Artificial life on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Artificial life (ALife or A-Life) is a field of study wherein researchers examine
Artificial life (ALife or A-Life) is a field of study wherein researchers examine
 Black-box models are completely nonmechanistic. They are phenomenological and ignore a composition and internal structure of a complex system. Due to the non-transparent nature of the model, interactions of subsystems cannot be investigated. In contrast, a white-box model of a complex dynamic system has ‘transparent walls’ and directly shows underlying mechanisms. All events at the micro-, meso- and macro-levels of a dynamic system are directly visible at all stages of a white-box model's evolution. In most cases, mathematical modelers use the heavy black-box mathematical methods, which cannot produce mechanistic models of complex dynamic systems. Grey-box models are intermediate and combine black-box and white-box approaches.
Black-box models are completely nonmechanistic. They are phenomenological and ignore a composition and internal structure of a complex system. Due to the non-transparent nature of the model, interactions of subsystems cannot be investigated. In contrast, a white-box model of a complex dynamic system has ‘transparent walls’ and directly shows underlying mechanisms. All events at the micro-, meso- and macro-levels of a dynamic system are directly visible at all stages of a white-box model's evolution. In most cases, mathematical modelers use the heavy black-box mathematical methods, which cannot produce mechanistic models of complex dynamic systems. Grey-box models are intermediate and combine black-box and white-box approaches. 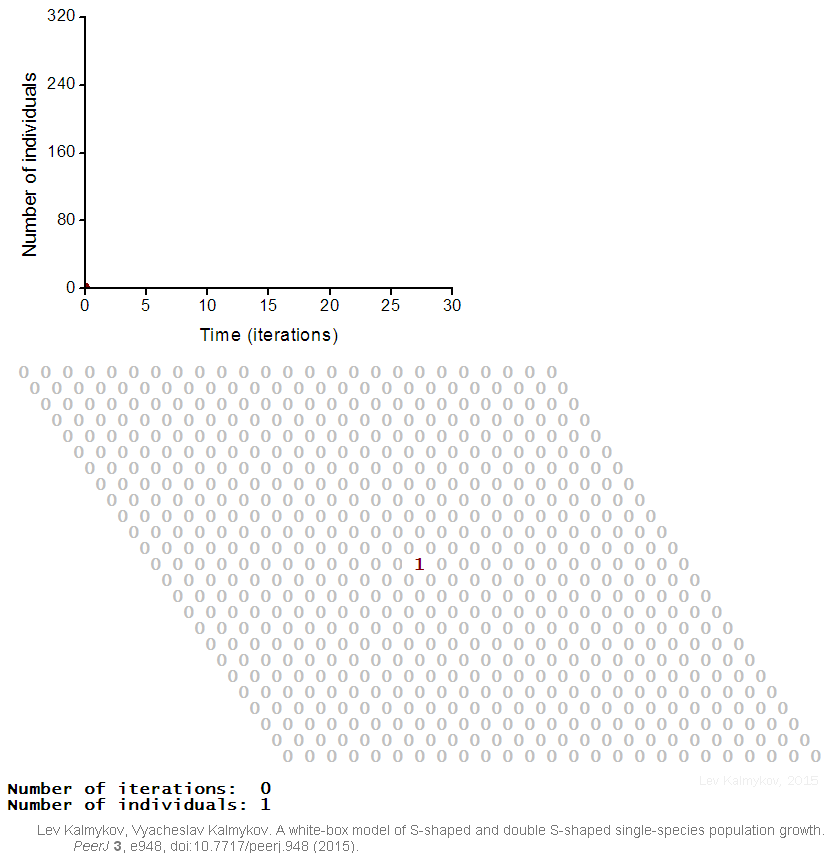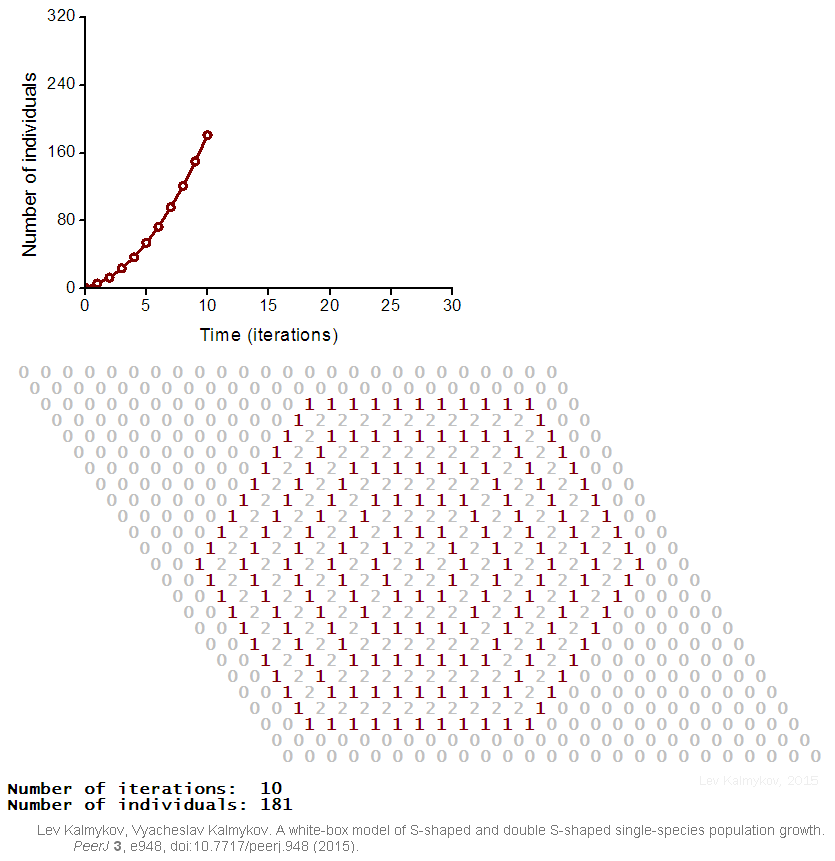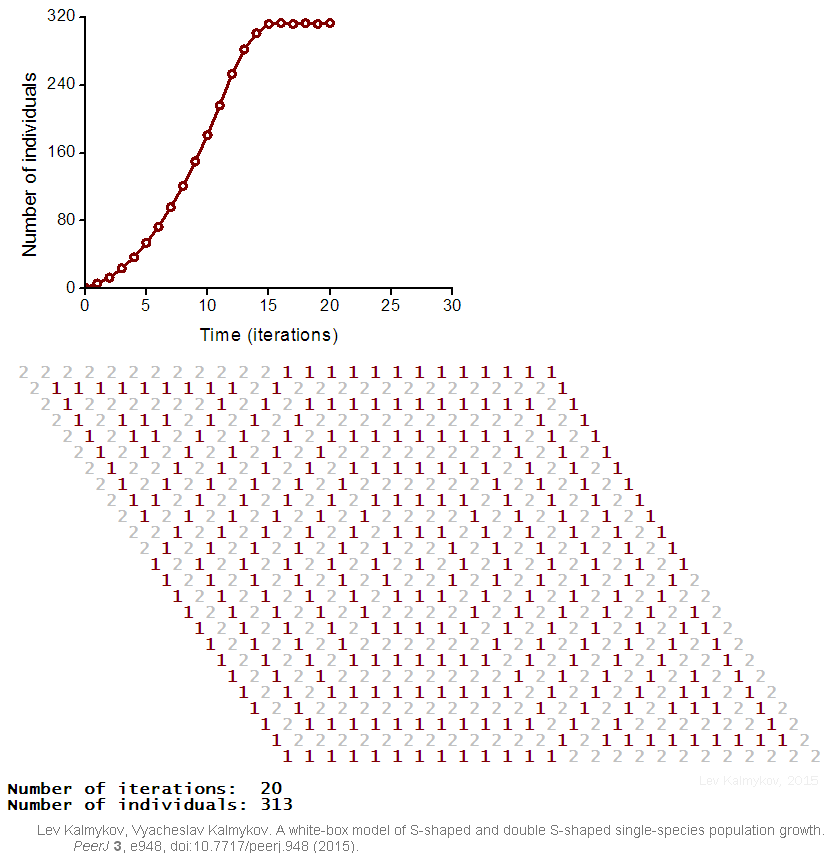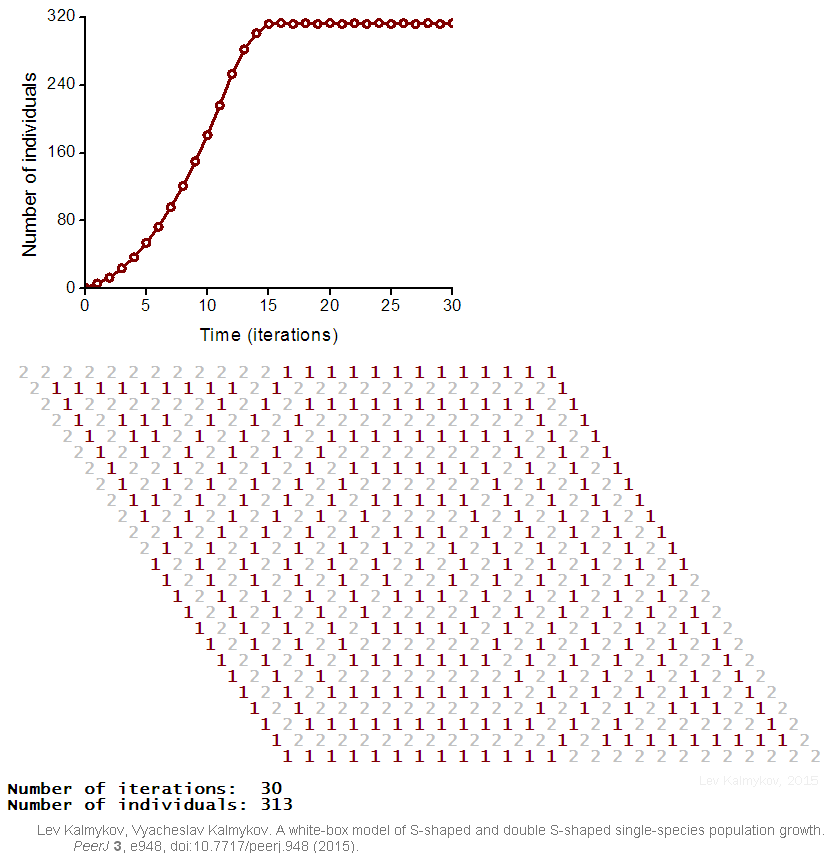 Creation of a white-box model of complex system is associated with the problem of the necessity of an a priori basic knowledge of the modeling subject. The deterministic logical cellular automata are necessary but not sufficient condition of a white-box model. The second necessary prerequisite of a white-box model is the presence of the physical
Creation of a white-box model of complex system is associated with the problem of the necessity of an a priori basic knowledge of the modeling subject. The deterministic logical cellular automata are necessary but not sufficient condition of a white-box model. The second necessary prerequisite of a white-box model is the presence of the physical 
International Society of Artificial Life
''Artificial Life''
journal, at MIT Press Journal
a virtual environment lab
The Bibites Project
{{Authority control Simulation
 Artificial life (ALife or A-Life) is a field of study wherein researchers examine
Artificial life (ALife or A-Life) is a field of study wherein researchers examine system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, str ...
s related to natural life
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, met ...
, its processes, and its evolution, through the use of simulation
A simulation is an imitative representation of a process or system that could exist in the real world. In this broad sense, simulation can often be used interchangeably with model. Sometimes a clear distinction between the two terms is made, in ...
s with computer models
Computer simulation is the running of a mathematical model on a computer, the model being designed to represent the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be determin ...
, robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
, and biochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, a ...
. The discipline was named by Christopher Langton, an American computer scientist
A computer scientist is a scientist who specializes in the academic study of computer science.
Computer scientists typically work on the theoretical side of computation. Although computer scientists can also focus their work and research on ...
, in 1986. In 1987, Langton organized the first conference on the field, in Los Alamos, New Mexico
Los Alamos (, meaning ''The Poplars'') is a census-designated place in Los Alamos County, New Mexico, United States, that is recognized as one of the development and creation places of the Nuclear weapon, atomic bomb—the primary objective of ...
. There are three main kinds of alife, named for their approaches: ''soft'', from software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
; ''hard'', from hardware; and '' wet'', from biochemistry. Artificial life researchers study traditional biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
by trying to recreate aspects of biological phenomena.
Overview
Artificial life studies the fundamental processes of living systems in artificial environments in order to gain a deeper understanding of the complex information processing that define such systems. These topics are broad, but often include evolutionary dynamics,emergent properties
In philosophy, systems theory, science, and art, emergence occurs when a complex entity has properties or behaviors that its parts do not have on their own, and emerge only when they interact in a wider whole.
Emergence plays a central role ...
of collective systems, biomimicry
Biomimetics or biomimicry is the emulation of the models, systems, and elements of nature for the purpose of solving complex human problems. The terms "biomimetics" and "biomimicry" are derived from (''bios''), life, and μίμησις ('' mīm ...
, as well as related issues about the philosophy of the nature of life and the use of lifelike properties in artistic works.
Philosophy
The modeling philosophy of artificial life strongly differs from traditional modeling by studying not only "life as we know it" but also "life as it could be". A traditional model of a biological system will focus on capturing its most important parameters. In contrast, an alife modeling approach will generally seek to decipher the most simple and general principles underlying life and implement them in a simulation. The simulation then offers the possibility to analyse new and different lifelike systems. Vladimir Georgievich Red'ko proposed to generalize this distinction to the modeling of any process, leading to the more general distinction of "processes as we know them" and "processes as they could be". At present, the commonly accepted definition of life does not consider any current alife simulations orsoftware
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
to be alive, and they do not constitute part of the evolutionary process of any ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
. However, different opinions about artificial life's potential have arisen:
* The ''strong alife'' (cf. Strong AI) position states that "life is a process which can be abstracted away from any particular medium" (John von Neumann
John von Neumann ( ; ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian and American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist and engineer. Von Neumann had perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time, in ...
) . Notably, Tom Ray declared that his program Tierra is not simulating life in a computer but synthesizing it.
* The ''weak alife'' position denies the possibility of generating a "living process" outside of a chemical solution. Its researchers try instead to simulate life processes to understand the underlying mechanics of biological phenomena.
Software-based ("soft")
Techniques
* Cellular automata were used in the early days of artificial life, and are still often used for ease ofscalability
Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work. One definition for software systems specifies that this may be done by adding resources to the system.
In an economic context, a scalable business model implies that ...
and parallelization
Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different for ...
. Alife and cellular automata share a closely tied history.
* Artificial neural network
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks.
A neural network consists of connected ...
s are sometimes used to model the brain of an agent. Although traditionally more of an artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
technique, neural nets can be important for simulating population dynamics
Population dynamics is the type of mathematics used to model and study the size and age composition of populations as dynamical systems. Population dynamics is a branch of mathematical biology, and uses mathematical techniques such as differenti ...
of organisms that can ''learn''. The symbiosis between learning and evolution is central to theories about the development of instincts in organisms with higher neurological complexity, as in, for instance, the Baldwin effect.
* Neuroevolution
Neuroevolution, or neuro-evolution, is a form of artificial intelligence that uses evolutionary algorithms to generate artificial neural networks (ANN), parameters, and rules. It is most commonly applied in artificial life, general game playing ...
