Asuka-kyŇć on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 was the Imperial
was the Imperial
 In the
In the
Palaces of the Asuka Period,"
1995; retrieved 2011-11-25. in the reign of
exterior view
 was the Imperial
was the Imperial capital of Japan
The capital of Japan is Tokyo."About Japan"
The Government of Japan. Retrieved 9 March 2022.
during the The Government of Japan. Retrieved 9 March 2022.
Asuka period
The was a period in the history of Japan lasting from 538 to 710, although its beginning could be said to overlap with the preceding Kofun period. The Yamato period, Yamato polity evolved greatly during the Asuka period, which is named after the ...
(538 ‚Äď 710 AD), which takes its name from this place. It is located in the present-day village of Asuka, Nara Prefecture.
Etymology
Some of the many theories of what the place was named after include the birdcommon crossbill
The red crossbill or common crossbill (''Loxia curvirostra'') is a small passerine bird in the finch family Fringillidae. Crossbills have distinctive mandibles, crossed at the tips, which enable them to extract seeds from conifer cones and other ...
, or ''isuka'' in Japanese, or local geological features, e.g. śī≤Śá¶ (''suka'', meaning sandbar, sandbank or delta) or Śī©Śúį (''asu'') + Śá¶ (''ka''). Or it may have been named in honor of Asuka (or Ashuku) Nyorai, the Japanese equivalent of Akshobhya
Akshobhya (, ''AkŠĻ£obhya'', "Immovable One"; ) is one of the Five Wisdom Buddhas, a product of the Adibuddha, who represents consciousness as an aspect of reality. By convention he is located in the east of the Diamond Realm and is the lor ...
, one of the Five Buddhas of Wisdom, who is still worshiped in the Asuka-dera
, also known as , is a Buddhist temple located in the village of Asuka, Nara Prefecture, Japan. It currently belongs to the Shingon-shŇę Buzan-ha sect. Asuka-dera is regarded as one of the oldest temples in Japan. Its precincts were designat ...
(Asuka Temple), the Asuka-niimasu-jinja (the shrine for his manifestation as a Shinto god), and several other structures from those days.
Archaeology
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
projects continue to uncover relics from these ruins. Recent discoveries in the area include Wado coins, believed to be some of the oldest coins in Japan, and paintings in the Kitora and Takamatsuzuka Kofun
are megalithic tombs or tumulus, tumuli in Northeast Asia. ''Kofun'' were mainly constructed in the Japanese archipelago between the middle of the 3rd century to the early 7th century AD.Ś≤°ÁĒįŤ£ēšĻč„ÄĆŚČćśĖĻŚĺĆŚÜÜŚĘ≥„Äć„Äéśó•śú¨ŚŹ§šĽ£ŚŹ≤Ś§ßŤĺě ...
, or tombs.
The Ishibutai Kofun
is a Kofun period burial mound, located in the village of Asuka, Nara in the Kansai region of Japan. The tumulus was designated a National Historic Site of Japan in 1935. In 1954 the designation was elevated to a , The ''kofun'' is also known ...
is also located in Asuka. On March 12, 2004, the discovery of the remains of a residence's main building adjacent to the kofun was announced. It is likely that the residence belonged to Soga no Umako
was the son of Soga no Iname and a member of the powerful Soga clan of Japan. Conflicting evidence has suggested that Soga no Umako was actually an emperor during the Asuka period.
Umako conducted political reforms with Prince ShŇćtoku during t ...
, who is believed to have been entombed in the kofun.
Access
Asuka can be reached from either Okadera Station orAsuka Station
is a railway station located in Asuka, Takaichi, Nara, Japan, on the Kintetsu Railway Yoshino Line.
Lines
* Kintetsu Railway
** Yoshino Line
Platforms and tracks
Surroundings
*
*Takamatsuzuka Tomb
*Ishibutai Kofun
*Oni no Manaita, Oni ...
on the Kintetsu train line, or by car on Route 169.
