierre-Simon Laplace
Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace (; ; 23 March 1749 – 5 March 1827) was a French scholar and polymath whose work was important to the development of engineering, mathematics, statistics, physics, astronomy, and philosophy. He summarized ...
and Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( , ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794),
CNRS (
CNRS (
John Dalton in his ''Chemical Philosophy'' gave ten calculations of this value, and finally adopted −3,000 °C as the natural zero of temperature.
 With a better theoretical understanding of absolute zero, scientists were eager to reach this temperature in the lab. By 1845,
With a better theoretical understanding of absolute zero, scientists were eager to reach this temperature in the lab. By 1845,
 The average temperature of the universe today is approximately , or about −270.42 ºC, based on measurements of
The average temperature of the universe today is approximately , or about −270.42 ºC, based on measurements of
BIPM Mise en pratique - Kelvin - Appendix 2 - SI Brochure
"Absolute zero"
a two part '' NOVA'' episode originally aired January 2008
"What is absolute zero?"
''Lansing State Journal'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Absolute Zero Cold Cryogenics Temperature
Lord Kelvin's work
AfterJames Prescott Joule
James Prescott Joule (; 24 December 1818 11 October 1889) was an English physicist, mathematician and brewer, born in Salford, Lancashire. Joule studied the nature of heat, and discovered its relationship to mechanical work (see energy). ...
had determined the mechanical equivalent of heat, Lord Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 182417 December 1907) was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, he did important ...
approached the question from an entirely different point of view, and in 1848 devised a scale of absolute temperature that was independent of the properties of any particular substance and was based on Carnot's theory of the Motive Power of Heat and data published by Henri Victor Regnault
Henri Victor Regnault (21 July 1810 – 19 January 1878) was a French chemist and physicist best known for his careful measurements of the thermal properties of gases. He was an early thermodynamicist and was mentor to William Thomson in ...
. It followed from the principles on which this scale was constructed that its zero was placed at −273 °C, at almost precisely the same point as the zero of the air thermometer. This value was not immediately accepted; values ranging from to , derived from laboratory measurements and observations of astronomical refraction, remained in use in the early 20th century.
The race to absolute zero
 With a better theoretical understanding of absolute zero, scientists were eager to reach this temperature in the lab. By 1845,
With a better theoretical understanding of absolute zero, scientists were eager to reach this temperature in the lab. By 1845, Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic inducti ...
had managed to liquefy most gases then known to exist, and reached a new record for lowest temperatures by reaching . Faraday believed that certain gases, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
, were permanent gases and could not be liquefied. Decades later, in 1873 Dutch theoretical scientist Johannes Diderik van der Waals
Johannes Diderik van der Waals (; 23 November 1837 – 8 March 1923) was a Dutch theoretical physicist and thermodynamicist famous for his pioneering work on the equation of state for gases and liquids. Van der Waals started his career as a sch ...
demonstrated that these gases could be liquefied, but only under conditions of very high pressure and very low temperatures. In 1877, Louis Paul Cailletet in France and Raoul Pictet in Switzerland succeeded in producing the first droplets of liquid air
Liquid air is air that has been cooled to very low temperatures ( cryogenic temperatures), so that it has condensed into a pale blue mobile liquid. To thermally insulate it from room temperature, it is stored in specialized containers ( vacuum in ...
. This was followed in 1883 by the production of liquid oxygen by the Polish professors Zygmunt Wróblewski Zygmunt, Zigmunt, Zigmund and spelling variations thereof are masculine given names and occasionally surnames. People so named include:
Given name Medieval period
* Sigismund I the Old (1467–1548), Zygmunt I Stary in Polish, King of Poland and Gr ...
and Karol Olszewski
Karol Stanisław Olszewski (29 January 1846 – 24 March 1915) was a Poles, Polish chemist, mathematician and physicist.
Biography
Olszewski was a graduate of Kazimierz Brodziński High School in Tarnów (I Liceum Ogólnokształcące im. Kazi ...
.
