Arleigh A. Burke on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Arleigh Albert Burke (October 19, 1901 – January 1, 1996) was an
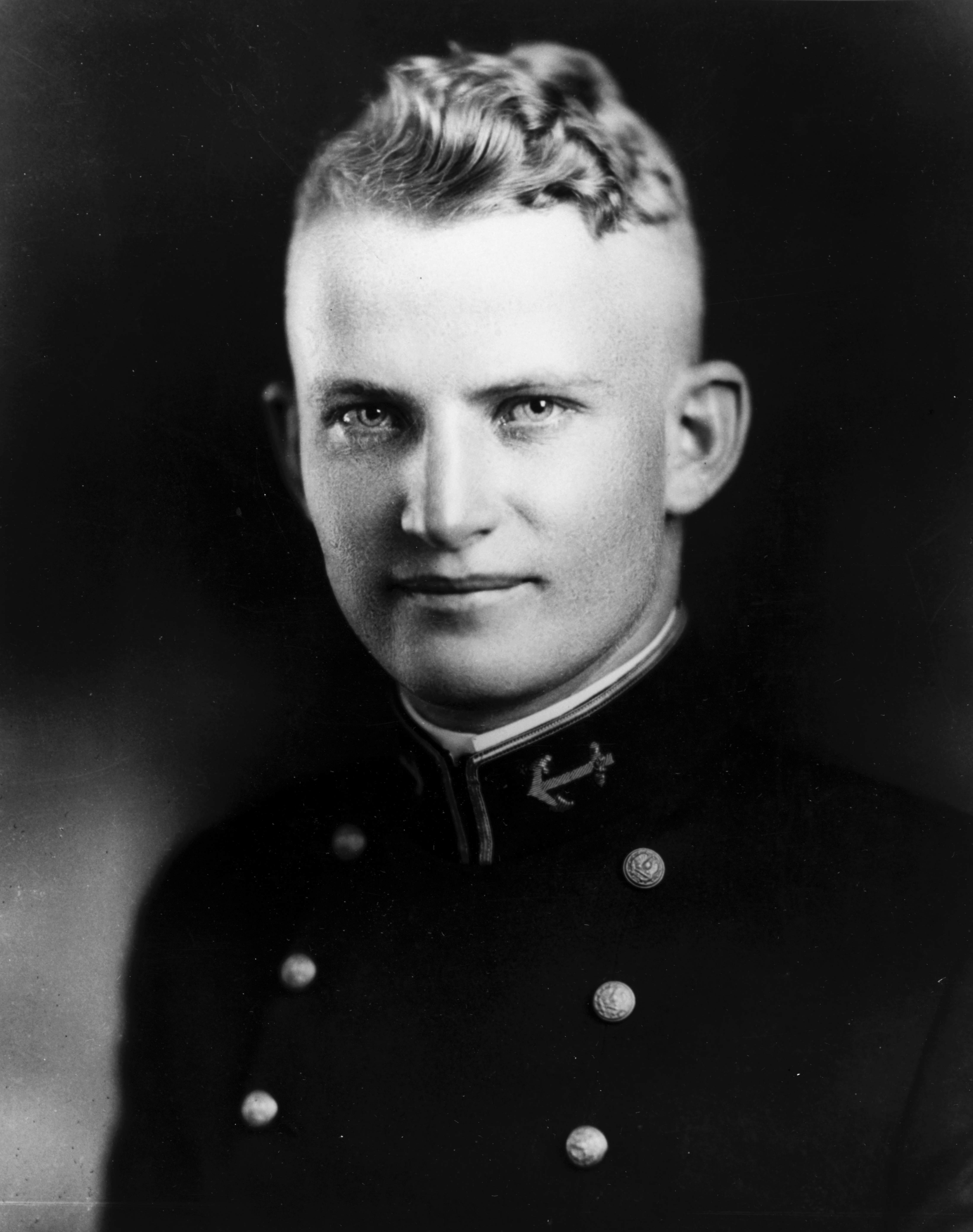 Burke was born in
Burke was born in
 In March 1944, Burke was promoted to Chief of Staff to the Commander of
In March 1944, Burke was promoted to Chief of Staff to the Commander of
National Security Archive Electronic Briefing Book No. 275 Burke further argued that land-based missiles and bombers were vulnerable to attack, which made the U.S.-Soviet nuclear balance dangerously unstable. By contrast, nuclear submarines were virtually undetectable and invulnerable. He was very critical of "hair trigger" or " launch on warning" nuclear strategies, and he warned that such strategies were "dangerous for any nation." Burke served an unprecedented three terms as Chief of Naval Operations during a period of growth and progress in the Navy. Upon completing his third term, he was transferred to the Retired List on August 1, 1961.
