Auisle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Auisle or Óisle ( non, Ásl or ; died c. 867) was a
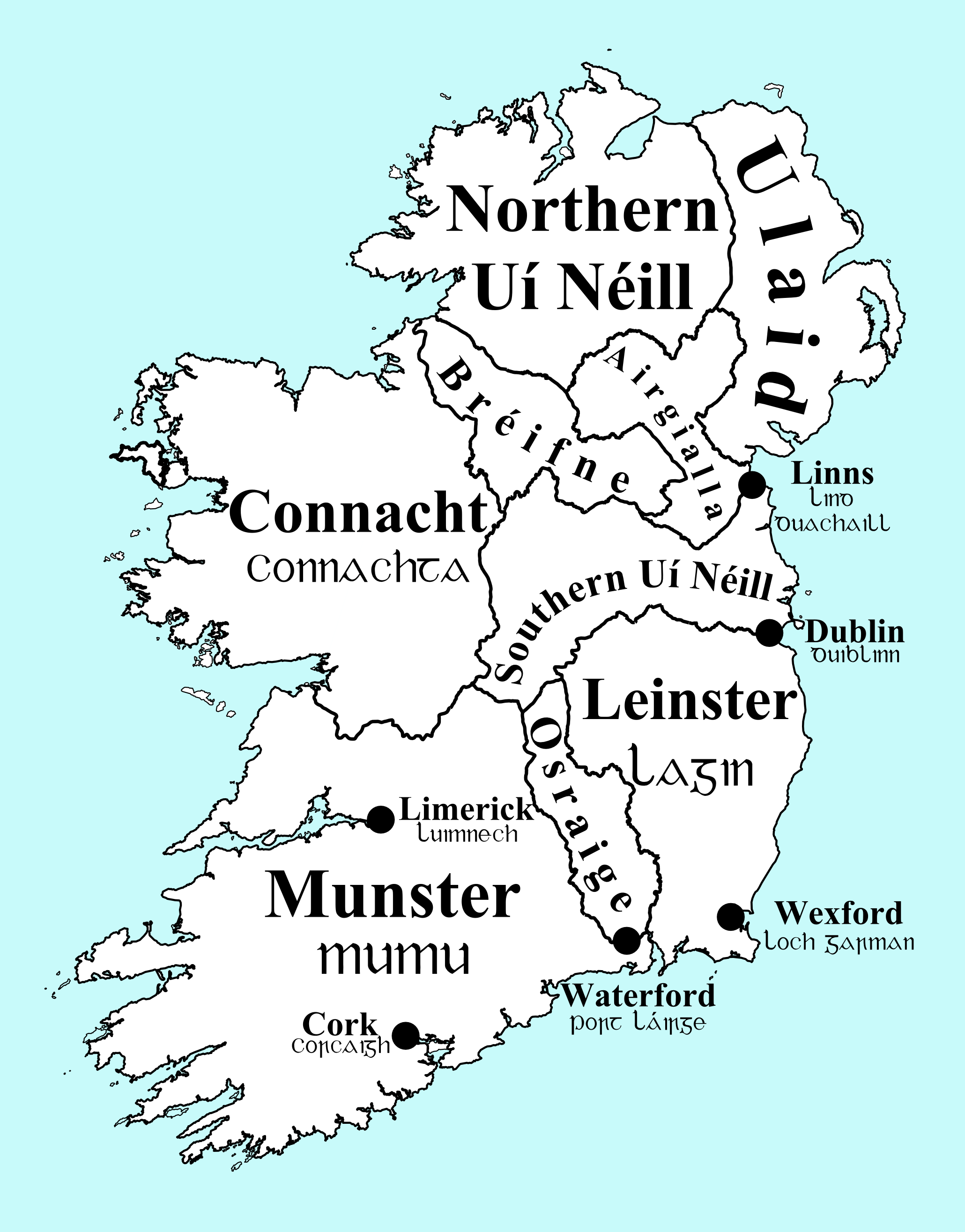 The earliest recorded Viking raids in Ireland occurred in 795. Over time, these raids increased in intensity, and they overwintered in Ireland for the first time in 840–841. Later in 841 a longphort was constructed at Áth Cliath (Irish for ''hurdled ford''), a site which would later develop into the city of Dublin. Longphorts were also established at other sites around Ireland, some of which developed into larger Viking settlements over time. The Viking population in Ireland was boosted in 851 with the arrival of a large group known as "dark foreigners" – a contentious term usually considered to mean the newly arrived Vikings, as opposed to the "fair foreigners", i.e. the Viking population which was resident prior to this influx. A kingdom in
The earliest recorded Viking raids in Ireland occurred in 795. Over time, these raids increased in intensity, and they overwintered in Ireland for the first time in 840–841. Later in 841 a longphort was constructed at Áth Cliath (Irish for ''hurdled ford''), a site which would later develop into the city of Dublin. Longphorts were also established at other sites around Ireland, some of which developed into larger Viking settlements over time. The Viking population in Ireland was boosted in 851 with the arrival of a large group known as "dark foreigners" – a contentious term usually considered to mean the newly arrived Vikings, as opposed to the "fair foreigners", i.e. the Viking population which was resident prior to this influx. A kingdom in
UK public library membership
required. * * * * * * *
at
Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
leader in Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
and Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
in the mid-late ninth century. He was the son of the king of Lochlann
In the modern Gaelic languages, () signifies Scandinavia or, more specifically, Norway. As such it is cognate with the Welsh name for Scandinavia, (). In both old Gaelic and old Welsh, such names literally mean 'land of lakes' or 'land of ...
