Arminius Vambery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Arminius ( 18/17 BC – 21 AD) was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the
 Born in 18 or 17 BC in Germania, Arminius was the son of the Cheruscan chief
Born in 18 or 17 BC in Germania, Arminius was the son of the Cheruscan chief
 In the autumn of 9 AD, the 25-year-old Arminius brought to Varus a false report of rebellion in northern Germany. He persuaded Varus to divert the three legions under his command (composed of the 17th,
In the autumn of 9 AD, the 25-year-old Arminius brought to Varus a false report of rebellion in northern Germany. He persuaded Varus to divert the three legions under his command (composed of the 17th,
 After the battle, the Germans quickly annihilated every trace of Roman presence east of the Rhine. Roman settlements such as the
After the battle, the Germans quickly annihilated every trace of Roman presence east of the Rhine. Roman settlements such as the 
 In the accounts of his Roman enemies, Arminius is highly regarded for his military leadership and as a defender of the liberty of his people. Based on these records, the story of Arminius was revived in the 16th century with the recovery of the histories of Tacitus, who wrote in his ''Annales II, 88'':
Arminius was not the only reason for Rome's change of policy towards Germania. Politics also played a factor; emperors found they could rarely trust a large army to a potential rival, though Augustus had enough loyal family members to wage his wars. Also, Augustus, in his 40-year reign, had annexed many territories still at the beginning of the process of Romanization. Tiberius, who succeeded Augustus in 14 AD, decided that Germania was a far less developed land, possessing few villages and only a small food surplus, and therefore was not currently important to Rome. Conquering Germania would require a commitment too burdensome for the imperial finances and an excessive expenditure of military force.
Modern scholars have pointed out that the Rhine was a more practical boundary for the Roman Empire than any other river in Germania. Armies on the Rhine could be supplied from the
In the accounts of his Roman enemies, Arminius is highly regarded for his military leadership and as a defender of the liberty of his people. Based on these records, the story of Arminius was revived in the 16th century with the recovery of the histories of Tacitus, who wrote in his ''Annales II, 88'':
Arminius was not the only reason for Rome's change of policy towards Germania. Politics also played a factor; emperors found they could rarely trust a large army to a potential rival, though Augustus had enough loyal family members to wage his wars. Also, Augustus, in his 40-year reign, had annexed many territories still at the beginning of the process of Romanization. Tiberius, who succeeded Augustus in 14 AD, decided that Germania was a far less developed land, possessing few villages and only a small food surplus, and therefore was not currently important to Rome. Conquering Germania would require a commitment too burdensome for the imperial finances and an excessive expenditure of military force.
Modern scholars have pointed out that the Rhine was a more practical boundary for the Roman Empire than any other river in Germania. Armies on the Rhine could be supplied from the
p. 329
/ref> In 1808,
In 1808,
''Deutsche Geschichte – Mythos einer Schlacht''
Zeit Online, 2008-11-04 (German) According to journalist David Crossland: "The old nationalism has been replaced by an easy-going patriotism that mainly manifests itself at sporting events like the soccer
Arminius
at the ''
Arminius
at the ''
"Arminius / Varus: Die Varusschlacht im Jahre 9 n. Chr."
– LWL-Institut für westfälische Regionalgeschichte (in German)
"Terry Jones' Barbarians: The Savage Goths"
– includes a portion on Arminius
(in German)
"They Need a Hero"
by Clay Risen in '' The National'', October 9, 2009 – article on modern German views of Hermann and the 2,000th anniversary of the battle {{DEFAULTSORT:Arminius 010s BC births 1st-century rulers in Europe 021 deaths Ancient Roman soldiers Cherusci rulers Cherusci warriors
Battle of the Teutoburg Forest
The Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, described as the Varian Disaster () by Roman historians, took place at modern Kalkriese in AD 9, when an alliance of Germanic peoples ambushed Roman legions and their auxiliaries, led by Publius Quinctilius ...
in 9 AD, in which three Roman legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period o ...
s under the command of general Publius Quinctilius Varus were destroyed. His victory at Teutoburg Forest would precipitate the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
's permanent strategic withdrawal from Germania Magna
Germania ( ; ), also called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman province of the same name, was a large historical region in north-c ...
. Modern historians have regarded Arminius' victory as one of Rome's greatest defeats. As it prevented the Romanization
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, a ...
of Germanic peoples east of the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, it has also been considered one of the most decisive battles in history and a turning point in human history
Human history, also called world history, is the narrative of humanity's past. It is understood and studied through anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and linguistics. Since the invention of writing, human history has been studied throug ...
.
