Arkansas State University on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Arkansas ( ) is a
 Before European settlement of North America, Arkansas, was inhabited by indigenous peoples for thousands of years. The
Before European settlement of North America, Arkansas, was inhabited by indigenous peoples for thousands of years. The

 In early antebellum Arkansas, the southeast Arkansas slave-based economy developed rapidly. On the eve of the American Civil War in 1860, enslaved African Americans numbered 111,115 people, just over 25% of the state's population. Plantation agriculture set the state and region behind the nation for decades. The wealth developed among planters of southeast Arkansas caused a political rift to form between the northwest and southeast.Bolton 1999, p. 22.
Many politicians were elected to office from the Family, the Southern rights political force in antebellum Arkansas. Residents generally wanted to avoid a civil war. When the Gulf states seceded in early 1861, Arkansas voted to remain in the Union. Arkansas did not secede until
In early antebellum Arkansas, the southeast Arkansas slave-based economy developed rapidly. On the eve of the American Civil War in 1860, enslaved African Americans numbered 111,115 people, just over 25% of the state's population. Plantation agriculture set the state and region behind the nation for decades. The wealth developed among planters of southeast Arkansas caused a political rift to form between the northwest and southeast.Bolton 1999, p. 22.
Many politicians were elected to office from the Family, the Southern rights political force in antebellum Arkansas. Residents generally wanted to avoid a civil war. When the Gulf states seceded in early 1861, Arkansas voted to remain in the Union. Arkansas did not secede until  Arkansas held a very important position for the Rebels, maintaining control of the
Arkansas held a very important position for the Rebels, maintaining control of the
accessed April 3, 2008. Five whites also died in the incident. The governor accompanied the troops to the scene; President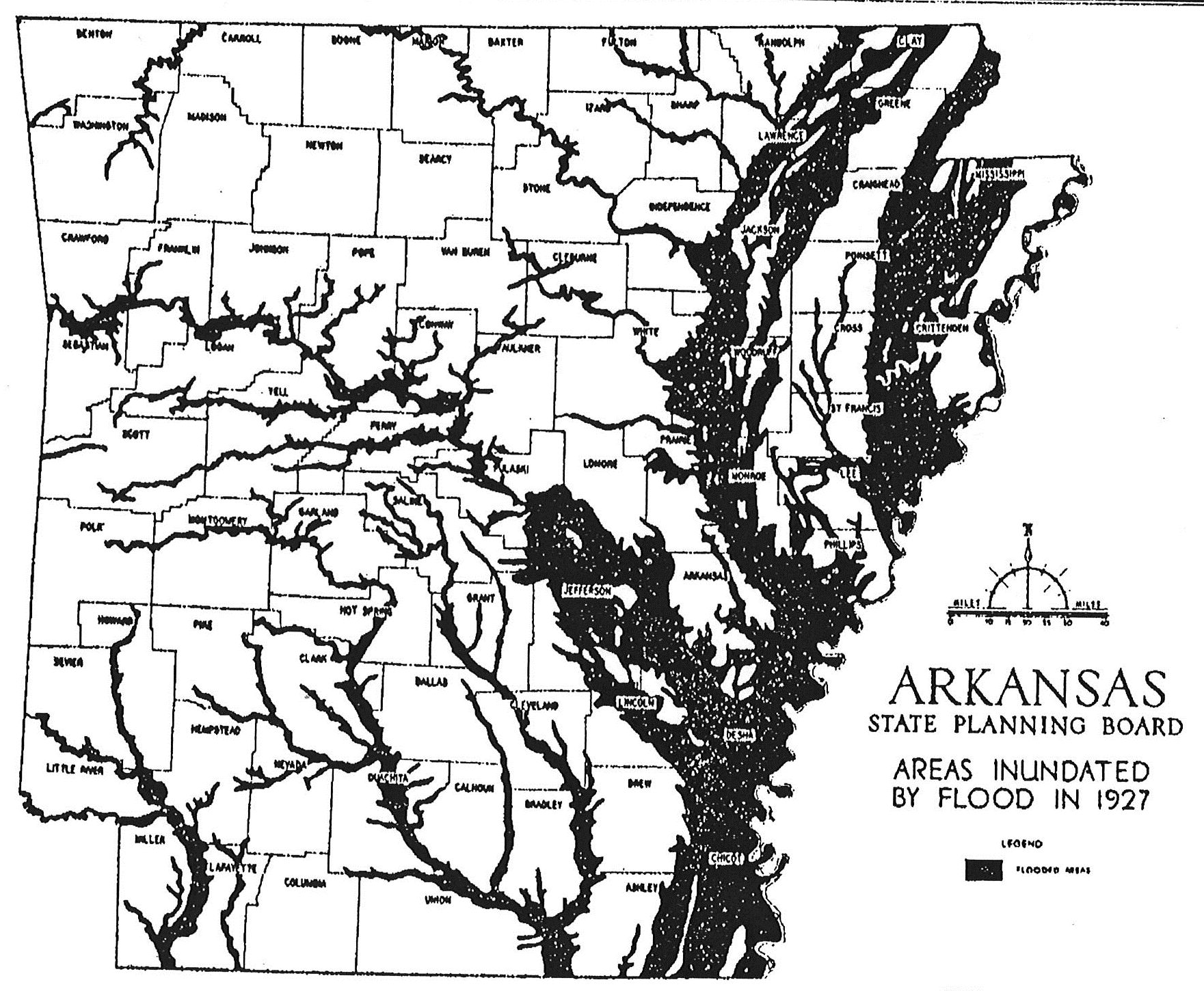 The
The

 Arkansas can generally be split into two halves, the highlands in the northwest and the lowlands of the southeast. The highlands are part of the Southern Interior Highlands, including The Ozarks and the
Arkansas can generally be split into two halves, the highlands in the northwest and the lowlands of the southeast. The highlands are part of the Southern Interior Highlands, including The Ozarks and the  The southeastern part of Arkansas along the Mississippi Alluvial Plain is sometimes called the Arkansas Delta. This region is a flat landscape of River delta, rich alluvial soils formed by repeated flooding of the adjacent Mississippi. Farther from the river, in the southeastern part of the state, the Grand Prairie has a more undulating landscape. Both are fertile agricultural areas. The Delta region is bisected by a geological formation known as Crowley's Ridge. A narrow band of rolling hills, Crowley's Ridge rises above the surrounding alluvial plain and underlies many of eastern Arkansas's major towns.
Northwest Arkansas is part of the Ozark Plateau including the Ozark Mountains, to the south are the
The southeastern part of Arkansas along the Mississippi Alluvial Plain is sometimes called the Arkansas Delta. This region is a flat landscape of River delta, rich alluvial soils formed by repeated flooding of the adjacent Mississippi. Farther from the river, in the southeastern part of the state, the Grand Prairie has a more undulating landscape. Both are fertile agricultural areas. The Delta region is bisected by a geological formation known as Crowley's Ridge. A narrow band of rolling hills, Crowley's Ridge rises above the surrounding alluvial plain and underlies many of eastern Arkansas's major towns.
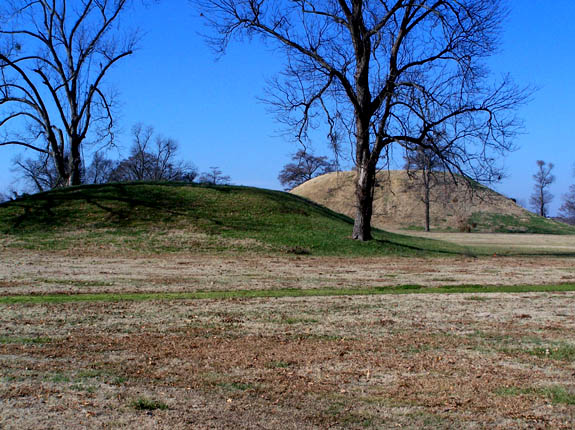
Northwest Arkansas is part of the Ozark Plateau including the Ozark Mountains, to the south are the  Arkansas is home to many List of caves in Arkansas, caves, such as Blanchard Springs Caverns. The State Archeologist has catalogued more than 43,000 Native American living, hunting and tool-making sites, many of them Pre-Columbian burial mounds and rock shelters. Crater of Diamonds State Park near Murfreesboro, Arkansas, Murfreesboro is the world's only diamond-bearing site accessible to the public for digging. Arkansas is home to a dozen Wilderness Areas totaling . These areas are set aside for outdoor recreation and are open to hunting, fishing, hiking, and primitive camping. No mechanized vehicles nor developed campgrounds are allowed in these areas.
Arkansas is home to many List of caves in Arkansas, caves, such as Blanchard Springs Caverns. The State Archeologist has catalogued more than 43,000 Native American living, hunting and tool-making sites, many of them Pre-Columbian burial mounds and rock shelters. Crater of Diamonds State Park near Murfreesboro, Arkansas, Murfreesboro is the world's only diamond-bearing site accessible to the public for digging. Arkansas is home to a dozen Wilderness Areas totaling . These areas are set aside for outdoor recreation and are open to hunting, fishing, hiking, and primitive camping. No mechanized vehicles nor developed campgrounds are allowed in these areas.
 Arkansas has many rivers, lakes, and reservoirs within or along its borders. Major tributaries to the Mississippi River include the
Arkansas has many rivers, lakes, and reservoirs within or along its borders. Major tributaries to the Mississippi River include the
 Arkansas's temperate deciduous forest is divided into three broad ecoregions: the ''Ozark, Ouachita-Appalachian Forests'', the ''Mississippi Alluvial and Southeast USA Coastal Plains'', and the ''Southeastern USA Plains''. The state is further divided into seven subregions: the Arkansas Valley, Boston Mountains, Mississippi Alluvial Plain, Crowley's Ridge, Mississippi Valley Loess Plain, Ozark Highlands, Ouachita Mountains, and the South Central Plains. A 2010 United States Forest Service survey determined of Arkansas's land is forestland, or 56% of the state's total area. Dominant species in Arkansas's forests include ''Oak, Quercus'' (oak), ''Hickory, Carya'' (hickory), ''Pinus echinata'' (shortleaf pine) and ''Pinus taeda'' (loblolly pine).
Arkansas's plant life varies with its climate and elevation. The Arkansas Timberlands, pine belt stretching from the Arkansas delta to Texas consists of dense oak-hickory-pine growth. Lumbering and paper milling activity is active throughout the region. In eastern Arkansas, one can find ''Taxodium '' (cypress), ''Quercus nigra'' (water oaks), and hickories with their roots submerged in the Mississippi Valley bayous indicative of the deep south. Nearby Crowley's Ridge is the only home of the Liriodendron, tulip tree in the state, and generally hosts more northeastern plant life such as the beech tree. The northwestern highlands are covered in an oak-hickory mixture, with Juniperus ashei, Ozark white cedars, ''Cornus (genus), cornus'' (dogwoods), and ''Cercis canadensis'' (redbuds) also present. The higher peaks in the Arkansas River Valley play host to scores of ferns, including the ''Woodsia scopulina'' and ''Adiantum'' (maidenhair fern) on Mount Magazine. Arkansas wildlife is famous for the white-tailed deer, elk, and bald eagle. The white-tailed deer is the official state mammal.
