Abigail Adams on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Abigail Adams ( ''née'' Smith; November 22, [ O.S. November 11] 1744 – October 28, 1818) was the wife and closest advisor of
 Abigail Adams was born on November 22, 1744, at the North Parish Congregational Church in
Abigail Adams was born on November 22, 1744, at the North Parish Congregational Church in
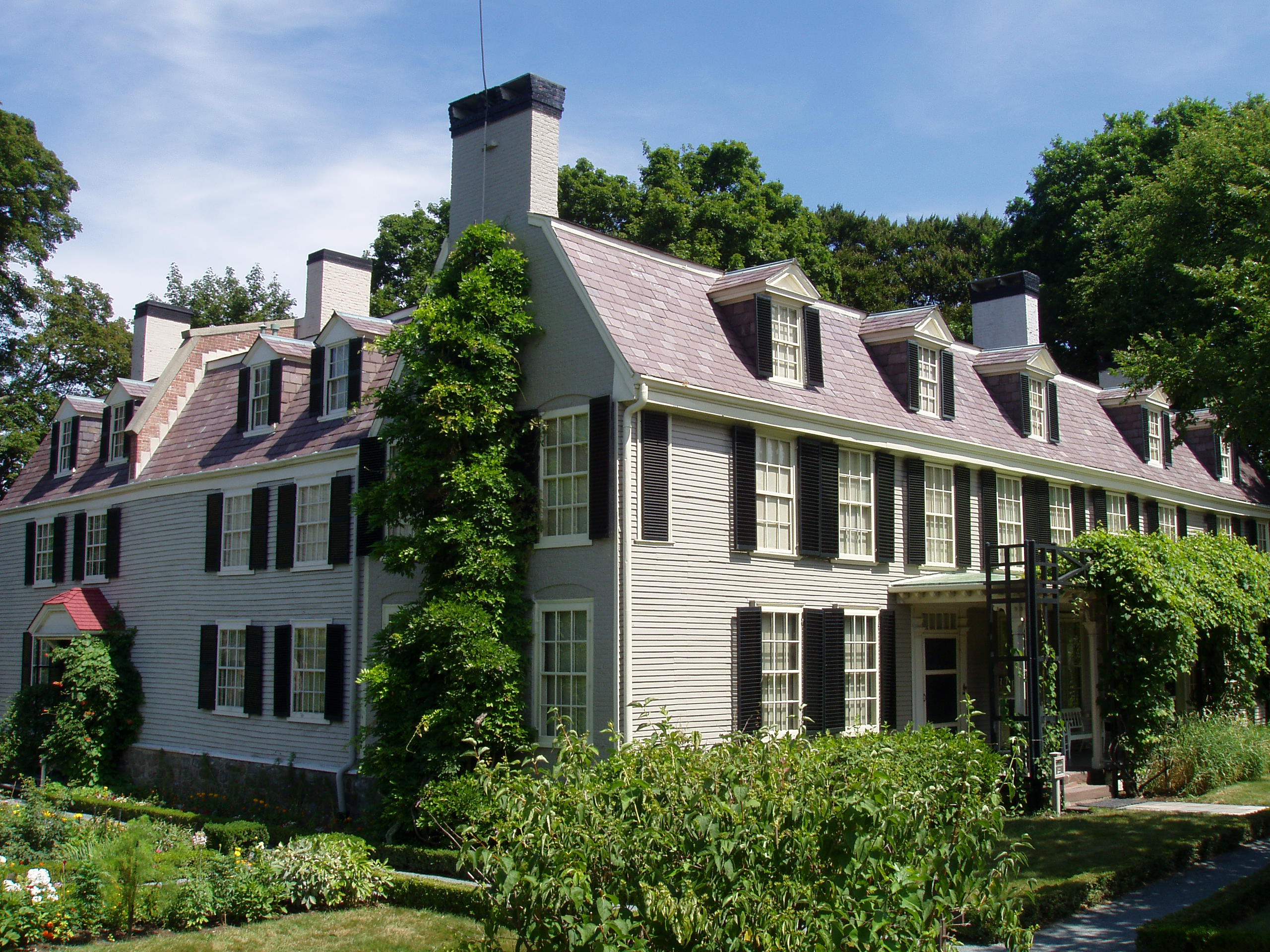 After John's defeat in his presidential re-election campaign, the family retired to
After John's defeat in his presidential re-election campaign, the family retired to
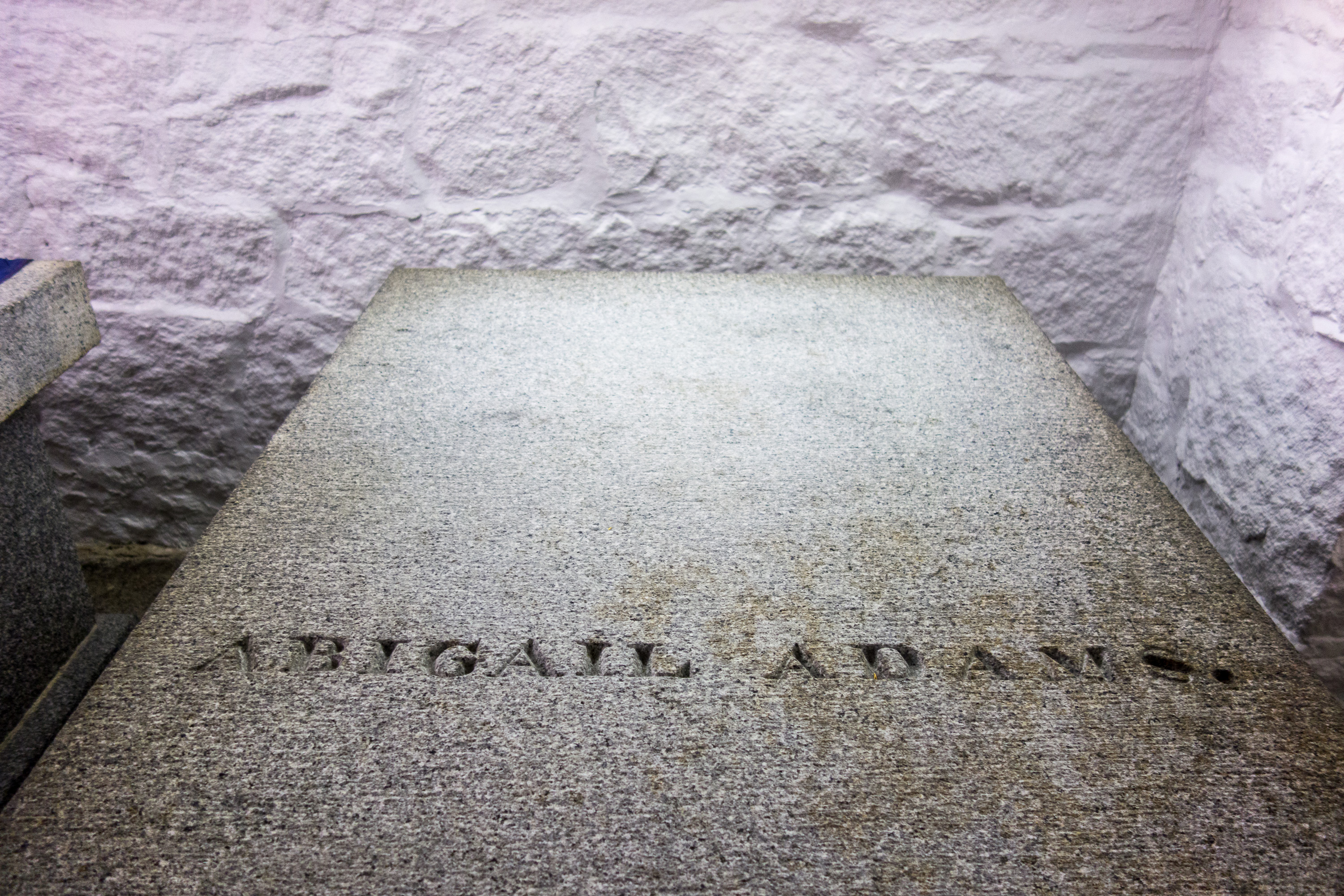 Adams died in her home on October 28, 1818, of
Adams died in her home on October 28, 1818, of
 John declined Abigail's "extraordinary code of laws", but acknowledged to Abigail, "We have only the name of masters, and rather than give up this, which would completely subject us to the despotism of the
John declined Abigail's "extraordinary code of laws", but acknowledged to Abigail, "We have only the name of masters, and rather than give up this, which would completely subject us to the despotism of the
File:Abigail Adams First Spouse Coin obverse.jpg, Obverse
File:Adams a-o.jpg, Obverse (bronze medal)
(New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 2010). * Gelles, Edith B. ''Portia: The World of Abigail Adams'' (Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 1991). * ——. ''First Thoughts: Life and Letters of Abigail Adams'' (New York: Twayne Publishers, 1998), reissued as ''Abigail Adams: A Writing Life'' (London and New York: Routledge, 2002). * ——. "The Adamses Retire". ''Early American Studies'' 4.1 (2006): 1–15. * ——. ''Abigail and John: Portrait of a Marriage'' (New York: William Morrow, 2009) – finalist for the 2010
''Dear Abigail: The Intimate Lives and Revolutionary Ideas of Abigail Adams and Her Two Remarkable Sisters''
(2014) * Kaminski, John P., editor ''The Quotable Abigail Adams'' (Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, 2009). * Levin, Phyllis Lee. ''Abigail Adams: A Biography'' (St. Martin's Press. 1987). 575pp * *
''The Adams Women: Abigail and Louisa Adams, Their Sisters and Daughters''
New York: . * Orihel, Michelle. "Remember The Ladies: Teaching the Correspondence of John and Abigail Adams in the Age of Social Media". ''Common-Place: The Interactive Journal of Early American Life'' (2018) 18#1 p 3+ * Sawyer, Kem Knapp.