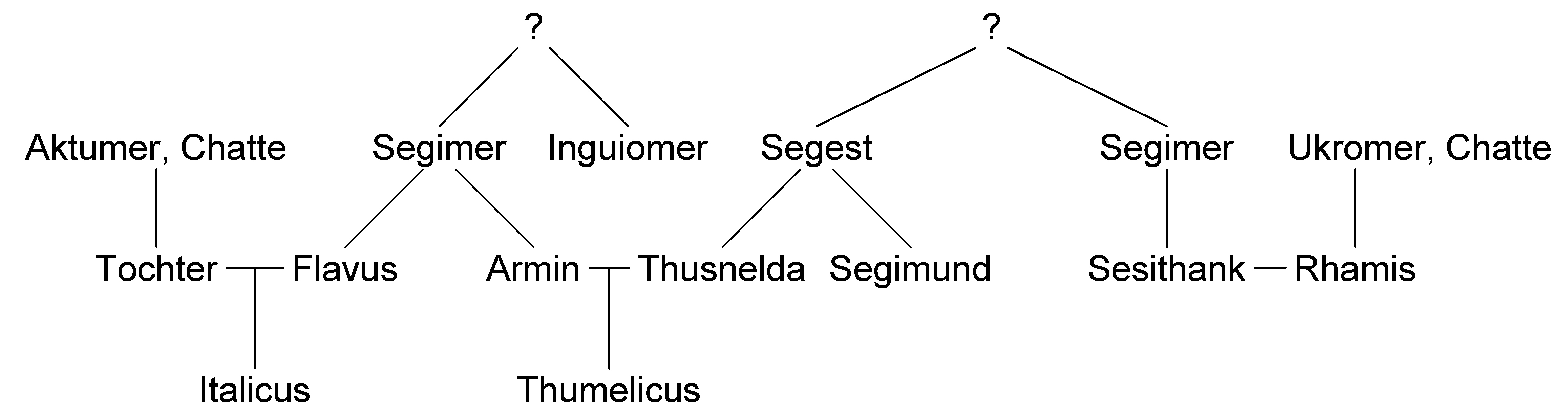
Born a prince of the Cherusci tribe, Arminius was part of the Roman friendly faction of the tribe. He learned Latin and served in the Roman military, which gained him Roman citizenship
Citizenship in ancient Rome (Latin: ''civitas'') was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in Ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, t ...
and the rank of ''eques''. After serving with distinction in the Great Illyrian Revolt
The (Latin for 'War of the Batos') was a military conflict fought in the Roman province of Illyricum in the 1st century AD, in which an alliance of native peoples of the two regions of Illyricum, Dalmatia and Pannonia, revolted against the Roma ...
, he was sent to Germania to aid the local governor Publius Quinctilius Varus in completing the Roman conquest of the Germanic tribes. While in this capacity, Arminius secretly plotted a Germanic revolt against Roman rule, which culminated in the ambush and destruction of three Roman legions in the Teutoburg Forest.
In the aftermath of the battle, Arminius fought retaliatory invasions by the Roman general Germanicus in the battles of Pontes Longi, Idistaviso Idistaviso is the location on the Weser river where forces commanded by Arminius fought those commanded by Germanicus at the Battle of the Weser River in 16 CE, attested in chapter 16 of Tacitus' ''Annales'' II. The name was amended by Karl Müllen ...
, and the Angrivarian Wall The so-called Angrivarian Wall (german: Angrivarierwall) was mentioned by the Roman historian, Tacitus (''Annals'' II, 19–21), in connection with the campaign by the Roman general Germanicus in 16 AD, which included the Battle of the Angrivarian ...
, and deposed a rival, the Marcomanni
The Marcomanni were a Germanic people
*
*
*
that established a powerful kingdom north of the Danube, somewhere near modern Bohemia, during the peak of power of the nearby Roman Empire. According to Tacitus and Strabo, they were Suebian.
Or ...
king Maroboduus. Germanic nobles, afraid of Arminius' growing power, assassinated him in 21 AD. He was remembered in Germanic legends for generations afterwards. The Roman historian Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
designated Arminius as the liberator of the Germanic tribes and commended him for having fought the Roman Empire to a standstill at the peak of its power.Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
. The Annals.2.88. "Assuredly he was the deliverer of Germany, one too who had defied Rome, not in her early rise, as other kings and generals, but in the height of her empire's glory, had fought, indeed, indecisive battles, yet in war remained unconquered. He completed thirty-seven years of life, twelve years of power, and he is still a theme of song among barbarous nations, though to Greek historians, who admire only their own achievements, he is unknown, and to Romans not as famous as he should be, while we extol the past and are indifferent to our own times."
During the unification of Germany
The unification of Germany (, ) was the process of building the modern German nation state with federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without multinational Austria), which commenced on 18 August 1866 with adoption of t ...
in the 19th century, Arminius was hailed by German nationalists
German nationalism () is an ideological notion that promotes the unity of Germans and German-speakers into one unified nation state. German nationalism also emphasizes and takes pride in the patriotism and national identity of Germans as one ...
as a symbol of German unity and freedom. Following World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, however, Arminius' significance was reduced in Germany due to his association with militaristic nationalism; the 2,000th anniversary of his victory at the Teutoburg Forest was only lightly commemorated in Germany.
Name
Theetymology
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the Phonological chan ...
of the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
name is unknown, and confusion is further created by contemporary scholars who alternately referred to him as . In his ''History'', Marcus Velleius Paterculus
Marcus Velleius Paterculus (; c. 19 BC – c. AD 31) was a Roman historian, soldier and senator. His Roman history, written in a highly rhetorical style, covered the period from the end of the Trojan War to AD 30, but is most useful for the per ...
mentions him as "Arminius, the son of Sigimer, a prince of the nation" and states he "attained the dignity of equestrian rank". Due to Roman naming conventions
Over the course of some fourteen centuries, the Romans and other peoples of Italy employed a system of nomenclature that differed from that used by other cultures of Europe and the Mediterranean Sea, consisting of a combination of personal and fam ...
of the time, it is likely is an adopted name granted to him upon citizenship or in any case not his Germanic name
Germanic languages, Germanic given names are traditionally wikt:dithematic, dithematic; that is, they are formed from two elements, by joining a prefix and a suffix. For example, Ethelred II of England, King Æþelred's name was derived from ', f ...