Arkansas's temperate deciduous forest is divided into three broad ecoregions: the ''Ozark, Ouachita-Appalachian Forests'', the ''Mississippi Alluvial and Southeast USA Coastal Plains'', and the ''Southeastern USA Plains''. The state is further divided into seven subregions: the Arkansas Valley, Boston Mountains, Mississippi Alluvial Plain, Crowley's Ridge, Mississippi Valley Loess Plain, Ozark Highlands, Ouachita Mountains, and the South Central Plains. A 2010 United States Forest Service survey determined of Arkansas's land is forestland, or 56% of the state's total area. Dominant species in Arkansas's forests include ''Oak, Quercus'' (oak), ''Hickory, Carya'' (hickory), ''Pinus echinata'' (shortleaf pine) and ''Pinus taeda'' (loblolly pine).
Arkansas's plant life varies with its climate and elevation. The Arkansas Timberlands, pine belt stretching from the Arkansas delta to Texas consists of dense oak-hickory-pine growth. Lumbering and paper milling activity is active throughout the region. In eastern Arkansas, one can find ''Taxodium '' (cypress), ''Quercus nigra'' (water oaks), and hickories with their roots submerged in the Mississippi Valley bayous indicative of the deep south. Nearby Crowley's Ridge is the only home of the Liriodendron, tulip tree in the state, and generally hosts more northeastern plant life such as the beech tree. The northwestern highlands are covered in an oak-hickory mixture, with Juniperus ashei, Ozark white cedars, ''Cornus (genus), cornus'' (dogwoods), and ''Cercis canadensis'' (redbuds) also present. The higher peaks in the Arkansas River Valley play host to scores of ferns, including the ''Woodsia scopulina'' and ''Adiantum'' (maidenhair fern) on Mount Magazine. Arkansas wildlife is famous for the white-tailed deer, elk, and bald eagle. The white-tailed deer is the official state mammal.
 Arkansas generally has a humid subtropical climate. While not bordering the Gulf of Mexico, Arkansas, is still close enough to the warm, large body of water for it to influence the weather in the state. Generally, Arkansas, has hot, humid summers and slightly drier, mild to cool winters. In
Arkansas generally has a humid subtropical climate. While not bordering the Gulf of Mexico, Arkansas, is still close enough to the warm, large body of water for it to influence the weather in the state. Generally, Arkansas, has hot, humid summers and slightly drier, mild to cool winters. In

 European Americans have a strong presence in the northwestern Ozarks and the central part of the state. African Americans live mainly in the southern and eastern parts of the state. Arkansans of Irish, English and German ancestry are mostly found in the far northwestern Ozarks near the Missouri border. Ancestors of the Irish in the Ozarks were chiefly Ulster Scots people, Scots-Irish, Protestants from Northern Ireland, the Scotland, Scottish lowlands and northern England part of the largest group of immigrants from Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland before the American Revolution. English American, English and Scots-Irish American, Scots-Irish immigrants settled throughout the back country of the South and in the more mountainous areas. Americans of English American, English stock are found throughout the state.
A 2010 survey of the principal ancestries of Arkansas's residents revealed the following: 15.5% African American, 12.3% Irish American, Irish, 11.5% German Americans, German, 11.0% American ethnicity, American, 10.1% English American, English, 4.7% Mexican American, Mexican, 2.1% French American, French, 1.7% Scottish American, Scottish, 1.7% Dutch American, Dutch, 1.6% Italian American, Italian, and 1.4% Scots-Irish American, Scots-Irish.
Most people identifying as "American" are of English descent and/or Scots-Irish descent. Their families have been in the state so long, in many cases since before statehood, that they choose to identify simply as having American ancestry or do not in fact know their ancestry. Their ancestry primarily goes back to the original 13 colonies and for this reason many of them today simply claim American ancestry. Many people who identify as of Irish descent are in fact of Scots-Irish descent.
According to the 2006ŌĆō2008 American Community Survey, 93.8% of Arkansas's population (over the age of five) spoke only English at home. About 4.5% of the state's population spoke Spanish at home. About 0.7% of the state's population spoke another Indo-European language. About 0.8% of the state's population spoke an Languages of Asia, Asian language, and 0.2% spoke other languages.
European Americans have a strong presence in the northwestern Ozarks and the central part of the state. African Americans live mainly in the southern and eastern parts of the state. Arkansans of Irish, English and German ancestry are mostly found in the far northwestern Ozarks near the Missouri border. Ancestors of the Irish in the Ozarks were chiefly Ulster Scots people, Scots-Irish, Protestants from Northern Ireland, the Scotland, Scottish lowlands and northern England part of the largest group of immigrants from Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland before the American Revolution. English American, English and Scots-Irish American, Scots-Irish immigrants settled throughout the back country of the South and in the more mountainous areas. Americans of English American, English stock are found throughout the state.
A 2010 survey of the principal ancestries of Arkansas's residents revealed the following: 15.5% African American, 12.3% Irish American, Irish, 11.5% German Americans, German, 11.0% American ethnicity, American, 10.1% English American, English, 4.7% Mexican American, Mexican, 2.1% French American, French, 1.7% Scottish American, Scottish, 1.7% Dutch American, Dutch, 1.6% Italian American, Italian, and 1.4% Scots-Irish American, Scots-Irish.
Most people identifying as "American" are of English descent and/or Scots-Irish descent. Their families have been in the state so long, in many cases since before statehood, that they choose to identify simply as having American ancestry or do not in fact know their ancestry. Their ancestry primarily goes back to the original 13 colonies and for this reason many of them today simply claim American ancestry. Many people who identify as of Irish descent are in fact of Scots-Irish descent.
According to the 2006ŌĆō2008 American Community Survey, 93.8% of Arkansas's population (over the age of five) spoke only English at home. About 4.5% of the state's population spoke Spanish at home. About 0.7% of the state's population spoke another Indo-European language. About 0.8% of the state's population spoke an Languages of Asia, Asian language, and 0.2% spoke other languages.
 Once a state with a cashless society in the uplands and Plantation economy, plantation agriculture in the lowlands, Arkansas's economy has evolved and diversified. The state's gross domestic product (GDP) was $119billion in 2015. Six Fortune 500 companies are based in Arkansas, including the world's #1 retailer,
Once a state with a cashless society in the uplands and Plantation economy, plantation agriculture in the lowlands, Arkansas's economy has evolved and diversified. The state's gross domestic product (GDP) was $119billion in 2015. Six Fortune 500 companies are based in Arkansas, including the world's #1 retailer,
 Transportation in Arkansas is overseen by the Arkansas Department of Transportation (ArDOT), headquartered in
Transportation in Arkansas is overseen by the Arkansas Department of Transportation (ArDOT), headquartered in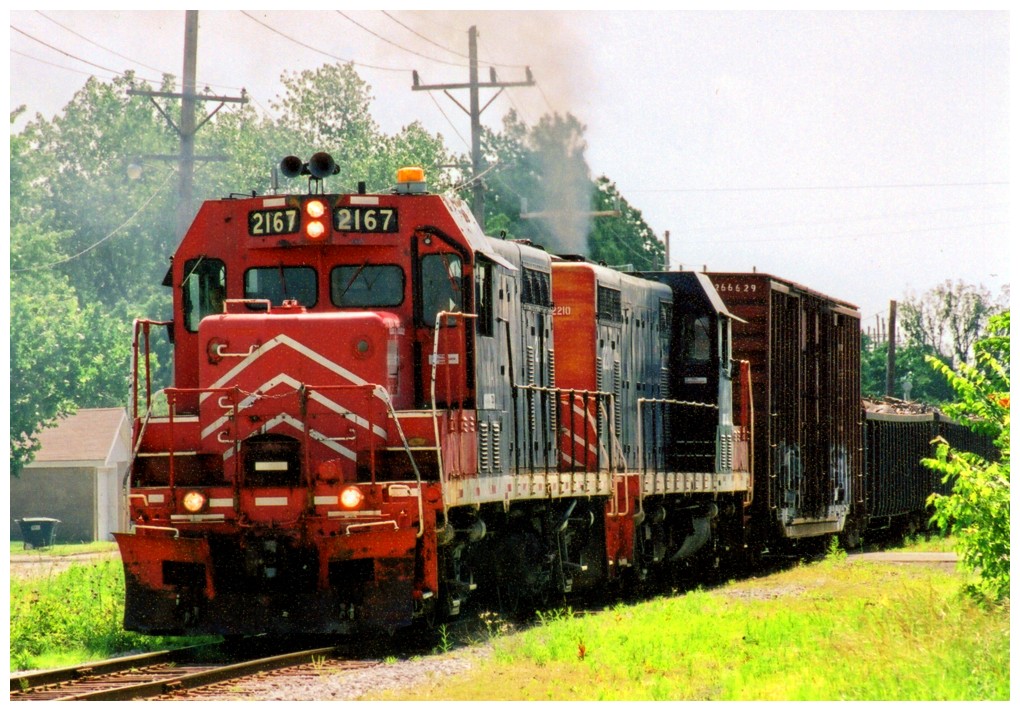  Arkansas is served by of railroad track divided among twenty-six railroad companies including three Class I railroads. Freight railroads are concentrated in southeast Arkansas to serve the industries in the region. The Texas Eagle, an Amtrak passenger train, serves five stations in the state Walnut Ridge (Amtrak station), Walnut Ridge, Little Rock (Amtrak station), Little Rock, Malvern (Amtrak station), Malvern, Arkadelphia (Amtrak station), Arkadelphia, and Texarkana (Amtrak station), Texarkana.
Arkansas also benefits from the use of its rivers for commerce. The
Arkansas is served by of railroad track divided among twenty-six railroad companies including three Class I railroads. Freight railroads are concentrated in southeast Arkansas to serve the industries in the region. The Texas Eagle, an Amtrak passenger train, serves five stations in the state Walnut Ridge (Amtrak station), Walnut Ridge, Little Rock (Amtrak station), Little Rock, Malvern (Amtrak station), Malvern, Arkadelphia (Amtrak station), Arkadelphia, and Texarkana (Amtrak station), Texarkana.
Arkansas also benefits from the use of its rivers for commerce. The
 The
The
 As of 2012, Arkansas, as with many Southern states, has a high incidence of premature death, infant mortality, cardiovascular deaths, and occupational fatalities compared to the rest of the United States. The state is tied for 43rd with New York (state), New York in percentage of adults who regularly exercise. Arkansas is usually ranked as one of the least healthy states due to high obesity, smoking, and sedentary lifestyle rates, but according to a Gallup poll, Arkansas made the most immediate progress in reducing its number of uninsured residents after the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, Affordable Care Act passed. The percentage of uninsured in Arkansas dropped from 22.5 in 2013 to 12.4 in August 2014.
The List of smoking bans in the United States#Arkansas, Arkansas Clean Indoor Air Act, a statewide smoking ban excluding bars and some restaurants, went into effect in 2006.