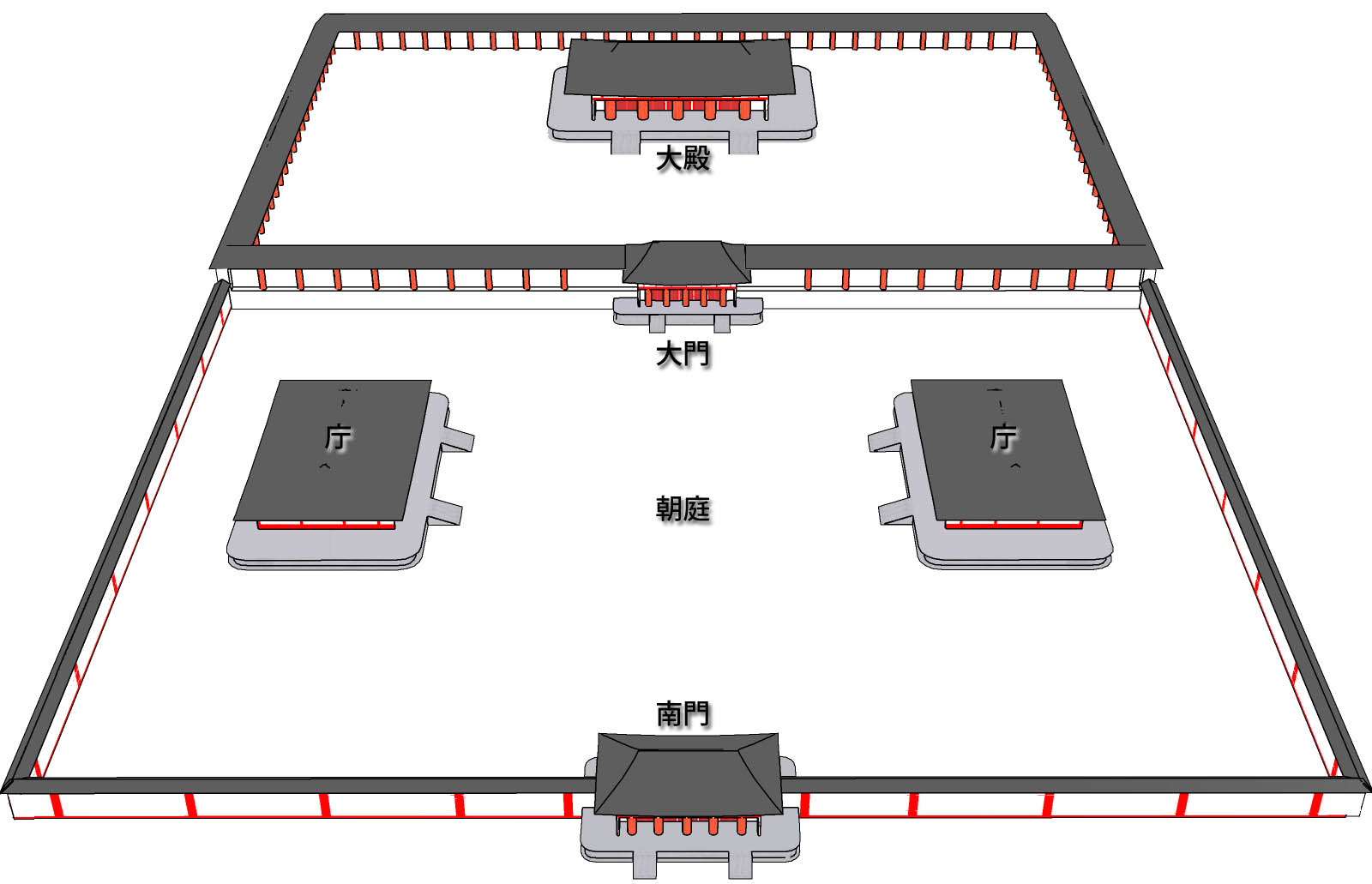
Imperial palaces
 In the
In the Asuka period
The was a period in the history of Japan lasting from 538 to 710, although its beginning could be said to overlap with the preceding Kofun period. The Yamato period, Yamato polity evolved greatly during the Asuka period, which is named after the ...
