Armenian People on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''
 The earliest attestations of the
The earliest attestations of the
hayer
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspor ...
'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora of around five million people of full or partial Armenian ancestry living outside modern Armenia. The largest Armenian populations today exist in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, and Syria. With the exceptions of Iran and the former Soviet states, the present-day Armenian diaspora was formed mainly as a result of the Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily through t ...
. Richard G. Hovannisian, ''The Armenian people from ancient to modern times: the fifteenth century to the twentieth century'', Volume 2, p. 421, Palgrave Macmillan, 1997.
Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
is an Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
language. It has two mutually intelligible spoken and written forms: Eastern Armenian, today spoken mainly in Armenia, Artsakh, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, and the former Soviet republics; and Western Armenian
Western Armenian ( Classical spelling: , ) is one of the two standardized forms of Modern Armenian, the other being Eastern Armenian. It is based mainly on the Istanbul Armenian dialect, as opposed to Eastern Armenian, which is mainly base ...
, used in the historical Western Armenia
Western Armenia (Western Armenian: Արեւմտեան Հայաստան, ''Arevmdian Hayasdan'') is a term to refer to the eastern parts of Turkey (formerly the Ottoman Empire) that are part of the historical homeland of the Armenians. Weste ...
and, after the Armenian genocide, primarily in the Armenian diasporan communities. The unique Armenian alphabet
The Armenian alphabet ( hy, Հայոց գրեր, ' or , ') is an alphabetic writing system used to write Armenian. It was developed around 405 AD by Mesrop Mashtots, an Armenian linguist and ecclesiastical leader. The system originally had ...
was invented in 405 AD by Mesrop Mashtots Mesrob or Mesrop ( hy, Մեսրոպ) is an Armenian given name.
Mesrob / Mesrop may refer to:
* Mesrop Mashtots, also Saint Mesrop, Armenian monk, theologian and linguist. Inventor of the Armenian alphabet
** Mesrop Mashtots Institute of Ancient M ...
.
Most Armenians adhere to the Armenian Apostolic Church
, native_name_lang = hy
, icon = Armenian Apostolic Church logo.svg
, icon_width = 100px
, icon_alt =
, image = Էջմիածնի_Մայր_Տաճար.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, a ...
, a non-Chalcedonian
Non-Chalcedonian Christianity comprises the branches of Christianity that do not accept theological resolutions of the Council of Chalcedon, the Fourth Ecumenical Council, held in 451. Non-Chalcedonian denominations reject the Christological ...
Christian church, which is also the world's oldest national church. Christianity began to spread in Armenia soon after Jesus' death, due to the efforts of two of his apostles, St. Thaddeus
Jude ( grc-gre, Ἰούδας Ἰακώβου translit. Ioúdas Iakóbou) was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. He is generally identified as Thaddeus ( grc-gre, Θαδδαῖος; cop, ⲑⲁⲇⲇⲉⲟⲥ; ...
and St. Bartholomew
Bartholomew (Aramaic: ; grc, Βαρθολομαῖος, translit=Bartholomaîos; la, Bartholomaeus; arm, Բարթողիմէոս; cop, ⲃⲁⲣⲑⲟⲗⲟⲙⲉⲟⲥ; he, בר-תולמי, translit=bar-Tôlmay; ar, بَرثُولَماو� ...
.see In the early 4th century, the Kingdom of Armenia became the first state to adopt Christianity as a state religion.
Etymology
 The earliest attestations of the
The earliest attestations of the exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
''Armenia'' date around the 6th century BC. In his trilingual Behistun Inscription dated to 517 BC, Darius I the Great
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his d ...
of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
refers to ''Urashtu'' (in Babylonian) as '' Armina'' ( Old Persian: 𐎠𐎼𐎷𐎡𐎴) and ''Harminuya'' (in Elamite).
In Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, ''Armenios'' () is attested from about the same time, perhaps the earliest reference being a fragment attributed to Hecataeus of Miletus (476 BC). Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Greek mercenary armies o ...
, a Greek general serving in some of the Persian expeditions, describes many aspects of Armenian village life and hospitality in around 401 BC.
Some have linked the name ''Armenia'' with the Early Bronze Age state of '' Armani (Armanum, Armi)'' or the Late Bronze Age state of '' Arme (Shupria)''. ''Armini'', Urartian for "inhabitant of Arme" or "Armean country," referring to the region of Shupria, to the immediate west of Lake Van. The Arme tribe of Urartian texts may have been the Urumu, who in the 12th century BC attempted to invade Assyria from the north with their allies the Mushki
The Mushki (sometimes transliterated as Muški) were an Iron Age people of Anatolia who appear in sources from Assyria but not from the Hittites. Several authors have connected them with the Moschoi (Μόσχοι) of Greek sources and the Geor ...
and the Kaskians
The Kaska (also Kaška, later Tabalian Kasku and Gasga,) were a loosely affiliated Bronze Age non-Indo-European tribal people, who spoke the unclassified Kaskian language and lived in mountainous East Pontic Anatolia, known from Hittite sour ...
. The Urumu apparently settled in the vicinity of Sason
Sason ( hy, Սասուն, translit=Sasun, ku, Qabilcewz, ar, قبل جوز; formerly known as Sasun or Sassoun) is a district and town in the Batman Province of Turkey. It was formerly part of the sanjak of Siirt, which was in Diyarbakır vi ...
, lending their name to the regions of Arme and the nearby lands of Urme and Inner Urumu. The location of the older site of Armani is a matter of debate. Some modern researchers have placed it in the same general area as Arme, near modern Samsat
Samsat ( ku, Samîsad), formerly Samosata ( grc, Σαμόσατα) is a small town in the Adıyaman Province of Turkey, situated on the upper Euphrates river. It is the seat of Samsat District.Indo-European-speaking people. The relationship between Armani and the later Arme-Shupria, if any, is undetermined. Additionally, their connections to Armenians is inconclusive as it is not known what languages were spoken in these regions.
It has also been speculated that the land of ''Ermenen'' (located in or near '' Minni''), mentioned by the Egyptian pharaoh
p. 6
. within this hypothetical dialect group, Proto-Armenian was situated between
 The first geographical entity that was called Armenia by neighboring peoples (such as by Hecataeus of Miletus and on the Achaemenid Behistun Inscription) was the
The first geographical entity that was called Armenia by neighboring peoples (such as by Hecataeus of Miletus and on the Achaemenid Behistun Inscription) was the
''Zoroastrians: Their Religious Beliefs and Practices''
Psychology Press, 2001 p 84 while later on adopting a few elements regarding identification of its pantheon with Greco-Roman deities). In the early years of the 4th century, likely 301 CE, partly in defiance of the
''Zoroastrians: Their Religious Beliefs and Practices''
Psychology Press, 2001 p 84 In the late Parthian period, Armenia was a predominantly Zoroastrian-adhering land, but by the Christianisation, previously predominant Zoroastrianism and paganism in Armenia gradually declined.Charl Wolhuter, Corene de Wet
''International Comparative Perspectives on Religion and Education''
AFRICAN SUN MeDIA, . 1 March 2014 p 31 Later on, in order to further strengthen Armenian national identity,

 In 885 CE the Armenians reestablished themselves as a sovereign kingdom under the leadership of Ashot I of the Bagratid Dynasty. A considerable portion of the Armenian nobility and peasantry fled the Byzantine occupation of Bagratid Armenia in 1045, and the subsequent invasion of the region by
In 885 CE the Armenians reestablished themselves as a sovereign kingdom under the leadership of Ashot I of the Bagratid Dynasty. A considerable portion of the Armenian nobility and peasantry fled the Byzantine occupation of Bagratid Armenia in 1045, and the subsequent invasion of the region by
 Armenians are believed to have had a presence in the Armenian Highland for over 4,000 years. According to legend, Hayk, the patriarch and founder of the Armenian nation, led Armenians to victory over Belus (Assyrian), Bel of Babylon and settled in the Armenian Highland. Today, with a population of 3.5 million (although more recent estimates place the population closer to 2.9 million), they not only constitute an overwhelming majority in Armenia, but also in the disputed region of Artsakh. Armenians in the diaspora informally refer to them as ''Hayastantsi''s ( hy, հայաստանցի), meaning those that are from Armenia (that is, those born and raised in Armenia). They, as well as the Armenians of Iran and Russia, speak the Eastern dialect of the Armenian language. The country itself is secular as a result of Soviet domination, but most of its citizens identify themselves as Apostolic Armenian Christian.
Armenians are believed to have had a presence in the Armenian Highland for over 4,000 years. According to legend, Hayk, the patriarch and founder of the Armenian nation, led Armenians to victory over Belus (Assyrian), Bel of Babylon and settled in the Armenian Highland. Today, with a population of 3.5 million (although more recent estimates place the population closer to 2.9 million), they not only constitute an overwhelming majority in Armenia, but also in the disputed region of Artsakh. Armenians in the diaspora informally refer to them as ''Hayastantsi''s ( hy, հայաստանցի), meaning those that are from Armenia (that is, those born and raised in Armenia). They, as well as the Armenians of Iran and Russia, speak the Eastern dialect of the Armenian language. The country itself is secular as a result of Soviet domination, but most of its citizens identify themselves as Apostolic Armenian Christian.
 Small Armenian trading and religious communities have existed outside Armenia for centuries. For example, a community survived for over a millennium in the Holy Land, and one of the four-quarters of the walled Old City (Jerusalem), Old City of Jerusalem has been called the Armenian Quarter. An Armenian Catholic San Lazzaro degli Armeni, monastic community of 35 founded in 1717 exists on an island near Venice, Italy. There are also remnants of formerly populous communities in Armenians in Turkey, Turkey (Armenians in Istanbul, Istanbul), Armenians in India, India, Armenians in Myanmar, Myanmar, Thailand, Belgium, Portugal, Italy, Israel, Poland, Austria, Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania, Serbia, Ethiopia, Sudan and Egypt.