Healthcare in Arkansas is provided by a network of hospitals as members of the Arkansas Hospital Association. Major institutions with multiple branches include Baptist Health, Community Health Systems, and HealthSouth. The University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS) in Little Rock operates the UAMS Medical Center, a teaching hospital ranked as high performing nationally in cancer and nephrology. The pediatric division of UAMS Medical Center is known as Arkansas Children's Hospital, nationally ranked in pediatric cardiology and heart surgery. Together, these two institutions are the state's only Level I trauma centers.
As of 2012, Arkansas, as with many Southern states, has a high incidence of premature death, infant mortality, cardiovascular deaths, and occupational fatalities compared to the rest of the United States. The state is tied for 43rd with New York (state), New York in percentage of adults who regularly exercise. Arkansas is usually ranked as one of the least healthy states due to high obesity, smoking, and sedentary lifestyle rates, but according to a Gallup poll, Arkansas made the most immediate progress in reducing its number of uninsured residents after the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, Affordable Care Act passed. The percentage of uninsured in Arkansas dropped from 22.5 in 2013 to 12.4 in August 2014.
The List of smoking bans in the United States#Arkansas, Arkansas Clean Indoor Air Act, a statewide smoking ban excluding bars and some restaurants, went into effect in 2006.
Healthcare in Arkansas is provided by a network of hospitals as members of the Arkansas Hospital Association. Major institutions with multiple branches include Baptist Health, Community Health Systems, and HealthSouth. The University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS) in Little Rock operates the UAMS Medical Center, a teaching hospital ranked as high performing nationally in cancer and nephrology. The pediatric division of UAMS Medical Center is known as Arkansas Children's Hospital, nationally ranked in pediatric cardiology and heart surgery. Together, these two institutions are the state's only Level I trauma centers.
 Arkansas ranks as the 32nd smartest state on the Morgan Quitno Smartest State Award, 44th in percentage of residents with at least a high school diploma, and 48th in percentage of bachelor's degree attainment. Arkansas has been making strides in education reform. ''Education Week'' has praised the state, ranking Arkansas in the top 10 of their Quality Counts Education Rankings every year since 2009 while scoring it in the top5 during 2012 and 2013. Arkansas specifically received an A in Transition and Policy Making for progress in this area consisting of early-childhood education, college readiness, and career readiness. Governor Mike Beebe has made improving education a major issue through his attempts to spend more on education. Through reforms, the state is a leader in requiring curricula designed to prepare students for postsecondary education, rewarding teachers for student achievement, and providing incentives for principals who work in lower-tier schools.
Arkansas ranks as the 32nd smartest state on the Morgan Quitno Smartest State Award, 44th in percentage of residents with at least a high school diploma, and 48th in percentage of bachelor's degree attainment. Arkansas has been making strides in education reform. ''Education Week'' has praised the state, ranking Arkansas in the top 10 of their Quality Counts Education Rankings every year since 2009 while scoring it in the top5 during 2012 and 2013. Arkansas specifically received an A in Transition and Policy Making for progress in this area consisting of early-childhood education, college readiness, and career readiness. Governor Mike Beebe has made improving education a major issue through his attempts to spend more on education. Through reforms, the state is a leader in requiring curricula designed to prepare students for postsecondary education, rewarding teachers for student achievement, and providing incentives for principals who work in lower-tier schools.
 The culture of Arkansas includes distinct cuisine, dialect, and traditional festivals. Sports are also very important to the culture, including football, baseball, basketball, hunting, and fishing. Perhaps the best-known aspect of Arkansas's culture is the stereotype that its citizens are shiftless hillbillies. The reputation began when early explorers characterized the state as a savage wilderness full of outlaws and thieves. The most enduring icon of Arkansas's hillbilly reputation is ''Edward Washburn, The Arkansas Traveller'', a painted depiction of a folk tale from the 1840s. Though intended to represent the divide between rich southeastern plantation Arkansas planters and the poor northwestern hill country, the meaning was twisted to represent a Northerner lost in the Ozarks on a white horse asking a backwoods Arkansan for directions. The state also suffers from the racial stigma common to former Confederate states, with historical events such as the
The culture of Arkansas includes distinct cuisine, dialect, and traditional festivals. Sports are also very important to the culture, including football, baseball, basketball, hunting, and fishing. Perhaps the best-known aspect of Arkansas's culture is the stereotype that its citizens are shiftless hillbillies. The reputation began when early explorers characterized the state as a savage wilderness full of outlaws and thieves. The most enduring icon of Arkansas's hillbilly reputation is ''Edward Washburn, The Arkansas Traveller'', a painted depiction of a folk tale from the 1840s. Though intended to represent the divide between rich southeastern plantation Arkansas planters and the poor northwestern hill country, the meaning was twisted to represent a Northerner lost in the Ozarks on a white horse asking a backwoods Arkansan for directions. The state also suffers from the racial stigma common to former Confederate states, with historical events such as the
 Sports have become an integral part of the culture of Arkansas, and her residents enjoy participating in and spectating various events throughout the year.
Team sports and especially collegiate football are important to Arkansans. College football in Arkansas began from humble beginnings, when the University of Arkansas first fielded a team in 1894 Arkansas Cardinals football team, 1894. Over the years, many Arkansans have looked to Arkansas Razorbacks football as the public image of the state. Although the University of Arkansas is based in Fayetteville, Arkansas, Fayetteville, the Razorbacks have always played at least one game per season at War Memorial Stadium (Arkansas), War Memorial Stadium in
Sports have become an integral part of the culture of Arkansas, and her residents enjoy participating in and spectating various events throughout the year.
Team sports and especially collegiate football are important to Arkansans. College football in Arkansas began from humble beginnings, when the University of Arkansas first fielded a team in 1894 Arkansas Cardinals football team, 1894. Over the years, many Arkansans have looked to Arkansas Razorbacks football as the public image of the state. Although the University of Arkansas is based in Fayetteville, Arkansas, Fayetteville, the Razorbacks have always played at least one game per season at War Memorial Stadium (Arkansas), War Memorial Stadium in
 Arkansas is home to many areas protected by the National Park System. These include:
* Arkansas Post National Memorial at Gillett, Arkansas, Gillett
* Blanchard Springs Caverns
* Buffalo National River
* Fort Smith National Historic Site
* Hot Springs National Park
* Little Rock Central High School National Historic Site
* Pea Ridge National Military Park
* President William Jefferson Clinton Birthplace Home National Historic Site
* Arkansas State Capitol Building
* List of Arkansas state parks
Arkansas is home to many areas protected by the National Park System. These include:
* Arkansas Post National Memorial at Gillett, Arkansas, Gillett
* Blanchard Springs Caverns
* Buffalo National River
* Fort Smith National Historic Site
* Hot Springs National Park
* Little Rock Central High School National Historic Site
* Pea Ridge National Military Park
* President William Jefferson Clinton Birthplace Home National Historic Site
* Arkansas State Capitol Building
* List of Arkansas state parks
Hamilton, Peter Joseph. ''The Reconstruction Period''
(1906), full length history of era; Dunning School approach; 570 pp; ch 13 on Arkansas * Hanson, Gerald T. and Carl H. Moneyhon. ''Historical Atlas of Arkansas'' (1992) * Key, V. O. ''Southern Politics'' (1949) * Kirk, John A., ''Redefining the Color Line: Black Activism in Little Rock, Arkansas, 1940ŌĆō1970'' (2002). * McMath, Sidney S. ''Promises Kept'' (2003) * Moore, Waddy W. ed., ''Arkansas in the Gilded Age, 1874ŌĆō1900'' (1976). * Peirce, Neal R. ''The Deep South States of America: People, Politics, and Power in the Seven Deep South States'' (1974). * Thompson, Brock. ''The Un-Natural State: Arkansas and the Queer South'' (2010) * Thompson, George H. ''Arkansas and Reconstruction'' (1976) * Whayne, Jeannie M. ''Arkansas Biography: A Collection of Notable Lives'' (2000) * White, Lonnie J. ''Politics on the Southwestern Frontier: Arkansas Territory, 1819ŌĆō1836'' (1964) * Williams, C. Fred. ed. ''A Documentary History Of Arkansas'' (2005)
Arkansas.gov
ĆöOfficial State Website
Arkansas State Facts from USDA
Official State tourism website
''Encyclopedia of Arkansas''
Energy & Environmental Data for Arkansas
2000 Census of Population and Housing for Arkansas
U.S. Census Bureau
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Arkansas
Arkansas Summer Camps
Arkansas Shakespeare Theatre
* * *
Arkansas State Code (the state statutes of Arkansas)
Arkansas State Databases
ĆöAnnotated list of searchable databases produced by Arkansas state agencies and compiled by the Government Documents Roundtable of the American Library Association. {{coord, 35, -92, dim:300000_region:US-AR_type:adm1st, name=State of Arkansas, display=title Arkansas, 1836 establishments in the United States South Central United States Southern United States States and territories established in 1836 States of the Confederate States of America States of the United States Contiguous United States
landlocked
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked de facto states. Kazakhstan is the world's largest ...
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in the South Central United States
The South Central United States or South Central states is a region in the south central portion of the Southern United States. It evolved out of the Old Southwest, which originally was the western portion of the South. The states of Arkansas, ...
. It is bordered by Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
to the north, Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
and Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
to the east, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
to the south, and Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
and Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ßÄŻßĦßÄ│ßÄ░ßÄ╣, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
to the west. Its name is from the Osage language
Osage (; Osage: ''Wa┼Š├Ī┼Še ie'') is a Siouan language that is spoken by the Osage people of Oklahoma. Their original territory was in present-day Missouri and Kansas but they were gradually pushed west by European-American pressure and treati ...
, a Dhegiha Siouan language, and referred to their relatives, the Quapaw
The Quapaw ( ; or Arkansas and Ugahxpa) people are a tribe of Native Americans that coalesced in what is known as the Midwest and Ohio Valley of the present-day United States. The Dhegiha Siouan-speaking tribe historically migrated from the Ohi ...
people. The state's diverse geography ranges from the mountainous regions of the Ozark
The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a physiographic region in the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma and the extreme southeastern corner of Kansas. The Ozarks cover a significant portio ...
and Ouachita Mountains
The Ouachita Mountains (), simply referred to as the Ouachitas, are a mountain range in western Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma. They are formed by a thick succession of highly deformed Paleozoic strata constituting the Ouachita Fold and Thru ...
, which make up the U.S. Interior Highlands, to the densely forested land in the south known as the Arkansas Timberlands
The Arkansas Timberlands (sometimes also called Southern Arkansas or Southwest Arkansas) is a region of the U.S. state of Arkansas generally encompassing the area south of the Ouachita Mountains, south of Central Arkansas and west of the Arkans ...
, to the eastern lowlands along the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
and the Arkansas Delta
The Arkansas Delta is one of the six natural regions of the state of Arkansas. Willard B. Gatewood Jr., author of ''The Arkansas Delta: Land of Paradox'', says that rich cotton lands of the Arkansas Delta make that area "The Deepest of the Deep ...
.
Arkansas is the 29th largest by area and the 34th most populous state, with a population of just over 3 million at the 2020 census. The capital and most populous city is Little Rock
( The "Little Rock")
, government_type = Council-manager
, leader_title = Mayor
, leader_name = Frank Scott Jr.
