
Astronomy is a
natural science
Natural science or empirical science is one of the branches of science concerned with the description, understanding and prediction of natural phenomena, based on empirical evidence from observation and experimentation. Mechanisms such as peer ...
that studies
celestial objects and the
phenomena
A phenomenon ( phenomena), sometimes spelled phaenomenon, is an observable Event (philosophy), event. The term came into its modern Philosophy, philosophical usage through Immanuel Kant, who contrasted it with the noumenon, which ''cannot'' be ...
that occur in the cosmos. It uses
mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
,
physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
, and
chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
in order to explain their origin and their overall
evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
. Objects of interest include
planets
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets by the most restrictive definition of the te ...
,
moons
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are colloquially referred to as moons, a deriva ...
,
star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
s,
nebulae
A nebula (; or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral, or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the Pillars of Creation in th ...
,
galaxies
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar Sys ...
,
meteoroid
A meteoroid ( ) is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.
Meteoroids are distinguished as objects significantly smaller than ''asteroids'', ranging in size from grains to objects up to wide. Objects smaller than meteoroids are classifie ...
s,
asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). As ...
s, and
comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding ...
s. Relevant phenomena include
supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion ...
explosions,
gamma ray burst
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are extremely energetic events occurring in distant galaxies which represent the brightest and most powerful class of explosion in the universe. These extreme electromagnetic emissions are second ...
s,
quasar
A quasar ( ) is an extremely Luminosity, luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. The emission from an AGN is powered by accretion onto a supermassive black hole with a mass rangi ...
s,
blazar
A blazar is an active galactic nucleus (AGN) with a relativistic jet (a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light) directed very nearly towards an observer. Relativistic beaming of electromagnetic radiation from the ...
s,
pulsar
A pulsar (''pulsating star, on the model of quasar'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its Poles of astronomical bodies#Magnetic poles, magnetic poles. This radiation can be obse ...
s, and
cosmic microwave background radiation
The cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR), or relic radiation, is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. With a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dar ...
. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weathe ...
.
Cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', with the meaning of "a speaking of the wo ...
is a branch of astronomy that studies the
universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents. It comprises all of existence, any fundamental interaction, physical process and physical constant, and therefore all forms of matter and energy, and the structures they form, from s ...
as a whole.
Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in
recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world h ...
made methodical observations of the
night sky
The night sky is the nighttime appearance of celestial objects like stars, planets, and the Moon, which are visible in a clear sky between sunset and sunrise, when the Sun is below the horizon.
Natural light sources in a night sky include moonlig ...
. These include the
Egyptians
Egyptians (, ; , ; ) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian identity is closely tied to Geography of Egypt, geography. The population is concentrated in the Nile Valley, a small strip of cultivable land stretchi ...
,
Babylonians
Babylonia (; , ) was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as an Akkadian-populated but Amorite-ru ...
,
Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
,
Indians
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Associated with India
* of or related to India
** Indian people
** Indian diaspora
** Languages of India
** Indian English, a dialect of the English language
** Indian cuisine
Associated with indigenous peoples o ...
,
Chinese
Chinese may refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China.
**'' Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic ...
,
Maya
Maya may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Mayan languages, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (East Africa), a p ...
, and many ancient
indigenous peoples of the Americas
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of ...
. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as
astrometry
Astrometry is a branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other Astronomical object, celestial bodies. It provides the kinematics and physical origin of the Solar System and this galaxy, th ...
,
celestial navigation
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is the practice of position fixing using stars and other celestial bodies that enables a navigator to accurately determine their actual current physical position in space or on the surface ...
,
observational astronomy
Observational astronomy is a division of astronomy that is concerned with recording data about the observable universe, in contrast with theoretical astronomy, which is mainly concerned with calculating the measurable implications of physical ...
, and the making of
calendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A calendar date, date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is ...
s.
Professional astronomy is split into
observational and
theoretical
A theory is a systematic and rational form of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the conclusions derived from such thinking. It involves contemplative and logical reasoning, often supported by processes such as observation, experimentation, ...
branches. Observational astronomy is focused on acquiring data from observations of astronomical objects. This data is then analyzed using basic principles of physics. Theoretical astronomy is oriented toward the development of computer or analytical models to describe astronomical objects and phenomena. These two fields complement each other. Theoretical astronomy seeks to explain observational results and observations are used to confirm theoretical results.
Astronomy is one of the few sciences in which amateurs play an
active role. This is especially true for the discovery and observation of
transient events.
Amateur astronomers
An amateur () is generally considered a person who pursues an avocation independent from their source of income. Amateurs and their pursuits are also described as popular, informal, self-taught, user-generated, DIY, and hobbyist.
History
...
have helped with many important discoveries, such as finding new comets.
Etymology
''Astronomy'' (from the
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
ἀστρονομία from
ἄστρον ''astron'', "star" and -νομία ''
-nomia'' from
νόμος ''nomos'', "law" or "culture") means "law of the stars" (or "culture of the stars" depending on the translation). Astronomy should not be confused with
astrology
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions ...
, the belief system which claims that human affairs are correlated with the positions of celestial objects. Although the
two fields share a common origin, they are now entirely distinct.
Use of terms "astronomy" and "astrophysics"
"Astronomy" and "
astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline, James Keeler, said, astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the ...
" are synonyms.
Based on strict dictionary definitions, "astronomy" refers to "the study of objects and matter outside the Earth's atmosphere and of their physical and chemical properties",
while "astrophysics" refers to the branch of astronomy dealing with "the behavior, physical properties, and dynamic processes of celestial objects and phenomena".
In some cases, as in the introduction of the introductory textbook ''The Physical Universe'' by
Frank Shu
Frank Hsia-San Shu (; June 2, 1943 – April 22, 2023) was a Chinese-American astrophysicist, astronomer, and author. He served as a Professor Emeritus at the University of California, Berkeley and University of California, San Diego. He is b ...
, "astronomy" may be used to describe the qualitative study of the subject, whereas "astrophysics" is used to describe the physics-oriented version of the subject.
However, since most modern astronomical research deals with subjects related to physics, modern astronomy could actually be called astrophysics.
Some fields, such as
astrometry
Astrometry is a branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other Astronomical object, celestial bodies. It provides the kinematics and physical origin of the Solar System and this galaxy, th ...
, are purely astronomy rather than also astrophysics. Various departments in which scientists carry out research on this subject may use "astronomy" and "astrophysics", partly depending on whether the department is historically affiliated with a physics department,
and many professional
astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. Astronomers observe astronomical objects, such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, galax ...
s have physics rather than astronomy degrees.
Some titles of the leading scientific journals in this field include ''
The Astronomical Journal
''The Astronomical Journal'' (often abbreviated ''AJ'' in scientific papers and references) is a peer-reviewed monthly scientific journal owned by the American Astronomical Society (AAS) and currently published by IOP Publishing. It is one of the p ...
'', ''
The Astrophysical Journal
''The Astrophysical Journal'' (''ApJ'') is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of astrophysics and astronomy, established in 1895 by American astronomers George Ellery Hale and James Edward Keeler. The journal discontinued its print edition and ...
'', and ''
Astronomy & Astrophysics
''Astronomy & Astrophysics (A&A)'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering theoretical, observational, and instrumental astronomy and astrophysics. It is operated by an editorial team under the supervision of a board of directors re ...
''.
History
Pre-historic astronomy

In early historic times, astronomy only consisted of the observation and predictions of the motions of objects visible to the naked eye. In some locations, early cultures assembled massive artifacts that may have had some astronomical purpose. In addition to their ceremonial uses, these
observatories
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysics, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed.
Th ...
could be employed to determine the seasons, an important factor in knowing when to plant crops and in understanding the length of the year.