Regardless, most of the modern days diaspora consists of Armenians scattered throughout the world as a direct consequence of the genocide of 1915, constituting the main portion of the Armenian diaspora. However, Armenian communities in the Georgian capital city of Tbilisi, in Syria and in
Small Armenian trading and religious communities have existed outside Armenia for centuries. For example, a community survived for over a millennium in the Holy Land, and one of the four-quarters of the walled Old City (Jerusalem), Old City of Jerusalem has been called the Armenian Quarter. An Armenian Catholic San Lazzaro degli Armeni, monastic community of 35 founded in 1717 exists on an island near Venice, Italy. There are also remnants of formerly populous communities in Armenians in Turkey, Turkey (Armenians in Istanbul, Istanbul), Armenians in India, India, Armenians in Myanmar, Myanmar, Thailand, Belgium, Portugal, Italy, Israel, Poland, Austria, Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania, Serbia, Ethiopia, Sudan and Egypt.
Regardless, most of the modern days diaspora consists of Armenians scattered throughout the world as a direct consequence of the genocide of 1915, constituting the main portion of the Armenian diaspora. However, Armenian communities in the Georgian capital city of Tbilisi, in Syria and in
 In 301 AD, Armenia adopted Christianity as a state religion, becoming the first state to do so. The claim is primarily based on the fifth-century work of Agathangelos titled "The History of the Armenians." Agathangelos witnessed at first hand the baptism of the Armenian King Trdat III (c. 301/314 A.D.) by St. Gregory the Illuminator. Trdat III decreed Christianity was the state religion.
Armenia established a Church that still exists independently of both the Roman Catholicism, Catholic and the Eastern Orthodox churches, having become so in 451 AD as a result of its stance regarding the Council of Chalcedon. Today this church is known as the
In 301 AD, Armenia adopted Christianity as a state religion, becoming the first state to do so. The claim is primarily based on the fifth-century work of Agathangelos titled "The History of the Armenians." Agathangelos witnessed at first hand the baptism of the Armenian King Trdat III (c. 301/314 A.D.) by St. Gregory the Illuminator. Trdat III decreed Christianity was the state religion.
Armenia established a Church that still exists independently of both the Roman Catholicism, Catholic and the Eastern Orthodox churches, having become so in 451 AD as a result of its stance regarding the Council of Chalcedon. Today this church is known as the  Armenia has, at times, constituted a Christian "island" in a mostly Muslim region. There are, however, a minority of ethnic Armenian Muslims, known as Hamshenis and Crypto-Armenians, although the former are often regarded as a distinct group or subgroup. In the late tsarist Caucasus, individual conversions of Muslims, Yazidis, Jews, and Assyrians into Armenian Christianity have been documented. The history of the Jews in Armenia dates back over 2,000 years. The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia had close ties to European Crusader States. Later on, the deteriorating situation in the region led the bishops of Armenia to elect a Catholicos in Etchmiadzin, the original seat of the Catholicosate. In 1441, a new Catholicos was elected in Etchmiadzin in the person of Kirakos Virapetsi, while Krikor Moussapegiants preserved his title as Catholicos of Cilicia. Therefore, since 1441, there have been two Catholicosates in the Armenian Church with equal rights and privileges, and with their respective jurisdictions. The primacy of honor of the Catholicosate of Etchmiadzin has always been recognized by the Catholicosate of Cilicia.
Armenia has, at times, constituted a Christian "island" in a mostly Muslim region. There are, however, a minority of ethnic Armenian Muslims, known as Hamshenis and Crypto-Armenians, although the former are often regarded as a distinct group or subgroup. In the late tsarist Caucasus, individual conversions of Muslims, Yazidis, Jews, and Assyrians into Armenian Christianity have been documented. The history of the Jews in Armenia dates back over 2,000 years. The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia had close ties to European Crusader States. Later on, the deteriorating situation in the region led the bishops of Armenia to elect a Catholicos in Etchmiadzin, the original seat of the Catholicosate. In 1441, a new Catholicos was elected in Etchmiadzin in the person of Kirakos Virapetsi, while Krikor Moussapegiants preserved his title as Catholicos of Cilicia. Therefore, since 1441, there have been two Catholicosates in the Armenian Church with equal rights and privileges, and with their respective jurisdictions. The primacy of honor of the Catholicosate of Etchmiadzin has always been recognized by the Catholicosate of Cilicia.
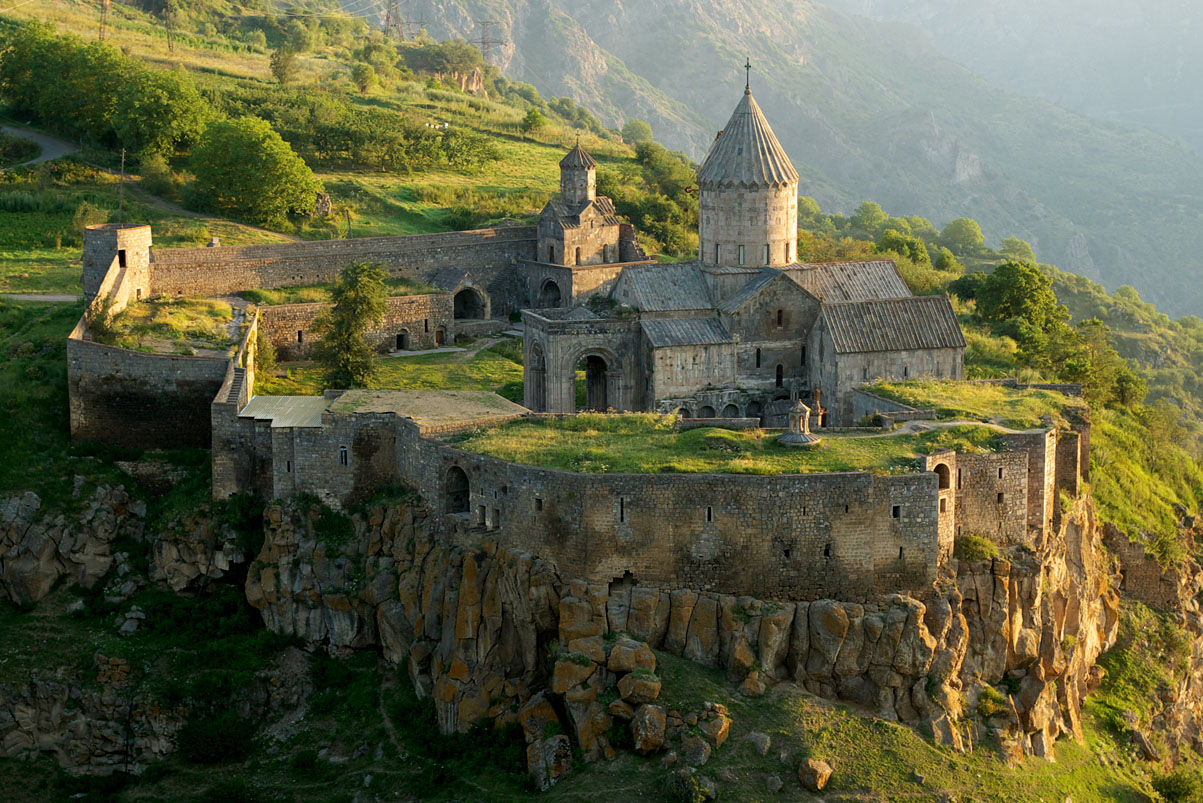 While the Armenian Apostolic Church remains the most prominent church in the Armenian community throughout the world, Armenians (especially in the diaspora) subscribe to any number of other Christian denominations. These include the Armenian Catholic Church (which follows its own liturgy but recognizes the Roman Catholicism, Roman Catholic Pope), the Armenian Evangelical Church, which started as a reformation in the Mother church but later broke away, and the Armenian Brotherhood Church, which was born in the Armenian Evangelical Church, but later broke apart from it. There are other numerous Armenian churches belonging to Protestant denominations of all kinds.
Through the ages many Armenians have collectively belonged to other faiths or Christian movements, including the Paulicians which is a form of Gnostic and Manichaean Christianity. Paulicians sought to restore the pure Christianity of Paul and in c.660 founded the first congregation in Kibossa, Armenia.
Another example is the Tondrakians, who flourished in medieval Armenia between the early 9th century and 11th century. Tondrakians advocated the abolishment of the church, denied the immortality of the soul, did not believe in an afterlife, supported property rights for peasants, and equality between men and women.
The Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Armenians or the Chalcedonian Armenians in the Byzantine Empire were called Iberians ("Georgians") or "Greeks". A notable Orthodox “Iberian” Armenian was the Byzantine General Gregory Pakourianos. The descendants of these Orthodox and Chalcedonic Armenians are the Hayhurum of Greece and Catholic Armenians of Georgia.
While the Armenian Apostolic Church remains the most prominent church in the Armenian community throughout the world, Armenians (especially in the diaspora) subscribe to any number of other Christian denominations. These include the Armenian Catholic Church (which follows its own liturgy but recognizes the Roman Catholicism, Roman Catholic Pope), the Armenian Evangelical Church, which started as a reformation in the Mother church but later broke away, and the Armenian Brotherhood Church, which was born in the Armenian Evangelical Church, but later broke apart from it. There are other numerous Armenian churches belonging to Protestant denominations of all kinds.
Through the ages many Armenians have collectively belonged to other faiths or Christian movements, including the Paulicians which is a form of Gnostic and Manichaean Christianity. Paulicians sought to restore the pure Christianity of Paul and in c.660 founded the first congregation in Kibossa, Armenia.
Another example is the Tondrakians, who flourished in medieval Armenia between the early 9th century and 11th century. Tondrakians advocated the abolishment of the church, denied the immortality of the soul, did not believe in an afterlife, supported property rights for peasants, and equality between men and women.
The Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Armenians or the Chalcedonian Armenians in the Byzantine Empire were called Iberians ("Georgians") or "Greeks". A notable Orthodox “Iberian” Armenian was the Byzantine General Gregory Pakourianos. The descendants of these Orthodox and Chalcedonic Armenians are the Hayhurum of Greece and Catholic Armenians of Georgia.
 Armenian literature dates back to 400 AD, when Mesrop Mashtots first invented the
Armenian literature dates back to 400 AD, when Mesrop Mashtots first invented the
 The first Armenian churches were built on the orders of St. Gregory the Illuminator, and were often built on top of pagan temples, and imitated some aspects of Armenian pre-Christian architecture.
Classical and Medieval Armenian Architecture is divided into four separate periods.
The first Armenian churches were built between the 4th and 7th century, beginning when Armenia converted to Christianity, and ending with the Arab invasion of Armenia. The early churches were mostly simple basilicas, but some with side apses. By the fifth century the typical cupola cone in the center had become widely used. By the seventh century, centrally planned churches had been built and a more complicated ''niched buttress'' and radiating ''Hrip'simé'' style had formed. By the time of the Arab invasion, most of what we now know as classical Armenian architecture had formed.
From the 9th to 11th century, Armenian architecture underwent a revival under the patronage of the Bagratuni dynasty, Bagratid Dynasty with a great deal of building done in the area of Lake Van, this included both traditional styles and new innovations. Ornately carved Armenian Khachkars were developed during this time.Armenia, Past and Present; Elisabeth Bauer, Jacob Schmidheiny, Frederick Leist, 1981 Many new cities and churches were built during this time, including a new capital at Lake Van and a new Cathedral on Akdamar Island to match. The Cathedral of Ani was also completed during this dynasty. It was during this time that the first major monasteries, such as Haghpat Monastery, Haghpat and Haritchavank Monastery, Haritchavank were built. This period was ended by the Great Seljuq Empire, Seljuk invasion.
The first Armenian churches were built on the orders of St. Gregory the Illuminator, and were often built on top of pagan temples, and imitated some aspects of Armenian pre-Christian architecture.
Classical and Medieval Armenian Architecture is divided into four separate periods.
The first Armenian churches were built between the 4th and 7th century, beginning when Armenia converted to Christianity, and ending with the Arab invasion of Armenia. The early churches were mostly simple basilicas, but some with side apses. By the fifth century the typical cupola cone in the center had become widely used. By the seventh century, centrally planned churches had been built and a more complicated ''niched buttress'' and radiating ''Hrip'simé'' style had formed. By the time of the Arab invasion, most of what we now know as classical Armenian architecture had formed.
From the 9th to 11th century, Armenian architecture underwent a revival under the patronage of the Bagratuni dynasty, Bagratid Dynasty with a great deal of building done in the area of Lake Van, this included both traditional styles and new innovations. Ornately carved Armenian Khachkars were developed during this time.Armenia, Past and Present; Elisabeth Bauer, Jacob Schmidheiny, Frederick Leist, 1981 Many new cities and churches were built during this time, including a new capital at Lake Van and a new Cathedral on Akdamar Island to match. The Cathedral of Ani was also completed during this dynasty. It was during this time that the first major monasteries, such as Haghpat Monastery, Haghpat and Haritchavank Monastery, Haritchavank were built. This period was ended by the Great Seljuq Empire, Seljuk invasion.
 Many types of sports are played in Armenia, among the most popular being association football, football, chess, boxing, basketball, ice hockey, Sambo (martial art), sambo, wrestling, Olympic weightlifting, weightlifting, and volleyball. Since independence, the Armenian government has been actively rebuilding its sports program in the country.
During Soviet rule, Armenian athletes rose to prominence winning plenty of medals and helping the USSR win the medal standings at the Olympics on numerous occasions. The first medal won by an Armenian in modern Olympic history was by Hrant Shahinyan, who won two golds and two silvers in gymnastics at the 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki. In football, their most successful team was FC Ararat Yerevan, Yerevan's FC Ararat, which had claimed most of the Soviet championships in the 70s and had also gone to post victories against professional clubs like FC Bayern Munich in the Euro cup.
Armenians have also been successful in chess, which is the most popular mind sport in Armenia. Some of the most prominent chess players in the world are Armenian such as Tigran Petrosian, Levon Aronian and Garry Kasparov. Armenians have also been successful in weightlifting and wrestling (Armen Nazaryan), winning medals in each sport at the Olympics. There are also successful Armenians in association football, football – Henrikh Mkhitaryan, boxing – Arthur Abraham and Vic Darchinyan.
Many types of sports are played in Armenia, among the most popular being association football, football, chess, boxing, basketball, ice hockey, Sambo (martial art), sambo, wrestling, Olympic weightlifting, weightlifting, and volleyball. Since independence, the Armenian government has been actively rebuilding its sports program in the country.
During Soviet rule, Armenian athletes rose to prominence winning plenty of medals and helping the USSR win the medal standings at the Olympics on numerous occasions. The first medal won by an Armenian in modern Olympic history was by Hrant Shahinyan, who won two golds and two silvers in gymnastics at the 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki. In football, their most successful team was FC Ararat Yerevan, Yerevan's FC Ararat, which had claimed most of the Soviet championships in the 70s and had also gone to post victories against professional clubs like FC Bayern Munich in the Euro cup.
Armenians have also been successful in chess, which is the most popular mind sport in Armenia. Some of the most prominent chess players in the world are Armenian such as Tigran Petrosian, Levon Aronian and Garry Kasparov. Armenians have also been successful in weightlifting and wrestling (Armen Nazaryan), winning medals in each sport at the Olympics. There are also successful Armenians in association football, football – Henrikh Mkhitaryan, boxing – Arthur Abraham and Vic Darchinyan.
 Carpet-weaving is historically a major traditional profession for the majority of Armenian women, including many Armenian families. Prominent Karabakh carpet weavers there were men too. The oldest extant Armenian carpet from the region, referred to as Artsakh (historic province), Artsakh (see also Karabakh carpet) during the medieval era, is from the village of Banants (near Gandzak, Armenia, Gandzak) and dates to the early 13th century. The first time that the Armenian word for carpet, ''kork'', was used in historical sources was in a 1242–1243 Armenian inscription on the wall of the Kaptavan Church in Artsakh.Hakobyan. ''Medieval Art of Artsakh'', p. 84.
Common themes and patterns found on Armenian carpets were the depiction of dragons and eagles. They were diverse in style, rich in color and ornamental motifs, and were even separated in categories depending on what sort of animals were depicted on them, such as ''artsvagorgs'' (eagle-carpets), ''vishapagorgs'' (dragon-carpets) and ''otsagorgs'' (serpent-carpets). The rug mentioned in the Kaptavan inscriptions is composed of three arches, "covered with vegatative ornaments", and bears an artistic resemblance to the illuminated manuscripts produced in Artsakh.
The art of carpet weaving was in addition intimately connected to the making of curtains as evidenced in a passage by Kirakos Gandzaketsi, a 13th-century Armenian historian from Artsakh, who praised Arzu-Khatun, the wife of regional prince Vakhtang Khachenatsi, and her daughters for their expertise and skill in weaving.
Armenian carpets were also renowned by foreigners who traveled to Artsakh; the Arab geographer and historian Al-Masudi noted that, among other works of art, he had never seen such carpets elsewhere in his life.
Carpet-weaving is historically a major traditional profession for the majority of Armenian women, including many Armenian families. Prominent Karabakh carpet weavers there were men too. The oldest extant Armenian carpet from the region, referred to as Artsakh (historic province), Artsakh (see also Karabakh carpet) during the medieval era, is from the village of Banants (near Gandzak, Armenia, Gandzak) and dates to the early 13th century. The first time that the Armenian word for carpet, ''kork'', was used in historical sources was in a 1242–1243 Armenian inscription on the wall of the Kaptavan Church in Artsakh.Hakobyan. ''Medieval Art of Artsakh'', p. 84.
Common themes and patterns found on Armenian carpets were the depiction of dragons and eagles. They were diverse in style, rich in color and ornamental motifs, and were even separated in categories depending on what sort of animals were depicted on them, such as ''artsvagorgs'' (eagle-carpets), ''vishapagorgs'' (dragon-carpets) and ''otsagorgs'' (serpent-carpets). The rug mentioned in the Kaptavan inscriptions is composed of three arches, "covered with vegatative ornaments", and bears an artistic resemblance to the illuminated manuscripts produced in Artsakh.
The art of carpet weaving was in addition intimately connected to the making of curtains as evidenced in a passage by Kirakos Gandzaketsi, a 13th-century Armenian historian from Artsakh, who praised Arzu-Khatun, the wife of regional prince Vakhtang Khachenatsi, and her daughters for their expertise and skill in weaving.
Armenian carpets were also renowned by foreigners who traveled to Artsakh; the Arab geographer and historian Al-Masudi noted that, among other works of art, he had never seen such carpets elsewhere in his life.
 Khorovats, an Armenian-styled barbecue, is arguably the favorite Armenian dish. Lavash is a very popular Armenian flat bread, and Armenian paklava is a popular dessert made from filo dough. Other famous Armenian foods include the kabob (a skewer of marinated roasted meat and vegetables), various dolmas (minced lamb, or beef meat and rice wrapped in grape leaves, cabbage leaves, or stuffed into hollowed vegetables), and pilaf, a rice dish. Also, ghapama, a rice-stuffed pumpkin dish, and many different salads are popular in Armenian culture. Fruits play a large part in the Armenian diet. Apricots (''Prunus armeniaca'', also known as Armenian Plum) have been grown in Armenia for centuries and have a reputation for having an especially good flavor. Peaches are popular as well, as are grapes, figs, pomegranates, and melons. Preserves are made from many fruits, including cornelian cherries, young walnuts, sea buckthorn, mulberries, sour cherries, and many others.
