Ayrton–Perry Winding on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
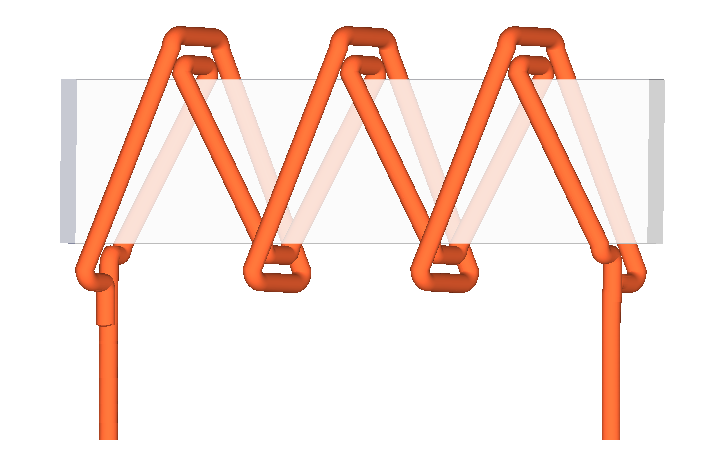 An Ayrton–Perry winding (named for
An Ayrton–Perry winding (named for
 An Ayrton–Perry winding (named for
An Ayrton–Perry winding (named for William Edward Ayrton
William Edward Ayrton, FRS (14 September 18478 November 1908) was an English physicist and electrical engineer.
Life
Early life and education
Ayrton was born in London, the son of Edward Nugent Ayrton, a barrister, and educated at Universit ...
and John Perry) is a type of bifilar winding
A bifilar coil is an electromagnetic coil that contains two closely spaced, parallel windings. In engineering, the word ''bifilar'' describes wire which is made of two filaments or strands. It is commonly used to denote special types of winding ...
pattern used in winding wire on forms to make electronic component
An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not ...
s. Its advantage is that the resulting coil of wire has low values of parasitic inductance
In electrical networks, a parasitic element is a circuit element ( resistance, inductance or capacitance) that is possessed by an electrical component but which it is not desirable for it to have for its intended purpose. For instance, a resis ...
and parasitic capacitance
Parasitic capacitance is an unavoidable and usually unwanted capacitance that exists between the parts of an electronic component or circuit simply because of their proximity to each other. When two electrical conductors at different voltages a ...
.K. Padmanabhan, Electronic Components, Laxmi Publications, , page 16 Ayrton–Perry windings of resistance wire
Resistance wire is wire intended for making electrical resistors (which are used to control the amount of current in a circuit). It is better if the alloy used has a high resistivity, since a shorter wire can then be used. In many situations, the ...
are used to make wirewound RF resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active el ...
s that are used at high frequencies, where inductance and capacitance are unwanted.
The winding is made of two separate wires wound in opposing directions along an insulating form and connected in parallel at the ends. Since there are the same number of turns of wire in either direction, the magnetic fields of the two wires cancel each other out, so the coil has little inductance; and since adjacent turns of the two wires are at approximately the same voltage, there is little parasitic capacitance between the turns.
One disadvantage is that because the two lengths of resistive wire are connected in parallel, four times the length of wire (twice the length for each coil) is needed to make a given resistance, compared to when a single coil is used.
See also
*Bifilar winding
A bifilar coil is an electromagnetic coil that contains two closely spaced, parallel windings. In engineering, the word ''bifilar'' describes wire which is made of two filaments or strands. It is commonly used to denote special types of winding ...
* Basket winding
Basket winding (or basket-weave winding or honeycomb winding or scatter winding) is a winding method for electrical wire in a coil. The winding pattern is used for radio-frequency electronic components with many parallel wires, such as inductors ...
References
Electromagnetic coils {{electronics-stub