Scottish chemist and physicist James Dewar
Sir James Dewar (20 September 1842 – 27 March 1923) was a British chemist and physicist. He is best known for his invention of the vacuum flask, which he used in conjunction with research into the liquefaction of gases. He also studied a ...
and Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes took on the challenge to liquefy the remaining gases, hydrogen and helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
. In 1898, after 20 years of effort, Dewar was first to liquefy hydrogen, reaching a new low-temperature record of . However, Kamerlingh Onnes, his rival, was the first to liquefy helium, in 1908, using several precooling stages and the Hampson–Linde cycle
The Hampson–Linde cycle is a process for the liquefaction of gases, especially for air separation. William Hampson and Carl von Linde independently filed for patents of the cycle in 1895: Hampson on 23 May 1895 and Linde on 5 June 1895.
The Ha ...
. He lowered the temperature to the boiling point of helium . By reducing the pressure of the liquid helium he achieved an even lower temperature, near 1.5 K. These were the coldest temperatures achieved on Earth at the time and his achievement earned him the Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
in 1913. Kamerlingh Onnes would continue to study the properties of materials at temperatures near absolute zero, describing superconductivity and superfluids for the first time.
Very low temperatures
 The average temperature of the universe today is approximately , or about −270.42 ºC, based on measurements of
The average temperature of the universe today is approximately , or about −270.42 ºC, based on measurements of cosmic microwave background
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all spac ...
radiation.
Absolute zero cannot be achieved, although it is possible to reach temperatures close to it through the use of cryocoolers, dilution refrigerator
A 3He/4He dilution refrigerator is a cryogenic device that provides continuous cooling to temperatures as low as 2 mK, with no moving parts in the low-temperature region. The cooling power is provided by the heat of mixing of the Hel ...
s, and nuclear adiabatic demagnetization. The use of laser cooling
Laser cooling includes a number of techniques in which atoms, molecules, and small mechanical systems are cooled, often approaching temperatures near absolute zero. Laser cooling techniques rely on the fact that when an object (usually an atom) a ...
has produced temperatures of less than a billionth of a kelvin. At very low temperatures in the vicinity of absolute zero, matter exhibits many unusual properties, including superconductivity, superfluidity
Superfluidity is the characteristic property of a fluid with zero viscosity which therefore flows without any loss of kinetic energy. When stirred, a superfluid forms vortices that continue to rotate indefinitely. Superfluidity occurs in two ...
, and Bose–Einstein condensation. To study such phenomena, scientists have worked to obtain even lower temperatures.
* In November 2000, nuclear spin temperatures below 100 pK were reported for an experiment at the Helsinki University of Technology
Helsinki University of Technology (TKK; fi, Teknillinen korkeakoulu; sv, Tekniska högskolan) was a technical university in Finland. It was located in Otaniemi, Espoo in the metropolitan area of Greater Helsinki. The university was founded in ...
's Low Temperature Lab in Espoo
Espoo (, ; sv, Esbo) is a city and municipality in the region of Uusimaa in the Republic of Finland. It is located on the northern shore of the Gulf of Finland, bordering the cities of Helsinki, Vantaa, Kirkkonummi, Vihti and Nurmijärvi ...
, Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
. However, this was the temperature of one particular degree of freedom
Degrees of freedom (often abbreviated df or DOF) refers to the number of independent variables or parameters of a thermodynamic system. In various scientific fields, the word "freedom" is used to describe the limits to which physical movement or ...
—a quantum property called nuclear spin—not the overall average thermodynamic temperature
Thermodynamic temperature is a quantity defined in thermodynamics as distinct from kinetic theory or statistical mechanics.
Historically, thermodynamic temperature was defined by Kelvin in terms of a macroscopic relation between thermodynamic ...
for all possible degrees in freedom.