, identified in the non-contemporary ''Fragmentary Annals of Ireland
The ''Fragmentary Annals of Ireland'' or ''Three Fragments'' are a Middle Irish combination of chronicles from various Irish annals and narrative history. They were compiled in the kingdom of Osraige, probably in the lifetime of Donnchad mac Gilla ...
'' as Gofraid
is an Irish masculine given name, arising in the Old Irish and Middle Irish/Middle Gaelic languages, as , and later partially Anglicised as Goffraid.
' corresponds to the Old Norse ', cognate with Gottfried or ', and Galfrid or '. ''Gofraid''/' ...
, and brother of Amlaíb Conung
Amlaíb Conung ( non, Óláfr ; died c. 874) was a Viking leader in Ireland and Scotland in the mid-late ninth century. He was the son of the king of Lochlann, identified in the non-contemporary ''Fragmentary Annals of Ireland'' as Gofraid, and br ...
and Ímar
Ímar ( non, Ívarr ; died c. 873), who may be synonymous with Ivar the Boneless, was a Viking leader in Ireland and Scotland in the mid-late ninth century who founded the Uí Ímair dynasty, and whose descendants would go on to dominate the Iri ...
, the latter of whom founded the Uí Ímair
The Uí Ímair (; meaning ‘''scions of Ivar’''), also known as the Ivar Dynasty or Ivarids was a royal Norse-Gael dynasty which ruled much of the Irish Sea region, the Kingdom of Dublin, the western coast of Scotland, including the Hebrides ...
dynasty, and whose descendants would go on to dominate the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
region for several centuries. Another Viking leader, Halfdan Ragnarsson
Halfdan Ragnarsson ( non, Hálfdan; oe, Halfdene or ''Healfdene''; sga, Albann; died 877) was a Viking leader and a commander of the Great Heathen Army which invaded the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England, starting in 865.
One of six sons of Ra ...
, is sometimes considered a brother. The Irish Annals
A number of Irish annals, of which the earliest was the Chronicle of Ireland, were compiled up to and shortly after the end of the 17th century. Annals were originally a means by which monks determined the yearly chronology of feast days. Over t ...
title Auisle, Ímar and Amlaíb "kings of the foreigners". Modern scholars use the title "kings of Dublin
Vikings invaded the territory around Dublin in the 9th century, establishing the Norsemen, Norse Kingdom of Dublin, the earliest and longest-lasting Norse kingdom in Ireland. Its territory corresponded to most of present-day County Dublin. The N ...
" after the Viking settlement which formed the base of their power.
Auisle is mentioned three times in contemporary annals. In the first entry, dated 863, he and his brothers are recorded as having raided Brega
Brega , also known as ''Mersa Brega'' or ''Marsa al-Brega'' ( ar, مرسى البريقة , i.e. "Brega Seaport"), is a complex of several smaller towns, industry installations and education establishments situated in Libya on the Gulf of Sidra, ...
, including underground tombs at Achad Aldai, Cnodba, and Dubad. The second, dated 866, records Auisle and Amlaíb raiding Pictland, taking away many hostages. In the final entry, dated 867, the death of Auisle at the hands of unnamed kinsmen is reported. According to the later '' Fragmentary Annals'' his brothers Amlaíb and Ímar plotted his death, with Amlaíb striking the killing blow.