Classical astronomy
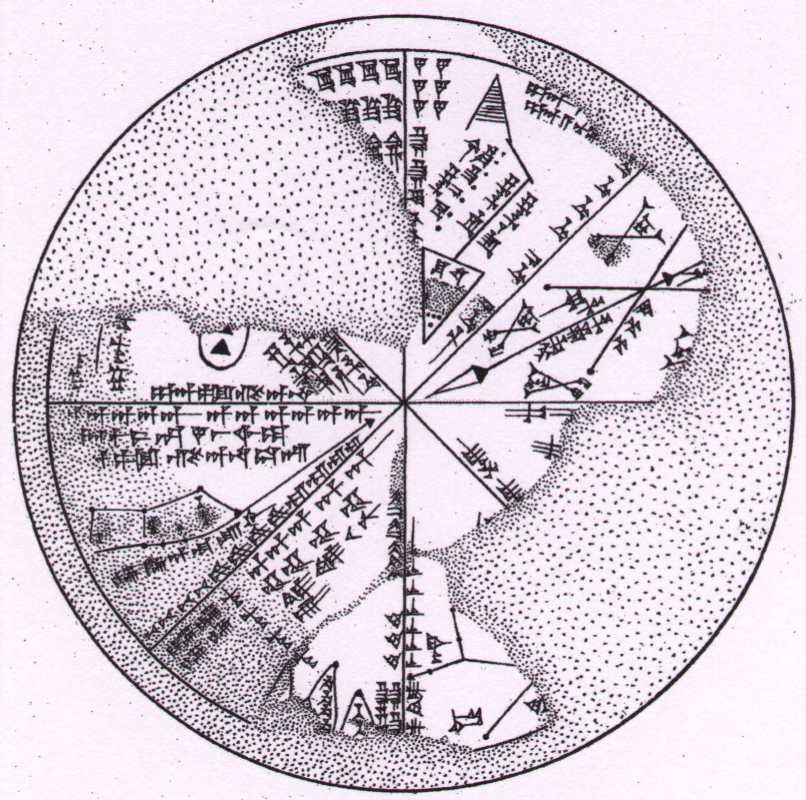
As civilizations developed, most notably in
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
,
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
,
Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
,
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
,
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
,
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, and
Central America
Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually ...
, astronomical observatories were assembled and ideas on the nature of the Universe began to develop. Most early astronomy consisted of mapping the positions of the stars and planets, a science now referred to as
astrometry
Astrometry is a branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other Astronomical object, celestial bodies. It provides the kinematics and physical origin of the Solar System and this galaxy, th ...
. From these observations, early ideas about the motions of the planets were formed, and the nature of the Sun, Moon and the Earth in the Universe were explored philosophically.
Mesopotamia is worldwide the place of the earliest known astronomer and poet by name:
Enheduanna
Enheduanna ( , also transliteration, transliterated as , , or variants; ) was the (high) priestess of the moon god Sin (mythology), Nanna (Sīn) in the Sumerian city-state of Ur in the reign of her father, Sargon of Akkad ( BCE). She was likely ...
,
Akkadian high priestess to the
lunar deity
A lunar deity or moon deity is a deity who represents the Moon, or an aspect of it. These deities can have a variety of functions and traditions depending upon the culture, but they are often related. Lunar deities and Moon worship can be foun ...
Nanna/Sin and princess, daughter of
Sargon the Great
Sargon of Akkad (; ; died 2279 BC), also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC.The date of the reign of Sargon is highly unc ...
( – BCE). She had the Moon tracked in her chambers and wrote poems about her divine Moon.
A particularly important early development was the beginning of mathematical and scientific astronomy, which began among
the Babylonians, who laid the foundations for the later astronomical traditions that developed in many other civilizations. The
Babylonians
Babylonia (; , ) was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as an Akkadian-populated but Amorite-ru ...
discovered that
lunar eclipses
A lunar eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase ...
recurred in a repeating cycle known as a
saros.
Following the Babylonians, significant advances in astronomy were made in ancient Greece and the Hellenistic civilization, Hellenistic world. Greek astronomy is characterized from the start by seeking a rational, physical explanation for celestial phenomena. In the 3rd century BC, Aristarchus of Samos estimated the Aristarchus On the Sizes and Distances, size and distance of the Moon and Sun, and he proposed a model of the Solar System where the Earth and planets rotated around the Sun, now called the heliocentrism, heliocentric model. In the 2nd century BC, Hipparchus discovered precession, calculated the size and distance of the Moon and invented the earliest known astronomical devices such as the astrolabe. Hipparchus also created a comprehensive catalog of 1020 stars, and most of the constellations of the northern hemisphere derive from Greek astronomy. The Antikythera mechanism (–80 BC) was an early analog computer designed to calculate the location of the Sun, Moon, and
planets
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets by the most restrictive definition of the te ...
for a given date. Technological artifacts of similar complexity did not reappear until the 14th century, when mechanical astronomical clocks appeared in Europe.
The Earth was believed to be the center of the Universe with the Sun, the Moon and the stars rotating around it. This is known as the geocentric model of the Universe, or the Ptolemaic system, named after Ptolemy.
Post-classical astronomy
Astronomy in medieval Islam, Astronomy flourished in the Islamic world and other parts of the world. This led to the emergence of the first astronomical
observatories
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysics, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed.
Th ...
in the Muslim world by the early 9th century.
In 964, the Andromeda Galaxy, the largest galaxy in the Local Group, was described by the Persian Muslim astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi in his ''Book of Fixed Stars''.
The SN 1006
supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion ...
, the brightest apparent magnitude stellar event in recorded history, was observed by the Egyptian Arabic astronomer Ali ibn Ridwan and Chinese astronomy, Chinese astronomers in 1006. Iranian scholar Al-Biruni observed that, contrary to Ptolemy, the Sun's apogee (highest point in the heavens) was mobile, not fixed. Some of the prominent Islamic (mostly Persian and Arab) astronomers who made significant contributions to the science include Al-Battani, Thebit, Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi, Abu Rayhan Biruni, Biruni, Abū Ishāq Ibrāhīm al-Zarqālī, Al-Birjandi, and the astronomers of the Maragheh observatory, Maragheh and Ulugh Beg Observatory, Samarkand observatories. Astronomers during that time introduced many List of Arabic star names, Arabic names now used for individual stars.
It is also believed that the ruins at Great Zimbabwe and Timbuktu may have housed astronomical observatories. In Post-classical West Africa, Astronomers studied the movement of stars and relation to seasons, crafting charts of the heavens as well as precise diagrams of orbits of the other planets based on complex mathematical calculations. Songhai Empire, Songhai historian Mahmud Kati documented a meteor shower in August 1583.
Europeans had previously believed that there had been no astronomical observation in sub-Saharan Africa during the pre-colonial Middle Ages, but modern discoveries show otherwise.
For over six centuries (from the recovery of ancient learning during the late Middle Ages into the Enlightenment), the Roman Catholic Church gave more financial and social support to the study of astronomy than probably all other institutions. Among the Church's motives was finding the Date of Easter, date for Easter.
Medieval Europe housed a number of important astronomers. Richard of Wallingford (1292–1336) made major contributions to astronomy and horology, including the invention of the first astronomical clock, the Rectangulus which allowed for the measurement of angles between planets and other astronomical bodies, as well as an equatorium called the ''Albion'' which could be used for astronomical calculations such as moon, lunar, sun, solar and planetary longitudes and could predict eclipses. Nicole Oresme (1320–1382) and Jean Buridan (1300–1361) first discussed evidence for the rotation of the Earth, furthermore, Buridan also developed the theory of impetus (predecessor of the modern scientific theory of inertia) which was able to show planets were capable of motion without the intervention of angels. Georg von Peuerbach (1423–1461) and Regiomontanus (1436–1476) helped make astronomical progress instrumental to Copernicus's development of the heliocentric model decades later.
Early telescopic astronomy
During the Renaissance, Nicolaus Copernicus proposed a heliocentric model of the solar system. His work was defended by Galileo Galilei and expanded upon by Johannes Kepler. Kepler was the first to devise a system that correctly described the details of the motion of the planets around the Sun. However, Kepler did not succeed in formulating a theory behind the laws he wrote down. It was Isaac Newton, with his invention of celestial dynamics and his gravity, law of gravitation, who finally explained the motions of the planets. Newton also developed the reflecting telescope.
Improvements in the size and quality of the telescope led to further discoveries. The English astronomer John Flamsteed catalogued over 3000 stars. More extensive star catalogues were produced by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille. The astronomer William Herschel made a detailed catalog of nebulosity and clusters, and in 1781 discovered the planet Uranus, the first new planet found.
During the 18–19th centuries, the study of the three-body problem by Leonhard Euler, Alexis Claude Clairaut, and Jean le Rond d'Alembert led to more accurate predictions about the motions of the Moon and planets. This work was further refined by Joseph-Louis Lagrange and Pierre Simon Laplace, allowing the masses of the planets and moons to be estimated from their perturbations.
Significant advances in astronomy came about with the introduction of new technology, including the spectroscope and Astrophotography, photography. Joseph von Fraunhofer discovered about 600 bands in the spectrum of the Sun in 1814–15, which, in 1859, Gustav Kirchhoff ascribed to the presence of different elements. Stars were proven to be similar to the Earth's own Sun, but with a wide range of temperatures, masses, and sizes.