. The name instead appears to ultimately be of Etruscan origin, appearing as and on inscriptions found at Volaterrae
Volterra (; Latin: ''Volaterrae'') is a walled mountaintop town in the Tuscany region of Italy. Its history dates from before the 8th century BC and it has substantial structures from the Etruscan, Roman, and Medieval periods.
History
Volt ...
. According to another theory, that name was given to Arminius for his service in Armenia.
The German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
translation of as the name ''Hermann'' dates from the 16th century, possibly first by Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Lutherani ...
. In German, Arminius was traditionally distinguished as ("Hermann the Cheruscan") or ("Hermann the Cheruscan Prince"). Hermann etymologically means "Man of War", coming from the Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050.
There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old High ...
meaning "war" and meaning "person" or "man".
Biography
 Born in 18 or 17 BC in Germania, Arminius was the son of the Cheruscan chief
Born in 18 or 17 BC in Germania, Arminius was the son of the Cheruscan chief Segimerus
Segimer or Sigimer ( la, Segimerus or ; fl. 1st century BC) was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe. He is chiefly remembered as the father of Arminius, who led the Germans to victory over the Romans at Teutoburg Forest in AD9.
Life
Seg ...
(German: ''Segimer''; Proto-Germanic: ''Sigimariz''; Old English: ''Sigemaer''), who was allied with Rome.
Arminius learned to speak Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
and joined the Roman military alongside his younger brother Flavus
Flavus is the Latin word for yellow or blond and has given the name to many, more or less yellow, objects:
* Subrius Flavus, a failed Roman conspirator against the Emperor Nero
* Flavus, brother of Arminius
See also
* Flavius
* Flava (disambi ...
. He served in the Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
between 1 and 6 AD, and received a military education as well as Roman citizenship
Citizenship in ancient Rome (Latin: ''civitas'') was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in Ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, t ...
and the status of equite
The ''equites'' (; literally "horse-" or "cavalrymen", though sometimes referred to as "knights" in English) constituted the second of the property-based classes of ancient Rome, ranking below the senatorial class. A member of the equestrian ...
before returning to Germania. These experiences gave him knowledge of Roman politics and military tactics, which allowed him to successfully anticipate enemy battle maneuvers during his later campaigns against the Roman army.
Battle of the Teutoburg Forest
Around the year 4 AD, Arminius assumed command of a Cheruscan detachment of Roman auxiliary forces, probably while fighting in thePannonian
Pannonia may refer to:
In geography:
* Basin of Pannonia, a geomorphological region (plain) in Central Europe
* Sea of Pannonia, an ancient (former) sea in Central Europe
* Steppe of Pannonia, a grassland ecosystem in the Pannonian Plain
In h ...
wars on the Balkan peninsula. He returned to northern Germania in 7 or 8 AD, where the Roman Empire had established secure control of the territories just east of the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, along the Lippe
Lippe () is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring districts are Herford, Minden-Lübbecke, Höxter, Paderborn, Gütersloh, and district-free Bielefeld, which forms the region Ostwestfalen-Lippe.
The ...
and Main
Main may refer to:
Geography
* Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries
...
rivers, and was now seeking to extend its hegemony eastward to the Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports o ...
and Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
rivers, under Publius Quinctilius Varus, a high-ranking administrative official appointed by Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
as governor. Arminius began plotting to unite various Germanic tribes in order to thwart Roman efforts to incorporate their lands into the empire. This proved a difficult task, as the tribes were strongly independent and many were traditionally enemies of each other.
Between 6 and 9 AD, the Romans were forced to move eight of the eleven legions present in Germania east of the Rhine to crush a rebellion in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, leaving Varus with only three legions to face the Germans, which was still 18,000 troops, or 6,000 men per legion. An additional two legions, under the command of Lucius Nonius Asprenas, were stationed in Moguntiacum. Arminius saw this as the perfect opportunity to defeat Varus.
 In the autumn of 9 AD, the 25-year-old Arminius brought to Varus a false report of rebellion in northern Germany. He persuaded Varus to divert the three legions under his command (composed of the 17th,
In the autumn of 9 AD, the 25-year-old Arminius brought to Varus a false report of rebellion in northern Germany. He persuaded Varus to divert the three legions under his command (composed of the 17th, 18th
18 (eighteen) is the natural number following 17 and preceding 19.
In mathematics
* Eighteen is a composite number, its divisors being 1, 2, 3, 6 and 9. Three of these divisors (3, 6 and 9) add up to 18, hence 18 is a semiperfect number. ...
, and 19th
19 (nineteen) is the natural number following 18 and preceding 20. It is a prime number.
Mathematics
19 is the eighth prime number, and forms a sexy prime with 13, a twin prime with 17, and a cousin prime with 23. It is the third full re ...
legions, plus three cavalry detachments and six cohorts of auxiliaries), which were at the time marching to winter quarters, to suppress the rebellion. Varus and his legions marched right into the trap that Arminius had set for them near Kalkriese
Kalkriese is a village now administratively part of the city of Bramsche in the district of Osnabrück, Lower Saxony, Germany. It is on the northern slope of the Wiehen Hills, a ridge-like range of hills, north of Osnabrück. The ''Kalkrieser Ber ...