''Abigail Adams''
(2009) for secondary schools. * Shields, David S., and Fredrika J. Teute. "The Court of Abigail Adams". ''Journal of the Early Republic'' 35.2 (2015): 227–235. *
Abigail Adams: Eyewitness to America's Birth
' (2009), for middle schools.
"Those Sentimental Americans"
''New York Review of Books''.
''Abigail Adams: Letters''
(Library of America, 2016). * Adams, Johns, and Abigail Adams
''My Dearest Friend: Letters of Abigail and John Adams''
(2007); 556 pp * Belton, Blair, ed
''Abigail Adams in Her Own Words''
(2014) * ''The Letters of John and Abigail Adams'' ed by Frank Shuffelton (2003).
Founders Online, searchable edition
** Adams Papers Editorial Project * * * *
Adams family biographies – Massachusetts Historical Society
Collection of Abigail Adams Letters
''The Adams Women: Abigail and Louisa Adams, Their Sisters and Daughters'', Harvard University Press
''Descent from Glory: Four Generations of the John Adams Family'', Harvard University Press
''Adams Family Correspondence''. Cambridge: Harvard University Press
Abigail Adams Birthplace – Museum in Weymouth, Massachusetts
Abigail Adams
at
"Abigail Adams"
National Women's History Museum. 2015. , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Adams, Abigail 1744 births 1818 deaths 18th-century American women writers 18th-century American writers 18th-century Unitarians 18th-century letter writers 19th-century American women 19th-century Unitarians Adams political family American Congregationalists American Unitarians American feminists American letter writers American people of English descent Burials in Massachusetts Colonial American women Deaths from typhoid fever First Ladies of the United States Infectious disease deaths in Massachusetts Mothers of presidents of the United States People from Braintree, Massachusetts People from Weymouth, Massachusetts People of Massachusetts in the American Revolution People of colonial Massachusetts Quincy family Second Ladies of the United States Women in the American Revolution Women letter writers
John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Before his presidency, he was a leader of t ...
, as well as the mother of John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, and diarist who served as the sixth president of the United States, from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States ...
