AIM-4 Falcon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Hughes AIM-4 Falcon was the first operational guided
The Hughes AIM-4 Falcon was the first operational guided
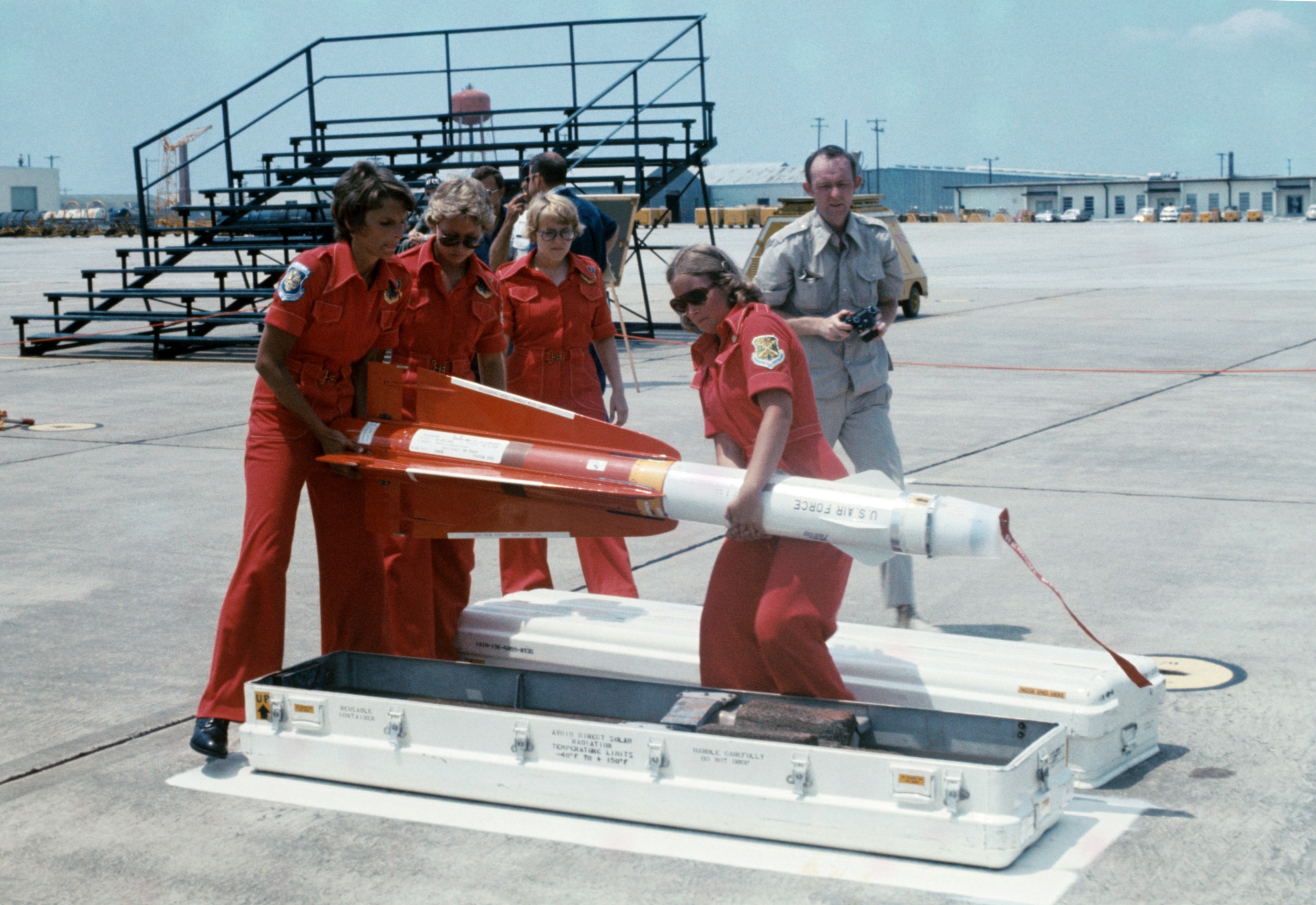
 All of the early Falcons had a small 7.6 lb (3.4 kg) warhead, limiting their lethal radius. Also limiting them tactically was the fact that Falcon lacked a
All of the early Falcons had a small 7.6 lb (3.4 kg) warhead, limiting their lethal radius. Also limiting them tactically was the fact that Falcon lacked a
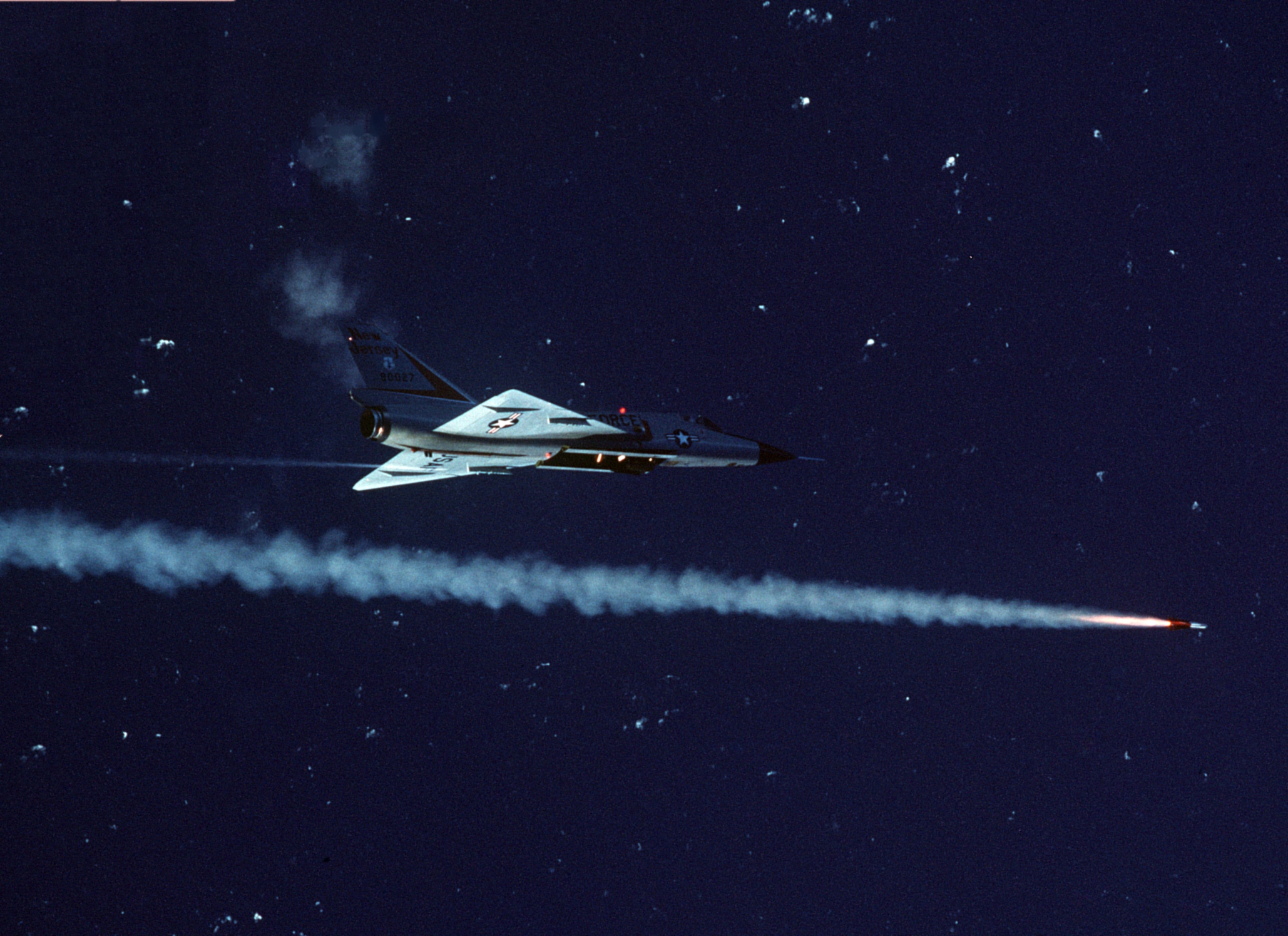
 The weapon was unpopular with pilots from the onset and was supplemented or partially withdrawn in 1969, to be replaced in the F-4D by the Sidewinder after retrofitting the proper wiring. Colonel Robin Olds, USAF, commanding the F-4D-equipped
The weapon was unpopular with pilots from the onset and was supplemented or partially withdrawn in 1969, to be replaced in the F-4D by the Sidewinder after retrofitting the proper wiring. Colonel Robin Olds, USAF, commanding the F-4D-equipped
 *Length: /
*Wingspan:
*Diameter:
*Weight: /
*Speed: Mach 3
*Range
*Guidance:
*Length: /
*Wingspan:
*Diameter:
*Weight: /
*Speed: Mach 3
*Range
*Guidance:
 The Hughes AIM-4 Falcon was the first operational guided
The Hughes AIM-4 Falcon was the first operational guided air-to-air missile
The newest and the oldest member of Rafael's Python family of AAM for comparisons, Python-5 (displayed lower-front) and Shafrir-1 (upper-back)
An air-to-air missile (AAM) is a missile fired from an aircraft for the purpose of destroying a ...