 Arleigh Burke died on January 1, 1996, at the
Arleigh Burke died on January 1, 1996, at the
 , the
, the
"Arleigh Burke: The Last CNO" by David Alan Rosenberg
– Biographies in Naval History –
admiral
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in some navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force, and is above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet, ...
of the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
who distinguished himself during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
and the Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
, and who served as Chief of Naval Operations
The chief of naval operations (CNO) is the professional head of the United States Navy. The position is a statutory office () held by an admiral who is a military adviser and deputy to the secretary of the Navy. In a separate capacity as a memb ...
during the Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
and Kennedy administrations.
, the lead ship
The lead ship, name ship, or class leader is the first of a series or class of ships all constructed according to the same general design. The term is applicable to naval ships and large civilian vessels.
Large ships are very complex and may ...
of its class of Aegis
The aegis ( ; grc, αἰγίς ''aigís''), as stated in the ''Iliad'', is a device carried by Athena and Zeus, variously interpreted as an animal skin or a shield and sometimes featuring the head of a Gorgon. There may be a connection with a d ...
-equipped guided missile destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in ...
s, was commissioned in Burke's honor in 1991. The honor of naming a vessel after a living figure was only the fourth time it had been bestowed since 1861.
Early life and naval career
 Burke was born in
Burke was born in Boulder, Colorado
Boulder is a home rule city that is the county seat and most populous municipality of Boulder County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 108,250 at the 2020 United States census, making it the 12th most populous city in Color ...
, on October 19, 1901, to Oscar Burke and Clara Mokler. His grandfather, August Björkgren, was a Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
immigrant to the US and changed his surname to 'Burke', a common Irish surname, to sound more 'American'. Due to the 1918 influenza outbreak, schools were closed in Boulder and he never graduated from high school. Burke won an alternate appointment to the United States Naval Academy
The United States Naval Academy (US Naval Academy, USNA, or Navy) is a federal service academy in Annapolis, Maryland. It was established on 10 October 1845 during the tenure of George Bancroft as Secretary of the Navy. The Naval Academy ...
given by his local congressman. During his time at the Academy, Burke was a member of 23rd Company. He graduated from the Academy in June 1923, and was commissioned as an ensign
An ensign is the national flag flown on a vessel to indicate nationality. The ensign is the largest flag, generally flown at the stern (rear) of the ship while in port. The naval ensign (also known as war ensign), used on warships, may be diffe ...
in the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
. He married Roberta Gorsuch (1899–1997) of Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
Over the next 18 years, Burke served aboard battleship
A battleship is a large armored warship with a main battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1880s to describe a type of ...
s and destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in ...
s, and earned a Master of Science
A Master of Science ( la, Magisterii Scientiae; abbreviated MS, M.S., MSc, M.Sc., SM, S.M., ScM or Sc.M.) is a master's degree in the field of science awarded by universities in many countries or a person holding such a degree. In contrast to ...
degree in chemical engineering
Chemical engineering is an engineering field which deals with the study of operation and design of chemical plants as well as methods of improving production. Chemical engineers develop economical commercial processes to convert raw materials int ...
at the University of Michigan
, mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth"
, former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817–1821)
, budget = $10.3 billion (2021)
, endowment = $17 billion (2021)As o ...
in 1931. When World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
came, he found himself, to his great disappointment, in a shore billet at the Naval Gun Factory
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It inc ...
in Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
After persistent efforts on his part, in 1943 he received orders to join the fighting in the South Pacific.