Khorovats, an Armenian-styled barbecue, is arguably the favorite Armenian dish. Lavash is a very popular Armenian flat bread, and Armenian paklava is a popular dessert made from filo dough. Other famous Armenian foods include the kabob (a skewer of marinated roasted meat and vegetables), various dolmas (minced lamb, or beef meat and rice wrapped in grape leaves, cabbage leaves, or stuffed into hollowed vegetables), and pilaf, a rice dish. Also, ghapama, a rice-stuffed pumpkin dish, and many different salads are popular in Armenian culture. Fruits play a large part in the Armenian diet. Apricots (''Prunus armeniaca'', also known as Armenian Plum) have been grown in Armenia for centuries and have a reputation for having an especially good flavor. Peaches are popular as well, as are grapes, figs, pomegranates, and melons. Preserves are made from many fruits, including cornelian cherries, young walnuts, sea buckthorn, mulberries, sour cherries, and many others.
Sacred Transformation: Armenian Churches in Los Angeles
a project of the University of Southern California, USC School of Policy, Planning, and Development. *Some of the information about the history of the Armenians comes from the multi-volume ''History of the Armenian People,'' Yerevan, Armenia, 1971.
Thutmose III
Thutmose III (variously also spelt Tuthmosis or Thothmes), sometimes called Thutmose the Great, was the sixth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. Officially, Thutmose III ruled Egypt for almost 54 years and his reign is usually dated from 2 ...
in 1446 BCE, could be a reference to Armenia.
Armenians call themselves ''Hay
Hay is grass, legumes, or other herbaceous plants that have been cut and dried to be stored for use as animal fodder, either for large grazing animals raised as livestock, such as cattle, horses, goats, and sheep, or for smaller domesticat ...
'' ( hy, հայ, pronounced �haj plural: հայեր, aˈjɛɾ. The name has traditionally been derived from '' Hayk'' ( hy, Հայկ), the legendary patriarch of the Armenians and a great-great-grandson of Noah, who, according to Movses Khorenatsi (Moses of Khorene), defeated the Babylonian king
The king of Babylon ( Akkadian: ''šakkanakki Bābili'', later also ''šar Bābili'') was the ruler of the ancient Mesopotamian city of Babylon and its kingdom, Babylonia, which existed as an independent realm from the 19th century BC to its fall ...
Bel in 2492 BC and established his nation in the Ararat region. It is also further postulatedElisabeth Bauer. ''Armenia: Past and Present'' (1981), p. 49 that the name ''Hay'' comes from, or is related to, one of the two confederated, Hittite vassal states—Hayasa
Hayasa-Azzi or Azzi-Hayasa ( hit, URUḪaiaša-, hy, Հայասա) was a Late Bronze Age confederation in the Armenian Highlands and/or Pontic region of Asia Minor. The Hayasa-Azzi confederation was in conflict with the Hittite Empire in th ...
-Azzi (1600–1200 BC). Ultimately, ''Hay'' may derive from the Proto Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
words ''póti'' (meaning "lord" or "master") or ''*h₂éyos''/''*áyos'' (meaning "metal").
Khorenatsi wrote that the word ''Armenian'' originated from the name Armenak or Aram
Aram may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Aram'' (film), 2002 French action drama
* Aram, a fictional character in Japanese manga series '' MeruPuri''
* Aram Quartet, an Italian music group
* ''Aram'' (Kural book), the first of the three ...
(the descendant of Hayk). Khorenatsi refers to both Armenia and Armenians as ''Hayk‘'' (Armenian: Հայք) (not to be confused with the aforementioned patriarch, Hayk).
History
Origin
While theArmenian language
Armenian ( classical: , reformed: , , ) is an Indo-European language and an independent branch of that family of languages. It is the official language of Armenia. Historically spoken in the Armenian Highlands, today Armenian is widely spoken th ...
is classified as an Indo-European language, its placement within the broader Indo-European language family is a matter of debate. Until fairly recently, scholars believed Armenian to be most closely related to Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Ancient Macedonian. Eric P. Hamp
Eric Pratt Hamp (November 16, 1920 – February 17, 2019) was an American linguist widely respected as a leading authority on Indo-European linguistics, with particular interests in Celtic languages and Albanian. Unlike many Indo-Europeanists, wh ...
placed Armenian in the "Pontic Indo-European" (also called Graeco-Armenian
Graeco-Armenian (or Helleno-Armenian) is the hypothetical common ancestor of Greek and Armenian that postdates Proto-Indo-European. Its status is somewhat similar to that of the Italo-Celtic grouping: each is widely considered plausible without b ...
or Helleno-Armenian) subgroup of Indo-European languages in his 2012 Indo-European family tree. There are two possible explanations, not mutually exclusive, for a common origin of the Armenian and Greek languages.
* In Hamp's view, the homeland of the proposed Graeco-Armenian subgroup is the northeast coast of the Black Sea and its hinterlands. He assumes that they migrated from there southeast through the Caucasus with the Armenians remaining after Batumi
Batumi (; ka, ბათუმი ) is the second largest city of Georgia and the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Adjara, located on the coast of the Black Sea in Georgia's southwest. It is situated in a subtropical zone at the foot of t ...
while the pre-Greeks proceeded westward along the southern coast of the Black Sea.
* Ancient Greek historian Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
(writing circa 440 BCE), suggested that Armenians migrated from Phrygia, a region that encompassed much of western and central Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
during the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
: "the Armenians were equipped like Phrygians, being Phrygian colonists" (7.73) ('). This statement was interpreted by later scholars as meaning that Armenians spoke a language derived from Phrygian, a poorly attested Indo-European language. However, this theory has been discredited. Ancient Greek writers believed that the Phrygians had originated in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, in an area adjoining Macedonia, from where they had emigrated to Anatolia during the Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a time of widespread societal collapse during the 12th century BC, between c. 1200 and 1150. The collapse affected a large area of the Eastern Mediterranean (North Africa and Southeast Europe) and the Near ...
. This led later scholars to theorize that Armenians also originated in the Balkans. However, an Armenian origin in the Balkans, although once widely accepted, has been facing increased scrutiny in recent years due to discrepancies in the timeline and lack of genetic and archeological evidence. The view that Armenians are native to the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
is supported by ancient Armenian historical accounts and legends, which place the Ararat Plain as the cradle of Armenian culture, as well as modern genetic research. In fact, some scholars have suggested that the Phrygians and/or the apparently related Mushki
The Mushki (sometimes transliterated as Muški) were an Iron Age people of Anatolia who appear in sources from Assyria but not from the Hittites. Several authors have connected them with the Moschoi (Μόσχοι) of Greek sources and the Geor ...
people were originally from Armenia and moved westward.
Some linguists tentatively conclude that Armenian, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
(and Phrygian) and Indo-Iranian were dialectally close to each other;''Handbook of Formal Languages'' (1997p. 6
. within this hypothetical dialect group, Proto-Armenian was situated between
Proto-Greek
The Proto-Greek language (also known as Proto-Hellenic) is the Indo-European language which was the last common ancestor of all varieties of Greek, including Mycenaean Greek, the subsequent ancient Greek dialects (i.e., Attic, Ionic, Aeo ...
(centum
Languages of the Indo-European family are classified as either centum languages or satem languages according to how the dorsal consonants (sounds of "K", "G" and "Y" type) of the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) developed. An e ...
subgroup) and Proto-Indo-Iranian (satem
Languages of the Indo-European family are classified as either centum languages or satem languages according to how the dorsal consonants (sounds of "K", "G" and "Y" type) of the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) developed. An ...
subgroup). This has led some scholars to propose a hypothetical Graeco-Armenian-Aryan clade within the Indo-European language family from which the Armenian, Greek, Indo-Iranian, and possibly Phrygian languages all descend. According to Kim (2018), however, there is insufficient evidence for a cladistic connection between Armenian and Greek, and common features between these two languages can be explained as a result of contact. Contact is also the most likely explanation for morphological features shared by Armenian with Indo-Iranian and Balto-Slavic languages
The Balto-Slavic languages form a branch of the Indo-European family of languages, traditionally comprising the Baltic and Slavic languages. Baltic and Slavic languages share several linguistic traits not found in any other Indo-European branc ...
.
It has been suggested that the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
Trialeti-Vanadzor culture
The Trialeti-Vanadzor culture, previously known as the Trialeti-Kirovakan culture, is named after the Trialeti region of Georgia (country), Georgia and the city of Vanadzor, Vanadzor, Armenia. It is attributed to the late 3rd and early 2nd mille ...
and sites such as the burial complexes at Verin and Nerkin Naver are indicative of an Indo-European presence in Armenia by the end of the 3rd millennium BCE. The controversial Armenian hypothesis
The Armenian hypothesis, also known as the Near Eastern model, is a theory of the Proto-Indo-European homeland, initially proposed by linguists Tamaz V. Gamkrelidze and Vyacheslav Ivanov in the early 1980s, which suggests that the Proto-Indo-Eu ...
, put forward by some scholars, such as Thomas Gamkrelidze and Vyacheslav V. Ivanov, proposes that the Indo-European homeland
The Proto-Indo-European homeland (or Indo-European homeland) was the prehistoric linguistic homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). From this region, its speakers migrated east and west, and went on to form the proto-communities of ...
was around the Armenian Highland. This theory was partially confirmed by the research of geneticist David Reich (et al. 2018), among others. Similarly Grolle (et al. 2018) supports not only a homeland for Armenians on the Armenian highlands, but also that the Armenian highlands are the homeland for the "pre-proto-Indo-Europeans". A large genetic study in 2022 showed that many Armenians are "direct patrilineal descendants of the Yamnaya
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archa ...