Deep space astronomy
The existence of the Earth's galaxy, the Milky Way, as its own group of stars was only proven in the 20th century, along with the existence of "external" galaxies. The observed recession of those galaxies led to the discovery of the expansion of the Universe.
In 1919, when the Hooker Telescope was completed, the prevailing view was that the universe consisted entirely of the Milky Way Galaxy. Using the Hooker Telescope, Edwin Hubble identified Cepheid variables in several spiral nebulae and in 1922–1923 proved conclusively that Andromeda Galaxy, Andromeda Nebula and Triangulum Nebula, Triangulum among others, were entire galaxies outside our own, thus proving that the universe consists of a multitude of galaxies.
With this Hubble formulated the Hubble constant, which allowed for the first time a calculation of the age of the Universe and size of the Observable Universe, which became increasingly precise with better meassurements, starting at 2 billion years and 280 million light-years, until 2006 when data of the Hubble Space Telescope allowed a very accurate calculation of the age of the Universe and size of the Observable Universe.

Theoretical astronomy led to speculations on the existence of objects such as black holes and neutron stars, which have been used to explain such observed phenomena as
quasar
A quasar ( ) is an extremely Luminosity, luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. The emission from an AGN is powered by accretion onto a supermassive black hole with a mass rangi ...
s,
pulsar
A pulsar (''pulsating star, on the model of quasar'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its Poles of astronomical bodies#Magnetic poles, magnetic poles. This radiation can be obse ...
s,
blazar
A blazar is an active galactic nucleus (AGN) with a relativistic jet (a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light) directed very nearly towards an observer. Relativistic beaming of electromagnetic radiation from the ...
s, and radio galaxy, radio galaxies. Physical cosmology made huge advances during the 20th century. In the early 1900s the model of the Big Bang theory was formulated, heavily evidenced by
cosmic microwave background radiation
The cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR), or relic radiation, is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. With a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dar ...
, Hubble's law, and the Big Bang nucleosynthesis, cosmological abundances of elements. Space telescopes have enabled measurements in parts of the electromagnetic spectrum normally blocked or blurred by the atmosphere. In February 2016, it was revealed that the LIGO project had first observation of gravitational waves, detected evidence of gravitational waves in the previous September.
Observational astronomy

The main source of information about celestial body, celestial bodies and other objects is visible light, or more generally electromagnetic radiation. Observational astronomy may be categorized according to the corresponding region of the electromagnetic spectrum on which the observations are made. Some parts of the spectrum can be observed from the Earth's surface, while other parts are only observable from either high altitudes or outside the Earth's atmosphere. Specific information on these subfields is given below.
Radio astronomy

Radio astronomy uses radiation with wavelengths greater than approximately one millimeter, outside the visible range.
Radio astronomy is different from most other forms of observational astronomy in that the observed radio waves can be treated as waves rather than as discrete photons. Hence, it is relatively easier to measure both the amplitude and Phase (waves), phase of radio waves, whereas this is not as easily done at shorter wavelengths.
Although some radio waves are emitted directly by astronomical objects, a product of black-body radiation, thermal emission, most of the radio emission that is observed is the result of synchrotron radiation, which is produced when electrons orbit magnetic fields.
Additionally, a number of spectral lines produced by interstellar gas, notably the hydrogen spectral line at 21 cm, are observable at radio wavelengths.
A wide variety of other objects are observable at radio wavelengths, including
supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion ...
e, interstellar gas,
pulsar
A pulsar (''pulsating star, on the model of quasar'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its Poles of astronomical bodies#Magnetic poles, magnetic poles. This radiation can be obse ...
s, and active galactic nuclei.
Infrared astronomy

Infrared astronomy is founded on the detection and analysis of infrared radiation, wavelengths longer than red light and outside the range of our vision. The infrared spectrum is useful for studying objects that are too cold to radiate visible light, such as planets, circumstellar disks or nebulae whose light is blocked by dust. The longer wavelengths of infrared can penetrate clouds of dust that block visible light, allowing the observation of young stars embedded in molecular clouds and the cores of galaxies. Observations from the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) have been particularly effective at unveiling numerous galactic protostars and their host star clusters.
With the exception of infrared wavelengths close to visible light, such radiation is heavily absorbed by the atmosphere, or masked, as the atmosphere itself produces significant infrared emission. Consequently, infrared observatories have to be located in high, dry places on Earth or in space. Some molecules radiate strongly in the infrared. This allows the study of the chemistry of space; more specifically it can detect water in comets.
Optical astronomy

Historically, optical astronomy, which has been also called visible light astronomy, is the oldest form of astronomy.
Images of observations were originally drawn by hand. In the late 19th century and most of the 20th century, images were made using photographic equipment. Modern images are made using digital detectors, particularly using charge-coupled devices (CCDs) and recorded on modern medium. Although visible light itself extends from approximately 4000 Ångstrom, Å to 7000 Å (400 nanometre, nm to 700 nm),
that same equipment can be used to observe some near-ultraviolet and near-infrared radiation.
Ultraviolet astronomy
Ultraviolet astronomy employs ultraviolet wavelengths between approximately 100 and 3200 Å (10 to 320 nm).
Light at those wavelengths is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, requiring observations at these wavelengths to be performed from the upper atmosphere or from space. Ultraviolet astronomy is best suited to the study of thermal radiation and spectral emission lines from hot blue
star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
s (OB stars) that are very bright in this wave band. This includes the blue stars in other galaxies, which have been the targets of several ultraviolet surveys. Other objects commonly observed in ultraviolet light include planetary nebulae, supernova remnants, and active galactic nuclei.
However, as ultraviolet light is easily absorbed by interstellar dust, an adjustment of ultraviolet measurements is necessary.
X-ray astronomy
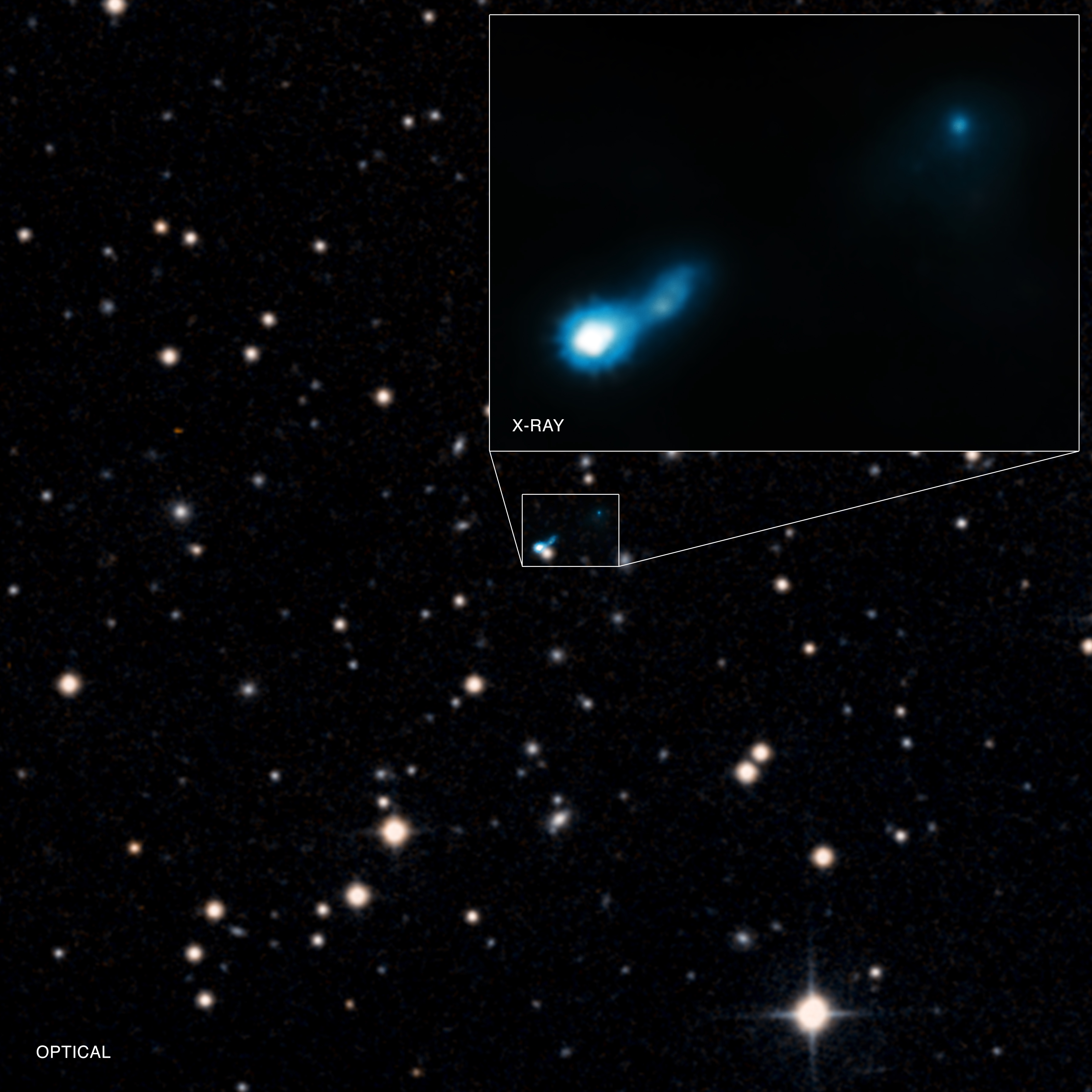

X-ray astronomy uses X-radiation, X-ray wavelengths. Typically, X-ray radiation is produced by synchrotron emission (the result of electrons orbiting magnetic field lines), bremsstrahlung radiation, thermal emission from thin gases above 10
7 (10 million) kelvins, and blackbody radiation, thermal emission from thick gases above 10
