Austroposeidon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Austroposeidon'' is a
 ''Austroposeidon'' was a large sauropod, the largest dinosaur discovered in Brazil, with the only known specimen, an adult, having a length of about .
Several traits show that ''Austroposeidon'' was a
''Austroposeidon'' was a large sauropod, the largest dinosaur discovered in Brazil, with the only known specimen, an adult, having a length of about .
Several traits show that ''Austroposeidon'' was a

 A phylogenetic analysis in 2016 recovered ''Austroposeidon'' as the sister taxon of the Lognkosauria. An updated version was published by Silva ''et al.'' (2019), where the only significant changes from the original, based on a redescription of '' Uberabatitan'', was the movement of ''Uberabatitan'' and ''Brasilotitan'' from Saltasaurinae to Aeolosaurini.
A phylogenetic analysis in 2016 recovered ''Austroposeidon'' as the sister taxon of the Lognkosauria. An updated version was published by Silva ''et al.'' (2019), where the only significant changes from the original, based on a redescription of '' Uberabatitan'', was the movement of ''Uberabatitan'' and ''Brasilotitan'' from Saltasaurinae to Aeolosaurini.
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
of titanosaur
Titanosaurs (or titanosaurians; members of the group Titanosauria) were a diverse group of sauropod dinosaurs, including genera from all seven continents. The titanosaurs were the last surviving group of long-necked sauropods, with taxa still thr ...
ian sauropod dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
from the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
Presidente Prudente Formation
The Presidente Prudente Formation is a geological formation of the Bauru Group in the Paraná Basin, located in Brazil whose strata date back to the Late Campanian to Early Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, ...
of Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
. It contains one species, ''Austroposeidon magnificus'' (meaning "Magnificent Southern Poseidon").
Discovery and naming
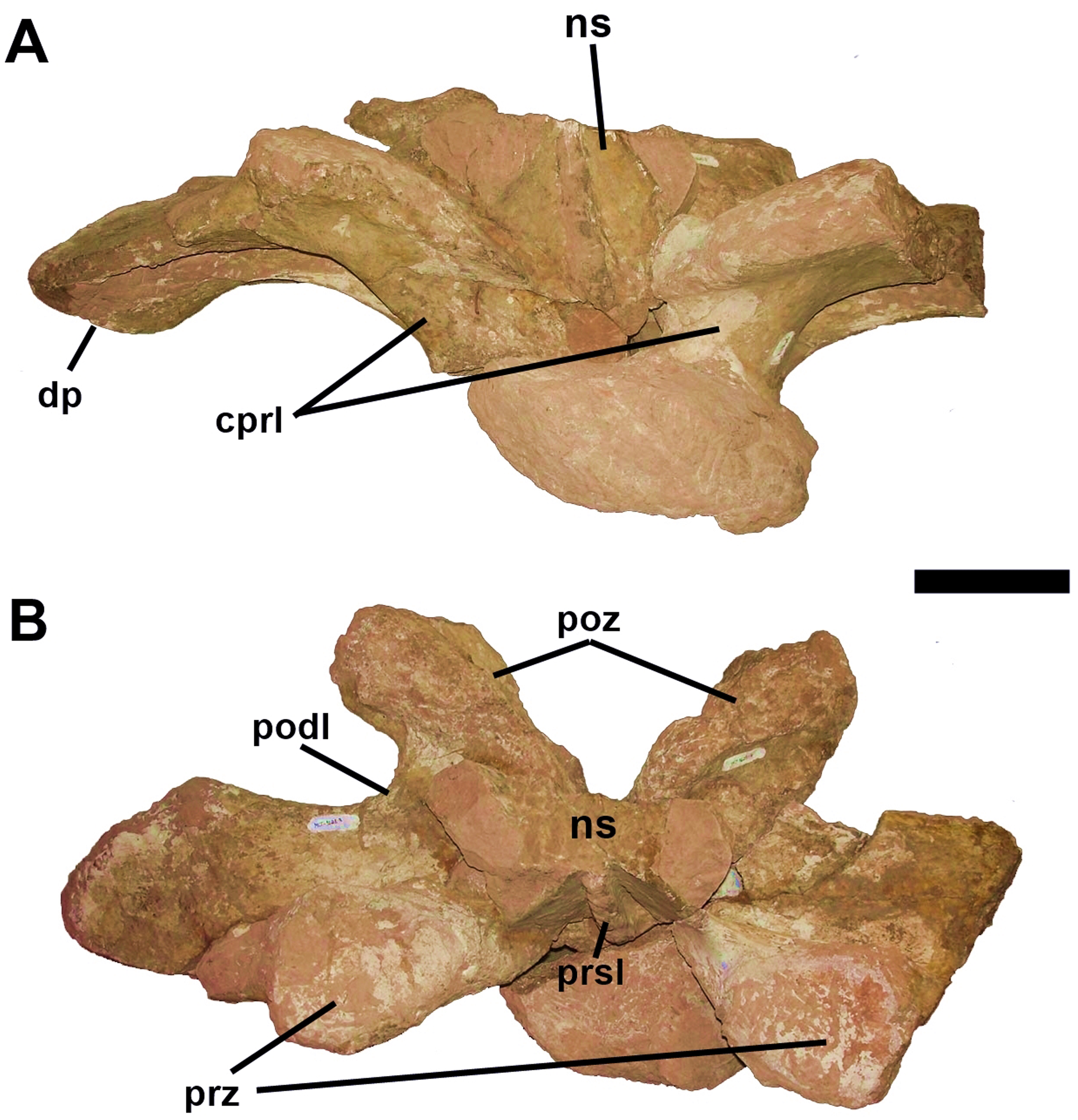
''Austroposeidon'' is known from a single specimen, MCT 1628-R, which consists of portions of the cervical (neck), dorsal (back), and sacral (hip) vertebrae (including a cervical rib and one complete dorsal vertebra). The specimen was discovered in theCampanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campani ...
-Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval ...
Presidente Prudente Formation
The Presidente Prudente Formation is a geological formation of the Bauru Group in the Paraná Basin, located in Brazil whose strata date back to the Late Campanian to Early Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, ...
of the Bauru Group
The Bauru Group is a geological group of the Bauru Sub-basin, Paraná Basin in Minas Gerais, São Paulo, General Salgado, Itapecuru-Mirim, Mato Grosso, Brazil whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils ...
by palaeontologist Llewellyn Ivor Price
Llewellyn Ivor Price (October 9, 1905 – June 9, 1980) was one of the first Brazilian paleontologists. His work contributed not only to the development of Brazilian but also to global paleontology. He collected '' Staurikosaurus'', the first ...
in 1953, but the remains were not described until 2016. The animal was likely preserved by a crevasse splay
A crevasse splay is a sedimentary fluvial deposit which forms when a stream breaks its natural or artificial levees and deposits sediment on a floodplain. A breach that forms a crevasse splay deposits sediments in similar pattern to an alluvial f ...
on a floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river which stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls, and which experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.Goudi ...
, judging by the fine sandstone that the specimen was found in. Unfortunately, the site where the specimen was recovered has now been lost to urban development.
The genus name combines ''austro'' ("southern", as in South America, from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''Auster'', the southern wind) and ''poseidon'', a reference to the Greek god of earthquakes of the same name. The specific name is the Latin word ''magnificus'' ("great, elevated, noble"), referring to the large size of the specimen.
Description
titanosaur
Titanosaurs (or titanosaurians; members of the group Titanosauria) were a diverse group of sauropod dinosaurs, including genera from all seven continents. The titanosaurs were the last surviving group of long-necked sauropods, with taxa still thr ...
; the hyposphene-hypantrum articulation The hyposphene-hypantrum articulation is an accessory joint found in the vertebrae of several fossil reptiles of the group Archosauromorpha. It consists of a process on the backside of the vertebrae, the hyposphene, that fits in a depression in the ...
s are missing from the vertebrae, the cervical and dorsal vertebrae do not have forked neural spine
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic ...
s, and the internal texture of the bone is camellate (punctuated by many small air chambers). The describers determined that ''Austroposeidon'' was a new genus based on a number of autapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an autapomorphy is a distinctive feature, known as a derived trait, that is unique to a given taxon. That is, it is found only in one taxon, but not found in any others or outgroup taxa, not even those most closely related to t ...
(traits unique to the known fossils) in the vertebrae: the thirteenth cervical vertebra has columnar centropostzygapophyseal laminae, and its rear centrodiapophyseal lamina splits into two prongs; the first dorsal vertebra has front and back centrodiapophyseal laminae that curve downwards and outwards, and its diapophysis stretches down to the top margin of the centrum
(Latin for ''center'') may refer to:
Places In Greenland
* Nuuk Centrum, a district of Nuuk, Greenland
* Centrum Lake, Greenland In the Netherlands
* Amsterdam-Centrum, the inner-most borough of Amsterdam, Netherlands
* Rotterdam Centrum, a borou ...
; and the frontmost part of the spinoprezygapophyseal laminae forks in the dorsal vertebrae positioned towards the back of the torso. Additionally, ''Austroposeidon'' possesses a unique combination of other vertebral traits, not seen elsewhere among titanosaurs.
A CT scan showed that the internal bone texture of the vertebrae possessed concentric, alternating rings of camellate tissue and dense tissue; the describers interpreted these as rings of growth within the bone.
Classification
See also
*2016 in paleontology
Flora Plants
Fungi
Cnidarians
Research
* '' Yunnanoascus haikouensis'', previously thought to be a member of Ctenophora, is reinterpreted as a crown-group medusozoan by Han ''et al.'' (2016).
* A study on the fossil corals from the Late Tr ...
References
{{Portal bar, Paleontology, Dinosaurs, Cretaceous Lithostrotians Campanian life Maastrichtian life Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of South America Cretaceous Brazil Fossils of Brazil Paraná Basin Fossil taxa described in 2016