Internet and e-commerce
Search engines
Recommendation systems
A recommendation system predicts the "rating" or "preference" a user would give to an item.Francesco Ricci and Lior Rokach and Bracha ShapiraIntroduction to Recommender Systems Handbook
Recommender Systems Handbook, Springer, 2011, pp. 1-35 Recommender systems are used in a variety of areas, such as generating playlists for video and music services, product recommendations for online stores, or content recommendations for social media platforms and open web content recommenders.Pankaj Gupta, Ashish Goel, Jimmy Lin, Aneesh Sharma, Dong Wang, and Reza Bosagh Zade
WTF:The who-to-follow system at Twitter
Proceedings of the 22nd international conference on World Wide Web
Web feeds and posts
Machine learning is also used in Web feeds such as for determining which posts show up in social media feeds. Various typesTargeted advertising and increasing internet engagement
AI is used to target web advertisements to those most likely to click or engage on them. It is also used to increase time spent on a website by selecting attractive content for the viewer. It can predict or generalize the behavior of customers from theirVirtual assistants
Intelligent personal assistants use AI to understand many natural language requests in other ways than rudimentary commands.Spam filtering
Language translation
AI has been used to automatically translate spoken language and textual documents-based context. There also is research and development to decode and conduct animal communication.Facial recognition and image labeling
AI has been used in facial recognition systems, with a 99% accuracy rate. AI has also been demonstrated to generate speech to describe images to blind people.Games
Games have been a major application of AI's capabilities since the 1950s. In the 21st century, AIs have produced superhuman results in many games, including chess (Economic and social challenges
AI for Good is an ITU initiative supporting institutions employing AI to tackle some of the world's greatest economic and social challenges. For example, the University of Southern California launched the Center for Artificial Intelligence in Society, with the goal of using AI to address problems such as homelessness. At Stanford, researchers use AI to analyze satellite images to identify high poverty areas.Agriculture
In agriculture, AI has helped farmers identify areas that need irrigation, fertilization, pesticide treatments or increasing yield. Agronomists use AI to conduct research and development. AI has been used to predict the ripening time for crops such as tomatoes, monitor soil moisture, operate agricultural robots, conduct predictive analytics, classify livestock pig call emotions, automateCyber security
Cyber security companies are adoptingEducation
AI tutors allow students to get one-on-one help. They can reduce anxiety and stress for students stemming from tutor labs or human tutors. AI can also create a dysfunctional environment with revenge effects such as technology that hinders students' ability to stay on task. In other scenario, AI can help educator for student early prediction in virtual learning environment (VLE) such as Moodle. Especially, during the COVID-19 pandemic, learning activity has been required to be conducted online to reduce the virus spread through face-to-face meeting.Finance
Financial institutions have long used artificial neural network systems to detect charges or claims outside of the norm, flagging these for human investigation. The use of AI in banking can be began in 1987 when Security Pacific National Bank launched a fraud prevention taskforce to counter the unauthorized use of debit cards. Kasisto and Moneystream use AI. Banks use AI to organize operations, for bookkeeping, invest in stocks, and manage properties. AI can react to changes when business is not taking place. AI is used to combat fraud and financial crimes by monitoring behavioral patterns for any abnormal changes or anomalies. The use of AI in applications such as online trading and decision making has changed major economic theories. For example, AI-based buying and selling platforms estimate individualized demand and supply curves and thus enable individualized pricing. AI machines reduce information asymmetry in the market and thus make markets more efficient.Trading and investment
Audit
AI makes continuous auditing possible. Potential benefits include reducing audit risk, increasing the level of assurance, and reducing audit duration.History
In the 1980s, AI started to become prominent in finance as expert systems were commercialized. For example, Dupont created 100 expert systems, which helped them to save almost $10 million per year. One of the first systems was the Protrader expert system that predicted the 87-point drop in the Dow Jones Industrial Average in 1986. "The major junctions of the system were to monitor premiums in the market, determine the optimum investment strategy, execute transactions when appropriate and modify the knowledge base through a learning mechanism." One of the first expert systems to help with financial plans was PlanPowerm and Client Profiling System, created by Applied Expert Systems (APEX). It was launched in 1986. It helped create personal financial plans for people. In the 1990s AI was applied to fraud detection. In 1993 FinCEN Artificial Intelligence System (FAIS) launched. It was able to review over 200,000 transactions per week and over two years it helped identify 400 potential cases ofGovernment
AI facial recognition systems are used for mass surveillance, notably in China. In 2019, Bangalore, Bengaluru, India deployed AI-managed traffic signal. This system uses cameras to monitor traffic density and adjust signal timing based on the interval needed to clear traffic.Military
Various countries are deploying AI military applications.Template:PD-notice, PD-notice The main applications enhance command and control, communications, sensors, integration and interoperability. Research is targeting intelligence collection and analysis, logistics, cyber operations, information operations, and semiautonomous and Vehicular automation, autonomous vehicles. AI technologies enable coordination of sensors and effectors, threat detection and identification, marking of enemy positions, target acquisition, coordination and deconfliction of distributed Forward observers in the U.S. military, Joint Fires between networked combat vehicles involving manned and unmanned teams. AI was incorporated into military operations in Iraq and Syria. Worldwide annual military spending on robotics rose from US$5.1 billion in 2010 to US$7.5 billion in 2015. Military drones capable of autonomous action are in wide use. Many researchers avoid military applications.Health
Healthcare
 AI in healthcare is often used for classification, to evaluate a CT scan or Electrocardiography, electrocardiogram or to identify high-risk patients for population health. AI is helping with the high-cost problem of dosing. One study suggested that AI could save $16 billion. In 2016, a study reported that an AI-derived formula derived the proper dose of immunosuppressant drugs to give to transplant patients.