7 Kelvin.
Since X-rays are absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, all X-ray observations must be performed from high-altitude balloons, rockets, or X-ray astronomy satellites. Notable Astrophysical X-ray source, X-ray sources include X-ray binaries,
pulsar
A pulsar (''pulsating star, on the model of quasar'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its Poles of astronomical bodies#Magnetic poles, magnetic poles. This radiation can be obse ...
s, supernova remnants, elliptical galaxies, clusters of galaxies, and active galactic nuclei.
Gamma-ray astronomy
Gamma ray astronomy observes astronomical objects at the shortest wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma rays may be observed directly by satellites such as the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory or by specialized telescopes called atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes.
The Cherenkov telescopes do not detect the gamma rays directly but instead detect the flashes of visible light produced when gamma rays are absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere.
Most Gamma ray, gamma-ray emitting sources are actually gamma-ray bursts, objects which only produce gamma radiation for a few milliseconds to thousands of seconds before fading away. Only 10% of gamma-ray sources are non-transient sources. These steady gamma-ray emitters include pulsars, neutron stars, and black hole candidates such as active galactic nuclei.
Fields not based on the electromagnetic spectrum
In addition to electromagnetic radiation, a few other events originating from great distances may be observed from the Earth.
In neutrino astronomy, astronomers use heavily shielded Neutrino observatory, underground facilities such as SAGE (ruSsian American Gallium Experiment), SAGE, GALLEX, and Kamioka Observatory, Kamioka II/III for the detection of neutrinos. The vast majority of the neutrinos streaming through the Earth originate from the Sun, but 24 neutrinos were also detected from supernova 1987A.
Cosmic rays, which consist of very high energy particles (atomic nuclei) that can decay or be absorbed when they enter the Earth's atmosphere, result in a cascade of secondary particles which can be detected by current observatories. Some future neutrino detectors may also be sensitive to the particles produced when cosmic rays hit the Earth's atmosphere.
Gravitational-wave astronomy is an emerging field of astronomy that employs gravitational-wave detectors to collect observational data about distant massive objects. A few observatories have been constructed, such as the ''Laser Interferometer Gravitational Observatory'' LIGO. LIGO made its First observation of gravitational waves, first detection on 14 September 2015, observing gravitational waves from a binary black hole.
A second gravitational wave was detected on 26 December 2015 and additional observations should continue but gravitational waves require extremely sensitive instruments.
The combination of observations made using electromagnetic radiation, neutrinos or gravitational waves and other complementary information, is known as multi-messenger astronomy.
Astrometry and celestial mechanics

One of the oldest fields in astronomy, and in all of science, is the measurement of the positions of celestial objects. Historically, accurate knowledge of the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets and stars has been essential in
celestial navigation
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is the practice of position fixing using stars and other celestial bodies that enables a navigator to accurately determine their actual current physical position in space or on the surface ...
(the use of celestial objects to guide navigation) and in the making of
calendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A calendar date, date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is ...
s.
Careful measurement of the positions of the planets has led to a solid understanding of gravitational Perturbation theory, perturbations, and an ability to determine past and future positions of the planets with great accuracy, a field known as celestial mechanics. More recently the tracking of near-Earth objects will allow for predictions of close encounters or potential collisions of the Earth with those objects.
The measurement of stellar parallax of nearby stars provides a fundamental baseline in the cosmic distance ladder that is used to measure the scale of the Universe. Parallax measurements of nearby stars provide an absolute baseline for the properties of more distant stars, as their properties can be compared. Measurements of the radial velocity and proper motion of stars allow astronomers to plot the movement of these systems through the Milky Way galaxy. Astrometric results are the basis used to calculate the distribution of speculated dark matter in the galaxy.
During the 1990s, the measurement of the stellar wobble of nearby stars was Methods of detecting extrasolar planets#Astrometry, used to detect large extrasolar planets orbiting those stars.
Theoretical astronomy
Theoretical astronomers use several tools including mathematical model, analytical models and computational Numerical analysis, numerical simulations; each has its particular advantages. Analytical models of a process are better for giving broader insight into the heart of what is going on. Numerical models reveal the existence of phenomena and effects otherwise unobserved.
Theorists in astronomy endeavor to create theoretical models that are based on existing observations and known physics, and to predict observational consequences of those models. The observation of phenomena predicted by a model allows astronomers to select between several alternative or conflicting models. Theorists also modify existing models to take into account new observations. In some cases, a large amount of observational data that is inconsistent with a model may lead to abandoning it largely or completely, as for geocentric theory, the existence of luminiferous aether, and the steady-state model of cosmic evolution.
Phenomena modeled by theoretical astronomers include:
* stellar dynamics and Stellar evolution, evolution
* galaxy formation and evolution, galaxy formation
* large-scale structure of the universe, large-scale distribution of matter in the Universe
* the origin of cosmic rays
* general relativity and physical cosmology, including string cosmology and astroparticle physics.
Modern theoretical astronomy reflects dramatic advances in observation since the 1990s, including studies of the cosmic microwave background, distant supernovae and redshift survey, galaxy redshifts, which have led to the development of a Lambda-CDM model, standard model of cosmology. This model requires the universe to contain large amounts of dark matter and dark energy whose nature is currently not well understood, but the model gives detailed predictions that are in excellent agreement with many diverse observations.
Specific subfields
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is the branch of astronomy that employs the principles of physics and
chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
"to ascertain the nature of the astronomical objects, rather than their positions or motions in space". Among the objects studied are the Sun, other
star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
s,
galaxies
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar Sys ...
, extrasolar planets, the interstellar medium and the cosmic microwave background.
Their emissions are examined across all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, and the properties examined include luminosity, density, temperature, and chemistry, chemical composition. Because astrophysics is a very broad subject, ''astrophysicists'' typically apply many disciplines of physics, including mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, thermodynamics, quantum mechanics, theory of relativity, relativity, nuclear physics, nuclear and particle physics, and atomic, molecular, and optical physics, atomic and molecular physics.
In practice, modern astronomical research often involves a substantial amount of work in the realms of Theoretical physics, theoretical and observational physics. Some areas of study for astrophysicists include their attempts to determine the properties of dark matter, dark energy, and black holes; whether or not time travel is possible, wormholes can form, or the multiverse exists; and the Cosmogony, origin and ultimate fate of the universe.
Topics also studied by theoretical astrophysicists include Formation and evolution of the Solar System, Solar System formation and evolution; stellar dynamics and Stellar evolution, evolution; galaxy formation and evolution; magnetohydrodynamics; large-scale structure of the universe, large-scale structure of matter in the universe; origin of cosmic rays; general relativity and physical cosmology, including string theory, string cosmology and astroparticle physics.
Astrochemistry
Astrochemistry is the study of the abundance and reactions of molecules in the Universe, and their interaction with radiation. The discipline is an overlap of astronomy and
chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
. The word "astrochemistry" may be applied to both the Solar System and the interstellar medium. The study of the abundance of elements and isotope ratios in Solar System objects, such as meteorites, is also called cosmochemistry, while the study of interstellar atoms and molecules and their interaction with radiation is sometimes called molecular astrophysics. The formation, atomic and chemical composition, evolution and fate of molecular cloud, molecular gas clouds is of special interest, because it is from these clouds that solar systems form. Studies in this field contribute to the understanding of the formation of the Solar System, Earth's origin and geology, abiogenesis, and the origin of climate and oceans.