. She was a founder of the United States, and was the first second lady of the United States
The second gentleman or second lady of the United States (SGOTUS or SLOTUS respectively) is the informal title held by the spouse of the vice president of the United States, concurrent with the vice president's term of office. Coined in contrast ...
and second first lady of the United States, although such titles were not used at the time. She and Barbara Bush
Barbara Pierce Bush (June 8, 1925 – April 17, 2018) was First Lady of the United States from 1989 to 1993, as the wife of President George H. W. Bush, and the founder of the Barbara Bush Foundation for Family Literacy. She previously w ...
are the only two women to have been married to U.S. presidents and to have been the mothers of other U.S. presidents.
Adams's life is one of the most documented of the first ladies: she is remembered for the many letters she wrote to her husband john adams while he stayed in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, during the Continental Congresses. John frequently sought the advice of Abigail on many matters, and their letters are filled with intellectual discussions on government and politics. Her letters also serve as eyewitness accounts of the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
home front.
Surveys of historians conducted periodically by the Siena College Research Institute
Siena College Research Institute (SCRI) is an affiliate of Siena College, located originally in Friars Hall and now in Hines Hall on the college's campus, in Loudonville, New York, in suburban Albany. It was founded in 1980.
It conducts both exp ...
since 1982 have consistently found Adams to rank among the three most highly regarded first ladies by the assessments of historians.
Early life and family
 Abigail Adams was born on November 22, 1744, at the North Parish Congregational Church in
Abigail Adams was born on November 22, 1744, at the North Parish Congregational Church in Weymouth, Massachusetts ("To Work Is to Conquer")
, image_map = Norfolk County Massachusetts incorporated and unincorporated areas Weymouth highlighted.svg
, mapsize = 250px
, map_caption = Location in Norfolk County in Massa ...
, to William Smith (1707–1783) and Elizabeth (née Quincy) Smith. On her mother's side, she was descended from the Quincy family
The Quincy family was a prominent political family in Massachusetts from the mid-17th century through to the early 20th century. It is connected to the Adams political family through Abigail Adams.
The family estate was in Mount Wollaston, first ...
, a well-known political family in the Massachusetts colony
The Province of Massachusetts Bay was a colony in British America which became one of the Thirteen Colonies, thirteen original states of the United States. It was chartered on October 7, 1691, by William III of England, William III and Mary II ...
. Through her mother she was a cousin of Dorothy Quincy
Dorothy Quincy Hancock Scott (; May 21 (May 10 O.S.) 1747 – February 3, 1830) was an American hostess, daughter of Justice Edmund Quincy of Braintree and Boston, and the wife of Founding Father John Hancock. Her aunt, also named Dorothy ...
, who was married to John Hancock
John Hancock ( – October 8, 1793) was an American Founding Father, merchant, statesman, and prominent Patriot of the American Revolution. He served as president of the Second Continental Congress and was the first and third Governor of t ...
. Adams was also the great-granddaughter of John Norton, founding pastor of Old Ship Church
The Old Ship Church (also known as the Old Ship Meetinghouse) is a Puritan Church (building), church built in 1681 in Hingham, Massachusetts, Hingham, Massachusetts. It is the only surviving 17th-century Puritan Meeting house, meetinghouse in A ...
in Hingham, Massachusetts
Hingham ( ) is a town in metropolitan Greater Boston on the South Shore (Massachusetts), South Shore of the U.S. state of Massachusetts in northern Plymouth County, Massachusetts, Plymouth County. At the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, t ...
, the only remaining 17th-century Puritan meetinghouse in Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
. Smith married Elizabeth Quincy in 1740, and together they had three daughters: Mary born in 1741, Abigail born in 1744 and Elizabeth born on November 22, 1744. As with several of her ancestors, Adams's father was a liberal Congregational
Congregational churches (also Congregationalist churches or Congregationalism) are Protestant churches in the Calvinist tradition practising congregationalist church governance, in which each congregation independently and autonomously runs its ...
minister: a leader in a Yankee
The term ''Yankee'' and its contracted form ''Yank'' have several interrelated meanings, all referring to people from the United States. Its various senses depend on the context, and may refer to New Englanders, residents of the Northern United S ...
society that held its clergy in high esteem. Smith did not focus his preaching on predestination
Predestination, in theology, is the doctrine that all events have been willed by God, usually with reference to the eventual fate of the individual soul. Explanations of predestination often seek to address the paradox of free will, whereby G ...
or original sin; instead he emphasized the importance of reason and morality. In July 1775 his wife Elizabeth, with whom he had been married for 35 years, died of smallpox. In 1784, at age 77, Smith died.
The Smith family were slaveholders and are known to have enslaved at least four people. An enslaved woman named Phoebe took a caretaking role to Abigail and other children; later on she would work as a paid servant for Abigail after she became free. Abigail would come to express anti-slavery beliefs as an adult.
Abigail did not receive formal schooling; she was frequently sick as a child, something which may have been a factor preventing her from receiving an education. Later in life, Adams would also consider that she was deprived an education because females were rarely given such an opportunity. Although she did not receive a formal education, her mother taught her and her sisters Mary (1739–1811) and Elizabeth (1742–1816, known as Betsy) to read, write and cipher; her father's, uncle's and grandfather's large libraries enabled the sisters to study English and French literature. Her grandmother, Elizabeth Quincy, also contributed to Adams's education. As she grew up, Adams read with friends in an effort to further her learning. She became one of the most erudite women ever to serve as first lady.
Marriage and children
Abigail Smith first met John Adams when she was 15 years old in 1759. John accompanied his friend Richard Cranch to the Smith household. Cranch was engaged to Abigail's older sister, Mary Smith, and they would be the parents of federal judgeWilliam Cranch
William Cranch (July 17, 1769 – September 1, 1855) was a United States circuit judge and chief judge of the United States Circuit Court of the District of Columbia. A staunch Federalist and nephew of President John Adams, Cranch moved his le ...
. Adams reported finding the Smith sisters neither "fond, nor frank, nor candid".
