ANRORC mechanism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ANRORC mechanism in  The exclusion of a second intermediate in this reaction, the
The exclusion of a second intermediate in this reaction, the  More evidence is gained by
More evidence is gained by 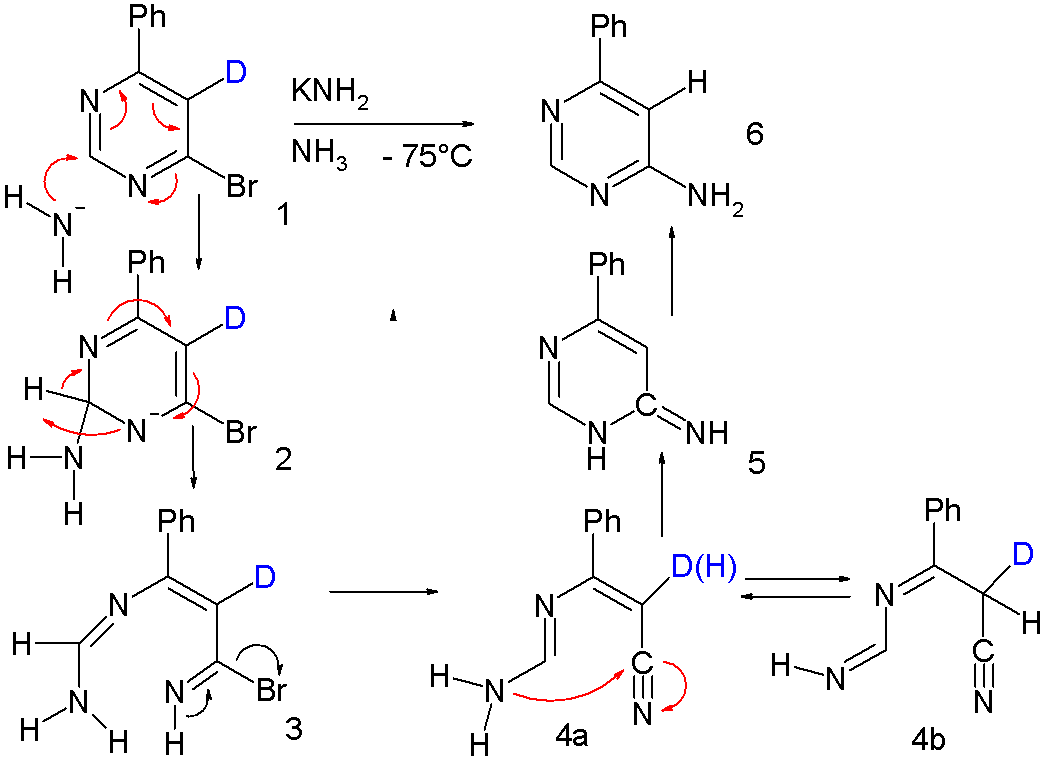 The final piece of evidence is provided by an isotope scrambling experiment with both nitrogen atoms in the pyrimidine core replaced by the 14N
The final piece of evidence is provided by an isotope scrambling experiment with both nitrogen atoms in the pyrimidine core replaced by the 14N  In the final product 4 (reversed to the reactant, after acid hydrolysis and bromination of 2) roughly half the isotope content is lost, clearly demonstrating that one internal nitrogen atom has been displaced to an external nitrogen atom.
The
In the final product 4 (reversed to the reactant, after acid hydrolysis and bromination of 2) roughly half the isotope content is lost, clearly demonstrating that one internal nitrogen atom has been displaced to an external nitrogen atom.
The
organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; ...
describes a special type of substitution reaction
A substitution reaction (also known as single displacement reaction or single substitution reaction) is a chemical reaction during which one functional group in a chemical compound is replaced by another functional group. Substitution reactions ar ...