Program-based
Program-based simulations contain organisms with a "genome" language. This language is more often in the form of aTuring complete
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher and theoretical biologist. He was highly influential in the development of theoretical comput ...
computer program than actual biological DNA. Assembly derivatives are the most common languages used. An organism "lives" when its code is executed, and there are usually various methods allowing self-replication
Self-replication is any behavior of a dynamical system that yields construction of an identical or similar copy of itself. Biological cells, given suitable environments, reproduce by cell division. During cell division, DNA is replicated and c ...
. Mutations are generally implemented as random changes to the code. Use of cellular automata is common but not required. Another example could be an artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
and multi-agent system/program.
Module-based
Individual modules are added to a creature. These modules modify the creature's behaviors and characteristics either directly, by hard coding into the simulation (leg type A increases speed and metabolism), or indirectly, through the emergent interactions between a creature's modules (leg type A moves up and down with a frequency of X, which interacts with other legs to create motion). Generally, these are simulators that emphasize user creation and accessibility over mutation and evolution.Parameter-based
Organisms are generally constructed with pre-defined and fixed behaviors that are controlled by various parameters that mutate. That is, each organism contains a collection of numbers or other ''finite'' parameters. Each parameter controls one or several aspects of an organism in a well-defined way.Neural net–based
These simulations have creatures that learn and grow using neural nets or a close derivative. Emphasis is often, although not always, on learning rather than on natural selection.Complex systems modeling
Mathematical models of complex systems are of three types:black-box
In science, computing, and engineering, a black box is a system which can be viewed in terms of its inputs and outputs (or transfer characteristics), without any knowledge of its internal workings. Its implementation is "opaque" (black). The te ...
(phenomenological), white-box (mechanistic, based on the first principles
In philosophy and science, a first principle is a basic proposition or assumption that cannot be deduced from any other proposition or assumption. First principles in philosophy are from first cause attitudes and taught by Aristotelians, and nuan ...
) and grey-box (mixtures of phenomenological and mechanistic models).
In black-box models, the individual-based (mechanistic) mechanisms of a complex dynamic system remain hidden.  Black-box models are completely nonmechanistic. They are phenomenological and ignore a composition and internal structure of a complex system. Due to the non-transparent nature of the model, interactions of subsystems cannot be investigated. In contrast, a white-box model of a complex dynamic system has ‘transparent walls’ and directly shows underlying mechanisms. All events at the micro-, meso- and macro-levels of a dynamic system are directly visible at all stages of a white-box model's evolution. In most cases, mathematical modelers use the heavy black-box mathematical methods, which cannot produce mechanistic models of complex dynamic systems. Grey-box models are intermediate and combine black-box and white-box approaches.
Black-box models are completely nonmechanistic. They are phenomenological and ignore a composition and internal structure of a complex system. Due to the non-transparent nature of the model, interactions of subsystems cannot be investigated. In contrast, a white-box model of a complex dynamic system has ‘transparent walls’ and directly shows underlying mechanisms. All events at the micro-, meso- and macro-levels of a dynamic system are directly visible at all stages of a white-box model's evolution. In most cases, mathematical modelers use the heavy black-box mathematical methods, which cannot produce mechanistic models of complex dynamic systems. Grey-box models are intermediate and combine black-box and white-box approaches.  Creation of a white-box model of complex system is associated with the problem of the necessity of an a priori basic knowledge of the modeling subject. The deterministic logical cellular automata are necessary but not sufficient condition of a white-box model. The second necessary prerequisite of a white-box model is the presence of the physical
Creation of a white-box model of complex system is associated with the problem of the necessity of an a priori basic knowledge of the modeling subject. The deterministic logical cellular automata are necessary but not sufficient condition of a white-box model. The second necessary prerequisite of a white-box model is the presence of the physical ontology
Ontology is the philosophical study of existence, being. It is traditionally understood as the subdiscipline of metaphysics focused on the most general features of reality. As one of the most fundamental concepts, being encompasses all of realit ...