Background
 The earliest recorded Viking raids in Ireland occurred in 795. Over time, these raids increased in intensity, and they overwintered in Ireland for the first time in 840–841. Later in 841 a longphort was constructed at Áth Cliath (Irish for ''hurdled ford''), a site which would later develop into the city of Dublin. Longphorts were also established at other sites around Ireland, some of which developed into larger Viking settlements over time. The Viking population in Ireland was boosted in 851 with the arrival of a large group known as "dark foreigners" – a contentious term usually considered to mean the newly arrived Vikings, as opposed to the "fair foreigners", i.e. the Viking population which was resident prior to this influx. A kingdom in
The earliest recorded Viking raids in Ireland occurred in 795. Over time, these raids increased in intensity, and they overwintered in Ireland for the first time in 840–841. Later in 841 a longphort was constructed at Áth Cliath (Irish for ''hurdled ford''), a site which would later develop into the city of Dublin. Longphorts were also established at other sites around Ireland, some of which developed into larger Viking settlements over time. The Viking population in Ireland was boosted in 851 with the arrival of a large group known as "dark foreigners" – a contentious term usually considered to mean the newly arrived Vikings, as opposed to the "fair foreigners", i.e. the Viking population which was resident prior to this influx. A kingdom in Viking Scotland
Scandinavian Scotland was the period from the 8th to the 15th centuries during which Vikings and Norse settlers, mainly Norwegians and to a lesser extent other Scandinavians, and their descendants colonised parts of what is now the periphery of ...
was established by the mid ninth-century, and it exerted control over some of the Vikings in Ireland. By 853 a separate kingdom of Dublin
Vikings invaded the territory around Dublin in the 9th century, establishing the Norse Kingdom of Dublin, the earliest and longest-lasting Norse kingdom in Ireland. Its territory corresponded to most of present-day County Dublin. The Norse refe ...
had been set up which claimed control over all the Vikings in Ireland.
Auisle's brother Amlaíb arrived in Ireland in 853 according to the ''Annals of Ulster
The ''Annals of Ulster'' ( ga, Annála Uladh) are annals of medieval Ireland. The entries span the years from 431 AD to 1540 AD. The entries up to 1489 AD were compiled in the late 15th century by the scribe Ruaidhrí Ó Luinín, ...
'':
Amlaíb is named in the annals as a "king of the foreigners", but in modern texts he is usually labelled the first king of Dublin, after the Viking settlement which was the base of his power. His brothers arrived in Ireland later, and they ruled together as co-kings. The '' Fragmentary Annals'' go into more detail regarding Amlaíb's arrival:
Lochlann
In the modern Gaelic languages, () signifies Scandinavia or, more specifically, Norway. As such it is cognate with the Welsh name for Scandinavia, (). In both old Gaelic and old Welsh, such names literally mean 'land of lakes' or 'land of ...
, originally Laithlinn or Lothlend, the land where Amlaíb's father was king, is often identified with Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
, but it is not universally accepted that it had such a meaning in early times. Several historians have proposed instead that in early times, and certainly as late as the Battle of Clontarf
The Battle of Clontarf ( ga, Cath Chluain Tarbh) took place on 23 April 1014 at Clontarf, near Dublin, on the east coast of Ireland. It pitted an army led by Brian Boru, High King of Ireland, against a Norse-Irish alliance comprising the forc ...
in 1014, Laithlinn refers to the Norse and Norse-Gael lands in the Hebrides
The Hebrides (; gd, Innse Gall, ; non, Suðreyjar, "southern isles") are an archipelago off the west coast of the Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner and Outer Hebrid ...
, the Isle of Man
)
, anthem = "O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europe ...
, the Northern Isles
The Northern Isles ( sco, Northren Isles; gd, Na h-Eileanan a Tuath; non, Norðreyjar; nrn, Nordøjar) are a pair of archipelagos off the north coast of mainland Scotland, comprising Orkney and Shetland. They are part of Scotland, as are th ...
and parts of mainland Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
. Whatever the original sense, by the twelfth century, when Magnus Barefoot
Magnus Olafsson (Old Norse: ''Magnús Óláfsson'', Norwegian: ''Magnus Olavsson''; 1073 – 24 August 1103), better known as Magnus Barefoot (Old Norse: ''Magnús berfœttr'', Norwegian: ''Magnus Berrføtt''), was King of Norway (being Ma ...
undertook his expedition to the West, it had come to mean Norway.