Microsoft's AI project Hanover helps doctors choose Treatment of cancer, cancer treatments from among the more than 800 medicines and vaccines. Its goal is to memorize all the relevant papers to predict which (combinations of) drugs will be most effective for each patient. Acute myeloid leukemia, Myeloid leukemia is one target. Another study reported on an AI that was as good as doctors in identifying skin cancers. Another project monitors multiple high-risk patients by asking each patient questions based on data acquired from doctor/patient interactions. In one study done with transfer learning, an AI diagnosed eye conditions similar to an ophthalmologist and recommended treatment referrals.
Another study demonstrated surgery with an autonomous robot. The team supervised the robot while it performed soft-tissue surgery, stitching together a pig's bowel judged better than a surgeon.
Artificial neural networks are used as clinical decision support systems for medical diagnosis, such as in concept processing technology in electronic medical record, EMR software.
Other healthcare tasks thought suitable for an AI that are in development include:
*Screening (medicine), Screening
*Heart sound analysis
* Companion robots for elderly care, elder care
* Electronic health record#Usefulness for research, Medical record analysis
* Treatment plan design
* Medication management
* Assisting blind people
* Consultations
* Drug creation (e.g. by identifying candidate drugs and by using existing drug screening data such as in life extension research)
* Clinical training
* Outcome prediction for surgical procedures
* HIV prognosis
* Identifying genomic pathogen signatures of novel pathogens or identifying pathogens via physics-based fingerprints (including pandemic pathogens)
* Helping link genes to their functions, otherwise analyzing genes and identification of novel biological targets
* Help development of biomarker (medicine), biomarkers
* Help tailor therapies to individuals in personalized medicine/precision medicine
AI in healthcare is often used for classification, to evaluate a CT scan or Electrocardiography, electrocardiogram or to identify high-risk patients for population health. AI is helping with the high-cost problem of dosing. One study suggested that AI could save $16 billion. In 2016, a study reported that an AI-derived formula derived the proper dose of immunosuppressant drugs to give to transplant patients.
Microsoft's AI project Hanover helps doctors choose Treatment of cancer, cancer treatments from among the more than 800 medicines and vaccines. Its goal is to memorize all the relevant papers to predict which (combinations of) drugs will be most effective for each patient. Acute myeloid leukemia, Myeloid leukemia is one target. Another study reported on an AI that was as good as doctors in identifying skin cancers. Another project monitors multiple high-risk patients by asking each patient questions based on data acquired from doctor/patient interactions. In one study done with transfer learning, an AI diagnosed eye conditions similar to an ophthalmologist and recommended treatment referrals.
Another study demonstrated surgery with an autonomous robot. The team supervised the robot while it performed soft-tissue surgery, stitching together a pig's bowel judged better than a surgeon.
Artificial neural networks are used as clinical decision support systems for medical diagnosis, such as in concept processing technology in electronic medical record, EMR software.
Other healthcare tasks thought suitable for an AI that are in development include:
*Screening (medicine), Screening
*Heart sound analysis
* Companion robots for elderly care, elder care
* Electronic health record#Usefulness for research, Medical record analysis
* Treatment plan design
* Medication management
* Assisting blind people
* Consultations
* Drug creation (e.g. by identifying candidate drugs and by using existing drug screening data such as in life extension research)
* Clinical training
* Outcome prediction for surgical procedures
* HIV prognosis
* Identifying genomic pathogen signatures of novel pathogens or identifying pathogens via physics-based fingerprints (including pandemic pathogens)
* Helping link genes to their functions, otherwise analyzing genes and identification of novel biological targets
* Help development of biomarker (medicine), biomarkers
* Help tailor therapies to individuals in personalized medicine/precision medicine
Workplace health and safety
AI-enabled chatbots decrease the need for humans to perform basic call center tasks. Machine learning in sentiment analysis can spot fatigue in order to prevent overwork. Similarly, decision support systems can prevent industrial disasters and make disaster response more efficient. For manual workers in material handling, predictive analytics may be used to reduce musculoskeletal injury. Data collected from Wearable technology, wearable sensors can improve workplace health surveillance, Occupational risk assessment, risk assessment, and research. AI can auto-Coding (social sciences), code workers' compensation claims. AI-enabled virtual reality systems can enhance safety training for hazard recognition. AI can more efficiently detect accident Near miss (safety), near misses, which are important in reducing accident rates, but are often underreported.Biochemistry
AlphaFold 2 can determine the 3D structure of a (Protein folding, folded) protein in hours rather than the months required by earlier automated approaches and was used to provide the likely structures of all proteins in the human body and essentially all proteins known to science (more than 200 million).Jeremy KahnLessons from DeepMind's breakthrough in protein-folding A.I.
''Fortune (magazine), Fortune'', 1 December 2020
Chemistry and biology
Machine learning has been used for Drug design#Computer-aided drug design, drug design. It has also been used for predicting molecular properties and exploring large chemical/reaction spaces. Computer-planned syntheses via computational reaction networks, described as a platform that combines "computational synthesis with AI algorithms to predict molecular properties", have been used to explore the abiogenesis, origins of life on Earth, drug-syntheses and developing routes for circular economy, recycling 200 industrial Chemical waste#Methods of disposal of laboratory chemical wastes, waste chemicals into important drugs and agrochemicals (chemical synthesis design). There is research about which types of computer-aided chemistry would benefit from machine learning. It can also be used for "drug discovery and development, drug repurposing, improving pharmaceutical productivity, and clinical trials". It has been used for the protein design, design of proteins with prespecified functional sites. It has been used with databases for the development of a 46-day process to design, synthesize and test a drug which inhibits enzymes of a particular gene, DDR1. DDR1 is involved in cancers and fibrosis which is one reason for the high-quality datasets that enabled these results. There are various types of applications for machine learning in decoding human biology, such as helping to map gene expression patterns to functional activation patterns or identifying functional DNA motifs. It is widely used in genetic research. There also is some use of machine learning in synthetic biology, disease biology, nanotechnology (e.g. nanostructured materials and bionanotechnology), and materials science.Novel types of machine learning
 There are also Laboratory robotics#Applications, prototype robot scientists, including robot-embodied ones like the two Robot Scientists, which show a form of "machine learning" not commonly associated with the term.