Although Adams's father approved of the match, her mother was appalled that her daughter would marry a country lawyer
In the United States, a country lawyer or county-seat lawyer is an attorney at law living and practicing primarily in a rural area or town, or an attorney pursuing a rural or small-town legal practice. In such areas, the county seat is an importa ...
whose manner still reeked of the farm, but eventually she gave in. The couple married on October 25, 1764, in the Smiths' home in Weymouth. Smith, Abigail's father, presided over the marriage of John Adams and his daughter. After the reception, the couple mounted a single horse and rode off to their new home, the saltbox house and farm John had inherited from his father in Braintree, Massachusetts
Braintree (), officially the Town of Braintree, is a municipality in Norfolk County, Massachusetts, United States. Although officially known as a towBraintree is a city, with a mayor-council government, mayor-council form of government, and ...
(a location that is now part of Quincy). Later they moved to a second home in Boston, where his law practice expanded. The couple welcomed their first child nine months into their marriage.
In 12 years, she gave birth to six children:
* Abigail
Abigail () was an Israelite woman in the Hebrew Bible married to Nabal; she married the future King David after Nabal's death ( 1 Samuel ). Abigail was David's second wife, after Saul and Ahinoam's daughter, Michal, whom Saul later marri ...
("Nabby"; 1765–1813)
* John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, and diarist who served as the sixth president of the United States, from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States ...
(1767–1848)
* Grace Susanna ("Susanna", nicknamed "Suky") (1768–1770)
* Charles (1770–1800)
* Thomas Boylston Adams (1772–1832)
Thomas Boylston Adams (September 15, 1772 to March 12, 1832) was the third and youngest son of second United States president John Adams and Abigail (Smith) Adams. He worked as a lawyer, a secretary to his brother John Quincy Adams while the latt ...
* Elizabeth (stillborn in 1777)
Her childrearing style included relentless and continual reminders of what the children owed to virtue and the Adams tradition.Garry Wills
Garry Wills (born May 22, 1934) is an American author, journalist, political philosopher, and historian, specializing in American history, politics, and religion, especially the history of the Catholic Church. He won a Pulitzer Prize for Genera ...
, ''Henry Adams and the Making of America'', 2005; p. 24; Wills cites the criticisms of Paul Nagel "and others" Adams was responsible for family and farm when her husband was on his long trips. "Alas!", she wrote in December 1773, "How many snow banks divide thee and me." Abigail and John's marriage is well documented through their correspondence and other writings. Letters exchanged throughout John's political obligations indicate his trust in Abigail's knowledge was sincere. Like her husband, Abigail often quoted literature in her letters. Historian David McCullough
David Gaub McCullough (; July 7, 1933 – August 7, 2022) was an American popular historian. He was a two-time winner of the Pulitzer Prize and the National Book Award. In 2006, he was given the Presidential Medal of Freedom, the United States ...
claims that she did so "more readily" than her husband. Their correspondence illuminated their mutual emotional and intellectual respect. John often excused himself to Abigail for his "vanity", exposing his need for her approval.
He moved the family to Boston in April 1768, renting a clapboard house on Brattle Street that was known locally as the "White House". He and Abigail and the children lived there for a year, then moved to Cold Lane; still later, they moved again to a larger house in Brattle Square in the center of the city.
John's growing law practice required changes for the family. In 1771, he moved Abigail and the children to Braintree, but he kept his office in Boston, hoping the time away from his family would allow him to focus on his work. Nevertheless, after some time in the capital, he became disenchanted with the rural and "vulgar" Braintree as a home for his family. In August 1772, therefore, Adams moved his family back to Boston. He purchased a large brick house on Queen Street, not far from his office. In 1774, Abigail and John returned the family to the farm due to the increasingly unstable situation in Boston, and Braintree remained their permanent Massachusetts home.
Abigail also took responsibility for the family's financial matters, including investments. Investments made through her uncle Cotton Tufts
Cotton Tufts (30 May 1734 in Medford, Province of Massachusetts – 8 December 1815 in Weymouth, Massachusetts) was a Massachusetts physician. He was a cousin of Abigail Adams.
Biography
He was the grandson of Peter Tufts, who emigrated to Mas ...
in debt instruments issued to finance the Revolutionary War were rewarded after Alexander Hamilton's First Report on the Public Credit
The First Report on the Public Credit was one of four major reports on fiscal and economic policy submitted by Founding Father and first US Treasury Secretary Alexander Hamilton on the request of Congress. The report analyzed the financial standi ...
endorsed full federal payment at face value to holders of government securities. One recent researcher even credits Abigail's financial acumen with providing for the Adams family's wealth through the end of John's lifetime.
Europe
In 1784, she and her daughter Nabby joined her husband and her eldest son, John Quincy, at her husband's diplomatic post inParis
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
. Abigail had dreaded the thought of the long sea voyage, but in fact found the journey interesting. At first she found life in Paris difficult, and was rather overwhelmed by the novel experience of running a large house with a retinue of servants. However, as the months passed she began to enjoy herself: she made numerous friends, discovered a fondness for the theatre and opera, and was fascinated by Parisian women's fashions, although she ruefully admitted that she "would never be in the mode".
After 1785, she filled the role of wife of the first U.S. minister to the Court of St James's (Britain). In contrast to Paris, Abigail disliked London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, where she had few friends and was, in general, cold-shouldered by polite society. One pleasant experience was her temporary guardianship of Thomas Jefferson's young daughter Mary (Polly), for whom Abigail came to feel a deep and lifelong love.
She and John returned in 1788 to their home in Quincy, Peacefield
Peacefield, also called Peace field or Old House, is a historic home formerly owned by the Adams family of Quincy, Massachusetts. It was the home of United States Founding Father and U.S. president John Adams and First Lady Abigail Adams, and o ...
(also known as the " Old House"), which she set about vigorously enlarging and remodeling. It still stands and is open to the public as part of Adams National Historical Park
Adams National Historical Park, formerly Adams National Historic Site, in Quincy, Massachusetts
Quincy ( ) is a coastal U.S. city in Norfolk County, Massachusetts, United States. It is the largest city in the county and a part of Metropolit ...
.
First Lady
John Adams was inaugurated as the secondpresident of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
on March 4, 1797, in Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
. Abigail was not present at her husband's inauguration as she was tending to his dying 89-year-old mother. When John was elected President of the United States, Abigail continued a formal pattern of entertaining. She held a large dinner each week, made frequent public appearances, and provided for entertainment for the city of Philadelphia each Fourth of July
Independence Day (colloquially the Fourth of July) is a federal holiday in the United States commemorating the Declaration of Independence, which was ratified by the Second Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, establishing the United States ...
