Assassination Of President James Garfield on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 James A. Garfield, the 20th president of the United States, was shot at the Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station in Washington, D.C., at 9:30 am on Saturday, July 2, 1881. He died in Elberon, New Jersey, 79 days later on September 19, 1881. The shooting occurred less than four months into his term as president. Garfield's assassin was Charles J. Guiteau, whose motive was revenge against Garfield for an imagined political debt, and getting Chester A. Arthur elevated to president. Guiteau was convicted of Garfield's murder and executed by hanging one year after the shooting.
James A. Garfield, the 20th president of the United States, was shot at the Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station in Washington, D.C., at 9:30 am on Saturday, July 2, 1881. He died in Elberon, New Jersey, 79 days later on September 19, 1881. The shooting occurred less than four months into his term as president. Garfield's assassin was Charles J. Guiteau, whose motive was revenge against Garfield for an imagined political debt, and getting Chester A. Arthur elevated to president. Guiteau was convicted of Garfield's murder and executed by hanging one year after the shooting.
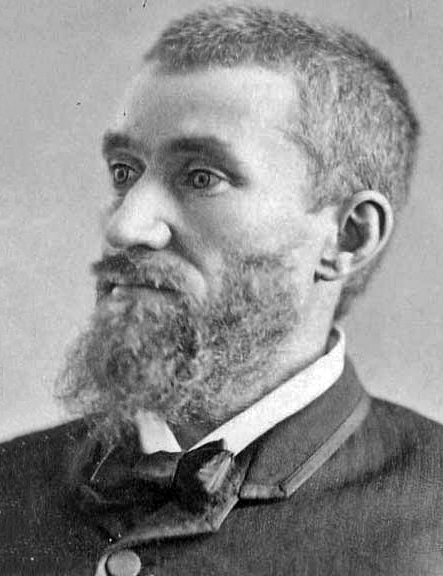 Guiteau arrived in Washington, D.C., on March 5, 1881, the day after Garfield's inauguration, still believing that he would be rewarded. He obtained entrance to the White House and saw the President on March 8, 1881, dropping off a copy of his speech as a reminder of the campaign work which he had done on Garfield's behalf. Guiteau spent the next two months roaming around Washington, staying at rooming houses and sneaking away without paying for his meals and lodging. He passed his days loitering in hotel lobbies to read old newspapers and using hotel stationery to write letters to those who he thought could help him obtain an appointment from Garfield. In addition, he spent time shuffling back and forth between the
Guiteau arrived in Washington, D.C., on March 5, 1881, the day after Garfield's inauguration, still believing that he would be rewarded. He obtained entrance to the White House and saw the President on March 8, 1881, dropping off a copy of his speech as a reminder of the campaign work which he had done on Garfield's behalf. Guiteau spent the next two months roaming around Washington, staying at rooming houses and sneaking away without paying for his meals and lodging. He passed his days loitering in hotel lobbies to read old newspapers and using hotel stationery to write letters to those who he thought could help him obtain an appointment from Garfield. In addition, he spent time shuffling back and forth between the
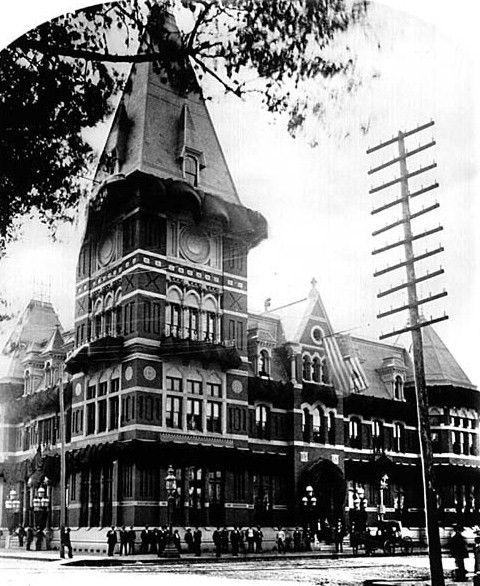

 Garfield was scheduled to leave Washington on July 2, 1881, for his summer vacation, which was reported in the Washington newspapers, and Guiteau lay in wait for him at the Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station on the southwest corner of Sixth Street and Constitution Avenue NW in Washington. Garfield came to the station on his way to his alma mater Williams College, where he was scheduled to deliver a speech before beginning his vacation. He was accompanied by his sons James and Harry, and by Secretary of State James G. Blaine; Secretary of War Robert Todd Lincoln waited at the station to see him off. Garfield had no bodyguard or security detail; early presidents did not employ them, with the exception of Abraham Lincoln during the Civil War.
As Garfield entered the station's waiting room, Guiteau stepped forward and shot the president at point-blank range from behind. Garfield cried out, "My God, what is that?", flinging up his arms. Guiteau fired again, and Garfield collapsed. The first bullet grazed the President's shoulder, and the other struck him in the back, passing the first lumbar vertebra but missing the spinal cord before coming to rest behind his pancreas. Guiteau put his pistol back in his pocket and turned to leave via a cab that he had waiting for him outside the station, but he collided with policeman Patrick Kearney, who was entering the station after hearing the gunfire.
Kearney apprehended Guiteau and was so excited at having arrested the man who had shot the president that he neglected to take the gun from him until after they arrived at the police station. Kearney demanded, "In God's name, man, what did you shoot the President for?" Guiteau responded, "I am a Stalwart, and want Arthur for President." The rapidly gathering crowd screamed, "
Garfield was scheduled to leave Washington on July 2, 1881, for his summer vacation, which was reported in the Washington newspapers, and Guiteau lay in wait for him at the Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station on the southwest corner of Sixth Street and Constitution Avenue NW in Washington. Garfield came to the station on his way to his alma mater Williams College, where he was scheduled to deliver a speech before beginning his vacation. He was accompanied by his sons James and Harry, and by Secretary of State James G. Blaine; Secretary of War Robert Todd Lincoln waited at the station to see him off. Garfield had no bodyguard or security detail; early presidents did not employ them, with the exception of Abraham Lincoln during the Civil War.