".
Genetic studies explain Armenian diversity by several mixtures of Eurasian populations that occurred between 3000 and 2000 BCE. But genetic signals of population mixture cease after 1200 BCE when Bronze Age civilizations in the Eastern Mediterranean world suddenly and violently collapsed. Armenians have since remained isolated and genetic structure within the population developed ~500 years ago when Armenia was divided between the Ottomans and the Safavid Empire in Iran. A genetic study (Wang et al. 2018) supports the indigenous origin for Armenians in a region south of the Caucasus which he calls "Greater Caucasus".
In the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
, several states flourished in the area of Greater Armenia, including the Hittite Empire
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-centr ...
(at the height of its power in the 14th century BCE), (Mitanni
Mitanni (; Hittite cuneiform ; ''Mittani'' '), c. 1550–1260 BC, earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, c. 1600 BC; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat (''Hanikalbat'', ''Khanigalbat'', cuneiform ') in Assyrian records, or ''Naharin'' in ...
(South-Western historical Armenia, 1500–1300 BCE), and Hayasa-Azzi
Hayasa-Azzi or Azzi-Hayasa ( hit, URUḪaiaša-, hy, Հայասա) was a Late Bronze Age confederation in the Armenian Highlands and/or Pontic region of Asia Minor. The Hayasa-Azzi confederation was in conflict with the Hittite Empire in t ...
(1500–1200 BCE). Soon after Hayasa-Azzi came Arme-Shupria (1300s–1190 BCE), the Nairi Confederation (1200–900 BCE), and the Kingdom of Urartu
Urartu (; Assyrian: ',Eberhard Schrader, ''The Cuneiform inscriptions and the Old Testament'' (1885), p. 65. Babylonian: ''Urashtu'', he, אֲרָרָט ''Ararat'') is a geographical region and Iron Age kingdom also known as the Kingdom of V ...
(860–590 BCE), who successively established their sovereignty over the Armenian Highland. Each of the aforementioned nations and tribes participated in the ethnogenesis of the Armenian people. Under Ashurbanipal (669–627 BCE), the Assyrian empire
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyr ...
reached the Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains,
: pronounced
* hy, Կովկասյան լեռներ,
: pronounced
* az, Qafqaz dağları, pronounced
* rus, Кавка́зские го́ры, Kavkázskiye góry, kɐfˈkasːkʲɪje ˈɡorɨ
* tr, Kafkas Dağla ...
(modern Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
, Georgia and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of t ...
).
Luwianologist John D. Hawkins proposed that "Hai" people were possibly mentioned in the 10th century BCE Hieroglyphic Luwian
Hieroglyphic Luwian (''luwili'') is a variant of the Luwian language, recorded in official and royal seals and a small number of monumental inscriptions. It is written in a hieroglyphic script known as Anatolian hieroglyphs.
A decipherment was pr ...
inscriptions from Carchemish
Carchemish ( Turkish: ''Karkamış''; or ), also spelled Karkemish ( hit, ; Hieroglyphic Luwian: , /; Akkadian: ; Egyptian: ; Hebrew: ) was an important ancient capital in the northern part of the region of Syria. At times during it ...
. A.E. Redgate later clarified that these "Hai" people may have been Armenians.
Antiquity
 The first geographical entity that was called Armenia by neighboring peoples (such as by Hecataeus of Miletus and on the Achaemenid Behistun Inscription) was the
The first geographical entity that was called Armenia by neighboring peoples (such as by Hecataeus of Miletus and on the Achaemenid Behistun Inscription) was the Satrapy of Armenia
The Satrapy of Armenia (Old Persian: 𐎠𐎼𐎷𐎡𐎴 or 𐎠𐎼𐎷𐎡𐎴𐎹 ), a region controlled by the Orontid dynasty (570–201 BC), was one of the satrapies of the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC that later became an ind ...
, established in the late 6th century BCE under the Orontid (Yervanduni) dynasty within the Achaemenid Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
. The Orontids later ruled the independent Kingdom of Armenia. At its zenith (95–65 BCE), under the imperial reign of Tigran the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
, a member of the Artaxiad (Artashesian) dynasty, the Kingdom of Armenia extended from the Caucasus all the way to what is now central Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
, Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
, and northern Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
.
The Arsacid Kingdom of Armenia, itself a branch of the Arsacid dynasty of Parthia, was the first state to adopt Christianity as its religion (it had formerly been adherent to Armenian paganism
Armenian mythology originated in ancient Indo-European traditions, specifically Proto-Armenian, and gradually incorporated Hurro-Urartian, Mesopotamian, Iranian, and Greek beliefs and deities."Armenia (Vannic)" by A.H. Sayce, p.793-4; "Armen ...
, which was influenced by Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
,Mary Boyce''Zoroastrians: Their Religious Beliefs and Practices''
Psychology Press, 2001 p 84 while later on adopting a few elements regarding identification of its pantheon with Greco-Roman deities). In the early years of the 4th century, likely 301 CE, partly in defiance of the
Sassanids
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
it seems.Mary Boyce''Zoroastrians: Their Religious Beliefs and Practices''
Psychology Press, 2001 p 84 In the late Parthian period, Armenia was a predominantly Zoroastrian-adhering land, but by the Christianisation, previously predominant Zoroastrianism and paganism in Armenia gradually declined.Charl Wolhuter, Corene de Wet
''International Comparative Perspectives on Religion and Education''
AFRICAN SUN MeDIA, . 1 March 2014 p 31 Later on, in order to further strengthen Armenian national identity,
Mesrop Mashtots Mesrob or Mesrop ( hy, Մեսրոպ) is an Armenian given name.
Mesrob / Mesrop may refer to:
* Mesrop Mashtots, also Saint Mesrop, Armenian monk, theologian and linguist. Inventor of the Armenian alphabet
** Mesrop Mashtots Institute of Ancient M ...
invented the Armenian alphabet
The Armenian alphabet ( hy, Հայոց գրեր, ' or , ') is an alphabetic writing system used to write Armenian. It was developed around 405 AD by Mesrop Mashtots, an Armenian linguist and ecclesiastical leader. The system originally had ...
, in 405 CE. This event ushered the Golden Age of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
, during which many foreign books and manuscripts were translated to Armenian by Mesrop's pupils. Armenia lost its sovereignty again in 428 CE to the rivaling Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
and Sassanid Persian empires, until the Muslim conquest of Persia
The Muslim conquest of Persia, also known as the Arab conquest of Iran, was carried out by the Rashidun Caliphate from 633 to 654 AD and led to the fall of the Sasanian Empire as well as the eventual decline of the Zoroastrian religion.
Th ...
overran also the regions in which Armenians lived.
Middle Ages

 In 885 CE the Armenians reestablished themselves as a sovereign kingdom under the leadership of Ashot I of the Bagratid Dynasty. A considerable portion of the Armenian nobility and peasantry fled the Byzantine occupation of Bagratid Armenia in 1045, and the subsequent invasion of the region by
In 885 CE the Armenians reestablished themselves as a sovereign kingdom under the leadership of Ashot I of the Bagratid Dynasty. A considerable portion of the Armenian nobility and peasantry fled the Byzantine occupation of Bagratid Armenia in 1045, and the subsequent invasion of the region by Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
in 1064. They settled in large numbers in Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coa ...
, an Anatolian region where Armenians were already established as a minority since Roman times. In 1080, they founded an independent Armenian Principality then Kingdom of Cilicia, which became the focus of Armenian nationalism. The Armenians developed close social, cultural, military, and religious ties with nearby Crusader States, but eventually succumbed to Mamluk
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
invasions. In the next few centuries, Djenghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
, Timurids, and the tribal Turkic federations of the Ak Koyunlu and the Kara Koyunlu ruled over the Armenians.
Early modern history
From the early 16th century, bothWestern Armenia
Western Armenia (Western Armenian: Արեւմտեան Հայաստան, ''Arevmdian Hayasdan'') is a term to refer to the eastern parts of Turkey (formerly the Ottoman Empire) that are part of the historical homeland of the Armenians. Weste ...
and Eastern Armenia fell under Iranian Safavid dynasty, Safavid rule. Owing to the century long Turco-Iranian geo-political rivalry that would last in Western Asia, significant parts of the region were frequently fought over between the two rivalling empires. From the mid 16th century with the Peace of Amasya, and decisively from the first half of the 17th century with the Treaty of Zuhab until the first half of the 19th century, Eastern Armenia was ruled by the successive Iranian Safavid, Afsharid dynasty, Afsharid and Qajar dynasty, Qajar empires, while Western Armenia remained under Ottoman Turkey, Ottoman rule. In the late 1820s, the parts of historic Armenia under Iranian control centering on Yerevan and Lake Sevan (all of Eastern Armenia) were incorporated into the Russian Empire following Qajar dynasty, Iran's forced ceding of the territories after its loss in the Russo-Persian War (1826-1828) and the outcoming Treaty of Turkmenchay. Western Armenia however, remained in Ottoman hands.
Modern history
The ethnic cleansing of Armenians during the final years of the Ottoman Empire is widely considered a Armenian genocide, genocide, resulting in an estimated 1.5 million victims. The first wave of persecution was in the years 1894 to 1896, the second one culminating in the events of theArmenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily through t ...
in 1915 and 1916. With World War I in progress, the Ottoman Empire accused the (Christian) Armenians as liable to ally with Imperial Russia, and used it as a pretext to deal with the entire Armenian population as an enemy within their empire.