of the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Si ...
. Development began in 1946; the weapon was first tested in 1949. The missile entered service with the USAF in 1956.
Produced in both heat-seeking and radar-guided versions, the missile served during the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
with USAF McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II
The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II is an American tandem two-seat, twin-engine, all-weather, long-range supersonic jet interceptor and fighter-bomber originally developed by McDonnell Aircraft for the United States Navy.Swanborough and B ...
units. Designed to shoot down slow bombers with limited maneuverability, it was ineffective against maneuverable fighters over Vietnam. Lacking proximity fusing, the missile would only detonate if a direct hit was scored. Only five kills were recorded.
With the AIM-4's poor kill record rendering the F-4 ineffective at air-to-air combat, the fighters were modified to carry the USN-designed AIM-9 Sidewinder
The AIM-9 Sidewinder (where "AIM" stands for "Air Intercept Missile") is a short-range air-to-air missile which entered service with the US Navy in 1956 and subsequently was adopted by the US Air Force in 1964. Since then the Sidewinder has prove ...
missile instead, which was already carried on USN and USMC F-4 Phantom II
The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II is an American tandem two-seat, twin-engine, all-weather, long-range supersonic jet interceptor and fighter-bomber originally developed by McDonnell Aircraft for the United States Navy.Swanborough and ...
and F-8 Crusader jet fighters. The Sidewinder was much more effective and improved versions continue to serve the armed forces of the United States and numerous allied nations to this day.
Development
Defensive concept
Development of a guided air-to-air missile began in 1946.Hughes Aircraft
The Hughes Aircraft Company was a major American aerospace and defense contractor founded on February 14, 1934 by Howard Hughes in Glendale, California, as a division of Hughes Tool Company. The company was known for producing, among other pro ...
was awarded a contract for a subsonic missile under the project designation MX-798, which soon gave way to the supersonic
Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound ( Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately . Speeds greater than five times ...
MX-904 in 1947.
The original purpose of the weapon was as a self-defense weapon for bomber aircraft
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped from an air ...
, which would carry a magazine of three missiles in the rear fuselage, and fire them through a long tube that led through the area that normally held the tail turret. In the case of the B-52
The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress is an American long-range, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber. The B-52 was designed and built by Boeing, which has continued to provide support and upgrades. It has been operated by the United States Air ...
, the missile contained a tuner for the bomber's A-3 rear-facing radar, and would follow the signal being reflected off the target aircraft using a semi-active radar homing
Semi-active radar homing (SARH) is a common type of missile guidance system, perhaps the most common type for longer-range air-to-air and surface-to-air missile systems. The name refers to the fact that the missile itself is only a passive de ...
(SARH) system.
Anti-bomber development
At the same time that the original MX-798 had been released, a specification for a forward-firing missile forfighter aircraft
Fighter aircraft are fixed-wing military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield ...
had been released as MX-799. This had progressed to the point of testing prototype rounds, as the AAM-A-1 Firebird, when its subsonic speed and manual guidance were realized to be serious problems.
The project was cancelled, and the recently released MX-904 was redirected to replace Firebird in the anti-bomber role. At this stage the weapon was still designed to be fired out of a tube, now leading from a weapon bay behind the nose-mounted radar with the launch tube exiting below the radar antenna. Instead of a magazine with multiple missiles, three missiles were placed in the tube tip-to-tail.
Housing in a tube presented several problems, but primary among them was that there was no way for the missile's seeker to lock-on before launch. The original concept would be firing against interceptor aircraft
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are ...
that were slowly approaching the B-52 and would be somewhere fairly close to directly behind the aircraft. In the case of a fighter, the target might not be so conveniently located, and with no way to know if it could see the target while inside the tube, this meant it might never lock-on properly.