As Garfield entered the station's waiting room, Guiteau stepped forward and shot the president at point-blank range from behind. Garfield cried out, "My God, what is that?", flinging up his arms. Guiteau fired again, and Garfield collapsed. The first bullet grazed the President's shoulder, and the other struck him in the back, passing the first lumbar vertebra but missing the spinal cord before coming to rest behind his pancreas. Guiteau put his pistol back in his pocket and turned to leave via a cab that he had waiting for him outside the station, but he collided with policeman Patrick Kearney, who was entering the station after hearing the gunfire.
Kearney apprehended Guiteau and was so excited at having arrested the man who had shot the president that he neglected to take the gun from him until after they arrived at the police station. Kearney demanded, "In God's name, man, what did you shoot the President for?" Guiteau responded, "I am a Stalwart, and want Arthur for President." The rapidly gathering crowd screamed, "
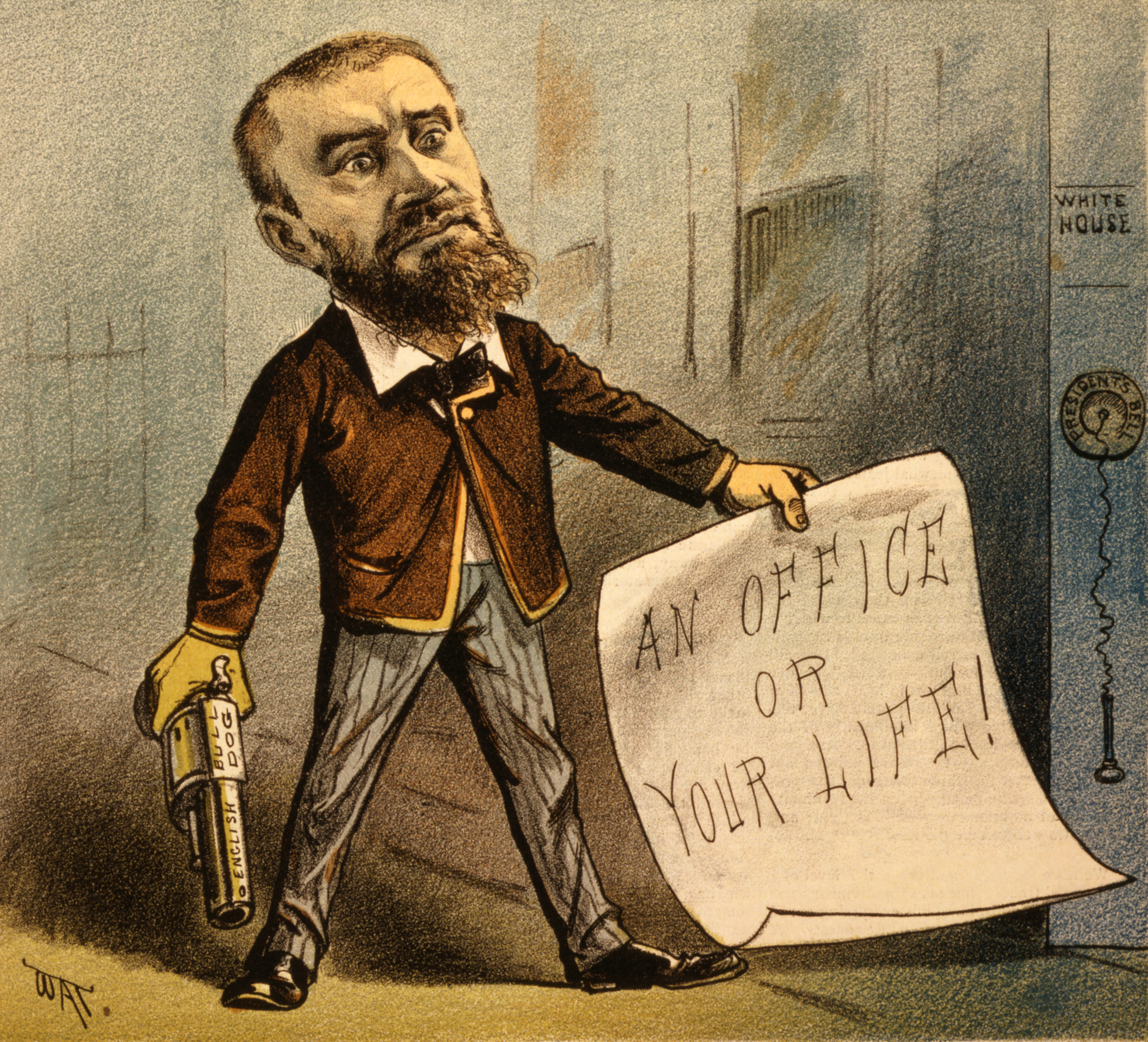 Garfield was carried to an upstairs floor of the railway station, conscious but in shock. One bullet remained lodged in his body, but doctors could not find it. Robert Lincoln was deeply upset, thinking back to the assassination of his father, Abraham Lincoln, sixteen years earlier; he said, "How many hours of sorrow I have passed in this town."