Biography
Auisle is first mentioned by the Irish Annals in 863: Prior to this raid, Auisle's brother Amlaíb had been involved in a protracted war withMáel Sechnaill Máel Sechnaill, an early Irish personal name meaning "Devotee of St Sechnall" who is thought to be a 5th century Italian Bishop that preceded St Patrick. It may refer to:
*Máel Sechnaill mac Máele Ruanaid (d. 862), high-king of Ireland
*Máel S ...
, overking of the Southern Uí Néill
The Southern Uí Néill ( ga, Uí Néill an Deiscirt, IPA: �iːˈnʲeːl̪ʲˈanˠˈdʲɛʃcəɾˠtʲ were that branch of the Uí Néill dynasty that invaded and settled in the Kingdom of Mide and its associated kingdoms.
In the initial decades t ...
, and a group of Vikings sometimes known as the Norse-Irish. Máel Sechnaill was the most powerful king in Ireland at the time and his lands lay close to the Viking settlement of Dublin.Downham
Downham is a district of south-east London, England, within the London Borough of Lewisham. It borders the London Borough of Bromley, and is located north of Bromley and south of Catford.
Downham was named in honour of Lord Downham, who was ...
, p. 17 Máel Sechnaill died in 862, and his territory in Meath was split between two rulers, Lorcán mac Cathail
Lorcán mac Cathail (blinded 864) was a King of Uisnech and Mide of the Clann Cholmáin. Lorcán ruled in as King of Mide from 862–864.
His exact dynastic affiliations are unknown. The death of a certain Cathal mac Conchobair is mentioned in ...
and Conchobar mac Donnchada. The raids on various underground tombs in Brega
Brega , also known as ''Mersa Brega'' or ''Marsa al-Brega'' ( ar, مرسى البريقة , i.e. "Brega Seaport"), is a complex of several smaller towns, industry installations and education establishments situated in Libya on the Gulf of Sidra, ...
mentioned by the annals in 863 were likely an attempt to increase the influence of the Vikings of Dublin.Downham
Downham is a district of south-east London, England, within the London Borough of Lewisham. It borders the London Borough of Bromley, and is located north of Bromley and south of Catford.
Downham was named in honour of Lord Downham, who was ...
, p. 20 Muirecán mac Diarmata
Muirecán mac Diarmata (died 863) was a King of Leinster of the Uí Fáeláin sept of the Uí Dúnlainge branch of the Laigin. This sept had their royal seat at Naas in the eastern part of the Liffey plain, Airthir Liphi. He was the son of Diar ...
, overking of the Uí Dúnchada, was killed by Vikings in 863, probably by Auisle and his kin trying to expand into Leinster.
Beginning around 864 the three brothers halted their campaigns of conquest in Ireland, and instead campaigned in Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
.Downham
Downham is a district of south-east London, England, within the London Borough of Lewisham. It borders the London Borough of Bromley, and is located north of Bromley and south of Catford.
Downham was named in honour of Lord Downham, who was ...
, p. 21 Ímar disappears from the Irish Annals in 864, and does not reappear until 870. This has led some scholars to conclude he is identical to Ivar the Boneless
Ivar the Boneless ( non, Ívarr hinn Beinlausi ; died c. 873), also known as Ivar Ragnarsson, was a Viking leader who invaded England and Ireland. According to the ''Tale of Ragnar Lodbrok'', he was the son of Ragnar Loðbrok and his wife Aslau ...
, a Viking leader who was active in England during this period as a commander of the Great Heathen Army
The Great Heathen Army,; da, Store Hedenske Hær also known as the Viking Great Army,Hadley. "The Winter Camp of the Viking Great Army, AD 872–3, Torksey, Lincolnshire", ''Antiquaries Journal''. 96, pp. 23–67 was a coalition of Scandin ...
. In 866 Amlaíb and Auisle led a large army to Pictland
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Sub-Roman Britain, Late Antiquity and the Scotland in the Early Middle Ages, Early Middle Ages. Where they lived an ...
and raided much of the country, taking away many hostages.
Auisle is mentioned for the third and final time by contemporary annals in 867.Downham
Downham is a district of south-east London, England, within the London Borough of Lewisham. It borders the London Borough of Bromley, and is located north of Bromley and south of Catford.
Downham was named in honour of Lord Downham, who was ...