Eventually, it was decided to abandon the tube-launched concept and mount the missile on the wings or in weapon bays that would point the missile at the target prior to launch. This change also allowed the seeker to use infrared homing
Infrared homing is a passive weapon guidance system which uses the infrared (IR) light emission from a target to track and follow it seamlessly. Missiles which use infrared seeking are often referred to as "heat-seekers" since infrared is rad ...
as well as SARH. Interchangeable seekers were developed, allowing an aircraft to carry either type, or both. Additionally, freed from the tube, the missile's wings were allowed to grow larger and took on the long delta form that it and its various descendants would carry into the 2000s.
Testing and service
The first test firings took place in 1949, at which time it was designated AAM-A-2 and given the popular name Falcon. A brief policy of assigning fighter and bomber designations to missiles led it to be redesignated F-98 in 1951. In 1955, the policy changed again, and the missile was again redesignated GAR-1. The initial GAR-1 and GAR-2 models entered service in 1956. It armed theNorthrop F-89 Scorpion
The Northrop F-89 Scorpion was an American all-weather, twin-engined interceptor aircraft built during the 1950s, the first jet-powered aircraft designed for that role from the outset to enter service. Though its straight wings limited its per ...
, McDonnell F-101B Voodoo
The McDonnell F-101 Voodoo is a supersonic jet fighter which served the United States Air Force (USAF) and the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF).
Initially designed by McDonnell Aircraft Corporation as a long-range bomber escort (known as a '' ...
and Convair F-102 Delta Dagger
The Convair F-102 Delta Dagger was an American interceptor aircraft designed and manufactured by Convair.
Built as part of the backbone of the United States Air Force's air defenses in the late 1950s, it entered service in 1956. Its main purpo ...
and F-106 Delta Dart
The Convair F-106 Delta Dart was the primary all-weather interceptor aircraft of the United States Air Force from the 1960s through to the 1980s. Designed as the so-called "Ultimate Interceptor", it proved to be the last specialist interceptor ...
interceptors. The only other users were Canada, Finland, Sweden and Switzerland, whose CF-101 Voodoo, Saab 35 Draken
The Saab 35 Draken (; 'The Kite' or 'The Dragon') is a Swedish fighter-interceptor developed and manufactured by Svenska Aeroplan Aktiebolaget ( SAAB) between 1955 and 1974. Development of the Saab 35 Draken started in 1948 as the Swedish air f ...
and Dassault Mirage III
The Dassault Mirage III () is a family of single/dual-seat, single-engine, fighter aircraft developed and manufactured by French aircraft company Dassault Aviation. It was the first Western European combat aircraft to exceed Mach number, Mach 2 ...
S carried the Falcon. Canada also hoped to use them on the Avro Canada CF-105 Arrow interceptor; however, this was never realized because of the Arrow's cancellation.
Fighters carrying the Falcon were often designed with internal weapons bays for carrying this missile. The Scorpion carried them on wingtip pods, while the Delta Dagger and Delta Dart had belly bays with a trapeze mechanism to move them into the airstream for launch. The F-101B had an unusual bay arrangement where two were stored externally, and then the bay door would rotate to expose two more missiles. It is likely the General Dynamics F-111's internal bay would have accommodated the missile as well, but by the time of service the Air Force had already dropped the Falcon for use against fighters, as well as the idea of using the F-111 as an air combat fighter.
The GAR-1 had semi-active radar homing
Semi-active radar homing (SARH) is a common type of missile guidance system, perhaps the most common type for longer-range air-to-air and surface-to-air missile systems. The name refers to the fact that the missile itself is only a passive de ...
(SARH), giving a range of about . About 4,000 missiles were produced. It was replaced in production by the GAR-1D (later AIM-4A), with larger control surfaces. About 12,000 of this variant were produced, the major production version of the SARH Falcon.
The GAR-2 (later AIM-4B) was a heat-seeker, generally limited to rear-aspect engagements, but with the advantage of being a ' fire and forget' weapon. As would also be Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
practice, it was common to fire the weapon in salvos of both types to increase the chances of a hit (a heat-seeking missile fired first, followed moments later by a radar-guided missile). The GAR-2 was about 1.5 in (40 mm) longer and 16 lb (7 kg) heavier than its SARH counterpart. Its range was similar. It was replaced in production by the GAR-2A (later AIM-4C), with a more sensitive infrared seeker. A total of about 26,000 of the infrared-homing Falcons were built.