. Arminius' tribe, the Cherusci, and their allies the Marsi
The Marsi were an Italic people of ancient Italy, whose chief centre was Marruvium, on the eastern shore of Lake Fucinus (which was drained for agricultural land in the late 19th century). The area in which they lived is now called Marsica. ...
, Chatti
The Chatti (also Chatthi or Catti) were an ancient Germanic tribe
whose homeland was near the upper Weser (''Visurgis''). They lived in central and northern Hesse and southern Lower Saxony, along the upper reaches of that river and in the va ...
, Bructeri
The Bructeri (from Latin; Greek: Βρούκτεροι, ''Broukteroi'', or Βουσάκτεροι, ''Bousakteroi''; Old English: ''Boruhtware'') were a Germanic tribe*
*
in Roman imperial times, located in northwestern Germany, in present-day ...
, Chauci
The Chauci (german: Chauken, and identical or similar in other regional modern languages) were an ancient Germanic tribe living in the low-lying region between the Rivers Ems and Elbe, on both sides of the Weser and ranging as far inland as the ...
, and Sicambri
The Sicambri, also known as the Sugambri or Sicambrians, were a Germanic people who during Roman times lived on the east bank of the river Rhine, in what is now Germany, near the border with the Netherlands. They were first reported by Julius C ...
(five out of at least fifty Germanic tribes at the time) ambushed and annihilated Varus' entire army, totaling over 20,000 men, as it marched along a narrow road through a dense forest. Recent archaeological finds show the long-debated location of the three-day battle was almost certainly near Kalkriese Hill, about north of present-day Osnabrück
Osnabrück (; wep, Ossenbrügge; archaic ''Osnaburg'') is a city in the German state of Lower Saxony. It is situated on the river Hase in a valley penned between the Wiehen Hills and the northern tip of the Teutoburg Forest. With a population ...
. When defeat was certain, Varus committed suicide. The battle was one of the most devastating defeats Rome suffered in its history. Arminius' success in destroying three entire legions and driving the Romans out of Germany marked a high point of Germanic power for centuries. Roman attempts to reconquer Germania failed, although they did eventually manage to break Arminius' carefully coordinated alliance.
Roman retaliation, inter-tribal conflicts, and death
 After the battle, the Germans quickly annihilated every trace of Roman presence east of the Rhine. Roman settlements such as the
After the battle, the Germans quickly annihilated every trace of Roman presence east of the Rhine. Roman settlements such as the Waldgirmes Forum
The Roman Forum of Lahnau-Waldgirmes (german: Römisches Forum Lahnau-Waldgirmes) is a fortified Roman trading place, located at the edge of the modern village Waldgirmes, part of Lahnau on the Lahn, Hesse, Germany. The site has the oldest known st ...
were abandoned. The vastly outnumbered Roman garrison of Aliso (present-day Haltern am See
Haltern am See (''Haltern at the lake'', before December 2001 only Haltern) is a town and a municipality in the district of Recklinghausen, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is situated on the Lippe and the Wesel–Datteln Canal, approx. no ...
), under the command of the prefect Lucius Cedicius, inflicted heavy losses on the Germans before retreating into Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
, resisting long enough for Lucius Nonius Asprenas to organize the Roman defense on the Rhine and Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
to arrive with a new army. This prevented Arminius from crossing the Rhine and invading Gaul.
Between 14 and 16 AD, Germanicus led punitive operations into Germany, fighting Arminius to a draw in the Battle at Pontes Longi
The Battle at Pontes Longi was fought near Bramsche, Germany in 15 AD between the Roman general Aulus Caecina Severus and an alliance of Germanic peoples commanded by Arminius. It was part of a three-year series of campaigns by Germanicus in ...
and twice defeating him (according to Tacitus): first in the Battle of Idistaviso
The Battle of the Weser River, sometimes known as the First Battle of Minden or Battle of Idistaviso, was fought in 16 AD between Roman legions commanded by Roman Emperor Tiberius's heir and adopted son, Germanicus, and an alliance of Germanic p ...
and later at the Battle of the Angrivarian Wall
The Battle of the Angrivarian Wall was fought near Porta Westfalica, Germany in 16 AD between the Roman general Germanicus and an alliance of Germanic tribes commanded by Arminius. This battle followed immediately after the Battle of Idistavi ...
. In 15 AD, Roman troops managed to recapture one of the three legionary eagles lost in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. In 16 AD, a second eagle was retrieved. Tiberius denied the request of Germanicus to launch an additional campaign for 17 AD, however, having decided the frontier with Germania would stand at the Rhine river. Instead, he offered Germanicus the honor of a triumph for his two victories. The third Roman eagle was recovered in 41 AD by Publius Gabinius, under the emperor Claudius. Arminius also faced opposition from his father-in-law and other pro-Roman Germanic leaders. His brother Flavus, who had been raised alongside him in Rome, remained loyal to the Roman Empire and fought under Germanicus against Arminius at the Battle of Idistaviso. With the end of the Roman threat, a war broke out between Arminius and Marbod
Maroboduus (d. AD 37) was a king of the Marcomanni, who were a Germanic Suebian people. He spent part of his youth in Rome, and returning, found his people under pressure from invasions by the Roman empire between the Rhine and Elbe. He led th ...