Similarly, there is research and development of biological "wetware computers" that can learn (e.g. for use as biosensors) and/or implantation into an organism's body (e.g. for use to control prosthetics). Polymer-based artificial neurons operate directly in biological environments and define biohybrid neurons made of artificial and living components.
Moreover, if whole brain emulation is possible via both scanning and replicating the, at least, bio-chemical brain – as premised in the form of digital replication in ''The Age of Em'', possibly using physical neural networks – that may have applications as or more extensive than e.g. valued human activities and may imply that society would face substantial moral choices, societal risks and ethical problems such as whether (and how) such are built, Mind uploading#Space exploration, sent through space and used compared to potentially competing e.g. potentially more synthetic and/or less human and/or non/less-sentient types of artificial/semi-artificial intelligence. An alternative or additive approach to scanning are types of reverse engineering of the brain.
A subcategory of artificial intelligence is embodied, some of which are mobile robotic systems that each consist of one or multiple robots that are able to learn in the physical world.
There are also Laboratory robotics#Applications, prototype robot scientists, including robot-embodied ones like the two Robot Scientists, which show a form of "machine learning" not commonly associated with the term.
Similarly, there is research and development of biological "wetware computers" that can learn (e.g. for use as biosensors) and/or implantation into an organism's body (e.g. for use to control prosthetics). Polymer-based artificial neurons operate directly in biological environments and define biohybrid neurons made of artificial and living components.
Moreover, if whole brain emulation is possible via both scanning and replicating the, at least, bio-chemical brain – as premised in the form of digital replication in ''The Age of Em'', possibly using physical neural networks – that may have applications as or more extensive than e.g. valued human activities and may imply that society would face substantial moral choices, societal risks and ethical problems such as whether (and how) such are built, Mind uploading#Space exploration, sent through space and used compared to potentially competing e.g. potentially more synthetic and/or less human and/or non/less-sentient types of artificial/semi-artificial intelligence. An alternative or additive approach to scanning are types of reverse engineering of the brain.
A subcategory of artificial intelligence is embodied, some of which are mobile robotic systems that each consist of one or multiple robots that are able to learn in the physical world.
Biological computing in AI and as AI
However, biological computing, biological computers, even if both highly artificial and intelligent, are typically distinguished from synthetic, often silicon-based, computers – they could however be combined or used for the design of either. Moreover, many tasks may be carried out inadequately by artificial intelligence even if its algorithms were transparent, understood, bias-free, apparently effective, and goal-aligned and its trained data sufficiently large and data cleansing, cleansed – such as in cases were the underlying or available metrics, value (ethics), values or data are inappropriate. Computer-aided is a phrase used to describe human activities that make use of computing as tool in more comprehensive activities and systems such as AI for narrow tasks or making use of such without substantially relying on its results (see also: human-in-the-loop). A study described the biological as a limitation of AI with "as long as the biological system cannot be understood, formalized, and imitated, we will not be able to develop technologies that can mimic it" and that if it was understood this doesn't mean there being "a technological solution to imitate natural intelligence". Technologies that integrate biology and are often AI-based include biorobotics.Astronomy, space activities and ufology
Artificial intelligence is used in astronomy to analyze increasing amounts of available data and applications, mainly for "classification, regression, clustering, forecasting, generation, discovery, and the development of new scientific insights" for example for discovering exoplanets, forecasting solar activity, and distinguishing between signals and instrumental effects in gravitational wave astronomy. It could also be used for activities in space such as space exploration, including analysis of data from space missions, real-time science decisions of spacecraft, space debris avoidance, and more autonomous operation. In the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI), machine learning has been used in attempts to identify artificially generated electromagnetic waves in available data – such as real-time observations – and other technosignatures, e.g. via anomaly detection. In ufology, the SkyCAM-5 project headed by Prof. Hakan Kayal and the Avi Loeb#The Galileo Project, Galileo Project headed by Prof. Avi Loeb use machine learning to detect and classify peculiar types of UFOs. The Galileo Project also seeks to detect two further types of potential extraterrestrial technological signatures with the use of AI: 'Oumuamua-like interstellar objects, and non-manmade artificial satellites.Future or non-human applications
Loeb has speculated that one type of technological equipment the project may detect could be "AI astronauts" and in 2021 – in an opinion piece – that AI "will" "supersede natural intelligence", while Martin Rees stated that there "may" be more civilizations than thought with the "majority of them" being artificial. In particular, Hypothetical technology, mid/far future or non-human applications of artificial intelligence could include advanced forms of artificial general intelligence that engages in space colonization or more narrow spaceflight-specific types of AI. In contrast, there have been concerns in relation to potential AGI or AI capable of embryo space colonization, or more generally natural intelligence-based space colonization, such as "safety of encounters with an alien AI", suffering risks (or inverse goals), moral license/responsibility in respect to colonization-effects, or AI gone rogue (e.g. as portrayed with fictional David 8, David8 and HAL 9000). See also: space law and space ethics. Loeb has described the possibility of "AI astronauts" that engage in "supervised evolution" (see also: Directed evolution (transhumanism), directed evolution, Uplift (science fiction), Uplift, directed panspermia, space colonization).Astrochemistry