proximity fuze
A proximity fuze (or fuse) is a fuze that detonates an explosive device automatically when the distance to the target becomes smaller than a predetermined value. Proximity fuzes are designed for targets such as planes, missiles, ships at sea, an ...
: the fuzing for the missile was in the leading edges of the wings, requiring a direct hit to detonate.
In 1958, Hughes introduced a slightly enlarged version of the Falcon, initially dubbed Super Falcon, with a more powerful, longer-burning rocket engine, increasing speed and range. It had a larger warhead (28.7 lb / 13 kg) and better guidance systems. The SARH versions were GAR-3 (AIM-4E) and the improved GAR-3A (AIM-4F). The infrared version was the GAR-4A (AIM-4G). About 2,700 SARH missiles and 3,400 IR Super Falcons were produced, replacing most earlier versions of the weapon in service.
The Falcon was redesignated AIM-4 in September 1962.
The final version of the original Falcon was the GAR-2B (later AIM-4D), which entered service in 1963. This was intended as a fighter combat weapon, combining the lighter, smaller airframe of the earlier GAR-1/GAR-2 weapon with the improved IR seeker of the GAR-4A/AIM-4G.
An effort to address the limitations of AIM-4D led to the development in 1970 of the XAIM-4H, which had a laser proximity fuze
A proximity fuze (or fuse) is a fuze that detonates an explosive device automatically when the distance to the target becomes smaller than a predetermined value. Proximity fuzes are designed for targets such as planes, missiles, ships at sea, an ...
, new warhead, and better maneuverability. It was cancelled the following year without entering service.
A larger version of the Falcon carrying a 0.25-kiloton nuclear warhead was developed as the GAR-11 (later designated the AIM-26 Falcon
The AIM-26 Falcon was a larger, more powerful version of the AIM-4 Falcon air-to-air missile built by Hughes. It is the only guided American air-to-air missile with a nuclear warhead to be produced; the unguided AIR-2 Genie rocket was also nucle ...
), while a long-range version was developed for the North American XF-108 Rapier
The North American XF-108 Rapier was a proposed long-range, high-speed interceptor aircraft designed by North American Aviation intended to defend the United States from supersonic Soviet strategic bombers. The aircraft would have cruised at ...
and Lockheed YF-12
The Lockheed YF-12 was an American Mach 3+ capable, high-altitude interceptor prototype, developed and manufactured by American aerospace company Lockheed Corporation.
It was developed during the late 1950s and early 1960s as a potent ...
interceptors as the GAR-9 (later AIM-47 Falcon
The Hughes AIM-47 Falcon, originally GAR-9, was a very long-range high-performance air-to-air missile that shared the basic design of the earlier AIM-4 Falcon. It was developed in 1958 along with the new Hughes AN/ASG-18 radar fire-control syst ...
).
Operational history
The Air Force deployed AIM-4 in May 1967 during theVietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
on the new F-4D Phantom II
The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II is an American tandem two-seat, twin-engine, all-weather, long-range supersonic jet interceptor and fighter-bomber originally developed by McDonnell Aircraft for the United States Navy.Swanborough and ...
, which carried it on the inner wing pylons and was not wired to carry the AIM-9 Sidewinder
The AIM-9 Sidewinder (where "AIM" stands for "Air Intercept Missile") is a short-range air-to-air missile which entered service with the US Navy in 1956 and subsequently was adopted by the US Air Force in 1964. Since then the Sidewinder has prove ...
. The missile's combat performance was very poor. The Falcon, already operational on Air Defense Command
Aerospace Defense Command was a major command of the United States Air Force, responsible for continental air defense. It was activated in 1968 and disbanded in 1980. Its predecessor, Air Defense Command, was established in 1946, briefly inac ...
aircraft, was designed to be used against bombers, and its slow seeker cooling times (as much as six or seven seconds to obtain a lock on a target) rendered it largely ineffective against maneuvering fighters. Moreover, it could only be cooled once. Limited coolant supply meant that once cooled, the missile would expend its supply of liquid nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen—LN2—is nitrogen in a liquid state at low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, low viscosity liquid that is wid ...
in two minutes, rendering it useless on the rail. The missile also had a small warhead, and lacked proximity fusing. As a result, only five kills were scored, all with the AIM-4D version. (The Falcon was also experimentally fired by the F-102 Delta Dagger against ground targets at night using its infrared seeker.)