World War II
Burke spent the remainder of the war in the South Pacific. He successively commanded Destroyer Division 43, Destroyer Division 44, Destroyer Squadron 12, andDestroyer Squadron 23
Destroyer Squadron 23 (DESRON 23) is a squadron of United States Navy destroyers based out of San Diego, California. The squadron is best known for its actions during World War II, most notably the Battle of Cape St. George, under the command of ...
. DesRon 23, known as the "Little Beavers", covered the initial landings in Bougainville in November 1943, and fought in 22 separate engagements during the next four months. During this time, the Little Beavers were credited with destroying one Japanese cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several roles.
The term "cruiser", which has been in use for several hu ...
, nine destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in ...
s, one submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
, several smaller ships, and approximately 30 aircraft. Burke's standing orders to his task force were, "Destroyers to attack on enemy contact WITHOUT ORDERS from the task force commander." After reviewing the Navy's early unsuccessful engagements with the Japanese, he concluded that uncertainty and hesitation had cost them dearly. The lesson was driven home to him at the Battle of Blackett Strait
The Battle of Blackett Strait (Japanese: ビラ・スタンモーア夜戦 (Battle of Vila–Stanmore)) was a naval battle of the Pacific War, Pacific campaign of World War II, fought on 6 March 1943 in the Blackett Strait, between Kolombangara ...
, when his radar operator made first contact with a ship near the shore but Burke hesitated to fire. A battle soon unfolded which ended in a US victory, which only Burke was unhappy with. Reflecting on the events Burke asked a nearby ensign what the difference was between a good officer and a poor one. After listening to the ensign's response, Burke offered his own: "The difference between a good officer and a poor one," said Burke, "is about ten seconds."
Burke usually pushed his destroyers to just under boiler-bursting speed, but while en route to a rendezvous prior to the Battle of Cape St. George
The Battle of Cape St. George was a naval battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II fought on 25 November 1943, between Cape St. George, New Ireland, and Buka Island (now part of the North Solomons Province in Papua New Guinea). It was ...
, a boiler casualty to (a jammed boiler tube by a brush used for cleaning) limited his squadron to 31 knots, rather than the 34+ of which they were otherwise capable. His nickname was "31 Knot Burke," originally a taunt, later a popular symbol of his hard-charging nature. An alternative explanation is provided by Jean Edward Smith in his biography of Eisenhower: "During World War Two, Burke mistakenly led his destroyer squadron into a Japanese minefield. Admiral Halsey radioed to ask what he was doing in a Japanese minefield. ‘Thirty-one knots,’ replied Burke”.
 In March 1944, Burke was promoted to Chief of Staff to the Commander of
In March 1944, Burke was promoted to Chief of Staff to the Commander of Task Force 58
The Fast Carrier Task Force (TF 38 when assigned to Third Fleet, TF 58 when assigned to Fifth Fleet), was the main striking force of the United States Navy in the Pacific War from January 1944 through the end of the war in August 1945. The task ...
, the Fifth Fleet's Fast Carrier Task Force
The Fast Carrier Task Force (TF 38 when assigned to Third Fleet, TF 58 when assigned to Fifth Fleet), was the main striking force of the United States Navy in the Pacific War from January 1944 through the end of the war in August 1945. The task ...
, which was commanded by Admiral Marc Mitscher
Marc Andrew "Pete" Mitscher (January 26, 1887 – February 3, 1947) was a pioneer in naval aviation who became an admiral in the United States Navy, and served as commander of the Fast Carrier Task Force in the Pacific during the latter half of ...
. The transfer stemmed from a directive from the Chief of Naval Operations
The chief of naval operations (CNO) is the professional head of the United States Navy. The position is a statutory office () held by an admiral who is a military adviser and deputy to the secretary of the Navy. In a separate capacity as a memb ...