, p. 246 The ''Annals of Ulster'' relate his death:
The ''Fragmentary Annals'' state explicitly that Amlaíb and Ímar were responsible for their brother's death:
Family
Auisle's father is identified as Gofraid by the ''Fragmentary Annals''.Fragmentary Annals of Ireland
The ''Fragmentary Annals of Ireland'' or ''Three Fragments'' are a Middle Irish combination of chronicles from various Irish annals and narrative history. They were compiled in the kingdom of Osraige, probably in the lifetime of Donnchad mac Gilla ...
, § 400 Auisle, Amlaíb, and Ímar are identified as "kings of the foreigners" by the ''Annals of Ulster'' in 863, and as brothers by the ''Fragmentary Annals'':
Some scholars identify Halfdan Ragnarsson
Halfdan Ragnarsson ( non, Hálfdan; oe, Halfdene or ''Healfdene''; sga, Albann; died 877) was a Viking leader and a commander of the Great Heathen Army which invaded the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England, starting in 865.
One of six sons of Ra ...
as another brother. This identification is contingent upon Ímar being identical to Ivar the Boneless: Halfdan and Ivar are named as brothers in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alf ...
''.Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alf ...
, s.a. 878 According to the ''Annals of Ulster'' Amlaíb's son Oistin was slain in battle by "Albann" in 875. This figure is generally agreed to be Halfdan. If that is correct, then it may explain the reason for the conflict: it was a dynastic squabble for control of the kingdom. One potential problem is that according to Norse tradition Ivar and Halfdan were the sons of Ragnar Lodbrok
according to legends, was a Viking hero and a Danish and Swedish king.Gutenberg Projec ...
, whereas Ímar and Amlaíb are named as sons of Gofraid in the ''Fragmentary Annals''. However, the historicity of Ragnar is uncertain and the identification of Ragnar as the father of Ivar and Halfdan is not to be relied upon.
A figure called "mac Auisli" in the original Old Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic ( sga, Goídelc, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ga, Sean-Ghaeilge; gd, Seann-Ghàidhlig; gv, Shenn Yernish or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive writt ...
, mentioned by the ''Annals of Ulster'' in 883 may have been a son of Auisle. The entry in the annals reads:
The much later ''Chronicon Scotorum
''Chronicon Scotorum'', also known as ''Chronicum Scotorum'', is a medieval Irish chronicle.
Overview
According to Nollaig Ó Muraíle, it is "a collection of annals belonging to the ' Clonmacnoise group', covering the period from prehistoric tim ...
'' says something similar, stating that it was Ottár son of Járnkné, possibly identical with Ottir Iarla
Earl Ottir ( non, Óttar jarl; lat-med, Oter comes, lit=Count Oter; died 918), also known as Ottir the Black ( sga, Ottir Dub), was a jarl who occupied a prominent position among the Norse of Britain and Ireland in the early 10th century. He is ...
, and Muirgel daughter of Máel Sechnaill mac Máele Ruanaid
Máel Sechnaill mac Máel Ruanaida (Modern Irish: ''Maolsheachlann Mac Maolruanaidh''), also known as Máel Sechnaill I, anglicised as Malachy MacMulrooney (died 27 November 862) was High King of Ireland. The Annals of Ulster use the Old Irish ti ...
who arranged the killing, but no motive is given.Downham
Downham is a district of south-east London, England, within the London Borough of Lewisham. It borders the London Borough of Bromley, and is located north of Bromley and south of Catford.
Downham was named in honour of Lord Downham, who was ...
, pp. 25, 257, 263 & 266.
Family tree
Notes
References
Citations
Primary Sources
* Accessed viaInternet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, ...
.
*
*
*
*
* Accessed via Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, ...
.
Secondary Sources
* Accessed viaInternet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, ...
.
*
* Subscription oUK public library membership
required. * * * * * * *
External links
at
University College Cork
University College Cork – National University of Ireland, Cork (UCC) ( ga, Coláiste na hOllscoile Corcaigh) is a constituent university of the National University of Ireland, and located in Cork.
The university was founded in 1845 as one of ...
. The Corpus of Electronic Texts includes the ''Annals of Ulster'' and ''the Four Masters'', the ''Chronicon Scotorum'' and the ''Book of Leinster'' as well as Genealogies, and various Saints' Lives. Most are translated into English, or translations are in progress.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Auisle
Rulers of Lochlann
867 deaths
9th-century Irish monarchs
Monarchs of Dublin
9th-century Irish people
Year of birth unknown