, leader_party = D
, leader_title2 = Council
, leader_name2 ...
, in the central part of the state, a hub for transportation, business, culture, and government. The northwestern corner of the state, including the FayettevilleŌĆōSpringdaleŌĆōRogers Metropolitan Area
Northwest Arkansas (NWA) is a metropolitan area and region in Arkansas within the Ozark Mountains. It includes four of the ten largest cities in the state: Fayetteville, Springdale, Rogers, and Bentonville, the surrounding towns of Benton a ...
and Fort Smith metropolitan area
The Fort Smith Metropolitan Statistical Area, as defined by the United States Census Bureau, is a five-county area including three Arkansas counties and two Oklahoma counties, and anchored by the city of Fort Smith, Arkansas. The total MSA populati ...
, is a population, education, and economic center. The largest city in the state's eastern part is Jonesboro. The largest city in the state's southeastern part is Pine Bluff.
Previously part of French Louisiana
The term French Louisiana refers to two distinct regions:
* first, to Louisiana (New France), colonial French Louisiana, comprising the massive, middle section of North America claimed by Early Modern France, France during the 17th and 18th centu ...
and the Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase (french: Vente de la Louisiane, translation=Sale of Louisiana) was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or app ...
, the Territory of Arkansas
The Arkansas Territory was a territory of the United States that existed from July 4, 1819, to June 15, 1836, when the final extent of Arkansas Territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Arkansas. Arkansas Post was the first territo ...
was admitted to the Union
''Admitted'' is a 2020 Indian Hindi-language docudrama film directed by Chandigarh-based director Ojaswwee Sharma. The film is about Dhananjay Chauhan, the first transgender student at Panjab University. The role of Dhananjay Chauhan has been p ...
as the 25th state on June 15, 1836. Much of the Delta had been developed for cotton plantations, and landowners there largely depended on enslaved African Americans' labor. In 1861, Arkansas seceded from the United States and joined the Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 ŌĆō May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
. On returning to the Union in 1868, Arkansas continued to suffer economically, due to its overreliance on the large-scale plantation economy
A plantation economy is an economy based on agricultural mass production, usually of a few commodity crops, grown on large farms worked by laborers or slaves. The properties are called plantations. Plantation economies rely on the export of cas ...
. Cotton remained the leading commodity crop, and the cotton market declined. Because farmers and businessmen did not diversify and there was little industrial investment, the state fell behind in economic opportunity. In the late 19th century, the state instituted various Jim Crow laws
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws enforcing racial segregation in the Southern United States. Other areas of the United States were affected by formal and informal policies of segregation as well, but many states outside the Sout ...
to disenfranchise and segregate the African-American population. During the civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination ...
of the 1950s and 1960s, Arkansas and particularly Little Rock were major battlegrounds for efforts to integrate schools.
White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
interests dominated Arkansas's politics, with disfranchisement of African Americans and refusal to reapportion the legislature. Only after the civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination ...
and federal legislation passed were more African Americans able to vote. The Supreme Court overturned rural domination in the South and other states that had refused to reapportion their state legislatures or retained rules based on geographic districts. In a series of cases in the 1960s during the height of related civil rights activities, the Warren Court
The Warren Court was the period in the history of the Supreme Court of the United States during which Earl Warren served as Chief Justice. Warren replaced the deceased Fred M. Vinson as Chief Justice in 1953, and Warren remained in office until ...
invoked a ''one person, one vote
"One man, one vote", or "one person, one vote", expresses the principle that individuals should have equal representation in voting. This slogan is used by advocates of political equality to refer to such electoral reforms as universal suffrage, ...
'' principle, applying the Equal Protection Clause
The Equal Protection Clause is part of the first section of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. The clause, which took effect in 1868, provides "''nor shall any State ... deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal ...
of the constitution and holding that states had to organize their legislatures by districts that held approximately equal populations, and that these had to be redefined as necessary after each decade's census.
Following World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposin ...
in the 1940s, Arkansas began to diversify its economy and see prosperity. During the 1960s, the state became the base of the Walmart
Walmart Inc. (; formerly Wal-Mart Stores, Inc.) is an American multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of hypermarkets (also called supercenters), discount department stores, and grocery stores from the United States, headquarter ...
corporation, the world's largest company by revenue, headquartered in Bentonville. In the 21st century, Arkansas's economy is based on service industries, aircraft, poultry, steel, and tourism, along with important commodity crops of cotton, soybeans
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu and ...
and rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
.
Arkansas's culture is observable in museums, theaters, novels, television shows, restaurants, and athletic venues across the state. Notable people from the state include politician and educational advocate William Fulbright
James William Fulbright (April 9, 1905 ŌĆō February 9, 1995) was an American politician, academic, and statesman who represented Arkansas in the United States Senate from 1945 until his resignation in 1974. , Fulbright is the longest serving chair ...
; former president Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( n├® Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
, who also served as the 40th and 42nd governor of Arkansas; general Wesley Clark
Wesley Kanne Clark (born December 23, 1944) is a retired United States Army officer. He graduated as valedictorian of the class of 1966 at West Point and was awarded a Rhodes Scholarship to the University of Oxford, where he obtained a degree ...
, former NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du trait├® de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states ŌĆō 28 European and two No ...
Supreme Allied Commander; Walmart
Walmart Inc. (; formerly Wal-Mart Stores, Inc.) is an American multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of hypermarkets (also called supercenters), discount department stores, and grocery stores from the United States, headquarter ...
founder and magnate Sam Walton
Samuel Moore Walton (March 29, 1918 ŌĆō April 5, 1992)
was an American business magnate best known for founding the retailers Walmart and Sam's Club, which he started in 1962 and 1983 respectively. Wal-Mart Stores Inc. grew to be the world's l ...
; singer-songwriters Johnny Cash
John R. Cash (born J. R. Cash; February 26, 1932 ŌĆō September 12, 2003) was an American country singer-songwriter. Much of Cash's music contained themes of sorrow, moral tribulation, and redemption, especially in the later stages of his ca ...
, Charlie Rich
Charles Allan Rich (December 14, 1932July 25, 1995) was an American country music singer, songwriter, and musician. His eclectic style of music was often difficult to classify, encompassing the rockabilly, jazz, blues, country music, country, sou ...
, Jimmy Driftwood
James Corbitt Morris (June 20, 1907 ŌĆō July 12, 1998), known professionally as Jimmy Driftwood or Jimmie Driftwood, was an American folk music songwriter and musician, most famous for his songs "The Battle of New Orleans" and " Tennessee Stud ...
, and Glen Campbell
Glen Travis Campbell (April 22, 1936 ŌĆō August 8, 2017) was an American guitarist, singer, songwriter, actor and television host. He was best known for a series of hit songs in the 1960s and 1970s, and for hosting ''The Glen Campbell Goodt ...
; actor-filmmaker Billy Bob Thornton
Billy Bob Thornton (born August 4, 1955) is an American actor, filmmaker and musician. He had his first break when he co-wrote and starred in the 1992 thriller ''One False Move'', and received international attention after writing, directing, a ...
; poet C. D. Wright; physicist William L. McMillan
William L. McMillan (January 13, 1936 ŌĆō August 30, 1984) was an American physicist noted for his research of condensed matter physics.
McMillan was a member of the National Academy of Sciences, Professor of Physics at University of Illinois, ...
, a pioneer in superconductor research; poet laureate Maya Angelou
Maya Angelou ( ; born Marguerite Annie Johnson; April 4, 1928 ŌĆō May 28, 2014) was an American memoirist, popular poet, and civil rights activist. She published seven autobiographies, three books of essays, several books of poetry, and ...
; Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He had served with distinction in World War I, was C ...
; musician Al Green; actor Alan Ladd; basketball player Scottie Pippen
Scotty Maurice Pippen Sr. (born September 25, 1965), usually spelled Scottie Pippen, is an American former professional basketball player. He played 17 seasons in the National Basketball Association (NBA), winning six NBA championships with the ...
; singer Ne-Yo
Shaffer Chimere Smith (born October 18, 1979), known professionally as Ne-Yo, is an American singer, songwriter, actor, dancer, and record producer. He gained fame for his songwriting abilities when he penned Mario's 2004 hit " Let Me Love You ...
; Chelsea Clinton
Chelsea Victoria Clinton (born February 27, 1980) is an American writer and global health advocate. She is the only child of former U.S. President Bill Clinton and former U.S. Secretary of State and 2016 presidential candidate Hillary Clinton ...
; actress Sheryl Underwood
Sheryl Patrice Underwood (born October 28, 1963) is an American comedian, actress and television host. She first rose to prominence in the comedy world as the first female finalist in 1989's Miller Lite Comedy Search. Currently, Underwood is one ...
; and author John Grisham
John Ray Grisham Jr. (; born February 8, 1955 in Jonesboro, Arkansas) is an American novelist, lawyer and former member of the 7th district of the Mississippi House of Representatives, known for his popular legal thrillers. According to the Am ...
.
Etymology
The name ''Arkansas'' initially applied to theArkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in the western United Stat ...
. It derives from a French term, ''Arcansas'', their plural term for their transliteration of ''akansa'', an Algonquian term for the Quapaw
The Quapaw ( ; or Arkansas and Ugahxpa) people are a tribe of Native Americans that coalesced in what is known as the Midwest and Ohio Valley of the present-day United States. The Dhegiha Siouan-speaking tribe historically migrated from the Ohi ...
people. These were a Dhegiha Siouan
The Dhegihan languages are a group of Siouan languages that include KansaŌĆō Osage, OmahaŌĆōPonca, and Quapaw. Their historical region included parts of the Ohio and Mississippi River Valleys, the Great Plains, and southeastern North America. ...
-speaking people who settled in Arkansas around the 13th century. ''Akansa'' is likely also the root term for Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
, which was named after the related Kaw people
The Kaw Nation (or Kanza or Kansa) is a federally recognized Native American tribe in Oklahoma and parts of Kansas. It comes from the central Midwestern United States. It has also been called the "People of the South wind",
.
The name has been pronounced and spelled in a variety of ways. In 1881, the state legislature defined the official pronunciation of Arkansas as having the final "s" be silent (as it would be in French). A dispute had arisen between the state's two senators over the pronunciation issue. One favored (), the other ().
In 2007, the state legislature passed a non-binding resolution declaring that the possessive form of the state's name is ''Arkansas's'', which the state government has increasingly followed.
History
Early history
 Before European settlement of North America, Arkansas, was inhabited by indigenous peoples for thousands of years. The
Before European settlement of North America, Arkansas, was inhabited by indigenous peoples for thousands of years. The Caddo
The Caddo people comprise the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma, a federally recognized tribe headquartered in Binger, Oklahoma. They speak the Caddo language.
The Caddo Confederacy was a network of Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, wh ...