, king of the Marcomanni
The Marcomanni were a Germanic people
*
*
*
that established a powerful kingdom north of the Danube, somewhere near modern Bohemia, during the peak of power of the nearby Roman Empire. According to Tacitus and Strabo, they were Suebian.
Or ...
. It ended with Marbod fleeing to Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the ca ...
and Roman protection, but Arminius failed to break into the "natural fortification" of Bohemia, and the war ended in stalemate.
In 19 AD, Germanicus died in Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
under circumstances which led many to believe he had been poisoned by his opponents. Arminius died two years later, in 21 AD, murdered by opponents within his own tribe who felt that he was becoming too powerful.Tacitus, The Annals 2.88 Tiberius allegedly had refused an earlier offer from a Chatti nobleman to poison Arminius: "It was not by secret treachery but openly and by arms that the people of Rome avenged themselves on their enemies."
Marriage to Thusnelda
Arminius married a Germanic princess namedThusnelda
Thusnelda (; 10 BC – after AD 17) was a Germanic Cheruscan noblewoman who was captured by the Roman general Germanicus during his invasion of Germania. She was the wife of Arminius. Tacitus and Strabo cite her capture as evidence of both the ...
. Her father was the Cheruscan prince Segestes
Segestes was a nobleman of the Germanic tribe of the Cherusci involved in the events surrounding the Roman attempts to conquer northern Germany during the reign of Roman Emperor Augustus.
Arminius, the Cheruscan noble and military leader, had m ...
, who was pro-Roman. After the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, Arminius abducted and then impregnated Thusnelda circa 14 AD. This elopement
Elopement is a term that is used in reference to a marriage which is conducted in a sudden and secretive fashion, usually involving a hurried flight away from one's place of residence together with one's beloved with the intention of getting ma ...
was likely a result of a dispute between Arminius and Segestes who was against their relationship. In May 15 AD the Roman general Germanicus captured Thusnelda. At the point of her capture she was pregnant and living with her father, who had taken her back. Arminius deeply grieved the capture of Thusnelda and did not marry again. Tacitus recorded that Arminius was "driven to frenzy" by the loss of his beloved wife.Tacitus, The Annals 1.59 Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
states in the ''Annals
Annals ( la, annāles, from , "year") are a concise historical record in which events are arranged chronologically, year by year, although the term is also used loosely for any historical record.
Scope
The nature of the distinction between ann ...
'':Arminius, with his naturally furious temper, was driven to frenzy by the seizure of his wife and the foredooming to slavery of his wife's unborn child. He flew hither and thither among the Cherusci, demanding "war against Segestes, war against Cæsar." And he refrained not from taunts.Thusnelda gave birth to a son named
Thumelicus
Thumelicus (born 15 AD; died before 47 AD, probably in 30 or 31) was the only son of the Cherusci leader Arminius and his wife Thusnelda, daughter of the pro-Roman tribal leader Segestes.
In May 15 AD, Arminius besieged Segestes at his stronghol ...
who grew up in Roman captivity. Tacitus describes him as having an unusual story, which he promises to tell in his later writings, but these writings have never been found.
Legacy
Arminius' victory against the Roman legions in the Teutoburg Forest had a far-reaching effect on the subsequent history of both the ancientGermanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
and on the Roman Empire. The Romans made no further concerted efforts to conquer and permanently hold Germania beyond the Rhine and the ''Agri Decumates
The ''Agri Decumates'' or ''Decumates Agri'' ("Decumatian Fields") were a region of the Roman Empire's provinces of Germania Superior and Raetia, covering the Black Forest, Swabian Jura, and Franconian Jura areas between the Rhine, Main, and Da ...
''. Numerous modern historians have regarded Arminius' victory as one of the most decisive battles in history, with some calling it "Rome's greatest defeat".
Rome
 In the accounts of his Roman enemies, Arminius is highly regarded for his military leadership and as a defender of the liberty of his people. Based on these records, the story of Arminius was revived in the 16th century with the recovery of the histories of Tacitus, who wrote in his ''Annales II, 88'':
Arminius was not the only reason for Rome's change of policy towards Germania. Politics also played a factor; emperors found they could rarely trust a large army to a potential rival, though Augustus had enough loyal family members to wage his wars. Also, Augustus, in his 40-year reign, had annexed many territories still at the beginning of the process of Romanization. Tiberius, who succeeded Augustus in 14 AD, decided that Germania was a far less developed land, possessing few villages and only a small food surplus, and therefore was not currently important to Rome. Conquering Germania would require a commitment too burdensome for the imperial finances and an excessive expenditure of military force.
Modern scholars have pointed out that the Rhine was a more practical boundary for the Roman Empire than any other river in Germania. Armies on the Rhine could be supplied from the
In the accounts of his Roman enemies, Arminius is highly regarded for his military leadership and as a defender of the liberty of his people. Based on these records, the story of Arminius was revived in the 16th century with the recovery of the histories of Tacitus, who wrote in his ''Annales II, 88'':
Arminius was not the only reason for Rome's change of policy towards Germania. Politics also played a factor; emperors found they could rarely trust a large army to a potential rival, though Augustus had enough loyal family members to wage his wars. Also, Augustus, in his 40-year reign, had annexed many territories still at the beginning of the process of Romanization. Tiberius, who succeeded Augustus in 14 AD, decided that Germania was a far less developed land, possessing few villages and only a small food surplus, and therefore was not currently important to Rome. Conquering Germania would require a commitment too burdensome for the imperial finances and an excessive expenditure of military force.