, Admiral Ernest King
Ernest Joseph King (23 November 1878 – 25 June 1956) was an American naval officer who served as Commander in Chief, United States Fleet (COMINCH) and Chief of Naval Operations (CNO) during World War II. As COMINCH-CNO, he directed the U ...
, that required a surface commander such as Admiral Raymond A. Spruance to have an aviator as Chief of Staff, and an air commander, such as Mitscher, to have a surface officer as Chief of Staff. Neither Mitscher nor Burke were happy with the arrangement, but as time passed Burke realized he had been given one of the most important assignments in the Navy, and his hard work and diligence eventually warmed Mitscher to him. Burke was promoted to the temporary rank of Commodore
Commodore may refer to:
Ranks
* Commodore (rank), a naval rank
** Commodore (Royal Navy), in the United Kingdom
** Commodore (United States)
** Commodore (Canada)
** Commodore (Finland)
** Commodore (Germany) or ''Kommodore''
* Air commodore ...
, and participated in all the force's naval engagements until June 1945, near the end of the war. He was aboard both and when they were hit by Japanese kamikaze
, officially , were a part of the Japanese Special Attack Units of military aviators who flew suicide attacks for the Empire of Japan against Allied naval vessels in the closing stages of the Pacific campaign of World War II, intending t ...
aircraft during the Okinawa
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest city ...
campaign.
After the end of the war, Burke reverted to his permanent rank of captain and continued his naval career by serving in a number of capacities, including once more as Admiral Mitscher's chief of staff, until the latter's death in 1947. Burke then took command of the cruiser for a cruise down the east coast of Africa. He was promoted to rear admiral in 1949 and served as Navy Secretary on the Defense Research and Development Board.
Korean War
At the outbreak of theKorean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
, Admiral Forrest Sherman
Forrest Percival Sherman (October 30, 1896 – July 22, 1951) was an Admiral (United States), admiral in the United States Navy and the youngest person to serve as Chief of Naval Operations until Admiral Elmo Zumwalt in 1970. The was named ...
, then Chief of Naval Operations, ordered Burke to duty as Deputy Chief of Staff to Commander Naval Forces Far East
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It inc ...
. From there, he assumed command of Cruiser Division Five, and, in July 1951, was made a member of the United Nations Truce Delegation which negotiated with the Communists for military armistice in Korea. After six months in the truce tents, he returned to the Office of Chief of Naval Operations where he served as Director of Strategic Plans Division until 1954.
In April 1954, he took command of Cruiser Division Six, then moved in January 1955 to command Destroyer Force Atlantic Fleet ( DesLant). In August 1955, Burke succeeded Admiral Robert B. Carney
Robert Bostwick Carney (March 26, 1895 – June 25, 1990) was an admiral in the United States Navy who served as commander-in-chief of the NATO forces in Southern Europe (1951–1953) and then as Chief of Naval Operations (1953–1954) du ...
as Chief of Naval Operations. At the time of his appointment as Chief of Naval Operations, Burke was still a rear admiral (two stars) and was promoted over the heads of many Flag Officers who were senior to him. Burke had never served as a vice admiral (three stars), so he was promoted two grades at the time of his appointment.
Chief of Naval Operations
Burke took the post of Chief of Naval Operations with significant reservations. He served at a critical time in world history, during the depths of theCold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
. He was relatively young compared to other Flag Officers at the time. He was a hard worker, and seemingly tireless, working fifteen-hour work days six days a week as a norm. He was also an excellent leader and manager, and his ability to create an effective organization were keys to his success. He supported the notoriously demanding Admiral Hyman Rickover
Hyman G. Rickover (January 27, 1900 – July 8, 1986) was an admiral in the U.S. Navy. He directed the original development of naval nuclear propulsion and controlled its operations for three decades as director of the U.S. Naval Reactors off ...