Garfield was carried back to the White House, and doctors told him that he would not survive the night; nevertheless, he remained conscious and alert. The next morning, his vital signs were good and doctors began to hope for recovery. A long
Garfield was carried to an upstairs floor of the railway station, conscious but in shock. One bullet remained lodged in his body, but doctors could not find it. Robert Lincoln was deeply upset, thinking back to the assassination of his father, Abraham Lincoln, sixteen years earlier; he said, "How many hours of sorrow I have passed in this town."
Garfield was carried back to the White House, and doctors told him that he would not survive the night; nevertheless, he remained conscious and alert. The next morning, his vital signs were good and doctors began to hope for recovery. A long 
 On July 29, Garfield met with his Cabinet for the only time during his illness; the members were under strict instruction from the doctors not to discuss anything upsetting. Garfield became increasingly ill over a period of several weeks due to infection, which caused his heart to weaken. He remained bedridden in the White House with fevers and extreme pains. His weight dropped from 210 pounds (95 kilograms) to 130 pounds (58 kilograms) as his inability to keep down and digest food took its toll. Nutrient enemas were given in an attempt to extend his life because he could not digest food. Sepsis and infection set in, and the President suffered from hallucinations for a time. Pus-filled abscesses spread all over his body as the infections raged.
Garfield's condition worsened under the oppressive summer weather in Washington. On September 6, Garfield was taken by train to Elberon (then part of Long Branch) at the
On July 29, Garfield met with his Cabinet for the only time during his illness; the members were under strict instruction from the doctors not to discuss anything upsetting. Garfield became increasingly ill over a period of several weeks due to infection, which caused his heart to weaken. He remained bedridden in the White House with fevers and extreme pains. His weight dropped from 210 pounds (95 kilograms) to 130 pounds (58 kilograms) as his inability to keep down and digest food took its toll. Nutrient enemas were given in an attempt to extend his life because he could not digest food. Sepsis and infection set in, and the President suffered from hallucinations for a time. Pus-filled abscesses spread all over his body as the infections raged.
Garfield's condition worsened under the oppressive summer weather in Washington. On September 6, Garfield was taken by train to Elberon (then part of Long Branch) at the  Most historians and medical experts now believe that Garfield probably would have survived his wound had the doctors been more capable. However, most American doctors of the day did not believe in anti-sepsis measures or the need for cleanliness to prevent infection. Several inserted their unwashed fingers into the wound to probe for the bullet, and one doctor punctured Garfield's liver in doing so. Also, Bliss had supplanted Garfield's physician Jedediah Hyde Baxter. Bliss and the other doctors who attended Garfield had guessed wrong about the path of the bullet in his body; they had probed rightward into his back instead of leftward, missing the location of the bullet but creating a new channel which filled with pus. The
Most historians and medical experts now believe that Garfield probably would have survived his wound had the doctors been more capable. However, most American doctors of the day did not believe in anti-sepsis measures or the need for cleanliness to prevent infection. Several inserted their unwashed fingers into the wound to probe for the bullet, and one doctor punctured Garfield's liver in doing so. Also, Bliss had supplanted Garfield's physician Jedediah Hyde Baxter. Bliss and the other doctors who attended Garfield had guessed wrong about the path of the bullet in his body; they had probed rightward into his back instead of leftward, missing the location of the bullet but creating a new channel which filled with pus. The
 Guiteau went on trial in November, represented by his brother-in-law George Scolville. He received ample media attention during his trial for his bizarre behavior, including constantly insulting his
Guiteau went on trial in November, represented by his brother-in-law George Scolville. He received ample media attention during his trial for his bizarre behavior, including constantly insulting his
 Part of Guiteau's preserved brain is on display at the Mütter Museum at the College of Physicians of Philadelphia. Guiteau's bones and more of his brain, along with Garfield's backbone and a few ribs, are kept at the National Museum of Health and Medicine, at the Army's Forest Glen Annex in Silver Spring, Maryland.
Garfield's assassination was instrumental to the passage of the Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act on January 16, 1883. Garfield himself had called for civil service reform in his inaugural address and supported it as president in the belief that it would make government more efficient. It was passed as something of a memorial to the fallen President. Arthur lost the Republican nomination in 1884 to Blaine, who went on to lose a close election to Democrat Grover Cleveland.
Part of Guiteau's preserved brain is on display at the Mütter Museum at the College of Physicians of Philadelphia. Guiteau's bones and more of his brain, along with Garfield's backbone and a few ribs, are kept at the National Museum of Health and Medicine, at the Army's Forest Glen Annex in Silver Spring, Maryland.
Garfield's assassination was instrumental to the passage of the Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act on January 16, 1883. Garfield himself had called for civil service reform in his inaugural address and supported it as president in the belief that it would make government more efficient. It was passed as something of a memorial to the fallen President. Arthur lost the Republican nomination in 1884 to Blaine, who went on to lose a close election to Democrat Grover Cleveland.
 The Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station was later demolished. The site is now occupied by the West Building of the
The Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station was later demolished. The site is now occupied by the West Building of the
History House
s account of Guiteau's life and the assassination of Garfield
part 12
an
3
James A. Garfield On Prospect of Being Assassinated: Original Letters and Manuscripts
Shapell Manuscript Foundation
New York Times article reprinting indictment
New York Times article on shooting at time of shooting
at the Crime Library
homepage at the University of Missouri–Kansas City
Charles J. Guiteau collection
at Georgetown University * *
The Attempt on the President's Life
, a September 1881 article about the shooting, printed in ''The Atlantic'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Garfield, James A., assassination Deaths by person in New Jersey History of Washington, D.C. 1881 murders in the United States
 James A. Garfield, the 20th president of the United States, was shot at the Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station in Washington, D.C., at 9:30 am on Saturday, July 2, 1881. He died in Elberon, New Jersey, 79 days later on September 19, 1881. The shooting occurred less than four months into his term as president. Garfield's assassin was Charles J. Guiteau, whose motive was revenge against Garfield for an imagined political debt, and getting Chester A. Arthur elevated to president. Guiteau was convicted of Garfield's murder and executed by hanging one year after the shooting.
