Arrephorion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
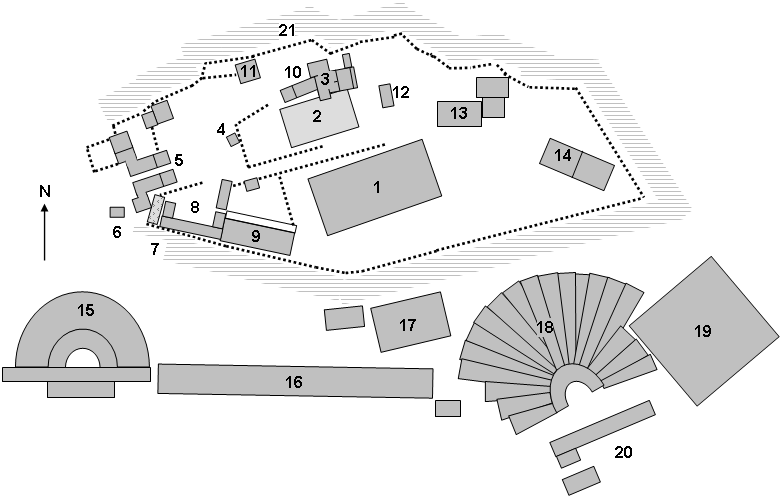 The Arrephorion or House of the Arrephoroi is a building conjectured to have been on the
The Arrephorion or House of the Arrephoroi is a building conjectured to have been on the
 The Arrephorion or House of the Arrephoroi is a building conjectured to have been on the
The Arrephorion or House of the Arrephoroi is a building conjectured to have been on the Acropolis of Athens
The Acropolis of Athens is an ancient citadel located on a rocky outcrop above the city of Athens and contains the remains of several ancient buildings of great architectural and historical significance, the most famous being the Parthenon. Th ...
based on a passage in Pausanias Pausanias ( el, Παυσανίας) may refer to:
*Pausanias of Athens, lover of the poet Agathon and a character in Plato's ''Symposium''
*Pausanias the Regent, Spartan general and regent of the 5th century BC
* Pausanias of Sicily, physician of t ...
. The discovery of the foundations of a substantial building on the north-west edge of the Acropolis has led to the identification of this structure with the Arrephorion.
Pausanias reports that:
I was much amazed at something which is not generally known, and so I will describe the circumstances. Two maidens dwell not far from the temple of Athena Polias, called by the Athenians Bearers of the Sacred Offerings. For a time they live with the goddess, but when the festival comes round they perform at night the following rites. Having placed on their heads what the priestess of Athena gives them to carry—neither she who gives nor they who carry have any knowledge what it is—the maidens descend by the natural underground passage that goes across the adjacent precincts, within the city, of Aphrodite in the Gardens. They leave down below what they carry and receive something else which they bring back covered up. These maidens they henceforth let go free, and take up to the Acropolis others in their place.Additionally, Plutarch remarks on the existence of a ballcourt adjacent to the house. The physical remains fit what we know of the House of the Arrephoroi but the evidence is still circumstantial that this was in fact the residence of the Arrephoroi. The dimensions of the building are 12.2 m square, and it was erected on a foundation of limestone blocks. It was divided into a south-facing portico of 4.4 m deep and a single rectangular room of approximately 8m by 12m. The terrace immediately around the building is an artificial one created by infill, which along with the foundation is dated to the last half of the 5th century or contemporary with the
Erechtheion
The Erechtheion (latinized as Erechtheum /ɪˈrɛkθiəm, ˌɛrɪkˈθiːəm/; Ancient Greek: Ἐρέχθειον, Greek: Ερέχθειο) or Temple of Athena Polias is an ancient Greek Ionic temple- telesterion on the north side of the Acropoli ...
.
The reconstruction of the architecture is controversial. While Dörpfeld assumed a south-facing front with two columns in antis
An anta (pl. antæ, antae, or antas; Latin, possibly from ''ante'', "before" or "in front of"), or sometimes parastas (pl. parastades), is an architectural term describing the posts or pillars on either side of a doorway or entrance of a Greek ...
- a conjecture that has recently been taken up again - four columns between the antae were later reconstructed. However, since no other four-column antae
The Antes, or Antae ( gr, Ἄνται), were an early East Slavic tribal polity of the 6th century CE. They lived on the lower Danube River, in the northwestern Black Sea region (present-day Moldova and central Ukraine), and in the regions aro ...
structures are known, a reconstruction with a six-column prostyle
Prostyle is an architectural term designating temples (especially Greek and Roman) featuring a row of columns on the front. The term is often used as an adjective when referring to the portico of a classical building, which projects from th ...
porch was recently proposed. Because of the wide foundations, it can be assumed that there was a step substructure, a crepidoma
Crepidoma is an architectural term for part of the structure of ancient Greek buildings. The crepidoma is the multilevel platform on which the superstructure of the building is erected. The crepidoma usually has three levels. Each level typic ...
, on which the actual building stood. Only a gable with a corresponding roof can have risen above the six-columned, prostyle portico. Older reconstructions with a hipped, pyramidal roof would therefore have to be discarded. The order of the columns in the building is unclear. An Ionic order is to be considered, although most available reconstructions assume a Doric order
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of c ...
.Helge Olaf Svenshon, Studien zum hexastylen Prostylos archaischer und klassischer Zeit. Darmstadt 2002, p.106 n.141.
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * {{Acropolis of Athens, state=collapsed Acropolis of Athens Ancient Greek buildings and structures in Athens