It can also be used to produce datasets of spectral signatures of molecules that may be involved in the atmospheric production or consumption of particular chemicals – such as Life on Venus#Phosphine, phosphine possibly detected on Venus – which could prevent miss assignments and, if accuracy is improved, be used in future detections and identifications of molecules on other planets.Other fields of research
Archaeology, history and imaging of sites
Machine learning can help to restore and attribute ancient texts. It can help to index texts for example to enable better and easier searching and classify of fragments. Artificial intelligence can also be used to investigate genomes to uncover genetic history, such as interbreeding between archaic and modern humans by which for example the past existence of a ghost population, not Neanderthal or Denisovan, was inferred. It can also be used for "non-invasive and non-destructive access to internal structures of archaeological remains".Physics
A deep learning system was reported to learn intuitive physics from visual data (of virtual 3D environments) based on an reproducibility, unpublished approach inspired by studies of visual cognition in infants. Other researchers have developed a machine learning algorithm that could discover sets of basic variables of various physical systems and predict the systems' future dynamics from video recordings of their behavior. In the future, it may be possible that such can be used to automate the discovery of physical laws of complex systems.Materials science
AI could be used for materials optimization and discovery such as the discovery of stable materials and the prediction of their crystal structure.Reverse engineering
Machine learning is used in diverse types of reverse engineering. For example, machine learning has been used to reverse engineer a composite material part, enabling unauthorized production of high quality parts, and for quickly understanding the behavior of malware. It can also design components by engaging in a type of reverse engineering of not-yet existent virtual components such as inverse molecular design for particular desired functionality or protein design for prespecified functional sites.Law
Legal analysis
AI is a mainstay of law-related professions. Algorithms and machine learning do some tasks previously done by entry-level lawyers. While its use is common, it is not expected to replace most work done by lawyers in the near future. The electronic discovery industry uses machine learning to reduce manual searching.Law enforcement and legal proceedings
COMPAS (software), COMPAS is a commercial system used by U.S. courts to assess the likelihood of recidivist, recidivism. One concern relates to algorithmic bias, AI programs may become biased after processing data that exhibits bias. ProPublica claims that the average COMPAS-assigned recidivism risk level of black defendants is significantly higher than that of white defendants.Services
Human resources
Another application of AI is in human resources. AI can screen resumes and rank candidates based on their qualifications, predict candidate success in given roles, and automate repetitive communication tasks via chatbots.Job search
AI has simplified the recruiting /job search process for both recruiters and job seekers. According to Raj Mukherjee from Indeed, 65% of job searchers search again within 91 days after hire. An AI-powered engine streamlines the complexity of job hunting by accessing information on job skills, salaries, and user tendencies, matching job seekers to the most relevant positions. Machine intelligence calculates appropriate wages and highlights resume information for recruiters using NLP, which extracts relevant words and phrases from text. Another application is an AI resume builder that compiles a CV in 5 minutes. Chatbots assist website visitors and refine workflows.Online and telephone customer service
 AI underlies Avatar (computing)#Artificial intelligence, avatars (automated online assistants) on web pages. It can reduce operation and training costs. Pypestream automated customer service for its mobile application to streamline communication with customers.
A Google app analyzes language and converts speech into text. The platform can identify angry customers through their language and respond appropriately. Amazon uses a chatbot for customer service that can perform tasks like checking the status of an order, cancelling orders, offering refunds and connecting the customer with a human representative.
AI underlies Avatar (computing)#Artificial intelligence, avatars (automated online assistants) on web pages. It can reduce operation and training costs. Pypestream automated customer service for its mobile application to streamline communication with customers.
A Google app analyzes language and converts speech into text. The platform can identify angry customers through their language and respond appropriately. Amazon uses a chatbot for customer service that can perform tasks like checking the status of an order, cancelling orders, offering refunds and connecting the customer with a human representative.
Hospitality
In the hospitality industry, AI is used to reduce repetitive tasks, analyze trends, interact with guests, and predict customer needs. AI hotel services come in the form of a chatbot, application, virtual voice assistant and service robots.Media
 AI applications analyze media content such as movies, TV programs, advertisement videos or user-generated content. The solutions often involve computer vision.
Typical scenarios include the analysis of images using object recognition or face recognition techniques, or the video content analysis, analysis of video for scene recognizing scenes, objects or faces. AI-based media analysis can facilitate media search, the creation of descriptive keywords for content, content policy monitoring (such as verifying the suitability of content for a particular TV viewing time), speech recognition, speech to text for archival or other purposes, and the detection of logos, products or celebrity faces for ad placement.
* Motion interpolation
* Pixel-art scaling algorithms
* Image scaling
* Image restoration
* Hand-colouring of photographs, Photo colorization
* Film restoration
* Photo tagging
* Automated species identification
AI applications analyze media content such as movies, TV programs, advertisement videos or user-generated content. The solutions often involve computer vision.
Typical scenarios include the analysis of images using object recognition or face recognition techniques, or the video content analysis, analysis of video for scene recognizing scenes, objects or faces. AI-based media analysis can facilitate media search, the creation of descriptive keywords for content, content policy monitoring (such as verifying the suitability of content for a particular TV viewing time), speech recognition, speech to text for archival or other purposes, and the detection of logos, products or celebrity faces for ad placement.