James A. Garfield, the 20th president of the United States, was shot at the Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station in Washington, D.C., at 9:30 am on Saturday, July 2, 1881. He died in Elberon, New Jersey, 79 days later on September 19, 1881. The shooting occurred less than four months into his term as president. Garfield's assassin was Charles J. Guiteau, whose motive was revenge against Garfield for an imagined political debt, and getting Chester A. Arthur elevated to president. Guiteau was convicted of Garfield's murder and executed by hanging one year after the shooting.
Assassination
Background
Charles Guiteau turned to politics after failing in several ventures, including theology, a law practice, bill collecting, and spending time in the utopian Oneida Community. Former President Ulysses S. Grant was the early front runner for the Republicanpresidential nomination
In United States politics and government, the term presidential nominee has two different meanings:
# A candidate for president of the United States who has been selected by the delegates of a political party at the party's national convention (al ...
in 1880 and was supported by the Stalwart faction. Guiteau became a Stalwart and a Grant supporter, and authored a speech, "Grant against Hancock".
When Grant lost the nomination to dark horse
A dark horse is a previously lesser-known person or thing that emerges to prominence in a situation, especially in a competition involving multiple rivals, or a contestant that on paper should be unlikely to succeed but yet still might.
Origin
Th ...
candidate James Garfield
James Abram Garfield (November 19, 1831 – September 19, 1881) was the 20th president of the United States, serving from March 4, 1881 until his death six months latertwo months after he was shot by an assassin. A lawyer and Civil War gene ...
, who was not affiliated with either the Stalwarts or their rivals the Half-Breeds, Guiteau revised his speech to "Garfield against Hancock" and tried to sign on as a campaigner for the Republican ticket. He never delivered the speech in a public setting, but had it printed (he never paid the bill) and distributed several hundred copies. The speech was ineffective, even in written form; among other problems, Guiteau had made a hurried but incomplete effort to replace references to Grant with references to Garfield. The result was that Guiteau appeared to give Garfield credit for accomplishments that he had originally ascribed to Grant, yet he convinced himself that his speech was largely responsible for Garfield's narrow victory over Democratic
Democrat, Democrats, or Democratic may refer to:
Politics
*A proponent of democracy, or democratic government; a form of government involving rule by the people.
*A member of a Democratic Party:
**Democratic Party (United States) (D)
**Democratic ...
nominee Winfield Scott Hancock. Guiteau believed he should be awarded a diplomatic post for his supposedly vital assistance, first asking for a consulship in Vienna, then expressing a willingness to "settle" for one in Paris. He loitered around Republican headquarters in New York City during the winter of 1880–1881, expecting rewards for his speech, but to no avail.
 Guiteau arrived in Washington, D.C., on March 5, 1881, the day after Garfield's inauguration, still believing that he would be rewarded. He obtained entrance to the White House and saw the President on March 8, 1881, dropping off a copy of his speech as a reminder of the campaign work which he had done on Garfield's behalf. Guiteau spent the next two months roaming around Washington, staying at rooming houses and sneaking away without paying for his meals and lodging. He passed his days loitering in hotel lobbies to read old newspapers and using hotel stationery to write letters to those who he thought could help him obtain an appointment from Garfield. In addition, he spent time shuffling back and forth between the
Guiteau arrived in Washington, D.C., on March 5, 1881, the day after Garfield's inauguration, still believing that he would be rewarded. He obtained entrance to the White House and saw the President on March 8, 1881, dropping off a copy of his speech as a reminder of the campaign work which he had done on Garfield's behalf. Guiteau spent the next two months roaming around Washington, staying at rooming houses and sneaking away without paying for his meals and lodging. He passed his days loitering in hotel lobbies to read old newspapers and using hotel stationery to write letters to those who he thought could help him obtain an appointment from Garfield. In addition, he spent time shuffling back and forth between the State Department
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government responsible for the country's fore ...
and the White House and approaching various Cabinet members and prominent Republicans to press his claim, all without success. Guiteau was destitute and increasingly slovenly because he was wearing the same clothes every day, and forced to walk through the cold, snowy city without overcoat, hat, gloves, or boots. On May 13, 1881, he was banned from the White House waiting room. The following day, he encountered Secretary of State James G. Blaine
James Gillespie Blaine (January 31, 1830January 27, 1893) was an American statesman and Republican politician who represented Maine in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1863 to 1876, serving as Speaker of the U.S. House of Representative ...
, who told him, "Never speak to me again on the Paris consulship as long as you live."
Guiteau's family had judged him to be insane in 1875 and attempted to have him committed, but he had escaped. Now his mania took a violent turn, and he decided that he had been commanded by a higher power to kill the President. He later stated, "I leave my justification to God."
Guiteau borrowed $15 () from George Maynard, a relative by marriage, then went out to purchase a revolver
A revolver (also called a wheel gun) is a repeating handgun that has at least one barrel and uses a revolving cylinder containing multiple chambers (each holding a single cartridge) for firing. Because most revolver models hold up to six roun ...