Governments of the Republic of Turkey since that time have consistently rejected charges of genocide, typically arguing either that those Armenians who died were simply in the way of a war, or that killings of Armenians were justified by their individual or collective support for the enemies of the Ottoman Empire. Passage of legislation in various foreign countries, condemning the persecution of the Armenians as genocide, has often provoked diplomatic conflict. (See Armenian genocide recognition, Recognition of the Armenian genocide)
Following the breakup of the Russian Empire in the aftermath of World War I for a brief period, from 1918 to 1920, Armenia was an First Republic of Armenia, independent republic plagued by socio-economic crises such as Muslim uprisings in Kars and Sharur–Nakhichevan, large-scale Muslim uprisings. In late 1920, the Communist Party of Armenia (Soviet Union), communists came to power following an invasion of Armenia by the Red Army; in 1922, Armenia became part of the Transcaucasian SFSR of the Soviet Union, later on forming the Armenian SSR, Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic (1936 to 21 September 1991). In 1991, Armenia declared independence from the USSR and established the second Republic of Armenia.
Geographic distribution
Armenia
 Armenians are believed to have had a presence in the Armenian Highland for over 4,000 years. According to legend, Hayk, the patriarch and founder of the Armenian nation, led Armenians to victory over Belus (Assyrian), Bel of Babylon and settled in the Armenian Highland. Today, with a population of 3.5 million (although more recent estimates place the population closer to 2.9 million), they not only constitute an overwhelming majority in Armenia, but also in the disputed region of Artsakh. Armenians in the diaspora informally refer to them as ''Hayastantsi''s ( hy, հայաստանցի), meaning those that are from Armenia (that is, those born and raised in Armenia). They, as well as the Armenians of Iran and Russia, speak the Eastern dialect of the Armenian language. The country itself is secular as a result of Soviet domination, but most of its citizens identify themselves as Apostolic Armenian Christian.
Armenians are believed to have had a presence in the Armenian Highland for over 4,000 years. According to legend, Hayk, the patriarch and founder of the Armenian nation, led Armenians to victory over Belus (Assyrian), Bel of Babylon and settled in the Armenian Highland. Today, with a population of 3.5 million (although more recent estimates place the population closer to 2.9 million), they not only constitute an overwhelming majority in Armenia, but also in the disputed region of Artsakh. Armenians in the diaspora informally refer to them as ''Hayastantsi''s ( hy, հայաստանցի), meaning those that are from Armenia (that is, those born and raised in Armenia). They, as well as the Armenians of Iran and Russia, speak the Eastern dialect of the Armenian language. The country itself is secular as a result of Soviet domination, but most of its citizens identify themselves as Apostolic Armenian Christian.
Diaspora
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
existed since ancient history, antiquity.
Within the diasporan Armenian community, there is an unofficial classification of the different ''kinds'' of Armenians. For example, Armenians who originate from Iran are referred to as Iranian Armenians, ''Parskahay'' ( hy, պարսկահայ), while Armenians from Lebanon are usually referred to as Armenians in Lebanon, ''Lipananahay'' ( hy, լիբանանահայ). Armenians of the Diaspora are the primary speakers of the Western dialect of the Armenian language. This dialect has considerable differences with Eastern Armenian, but speakers of either of the two variations can usually understand each other. Eastern Armenian in the diaspora is primarily spoken in Iran and European countries such as Ukraine, Russia, and Georgia (country), Georgia (where they form a majority in the Samtskhe-Javakheti province). In diverse communities (such as in Canada and the U.S.) where many different kinds of Armenians live together, there is a tendency for the different groups to cluster together.
Culture
Religion
Before Christianity, Armenians adhered to Armenian paganism, Armenian Indo-European native religion: a type of indigenous polytheism that pre-dated the Urartu period but which subsequently adopted several Greco-Roman and Iranian religious characteristics. In 301 AD, Armenia adopted Christianity as a state religion, becoming the first state to do so. The claim is primarily based on the fifth-century work of Agathangelos titled "The History of the Armenians." Agathangelos witnessed at first hand the baptism of the Armenian King Trdat III (c. 301/314 A.D.) by St. Gregory the Illuminator. Trdat III decreed Christianity was the state religion.
Armenia established a Church that still exists independently of both the Roman Catholicism, Catholic and the Eastern Orthodox churches, having become so in 451 AD as a result of its stance regarding the Council of Chalcedon. Today this church is known as the
In 301 AD, Armenia adopted Christianity as a state religion, becoming the first state to do so. The claim is primarily based on the fifth-century work of Agathangelos titled "The History of the Armenians." Agathangelos witnessed at first hand the baptism of the Armenian King Trdat III (c. 301/314 A.D.) by St. Gregory the Illuminator. Trdat III decreed Christianity was the state religion.
Armenia established a Church that still exists independently of both the Roman Catholicism, Catholic and the Eastern Orthodox churches, having become so in 451 AD as a result of its stance regarding the Council of Chalcedon. Today this church is known as the Armenian Apostolic Church
, native_name_lang = hy
, icon = Armenian Apostolic Church logo.svg
, icon_width = 100px
, icon_alt =
, image = Էջմիածնի_Մայր_Տաճար.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, a ...
, which is a part of the Oriental Orthodox communion, not to be confused with the Eastern Orthodox communion. During its later political eclipses, Armenia depended on the church to preserve and protect its unique identity. The original location of the Armenian Catholicosate is Echmiadzin. However, the continuous upheavals, which characterized the political scenes of Armenia, made the political power move to safer places. The Church center moved as well to different locations together with the political authority. Therefore, it eventually moved to Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coa ...
as the Holy See of Cilicia.
 Armenia has, at times, constituted a Christian "island" in a mostly Muslim region. There are, however, a minority of ethnic Armenian Muslims, known as Hamshenis and Crypto-Armenians, although the former are often regarded as a distinct group or subgroup. In the late tsarist Caucasus, individual conversions of Muslims, Yazidis, Jews, and Assyrians into Armenian Christianity have been documented. The history of the Jews in Armenia dates back over 2,000 years. The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia had close ties to European Crusader States. Later on, the deteriorating situation in the region led the bishops of Armenia to elect a Catholicos in Etchmiadzin, the original seat of the Catholicosate. In 1441, a new Catholicos was elected in Etchmiadzin in the person of Kirakos Virapetsi, while Krikor Moussapegiants preserved his title as Catholicos of Cilicia. Therefore, since 1441, there have been two Catholicosates in the Armenian Church with equal rights and privileges, and with their respective jurisdictions. The primacy of honor of the Catholicosate of Etchmiadzin has always been recognized by the Catholicosate of Cilicia.
Armenia has, at times, constituted a Christian "island" in a mostly Muslim region. There are, however, a minority of ethnic Armenian Muslims, known as Hamshenis and Crypto-Armenians, although the former are often regarded as a distinct group or subgroup. In the late tsarist Caucasus, individual conversions of Muslims, Yazidis, Jews, and Assyrians into Armenian Christianity have been documented. The history of the Jews in Armenia dates back over 2,000 years. The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia had close ties to European Crusader States. Later on, the deteriorating situation in the region led the bishops of Armenia to elect a Catholicos in Etchmiadzin, the original seat of the Catholicosate. In 1441, a new Catholicos was elected in Etchmiadzin in the person of Kirakos Virapetsi, while Krikor Moussapegiants preserved his title as Catholicos of Cilicia. Therefore, since 1441, there have been two Catholicosates in the Armenian Church with equal rights and privileges, and with their respective jurisdictions. The primacy of honor of the Catholicosate of Etchmiadzin has always been recognized by the Catholicosate of Cilicia.
 While the Armenian Apostolic Church remains the most prominent church in the Armenian community throughout the world, Armenians (especially in the diaspora) subscribe to any number of other Christian denominations. These include the Armenian Catholic Church (which follows its own liturgy but recognizes the Roman Catholicism, Roman Catholic Pope), the Armenian Evangelical Church, which started as a reformation in the Mother church but later broke away, and the Armenian Brotherhood Church, which was born in the Armenian Evangelical Church, but later broke apart from it. There are other numerous Armenian churches belonging to Protestant denominations of all kinds.
Through the ages many Armenians have collectively belonged to other faiths or Christian movements, including the Paulicians which is a form of Gnostic and Manichaean Christianity. Paulicians sought to restore the pure Christianity of Paul and in c.660 founded the first congregation in Kibossa, Armenia.
Another example is the Tondrakians, who flourished in medieval Armenia between the early 9th century and 11th century. Tondrakians advocated the abolishment of the church, denied the immortality of the soul, did not believe in an afterlife, supported property rights for peasants, and equality between men and women.
The Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Armenians or the Chalcedonian Armenians in the Byzantine Empire were called Iberians ("Georgians") or "Greeks". A notable Orthodox “Iberian” Armenian was the Byzantine General Gregory Pakourianos. The descendants of these Orthodox and Chalcedonic Armenians are the Hayhurum of Greece and Catholic Armenians of Georgia.
While the Armenian Apostolic Church remains the most prominent church in the Armenian community throughout the world, Armenians (especially in the diaspora) subscribe to any number of other Christian denominations. These include the Armenian Catholic Church (which follows its own liturgy but recognizes the Roman Catholicism, Roman Catholic Pope), the Armenian Evangelical Church, which started as a reformation in the Mother church but later broke away, and the Armenian Brotherhood Church, which was born in the Armenian Evangelical Church, but later broke apart from it. There are other numerous Armenian churches belonging to Protestant denominations of all kinds.
Through the ages many Armenians have collectively belonged to other faiths or Christian movements, including the Paulicians which is a form of Gnostic and Manichaean Christianity. Paulicians sought to restore the pure Christianity of Paul and in c.660 founded the first congregation in Kibossa, Armenia.
Another example is the Tondrakians, who flourished in medieval Armenia between the early 9th century and 11th century. Tondrakians advocated the abolishment of the church, denied the immortality of the soul, did not believe in an afterlife, supported property rights for peasants, and equality between men and women.
The Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Armenians or the Chalcedonian Armenians in the Byzantine Empire were called Iberians ("Georgians") or "Greeks". A notable Orthodox “Iberian” Armenian was the Byzantine General Gregory Pakourianos. The descendants of these Orthodox and Chalcedonic Armenians are the Hayhurum of Greece and Catholic Armenians of Georgia.