* Motion interpolation
* Pixel-art scaling algorithms
* Image scaling
* Image restoration
* Hand-colouring of photographs, Photo colorization
* Film restoration
* Photo tagging
* Automated species identification
Deep-fakes
Deepfakes, Deep-fakes can be used for comedic purposes but are better known for fake news and hoaxes. In January 2016, the Horizon 2020 program financed the InVID Project to help journalists and researchers detect fake documents, made available as browser plugins. In June 2016, the visual computing group of the Technical University of Munich and from Stanford University developed Face2Face, a program that animates photographs of faces, mimicking the facial expressions of another person. The technology has been demonstrated animating the faces of people including Barack Obama and Vladimir Putin. Other methods have been demonstrated based on deep neural networks, from which the name ''deep fake'' was taken. In September 2018, U.S. Senator Mark Warner proposed to penalize social media companies that allow sharing of deep-fake documents on their platforms. In 2018, Vincent Nozick found a way to detect faked content by analyzing eyelid movements. DARPA gave 68 million dollars to work on deep-fake detection. Audio deep-fakes and AI software capable of detecting deep-fakes and cloning human voices have been developed.Video content analysis, surveillance and manipulated media detection
AI algorithms have been used to detect deepfake videos.Music
AI has been used to compose music of various genres. David Cope created an AI called Emily Howell that managed to become well known in the field of algorithmic computer music. The algorithm behind Emily Howell is registered as a US patent. In 2012, AI Iamus (computer), Iamus created the first complete classical album. AIVA (Artificial Intelligence Virtual Artist), composes symphonic music, mainly classical music for film scores. It achieved a world first by becoming the first virtual composer to be recognized by a musical Société des auteurs, compositeurs et éditeurs de musique, professional association. Melomics creates computer-generated music for stress and pain relief. At Sony CSL Research Laboratory, the Flow Machines software creates pop songs by learning music styles from a huge database of songs. It can compose in multiple styles. The Watson Beat uses reinforcement learning and deep belief networks to compose music on a simple seed input melody and a select style. The software was open sourced and musicians such as Taryn Southern collaborated with the project to create music. South Korean singer Hayeon's debut song, "Eyes on You" was composed using AI which was supervised by real composers, including NUVO.Writing and reporting
Narrative Science sells computer generated journalism, computer-generated news and reports. It summarizes sporting events based on statistical data from the game. It also creates financial reports and real estate analyses. Automated Insights generates personalized recaps and previews for Yahoo Sports Fantasy football (American), Fantasy Football. Yseop, uses AI to turn structured data into natural language comments and recommendations. Yseop writes financial reports, executive summaries, personalized sales or marketing documents and more in multiple languages, including English, Spanish, French, and German. TALESPIN made up stories similar to the Aesop's Fables, fables of Aesop. The program started with a set of characters who wanted to achieve certain goals. The story narrated their attempts to satisfy these goals. Mark Riedl and Vadim Bulitko asserted that the essence of storytelling was experience management, or "how to balance the need for a coherent story progression with user agency, which is often at odds". While AI storytelling focuses on story generation (character and plot), story communication also received attention. In 2002, researchers developed an architectural framework for narrative prose generation. They faithfully reproduced text variety and complexity on stories such as Little Red Riding Hood. In 2016, a Japanese AI co-wrote a short story and almost won a literary prize. South Korean company Hanteo Global uses a journalism bot to write articles. Literary authors are also exploring uses of AI. An example is David Jhave Johnston's work ''ReRites'' (2017-2019), where the poet created a daily rite of editing the poetic output of a neural network to create a series of performances and publications.Video games
In video games, AI is routinely used to generate behavior in non-player characters (NPCs). In addition, AI is used for pathfinding. Some researchers consider NPC AI in games to be a "solved problem" for most production tasks. Games with less typical AI include the AI director of ''Left 4 Dead'' (2008) and the neuroevolutionary training of platoons in ''Supreme Commander 2'' (2010). AI is also used in Alien: Isolation, ''Alien Isolation'' (2014) as a way to control the actions the Alien will perform next. Kinect, which provides a 3D body–motion interface for the Xbox 360 and the Xbox One, uses algorithms that emerged from AI research.Art
Art from language input

 AI like "Disco Diffusion", "DALL-E, DALL·E" (1 and 2), Stable Diffusion, Imagen, "Dream by Wombo", Midjourney has also been used for visualizing conceptual inputs such as song lyrics, certain texts or specific imagined concepts (or imaginations) in artistic ways or artistic images in general. Some of the tools also allow users to input images and various parameters e.g. to display an object or product photography, product in various environments, some can replicate artistic styles of popular artists, and some can create elaborate artistic images from rough sketches.
AI like "Disco Diffusion", "DALL-E, DALL·E" (1 and 2), Stable Diffusion, Imagen, "Dream by Wombo", Midjourney has also been used for visualizing conceptual inputs such as song lyrics, certain texts or specific imagined concepts (or imaginations) in artistic ways or artistic images in general. Some of the tools also allow users to input images and various parameters e.g. to display an object or product photography, product in various environments, some can replicate artistic styles of popular artists, and some can create elaborate artistic images from rough sketches.