, various palaces were constructed for each monarch. As soon as one emperor died, the whole court moved to a newly constructed palace, since it was considered dangerous and ominous to remain in a place where a deceased monarch's spirit might reside. Sometimes even during a single emperor's reign, palaces were changed multiple times due to destruction by fire or ill omens. Since these palaces were entirely constructed from wood, none of them have survived, although some archaeological work in modern times has uncovered such remains as stone bases for pillars.
Sakurai was briefly the capital of Japan
The capital of Japan is Tokyo."About Japan"
The Government of Japan. Retrieved 9 March 2022.
during the reign of The Government of Japan. Retrieved 9 March 2022.
Emperor IngyŇć
was the 19th Emperor of Japan, according to the traditional List of Emperors of Japan, order of succession. Both the ''Kojiki'', and the ''Nihon Shoki'' (collectively known as the ''Kiki'') recorded events that took place during IngyŇć's alleged ...
. The life of the Imperial court was centered at the Palace of ''Tohotsu'' where the emperor lived in 457‚Äď479. Other emperors also built palaces at Asuka, including
* ''Chikatsu-Asuka-Yatsuri'' Palace, 485‚Äď487 in reign of Emperor KenzŇć
(450 ‚Äď 2 June 487) was the 23rd legendary emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''KunaichŇć'') ť°ēŚģ󌧩Áöá (23) retrieved 2013-8-29. according to the traditional order of succession.
No firm dates can be assigned to this emperor's life ...
* ''Shikishima no Kanasashi'' Palace, 540‚Äď571 in reign of Emperor Kinmei
was the 29th emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''KunaichŇć'') ś¨Ĺśė錧©Áöá (29) retrieved 2013-8-22. according to the traditional order of succession. Titsingh, Isaac. (1834)pp. 34‚Äď36 Brown, Delmer. (1979) ''GukanshŇć,'' pp. 261‚Äď2 ...
* ''Toyura'' Palace or ''Toyura-no-miya'', 593‚Äď603Asuka Historical MuseumPalaces of the Asuka Period,"
1995; retrieved 2011-11-25. in the reign of
Empress Suiko
(554 ‚Äď 15 April 628) was the 33rd monarch of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''KunaichŇć''):
She introduced Buddhism in Japan and built many Buddhist temples, but she held the balance between Buddhism and Shintoism. Under her rule, Japan ...
Ponsonby-Fane, p. 20.
* ''Oharida'' Palace or ''Oharida-no-miya'', 603‚Äď629 in the Suiko's reign
* ''Okamoto'' Palace or ''Okamoto-no-miya'', 630‚Äď636 in the reign of Emperor Jomei
was the 34th emperor of Japan,KunaichŇć śĖČśė錧©Áöá (34)/ref> according to the traditional order of succession.
Jomei's reign spanned the years from 629 through 641.
Traditional narrative
Before Jomei's ascension to the Chrysanthemum Throne, ...
Ponsonby-Fane, p. 21.
* ''Tanaka'' Palace, 636‚Äď40
* ''Umayasaka'' Palace, 640
In 640‚Äď642, the Imperial court briefly moved to the ''Kudara'' Palace in KŇćryŇć, Nara
280px, ÁęĻŚŹĖŚÖ¨Śúí Taketori Park
280px, ÁęĻŚŹĖŚÖ¨Śúí Suyama Kofun
280px, ÁęĻŚŹĖŚÖ¨Śúí Kudara-ji
is a town located in Kitakatsuragi District, Nara Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 35,035 in 14106 households, and a p ...