Astrobiology
Astrobiology is an interdisciplinary scientific field concerned with the abiogenesis, origins, Protocell, early evolution, distribution, and future of life in the
universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents. It comprises all of existence, any fundamental interaction, physical process and physical constant, and therefore all forms of matter and energy, and the structures they form, from s ...
. Astrobiology considers the question of whether extraterrestrial life exists, and how humans can detect it if it does.
The term exobiology is similar.
Astrobiology makes use of molecular biology, biophysics, biochemistry,
chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
, astronomy, physical cosmology, exoplanetology and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from that on Earth. Abiogenesis, The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing Scientific method, scientific data, and although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.
This interdisciplinary field encompasses research on the origin of planetary systems, origins of List of interstellar and circumstellar molecules, organic compounds in space, rock-water-carbon interactions, abiogenesis on Earth, planetary habitability, research on biosignatures for life detection, and studies on the potential for extremophile, life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space.
Physical cosmology
Cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', with the meaning of "a speaking of the wo ...
(from the Greek () "world, universe" and () "word, study" or literally "logic") could be considered the study of the Universe as a whole.
Observations of the large-scale structure of the Universe, a branch known as physical cosmology, have provided a deep understanding of the formation and evolution of the cosmos. Fundamental to modern cosmology is the well-accepted theory of the Big Bang, wherein our Universe began at a single point in time, and thereafter metric expansion of space, expanded over the course of 13.8 billion years to its present condition.
[ The concept of the Big Bang can be traced back to the discovery of the Cosmic microwave background radiation, microwave background radiation in 1965.][ (See also nucleocosmochronology.)
When the first neutral atoms formed from a sea of primordial ions, space became transparent to radiation, releasing the energy viewed today as the microwave background radiation. The expanding Universe then underwent a Dark Age due to the lack of stellar energy sources.]
Extragalactic astronomy
The study of objects outside our galaxy is a branch of astronomy concerned with the Galaxy formation and evolution, formation and evolution of galaxies, their morphology (description) and Galaxy morphological classification, classification, the observation of Active galaxy, active galaxies, and at a larger scale, the Galaxy groups and clusters, groups and clusters of galaxies. Finally, the latter is important for the understanding of the large-scale structure of the cosmos.galaxies
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar Sys ...
are organized into distinct shapes that allow for classification schemes. They are commonly divided into spiral galaxy, spiral, elliptical galaxy, elliptical and irregular galaxy, Irregular galaxies.
As the name suggests, an elliptical galaxy has the cross-sectional shape of an ellipse. The stars move along randomness, random orbits with no preferred direction. These galaxies contain little or no interstellar dust, few star-forming regions, and older stars.quasar
A quasar ( ) is an extremely Luminosity, luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. The emission from an AGN is powered by accretion onto a supermassive black hole with a mass rangi ...
s, and blazar
A blazar is an active galactic nucleus (AGN) with a relativistic jet (a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light) directed very nearly towards an observer. Relativistic beaming of electromagnetic radiation from the ...
s. Quasars are believed to be the most consistently luminous objects in the known universe.
The large-scale structure of the cosmos is represented by groups and clusters of galaxies. This structure is organized into a hierarchy of groupings, with the largest being the superclusters. The collective matter is formed into Galaxy filament, filaments and walls, leaving large Void (astronomy), voids between.
Galactic astronomy
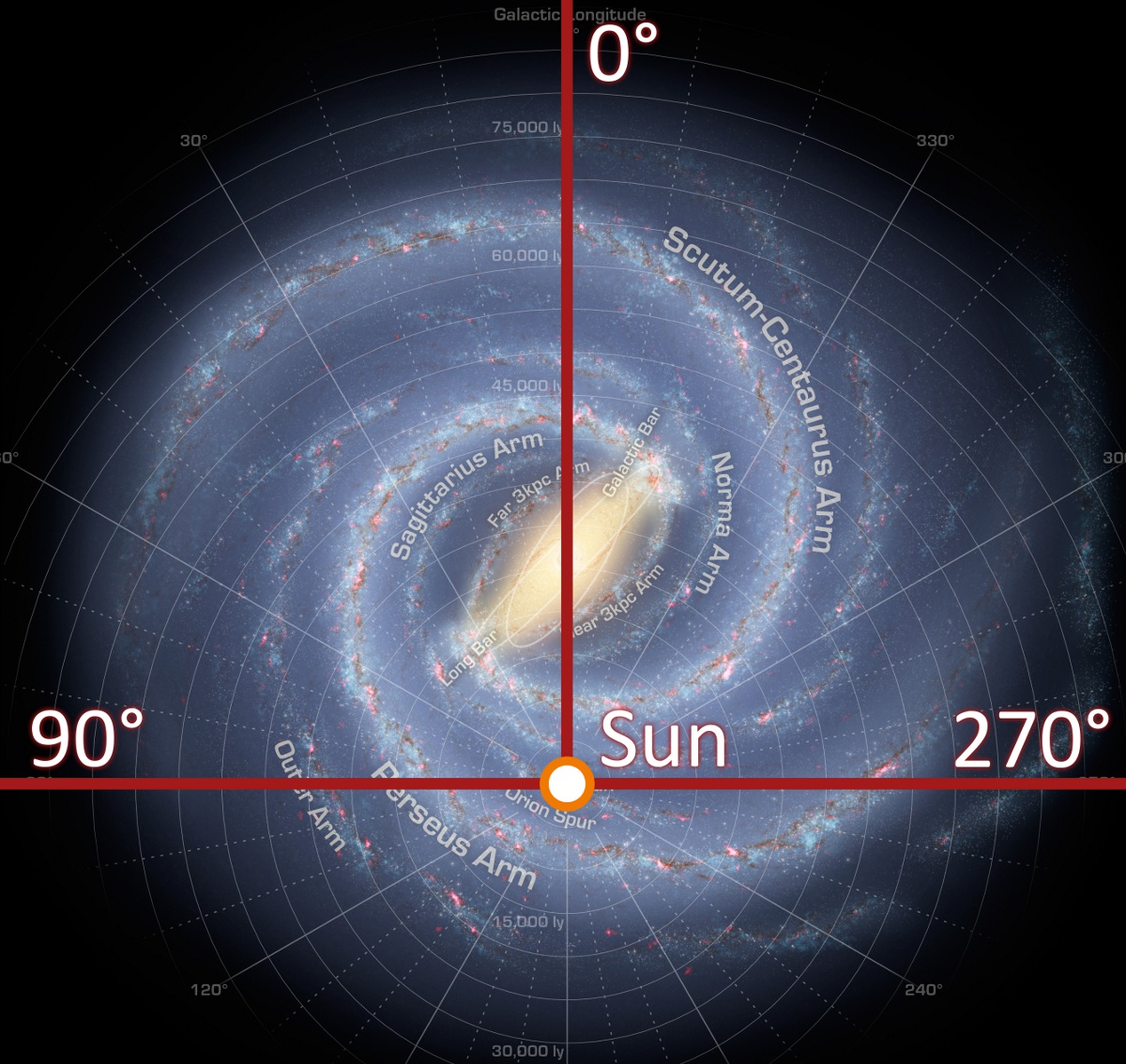 The Solar System orbits within the Milky Way, a barred spiral galaxy that is a prominent member of the Local Group of galaxies. It is a rotating mass of gas, dust, stars and other objects, held together by mutual gravitational attraction. As the Earth is located within the dusty outer arms, there are large portions of the Milky Way that are obscured from view.
The Solar System orbits within the Milky Way, a barred spiral galaxy that is a prominent member of the Local Group of galaxies. It is a rotating mass of gas, dust, stars and other objects, held together by mutual gravitational attraction. As the Earth is located within the dusty outer arms, there are large portions of the Milky Way that are obscured from view.
Stellar astronomy
 The study of stars and stellar evolution is fundamental to our understanding of the Universe. The astrophysics of stars has been determined through observation and theoretical understanding; and from computer simulations of the interior.