of the object under study. The white-box modeling represents an automatic hyper-logical inference from the first principle
In philosophy and science, a first principle is a basic proposition or assumption that cannot be deduced from any other proposition or assumption. First principles in philosophy are from first cause attitudes and taught by Aristotelians, and nuan ...
s because it is completely based on the deterministic logic and axiomatic theory of the subject. The purpose of the white-box modeling is to derive from the basic axioms a more detailed, more concrete mechanistic knowledge about the dynamics of the object under study. The necessity to formulate an intrinsic axiomatic system
In mathematics and logic, an axiomatic system is a set of formal statements (i.e. axioms) used to logically derive other statements such as lemmas or theorems. A proof within an axiom system is a sequence of deductive steps that establishes ...
of the subject before creating its white-box model distinguishes the cellular automata models of white-box type from cellular automata models based on arbitrary logical rules. If cellular automata rules have not been formulated from the first principles of the subject, then such a model may have a weak relevance to the real problem.

Notable simulators
This is a list of artificial life and digital organism simulators:Hardware-based ("hard")
Hardware-based artificial life mainly consist of ''robots'', that is, automatically guidedmachine
A machine is a physical system that uses power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromol ...
s able to do tasks on their own.
Biochemical-based ("wet")
Biochemical-based life is studied in the field ofsynthetic biology
Synthetic biology (SynBio) is a multidisciplinary field of science that focuses on living systems and organisms. It applies engineering principles to develop new biological parts, devices, and systems or to redesign existing systems found in nat ...
. It involves research such as the creation of synthetic DNA. The term "wet" is an extension of the term " wetware". Efforts toward "wet" artificial life focus on engineering live minimal cells from living bacteria ''Mycoplasma laboratorium
''Mycoplasma laboratorium'' or Synthia refers to a plan to produce a synthetic biology, synthetic strain of bacterium. The project to build the new bacterium has evolved since its inception. Initially the goal was to identify a minimal set of ge ...
'' and in building non-living biochemical cell-like systems from scratch.
In May 2019, researchers reported a new milestone in the creation of a new synthetic (possibly artificial
Artificiality (the state of being artificial, anthropogenic, or man-made) is the state of being the product of intentional human manufacture, rather than occurring naturally through processes not involving or requiring human activity.
Connotati ...
) form of viable
Viability or viable may refer to:
Biology, medicine or ecology
* Viability selection, the selection of individual organisms who can survive until they are able to reproduce
* Fetal viability, the ability of a fetus to survive outside of the uter ...
life
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, met ...
, a variant of the bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
'', by reducing the natural number of 64 codon
Genetic code is a set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links prote ...
s in the bacterial genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
to 59 codons instead, in order to encode 20 amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s.
Open problems
;How does life arise from the nonliving? * Generate a molecular proto-organismin vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in ...
.
* Achieve the transition to life in an artificial chemistry in silico
In biology and other experimental sciences, an ''in silico'' experiment is one performed on a computer or via computer simulation software. The phrase is pseudo-Latin for 'in silicon' (correct ), referring to silicon in computer chips. It was c ...
.
* Determine whether fundamentally novel living organizations can exist.
* Simulate a unicellular organism
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and ...
over its entire life cycle.
* Explain how rules and symbols are generated from physical dynamics in living systems.
;What are the potentials and limits of living systems?
* Determine what is inevitable in the open-ended evolution of life.
* Determine minimal conditions for evolutionary transitions from specific to generic response systems.
* Create a formal framework for synthesizing dynamical hierarchies at all scales.
* Determine the predictability of evolutionary consequences of manipulating organisms and ecosystems.
* Develop a theory of information processing, information flow
In discourse-based grammatical theory, information flow is any tracking of referential information by speakers. Information may be ''new,'' i.e., just introduced into the conversation''; given,'' i.e., already active in the speakers' consciousne ...
, and information generation for evolving systems.
;How is life related to mind, machines, and culture?