.
She took an active role in politics and policy, unlike the quiet presence of Martha Washington
Martha Dandridge Custis Washington (June 21, 1731 — May 22, 1802) was the wife of George Washington, the first president of the United States. Although the title was not coined until after her death, Martha Washington served as the inaugural ...
. She was so politically active, her political opponents came to refer to her as "Mrs. President". As John's confidant, Abigail was often well informed on issues facing her husband's administration, at times including details of current events not yet known to the public in letters to her sister Mary and her son John Quincy. Some people used Abigail to contact the president. At times Abigail planted favorable stories about her husband in the press. Abigail remained a staunch supporter of her husband's political career, supporting his policies, such as passing the Alien and Sedition Acts
The Alien and Sedition Acts were a set of four laws enacted in 1798 that applied restrictions to immigration and speech in the United States. The Naturalization Act increased the requirements to seek citizenship, the Alien Friends Act allowed th ...
.
Adams brought the children of her brother William Smith, her brother-in-law John Shaw, and her son Charles to live in the President's House during her husband's presidency because the children's respective fathers all struggled with alcoholism. Charles's daughter, Suzannah, was just 3 years old in 1800 when Adams brought her to live in the President's House in Philadelphia days before Charles's death.
With the relocation of the capital to Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, in 1800, she became the first First Lady to reside at the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in 1800. ...
, or President's House as it was then known. Adams moved into the White House in November 1800, living there for only the last four months of her husband's term. The city was wilderness, the President's House far from completion. She found the unfinished mansion in Washington "habitable" and the location "beautiful"; but she complained that, despite the thick woods nearby, she could find no one willing to chop and haul firewood for the First Family. Abigail used the East Room of the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in 1800. ...
to hang up the laundry. Adams's health, never robust, suffered in Washington.
Later life
Peacefield
Peacefield, also called Peace field or Old House, is a historic home formerly owned by the Adams family of Quincy, Massachusetts. It was the home of United States Founding Father and U.S. president John Adams and First Lady Abigail Adams, and o ...
in Quincy in 1800. Abigail followed her son's political career earnestly, as her letters to her contemporaries show. In later years, she renewed correspondence with Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was previously the natio ...
, having reached out to him upon the death of his daughter Maria Jefferson Eppes (Polly), whom Abigail had cared for and come to love when Polly was a small child in London, even though Jefferson's political opposition to her husband had hurt her deeply. She continued to raise her granddaughter Susanna. She also raised her elder grandchildren, including George Washington Adams and a younger John Adams, while their father John Quincy Adams was minister to Russia. Adams's 48-year-old daughter, Nabby, died of breast cancer in 1813, after having endured three years of severe pain.
Death
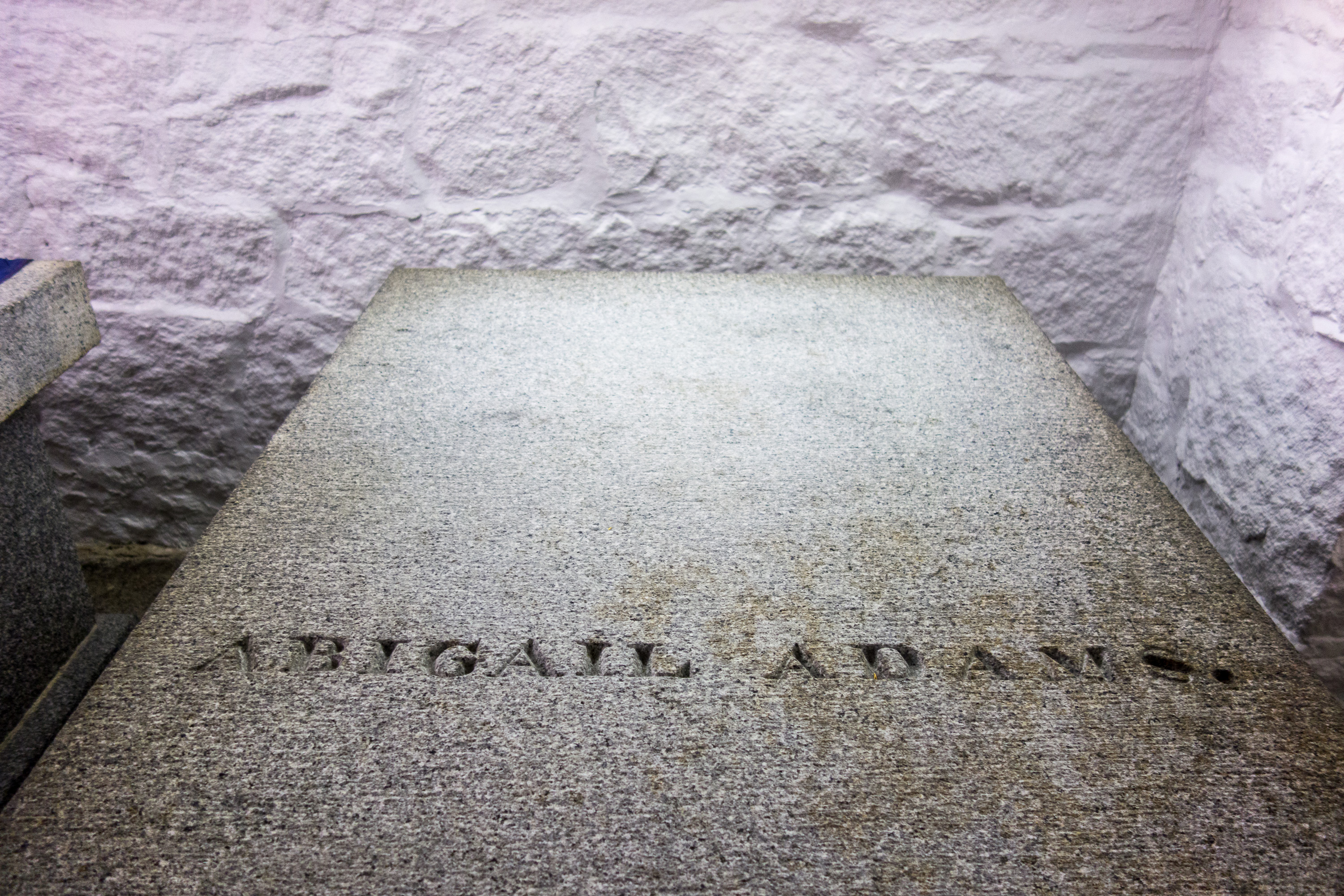 Adams died in her home on October 28, 1818, of
Adams died in her home on October 28, 1818, of typhoid fever
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several ...