. He knew little about firearms, but he believed that he would need a large caliber gun. O'Meara's store in Washington provided a choice between two versions of the .442 Webley
The .442 Webley (also known as the ".442 Revolver Centre Fire" in Great Britain, the .442 Rook long (kangaroo) in Australia, the "10.5x17mmR" or ".442 ''Kurz''" in Europe, and ".44 Webley" or ".442 R.I.C." in the United States) is a British cen ...
caliber British Bulldog revolver
The British Bull Dog was a popular type of solid-frame pocket revolver introduced by Philip Webley & Son of Birmingham, England, in 1872, and subsequently copied by gunmakers in continental Europe and the United States.Dowell, p. 68. It featured ...
, one with a wooden grip and another with an ivory grip. He favored ivory because he thought that it would look better as a museum exhibit after the assassination, but could not afford the extra dollar, so the store owner dropped the price for him. Another source describes the pistol that Guiteau purchased as in fact having wooden grips. The revolver was recovered and displayed by the Smithsonian in the early 20th century, but it has since been lost. Guiteau spent the next few weeks stalking Garfield and in target practice; the kick from the revolver almost knocked him over the first time that he fired it. He wrote a letter to Garfield, saying that he should fire Blaine or "you and the Republican party will come to grief". The letter was ignored, as was all the correspondence that Guiteau sent to the White House.
Guiteau continued to prepare carefully; he wrote a letter to William Tecumseh Sherman, the Commanding General of the Army, asking for protection from the mob that he assumed would gather after he killed the President, and he wrote other letters justifying his action as necessary to heal dissension between the factions of the Republican Party. He went to the District of Columbia jail to ask for a tour of the facility where he expected to be incarcerated, but he was told to come back later. He spent the whole month of June following Garfield around Washington. On one occasion, Guiteau trailed Garfield to the railway station as he was seeing his wife, Lucretia Garfield, off to a beach resort in Long Branch, New Jersey
Long Branch is a beachside City (New Jersey), city in Monmouth County, New Jersey, Monmouth County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2010 United States census, 2010 U.S. census, the city's population was 30,719,< ...
; he decided not to shoot the President then, as Lucretia was known to be in poor health and he did not want to upset her.
Shooting

Lynch
Lynch may refer to:
Places Australia
* Lynch Island, South Orkney Islands, Antarctica
* Lynch Point, Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica
* Lynch's Crater, Queensland, Australia
England
* River Lynch, Hertfordshire
* The Lynch, an island in the River T ...
him", but Kearney and several other police officers took the assassin to the police station a few blocks away. As he surrendered to authorities, Guiteau uttered the exulting words, repeated everywhere: "I am a Stalwart of the Stalwarts! I did it, and I want to be arrested! Arthur is President now!" This statement briefly led to unfounded suspicions that either Vice President Chester A. Arthur or his supporters had put Guiteau up to the crime.
The Stalwarts were a Republican faction loyal to Senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
Roscoe Conkling; they supported Grant for a third term in 1880 and strongly opposed Blaine's Half-Breeds. Garfield was unaffiliated with either faction, but Blaine had given his support to Garfield once it became clear that Blaine could not win the presidential nomination. Arthur, a Conkling ally, had been selected as Garfield's running mate to placate the Stalwart faction. As a self-professed Stalwart, Guiteau convinced himself that by removing Garfield, he was striking a blow to unite the two factions of the Republican Party.
Treatment and death
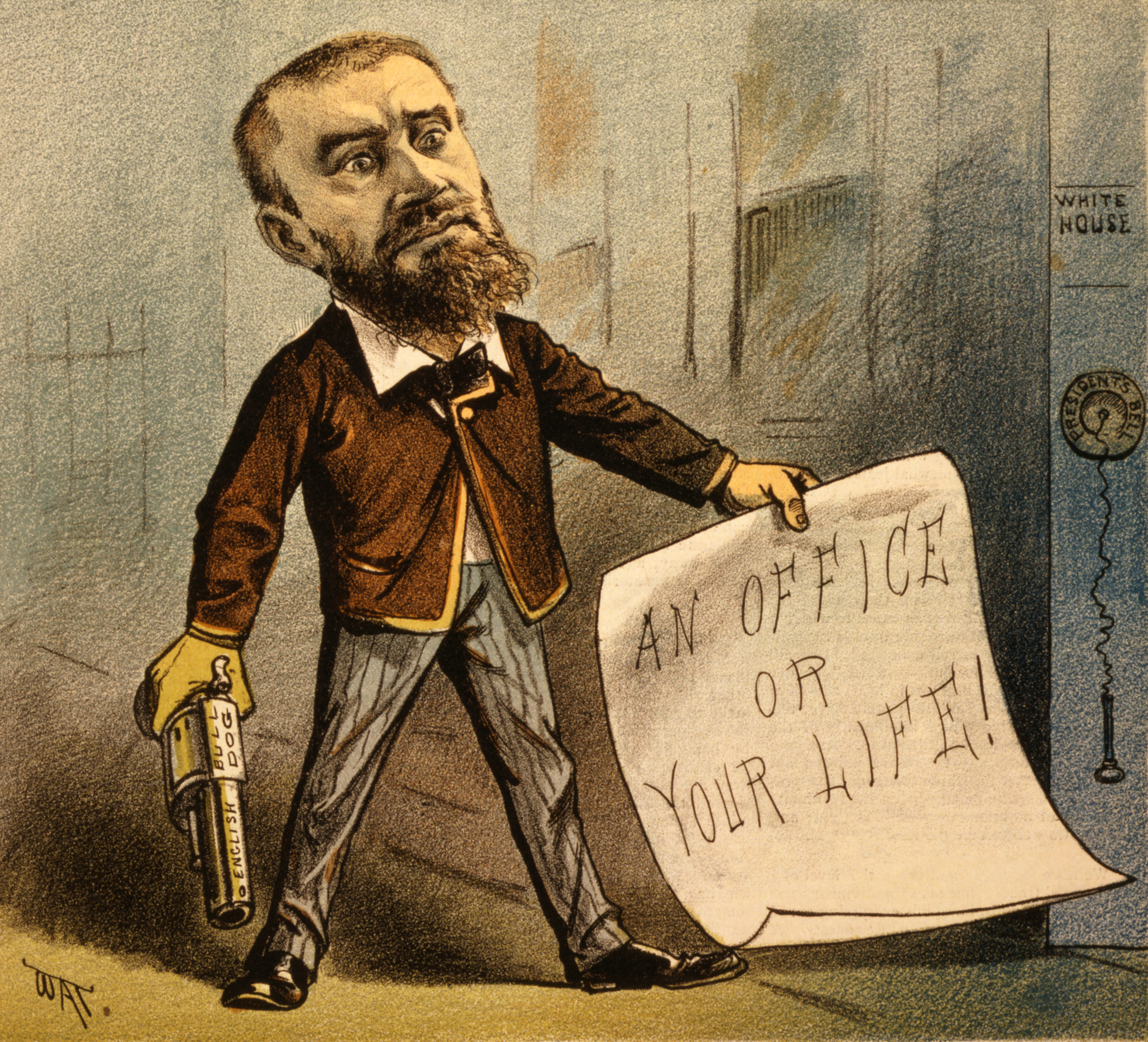 Garfield was carried to an upstairs floor of the railway station, conscious but in shock. One bullet remained lodged in his body, but doctors could not find it. Robert Lincoln was deeply upset, thinking back to the assassination of his father, Abraham Lincoln, sixteen years earlier; he said, "How many hours of sorrow I have passed in this town."