, Osage, and Quapaw
The Quapaw ( ; or Arkansas and Ugahxpa) people are a tribe of Native Americans that coalesced in what is known as the Midwest and Ohio Valley of the present-day United States. The Dhegiha Siouan-speaking tribe historically migrated from the Ohi ...
peoples encountered European explorers. The first of these Europeans was Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1500 ŌĆō 21 May, 1542) was a Spanish explorer and '' conquistador'' who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire ...
in 1541, who crossed the Mississippi and marched across central Arkansas and the Ozark Mountains. After finding nothing he considered of value and encountering native resistance the entire way, he and his men returned to the Mississippi River where de Soto fell ill. From his deathbed he ordered his men to massacre all the men of the nearby village of Anilco, who he feared had been plotting with a powerful polity down the Mississippi River, '' Quigualtam''. His men obeyed and did not stop with the men, but were said to have massacred women and children as well. He died the following day in what is believed to be the vicinity of modern-day McArthur, Arkansas
McArthur is an unincorporated community in Clayton Township, Desha County, Arkansas. It is located on Arkansas Highway 1 northeast of McGehee.
McArthur is one of two possible sites of the death of Hernando de Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1 ...
, in May 1542. His body was weighted down with sand and he was consigned to a watery grave in the Mississippi River under cover of darkness by his men. De Soto had attempted to deceive the native population into thinking he was an immortal deity, sun of the sun, in order to forestall attack by outraged Native Americans on his by then weakened and bedraggled army. In order to keep the ruse up, his men informed the locals that de Soto had ascended into the sky. His will at the time of his death listed "four Indian slaves, three horses and 700 hogs" which were auctioned off. The starving men, who had been living off maize stolen from natives, immediately started butchering the hogs and later, commanded by former aide-de-camp Moscoso, attempted an overland return to Mexico. They made it as far as Texas before running into territory too dry for maize farming and too thinly populated to sustain themselves by stealing food from the locals. The expedition promptly backtracked to Arkansas. After building a small fleet of boats they then headed down the Mississippi River and eventually on to Mexico by water.
Later explorers included the French Jacques Marquette
Jacques Marquette S.J. (June 1, 1637 ŌĆō May 18, 1675), sometimes known as P├©re Marquette or James Marquette, was a French Jesuit missionary who founded Michigan's first European settlement, Sault Sainte Marie, and later founded Saint Ign ...
and Louis Jolliet
Louis Jolliet (September 21, 1645after May 1700) was a French-Canadian explorer known for his discoveries in North America. In 1673, Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, a Jesuit Catholic priest and missionary, were the first non-Natives to explore an ...
in 1673, and Frenchmen Robert La Salle
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hr┼Ź├Šiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hr├│├░r) "fame, glory, honou ...
and Henri de Tonti
Henri de Tonti (''n├®'' Enrico Tonti; ŌĆō September 1704), also spelled Henri de Tonty, was an Italian-born French military officer, explorer, and ''voyageur'' who assisted Ren├®-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle, with North American explora ...
in 1681. Tonti established Arkansas Post at a Quapaw village in 1686, making it the first European settlement in the territory.Arnold 1992, p. 75. The early Spanish or French explorers of the state gave it its name, which is probably a phonetic spelling of the Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
tribe's name for the Quapaw
The Quapaw ( ; or Arkansas and Ugahxpa) people are a tribe of Native Americans that coalesced in what is known as the Midwest and Ohio Valley of the present-day United States. The Dhegiha Siouan-speaking tribe historically migrated from the Ohi ...
people, who lived downriver from them. The name Arkansas has been pronounced and spelled in a variety of fashions. The region was organized as the Territory of Arkansaw
The Arkansas Territory was a territory of the United States that existed from July 4, 1819, to June 15, 1836, when the final extent of Arkansas Territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Arkansas. Arkansas Post was the first territo ...
on July 4, 1819, with the territory admitted to the United States as the state of Arkansas on June 15, 1836. The name was historically , , and several other variants. Historically and modernly, the people of Arkansas call themselves either "Arkansans" or "Arkansawyers". In 1881, the Arkansas General Assembly
The General Assembly of Arkansas is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The legislature is a bicameral body composed of the upper house Arkansas Senate with 35 members, and the lower Arkansas House of Representatives with 100 ...
passed Arkansas Code 1-4-105 (official text):
Whereas, confusion of practice has arisen in the pronunciation of the name of our state and it is deemed important that the true pronunciation should be determined for use in oral official proceedings.
And, whereas, the matter has been thoroughly investigated by the State Historical Society and the Eclectic Society of Little Rock, which have agreed upon the correct pronunciation as derived from history, and the early usage of the American immigrants.
Be it therefore resolved by both houses of the General Assembly, that the only true pronunciation of the name of the state, in the opinion of this body, is that received by the French from the native Indians and committed to writing in the French word representing the sound. It should be pronounced in three (3) syllables, with the final "s" silent, the "a" in each syllable with the Italian sound, and the accent on the first and last syllables. The pronunciation with the accent on the second syllable with the sound of "a" in "man" and the sounding of the terminal "s" is an innovation to be discouraged.Citizens of the
state of Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
often pronounce the Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in the western United Stat ...
as , in a manner similar to the common pronunciation of the name of their state.
Settlers, such as fur trappers, moved to Arkansas in the early 18th century. These people used Arkansas Post as a home base and entrep├┤t
An ''entrep├┤t'' (; ) or transshipment port is a port, city, or trading post where merchandise may be imported, stored, or traded, usually to be exported again. Such cities often sprang up and such ports and trading posts often developed into c ...
. During the colonial period, Arkansas changed hands between France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de Espa├▒a.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de Espa├▒a (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
following the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756ŌĆō1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754ŌĆ ...
, although neither showed interest in the remote settlement of Arkansas Post. In April 1783, Arkansas saw its only battle of the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 ŌĆō September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, a brief siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition warfare, attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity con ...
of the post by British Captain James Colbert with the assistance of the Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
and Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands. Their traditional territory was in the Southeastern United States of Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee as well in southwestern Kentucky. Their language is classified as ...
.
Purchase and statehood
Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 ŌĆō 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
sold French Louisiana
The term French Louisiana refers to two distinct regions:
* first, to Louisiana (New France), colonial French Louisiana, comprising the massive, middle section of North America claimed by Early Modern France, France during the 17th and 18th centu ...
to the United States in 1803, including all of Arkansas, in a transaction known today as the Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase (french: Vente de la Louisiane, translation=Sale of Louisiana) was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or app ...
. French soldiers remained as a garrison at Arkansas Post. Following the purchase, the balanced give-and-take relationship between settlers and Native Americans began to change all along the frontier, including in Arkansas. Following a controversy over allowing slavery in the territory, the Territory of Arkansas
The Arkansas Territory was a territory of the United States that existed from July 4, 1819, to June 15, 1836, when the final extent of Arkansas Territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Arkansas. Arkansas Post was the first territo ...
was organized on July 4, 1819. Gradual emancipation in Arkansas was struck down by one vote, the Speaker of the House
The speaker of a deliberative assembly, especially a legislative body, is its presiding officer, or the chair. The title was first used in 1377 in England.
Usage
The title was first recorded in 1377 to describe the role of Thomas de Hungerf ...
Henry Clay
Henry Clay Sr. (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American attorney and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the U.S. Senate and House of Representatives. He was the seventh House speaker as well as the ninth secretary of state, al ...
, allowing Arkansas to organize as a slave territory.
Slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slaveŌĆösomeone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
became a wedge issue in Arkansas, forming a geographic divide that remained for decades. Owners and operators of the cotton plantation economy
A plantation economy is an economy based on agricultural mass production, usually of a few commodity crops, grown on large farms worked by laborers or slaves. The properties are called plantations. Plantation economies rely on the export of cas ...
in southeast Arkansas firmly supported slavery, as they perceived slave labor
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slaveŌĆösomeone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
as the best or "only" economically viable method of harvesting their commodity crops. The "hill country" of northwest Arkansas was unable to grow cotton and relied on a cash-scarce, subsistence farming
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow food crops to meet the needs of themselves and their families on smallholdings. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements, with little or no su ...
economy.
As European Americans settled throughout the East Coast and into the Midwest, in the 1830s the United States government forced the removal of many Native American tribes to Arkansas and Indian Territory
The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United St ...
west of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
.
Additional Native American removals began in earnest during the territorial period, with final Quapaw removal complete by 1833 as they were pushed into Indian Territory. The capital was relocated from Arkansas Post to Little Rock
( The "Little Rock")
, government_type = Council-manager
, leader_title = Mayor
, leader_name = Frank Scott Jr.
, leader_party = D
, leader_title2 = Council
, leader_name2 ...
in 1821, during the territorial period.
When Arkansas applied for statehood, the slavery issue was again raised in Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
Congress eventually approved the Arkansas Constitution
The Constitution of Arkansas is the primary organizing law for the U.S. state of Arkansas delineating the duties, powers, structures, and functions of the state government. Arkansas' original constitution was adopted at a constitutional conv ...
after a 25-hour session, admitting Arkansas on June 15, 1836, as the 25th state and the 13th slave state
In the United States before 1865, a slave state was a state in which slavery and the internal or domestic slave trade were legal, while a free state was one in which they were not. Between 1812 and 1850, it was considered by the slave states ...
, having a population of about 60,000. Arkansas struggled with taxation to support its new state government, a problem made worse by a state banking scandal and worse yet by the Panic of 1837.
Civil War and reconstruction
 In early antebellum Arkansas, the southeast Arkansas slave-based economy developed rapidly. On the eve of the American Civil War in 1860, enslaved African Americans numbered 111,115 people, just over 25% of the state's population. Plantation agriculture set the state and region behind the nation for decades. The wealth developed among planters of southeast Arkansas caused a political rift to form between the northwest and southeast.Bolton 1999, p. 22.
Many politicians were elected to office from the Family, the Southern rights political force in antebellum Arkansas. Residents generally wanted to avoid a civil war. When the Gulf states seceded in early 1861, Arkansas voted to remain in the Union. Arkansas did not secede until
In early antebellum Arkansas, the southeast Arkansas slave-based economy developed rapidly. On the eve of the American Civil War in 1860, enslaved African Americans numbered 111,115 people, just over 25% of the state's population. Plantation agriculture set the state and region behind the nation for decades. The wealth developed among planters of southeast Arkansas caused a political rift to form between the northwest and southeast.Bolton 1999, p. 22.
Many politicians were elected to office from the Family, the Southern rights political force in antebellum Arkansas. Residents generally wanted to avoid a civil war. When the Gulf states seceded in early 1861, Arkansas voted to remain in the Union. Arkansas did not secede until Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 ŌĆō April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
demanded Arkansas troops be sent to Fort Sumter
Fort Sumter is a sea fort built on an artificial island protecting Charleston, South Carolina from naval invasion. Its origin dates to the War of 1812 when the British invaded Washington by sea. It was still incomplete in 1861 when the Battl ...
to quell the rebellion there. On May 6, a state convention voted to terminate Arkansas's membership in the Union and join the Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
.