Language and literature
Armenian is a sub-branch of theIndo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
family, and with some 8 million speakers one of the smallest surviving branches, comparable to Albanian language, Albanian or the somewhat more widely spoken Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, with which it may be connected (see Graeco-Armenian
Graeco-Armenian (or Helleno-Armenian) is the hypothetical common ancestor of Greek and Armenian that postdates Proto-Indo-European. Its status is somewhat similar to that of the Italo-Celtic grouping: each is widely considered plausible without b ...
). Today, that branch has just one language – Armenian.
Five million Eastern Armenian speakers live in the Caucasus, Russia, and Iran, and approximately two to three million people in the rest of the Armenian diaspora speak Western Armenian. According to US Census figures, there are 300,000 Americans who speak Armenian at home. It is in fact the twentieth most commonly spoken language in the United States, having slightly fewer speakers than Haitian Creole, and slightly more than Navajo language, Navajo.
 Armenian literature dates back to 400 AD, when Mesrop Mashtots first invented the
Armenian literature dates back to 400 AD, when Mesrop Mashtots first invented the Armenian alphabet
The Armenian alphabet ( hy, Հայոց գրեր, ' or , ') is an alphabetic writing system used to write Armenian. It was developed around 405 AD by Mesrop Mashtots, an Armenian linguist and ecclesiastical leader. The system originally had ...
. This period of time is often viewed as the Golden Age of Armenian literature. Early Armenian literature was written by the "father of Armenian history", Moses of Chorene, who authored ''The History of Armenia''. The book covers the time-frame from the formation of the Armenian people to the fifth century AD. The nineteenth century beheld a great literary movement that was to give rise to modern Armenian literature. This period of time, during which Armenian culture flourished, is known as the Revival period (Zartonki sherchan). The Revivalist authors of Constantinople and Tiflis, almost identical to the Romanticists of Europe, were interested in encouraging Armenian nationalism. Most of them adopted the newly created Eastern or Western variants of the Armenian language depending on the targeted audience, and preferred them over classical Armenian (grabar). This period ended after the Hamidian massacres, when Armenians experienced turbulent times. As Armenian history of the 1920s and of the Genocide came to be more openly discussed, writers like Paruyr Sevak, Gevork Emin, Silva Kaputikyan and Hovhannes Shiraz began a new era of literature.
Architecture
 The first Armenian churches were built on the orders of St. Gregory the Illuminator, and were often built on top of pagan temples, and imitated some aspects of Armenian pre-Christian architecture.
Classical and Medieval Armenian Architecture is divided into four separate periods.
The first Armenian churches were built between the 4th and 7th century, beginning when Armenia converted to Christianity, and ending with the Arab invasion of Armenia. The early churches were mostly simple basilicas, but some with side apses. By the fifth century the typical cupola cone in the center had become widely used. By the seventh century, centrally planned churches had been built and a more complicated ''niched buttress'' and radiating ''Hrip'simé'' style had formed. By the time of the Arab invasion, most of what we now know as classical Armenian architecture had formed.
From the 9th to 11th century, Armenian architecture underwent a revival under the patronage of the Bagratuni dynasty, Bagratid Dynasty with a great deal of building done in the area of Lake Van, this included both traditional styles and new innovations. Ornately carved Armenian Khachkars were developed during this time.Armenia, Past and Present; Elisabeth Bauer, Jacob Schmidheiny, Frederick Leist, 1981 Many new cities and churches were built during this time, including a new capital at Lake Van and a new Cathedral on Akdamar Island to match. The Cathedral of Ani was also completed during this dynasty. It was during this time that the first major monasteries, such as Haghpat Monastery, Haghpat and Haritchavank Monastery, Haritchavank were built. This period was ended by the Great Seljuq Empire, Seljuk invasion.
The first Armenian churches were built on the orders of St. Gregory the Illuminator, and were often built on top of pagan temples, and imitated some aspects of Armenian pre-Christian architecture.
Classical and Medieval Armenian Architecture is divided into four separate periods.
The first Armenian churches were built between the 4th and 7th century, beginning when Armenia converted to Christianity, and ending with the Arab invasion of Armenia. The early churches were mostly simple basilicas, but some with side apses. By the fifth century the typical cupola cone in the center had become widely used. By the seventh century, centrally planned churches had been built and a more complicated ''niched buttress'' and radiating ''Hrip'simé'' style had formed. By the time of the Arab invasion, most of what we now know as classical Armenian architecture had formed.
From the 9th to 11th century, Armenian architecture underwent a revival under the patronage of the Bagratuni dynasty, Bagratid Dynasty with a great deal of building done in the area of Lake Van, this included both traditional styles and new innovations. Ornately carved Armenian Khachkars were developed during this time.Armenia, Past and Present; Elisabeth Bauer, Jacob Schmidheiny, Frederick Leist, 1981 Many new cities and churches were built during this time, including a new capital at Lake Van and a new Cathedral on Akdamar Island to match. The Cathedral of Ani was also completed during this dynasty. It was during this time that the first major monasteries, such as Haghpat Monastery, Haghpat and Haritchavank Monastery, Haritchavank were built. This period was ended by the Great Seljuq Empire, Seljuk invasion.
Sports
 Many types of sports are played in Armenia, among the most popular being association football, football, chess, boxing, basketball, ice hockey, Sambo (martial art), sambo, wrestling, Olympic weightlifting, weightlifting, and volleyball. Since independence, the Armenian government has been actively rebuilding its sports program in the country.
During Soviet rule, Armenian athletes rose to prominence winning plenty of medals and helping the USSR win the medal standings at the Olympics on numerous occasions. The first medal won by an Armenian in modern Olympic history was by Hrant Shahinyan, who won two golds and two silvers in gymnastics at the 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki. In football, their most successful team was FC Ararat Yerevan, Yerevan's FC Ararat, which had claimed most of the Soviet championships in the 70s and had also gone to post victories against professional clubs like FC Bayern Munich in the Euro cup.
Armenians have also been successful in chess, which is the most popular mind sport in Armenia. Some of the most prominent chess players in the world are Armenian such as Tigran Petrosian, Levon Aronian and Garry Kasparov. Armenians have also been successful in weightlifting and wrestling (Armen Nazaryan), winning medals in each sport at the Olympics. There are also successful Armenians in association football, football – Henrikh Mkhitaryan, boxing – Arthur Abraham and Vic Darchinyan.
Many types of sports are played in Armenia, among the most popular being association football, football, chess, boxing, basketball, ice hockey, Sambo (martial art), sambo, wrestling, Olympic weightlifting, weightlifting, and volleyball. Since independence, the Armenian government has been actively rebuilding its sports program in the country.
During Soviet rule, Armenian athletes rose to prominence winning plenty of medals and helping the USSR win the medal standings at the Olympics on numerous occasions. The first medal won by an Armenian in modern Olympic history was by Hrant Shahinyan, who won two golds and two silvers in gymnastics at the 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki. In football, their most successful team was FC Ararat Yerevan, Yerevan's FC Ararat, which had claimed most of the Soviet championships in the 70s and had also gone to post victories against professional clubs like FC Bayern Munich in the Euro cup.
Armenians have also been successful in chess, which is the most popular mind sport in Armenia. Some of the most prominent chess players in the world are Armenian such as Tigran Petrosian, Levon Aronian and Garry Kasparov. Armenians have also been successful in weightlifting and wrestling (Armen Nazaryan), winning medals in each sport at the Olympics. There are also successful Armenians in association football, football – Henrikh Mkhitaryan, boxing – Arthur Abraham and Vic Darchinyan.
Music and dance
Armenian music is a mix of indigenous folk music, perhaps best-represented by Djivan Gasparyan's well-known duduk music, as well as light pop, and extensive Christian music. Instruments like the duduk, the dhol, the zurna and the Qanun (instrument), kanun are commonly found in Armenian folk music. Artists such as Sayat Nova are famous due to their influence in the development of Armenian folk music. One of the oldest types of Armenian music is the Armenian chant which is the most common kind of religious music in Armenia. Many of these chants are ancient in origin, extending to pre-Christian times, while others are relatively modern, including several composed by Saint Mesrop Mashtots, the inventor of the Armenian alphabet. Whilst under Soviet rule, Armenian classical music composer Aram Khatchaturian became internationally well known for his music, for various ballets and the Sabre Dance from his composition for the ballet Gayane (ballet), Gayane. The Armenian Genocide caused widespread emigration that led to the settlement of Armenians in various countries in the world. Armenians kept to their traditions and certain diasporans rose to fame with their music. In the post-Genocide Armenian community of the United States, the so-called "kef" style Armenian dance music, using Armenian and Middle Eastern folk instruments (often electrified/amplified) and some western instruments, was popular. This style preserved the folk songs and dances ofWestern Armenia
Western Armenia (Western Armenian: Արեւմտեան Հայաստան, ''Arevmdian Hayasdan'') is a term to refer to the eastern parts of Turkey (formerly the Ottoman Empire) that are part of the historical homeland of the Armenians. Weste ...