. She is buried beside her husband and near their son John Quincy and his wife Louisa in a crypt located in the United First Parish Church
United First Parish Church is a Unitarian Universalist congregation in Quincy, Massachusetts, established as the parish church of Quincy in 1639. The current building was constructed in 1828 by noted Boston stonecutter Abner Joy to designs by ...
(also known as the "Church of the Presidents") in Quincy, Massachusetts. She was 73 years old, exactly two weeks shy of her 74th birthday. Her last words
Last words are the final utterances before death. The meaning is sometimes expanded to somewhat earlier utterances.
Last words of famous or infamous people are sometimes recorded (although not always accurately) which became a historical and liter ...
were, "Do not grieve, my friend, my dearest friend. I am ready to go. And John, it will not be long." Less than eight years later, on July 4, 1826, the fiftieth anniversary of the Declaration of Independence, her husband died of heart failure at the age of 90. He was buried with his late wife and is not far from the grave of their son, John Quincy.
Political viewpoints
Biographer Lynne Withey argues for her conservatism because she: "feared revolution; she valued stability, believed that family and religion were the essential props of social order, and considered inequality a social necessity". Her 18th-century mindset held that "improved legal and social status for women was not inconsistent with their essentially domestic role."Women's rights
Abigail Adams wrote about the troubles and concerns she had as an 18th-century woman. She was an advocate of married women'sproperty rights
The right to property, or the right to own property (cf. ownership) is often classified as a human right for natural persons regarding their possessions. A general recognition of a right to private property is found more rarely and is typically h ...
and more opportunities for women, particularly in the field of education. Women, she believed, should not submit to laws not made in their interest, nor should they be content with the simple role of being companions to their husbands. They should educate themselves and thus be recognized for their intellectual capabilities so they could guide and influence the lives of their children and husbands. She is known for her March 1776 letter to John and the Continental Congress, requesting that they, "remember the ladies, and be more generous and favorable to them than your ancestors. Do not put such unlimited power into the hands of the Husbands. Remember all Men would be tyrants if they could. If particular care and attention is not paid to the Ladies we are determined to foment a Rebellion, and will not hold ourselves bound by any Laws in which we have no voice, or Representation."
 John declined Abigail's "extraordinary code of laws", but acknowledged to Abigail, "We have only the name of masters, and rather than give up this, which would completely subject us to the despotism of the
John declined Abigail's "extraordinary code of laws", but acknowledged to Abigail, "We have only the name of masters, and rather than give up this, which would completely subject us to the despotism of the petticoat
A petticoat or underskirt is an article of clothing, a type of undergarment worn under a skirt or a dress. Its precise meaning varies over centuries and between countries.
According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', in current British En ...
, I hope General Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the ...
and all our brave heroes would fight."
Slavery
Adams believed thatslavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
was evil and a threat to the American democratic experiment. A letter written by her on March 31, 1776, explained that she doubted most of the Virginians had such "passion for Liberty" as they claimed they did, since they "deprive their fellow Creatures" of freedom.
A notable incident regarding this happened in Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
in 1791, when a free black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ...
youth came to her house asking to be taught how to write. Subsequently, she placed the boy in a local evening school, though not without objections from a neighbor. Adams responded that he was "a Freeman as much as any of the young Men and merely because his Face is Black, is he to be denied instruction? How is he to be qualified to procure a livelihood? ... I have not thought it any disgrace to my self to take him into my parlor and teach him both to read and write."
Religious beliefs
Adams was an active member of First Parish Church in Quincy, which became Unitarian in doctrine by 1753. Her theological views evolved over the course of her life. In a letter to her son near the end of her life, dated May 5, 1816, she wrote of her religious beliefs: She also askedLouisa Adams
Louisa Catherine Adams ( ''née'' Johnson; February 12, 1775 – May 15, 1852) was the First Lady of the United States from 1825 to 1829 during the presidency of John Quincy Adams.
Early life
Adams was born on February 12, 1775, in the City ...
in a letter dated January 3, 1818, "When will Mankind be convinced that true Religion is from the Heart, between Man and his creator, and not the imposition of Man or creeds and tests?"
Legacy
HistorianJoseph Ellis
Joseph John-Michael Ellis III (born July 18, 1943) is an American historian whose work focuses on the lives and times of the founders of the United States of America. '' American Sphinx: The Character of Thomas Jefferson'' won a National Boo ...
has found that the 1,200 letters between John and Abigail "constituted a treasure trove of unexpected intimacy and candor, more revealing than any other correspondence between a prominent American husband and wife in American history."Cited in Wood (2011) Ellis (2011) says that Abigail, although self-educated, was a better and more colorful letter-writer than John, even though John was one of the best letter-writers of the age. Ellis argues that Abigail was the more resilient and more emotionally balanced of the two, and calls her one of the most extraordinary women in American history.
Memorials
The Abigail Adams Cairn – a mound of rough stones – crowns the nearby Penn Hill from which she and her son, John Quincy Adams, watched the Battle of Bunker Hill and the burning of Charlestown. At that time she was minding the children of Dr. Joseph Warren, president of theMassachusetts Provincial Congress
The Massachusetts Provincial Congress (1774–1780) was a provisional government created in the Province of Massachusetts Bay early in the American Revolution. Based on the terms of the colonial charter, it exercised ''de facto'' control over the ...
, who was killed in the battle.
One of the subpeaks of New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
's Mount Adams (whose main peak is named for her husband) is named in her honor.