The study of stars and stellar evolution is fundamental to our understanding of the Universe. The astrophysics of stars has been determined through observation and theoretical understanding; and from computer simulations of the interior.[Harpaz, 1994, pp. 7–18] Star formation occurs in dense regions of dust and gas, known as Dark nebula, giant molecular clouds. When destabilized, cloud fragments can collapse under the influence of gravity, to form a protostar. A sufficiently dense, and hot, core region will trigger nuclear fusion, thus creating a main-sequence star.[
Almost all elements heavier than hydrogen and helium were nucleosynthesis, created inside the cores of stars.][
The characteristics of the resulting star depend primarily upon its starting mass. The more massive the star, the greater its luminosity, and the more rapidly it fuses its hydrogen fuel into helium in its core. Over time, this hydrogen fuel is completely converted into helium, and the star begins to Stellar evolution, evolve. The fusion of helium requires a higher core temperature. A star with a high enough core temperature will push its outer layers outward while increasing its core density. The resulting red giant formed by the expanding outer layers enjoys a brief life span, before the helium fuel in the core is in turn consumed. Very massive stars can also undergo a series of evolutionary phases, as they fuse increasingly heavier elements.][Harpaz, 1994]
The final fate of the star depends on its mass, with stars of mass greater than about eight times the Sun becoming core collapse supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion ...
e; while smaller stars blow off their outer layers and leave behind the inert core in the form of a white dwarf. The ejection of the outer layers forms a planetary nebula. The remnant of a supernova is a dense neutron star, or, if the stellar mass was at least three times that of the Sun, a black hole.
Solar astronomy
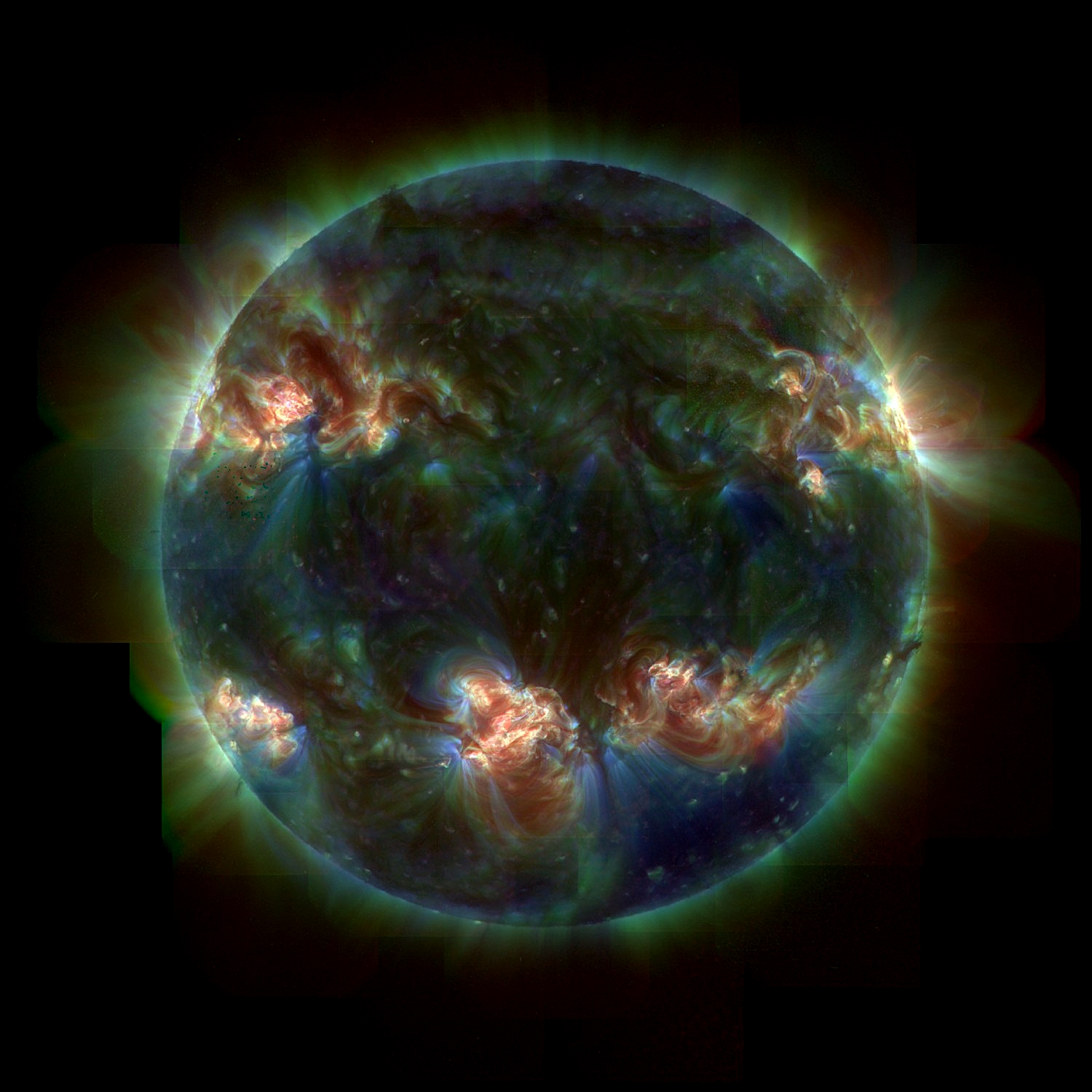 At a distance of about eight light-minutes, the most frequently studied star is the Sun, a typical main-sequence dwarf star of stellar class G2 V, and about 4.6 billion years (Gyr) old. The Sun is not considered a variable star, but it does undergo periodic changes in activity known as the sunspot cycle. This is an 11-year oscillation in Wolf number, sunspot number. Sunspots are regions of lower-than-average temperatures that are associated with intense magnetic activity.
At a distance of about eight light-minutes, the most frequently studied star is the Sun, a typical main-sequence dwarf star of stellar class G2 V, and about 4.6 billion years (Gyr) old. The Sun is not considered a variable star, but it does undergo periodic changes in activity known as the sunspot cycle. This is an 11-year oscillation in Wolf number, sunspot number. Sunspots are regions of lower-than-average temperatures that are associated with intense magnetic activity.
Planetary science
Planetary science is the study of the assemblage of planets, moons
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are colloquially referred to as moons, a deriva ...
, dwarf planets, comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding ...
s, asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). As ...
s, and other bodies orbiting the Sun, as well as extrasolar planets. The Solar System has been relatively well-studied, initially through telescopes and then later by spacecraft. This has provided a good overall understanding of the formation and evolution of the Sun's planetary system, although many new discoveries are still being made.
Interdisciplinary studies
Astronomy and astrophysics have developed significant interdisciplinary links with other major scientific fields. Archaeoastronomy is the study of ancient or traditional astronomies in their cultural context, utilizing archaeology, archaeological and anthropology, anthropological evidence. Astrobiology is the study of the advent and evolution of biological systems in the Universe, with particular emphasis on the possibility of non-terrestrial life. Astrostatistics is the application of statistics to astrophysics to the analysis of a vast amount of observational astrophysical data.
Amateur astronomy
 Astronomy is one of the sciences to which amateurs can contribute the most.
Collectively, amateur astronomers observe a variety of celestial objects and phenomena sometimes with consumer-level equipment or Amateur telescope making, equipment that they build themselves. Common targets of amateur astronomers include the Sun, the Moon, planets, stars, comets, meteor showers, and a variety of deep-sky objects such as star clusters, galaxies, and nebulae. Astronomy clubs are located throughout the world and many have programs to help their members set up and complete observational programs including those to observe all the objects in the Messier (110 objects) or Herschel 400 catalogues of points of interest in the night sky. One branch of amateur astronomy, astrophotography, involves the taking of photos of the night sky. Many amateurs like to specialize in the observation of particular objects, types of objects, or types of events that interest them.
Most amateurs work at visible wavelengths, but many experiment with wavelengths outside the visible spectrum. This includes the use of infrared filters on conventional telescopes, and also the use of radio telescopes. The pioneer of amateur radio astronomy was Karl Guthe Jansky, Karl Jansky, who started observing the sky at radio wavelengths in the 1930s. A number of amateur astronomers use either homemade telescopes or use radio telescopes which were originally built for astronomy research but which are now available to amateurs (''e.g.'' the One-Mile Telescope).
Amateur astronomers continue to make scientific contributions to the field of astronomy and it is one of the few scientific disciplines where amateurs can still make significant contributions. Amateurs can make occultation measurements that are used to refine the orbits of minor planets. They can also discover comets, and perform regular observations of variable stars. Improvements in digital technology have allowed amateurs to make impressive advances in the field of astrophotography.
Astronomy is one of the sciences to which amateurs can contribute the most.