, and many artists also played the contemporary popular songs of Turkey and other Middle Eastern countries from which the Armenians emigrated. Richard Hagopian is perhaps the most famous artist of the traditional "kef" style and the Vosbikian Band was notable in the 40s and 50s for developing their own style of "kef music" heavily influenced by the popular American Big Band Jazz of the time. Later, stemming from the Middle Eastern Armenian diaspora and influenced by Continental European (especially French) pop music, the Armenian pop music genre grew to fame in the 60s and 70s with artists such as Adiss Harmandian and Harout Pamboukjian performing to the Armenian diaspora and Armenia. Also with artists such as Sirusho, performing pop music combined with Armenian folk music in today's entertainment industry. Other Armenian diasporans that rose to fame in classical or international music circles are world-renowned List of French-Armenians, French-Armenian singer and composer Charles Aznavour, pianist Sahan Arzruni, prominent opera sopranos such as Hasmik Papian and more recently Isabel Bayrakdarian and Anna Kasyan. Certain Armenians settled to sing non-Armenian tunes such as the heavy metal band System of a Down (which nonetheless often incorporates traditional Armenian instrumentals and styling into their songs) or pop star Cher (whose father was Armenian). Ruben Hakobyan (Ruben Sasuntsi) is a well recognized Armenian ethnographic and patriotic folk singer who has achieved widespread national recognition due to his devotion to Armenian folk music and exceptional talent. In the Armenian diaspora, Armenian Revolutionary Songs are popular with the youth. These songs encourage Armenian patriotism and are generally about Armenian history and national heroes.
Carpet weaving
 Carpet-weaving is historically a major traditional profession for the majority of Armenian women, including many Armenian families. Prominent Karabakh carpet weavers there were men too. The oldest extant Armenian carpet from the region, referred to as Artsakh (historic province), Artsakh (see also Karabakh carpet) during the medieval era, is from the village of Banants (near Gandzak, Armenia, Gandzak) and dates to the early 13th century. The first time that the Armenian word for carpet, ''kork'', was used in historical sources was in a 1242–1243 Armenian inscription on the wall of the Kaptavan Church in Artsakh.Hakobyan. ''Medieval Art of Artsakh'', p. 84.
Common themes and patterns found on Armenian carpets were the depiction of dragons and eagles. They were diverse in style, rich in color and ornamental motifs, and were even separated in categories depending on what sort of animals were depicted on them, such as ''artsvagorgs'' (eagle-carpets), ''vishapagorgs'' (dragon-carpets) and ''otsagorgs'' (serpent-carpets). The rug mentioned in the Kaptavan inscriptions is composed of three arches, "covered with vegatative ornaments", and bears an artistic resemblance to the illuminated manuscripts produced in Artsakh.
The art of carpet weaving was in addition intimately connected to the making of curtains as evidenced in a passage by Kirakos Gandzaketsi, a 13th-century Armenian historian from Artsakh, who praised Arzu-Khatun, the wife of regional prince Vakhtang Khachenatsi, and her daughters for their expertise and skill in weaving.
Armenian carpets were also renowned by foreigners who traveled to Artsakh; the Arab geographer and historian Al-Masudi noted that, among other works of art, he had never seen such carpets elsewhere in his life.
Carpet-weaving is historically a major traditional profession for the majority of Armenian women, including many Armenian families. Prominent Karabakh carpet weavers there were men too. The oldest extant Armenian carpet from the region, referred to as Artsakh (historic province), Artsakh (see also Karabakh carpet) during the medieval era, is from the village of Banants (near Gandzak, Armenia, Gandzak) and dates to the early 13th century. The first time that the Armenian word for carpet, ''kork'', was used in historical sources was in a 1242–1243 Armenian inscription on the wall of the Kaptavan Church in Artsakh.Hakobyan. ''Medieval Art of Artsakh'', p. 84.
Common themes and patterns found on Armenian carpets were the depiction of dragons and eagles. They were diverse in style, rich in color and ornamental motifs, and were even separated in categories depending on what sort of animals were depicted on them, such as ''artsvagorgs'' (eagle-carpets), ''vishapagorgs'' (dragon-carpets) and ''otsagorgs'' (serpent-carpets). The rug mentioned in the Kaptavan inscriptions is composed of three arches, "covered with vegatative ornaments", and bears an artistic resemblance to the illuminated manuscripts produced in Artsakh.
The art of carpet weaving was in addition intimately connected to the making of curtains as evidenced in a passage by Kirakos Gandzaketsi, a 13th-century Armenian historian from Artsakh, who praised Arzu-Khatun, the wife of regional prince Vakhtang Khachenatsi, and her daughters for their expertise and skill in weaving.
Armenian carpets were also renowned by foreigners who traveled to Artsakh; the Arab geographer and historian Al-Masudi noted that, among other works of art, he had never seen such carpets elsewhere in his life.
Cuisine
 Khorovats, an Armenian-styled barbecue, is arguably the favorite Armenian dish. Lavash is a very popular Armenian flat bread, and Armenian paklava is a popular dessert made from filo dough. Other famous Armenian foods include the kabob (a skewer of marinated roasted meat and vegetables), various dolmas (minced lamb, or beef meat and rice wrapped in grape leaves, cabbage leaves, or stuffed into hollowed vegetables), and pilaf, a rice dish. Also, ghapama, a rice-stuffed pumpkin dish, and many different salads are popular in Armenian culture. Fruits play a large part in the Armenian diet. Apricots (''Prunus armeniaca'', also known as Armenian Plum) have been grown in Armenia for centuries and have a reputation for having an especially good flavor. Peaches are popular as well, as are grapes, figs, pomegranates, and melons. Preserves are made from many fruits, including cornelian cherries, young walnuts, sea buckthorn, mulberries, sour cherries, and many others.
Khorovats, an Armenian-styled barbecue, is arguably the favorite Armenian dish. Lavash is a very popular Armenian flat bread, and Armenian paklava is a popular dessert made from filo dough. Other famous Armenian foods include the kabob (a skewer of marinated roasted meat and vegetables), various dolmas (minced lamb, or beef meat and rice wrapped in grape leaves, cabbage leaves, or stuffed into hollowed vegetables), and pilaf, a rice dish. Also, ghapama, a rice-stuffed pumpkin dish, and many different salads are popular in Armenian culture. Fruits play a large part in the Armenian diet. Apricots (''Prunus armeniaca'', also known as Armenian Plum) have been grown in Armenia for centuries and have a reputation for having an especially good flavor. Peaches are popular as well, as are grapes, figs, pomegranates, and melons. Preserves are made from many fruits, including cornelian cherries, young walnuts, sea buckthorn, mulberries, sour cherries, and many others.
Institutions
* TheArmenian Apostolic Church
, native_name_lang = hy
, icon = Armenian Apostolic Church logo.svg
, icon_width = 100px
, icon_alt =
, image = Էջմիածնի_Մայր_Տաճար.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, a ...
, the world's oldest National Church
* The Armenian General Benevolent Union (AGBU) founded in 1906 and the largest Armenian non-profit organization in the world, with educational, cultural and humanitarian projects on all continents
* The Armenian Revolutionary Federation, founded in 1890. It is generally referred to as the ''Dashnaktsutyun'', which means ''Federation'' in Armenian. The ARF is the strongest worldwide Armenian political organization and the only diasporan Armenian organization with a significant political presence in Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
.
* Hamazkayin, an Armenian cultural and educational society founded in Cairo in 1928, and responsible for the founding of Armenian secondary schools and institutions of higher education in several countries
* The Armenian Catholic Church, representing small communities of Armeno-Catholics in different countries around the world, as well as important monastic and cultural institutions in Venice and Vienna
* Homenetmen, an Armenian Scouting and athletic organization founded in 1910 with a worldwide membership of about 25,000
* The Armenian Relief Society, founded in 1910
Genetics
Y-DNA
A 2012 study found that haplogroups R1b, J2, and T were the most notable haplogroups among Armenians.MtDNA
Most notable mtDNA haplogroups among the Armenian samples are H, U, T, J, K and X while the rest of remaining Mtdna of the Armenians are HV, I, X, W, R0 and N.Notable people
See also
* Ethnic groups in Europe * Ethnic groups in West Asia * Hayk * Hemshin peoples * Hidden Armenians * Peoples of the Caucasus * Prehistory of the Armenians * List of Armenian ethnic enclaves * Armenian diasporaReferences
Notes Inline General * * *The categorization of Armenian churches in Los Angeles used information froSacred Transformation: Armenian Churches in Los Angeles
a project of the University of Southern California, USC School of Policy, Planning, and Development. *Some of the information about the history of the Armenians comes from the multi-volume ''History of the Armenian People,'' Yerevan, Armenia, 1971.
Further reading
* * I. M. Diakonoff, ''The Pre-History of the Armenian People'' (revised, trans. Lori Jennings), Caravan Books, New York (1984), . * George A. Bournoutian, ''A History of the Armenian People'', 2 vol. (1994) * * * * Aleksandra Ziolkowska-Boehm, ''The Polish Experience through World War II: A Better Day Has Not Come'', Lanham, MD: Lexington Books, 2013, * Russell D. Gray and Quentin D. Atkinson, "Language-tree divergence times support the Anatolian theory of Indo-European origin", Nature, 426, 435–439 (2003) * George A. Bournoutian, ''A Concise History of the Armenian People'' (Mazda, 2003, 2004). * * * - on Brazil's Armenian diaspora. ;UCLA conference series proceedings The UCLA conference series titled "Historic Armenian Cities and Provinces" is organized by the Holder of the Armenian Educational Foundation Chair in Modern Armenian History. The conference proceedings are edited by Richard G. Hovannisian. Published in Costa Mesa, CA, by Mazda Publishers, they are: # ''Armenian Van/Vaspurakan'' (2000) # ''Armenian Baghesh/Bitlis and Taron/Mush'' (2001) # ''Armenian Tsopk/Kharpert'' (2002) # ''Armenian Karin/Erzerum'' (2003) # ''Armenian Sebastia/Sivas and Lesser Armenia'' (2004) # ''Armenian Tigranakert/Diarbekir and Edessa/Urfa'' (2006) # ''Armenian Cilicia'' (2008) # ''Armenian Pontus: the Trebizond-Black Sea communities'' (2009) {{Authority control Armenian people, Ethnic groups in Armenia Peoples of the Caucasus Ancient peoples of the Near East Indo-European peoples Modern Indo-European peoples Indigenous peoples of Western Asia Articles containing video clips Ethnic groups in the Middle East