In 2022, a seven-foot tall bronze statue of Adams was unveiled in Quincy, Massachusetts, on the Hancock Adams Common.
An Adams Memorial
The Adams Memorial is a proposed United States presidential memorial to honor the second President John Adams; his wife and prolific writer Abigail Adams; their son, the sixth President John Quincy Adams; John Quincy Adams' wife Louisa Catherine ...
has been proposed in Washington, D.C., honoring Adams, her husband, her son, and other members of their family.
Popular culture
Passages from Adams's letters to her husband figured prominently in songs from the Broadway musical '' 1776''. Virginia Vestoff played Adams in the original 1969 Broadway production of ''1776'' and recreated the role for thefilm version
A film adaptation is the transfer of a work or story, in whole or in part, to a feature film. Although often considered a type of derivative work, film adaptation has been conceptualized recently by academic scholars such as Robert Stam as a dia ...
in 1972. On television, Kathryn Walker
Kathryn Walker is an American theater, television and film actress.
Biography
Walker was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. She is a Phi Beta Kappa graduate of Wells College in Aurora, New York, and was a Fulbright Scholar in music and dra ...
and Leora Dana portrayed Adams in the 1976 PBS
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of educat ...
mini-series ''The Adams Chronicles
''The Adams Chronicles'' is a thirteen-episode miniseries by PBS that aired in 1976 to commemorate the American Bicentennial.
Synopsis
The series chronicles the story of the Adams political family over a 150-year span, including John Adams (dra ...
''. In the mini-series ''John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Before his presidency, he was a leader of t ...
'', which premiered in March 2008 on HBO, she was played by Laura Linney. Linney enjoyed portraying Adams, saying that "she is a woman of both passion and principle." A revolution-era Abigail, circa 1781, is portrayed by Michelle Trachtenberg
Michelle Trachtenberg (; born October 11, 1985) is an American actress and model. Trachtenberg began her career at age three, appearing in a number of commercials, films, and television series as a child. Her starring role on the Nickelodeon tel ...
, on the television series, '' Sleepy Hollow'', in the season 2 episode, "Pittura Infamante" (January 19, 2015), her assistance being crucial in ending a series of unexplained murders from the period. Adams is a featured figure on Judy Chicago
Judy Chicago (born Judith Sylvia Cohen; July 20, 1939) is an American feminist artist, art educator, and writer known for her large collaborative art installation pieces about birth and creation images, which examine the role of women in history ...
's installation piece ''The Dinner Party
''The Dinner Party'' is an installation artwork by feminist artist Judy Chicago. Widely regarded as the first epic feminist artwork, it functions as a symbolic history of women in civilization. There are 39 elaborate place settings on a triang ...
'', being represented as one of the 999 names on the '' Heritage Floor''.Chicago, Judy (2007). ''The Dinner Party: From Creation to Preservation''. London: Merrell. p. 169. Novelist Barbara Hambly
Barbara Hambly (born August 28, 1951) is an American novelist and screenwriter within the genres of fantasy, science fiction, mystery, and historical fiction. She is the author of the bestselling Benjamin January mystery series featuring a fre ...
, writing as Barbara Hamilton, wrote three historical mysteries set in the early 1770s told from Abigail Adams' perspective (and featuring Abigail as the detective): ''The Ninth Daughter'' (2009), ''A Marked Man'' (2010), and ''Sup with the Devil'' (2011).
Portrait on currency
The First Spouse Program under thePresidential $1 Coin Program
Presidential dollar coins (authorized by ) are a series of United States dollar coins with engravings of relief portraits of U.S. presidents on the obverse and the Statue of Liberty (''Liberty Enlightening the World'') on the reverse.
From 2007 ...
authorizes the United States Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bullion. It does not produce paper money; tha ...
to issue half-ounce
The ounce () is any of several different units of mass, weight or volume and is derived almost unchanged from the , an Ancient Roman unit of measurement.
The avoirdupois ounce (exactly ) is avoirdupois pound; this is the United States customa ...
$10 gold coins
A gold coin is a coin that is made mostly or entirely of gold. Most gold coins minted since 1800 are 90–92% gold (22 karat), while most of today's gold bullion coins are pure gold, such as the Britannia, Canadian Maple Leaf, and American Bu ...
and bronze medal duplicates to honor the first spouses of the United States. The Abigail Adams coin was released on June 19, 2007, and sold out in just hours. She is pictured on the back of the coin writing her most famous letter to John Adams. In February 2009 ''Coin World
''Coin World'' is an American numismatic magazine, with weekly and monthly issues. It is among the world’s most popular non-academic publications for coin collectors and is covering the entire numismatic field, including coins, paper money, me ...
'' reported that some 2007 Abigail Adams medals were struck using the reverse from the 2008 Louisa Adams
Louisa Catherine Adams ( ''née'' Johnson; February 12, 1775 – May 15, 1852) was the First Lady of the United States from 1825 to 1829 during the presidency of John Quincy Adams.
Early life
Adams was born on February 12, 1775, in the City ...
medal, apparently by mistake. These pieces, called mules, were contained within the 2007 First Spouse medal set. The U.S. Mint has not released an estimate of how many mules were made.
Regard by historians
Since 1982Siena College Research Institute
Siena College Research Institute (SCRI) is an affiliate of Siena College, located originally in Friars Hall and now in Hines Hall on the college's campus, in Loudonville, New York, in suburban Albany. It was founded in 1980.
It conducts both exp ...
has periodically conducted surveys asking historians to assess American first ladies according to a cumulative score on the independent criteria of their background, value to the country, intelligence, courage, accomplishments, integrity, leadership, being their own women, public image, and value to the president. Consistently, Adams has ranked among the three-most highly regarded first ladies in these surveys. In terms of cumulative assessment, Adams has been ranked:
*2nd-best of 42 in 1982
*3rd-best of 37 in 1993
*2nd-best of 38 in 2003
*2nd-best of 38 in 2008
*2nd-best of 39 in 2014
In the 2008 Siena Research Institute survey, Adams was ranked in the top-four of all criteria, ranking the 3rd-highest in of background, 2nd-highest in intelligence, 3rd-highest in value to the country, 3rd-highest in being her "own woman", 2nd-highest in integrity, 3rd-highest in her accomplishments, 3rd-highest in courage, 2nd-highest in leadership, 4th-highest in public image, and 2nd-highest in her value to the president. In the 2014 survey, Adams and her husband were ranked the 5th-highest out of 39 first couples in terms of being a "power couple".