 Arkansas held a very important position for the Rebels, maintaining control of the
Arkansas held a very important position for the Rebels, maintaining control of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
and surrounding Southern states. The bloody Battle of Wilson's Creek
The Battle of Wilson's Creek, also known as the Battle of Oak Hills, was the first major battle of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War. It was fought on August 10, 1861, near Springfield, Missouri, Springfield, Missou ...
just across the border in Missouri shocked many Arkansans who thought the war would be a quick and decisive Southern victory. Battles early in the war took place in northwest Arkansas, including the Battle of Cane Hill
The Battle of Cane Hill (also known as the Engagement at Cane Hill) was fought during the American Civil War on November 28, 1862, in northwestern Arkansas, near the town of Cane Hill, Arkansas, Cane Hill. Union Army, Union troops under Brigad ...
, Battle of Pea Ridge
The Battle of Pea Ridge (March 7ŌĆō8, 1862), also known as the Battle of Elkhorn Tavern, took place in the American Civil War near Leetown, northeast of Fayetteville, Arkansas. Federal forces, led by Brig. Gen. Samuel R. Curtis, moved south ...
, and Battle of Prairie Grove
The Battle of Prairie Grove was a battle of the American Civil War fought on December 7, 1862. While tactically indecisive, the battle secured the Union control of northwestern Arkansas.
A division of Union troops in the Army of the Front ...
. Union general Samuel Curtis
Samuel Curtis (born in Walworth, Surrey on 29 August 1779-died at La Chaire, Rozel Bay, Jersey, on 6 January 1860
swept across the state to Helena in the Delta in 1862. Little Rock was captured the following year. The government shifted the state Confederate capital to Hot Springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
, and then again to Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
from 1863 to 1865, for the remainder of the war. Throughout the state, guerrilla warfare ravaged the countryside and destroyed cities. Passion for the Confederate cause waned after implementation of programs such as the draft, high taxes, and martial law.
Under the Military Reconstruction Act, Congress declared Arkansas restored to the Union in June 1868, after the Legislature accepted the 14th Amendment. The Republican-controlled reconstruction legislature established universal male suffrage (though temporarily disfranchising former Confederate Army officers, who were all Democrats), a public education system for blacks and whites, and passed general issues to improve the state and help more of the population. The State soon came under control of the Radical Republicans
The Radical Republicans (later also known as " Stalwarts") were a faction within the Republican Party, originating from the party's founding in 1854, some 6 years before the Civil War, until the Compromise of 1877, which effectively ended Reco ...
and Unionists, and led by Governor Powell Clayton
Powell Foulk Clayton (August 7, 1833August 25, 1914) was an American politician, diplomat, and businessman who served as the 9th governor of Arkansas from 1868 to 1871, as a Republican member of the U.S. Senate for Arkansas from 1871 to 1877 ...
, they presided over a time of great upheaval as Confederate sympathizers and the Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to the KKK or the Klan, is an American white supremacist, right-wing terrorist, and hate group whose primary targets are African Americans, Jews, Latinos, Asian Americans, Native Americans, and ...
fought the new developments, particularly voting rights for African Americans.
End of Reconstruction and late 19th century
In 1874, the Brooks-Baxter War, a political struggle between factions of the Republican Party shook Little Rock and the state governorship. It was settled only when PresidentUlysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union Ar ...
ordered Joseph Brooks to disperse his militant supporters.
Following the Brooks-Baxter War, a new state constitution was ratified, re-enfranchising former Confederates.
In 1881, the Arkansas state legislature enacted a bill that adopted an official pronunciation of the state's name, to combat a controversy then simmering. (See Law and Government below.)
After Reconstruction, the state began to receive more immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, and ...
and migrants. Chinese, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, and Syrian
Syrians ( ar, ž│┘Å┘łž▒┘É┘Ŗ┘Å┘æ┘ł┘å, ''S┼½riyy─½n'') are an Eastern Mediterranean ethnic group indigenous to the Levant. They share common Levantine Semitic roots. The cultural and linguistic heritage of the Syrian people is a blend of both indi ...
men were recruited for farm labor in the developing Delta region. None of these nationalities stayed long at farm labor; the Chinese especially quickly became small merchants in towns around the Delta. Many Chinese became such successful merchants in small towns that they were able to educate their children at college.
Construction of railroads enabled more farmers to get their products to market. It also brought new development into different parts of the state, including the Ozarks, where some areas were developed as resorts. In a few years at the end of the 19th century, for instance, Eureka Springs
Eureka Springs is a city in Carroll County, Arkansas, United States, and one of two county seats for the county. It is located in the Ozark Mountains of northwest Arkansas, near the border with Missouri. As of the 2020 census, the city populat ...
in Carroll County grew to 10,000 people, rapidly becoming a tourist destination and the fourth-largest city of the state. It featured newly constructed, elegant resort hotels and spas planned around its natural springs, considered to have healthful properties. The town's attractions included horse racing and other entertainment. It appealed to a wide variety of classes, becoming almost as popular as Hot Springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
.
Rise of the Jim Crow laws and early 20th century
In the late 1880s, the worsening agricultural depression catalyzed Populist and third party movements, leading to interracial coalitions. Struggling to stay in power, in the 1890s the Democrats in Arkansas followed other Southern states in passing legislation and constitutional amendments that disfranchised blacks and poor whites. In 1891 state legislators passed a requirement for aliteracy test
A literacy test assesses a person's literacy skills: their ability to read and write have been administered by various governments, particularly to immigrants. In the United States, between the 1850s and 1960s, literacy tests were administered t ...
, knowing it would exclude many blacks and whites. At the time, more than 25% of the population could neither read nor write. In 1892, they amended the state constitution to require a poll tax
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources.
Head taxes were important sources of revenue for many governments fr ...
and more complex residency requirements, both of which adversely affected poor people and sharecroppers, forcing most blacks and many poor whites from voter rolls.
By 1900 the Democratic Party expanded use of the white primary
White primaries were primary elections held in the Southern United States in which only white voters were permitted to participate. Statewide white primaries were established by the state Democratic Party units or by state legislatures in South C ...
in county and state elections, further denying blacks a part in the political process. Only in the primary was there any competition among candidates, as Democrats held all the power. The state was a Democratic one-party state for decades, until after passage of the federal Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
and Voting Rights Act of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights movement ...
to enforce constitutional rights.
Between 1905 and 1911, Arkansas began to receive a small immigration of German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, Slovak, and Scots-Irish from Europe. The German and Slovak peoples settled in the eastern part of the state known as the Prairie
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the ...
, and the Irish founded small communities in the southeast part of the state. The Germans were mostly Lutheran and the Slovaks were primarily Catholic. The Irish were mostly Protestant from Ulster
Ulster (; ga, Ulaidh or ''C├║ige Uladh'' ; sco, label= Ulster Scots, Ulst├©r or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional Irish provinces. It is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United King ...
, of Scots and Northern Borders descent. Some early 20th-century immigration included people from eastern Europe. Together, these immigrants made the Delta more diverse than the rest of the state. In the same years, some black migrants moved into the area because of opportunities to develop the bottomlands and own their own property.
Black sharecroppers began to try to organize a farmers' union after World WarI. They were seeking better conditions of payment and accounting from white landowners of the area cotton plantations. Whites resisted any change and often tried to break up their meetings. On September 30, 1919, two white men, including a local deputy, tried to break up a meeting of black sharecroppers who were trying to organize a farmers' union. After a white deputy was killed in a confrontation with guards at the meeting, word spread to town and around the area. Hundreds of whites from Phillips and neighboring areas rushed to suppress the blacks, and started attacking blacks at large. Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
Charles Hillman Brough
Charles Hillman Brough (July 9, 1876 ŌĆō December 26, 1935) was an American politician who served as the 25th Governor of Arkansas from 1917 to 1921. He signed a bill for womenŌĆÖs suffrage in Arkansas and supported it nationally.
Biography
Ch ...
requested federal troops to stop what was called the Elaine massacre
The Elaine massacre occurred on September 30ŌĆōOctober 2, 1919 at Hoop Spur in the vicinity of Elaine, Arkansas, Elaine in rural Phillips County, Arkansas. As many as several hundred African Americans and five White people, white men were kille ...
. White mobs spread throughout the county, killing an estimated 237 blacks before most of the violence was suppressed after October 1.Elaine Massacre, Arkansas Encyclopedia of History and Cultureaccessed April 3, 2008. Five whites also died in the incident. The governor accompanied the troops to the scene; President
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
had approved their use.
 The
The Great Mississippi Flood of 1927
The Great Mississippi Flood of 1927 was the most destructive river flood in the history of the United States, with inundated in depths of up to over the course of several months in early 1927. The uninflated cost of the damage has been estimat ...
flooded the areas along the Ouachita Rivers along with many other rivers.
Based on the order of President Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
given shortly after Imperial Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent forma ...
's attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, j ...
, nearly 16,000 Japanese Americans
are Americans of Japanese ancestry. Japanese Americans were among the three largest Asian American ethnic communities during the 20th century; but, according to the 2000 census, they have declined in number to constitute the sixth largest Asi ...
were forcibly removed from the West Coast of the United States
The West Coast of the United States, also known as the Pacific Coast, Pacific states, and the western seaboard, is the coastline along which the Western United States meets the North Pacific Ocean. The term typically refers to the contiguous U.S ...
and incarcerated in two internment camps in the Arkansas Delta
The Arkansas Delta is one of the six natural regions of the state of Arkansas. Willard B. Gatewood Jr., author of ''The Arkansas Delta: Land of Paradox'', says that rich cotton lands of the Arkansas Delta make that area "The Deepest of the Deep ...
. The Rohwer Camp in Desha County operated from September 1942 to November 1945 and at its peak interned 8,475 prisoners. The Jerome War Relocation Center
The Jerome War Relocation Center was a Japanese American internment camp located in southeastern Arkansas, near the town of Jerome in the Arkansas Delta. Open from October 6, 1942, until June 30, 1944, it was the last American concentration camp ...
in Drew County
Drew County is a county located in the southeast region of the U.S. state of Arkansas. As of the 2010 census, the population was 18,509, making it the 39th most populous of Arkansas's 75 counties. The county seat and largest city is Monticello. ...
operated from October 1942 to June 1944 and held about 8,000.
Fall of segregation
After theSupreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
ruled segregation in public schools unconstitutional in ''Brown ''v.'' Board of Education of Topeka, Kansas'' (1954), some students worked to integrate schools in the state. The Little Rock Nine
The Little Rock Nine were a group of nine African American students enrolled in Little Rock Central High School in 1957. Their enrollment was followed by the Little Rock Crisis, in which the students were initially prevented from entering ...
brought Arkansas to national attention in 1957 when the federal government had to intervene to protect African-American students trying to integrate a high school in the capital. Governor Orval Faubus had ordered the Arkansas National Guard to help segregationists prevent nine African-American students from enrolling at Little Rock's Central High School. After attempting three times to contact Faubus, President Dwight D. Eisenhower sent 1,000 troops from the active-duty 101st Airborne Division to escort and protect the African-American students as they entered school on September 25, 1957. In defiance of federal court orders to integrate, the governor and city of Little Rock decided to close the high schools for the remainder of the school year. By the fall of 1959, the Little Rock high schools were completely integrated.