Collectively, amateur astronomers observe a variety of celestial objects and phenomena sometimes with consumer-level equipment or Amateur telescope making, equipment that they build themselves. Common targets of amateur astronomers include the Sun, the Moon, planets, stars, comets, meteor showers, and a variety of deep-sky objects such as star clusters, galaxies, and nebulae. Astronomy clubs are located throughout the world and many have programs to help their members set up and complete observational programs including those to observe all the objects in the Messier (110 objects) or Herschel 400 catalogues of points of interest in the night sky. One branch of amateur astronomy, astrophotography, involves the taking of photos of the night sky. Many amateurs like to specialize in the observation of particular objects, types of objects, or types of events that interest them.
Most amateurs work at visible wavelengths, but many experiment with wavelengths outside the visible spectrum. This includes the use of infrared filters on conventional telescopes, and also the use of radio telescopes. The pioneer of amateur radio astronomy was Karl Guthe Jansky, Karl Jansky, who started observing the sky at radio wavelengths in the 1930s. A number of amateur astronomers use either homemade telescopes or use radio telescopes which were originally built for astronomy research but which are now available to amateurs (''e.g.'' the One-Mile Telescope).
Amateur astronomers continue to make scientific contributions to the field of astronomy and it is one of the few scientific disciplines where amateurs can still make significant contributions. Amateurs can make occultation measurements that are used to refine the orbits of minor planets. They can also discover comets, and perform regular observations of variable stars. Improvements in digital technology have allowed amateurs to make impressive advances in the field of astrophotography.
Unsolved problems in astronomy
In the 21st century there remain important unanswered questions in astronomy. Some are cosmic in scope: for example, what are dark matter and dark energy? These dominate the evolution and fate of the cosmos, yet their true nature remains unknown.
See also
*
*
*
*
Lists
*
*
*
*
*
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
External links
NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED)NED-Distances
Core books
an
Core journals
in Astronomy, from the Smithsonian/NASA Astrophysics Data System
{{Use dmy dates, date=April 2019
Astronomy,
Solar System
 Astronomy is a
Astronomy is a  In early historic times, astronomy only consisted of the observation and predictions of the motions of objects visible to the naked eye. In some locations, early cultures assembled massive artifacts that may have had some astronomical purpose. In addition to their ceremonial uses, these
In early historic times, astronomy only consisted of the observation and predictions of the motions of objects visible to the naked eye. In some locations, early cultures assembled massive artifacts that may have had some astronomical purpose. In addition to their ceremonial uses, these  As civilizations developed, most notably in
As civilizations developed, most notably in  Theoretical astronomy led to speculations on the existence of objects such as black holes and neutron stars, which have been used to explain such observed phenomena as
Theoretical astronomy led to speculations on the existence of objects such as black holes and neutron stars, which have been used to explain such observed phenomena as  The main source of information about celestial body, celestial bodies and other objects is visible light, or more generally electromagnetic radiation. Observational astronomy may be categorized according to the corresponding region of the electromagnetic spectrum on which the observations are made. Some parts of the spectrum can be observed from the Earth's surface, while other parts are only observable from either high altitudes or outside the Earth's atmosphere. Specific information on these subfields is given below.
The main source of information about celestial body, celestial bodies and other objects is visible light, or more generally electromagnetic radiation. Observational astronomy may be categorized according to the corresponding region of the electromagnetic spectrum on which the observations are made. Some parts of the spectrum can be observed from the Earth's surface, while other parts are only observable from either high altitudes or outside the Earth's atmosphere. Specific information on these subfields is given below.
 Radio astronomy uses radiation with wavelengths greater than approximately one millimeter, outside the visible range. Radio astronomy is different from most other forms of observational astronomy in that the observed radio waves can be treated as waves rather than as discrete photons. Hence, it is relatively easier to measure both the amplitude and Phase (waves), phase of radio waves, whereas this is not as easily done at shorter wavelengths.
Although some radio waves are emitted directly by astronomical objects, a product of black-body radiation, thermal emission, most of the radio emission that is observed is the result of synchrotron radiation, which is produced when electrons orbit magnetic fields. Additionally, a number of spectral lines produced by interstellar gas, notably the hydrogen spectral line at 21 cm, are observable at radio wavelengths.
A wide variety of other objects are observable at radio wavelengths, including
Radio astronomy uses radiation with wavelengths greater than approximately one millimeter, outside the visible range. Radio astronomy is different from most other forms of observational astronomy in that the observed radio waves can be treated as waves rather than as discrete photons. Hence, it is relatively easier to measure both the amplitude and Phase (waves), phase of radio waves, whereas this is not as easily done at shorter wavelengths.
Although some radio waves are emitted directly by astronomical objects, a product of black-body radiation, thermal emission, most of the radio emission that is observed is the result of synchrotron radiation, which is produced when electrons orbit magnetic fields. Additionally, a number of spectral lines produced by interstellar gas, notably the hydrogen spectral line at 21 cm, are observable at radio wavelengths.
A wide variety of other objects are observable at radio wavelengths, including  Infrared astronomy is founded on the detection and analysis of infrared radiation, wavelengths longer than red light and outside the range of our vision. The infrared spectrum is useful for studying objects that are too cold to radiate visible light, such as planets, circumstellar disks or nebulae whose light is blocked by dust. The longer wavelengths of infrared can penetrate clouds of dust that block visible light, allowing the observation of young stars embedded in molecular clouds and the cores of galaxies. Observations from the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) have been particularly effective at unveiling numerous galactic protostars and their host star clusters.
With the exception of infrared wavelengths close to visible light, such radiation is heavily absorbed by the atmosphere, or masked, as the atmosphere itself produces significant infrared emission. Consequently, infrared observatories have to be located in high, dry places on Earth or in space. Some molecules radiate strongly in the infrared. This allows the study of the chemistry of space; more specifically it can detect water in comets.
Infrared astronomy is founded on the detection and analysis of infrared radiation, wavelengths longer than red light and outside the range of our vision. The infrared spectrum is useful for studying objects that are too cold to radiate visible light, such as planets, circumstellar disks or nebulae whose light is blocked by dust. The longer wavelengths of infrared can penetrate clouds of dust that block visible light, allowing the observation of young stars embedded in molecular clouds and the cores of galaxies. Observations from the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) have been particularly effective at unveiling numerous galactic protostars and their host star clusters.
With the exception of infrared wavelengths close to visible light, such radiation is heavily absorbed by the atmosphere, or masked, as the atmosphere itself produces significant infrared emission. Consequently, infrared observatories have to be located in high, dry places on Earth or in space. Some molecules radiate strongly in the infrared. This allows the study of the chemistry of space; more specifically it can detect water in comets.
 X-ray astronomy uses X-radiation, X-ray wavelengths. Typically, X-ray radiation is produced by synchrotron emission (the result of electrons orbiting magnetic field lines), bremsstrahlung radiation, thermal emission from thin gases above 107 (10 million) kelvins, and blackbody radiation, thermal emission from thick gases above 107 Kelvin. Since X-rays are absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, all X-ray observations must be performed from high-altitude balloons, rockets, or X-ray astronomy satellites. Notable Astrophysical X-ray source, X-ray sources include X-ray binaries,
X-ray astronomy uses X-radiation, X-ray wavelengths. Typically, X-ray radiation is produced by synchrotron emission (the result of electrons orbiting magnetic field lines), bremsstrahlung radiation, thermal emission from thin gases above 107 (10 million) kelvins, and blackbody radiation, thermal emission from thick gases above 107 Kelvin. Since X-rays are absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, all X-ray observations must be performed from high-altitude balloons, rockets, or X-ray astronomy satellites. Notable Astrophysical X-ray source, X-ray sources include X-ray binaries,  One of the oldest fields in astronomy, and in all of science, is the measurement of the positions of celestial objects. Historically, accurate knowledge of the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets and stars has been essential in
One of the oldest fields in astronomy, and in all of science, is the measurement of the positions of celestial objects. Historically, accurate knowledge of the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets and stars has been essential in  The study of stars and stellar evolution is fundamental to our understanding of the Universe. The astrophysics of stars has been determined through observation and theoretical understanding; and from computer simulations of the interior.Harpaz, 1994, pp. 7–18 Star formation occurs in dense regions of dust and gas, known as Dark nebula, giant molecular clouds. When destabilized, cloud fragments can collapse under the influence of gravity, to form a protostar. A sufficiently dense, and hot, core region will trigger nuclear fusion, thus creating a main-sequence star.
Almost all elements heavier than hydrogen and helium were nucleosynthesis, created inside the cores of stars.