Family tree
References
Bibliography
Secondary sources
* Abrams, Jeanne E. ''First Ladies of the Republic: Martha Washington, Abigail Adams, Dolley Madison, and the Creation of an Iconic American Role'' (NYU Press, 2018). * Barker-Benfield, G.J. ''Abigail and John Adams: The Americanization of Sensibility'' (University of Chicago Press; 2010). * Bober, Natalie S. 1995. ''Abigail Adams: Witness to a Revolution'' New York: Simon & Schuster Children's Publishing Division. * Ellis, Joseph J.br>''First Family: Abigail and John Adams''(New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 2010). * Gelles, Edith B. ''Portia: The World of Abigail Adams'' (Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 1991). * ——. ''First Thoughts: Life and Letters of Abigail Adams'' (New York: Twayne Publishers, 1998), reissued as ''Abigail Adams: A Writing Life'' (London and New York: Routledge, 2002). * ——. "The Adamses Retire". ''Early American Studies'' 4.1 (2006): 1–15. * ——. ''Abigail and John: Portrait of a Marriage'' (New York: William Morrow, 2009) – finalist for the 2010
George Washington Book Prize
The George Washington Book Prize was instituted in 2005 and is awarded annually to the best book on the founding era of the United States; especially ones that have the potential to advance broad public understanding of American history. It is admi ...
.
* ——. "Bonds of Friendship: The Correspondence of Abigail Adams and Mercy Otis Warren". ''Proceedings of the Massachusetts Historical Society'' (1996), Vol. 108, p35-71.
* Holton, Woody. ''Abigail Adams: A Life'' (New York: Free Press, 2009) – winner of the 2010 Bancroft Prize
The Bancroft Prize is awarded each year by the trustees of Columbia University for books about diplomacy or the history of the Americas.
It was established in 1948, with a bequest from Frederic Bancroft, in his memory and that of his brother, ...
.
* Jacobs, Diane''Dear Abigail: The Intimate Lives and Revolutionary Ideas of Abigail Adams and Her Two Remarkable Sisters''
(2014) * Kaminski, John P., editor ''The Quotable Abigail Adams'' (Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, 2009). * Levin, Phyllis Lee. ''Abigail Adams: A Biography'' (St. Martin's Press. 1987). 575pp * *
Nagel, Paul C.
Paul Chester Nagel (August 14, 1926 – May 22, 2011) was a historian and biographer who was best known for his works for general readers on the Adams and Lee political families, and who also wrote on the history of his home state of Missouri. ...
1987''The Adams Women: Abigail and Louisa Adams, Their Sisters and Daughters''
New York: . * Orihel, Michelle. "Remember The Ladies: Teaching the Correspondence of John and Abigail Adams in the Age of Social Media". ''Common-Place: The Interactive Journal of Early American Life'' (2018) 18#1 p 3+ * Sawyer, Kem Knapp.
''Abigail Adams''
(2009) for secondary schools. * Shields, David S., and Fredrika J. Teute. "The Court of Abigail Adams". ''Journal of the Early Republic'' 35.2 (2015): 227–235. *
Abigail Adams: Eyewitness to America's Birth
' (2009), for middle schools.
Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to ...
magazine.
* Waldstreicher, David, ed. ''A Companion to John Adams and John Quincy Adams'' (2013).
* Winner, Viola Hopkins. "Abigail Adams and 'The Rage of Fashion. ''Dress'' (Costume Society of America). 2001, Vol. 28, pp. 64-76.
*
*
Historiography
* Crane, Elaine Forman. "Abigail Adams and Feminism". in David Waldstreicher, ed. ''A Companion to John Adams and John Quincy Adams'' (2013) pp 199- * Hogan, Margaret A. "Abigail Adams: The Life and the biographers". in David Waldstreicher, ed. ''A Companion to John Adams and John Quincy Adams'' (2013) pp 218–38. * Wood, Gordon S. (May 12, 2011)"Those Sentimental Americans"
''New York Review of Books''.
Primary sources
* Adams, Abigail''Abigail Adams: Letters''
(Library of America, 2016). * Adams, Johns, and Abigail Adams
''My Dearest Friend: Letters of Abigail and John Adams''
(2007); 556 pp * Belton, Blair, ed
''Abigail Adams in Her Own Words''
(2014) * ''The Letters of John and Abigail Adams'' ed by Frank Shuffelton (2003).
External links
*Founders Online, searchable edition
** Adams Papers Editorial Project * * * *
Adams family biographies – Massachusetts Historical Society
Collection of Abigail Adams Letters
''The Adams Women: Abigail and Louisa Adams, Their Sisters and Daughters'', Harvard University Press
''Descent from Glory: Four Generations of the John Adams Family'', Harvard University Press
''Adams Family Correspondence''. Cambridge: Harvard University Press
Abigail Adams Birthplace – Museum in Weymouth, Massachusetts
Abigail Adams
at
C-SPAN
Cable-Satellite Public Affairs Network (C-SPAN ) is an American cable and satellite television network that was created in 1979 by the cable television industry as a nonprofit public service. It televises many proceedings of the United States ...
's '' First Ladies: Influence & Image''
* Michals, Debra"Abigail Adams"
National Women's History Museum. 2015. , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Adams, Abigail 1744 births 1818 deaths 18th-century American women writers 18th-century American writers 18th-century Unitarians 18th-century letter writers 19th-century American women 19th-century Unitarians Adams political family American Congregationalists American Unitarians American feminists American letter writers American people of English descent Burials in Massachusetts Colonial American women Deaths from typhoid fever First Ladies of the United States Infectious disease deaths in Massachusetts Mothers of presidents of the United States People from Braintree, Massachusetts People from Weymouth, Massachusetts People of Massachusetts in the American Revolution People of colonial Massachusetts Quincy family Second Ladies of the United States Women in the American Revolution Women letter writers