Modern scholars have pointed out that the Rhine was a more practical boundary for the Roman Empire than any other river in Germania. Armies on the Rhine could be supplied from the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
via the Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Ar ...
, Saône
The Saône ( , ; frp, Sona; lat, Arar) is a river in eastern France. It is a right tributary of the Rhône, rising at Vioménil in the Vosges department and joining the Rhône in Lyon, at the southern end of the Presqu'île.
The name ...
, and Mosel, with only a brief area of portage. Armies on the Elbe, however, would had to have been supplied by extensive overland routes or by ships travelling the hazardous Atlantic. Economically, the Rhine already had towns and sizable villages at the time of the Gallic conquest. The Rhine was significantly more accessible from Rome and better equipped to supply sizable garrisons than the regions beyond.
Rome chose no longer to rule directly in Germania east of the Rhine and north of the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
, instead preferring to exert indirect influence by appointing client king
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
s, which was cheaper than military campaigns. Italicus
Italicus Rosolio di Bergamotto is a bergamot rosolio (a type of aperitivo) manufactured in Italy. The liqueur uses bergamot from Calabria and citrons from Sicily, along with Italian flower varieties. The spirit was created by an Italian bartend ...
, nephew of Arminius, was appointed king of the Cherusci; Vangio and Sido
Vangio and Sido (flourished in 1st century AD) were two Quadian brothers who were the co-rulers of a Roman client kingdom in Bohemia in the 1st century AD.
According to The Annals of Tacitus, Vangio and Sido were the sons of a sister of Vannius, w ...
became vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain ...
princes of the powerful Suebi, etc. When indirect methods proved insufficient to control the Germanic tribes beyond the Rhine, Roman emperors occasionally led devastating punitive campaigns deep into Germania. One of them, led by the Roman emperor Maximinus Thrax
Gaius Julius Verus Maximinus "Thrax" ("the Thracian"; – 238) was Roman emperor from 235 to 238.
His father was an accountant in the governor's office and sprang from ancestors who were Carpi (a Dacian tribe), a people whom Diocleti ...
, resulted in a Roman victory in 235 at the Battle at the Harzhorn Hill, located in the modern German state of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
, east of the Weser river, between the towns of Kalefeld
Kalefeld is a municipality in the district of Northeim, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated approximately 10 km north of Northeim. It comprises the villages of Dögerode, Eboldshausen, Echte, Kalefeld, Oldenrode, Oldershausen, Sebexen ...
and Bad Gandersheim
Bad Gandersheim (Eastphalian dialect, Eastphalian: ''Ganderssen'') is a town in southern Lower Saxony, Germany, located in the district of Northeim (district), Northeim. , it had a population of 9,492.
Bad Gandersheim has many half-timbered hou ...
.
Old Germanic sagas
In the early 19th century, attempts were made to show that the story of Arminius and his victory may have lived on in theOld Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlemen ...
sagas, in the form of the dragon slayer Sigurd
Sigurd ( non, Sigurðr ) or Siegfried (Middle High German: ''Sîvrit'') is a legendary hero of Germanic heroic legend, who killed a dragon and was later murdered. It is possible he was inspired by one or more figures from the Frankish Merovin ...
of the Völsunga saga
The ''Völsunga saga'' (often referred to in English as the ''Volsunga Saga'' or ''Saga of the Völsungs'') is a legendary saga, a late 13th-century poetic rendition in Old Norse of the origin and decline of the Völsung clan (including the st ...
and the Nibelungenlied
The ( gmh, Der Nibelunge liet or ), translated as ''The Song of the Nibelungs'', is an epic poem written around 1200 in Middle High German. Its anonymous poet was likely from the region of Passau. The is based on an oral tradition of Germani ...
. An Icelandic account states that Sigurd "slew the dragon" in the Gnitaheidr—today the suburb Knetterheide of the city of Bad Salzuflen
Bad Salzuflen is a town and thermal spa resort in the Lippe district of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. At the end of 2013, it had 52,121 inhabitants.
Geography
Bad Salzuflen lies on the eastern edge of the Ravensberg Basin, at the confluence ...
, located at a strategic site on the Werre
The Werre is a river in the Detmold region (Regierungsbezirk) of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, left tributary of the Weser. Its source is near Horn-Bad Meinberg. The Werre flows generally north through the towns Detmold, Lage, Bad Salzuflen, ...
river which could very well have been the point of departure of Varus' legions on their way to their doom in the Teutoburg Forest. One of the foremost Scandinavian scholars of the 19th century, Guðbrandur Vigfússon
Guðbrandur Vigfússon, known in English as Gudbrand Vigfusson, (13 March 1827 – 31 January 1889Jón þorkelsson, "Nekrolog över Guðbrandur Vigfússon" in ''Arkiv för nordisk filologi'', Sjätte bandet (ny följd: andra bandet), Lund, 18 ...
, identified Sigurd as Arminius. This educated guess was also picked up by Otto Höfler
Otto Eduard Gotfried Ernst Höfler (10 May 1901 – 25 August 1987) was an Austrian philologist who specialized in Germanic studies. A student of Rudolf Much, Höfler was Professor and Chair of German Language and Old German Literature at the Uni ...