Geography

Boundaries
Arkansas bordersLouisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
to the south, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
to the southwest, Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ßÄŻßĦßÄ│ßÄ░ßÄ╣, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
to the west, Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
to the north, and Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
and Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
to the east. The United States Census Bureau classifies Arkansas as a Southern United States, southern state, sub-categorized among the West South Central States. The Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
forms most of its eastern border, except in Clay County, Arkansas, Clay and Greene County, Arkansas, Greene counties, where the St. Francis River forms the western boundary of the Missouri Bootheel, and in many places where the channel of the Mississippi has meandered (or been straightened by man) from its original 1836 course.
Terrain
 Arkansas can generally be split into two halves, the highlands in the northwest and the lowlands of the southeast. The highlands are part of the Southern Interior Highlands, including The Ozarks and the
Arkansas can generally be split into two halves, the highlands in the northwest and the lowlands of the southeast. The highlands are part of the Southern Interior Highlands, including The Ozarks and the Ouachita Mountains
The Ouachita Mountains (), simply referred to as the Ouachitas, are a mountain range in western Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma. They are formed by a thick succession of highly deformed Paleozoic strata constituting the Ouachita Fold and Thru ...
. The southern lowlands include the Gulf Coastal Plain and the Arkansas Delta
The Arkansas Delta is one of the six natural regions of the state of Arkansas. Willard B. Gatewood Jr., author of ''The Arkansas Delta: Land of Paradox'', says that rich cotton lands of the Arkansas Delta make that area "The Deepest of the Deep ...
. This split can yield to a regional division into northwest, southwest, northeast, southeast, and central Arkansas. These regions are broad and not defined along county lines. Arkansas has seven distinct natural regions: the Ozark Mountains, Ouachita Mountains, Arkansas River Valley, Gulf Coastal Plain, Crowley's Ridge, and the Arkansas Delta, with Central Arkansas sometimes included as a blend of multiple regions.
 The southeastern part of Arkansas along the Mississippi Alluvial Plain is sometimes called the Arkansas Delta. This region is a flat landscape of River delta, rich alluvial soils formed by repeated flooding of the adjacent Mississippi. Farther from the river, in the southeastern part of the state, the Grand Prairie has a more undulating landscape. Both are fertile agricultural areas. The Delta region is bisected by a geological formation known as Crowley's Ridge. A narrow band of rolling hills, Crowley's Ridge rises above the surrounding alluvial plain and underlies many of eastern Arkansas's major towns.
Northwest Arkansas is part of the Ozark Plateau including the Ozark Mountains, to the south are the
The southeastern part of Arkansas along the Mississippi Alluvial Plain is sometimes called the Arkansas Delta. This region is a flat landscape of River delta, rich alluvial soils formed by repeated flooding of the adjacent Mississippi. Farther from the river, in the southeastern part of the state, the Grand Prairie has a more undulating landscape. Both are fertile agricultural areas. The Delta region is bisected by a geological formation known as Crowley's Ridge. A narrow band of rolling hills, Crowley's Ridge rises above the surrounding alluvial plain and underlies many of eastern Arkansas's major towns.
Northwest Arkansas is part of the Ozark Plateau including the Ozark Mountains, to the south are the Ouachita Mountains
The Ouachita Mountains (), simply referred to as the Ouachitas, are a mountain range in western Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma. They are formed by a thick succession of highly deformed Paleozoic strata constituting the Ouachita Fold and Thru ...
, and these regions are divided by the Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in the western United Stat ...
; the southern and eastern parts of Arkansas are called the Lowlands. These mountain ranges are part of the U.S. Interior Highlands region, the only major mountainous region between the Rocky Mountains and the Appalachian Mountains. The state's highest point is Mount Magazine in the Ouachita Mountains
The Ouachita Mountains (), simply referred to as the Ouachitas, are a mountain range in western Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma. They are formed by a thick succession of highly deformed Paleozoic strata constituting the Ouachita Fold and Thru ...
, which is above sea level.
 Arkansas is home to many List of caves in Arkansas, caves, such as Blanchard Springs Caverns. The State Archeologist has catalogued more than 43,000 Native American living, hunting and tool-making sites, many of them Pre-Columbian burial mounds and rock shelters. Crater of Diamonds State Park near Murfreesboro, Arkansas, Murfreesboro is the world's only diamond-bearing site accessible to the public for digging. Arkansas is home to a dozen Wilderness Areas totaling . These areas are set aside for outdoor recreation and are open to hunting, fishing, hiking, and primitive camping. No mechanized vehicles nor developed campgrounds are allowed in these areas.
Arkansas is home to many List of caves in Arkansas, caves, such as Blanchard Springs Caverns. The State Archeologist has catalogued more than 43,000 Native American living, hunting and tool-making sites, many of them Pre-Columbian burial mounds and rock shelters. Crater of Diamonds State Park near Murfreesboro, Arkansas, Murfreesboro is the world's only diamond-bearing site accessible to the public for digging. Arkansas is home to a dozen Wilderness Areas totaling . These areas are set aside for outdoor recreation and are open to hunting, fishing, hiking, and primitive camping. No mechanized vehicles nor developed campgrounds are allowed in these areas.
Hydrology
 Arkansas has many rivers, lakes, and reservoirs within or along its borders. Major tributaries to the Mississippi River include the
Arkansas has many rivers, lakes, and reservoirs within or along its borders. Major tributaries to the Mississippi River include the Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in the western United Stat ...
, the White River (Arkansas), White River, and the St. Francis River.Federal Writers' Project 1987, p. 8. The Arkansas is fed by the Mulberry River (Arkansas), Mulberry and Fourche La Fave River, Fourche LaFave Rivers in the Arkansas River Valley, which is also home to Lake Dardanelle. The Buffalo National River, Buffalo, Little Red River (Arkansas), Little Red, Black River (Arkansas), Black and Cache River (Arkansas), Cache Rivers are all tributaries to the White River (Arkansas), White River, which also empties into the Mississippi. Bayou Bartholomew and the Saline River (Ouachita River), Saline, Little Missouri River (Arkansas), Little Missouri, and Caddo Rivers are all tributaries to the Ouachita River in south Arkansas, Old River Control Structure, which empties into the Mississippi in Louisiana. The Red River of the South, Red River briefly forms the state's boundary with Texas. Arkansas has few natural lakes and many reservoirs, such as Bull Shoals Lake, Lake Ouachita, Greers Ferry Lake, Millwood Lake, Beaver Lake (Arkansas), Beaver Lake, Norfork Lake, DeGray Lake, and Lake Conway.
Flora and fauna
 Arkansas's temperate deciduous forest is divided into three broad ecoregions: the ''Ozark, Ouachita-Appalachian Forests'', the ''Mississippi Alluvial and Southeast USA Coastal Plains'', and the ''Southeastern USA Plains''. The state is further divided into seven subregions: the Arkansas Valley, Boston Mountains, Mississippi Alluvial Plain, Crowley's Ridge, Mississippi Valley Loess Plain, Ozark Highlands, Ouachita Mountains, and the South Central Plains. A 2010 United States Forest Service survey determined of Arkansas's land is forestland, or 56% of the state's total area. Dominant species in Arkansas's forests include ''Oak, Quercus'' (oak), ''Hickory, Carya'' (hickory), ''Pinus echinata'' (shortleaf pine) and ''Pinus taeda'' (loblolly pine).
Arkansas's plant life varies with its climate and elevation. The Arkansas Timberlands, pine belt stretching from the Arkansas delta to Texas consists of dense oak-hickory-pine growth. Lumbering and paper milling activity is active throughout the region. In eastern Arkansas, one can find ''Taxodium '' (cypress), ''Quercus nigra'' (water oaks), and hickories with their roots submerged in the Mississippi Valley bayous indicative of the deep south. Nearby Crowley's Ridge is the only home of the Liriodendron, tulip tree in the state, and generally hosts more northeastern plant life such as the beech tree. The northwestern highlands are covered in an oak-hickory mixture, with Juniperus ashei, Ozark white cedars, ''Cornus (genus), cornus'' (dogwoods), and ''Cercis canadensis'' (redbuds) also present. The higher peaks in the Arkansas River Valley play host to scores of ferns, including the ''Woodsia scopulina'' and ''Adiantum'' (maidenhair fern) on Mount Magazine. Arkansas wildlife is famous for the white-tailed deer, elk, and bald eagle. The white-tailed deer is the official state mammal.
Arkansas's temperate deciduous forest is divided into three broad ecoregions: the ''Ozark, Ouachita-Appalachian Forests'', the ''Mississippi Alluvial and Southeast USA Coastal Plains'', and the ''Southeastern USA Plains''. The state is further divided into seven subregions: the Arkansas Valley, Boston Mountains, Mississippi Alluvial Plain, Crowley's Ridge, Mississippi Valley Loess Plain, Ozark Highlands, Ouachita Mountains, and the South Central Plains. A 2010 United States Forest Service survey determined of Arkansas's land is forestland, or 56% of the state's total area. Dominant species in Arkansas's forests include ''Oak, Quercus'' (oak), ''Hickory, Carya'' (hickory), ''Pinus echinata'' (shortleaf pine) and ''Pinus taeda'' (loblolly pine).
Arkansas's plant life varies with its climate and elevation. The Arkansas Timberlands, pine belt stretching from the Arkansas delta to Texas consists of dense oak-hickory-pine growth. Lumbering and paper milling activity is active throughout the region. In eastern Arkansas, one can find ''Taxodium '' (cypress), ''Quercus nigra'' (water oaks), and hickories with their roots submerged in the Mississippi Valley bayous indicative of the deep south. Nearby Crowley's Ridge is the only home of the Liriodendron, tulip tree in the state, and generally hosts more northeastern plant life such as the beech tree. The northwestern highlands are covered in an oak-hickory mixture, with Juniperus ashei, Ozark white cedars, ''Cornus (genus), cornus'' (dogwoods), and ''Cercis canadensis'' (redbuds) also present. The higher peaks in the Arkansas River Valley play host to scores of ferns, including the ''Woodsia scopulina'' and ''Adiantum'' (maidenhair fern) on Mount Magazine. Arkansas wildlife is famous for the white-tailed deer, elk, and bald eagle. The white-tailed deer is the official state mammal.
Climate
 Arkansas generally has a humid subtropical climate. While not bordering the Gulf of Mexico, Arkansas, is still close enough to the warm, large body of water for it to influence the weather in the state. Generally, Arkansas, has hot, humid summers and slightly drier, mild to cool winters. In
Arkansas generally has a humid subtropical climate. While not bordering the Gulf of Mexico, Arkansas, is still close enough to the warm, large body of water for it to influence the weather in the state. Generally, Arkansas, has hot, humid summers and slightly drier, mild to cool winters. In Little Rock
( The "Little Rock")
, government_type = Council-manager
, leader_title = Mayor
, leader_name = Frank Scott Jr.
, leader_party = D
, leader_title2 = Council
, leader_name2 ...
, the daily high temperatures average around with lows around in July. In January highs average around and lows around . In Siloam Springs, Arkansas, Siloam Springs in the northwest part of the state, the average high and low temperatures in July are and in January the average high and low are . Annual precipitation throughout the state averages between about ; it is somewhat wetter in the south and drier in the northern part of the state. Snowfall is infrequent but most common in the northern half of the state. The half of the state south of Little Rock is apter to see ice storms. Arkansas's record high is at Ozark, Arkansas, Ozark on August 10, 1936; the record low is at Gravette, Arkansas, Gravette, on February 13, 1905.
