Aryika on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
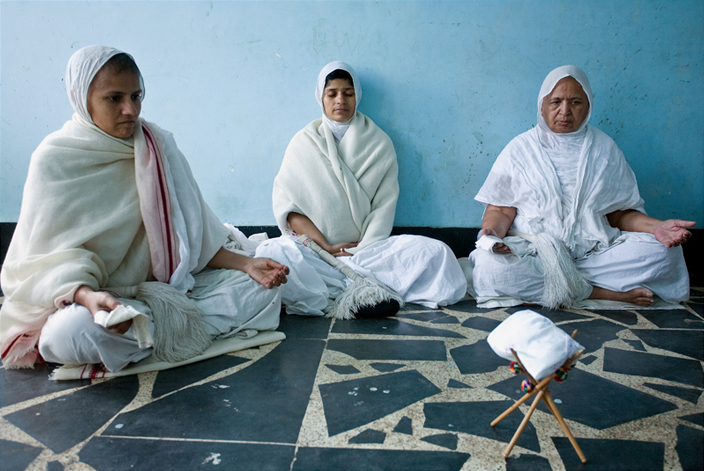 ''Aryika'', also known as ''Sadhvi'', is a female mendicant (
''Aryika'', also known as ''Sadhvi'', is a female mendicant (
 ''Aryika'', also known as ''Sadhvi'', is a female mendicant (
''Aryika'', also known as ''Sadhvi'', is a female mendicant (nun
A nun is a woman who vows to dedicate her life to religious service, typically living under vows of poverty, chastity, and obedience in the enclosure of a monastery or convent.''The Oxford English Dictionary'', vol. X, page 599. The term is o ...
) in Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current ...
.

History
In the traditionalDigambara
''Digambara'' (; "sky-clad") is one of the two major schools of Jainism, the other being ''Śvētāmbara'' (white-clad). The Sanskrit word ''Digambara'' means "sky-clad", referring to their traditional monastic practice of neither possessing n ...
tradition, a male human being is considered closest to the apex with the potential to achieve liberation, particularly through asceticism. Women must gain karmic merit, to be reborn as man, and only then can they achieve spiritual liberation in the Digambara sect of Jainism. This view is different from the Svetambara sect that believes that women too can achieve liberation from ''Saṃsāra
''Saṃsāra'' (Devanagari: संसार) is a Pali/Sanskrit word that means "world". It is also the concept of rebirth and "cyclicality of all life, matter, existence", a fundamental belief of most Indian religions. Popularly, it is the c ...
'' by being mendicants and through ascetic practices.
According to Svetambara Jain texts, from ''Kalpasutras'' onwards, Jainism has had more ''sadhvis'' than ''sadhus'' (female than male mendicants). In Tapa Gacch of the modern era, the ratio of sadhvis to sadhus (nuns to monks) is about 3.5 to 1. This is much higher, and in contrast to the gender ratio historically observed in Buddhism and Hinduism.
Traditionally, in contrast to Svetambara, the Digambara sect has had far less ''sadhvis''. In contemporary times, some Digambara organizations include ''sandhvis'', but the ratio of sadhvis to sadhus (nuns to monks) has been about 1 to 3.
Conduct
A Sadhvi, like a Sadhu, enters the mendicant order by making the Five vows: Ahimsa (Non-violence or Non-injury), Satya (Truthfulness), Asteya (Non-stealing), Brahmacharya (Abstinence from sex and sensual pleasures), and Aparigraha (Non-attachment). Describing the conduct of ''aryikas'',Champat Rai Jain
Champat Rai Jain (6 August 1867–2 June 1942) was a Digambara Jain born in Delhi and who studied and practised law in England. He became an influential Jainism scholar and comparative religion writer between 1910s and 1930s who translated and ...
in his book, ''Sannyāsa Dharma'' writes:
Jains supporting the spiritual liberation of womankind note that their conduct is inclusive in such a path: "It is by way of the Three Jewels that one attains moksa. Nowhere in the Agamas is it stated that women are unable to realise these Three Jewels
In Buddhism, refuge or taking refuge refers to a religious practice, which often includes a prayer or recitation performed at the beginning of the day or of a practice session. Since the period of Early Buddhism until present time, all Theravada ...
" (the right faith, right knowledge, and right conduct).
Gyanmati
Gyanmati Mataji is a Jain nun having the rank of ''Ganini Pramukha''.See also
*Jain monasticism
Jain monasticism refers to the order of monks and nuns in the Jain community and can be divided into two major denominations: the ''Digambara'' and the ''Śvētāmbara''. The monastic practices of the two major sects vary greatly, but the maj ...
* Jain schools and branches
Jainism is an Indian religion which is traditionally believed to be propagated by twenty-four spiritual teachers known as ''tirthankara''. Broadly, Jainism is divided into two major schools of thought, Digambara and Svetambara. These are furth ...
Notes
References
* * Jain monasticism Jainism and women {{Jainism-stub