, who was a prominent Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
academic during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
.
German nationalism
During theunification of Germany
The unification of Germany (, ) was the process of building the modern German nation state with federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without multinational Austria), which commenced on 18 August 1866 with adoption of t ...
in the 19th century, Arminius was hailed as a symbol of German unity and freedom. In Germany, the name ''Arminius'' was interpreted as reflecting the name ''Hermann'' by Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Lutherani ...
, who saw Arminius as a symbol of the German people and their fight against Rome. ''Hermann der Cheruskerfürst'' became an emblem of the revival of German nationalism
German nationalism () is an ideological notion that promotes the unity of Germans and German-speakers into one unified nation state. German nationalism also emphasizes and takes pride in the patriotism and national identity of Germans as one n ...
fueled by the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
in the 19th century, such as in Caspar David Friedrich's 1812 painting ''The Tombs of the Old Heroes
''The Tombs of the Old Heroes'' (German - ''Grabmale alter Helden'') is an oil on canvas painting by Caspar David Friedrich, painted between April and August 1812. It is also known as ''The Graves of the Fallen Freedom Fighters'' (''Gräber ge ...
''.Dorothea Klein (ed.), Lutz Käppel (ed.): ''Das diskursive Erbe Europas: Antike und Antikerezeption''. Peter Lang, 2008, p. 329
/ref>
 In 1808,
In 1808, Heinrich von Kleist
Bernd Heinrich Wilhelm von Kleist (18 October 177721 November 1811) was a German poet, dramatist, novelist, short story writer and journalist. His best known works are the theatre plays '' Das Käthchen von Heilbronn'', ''The Broken Jug'', ''Amph ...
wrote the play '' Die Hermannsschlacht'', but with Napoleon's victory at Wagram it remained in manuscript, being published in 1821 and not staged until 1860. The play has been revived repeatedly at moments propitious for raw expressions of National Romanticism and was especially popular in Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
.
In 1838, construction was started on a massive statue of Arminius, known as the ''Hermannsdenkmal
The ''Hermannsdenkmal'' (German for "Hermann Monument") is a monument located southwest of Detmold in the district of Lippe (North Rhine-Westphalia), in Germany. It stands on the densely forested ', sometimes also called the ''Teutberg'' or ''Te ...
'', on a hill near Detmold
Detmold () is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, with a population of . It was the capital of the small Principality of Lippe from 1468 until 1918 and then of the Free State of Lippe until 1947. Today it is the administrative center of t ...
in the Teutoburg Forest; it was finally completed and dedicated during the early years of the Second German Empire in the wake of the German victory over France in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871. The monument has been a major tourist attraction ever since, as has the Hermann Heights Monument
The Hermann Heights Monument is a statue erected in New Ulm, Minnesota. The statue depicts Arminius (german: Hermann), an ancient Cheruscan, but locals refer to the statue as Hermann the German. The only National Register of Historic Places prop ...
, a similar statue erected in New Ulm, Minnesota
New Ulm is a city in Brown County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 14,120 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Brown County. It is located on the triangle of land formed by the confluence of the Minnesota River and the ...
, in the United States in 1897. The Hermann Heights monument was erected by the Sons of Hermann
The Order of the Sons of Hermann (german: Der Orden der Hermanns-Soehne, also known as Hermann Sons ( ''Hermannssöhne'' ), is a mutual aid society for German immigrants that was formed in New York, New York on July 20, 1840,Fritz Schilo"Sons ...
, a fraternal organization formed by German Americans in New York City in 1840 that flourished during the 19th century in American cities with large populations of German origin. Hermann, Missouri
Hermann is a city in and the county seat of Gasconade County, Missouri, United States. It has been the county seat since 1842. It is near the center of the Missouri Rhineland and south of the Missouri River. The population was 2,185 at the 202 ...
, a town on the Missouri River founded in the 1830s and incorporated in 1845, was also named for Arminius.
Following the rise of Nazi Germany, fueled by aggressive German nationalism, and its subsequent defeat in World War II, Arminius became a lesser-known figure among West Germans and many schools shied away from teaching his story in any detail due to its previous association with nationalism. There was, however, a somewhat different perception in East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
. In East Germany, Arminius, based on a Marxist reading of history, came to be seen as a revolutionary figure of sorts, leading German tribes in a fight against the Roman slaveholder society (''Sklavenhaltergesellschaft''). In the context of the Cold War, Arminius was interpreted as symbolic of socialism
Socialism is a left-wing Economic ideology, economic philosophy and Political movement, movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to Private prop ...
, with Rome being a symbol of the capitalist
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, priva ...
United States as an oppressive empire.Tillmann Bendikowski''Deutsche Geschichte – Mythos einer Schlacht''
Zeit Online, 2008-11-04 (German) According to journalist David Crossland: "The old nationalism has been replaced by an easy-going patriotism that mainly manifests itself at sporting events like the soccer
World Cup
A world cup is a global sporting competition in which the participant entities – usually international teams or individuals representing their countries – compete for the title of world champion. The event most associated with the concept i ...