* Demonstrate the emergence of intelligence and mind in an artificial living system.
* Evaluate the influence of machines on the next major evolutionary transition of life.
* Provide a quantitative model of the interplay between cultural and biological evolution.
* Establish ethical
Ethics is the philosophical study of moral phenomena. Also called moral philosophy, it investigates normative questions about what people ought to do or which behavior is morally right. Its main branches include normative ethics, applied e ...
principles for artificial life.
Related subjects
# Agent-based modeling is used in artificial life and other fields to exploreemergence
In philosophy, systems theory, science, and art, emergence occurs when a complex entity has properties or behaviors that its parts do not have on their own, and emerge only when they interact in a wider whole.
Emergence plays a central rol ...
in systems.
# Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
has traditionally used a top down
"Top Down" is a song by American rapper and producer Swizz Beatz, included as the eighth track from his debut studio album ''One Man Band Man'' (2007). "Top Down" contains Sampling (music), samples of swirls and riotous bursts of 1970s-soul horns ...
approach, while alife generally works from the bottom up.
# Artificial chemistry started as a method within the alife community to abstract the processes of chemical reactions.
# Evolutionary algorithm
Evolutionary algorithms (EA) reproduce essential elements of the biological evolution in a computer algorithm in order to solve "difficult" problems, at least Approximation, approximately, for which no exact or satisfactory solution methods are k ...
s are a practical application of the weak alife principle applied to optimization problem
In mathematics, engineering, computer science and economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goo ...
s. Many optimization algorithms have been crafted which borrow from or closely mirror alife techniques. The primary difference lies in explicitly defining the fitness of an agent by its ability to solve a problem, instead of its ability to find food, reproduce, or avoid death. The following is a list of evolutionary algorithms closely related to and used in alife:
#* Ant colony optimization
#* Bacterial colony optimization
#* Genetic algorithm
In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to g ...
#* Genetic programming
Genetic programming (GP) is an evolutionary algorithm, an artificial intelligence technique mimicking natural evolution, which operates on a population of programs. It applies the genetic operators selection (evolutionary algorithm), selection a ...
#* Swarm intelligence
# Multi-agent system – A multi-agent system is a computerized system composed of multiple interacting intelligent agents within an environment.
# Evolutionary art
Evolutionary art is a branch of generative art, in which the artist does not do the work of constructing the artwork, but rather lets a system do the construction. In evolutionary art, initially generated art is put through an iterated process o ...
uses techniques and methods from artificial life to create new forms of art.
# Evolutionary music uses similar techniques, but applied to music instead of visual art.
# Abiogenesis
Abiogenesis is the natural process by which life arises from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothesis is that the transition from non-living to living entities on Earth was not a single even ...
and the origin of life sometimes employ alife methodologies as well.
# Quantum artificial life applies quantum algorithms to artificial life systems.
History
Criticism
Artificial life has had a controversial history.John Maynard Smith
John Maynard Smith (6 January 1920 – 19 April 2004) was a British mathematical and theoretical biology, theoretical and mathematical evolutionary biologist and geneticist. Originally an aeronautical engineer during the Second World War, he ...
criticized certain artificial life work in 1994 as "fact-free science". Mario Bunge
Mario Augusto Bunge ( ; ; September 21, 1919 – February 24, 2020) was an Argentine-Canadian philosopher and physicist. His philosophical writings combined scientific realism, systemism, materialism, emergentism, and other principles.
He was a ...
criticized the ideas of strong artificial life as part of his wider critique of computationalism
In philosophy of mind, the computational theory of mind (CTM), also known as computationalism, is a family of views that hold that the human mind is an information processing system and that cognition and consciousness together are a form of comp ...
. He wrote that proponents of strong alife are mistakenly erasing the distinction between a simulation and the process that is being simulated. He had no such objections to the weak alife program.
See also
References
External links
International Society of Artificial Life
''Artificial Life''
journal, at MIT Press Journal
a virtual environment lab
The Bibites Project
{{Authority control Simulation