 The weapon was unpopular with pilots from the onset and was supplemented or partially withdrawn in 1969, to be replaced in the F-4D by the Sidewinder after retrofitting the proper wiring. Colonel Robin Olds, USAF, commanding the F-4D-equipped
The weapon was unpopular with pilots from the onset and was supplemented or partially withdrawn in 1969, to be replaced in the F-4D by the Sidewinder after retrofitting the proper wiring. Colonel Robin Olds, USAF, commanding the F-4D-equipped 8th Tactical Fighter Wing
The United States Air Force 8th Fighter Wing is the host unit at Kunsan Air Base, Republic of Korea and is assigned to Seventh Air Force. Seventh Air Force falls under Pacific Air Forces (PACAF). The Wing's 8th Operations Group is the success ...
, was an outspoken critic of the missile and said of it:
By the beginning of June, we all hated the new AIM-4 Falcon missiles. I loathed the damned useless things. I wanted my Sidewinders back. In two missions I had fired seven or eight of the bloody things and not one guided. They were worse than I had anticipated. Sometimes they refused to launch; sometimes they just cruised off into the blue without guiding. In the thick of an engagement with my head twisting and turning, trying to keep track of friend and foe, I'd forget which of the four I had (already) selected and couldn't tell which of the remaining was perking and which head was already expiring on its launch rail. Twice upon returning to base I had the tech rep go over the switchology and firing sequences. We never discovered I was doing anything wrong.Colonel Olds became exasperated with the Falcon's poor combat performance. He ordered his entire fighter wing to rewire the F-4Ds to carry more reliable AIM-9 Sidewinders. Although it was an unauthorized field modification, the entire air force eventually followed his example.
Vietnam War: U.S. AIM-4 Falcon Air to Air Victories
Used from 1965 through 1972 in Vietnam, Falcons achieved their only kills duringOperation Rolling Thunder
Operation Rolling Thunder was a gradual and sustained aerial bombardment campaign conducted by the United States (U.S.) 2nd Air Division (later Seventh Air Force), U.S. Navy, and Republic of Vietnam Air Force (RVNAF) against the Democratic R ...
(1965–68) during which time only 5 successful hits were scored from 54 launchings during aerial combat.Michel III p. 156
The AIM-4 was also produced as the HM-55S (radar-guided) for the Swiss Air Force
The Swiss Air Force (german: Schweizer Luftwaffe; french: Forces aériennes suisses; it, Forze aeree svizzere; rm, Aviatica militara svizra) is the air component of the Swiss Armed Forces, established on 31 July 1914 as a part of the army an ...
for use on the Dassault Mirage III
The Dassault Mirage III () is a family of single/dual-seat, single-engine, fighter aircraft developed and manufactured by French aircraft company Dassault Aviation. It was the first Western European combat aircraft to exceed Mach number, Mach 2 ...
S, and license-manufactured in Sweden for the Swedish Air Force
The Swedish Air Force ( sv, Svenska flygvapnet or just ) is the air force branch of the Swedish Armed Forces.
History
The Swedish Air Force was created on 1 July, 1926 when the aircraft units of the Army and Navy were merged. Because of the e ...
(as the Rb 28) to equip the Saab 35 Draken
The Saab 35 Draken (; 'The Kite' or 'The Dragon') is a Swedish fighter-interceptor developed and manufactured by Svenska Aeroplan Aktiebolaget ( SAAB) between 1955 and 1974. Development of the Saab 35 Draken started in 1948 as the Swedish air f ...
and 37 Viggen. The seeker of the missile was also redesigned.
The AIM-4F/AIM-4G Super Falcon remained in USAF
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part ...
and ANG service, primarily with Convair F-102 Delta Dagger
The Convair F-102 Delta Dagger was an American interceptor aircraft designed and manufactured by Convair.
Built as part of the backbone of the United States Air Force's air defenses in the late 1950s, it entered service in 1956. Its main purpo ...
and F-106 Delta Dart
The Convair F-106 Delta Dart was the primary all-weather interceptor aircraft of the United States Air Force from the 1960s through to the 1980s. Designed as the so-called "Ultimate Interceptor", it proved to be the last specialist interceptor ...
interceptors, until the final retirement of the F-106 in 1988. These aircraft had been designed to carry the weapon and could not be easily converted to carry larger weapons like the Sidewinder or AIM-7 Sparrow
The AIM-7 Sparrow (Air Intercept Missile) is an American, medium-range semi-active radar homing air-to-air missile operated by the United States Air Force, United States Navy, and United States Marine Corps, as well as other various air forces ...