Garfield was carried back to the White House, and doctors told him that he would not survive the night; nevertheless, he remained conscious and alert. The next morning, his vital signs were good and doctors began to hope for recovery. A long
Garfield was carried to an upstairs floor of the railway station, conscious but in shock. One bullet remained lodged in his body, but doctors could not find it. Robert Lincoln was deeply upset, thinking back to the assassination of his father, Abraham Lincoln, sixteen years earlier; he said, "How many hours of sorrow I have passed in this town."
Garfield was carried back to the White House, and doctors told him that he would not survive the night; nevertheless, he remained conscious and alert. The next morning, his vital signs were good and doctors began to hope for recovery. A long vigil
A vigil, from the Latin ''vigilia'' meaning ''wakefulness'' (Greek: ''pannychis'', or ''agrypnia'' ), is a period of purposeful sleeplessness, an occasion for devotional watching, or an observance. The Italian word ''vigilia'' has become genera ...
began, and Garfield's doctors issued regular bulletins that the American public followed closely throughout the summer of 1881. Garfield's condition fluctuated; fevers came and went, he struggled to keep down solid food, and he spent most of the summer eating only liquids.
Navy engineers rigged up an air cooler in an effort to relieve Garfield from the heat of a Washington summer. Fans blew air over a large box of ice and into the President's sickroom, and the device worked well enough to lower the temperature 20 degrees (Fahrenheit). Doctors continued to probe Garfield's wound with unsterilized fingers and instruments, attempting to find the bullet, and Alexander Graham Bell
Alexander Graham Bell (, born Alexander Bell; March 3, 1847 – August 2, 1922) was a Scottish-born inventor, scientist and engineer who is credited with patenting the first practical telephone. He also co-founded the American Telephone and Te ...
devised a metal detector specifically to find it. He was unsuccessful, partly because Garfield's metal bed frame made the instrument malfunction, and partly because self-appointed chief physician Doctor Willard Bliss allowed Bell to use the device only on Garfield's right side, where Bliss insisted the bullet had lodged. Bell's subsequent tests indicated that his metal detector was in good working order and that he would have found the bullet had he been allowed to use the device on Garfield's left side.

 On July 29, Garfield met with his Cabinet for the only time during his illness; the members were under strict instruction from the doctors not to discuss anything upsetting. Garfield became increasingly ill over a period of several weeks due to infection, which caused his heart to weaken. He remained bedridden in the White House with fevers and extreme pains. His weight dropped from 210 pounds (95 kilograms) to 130 pounds (58 kilograms) as his inability to keep down and digest food took its toll. Nutrient enemas were given in an attempt to extend his life because he could not digest food. Sepsis and infection set in, and the President suffered from hallucinations for a time. Pus-filled abscesses spread all over his body as the infections raged.
Garfield's condition worsened under the oppressive summer weather in Washington. On September 6, Garfield was taken by train to Elberon (then part of Long Branch) at the
On July 29, Garfield met with his Cabinet for the only time during his illness; the members were under strict instruction from the doctors not to discuss anything upsetting. Garfield became increasingly ill over a period of several weeks due to infection, which caused his heart to weaken. He remained bedridden in the White House with fevers and extreme pains. His weight dropped from 210 pounds (95 kilograms) to 130 pounds (58 kilograms) as his inability to keep down and digest food took its toll. Nutrient enemas were given in an attempt to extend his life because he could not digest food. Sepsis and infection set in, and the President suffered from hallucinations for a time. Pus-filled abscesses spread all over his body as the infections raged.
Garfield's condition worsened under the oppressive summer weather in Washington. On September 6, Garfield was taken by train to Elberon (then part of Long Branch) at the Jersey Shore
The Jersey Shore (known by locals simply as the Shore) is the coastal region of the U.S. state of New Jersey. Geographically, the term encompasses about of oceanfront bordering the Atlantic Ocean, from Perth Amboy in the north to Cape May Po ...
