Atlantica Hotel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Atlantica ( gr, Ατλαντικα; ''Atlantika'') is an ancient continent that formed during the
Atlantica ( gr, Ατλαντικα; ''Atlantika'') is an ancient continent that formed during the
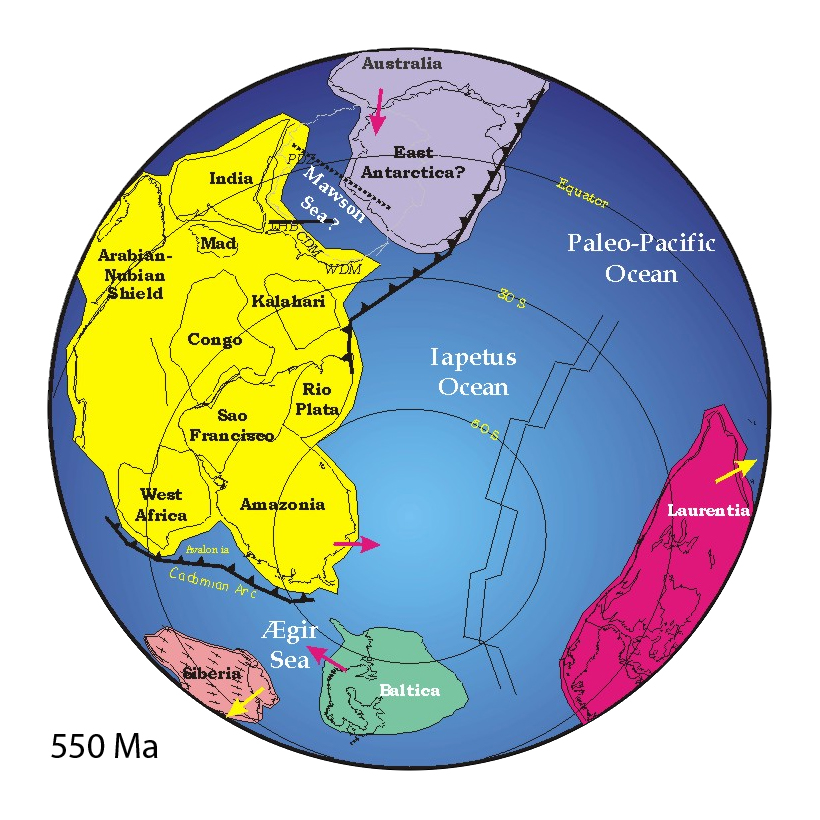 Atlantica separated from Nena between 1.6–1.4 Ga when
Atlantica separated from Nena between 1.6–1.4 Ga when
Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
about (two billion years ago, Ga) from various 2 Ga cratons located in what are now West Africa and eastern South America.
The name, introduced by , was chosen because the parts of the ancient continent are now located on opposite sides of the South Atlantic Ocean.
Formation
Atlantica formed simultaneously with Nena at about 1.9 Ga from Archaean cratons, includingAmazonia
The Amazon rainforest, Amazon jungle or ; es, Selva amazónica, , or usually ; french: Forêt amazonienne; nl, Amazoneregenwoud. In English, the names are sometimes capitalized further, as Amazon Rainforest, Amazon Forest, or Amazon Jungle. ...
in present-day South America, and the Congo, West Africa and North Africa Cratons in Africa.
Breakup
 Atlantica separated from Nena between 1.6–1.4 Ga when
Atlantica separated from Nena between 1.6–1.4 Ga when Columbia
Columbia may refer to:
* Columbia (personification), the historical female national personification of the United States, and a poetic name for America
Places North America Natural features
* Columbia Plateau, a geologic and geographic region in ...
— a supercontinent composed of Ur, Nena, and Atlantica — fragmented.
Atlantica and continents Nena and Ur and some minor plates formed the supercontinent Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago and broke up 750–633 million years ago.
were probably ...
about 1 Ga ago. Between 1–0.5 Ga Rodinia split into three new continents: Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pan ...
and East and West Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages ...
; Atlantica became the nucleus of West Gondwana.
During this later stage, the Neoproterozoic era, a Brasiliano- Pan African orogenic system developed. The central part of this system, the Araçuaí-West Congo orogen, has left a distinct pattern of deformations, still present on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean.
See also
* Plate tectonicsNotes
References
* * * * * {{Continents of the world Historical continents Proterozoic History of the Atlantic Ocean