in the development of a nuclear-powered submarine
A nuclear submarine is a submarine powered by a nuclear reactor, but not necessarily nuclear-armed. Nuclear submarines have considerable performance advantages over "conventional" (typically diesel-electric) submarines. Nuclear propulsion, ...
force, and instituted the development of submarine-launched ballistic missiles, which led to the Polaris missile program, headed by Burke's selectee Rear Admiral W. F. "Red" Raborn. Burke convened the Project Nobska
Project Nobska was a 1956 summer study on anti-submarine warfare (ASW) for the United States Navy ordered by Chief of Naval Operations Admiral Arleigh Burke. It is also referred to as the Nobska Study, named for its location on Nobska Point nea ...
anti-submarine warfare
Anti-submarine warfare (ASW, or in older form A/S) is a branch of underwater warfare that uses surface warships, aircraft, submarines, or other platforms, to find, track, and deter, damage, or destroy enemy submarines. Such operations are t ...
conference in 1956 at the suggestion of Columbus Iselin II, director of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI, acronym pronounced ) is a private, nonprofit research and higher education facility dedicated to the study of marine science and engineering.
Established in 1930 in Woods Hole, Massachusetts, it i ...
, where discussion ranged from oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamic ...
to nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
s. At the conference, a statement by Edward Teller
Edward Teller ( hu, Teller Ede; January 15, 1908 – September 9, 2003) was a Hungarian-American theoretical physicist who is known colloquially as "the father of the hydrogen bomb" (see the Teller–Ulam design), although he did not care for ...
that a physically small one-megaton warhead suitable for Polaris could be developed led to Burke's adoption of Polaris over Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but ...
. At a time when others in the Navy were very skeptical of the idea of a missile launched from a submarine, Burke succeeded in developing the single most effective deterrent to a nuclear attack on the United States. By 1961 routine Polaris deterrent patrols were in progress and a rapid construction program of Polaris submarines was underway.
Burke as Chief of Naval Operations was intimately involved in the Eisenhower administration
Dwight D. Eisenhower's tenure as the 34th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1953, and ended on January 20, 1961. Eisenhower, a Republican from Kansas, took office following a landslide victory ...
discussions on limiting the size of the submarine force. Asked "how much is enough?", as to the number of US ballistic missile submarines needed for deterrence
Deterrence may refer to:
* Deterrence theory, a theory of war, especially regarding nuclear weapons
* Deterrence (penology), a theory of justice
* Deterrence (psychology)
Deterrence in relation to criminal offending is the idea or theory that t ...
, Burke argued that a force of around 40 Polaris submarines (each with 16 missiles
In military terminology, a missile is a guided airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight usually by a jet engine or rocket motor. Missiles are thus also called guided missiles or guided rockets (when a previously unguided rocket i ...
) was a reasonable answer."How Much is Enough?": The U.S. Navy and "Finite Deterrence"National Security Archive Electronic Briefing Book No. 275 Burke further argued that land-based missiles and bombers were vulnerable to attack, which made the U.S.-Soviet nuclear balance dangerously unstable. By contrast, nuclear submarines were virtually undetectable and invulnerable. He was very critical of "hair trigger" or " launch on warning" nuclear strategies, and he warned that such strategies were "dangerous for any nation." Burke served an unprecedented three terms as Chief of Naval Operations during a period of growth and progress in the Navy. Upon completing his third term, he was transferred to the Retired List on August 1, 1961.
Last years
Burke, himself of Swedish descent, was the senior representative of the United States of America at the funeral of King Gustaf VI Adolf of Sweden in 1973. Arleigh Burke died on January 1, 1996, at the
Arleigh Burke died on January 1, 1996, at the National Naval Medical Center
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, ...
in Bethesda, Maryland
Bethesda () is an unincorporated, census-designated place in southern Montgomery County, Maryland. It is located just northwest of Washington, D.C. It takes its name from a local church, the Bethesda Meeting House (1820, rebuilt 1849), which in ...
. He was 94 years old. He is buried at the United States Naval Academy Cemetery
The United States Naval Academy Cemetery and Columbarium is a cemetery at the United States Naval Academy in Annapolis, Maryland.