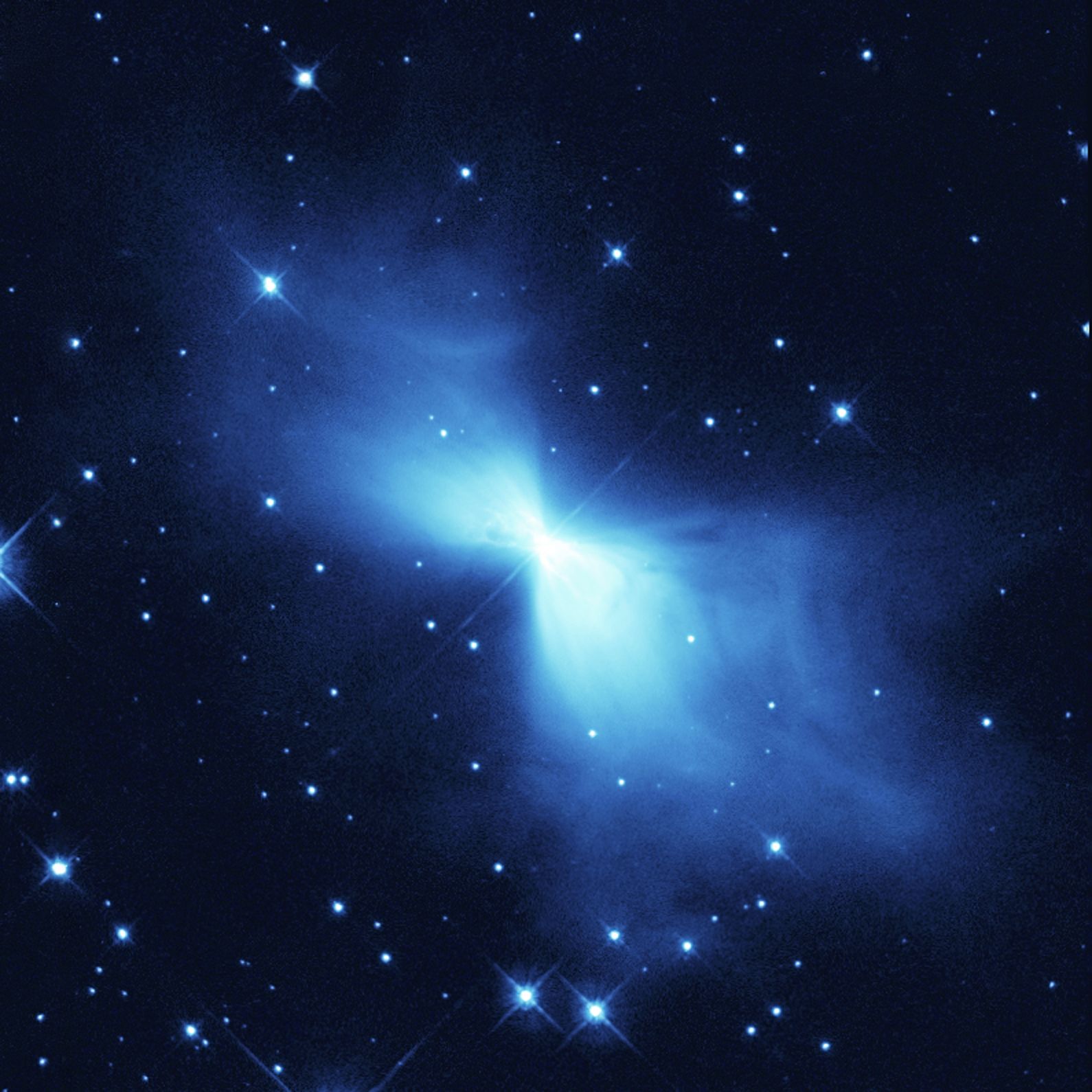
* In February 2003, the Boomerang Nebula
The Boomerang Nebula is a protoplanetary nebula located 5,000 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Centaurus. It is also known as the Bow Tie Nebula and catalogued as LEDA 3074547. The nebula's temperature is measured at making i ...
was observed to have been releasing gases at a speed of for the last 1,500 years. This has cooled it down to approximately 1 K, as deduced by astronomical observation, which is the lowest natural temperature ever recorded.