History
= GOFAI
= AI has been used to produce visual art. The first AI art program, called AARON, was developed by Harold Cohen (artist), Harold Cohen in 1968 at the University of California at San Diego. AARON is the most notable example of AI art in the era of Symbolic artificial intelligence, GOFAI programming because of its use of a symbolic rule-based approach to generate technical images. Cohen developed AARON with the goal of being able to code the act of drawing. In its primitive form, AARON created simple black and white drawings. Cohen would later finish the drawings by painting them. Throughout the years, he also began to develop a way for AARON to also paint. Cohen designed AARON to paint using special brushes and dyes that were chosen by the program itself without mediation from Cohen.= GAN/Modern
= In recent years, AI art has shifted into a new paradigm with the emergence of Generative adversarial network, GAN computer programming, which generates technical images through machine learning frameworks that surpass the need for human operators. One example iMagenta
which began as a research project in 2016 from the Google Brain team that aimed to build programs and algorithms that can generate art and music, without need of human intervention. Other examples of GAN programs that generate art include Artbreeder and DeepDream. AI art generated from GANs programming challenged the parameters of art and only recently entered the art auction market. On October 25, 2018, Portrait of Edmond Edmond de Belamy, Belamy by the Parisian collective, Obvious, was the first art piece created by artificial intelligence to be offered at Christie's, Christie's Auction House and was sold for $432,500. The exhibition "Thinking Machines: Art and Design in the Computer Age, 1959–1989" at Museum of Modern Art, MoMA provided an overview of AI applications for art, architecture, and design. Exhibitions showcasing the usage of AI to produce art include the 2016 Google-sponsored benefit and auction at the Gray Area Foundation in San Francisco, where artists experimented with the DeepDream algorithm and the 2017 exhibition "Unhuman: Art in the Age of AI", which took place in Los Angeles and Frankfurt. In spring 2018, the Association for Computing Machinery dedicated a magazine issue to the subject of computers and art. In June 2018, "Duet for Human and Machine", an art piece permitting viewers to interact with an artificial intelligence, premiered at the Beall Center for Art + Technology. The Austrian Ars Electronica and Museum of Applied Arts, Vienna opened exhibitions on AI in 2019. Ars Electronica's 2019 festival "Out of the box" explored art's role in a sustainable societal transformation.
Understanding art with AI
In addition to the creation of original art, research methods that utilize AI have been generated to quantitatively analyze digital art collections. This has been made possible due to large-scale digitization of artwork in the past few decades. Although the main goal of digitization was to allow for accessibility and exploration of these collections, the use of AI in analyzing them has brought about new research perspectives. Two computational methods, close reading and distant viewing, are the typical approaches used to analyze digitized art. Close reading focuses on specific visual aspects of one piece. Some tasks performed by machines in close reading methods include computational artist authentication and analysis of brushstrokes or texture properties. In contrast, through distant viewing methods, the similarity across an entire collection for a specific feature can be statistically visualized. Common tasks relating to this method include automatic classification, object detection, multimodal tasks, knowledge discovery in art history, and computational aesthetics. Whereas distant viewing includes the analysis of large collections, close reading involves one piece of artwork. Researchers have also introduced models that predict emotional responses to art such aArtEmis
a large-scale dataset with machine learning models that contain emotional reactions to visual art as well as predictions of emotion from images or text.
Utilities
Energy system
Power electronics converters are used in renewable energy, energy storage, electric vehicles and high-voltage direct current transmission. These converters are failure-prone, which can interrupt service and require costly maintenance or catastrophic consequences in mission critical applications. AI can guide the design process for reliable power electronics converters, by calculating exact design parameters that ensure the required lifetime. Machine learning can be used for energy consumption prediction and scheduling, e.g. to help with 100% renewable energy#Intermittency management, renewable energy intermittency management (see also: smart grid and Climate change mitigation#Smart grid and load management, climate change mitigation in the power grid).Telecommunications