History
In 1868 the Naval Academy purchased a 67-acre piece of land called Strawberry Hill as part of their effort ...
, in Annapolis, Maryland
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east o ...
.
Awards and honors
Ship class namesake
lead ship
The lead ship, name ship, or class leader is the first of a series or class of ships all constructed according to the same general design. The term is applicable to naval ships and large civilian vessels.
Large ships are very complex and may ...
of her class of Aegis
The aegis ( ; grc, αἰγίς ''aigís''), as stated in the ''Iliad'', is a device carried by Athena and Zeus, variously interpreted as an animal skin or a shield and sometimes featuring the head of a Gorgon. There may be a connection with a d ...
-equipped guided missile destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in ...
s, was commissioned in his honor in 1991. In 1985, a few months after the ship was ordered, an early keel-laying ceremony was held at Bath Iron Works
Bath Iron Works (BIW) is a major United States shipyard located on the Kennebec River in Bath, Maine, founded in 1884 as Bath Iron Works, Limited. Since 1995, Bath Iron Works has been a subsidiary of General Dynamics. It is the fifth-largest de ...
. Burke marked his initials on material that was later incorporated at the physical keel-laying on December 6, 1988. Burke was one of the very few individuals to be honored by a ship named after them during their lifetime.
The Assisted Living section of the Vinson Hall Retirement Community in McLean, Virginia
McLean ( ) is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Fairfax County in Northern Virginia. McLean is home to many diplomats, military, members of Congress, and high-ranking government officials partially due to its proxi ...
, is named the Arleigh Burke Pavilion in his honor.
Medals
Burke received numerous combat awards during his forty-two years in the Navy, including theNavy Cross
The Navy Cross is the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps' second-highest military decoration awarded for sailors and marines who distinguish themselves for extraordinary heroism in combat with an armed enemy force. The medal is eq ...
, Navy Distinguished Service Medal, Legion of Merit
The Legion of Merit (LOM) is a military award of the United States Armed Forces that is given for exceptionally meritorious conduct in the performance of outstanding services and achievements. The decoration is issued to members of the eight ...
, and the Purple Heart
The Purple Heart (PH) is a United States military decoration awarded in the name of the President to those wounded or killed while serving, on or after 5 April 1917, with the U.S. military. With its forerunner, the Badge of Military Merit, w ...
. None were more cherished than two awards that came early in his career. In 1928, while serving aboard , he was commended for the "rescue of shipwrecked and seafaring men." In 1939 during his first command, , he was commended when his destroyer won the fleet gunnery trophy with the highest score in many years. His ship also stood third in engineering competition and high in communication competition.
For his service in Destroyer Squadron 23, Burke was awarded the Navy Cross, the Navy Distinguished Service Medal, the Legion of Merit, and the Presidential Unit Citation awarded to the squadron. The citations follow in part:
;Navy Cross
;Navy Distinguished Service Medal
;Legion of Merit
As Chief of Staff, Commander Fast Carrier Task Force, Pacific (Task Force 38), Burke was awarded a Gold Star in lieu of a second Distinguished Service Medal, the Silver Star, a Gold Star in lieu of a second Legion of Merit, and a Letter of Commendation, with authorization to wear the Commendation Ribbon. The citations follow in part:
;Silver Star
;Gold Star in lieu of second Legion of Merit
;Letter of Commendation
From September 1950 until May 1951, Burke served as Deputy Chief of Staff to Commander U.S. Naval Forces, Far East, and, for "exceptionally meritorious conduct (in that capacity) from September 3, 1950, to January 1, 1951" he was awarded a Gold Star in lieu of a third Legion of Merit. The citation further states:
While serving as Commander Cruiser Division Five from May to September 1951, and also as a Member of the Military Armistice Commission
The United Nations Command Military Armistice Commission (UNCMAC) was established in July 1953 at the end of the Korean War to supervise the Korean Armistice Agreement
The Korean Armistice Agreement ( ko, 한국정전협정 / 조선정전� ...
in Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
, Burke was awarded an oak leaf cluster in lieu of a fourth Legion of Merit by the Army (Headquarters U.S. Army Forces, Far East) by General Order #5, as follows:
Burke was presented a Gold Star in lieu of a third Distinguished Service Medal by President John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination ...
at the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in 1800. ...
on July 26, 1961. On January 10, 1977, Burke was presented with the Presidential Medal of Freedom
The Presidential Medal of Freedom is the highest civilian award of the United States, along with the Congressional Gold Medal. It is an award bestowed by the president of the United States to recognize people who have made "an especially merito ...
by President Gerald Ford
Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. ( ; born Leslie Lynch King Jr.; July 14, 1913December 26, 2006) was an American politician who served as the 38th president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. He was the only president never to have been elected ...
.
Presidential Unit Citations
Burke was also entitled to wear the Presidential Unit Citations presented to Destroyer Squadron 23, , , and to . Those vessels were, at various times during his period of service, flagships of the Fast Carrier Task Forces in the Pacific. The citation for the citation to Destroyer Squadron 23 reads:Other awards
In addition to the above, Burke earned theAmerican Defense Service Medal
The American Defense Service Medal was a military award of the United States Armed Forces, established by , by President Franklin D. Roosevelt, on June 28, 1941.
The medal was intended to recognize those military service members who had served ...
with "Fleet" clasp, the Asiatic-Pacific Campaign Medal with two silver stars and two bronze stars (twelve engagements); the American Campaign Medal
The American Campaign Medal is a military award of the United States Armed Forces which was first created on November 6, 1942, by issued by President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The medal was intended to recognize those military members who had perfo ...
; World War II Victory Medal
The World War II Victory Medal is a service medal of the United States military which was established by an Act of Congress on 6 July 1945 (Public Law 135, 79th Congress) and promulgated by Section V, War Department Bulletin 12, 1945.
The Wo ...
; Navy Occupation Service Medal
The Navy Occupation Service Medal is a military award of the United States Navy which was "Awarded to commemorate the services of Navy, Marine Corps and Coast Guard personnel in the occupation of certain territories of the enemies of the U.S. durin ...
, the National Defense Service Medal
The National Defense Service Medal (NDSM) is a service award of the United States Armed Forces established by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1953. It is awarded to every member of the US Armed Forces who has served during any one of four sp ...
with bronze star (Admiral Burke became retroactively eligible for a second award after his retirement); Korean Service Medal
The Korean Service Medal (KSM) is a military award for service in the United States Armed Forces and was established November 8, 1950 by executive order of President Harry Truman. The Korean Service Medal is the primary US military award for s ...
with bronze battle star; the Philippine Liberation Medal
The Philippine Liberation Medal is a military award of the Republic of the Philippines which was created by an order of Commonwealth Army of the Philippines Headquarters on 20 December 1944, and was issued as the Philippine Liberation Ribbon. The d ...
with bronze service star; and the United Nations Korea Medal
The United Nations Service Medal for Korea (UNKM) is an international military decoration established by the United Nations on December 12, 1950 as the United Nations Service Medal. The decoration was the first international award ever created by t ...
. He was awarded the ''Ui Chi Medal'' and the Presidential Unit Citation from the Republic of Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korean Peninsula and sharing a land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its east ...
as well as the Order of the Rising Sun
The is a Japanese order, established in 1875 by Emperor Meiji. The Order was the first national decoration awarded by the Japanese government, created on 10 April 1875 by decree of the Council of State. The badge features rays of sunlight ...
, First Class by the Government of Japan. In 1960 he received the Grand Cross of the Royal Norwegian Order of St. Olav
Royal may refer to:
People
* Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name
* A member of a royal family
Places United States
* Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Royal, Illinois, a village
* Royal, Iowa, a ci ...
from the Norwegian King. In 1999 Admiral Burke became posthumously eligible for the Korean War Service Medal
The Korean War Service Medal (KWSM, ko, 6.25사변종군기장, ), also known as the Republic of Korea War Service Medal (ROKWSM), is a military award of South Korea which was first authorized in December 1950.