. ANRORC stands for Addition of the Nucleophile, Ring Opening, and Ring Closure in nucleophilic attack on ring systems and it helps to explain product formation and distribution in some nucleophilic substitution
In chemistry, a nucleophilic substitution is a class of chemical reactions in which an electron-rich chemical species (known as a nucleophile) replaces a functional group within another electron-deficient molecule (known as the electrophile). The ...
s especially in heterocyclic compound
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and ...
s. It is widely used in medicinal chemistry
Medicinal or pharmaceutical chemistry is a scientific discipline at the intersection of chemistry and pharmacy involved with designing and developing pharmaceutical drugs. Medicinal chemistry involves the identification, synthesis and developm ...
.
This reaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs.
A chemical mechanism is a theoretical conjecture that tries to describe in detail what takes place at each stage of ...
has been extensively studied in reactions of metal amide nucleophiles (such as sodium amide
Sodium amide, commonly called sodamide (systematic name sodium azanide), is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a salt composed of the sodium cation and the azanide anion. This solid, which is dangerously reactive toward water, is whit ...
) and substituted pyrimidine
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other ...
s (for instance 4-phenyl-6-bromopyrimidine 1) in ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
at low temperatures. The main reaction product is 4-phenyl-6-aminopyrimidine 2 with the bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table (halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simila ...
substituent
A substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces (one or more) atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule. (In organic chemistry and biochemistry, the terms ''substituent'' and ''functional group'', as well as ''side ...
replaced by an amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituen ...
. This rules out the formation of an aryne
Arynes and benzynes are highly reactive species derived from an aromatic ring by removal of two substituents. Arynes are examples of didehydroarenes (1,2-didehydroarenes in this case), although 1,3- and 1,4-didehydroarenes are also known. Arynes ar ...
intermediate A which would also give the 5-substituted isomer.
 The exclusion of a second intermediate in this reaction, the
The exclusion of a second intermediate in this reaction, the Meisenheimer complex A Meisenheimer complex or Jackson–Meisenheimer complex in organic chemistry is a 1:1 reaction adduct between an arene carrying electron withdrawing groups and a nucleophile. These complexes are found as reactive intermediates in nucleophilic aroma ...
B in favor of the ring-opened ANRORC intermediate is based on several pieces of evidence. With other amines such as piperidine
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)5NH. This heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene bridges (–CH2–) and one amine bridge (–NH–). It is a colorless ...
the ring-opened compound after loss of hydrogen bromide
Hydrogen bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a hydrogen halide consisting of hydrogen and bromine. A colorless gas, it dissolves in water, forming hydrobromic acid, which is saturated at 68.85% HBr by weight at room temper ...
to the nitrile
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a functional group. The prefix ''cyano-'' is used interchangeably with the term ''nitrile'' in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including met ...
is also the isolated reaction product:
 More evidence is gained by
More evidence is gained by isotope labeling
Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope (an atom with a detectable variation in neutron count) through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific ...
with deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two Stable isotope ratio, stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being Hydrogen atom, protium, or hydrogen-1). The atomic nucleus, nucleus of a deuterium ato ...
at C5:
The deuterium atom is no longer present in the reaction product and this is again explained by the ANRORC mechanism where the ring-opened intermediate 4 is a tautomer
Tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert.
The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydr ...
ic pair enabling fast H-D exchange:
 The final piece of evidence is provided by an isotope scrambling experiment with both nitrogen atoms in the pyrimidine core replaced by the 14N
The final piece of evidence is provided by an isotope scrambling experiment with both nitrogen atoms in the pyrimidine core replaced by the 14N isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) ...
to a degree of 3% each:
 In the final product 4 (reversed to the reactant, after acid hydrolysis and bromination of 2) roughly half the isotope content is lost, clearly demonstrating that one internal nitrogen atom has been displaced to an external nitrogen atom.
The
In the final product 4 (reversed to the reactant, after acid hydrolysis and bromination of 2) roughly half the isotope content is lost, clearly demonstrating that one internal nitrogen atom has been displaced to an external nitrogen atom.
The Zincke reaction
The Zincke reaction is an organic reaction, named after Theodor Zincke, in which a pyridine is transformed into a pyridinium salt by reaction with 2,4-dinitro-chlorobenzene and a primary amine.
The Zincke reaction should not be confused with th ...
is a named reaction involving an ANRORC mechanism.
References
{{Reflist Reaction mechanisms