* In November 2003, 90377 Sedna was discovered and is one of the Coldest known Objects in the Solar System. With an Average Surface Temperature of -400°F (-240°C), due to its extremely far orbit of 903 Astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits ...
s.
* In May 2005, the European Space Agency proposed research in space to achieve femtokelvin temperatures.
* In May 2006, the Institute of Quantum Optics at the University of Hannover gave details of technologies and benefits of femtokelvin research in space.
* In January 2013, physicist Ulrich Schneider of the University of Munich
The Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (simply University of Munich or LMU; german: Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München) is a public research university in Munich, Germany. It is Germany's sixth-oldest university in continuous operatio ...
in Germany reported to have achieved temperatures formally below absolute zero (" negative temperature") in gases. The gas is artificially forced out of equilibrium into a high potential energy state, which is, however, cold. When it then emits radiation it approaches the equilibrium, and can continue emitting despite reaching formal absolute zero; thus, the temperature is formally negative.
* In September 2014, scientists in the CUORE
The Cryogenic Underground Observatory for Rare Events (CUORE , also ) is a particle physics facility located underground at the Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso in Assergi, Italy. CUORE was designed primarily as a search for neutrinoless dou ...
collaboration at the Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso in Italy cooled a copper vessel with a volume of one cubic meter to for 15 days, setting a record for the lowest temperature in the known universe over such a large contiguous volume.
* In June 2015, experimental physicists at MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the m ...
cooled molecules in a gas of sodium potassium to a temperature of 500 nanokelvin, and it is expected to exhibit an exotic state of matter by cooling these molecules somewhat further.
* In 2017, Cold Atom Laboratory (CAL), an experimental instrument was developed for launch to the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ( ...
(ISS) in 2018. The instrument has created extremely cold conditions in the microgravity environment of the ISS leading to the formation of Bose–Einstein condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero (−273.15 °C or −459.6 ...
s. In this space-based laboratory, temperatures as low as 1 picokelvin (10−12 K) temperatures are projected to be achievable, and it could further the exploration of unknown quantum mechanical
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, qua ...
phenomena and test some of the most fundamental laws of physics
Scientific laws or laws of science are statements, based on repeated experiments or observations, that describe or predict a range of natural phenomena. The term ''law'' has diverse usage in many cases (approximate, accurate, broad, or narrow) ...
.
* The current world record for effective temperatures was set in 2021 at 38 picokelvin (pK), or 0.000000000038 of a kelvin, through matter-wave lensing of rubidium Bose–Einstein condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero (−273.15 °C or −459.6 ...
s.
See also
*Charles's law
Charles's law (also known as the law of volumes) is an experimental gas law that describes how gases tend to expand when heated. A modern statement of Charles's law is:
When the pressure on a sample of a dry gas is held constant, the Kelvin t ...
* Heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is ...
* International Temperature Scale of 1990
* Orders of magnitude (temperature)
List of orders of magnitude for temperature
Detailed list for 100 K to 1000 K
Most ordinary human activity takes place at temperatures of this order of magnitude. Circumstances where water naturally occurs in liquid form are shown in light gr ...
* Thermodynamic temperature
Thermodynamic temperature is a quantity defined in thermodynamics as distinct from kinetic theory or statistical mechanics.
Historically, thermodynamic temperature was defined by Kelvin in terms of a macroscopic relation between thermodynamic ...
* Triple point
In thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.. It is that temperature and pressure at which the sub ...
* Ultracold atom
Ultracold atoms are atoms that are maintained at temperatures close to 0 kelvin (absolute zero), typically below several tens of microkelvin (µK). At these temperatures the atom's quantum-mechanical properties become important.
To reach such low ...
* Kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acc ...
* Entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynam ...
References
Further reading
* * * *BIPM Mise en pratique - Kelvin - Appendix 2 - SI Brochure
External links
"Absolute zero"
a two part '' NOVA'' episode originally aired January 2008
"What is absolute zero?"
''Lansing State Journal'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Absolute Zero Cold Cryogenics Temperature