." The German Bundesliga football club DSC Arminia Bielefeld
DSC Arminia Bielefeld (; full name: ; commonly known as Arminia Bielefeld (), also known as ''Die Arminen'' or ''Die Blauen'' ), or just Arminia (), is a German sports club from Bielefeld, North Rhine-Westphalia. Arminia offers the sports of ...
is named after Arminius. The 2,000-year anniversary of the battle was also celebrated in New Ulm, Minnesota without restraint. There were mock battles between Romans and club-wielding barbarians and also a lecture series in an auditorium.
Cultural references
* '' Arminio'' is a 1692 opera about Arminius by the Bohemian-Austrian composerHeinrich Ignaz Franz Biber
Heinrich Ignaz Franz Biber ( bapt. 12 August 1644, Stráž pod Ralskem – 3 May 1704, Salzburg) was a Bohemian-Austrian composer and violinist. Biber worked in Graz and Kroměříž before he illegally left his employer, Prince-Bishop Karl L ...
.
* '' Arminio'' is a 1736 opera about Arminius by George Frideric Handel.
* '' Arminius'' is an 1877 oratorio about Arminius by the German composer Max Bruch
Max Bruch (6 January 1838 – 2 October 1920) was a German Romantic composer, violinist, teacher, and conductor who wrote more than 200 works, including three violin concertos, the first of which has become a prominent staple of the standard ...
.
* ''Barbarians
A barbarian (or savage) is someone who is perceived to be either uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by some to be les ...
'' is a 2020 TV show that features a fictionalized version of Arminius as one of the central characters.
See also
* Ariovistus *Bato the Breucian
Bato the Breucian or Bato of the Breuci was the chieftain of the Breuci, an Illyrian tribe that fought against the Roman Empire in a war known as ''Bellum Batonianum''. Bato joined his rebel forces with those led by Bato of the Daesitiates. A ...
* Bato the Daesitiate
Bato the Daesitiate (also known as Bato of the Daesitiates) was a chieftain of the Daesitiates, an Illyrian tribe which fought against the Roman Empire between 6 and 9 AD in a conflict known as '' Bellum Batonianum'' ("Bato's War").
Biography
...
* Boudica
* Divico
Divico was a Celtic king and the leader of the Helvetian tribe of the Tigurini. During the Cimbrian War, in which the Cimbri and Teutons invaded the Roman Republic, he led the Tigurini across the Rhine to invade Gaul in 109 BC. He defeated a Roma ...
* Gaius Julius Civilis
Gaius Julius Civilis was the leader of the Batavian rebellion against the Romans in 69 AD. His nomen shows that he (or one of his male ancestors) was made a Roman citizen (and thus, the tribe a Roman vassal) by either Augustus or Caligula.
Earl ...
* Teutobod
Teutobod was a king of the Teutons, who, together with the allied Cimbri, invaded the Roman Republic in the Cimbrian War and won a spectacular victory at the Battle of Arausio in 105 BC. He was later captured at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae in 10 ...
* Vercingetorix
Vercingetorix (; Greek: Οὐερκιγγετόριξ; – 46 BC) was a Gallic king and chieftain of the Arverni tribe who united the Gauls in a failed revolt against Roman forces during the last phase of Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. Despite ha ...
Citations
Sources
* * * * Dörner, Andreas, ''Politischer Mythos und symbolische Politik. Der Hermannmythos: Zur Entstehung des Nationalbewußtseins der Deutschen'' (Reinbek: Rowohlt, 1996). * * von Essen, Gesa, ''Hermannsschlachten. Germanen- und Römerbilder in der Literatur des 18. und 19. Jahrhunderts'' (Göttingen: Wallstein, 1998). * Kuehnemund, Richard, ''Arminius or the Rise of a National Symbol in Literature: From Hutten to Grabbe'' (New York: AMS Press, 1966). * Münkler Herfried, and Hans Grünberger: "Arminius/ Hermann als nationales Symbol im Diskurs der deutschen Humanisten 1500–1570", In: Herfried Münkler, Hans Grünberger, and Kathrin Mayer, ''Nationenbildung. Die Nationalisierung Europas im Diskurs humanistischer Intellektueller. Italien und Deutschland'' (Berlin: Akademie, 1998), pp. 263–308. * * * Wagner-Egelhaaf, Martina (ed.), ''Hermanns Schlachten. Zur Literaturgeschichte eines nationalen Mythos'' (Bielefeld: Aisthesis, 2008). * * Wolters, Reinhard ''Die Schlacht im Teutoburger Wald: Arminius, Varus und das roemische Germanien'' (München: Verlag C. H. Beck, 2008).External links
Arminius
at the ''
Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various t ...
''
Arminius
at the ''
Ancient History Encyclopedia
World History Encyclopedia (formerly Ancient History Encyclopedia) is a nonprofit educational company created in 2009 by Jan van der Crabben. The organization publishes and maintains articles, images, videos, podcasts, and interactive educational ...
''
"Arminius / Varus: Die Varusschlacht im Jahre 9 n. Chr."
– LWL-Institut für westfälische Regionalgeschichte (in German)
"Terry Jones' Barbarians: The Savage Goths"
– includes a portion on Arminius
(in German)
"They Need a Hero"
by Clay Risen in '' The National'', October 9, 2009 – article on modern German views of Hermann and the 2,000th anniversary of the battle {{DEFAULTSORT:Arminius 010s BC births 1st-century rulers in Europe 021 deaths Ancient Roman soldiers Cherusci rulers Cherusci warriors