, where volunteers built a spur line, overnight, from the station to the Francklyn Cottage, a seaside mansion given over to his use. The intent was to help the President escape the Washington heat and humidity, in the vain hope that the fresh air and quiet might aid his recovery. Garfield was propped up in bed before a window with a view of the beach and ocean. New infections set in, as well as spasms of angina
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by ischemia, insufficient blood flow to the Cardiac muscle, heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typical ...
. Garfield died of a ruptured splenic artery aneurysm, following sepsis and bronchial pneumonia at 10:35 pm on Monday, September 19, 1881, in Elberon, New Jersey, two months before his 50th birthday. During the 79 days between his shooting and death, Garfield's only official act was to sign a request for the extradition of a forger who had escaped and was apprehended after he fled to Canada.
 Most historians and medical experts now believe that Garfield probably would have survived his wound had the doctors been more capable. However, most American doctors of the day did not believe in anti-sepsis measures or the need for cleanliness to prevent infection. Several inserted their unwashed fingers into the wound to probe for the bullet, and one doctor punctured Garfield's liver in doing so. Also, Bliss had supplanted Garfield's physician Jedediah Hyde Baxter. Bliss and the other doctors who attended Garfield had guessed wrong about the path of the bullet in his body; they had probed rightward into his back instead of leftward, missing the location of the bullet but creating a new channel which filled with pus. The
Most historians and medical experts now believe that Garfield probably would have survived his wound had the doctors been more capable. However, most American doctors of the day did not believe in anti-sepsis measures or the need for cleanliness to prevent infection. Several inserted their unwashed fingers into the wound to probe for the bullet, and one doctor punctured Garfield's liver in doing so. Also, Bliss had supplanted Garfield's physician Jedediah Hyde Baxter. Bliss and the other doctors who attended Garfield had guessed wrong about the path of the bullet in his body; they had probed rightward into his back instead of leftward, missing the location of the bullet but creating a new channel which filled with pus. The autopsy
An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any di ...
discovered this error and revealed pneumonia in both lungs and a body that was filled with pus due to uncontrolled sepsis. The conventional narrative regarding Garfield's post-shooting medical condition was challenged by Theodore Pappas and Shahrzad Joharifard in a 2013 article in ''The American Journal of Surgery'', in which they argued that the President died from a late rupture of a splenic artery pseudoaneurysm, which developed secondary to the path of the bullet adjacent to the splenic artery. They also argued that his sepsis was actually caused by post-traumatic acute acalculous cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder). Based on the autopsy report, the authors speculate that Garfield's gallbladder subsequently ruptured, leading to the development of a large bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), or gall, is a dark-green-to-yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver (liver bile ...
-containing abscess adjacent to the gallbladder. Pappas and Joharifard say this caused the septic decline in Garfield's condition that was visible starting from July 23, 1881.
Vice President Arthur was at his home in New York City when word came the night of September 19 that Garfield had died. He said, "I hope—my God, I do hope it is a mistake", but confirmation by telegram came soon after. Arthur was inaugurated early in the morning on September 20, and he took the presidential oath of office from John R. Brady
John Riker Brady (March 9, 1822 – March 16, 1891) was an American judge, a justice of the New York Supreme Court, and best known for administering the presidential oath of office to Chester A. Arthur.
Life and career
John Riker Brady ...
, a New York Supreme Court judge. Arthur then left for Long Branch to pay his respects to Mrs. Garfield before going on to Washington.
Garfield's body was taken to Washington, where it lay in state in the Capitol Rotunda and in the United States House of Representatives chamber before being taken to Cleveland, Ohio, where the funeral was held on September 26.
Trial and execution
 Guiteau went on trial in November, represented by his brother-in-law George Scolville. He received ample media attention during his trial for his bizarre behavior, including constantly insulting his
Guiteau went on trial in November, represented by his brother-in-law George Scolville. He received ample media attention during his trial for his bizarre behavior, including constantly insulting his defense
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense industr ...
team, formatting his testimony in epic poems which he recited at length, and soliciting legal advice from random spectators in the audience via passed notes. Guiteau claimed that he was not guilty because Garfield's murder was the will of God and he was only an instrument of it. He sang " John Brown's Body" to the court. He dictated an autobiography to the ''New York Herald
The ''New York Herald'' was a large-distribution newspaper based in New York City that existed between 1835 and 1924. At that point it was acquired by its smaller rival the ''New-York Tribune'' to form the '' New York Herald Tribune''.
His ...
'', ending it with a personal ad for a nice Christian lady under 30. He was oblivious to the American public's outrage and hatred of him, even after he was almost killed twice himself—once while in prison, and again while being transported there. At one point, Guiteau argued that Garfield was killed not by him but by medical malpractice: "I deny the killing, if your honor please. We admit the shooting." He was housed at St. Elizabeths Hospital
St. Elizabeths Hospital is a psychiatric hospital in Southeast, Washington, D.C. operated by the District of Columbia Department of Behavioral Health. It opened in 1855 under the name Government Hospital for the Insane, the first federally oper ...
in the southeastern quadrant of Washington, D.C., throughout the trial and up until his execution.
Guiteau's trial was one of the first high-profile cases in the United States where the insanity defense
The insanity defense, also known as the mental disorder defense, is an affirmative defense by excuse in a criminal case, arguing that the defendant is not responsible for their actions due to an episodic psychiatric disease at the time of the cr ...
was considered. Guiteau vehemently insisted that he had been legally insane at the time of the shooting, but he was not really medically insane, which caused a major rift with his defense lawyers, and which probably contributed to the jury's impression that Guiteau was merely trying to deny responsibility.