History
6.25 Incident Participati ...
awarded by the Republic of Korea.
Legacy
In 1962, Burke co-founded theCenter for Strategic and International Studies
The Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) is an American think tank based in Washington, D.C. CSIS was founded as the Center for Strategic and International Studies of Georgetown University in 1962. The center conducts polic ...
(CSIS) in Washington, D.C., with David Abshire. CSIS hosts the Arleigh A. Burke Chair in Strategy
Strategy (from Greek στρατηγία ''stratēgia'', "art of troop leader; office of general, command, generalship") is a general plan to achieve one or more long-term or overall goals under conditions of uncertainty. In the sense of the "art ...
, which "provides political and military analysis of key strategic challenges facing the United States and the world." It is held as of 2013 by Anthony Cordesman
Anthony H. Cordesman (born August 1, 1939) holds the Arleigh A. Burke Chair in Strategy at the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) and is a national security analyst on a number of global conflicts.
Career
He earned his B.A. ...
.
Burke was elected as an honorary member of the New York State Society of Cincinnati
The Society of the Cincinnati is a fraternal, hereditary society founded in 1783 to commemorate the American Revolutionary War that saw the creation of the United States. Membership is largely restricted to descendants of military officers wh ...
in 1964.
In 1991 Burke was awarded the Lone Sailor Award by the U.S. Navy Memorial Foundation for his distinguished career during World War II and the Korean War.
, a guided-missile destroyer of the United States Navy and lead ship of its class, was named in his honor. The class is one of the most advanced in service and is one of only two destroyer classes currently in active US Navy service.
An elementary school was named in his honor in Boulder; it was closed in 1982. Thunderbird Park, also in Boulder, was renamed ''Admiral Arleigh A. Burke Memorial Park'' in 1997. In October 2001, a dedication of the memorial was held, featuring a 12-foot, 26,000-pound anchor from a World War II destroyer, a memorial wall containing a bronze relief sculpture of the admiral and a plaque with his biography.
The Navy annually awards the Arleigh Burke Fleet Trophy to "the ship or aircraft squadron from each coast selected for having achieved the greatest improvement in battle efficiency during the calendar year, based upon the Battle Efficiency Competition." Winning the Battle "E" is not a prerequisite.
The United States Postal Service issued a commemorative stamp pane on February 4, 2010, honoring distinguished sailors. In addition to Burke, the other persons on the stamp pane were Admiral William S. Sims, Lieutenant Commander John McCloy, and Officer's Cook Third Class Doris Miller
Doris Miller (October 12, 1919November 24, 1943) was a United States Navy cook third class who was killed in action during World War II. He was the first Black American to be awarded the Navy Cross, the highest decoration for valor presented by ...
."Distinguished Sailors Saluted On Stamps", USPS release no. 10-009,
Notes
References
* * *External links
"Arleigh Burke: The Last CNO" by David Alan Rosenberg
– Biographies in Naval History –
Naval Historical Center
The Naval History and Heritage Command, formerly the Naval Historical Center, is an Echelon II command responsible for the preservation, analysis, and dissemination of U.S. naval history and heritage located at the historic Washington Navy Yard. ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Burke, Arleigh
1901 births
1996 deaths
United States Navy admirals
United States Navy personnel of World War II
United States Navy personnel of the Korean War
Presidential Medal of Freedom recipients
Recipients of the Navy Cross (United States)
Recipients of the Navy Distinguished Service Medal
Recipients of the Legion of Merit
Recipients of the Silver Star
Grand Cordons of the Order of the Rising Sun
United States Naval Academy alumni
Chiefs of Naval Operations
People from Boulder, Colorado
University of Michigan College of Engineering alumni
American people of Swedish descent
Burials at the United States Naval Academy Cemetery
CSIS people
Military personnel from Colorado