Many telecommunications companies make use of Search algorithm, heuristic search to manage their workforces. For example, BT Group deployed heuristic searchSuccess Stories. in an application that schedules 20,000 engineers. Machine learning is also used for speech recognition (SR), including of voice-controlled devices, and SR-related transcription, including of videos.
Manufacturing
Sensors
Artificial intelligence has been combined with digital Spectrometer, spectrometry by IdeaCuria Inc., enable applications such as at-home water quality monitoring.Toys and games
In the 1990s early AIs controlled Tamagotchis and Giga Pets, the Internet, and the first widely released robot, Furby. Aibo was a domestic robot in the form of a robotic dog with intelligent features and autonomy. Mattel created an assortment of AI-enabled toys that "understand" conversations, give intelligent responses, and learn.Oil and gas
Oil and gas companies have used artificial intelligence tools to automate functions, foresee equipment issues, and increase oil and gas output.Transport
Automotive
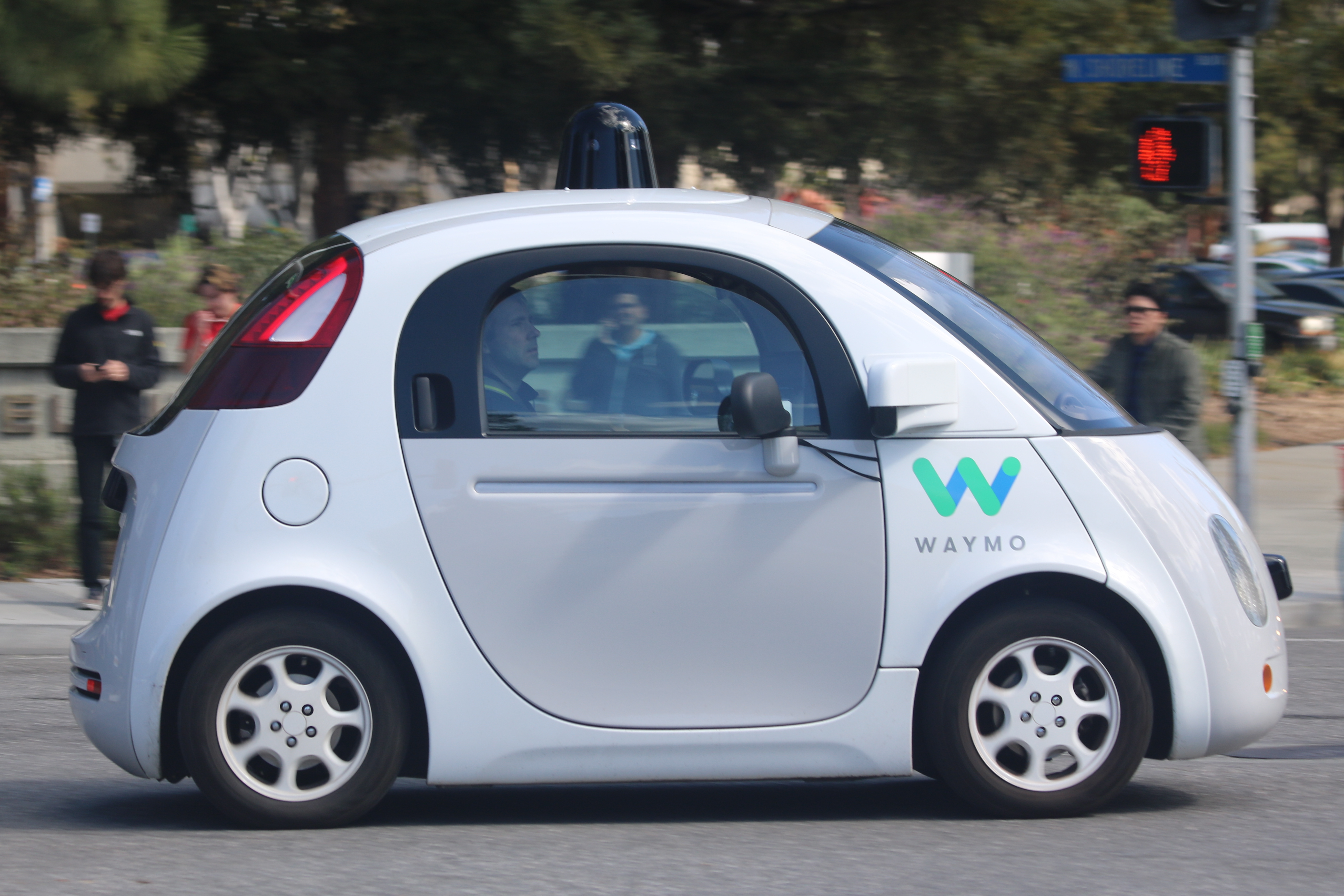 AI in transport is expected to provide safe, efficient, and reliable transportation while minimizing the impact on the environment and communities. The major development challenge is the complexity of transportation systems that involves independent components and parties, with potentially conflicting objectives.
AI-based fuzzy logic controllers operate Transmission (mechanics), gearboxes. For example, the 2006 Audi TT, Volkswagen Touareg, VW Touareg and Volkswagen Transporter (T5), VW Caravell feature the DSP transmission. A number of Škoda variants (Škoda Fabia) include a fuzzy logic-based controller. Cars have AI-based Advanced driver-assistance systems, driver-assist features such as Automatic parking, self-parking and adaptive cruise control.
There are also prototypes of autonomous automotive public transport vehicles such as electric mini-buses as well as Automatic train operation, autonomous rail transport in List of automated train systems, operation.
There also are prototypes of autonomous delivery vehicles, sometimes including delivery robots.
AI has been used to optimize traffic management, which reduces wait times, energy use, and emissions by as much as 25 percent.
Transportation's complexity means that in most cases training an AI in a real-world driving environment is impractical. Simulator-based testing can reduce the risks of on-road training.
AI underpins self-driving vehicles. Companies involved with AI include Tesla Motors, Tesla, WayMo, and General Motors. AI-based systems control functions such as braking, lane changing, collision prevention, navigation and mapping.
Autonomous trucks are in the testing phase. The UK government passed legislation to begin testing of autonomous truck platoons in 2018. A group of autonomous trucks follow closely behind each other. German corporation Daimler AG, Daimler is testing its Freightliner Inspiration.
Autonomous vehicles require accurate maps to be able to navigate between destinations. Some autonomous vehicles do not allow human drivers (they have no steering wheels or pedals).
AI in transport is expected to provide safe, efficient, and reliable transportation while minimizing the impact on the environment and communities. The major development challenge is the complexity of transportation systems that involves independent components and parties, with potentially conflicting objectives.
AI-based fuzzy logic controllers operate Transmission (mechanics), gearboxes. For example, the 2006 Audi TT, Volkswagen Touareg, VW Touareg and Volkswagen Transporter (T5), VW Caravell feature the DSP transmission. A number of Škoda variants (Škoda Fabia) include a fuzzy logic-based controller. Cars have AI-based Advanced driver-assistance systems, driver-assist features such as Automatic parking, self-parking and adaptive cruise control.
There are also prototypes of autonomous automotive public transport vehicles such as electric mini-buses as well as Automatic train operation, autonomous rail transport in List of automated train systems, operation.
There also are prototypes of autonomous delivery vehicles, sometimes including delivery robots.
AI has been used to optimize traffic management, which reduces wait times, energy use, and emissions by as much as 25 percent.
Transportation's complexity means that in most cases training an AI in a real-world driving environment is impractical. Simulator-based testing can reduce the risks of on-road training.
AI underpins self-driving vehicles. Companies involved with AI include Tesla Motors, Tesla, WayMo, and General Motors. AI-based systems control functions such as braking, lane changing, collision prevention, navigation and mapping.
Autonomous trucks are in the testing phase. The UK government passed legislation to begin testing of autonomous truck platoons in 2018. A group of autonomous trucks follow closely behind each other. German corporation Daimler AG, Daimler is testing its Freightliner Inspiration.