Guiteau was actively making plans to start a lecture tour after his release and to run for president himself in 1884; at the same time, he delighted in the media circus surrounding his trial. Guiteau was dismayed when the jury was unconvinced of his divine inspiration, convicting him of Garfield's murder on January 25, 1882, and sentencing him to death. He appeal
In law, an appeal is the process in which cases are reviewed by a higher authority, where parties request a formal change to an official decision. Appeals function both as a process for error correction as well as a process of clarifying and ...
ed, but his appeal was rejected, and he was hanged on June 30, 1882, just two days before the first anniversary of the shooting, in the District of Columbia. Guiteau famously danced his way up to the gallows and waved at the audience, shook hands with his executioner, and, as a last request, recited a poem that he had written called " I am Going to the Lordy". He requested an orchestra to play as he sang the poem; it was denied. As per request with the executioner, Guiteau signaled that he was ready to die by dropping the paper.
Aftermath
 The Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station was later demolished. The site is now occupied by the West Building of the
The Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station was later demolished. The site is now occupied by the West Building of the National Gallery of Art
The National Gallery of Art, and its attached Sculpture Garden, is a national art museum in Washington, D.C., United States, located on the National Mall, between 3rd and 9th Streets, at Constitution Avenue NW. Open to the public and free of char ...
. The National Park Service in 2018 placed permanent wayside signs to mark the spot of the assassination and to honor Garfield. A few blocks away the James A. Garfield Monument
The James A. Garfield Monument stands on the grounds of the United States Capitol in the circle at First Street, S.W., and Maryland Avenue, Washington, D.C. It is a memorial to United States President James A. Garfield, elected in 1880 and as ...
stands on the southwest corner of the U.S. Capitol grounds.
The question of Presidential disability was not addressed. Article II, section 1, clause 6 of the U.S. Constitution says that in case of the "Inability f the Presidentto discharge the Powers and Duties of the said Office, the same shall devolve on the Vice President", but gives no further instruction on what constitutes inability or how the President's inability should be determined. Garfield had lain on his sickbed for 79 days without performing any of the duties of his office except for the signing of an extradition paper, but this did not prove to be a difficulty because in the 19th century the federal government effectively shut down for the summer regardless. During Garfield's ordeal, Congress was not in session and there was little for a president to do. Blaine suggested the Cabinet declare Arthur acting president, but this option was rejected by all, including Arthur, who did not wish to be perceived as grasping for power.
Congress did not deal with the problem of what to do if a president were alive but incapacitated as Garfield was, nor did the Congress take up the question thirty-eight years later, when Woodrow Wilson suffered a stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
that put him in a coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
for days and left him partially paralyzed and blind in one eye for the last year and a half of his presidency. The Twenty-fifth Amendment
The Twenty-fifth Amendment (Amendment XXV) to the United States Constitution deals with presidential succession and disability.
It clarifies that the vice president becomes president if the president dies, resigns, or is removed from office, a ...
was ratified in 1967 and provides an official procedure when the incapacity of a president is recognized.
Lincoln's assassination had taken place roughly sixteen years before during the closing stages of the Civil War. On the other hand, Garfield's term was marked (for the most part) by peacetime, and a general complacency with respect to presidential security had developed by this time. Garfield, like many other presidents, often preferred to interact directly with the public, and although some form of security was almost certainly in place, a comprehensive security detail had not been seriously considered by either Congress or the president up to that point. Remarkably, it would not be until the assassination of William McKinley
William McKinley, the 25th president of the United States, was shot on the grounds of the Pan-American Exposition at the Temple of Music in Buffalo, New York, on September 6, 1901, six months into his second term. He was shaking hands with the ...
some twenty years later that Congress would finally task the United States Secret Service (founded to prevent counterfeiting
To counterfeit means to imitate something authentic, with the intent to steal, destroy, or replace the original, for use in illegal transactions, or otherwise to deceive individuals into believing that the fake is of equal or greater value tha ...
) with the responsibility of ensuring the president's personal safety.
See also
*Assassination of Abraham Lincoln
On April 14, 1865, Abraham Lincoln, the 16th president of the United States, was assassinated by well-known stage actor John Wilkes Booth, while attending the play ''Our American Cousin'' at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C.
Shot in the hea ...
*Assassination of William McKinley
William McKinley, the 25th president of the United States, was shot on the grounds of the Pan-American Exposition at the Temple of Music in Buffalo, New York, on September 6, 1901, six months into his second term. He was shaking hands with the ...
* Assassination of John F. Kennedy
* Garfield Tea House
* List of United States presidential assassination attempts and plots
*List of incidents of political violence in Washington, D.C.
There have been numerous incidents of political violence in Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States, as well as in the greater Washington Metropolitan area.
19th century
* August 24, 1814: Burning of Washington: The British Army inva ...
*'' Assassination Vacation'' (2005 book)
References
Cited works
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*External links
History House
s account of Guiteau's life and the assassination of Garfield
part 1
an
3
James A. Garfield On Prospect of Being Assassinated: Original Letters and Manuscripts
Shapell Manuscript Foundation
New York Times article reprinting indictment
New York Times article on shooting at time of shooting
at the Crime Library
homepage at the University of Missouri–Kansas City
Charles J. Guiteau collection
at Georgetown University * *
The Attempt on the President's Life
, a September 1881 article about the shooting, printed in ''The Atlantic'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Garfield, James A., assassination Deaths by person in New Jersey History of Washington, D.C. 1881 murders in the United States
Assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
Medical malpractice
1881 in Washington, D.C.
July 1881 events
Political violence in the United States
Murder in Washington, D.C.