, which were much longer.
Operators

Former operators
; *Royal Canadian Air Force
The Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF; french: Aviation royale canadienne, ARC) is the air and space force of Canada. Its role is to "provide the Canadian Forces with relevant, responsive and effective airpower". The RCAF is one of three environm ...
*Canadian Forces
}
The Canadian Armed Forces (CAF; french: Forces armées canadiennes, ''FAC'') are the unified military forces of Canada, including sea, land, and air elements referred to as the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army, and Royal Canadian Air Force.
...
;
*Finnish Air Force
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries =
, equipment = 159
, equipment_label ...
– (Swedish-built missiles)
;
*Hellenic Air Force
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = 8 November
, equipment =
, equipment_label ...
;
*Swedish Air Force
The Swedish Air Force ( sv, Svenska flygvapnet or just ) is the air force branch of the Swedish Armed Forces.
History
The Swedish Air Force was created on 1 July, 1926 when the aircraft units of the Army and Navy were merged. Because of the e ...
– (Licence built by SAAB)
;
*Swiss Air Force
The Swiss Air Force (german: Schweizer Luftwaffe; french: Forces aériennes suisses; it, Forze aeree svizzere; rm, Aviatica militara svizra) is the air component of the Swiss Armed Forces, established on 31 July 1914 as a part of the army an ...
;
*Turkish Air Force
The Turkish Air Force ( tr, ) is the aerial warfare service branch of the Turkish Armed Forces. The Turkish Air Force can trace its origins back to June 1911 when it was founded by the Ottoman Empire, however, the air force as it is known to ...
;
*United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Si ...
Specifications (GAR-1D/ -2B / AIM-4C/D)
 *Length: /
*Wingspan:
*Diameter:
*Weight: /
*Speed: Mach 3
*Range
*Guidance:
*Length: /
*Wingspan:
*Diameter:
*Weight: /
*Speed: Mach 3
*Range
*Guidance: semi-active radar homing
Semi-active radar homing (SARH) is a common type of missile guidance system, perhaps the most common type for longer-range air-to-air and surface-to-air missile systems. The name refers to the fact that the missile itself is only a passive de ...
/ rear-aspect infrared homing
Infrared homing is a passive weapon guidance system which uses the infrared (IR) light emission from a target to track and follow it seamlessly. Missiles which use infrared seeking are often referred to as "heat-seekers" since infrared is rad ...
*Warhead: high explosive
See also
Related Development: *AIM-26 Falcon
The AIM-26 Falcon was a larger, more powerful version of the AIM-4 Falcon air-to-air missile built by Hughes. It is the only guided American air-to-air missile with a nuclear warhead to be produced; the unguided AIR-2 Genie rocket was also nucle ...
*AIM-47 Falcon
The Hughes AIM-47 Falcon, originally GAR-9, was a very long-range high-performance air-to-air missile that shared the basic design of the earlier AIM-4 Falcon. It was developed in 1958 along with the new Hughes AN/ASG-18 radar fire-control syst ...
*AIM-54 Phoenix
The AIM-54 Phoenix is an American radar-guided, long-range air-to-air missile (AAM), carried in clusters of up to six missiles on the Grumman F-14 Tomcat, its only operational launch platform.
The Phoenix was the United States' only long-range ...
References
Notes
Bibliography
* *The history of the ''Falcon'' missile, and its various configurations, is examined in Gart, Jason H. "Electronics and Aerospace Industry in Cold War Arizona, 1945-1968: Motorola, Hughes Aircraft, Goodyear Aircraft." Phd diss., Arizona State University, 2006. *Leighton, David, ""The History of the Hughes Missile Plant in Tucson, 1947-1960," Private Publication, 2015 *McCarthy Jr. Donald J. ''MiG Killers, A Chronology of U.S. Air Victories in Vietnam 1965-1973.'' 2009, Specialty Press. . *Michel III, Marshall L. '' Clashes, Air Combat Over North Vietnam 1965-1972.'' 1997, Naval Institute Press. . {{DEFAULTSORT:Aim-4 Falcon Cold War air-to-air missiles of the United States Military equipment introduced in the 1950s