; then the emperor returned to Asuka where he lived at
* ''Oharida'' Palace, 642‚Äď643
* ''Itabuki'' Palace or ''Itabuki no miya'', 643‚Äď645 in the reign of Empress KŇćgyoku
, also known as , was the 35th and 37th monarch of Japan,KunaichŇć śĖČśė錧©Áöá (37)/ref> according to the traditional order of succession. Both her reigns were within the Asuka period.
KŇćgyoku's reign spanned the years from 642 to 645. Her r ...
In 645‚Äď654, the court moved to the ''Naniwa Nagara-Toyosaki'' Palace in Osaka
is a Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the List of cities in Japan, third-most populous city in J ...
; then the capital moved back to Asuka when the emperor lived at
* ''Itabuki'' Palace, 655‚Äď655 in the reign of Emperor KŇćtoku
was the 36th emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''KunaichŇć'') Ś≠ĚŚĺ≥Ś§©Áöá (33)/ref> according to the traditional List of emperors of Japan, order of succession.
The years of his reign lasted from Asuka period, 645 through 654.
Tradi ...
* ''Kawahara'' Palace or ''Kawahara-no-miya'', 655‚Äď655
* ''Okamoto'' Palace or ''Nochi no Asuka-Okamoto-no-miya'', 656‚Äď660 in the reign of Empress Saimei
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
Ponsonby-Fane, p. 24.
In 661‚Äď667, the court moved to the ''Tachibana no Hironiwa'' Palace (661‚Äď67) in Asakura, Fukuoka
file:Asakura city office.jpg, 270px, Asakura CIty Hall
is a Cities of Japan, city located in south central Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 50,488 in 22168 households, and a population density of 200 persons pe ...
. Then the court moved again to the ''ŇĆmi'' Palace or ''ŇĆtsu'' Palace (667‚Äď72) in ŇĆmi-kyŇć (today ŇĆtsu, Shiga). Once more, the court moved back to Asuka at
* ''Kiyomihara'' Palace or ''Kiomihara-no-miya'', 672‚Äď694 in the reign of Emperor Tenmu
was the 40th Emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''KunaichŇć'') Ś§©ś≠¶Ś§©Áöá (40) retrieved 2013-8-22. according to the traditional order of succession. Ponsonby-Fane, Richard. (1959). ''The Imperial House of Japan'', p. 53. He ascended ...
Ponsonby-Fane, p. 26. and in the reign of Empress JitŇć
was the 41st emperor of Japan, monarch of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''KunaichŇć'') śĆĀÁĶĪŚ§©Áöá (41)/ref> according to the traditional List of Emperors of Japan, order of succession.
JitŇć's reign spanned the years from JitŇć period, 68 ...
Ponsonby-Fane, p. 27.
Asuka was abandoned by Empress JitŇć
was the 41st emperor of Japan, monarch of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''KunaichŇć'') śĆĀÁĶĪŚ§©Áöá (41)/ref> according to the traditional List of Emperors of Japan, order of succession.
JitŇć's reign spanned the years from JitŇć period, 68 ...
when she and her court moved to Fujiwara-kyŇć
280px, Map of Fujiwara-kyŇć
was the Imperial capital of Japan for sixteen years, between 694 and 710. It was located in Yamato Province (present-day Kashihara in Nara Prefecture), having been moved from nearby Asuka, and remained the capital u ...
.
See also
*The 100 Views of Nature in Kansai
This is a list of 100 views of nature decided upon by the Kansai Global Environment Forum in Japan for their natural beauty, history and cultural significance.
Summary
See also
* List of Historic Sites of Japan (Osaka)
This list is of the H ...
External links
* Asuka Historical Museumexterior view
References
* {{coord, 34, 28, 56, N, 135, 48, 47, E, display=title, region:JP-29_type:landmark_source:dewiki Cities in Nara Prefecture Former capitals of Japan Asuka period