Autonomous vehicles require accurate maps to be able to navigate between destinations. Some autonomous vehicles do not allow human drivers (they have no steering wheels or pedals).
Smart traffic lights
Smart traffic lights have been developed at Carnegie Mellon University, Carnegie Mellon since 2009. Professor Stephen Smith has started a company since then Scalable Urban Traffic Control, Surtrac that has installed smart traffic control systems in 22 cities. It costs about $20,000 per intersection to install. Drive time has been reduced by 25% and traffic jam waiting time has been reduced by 40% at the intersections it has been installed.Military
The Royal Australian Air Force, Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) Air and Space Operations Center, Air Operations Division (AOD) uses AI for expert systems. AIs operate as surrogate operators for combat and training simulators, mission management aids, support systems for tactical decision making, and post processing of the simulator data into symbolic summaries. Aircraft simulators use AI for training aviators. Flight conditions can be simulated that allow pilots to make mistakes without risking themselves or expensive aircraft. Air combat can also be simulated. AI can also be used to operate planes analogously to their control of ground vehicles. Autonomous drones can fly independently or in Swarm robotics, swarms. AOD uses the Interactive Fault Diagnosis and Isolation System, or IFDIS, which is a rule-based expert system using information from TF-30 documents and expert advice from mechanics that work on the TF-30. This system was designed to be used for the development of the TF-30 for the F-111C. The system replaced specialized workers. The system allowed regular workers to communicate with the system and avoid mistakes, miscalculations, or having to speak to one of the specialized workers. Speech recognition allows traffic controllers to give verbal directions to drones. Artificial intelligence supported design of aircraft, or AIDA, is used to help designers in the process of creating conceptual designs of aircraft. This program allows the designers to focus more on the design itself and less on the design process. The software also allows the user to focus less on the software tools. The AIDA uses rule-based systems to compute its data. This is a diagram of the arrangement of the AIDA modules. Although simple, the program is proving effective.NASA
In 2003 a Dryden Flight Research Center project created software that could enable a damaged aircraft to continue flight until a safe landing can be achieved. The software compensated for damaged components by relying on the remaining undamaged components. The 2016 Intelligent Autopilot System combined apprenticeship learning and behavioral cloning whereby the autopilot observed low-level actions required to maneuver the airplane and high-level strategy used to apply those actions.Maritime
Neural networks are used by Situation awareness, situational awareness systems in ships and boats. There also are Unmanned surface vehicle, autonomous boats.Environmental monitoring
Autonomous ships that monitor the ocean, AI-driven satellite data analysis, passive acoustics or remote sensing and other applications of environmental monitoring make use of machine learning. For example, "Global Plastic Watch" is an AI-based Earth observation satellite#Environmental monitoring, satellite monitoring-platform for analysis/tracking of plastic waste sites to help waste management, prevention of plastic pollution – primarily ocean pollution – by helping identify who and where mismanages plastic waste, dumping it into oceans.Early-warning systems
Machine learning can be used to early warning system, spot early-warning signs of disasters and environmental issues, possibly including natural pandemic prevention, pandemics, earthquakes, landslides, heavy rainfall, long-term water supply vulnerability, tipping-points of ecosystem collapse, cyanobacterial bloom outbreaks, and droughts.Computer science
Programming assistance
GitHub Copilot is an artificial intelligence model developed by GitHub and OpenAI that is able to autocomplete code in multiple programming languages.Neural network design
AI can be used to create other AIs. For example, around November 2017, Google's AutoML project to evolve new neural net topologies created NASNet, a system optimized for ImageNet and POCO F1. NASNet's performance exceeded all previously published performance on ImageNet.Quantum computing
Machine learning has been used for noise-cancelling in quantum technology, including quantum sensors. Moreover, there is substantial research and development of using quantum computers with machine learning algorithms. For example, there is a prototype, photonic, for neuromorphic computing, neuromorphic (quantum-)computers (NC)/ artificial neural networks and NC-using quantum materials with some variety of potential neuromorphic computing-related applications, and quantum machine learning is a field with some variety of applications under development. AI could be used for quantum simulators which may have the application of solving physics and Quantum chemistry, chemistry problems as well as for quantum annealers for training of neural networks for AI applications. There may also be some usefulness in chemistry, e.g. for drug discovery, and in materials science, e.g. for materials optimization/discovery (with possible relevance to quantum materials manufacturing).Historical contributions
AI researchers have created many tools to solve the most difficult problems in computer science. Many of their inventions have been adopted by mainstream computer science and are no longer considered AI. All of the following were originally developed in AI laboratories: * Time sharing * Interpreted language, Interactive interpreters * Graphical user interfaces and the computer mouse * Rapid application development environments * The linked list data structure * Automatic storage management * Third-generation programming language, Symbolic programming * Functional programming * Dynamic programming * Object-oriented programming * Optical character recognition * Constraint satisfactionBusiness
Customer service
Business websites and social media platforms for businesses like use chatbots for customer interactions like helping in answering frequently asked questions. Chatbots offers 24/7 support and replaces humans thereby helping in cutting business costs.Content extraction
An Optical character recognition, optical character reader is used in the extraction of data in business documents like invoices and receipts. It can also be used in business contract documents e.g Employment contract, employment agreements to extract critical data like employment terms, delivery terms, termination clauses, etc.List of applications
See also
* Applications of artificial intelligence to legal informatics * Applications of deep learning * Applications of machine learning * Collective intelligence#Applications * List of artificial intelligence projects * Progress in artificial intelligence * Open data * Timeline of computing –presentFootnotes
Further reading
* * * * *External links
How AI can be applied in many fields
{{emerging technologies, topics=yes, infocom=yes Applications of artificial intelligence,