The characteristics of the resulting star depend primarily upon its starting mass. The more massive the star, the greater its luminosity, and the more rapidly it fuses its hydrogen fuel into helium in its core. Over time, this hydrogen fuel is completely converted into helium, and the star begins to Stellar evolution, evolve. The fusion of helium requires a higher core temperature. A star with a high enough core temperature will push its outer layers outward while increasing its core density. The resulting red giant formed by the expanding outer layers enjoys a brief life span, before the helium fuel in the core is in turn consumed. Very massive stars can also undergo a series of evolutionary phases, as they fuse increasingly heavier elements.Harpaz, 1994
The final fate of the star depends on its mass, with stars of mass greater than about eight times the Sun becoming core collapse
The study of stars and stellar evolution is fundamental to our understanding of the Universe. The astrophysics of stars has been determined through observation and theoretical understanding; and from computer simulations of the interior.Harpaz, 1994, pp. 7–18 Star formation occurs in dense regions of dust and gas, known as Dark nebula, giant molecular clouds. When destabilized, cloud fragments can collapse under the influence of gravity, to form a protostar. A sufficiently dense, and hot, core region will trigger nuclear fusion, thus creating a main-sequence star.
Almost all elements heavier than hydrogen and helium were nucleosynthesis, created inside the cores of stars.
The characteristics of the resulting star depend primarily upon its starting mass. The more massive the star, the greater its luminosity, and the more rapidly it fuses its hydrogen fuel into helium in its core. Over time, this hydrogen fuel is completely converted into helium, and the star begins to Stellar evolution, evolve. The fusion of helium requires a higher core temperature. A star with a high enough core temperature will push its outer layers outward while increasing its core density. The resulting red giant formed by the expanding outer layers enjoys a brief life span, before the helium fuel in the core is in turn consumed. Very massive stars can also undergo a series of evolutionary phases, as they fuse increasingly heavier elements.Harpaz, 1994
The final fate of the star depends on its mass, with stars of mass greater than about eight times the Sun becoming core collapse  At a distance of about eight light-minutes, the most frequently studied star is the Sun, a typical main-sequence dwarf star of stellar class G2 V, and about 4.6 billion years (Gyr) old. The Sun is not considered a variable star, but it does undergo periodic changes in activity known as the sunspot cycle. This is an 11-year oscillation in Wolf number, sunspot number. Sunspots are regions of lower-than-average temperatures that are associated with intense magnetic activity.
The Sun has steadily increased in luminosity by 40% since it first became a main-sequence star. The Sun has also undergone periodic changes in luminosity that can have a significant impact on the Earth. The Maunder minimum, for example, is believed to have caused the Little Ice Age phenomenon during the Middle Ages.
At the center of the Sun is the core region, a volume of sufficient temperature and pressure for nuclear fusion to occur. Above the core is the radiation zone, where the plasma conveys the energy flux by means of radiation. Above that is the convection zone where the gas material transports energy primarily through physical displacement of the gas known as convection. It is believed that the movement of mass within the convection zone creates the magnetic activity that generates sunspots. The visible outer surface of the Sun is called the photosphere. Above this layer is a thin region known as the chromosphere. This is surrounded by a transition region of rapidly increasing temperatures, and finally by the super-heated solar corona, corona.
A solar wind of plasma particles constantly streams outward from the Sun until, at the outermost limit of the Solar System, it reaches the heliopause (astronomy), heliopause. As the solar wind passes the Earth, it interacts with the Earth's magnetic field (magnetosphere) and deflects the solar wind, but traps some creating the Van Allen radiation belts that envelop the Earth. The aurora (astronomy), aurora are created when solar wind particles are guided by the magnetic flux lines into the Earth's polar regions where the lines then descend into the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere.
At a distance of about eight light-minutes, the most frequently studied star is the Sun, a typical main-sequence dwarf star of stellar class G2 V, and about 4.6 billion years (Gyr) old. The Sun is not considered a variable star, but it does undergo periodic changes in activity known as the sunspot cycle. This is an 11-year oscillation in Wolf number, sunspot number. Sunspots are regions of lower-than-average temperatures that are associated with intense magnetic activity.
The Sun has steadily increased in luminosity by 40% since it first became a main-sequence star. The Sun has also undergone periodic changes in luminosity that can have a significant impact on the Earth. The Maunder minimum, for example, is believed to have caused the Little Ice Age phenomenon during the Middle Ages.
At the center of the Sun is the core region, a volume of sufficient temperature and pressure for nuclear fusion to occur. Above the core is the radiation zone, where the plasma conveys the energy flux by means of radiation. Above that is the convection zone where the gas material transports energy primarily through physical displacement of the gas known as convection. It is believed that the movement of mass within the convection zone creates the magnetic activity that generates sunspots. The visible outer surface of the Sun is called the photosphere. Above this layer is a thin region known as the chromosphere. This is surrounded by a transition region of rapidly increasing temperatures, and finally by the super-heated solar corona, corona.
A solar wind of plasma particles constantly streams outward from the Sun until, at the outermost limit of the Solar System, it reaches the heliopause (astronomy), heliopause. As the solar wind passes the Earth, it interacts with the Earth's magnetic field (magnetosphere) and deflects the solar wind, but traps some creating the Van Allen radiation belts that envelop the Earth. The aurora (astronomy), aurora are created when solar wind particles are guided by the magnetic flux lines into the Earth's polar regions where the lines then descend into the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere.
 Astronomy is one of the sciences to which amateurs can contribute the most.
Collectively, amateur astronomers observe a variety of celestial objects and phenomena sometimes with consumer-level equipment or Amateur telescope making, equipment that they build themselves. Common targets of amateur astronomers include the Sun, the Moon, planets, stars, comets, meteor showers, and a variety of deep-sky objects such as star clusters, galaxies, and nebulae. Astronomy clubs are located throughout the world and many have programs to help their members set up and complete observational programs including those to observe all the objects in the Messier (110 objects) or Herschel 400 catalogues of points of interest in the night sky. One branch of amateur astronomy, astrophotography, involves the taking of photos of the night sky. Many amateurs like to specialize in the observation of particular objects, types of objects, or types of events that interest them.
Most amateurs work at visible wavelengths, but many experiment with wavelengths outside the visible spectrum. This includes the use of infrared filters on conventional telescopes, and also the use of radio telescopes. The pioneer of amateur radio astronomy was Karl Guthe Jansky, Karl Jansky, who started observing the sky at radio wavelengths in the 1930s. A number of amateur astronomers use either homemade telescopes or use radio telescopes which were originally built for astronomy research but which are now available to amateurs (''e.g.'' the One-Mile Telescope).
Amateur astronomers continue to make scientific contributions to the field of astronomy and it is one of the few scientific disciplines where amateurs can still make significant contributions. Amateurs can make occultation measurements that are used to refine the orbits of minor planets. They can also discover comets, and perform regular observations of variable stars. Improvements in digital technology have allowed amateurs to make impressive advances in the field of astrophotography.
Astronomy is one of the sciences to which amateurs can contribute the most.
Collectively, amateur astronomers observe a variety of celestial objects and phenomena sometimes with consumer-level equipment or Amateur telescope making, equipment that they build themselves. Common targets of amateur astronomers include the Sun, the Moon, planets, stars, comets, meteor showers, and a variety of deep-sky objects such as star clusters, galaxies, and nebulae. Astronomy clubs are located throughout the world and many have programs to help their members set up and complete observational programs including those to observe all the objects in the Messier (110 objects) or Herschel 400 catalogues of points of interest in the night sky. One branch of amateur astronomy, astrophotography, involves the taking of photos of the night sky. Many amateurs like to specialize in the observation of particular objects, types of objects, or types of events that interest them.
Most amateurs work at visible wavelengths, but many experiment with wavelengths outside the visible spectrum. This includes the use of infrared filters on conventional telescopes, and also the use of radio telescopes. The pioneer of amateur radio astronomy was Karl Guthe Jansky, Karl Jansky, who started observing the sky at radio wavelengths in the 1930s. A number of amateur astronomers use either homemade telescopes or use radio telescopes which were originally built for astronomy research but which are now available to amateurs (''e.g.'' the One-Mile Telescope).
Amateur astronomers continue to make scientific contributions to the field of astronomy and it is one of the few scientific disciplines where amateurs can still make significant contributions. Amateurs can make occultation measurements that are used to refine the orbits of minor planets. They can also discover comets, and perform regular observations of variable stars. Improvements in digital technology have allowed amateurs to make impressive advances in the field of astrophotography.