Arkansas is known for extreme weather and frequent storms. A typical year brings thunderstorms, tornadoes, hail, snow and ice storms. Between both the Great Plains and the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf States, Arkansas, receives around 60 days of thunderstorms. Arkansas is located in Tornado Alley, and as a result, a few of the most destructive tornadoes in U.S. history have struck the state. While sufficiently far from the coast to avoid a direct hit from a hurricane, Arkansas can often get the remnants of a tropical cyclone, tropical system, which dumps tremendous amounts of rain in a short time and often spawns smaller tornadoes.
Cities and towns

Little Rock
( The "Little Rock")
, government_type = Council-manager
, leader_title = Mayor
, leader_name = Frank Scott Jr.
, leader_party = D
, leader_title2 = Council
, leader_name2 ...
has been Arkansas's List of capitals in the United States, capital city since 1821 when it replaced Arkansas Post, Arkansas, Arkansas Post as the capital of the Territory of Arkansas
The Arkansas Territory was a territory of the United States that existed from July 4, 1819, to June 15, 1836, when the final extent of Arkansas Territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Arkansas. Arkansas Post was the first territo ...
. The state capitol was moved to Hot Springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
and later Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 ŌĆō May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
when the Union armies threatened the city in 1862, and state government did not return to Little Rock until after the war ended. Today, the Little RockŌĆōNorth Little RockŌĆōConway metropolitan area is the largest in the state, with a population of 724,385 in 2013.
The FayettevilleŌĆōSpringdaleŌĆōRogers Metropolitan Area
Northwest Arkansas (NWA) is a metropolitan area and region in Arkansas within the Ozark Mountains. It includes four of the ten largest cities in the state: Fayetteville, Springdale, Rogers, and Bentonville, the surrounding towns of Benton a ...
is the second-largest metropolitan area in Arkansas, growing at the fastest rate due to the influx of businesses and the growth of the University of Arkansas and Walmart
Walmart Inc. (; formerly Wal-Mart Stores, Inc.) is an American multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of hypermarkets (also called supercenters), discount department stores, and grocery stores from the United States, headquarter ...
.
The state has eight cities with populations above 50,000 (based on 2010 census). In descending order of size, they are Little Rock
( The "Little Rock")
, government_type = Council-manager
, leader_title = Mayor
, leader_name = Frank Scott Jr.
, leader_party = D
, leader_title2 = Council
, leader_name2 ...
, Fort Smith, Arkansas, Fort Smith, Fayetteville, Arkansas, Fayetteville, Springdale, Arkansas, Springdale, Jonesboro, North Little Rock, Arkansas, North Little Rock, Conway, Arkansas, Conway, and Rogers, Arkansas, Rogers. Of these, only Fort Smith and Jonesboro are outside the two largest metropolitan areas. Other cities in Arkansas include Pine Bluff, Crossett, Arkansas, Crossett, Bryant, Arkansas, Bryant, Lake Village, Arkansas, Lake Village, Hot Springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
, Bentonville, Texarkana, Arkansas, Texarkana, Sherwood, Arkansas, Sherwood, Jacksonville, Arkansas, Jacksonville, Russellville, Arkansas, Russellville, Bella Vista, Arkansas, Bella Vista, West Memphis, Arkansas, West Memphis, Paragould, Arkansas, Paragould, Cabot, Arkansas, Cabot, Searcy, Arkansas, Searcy, Van Buren, Arkansas, Van Buren, El Dorado, Arkansas, El Dorado, Blytheville, Arkansas, Blytheville, Harrison, Arkansas, Harrison, Dumas, Arkansas, Dumas, Rison, Arkansas, Rison, Warren, Arkansas, Warren, and Mountain Home, Arkansas, Mountain Home.
Demographics
Population
The United States Census Bureau estimated that the population of Arkansas was 3,017,804 on July 1, 2019, a 3.49% increase since the 2010 United States Census, 2010 United States census. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, Arkansas had a resident population of 3,011,524. From fewer than 15,000 in 1820, Arkansas's population grew to 52,240 during a special census in 1835, far exceeding the 40,000 required to apply for statehood. Following statehood in 1836, the population doubled each decade until the 1870 United States Census, 1870 census conducted following the American Civil War. The state recorded growth in each successive decade, although it gradually slowed in the 20th century. It recorded population losses in the 1950 United States Census, 1950 and 1960 United States Census, 1960 censusRace and ethnicity
Arkansas is 72.0% non-Hispanic white, 15.4% Black or African American, 0.5% American Indian and Alaska Native, 1.5% Asian, 0.4% Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander, 0.1% some other race, 2.4% two or more races, and 7.7% Hispanic or Latin American of any race. In 2011, the state was 80.1% white (74.2% non-Hispanic white), 15.6% Black or African American, 0.9% Native Americans in the United States, American Indian and Alaska Native, 1.3% Asian ethnicity, Asian, and 1.8% from two or more races. Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanics or Latinos of any race made up 6.6% of the population. As of 2011, 39.0% of Arkansas's population younger than age1 were minorities.Religion
Like most other Southern states, Arkansas is part of the Bible Belt and predominantly Protestantism, Protestant. The largest denominations by number of adherents in 2010 were the Southern Baptist Convention with 661,382; the United Methodist Church with 158,574; non-denominational Evangelical Protestants with 129,638; the Catholic Church with 122,662; and the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints with 31,254. Some residents of the state have other religions, such as Islam, Judaism, Wicca/Paganism, Hinduism, Buddhism, and some have no religious affiliation. In 2014, the Pew Research Center determined that 79% of the population was Christian, dominated by evangelicals in the Southern Baptist and independent Baptist churches. In contrast with many other states, the Catholic Church as of 2014 was not the largest Christian denomination in Arkansas. Of the unaffiliated population, 2% were Atheism, atheist in 2014. By 2020, the Public Religion Research Institute determined 71% of the population was Christian. Arkansas continued to be dominated by evangelicals, followed by mainline Protestants and Black church, historically black or African American churches.Economy
 Once a state with a cashless society in the uplands and Plantation economy, plantation agriculture in the lowlands, Arkansas's economy has evolved and diversified. The state's gross domestic product (GDP) was $119billion in 2015. Six Fortune 500 companies are based in Arkansas, including the world's #1 retailer,
Once a state with a cashless society in the uplands and Plantation economy, plantation agriculture in the lowlands, Arkansas's economy has evolved and diversified. The state's gross domestic product (GDP) was $119billion in 2015. Six Fortune 500 companies are based in Arkansas, including the world's #1 retailer, Walmart
Walmart Inc. (; formerly Wal-Mart Stores, Inc.) is an American multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of hypermarkets (also called supercenters), discount department stores, and grocery stores from the United States, headquarter ...
; Tyson Foods, J.B. Hunt, Dillard's, Murphy USA, and Windstream are also headquartered in the state. The List of U.S. states by GDP per capita (nominal), per capita personal income in 2015 was $39,107, ranking 45th in the nation. The median household income from 2011 to 2015 was $41,371, ranking 49th in the nation. The state's agriculture outputs are poultry and eggs, soybeans, sorghum, cattle, cotton, rice, hogs, and milk. Its industrial outputs are food processing, electric equipment, fabricated metal products, machinery, and paper products. Arkansas's mines produce natural gas, oil, crushed stone, bromine, and vanadium. According to CNBC, Arkansas is the 20th-best state for business, with the 2nd-lowest cost of doing business, 5th-lowest cost of living, 11th-best workforce, 20th-best economic climate, 28th-best-educated workforce, 31st-best infrastructure and the 32nd-friendliest regulatory environment. Arkansas gained 12 spots in the best state for business rankings since 2011. As of 2014, it was the most affordable state to live in.
As of June 2021, the state's unemployment rate was 4.4%; the preliminary rate for November 2021 is 3.4%.
Industry and commerce
Arkansas's earliest industries were fur trading and agriculture, with development of cotton plantations in the American South, plantations in the areas near the Mississippi River. They were dependent on slave labor through theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 ŌĆō May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
.
Today only about three percent of the population are employed in the agricultural sector, it remains a major part of the state's economy, ranking 13th in the nation in the value of products sold. Arkansas is the nation's largest producer of rice, broilers, and turkeys, and ranks in the top three for cotton, pullets, and aquaculture (catfish). Forestry remains strong in the Arkansas Timberlands
The Arkansas Timberlands (sometimes also called Southern Arkansas or Southwest Arkansas) is a region of the U.S. state of Arkansas generally encompassing the area south of the Ouachita Mountains, south of Central Arkansas and west of the Arkans ...
, and the state ranks fourth nationally and first in the South in softwood lumber production. Automobile parts manufacturers have opened factories in eastern Arkansas to support auto plants in other states. Bauxite was formerly a large part of the state's economy, mined mostly around Saline County, Arkansas, Saline County.
Tourism is also very important to the Arkansas economy; the official state nickname "The Natural State" was created for state tourism advertising in the 1970s, and is still used to this day. The state maintains List of Arkansas state parks, 52 state parks and the National Park Service maintains seven properties in Arkansas. The completion of the William Jefferson Clinton Presidential Library in Little Rock has drawn many visitors to the city and revitalized the nearby River Market District (Little Rock, Arkansas), River Market District. Many cities also hold festivals, which draw tourists to Arkansas culture, such as The Bradley County Pink Tomato Festival in Warren, King Biscuit Blues Festival, Ozark Folk Center, Ozark Folk Festival, Toad Suck Daze, and Tontitown, Arkansas, Tontitown Grape Festival.
Transportation
 Transportation in Arkansas is overseen by the Arkansas Department of Transportation (ArDOT), headquartered in
Transportation in Arkansas is overseen by the Arkansas Department of Transportation (ArDOT), headquartered in Little Rock
( The "Little Rock")
, government_type = Council-manager
, leader_title = Mayor
, leader_name = Frank Scott Jr.
, leader_party = D
, leader_title2 = Council
, leader_name2 ...
. Several main corridors pass through Little Rock, including Interstate 30 in Arkansas, Interstate30 (I-30) and Interstate 40 in Arkansas, I-40 (the nation's 3rd-busiest trucking corridor). Arkansas first designated a state highway system in 1924, and first numbered its roads in 1926. Arkansas had one of the first paved roads, the Dollarway Road, and one of the first members of the Interstate Highway System. The state maintains a large system of List of Arkansas state highways, state highways today, in addition to eight List of Interstate Highways in Arkansas, Interstates and 20 List of U.S. Routes in Arkansas, U.S. Routes.
In northeast Arkansas, Interstate 55 in Arkansas, I-55 travels north from Memphis, Tennessee, Memphis to Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
, with a new spur to Jonesboro (Interstate 555, I-555). Northwest Arkansas is served by the segment of Interstate 49 in Arkansas, I-49 from Fort Smith to the beginning of the Arkansas Highway 549, Bella Vista Bypass. This segment of I-49 currently follows mostly the same route as the Interstate 540 (Arkansas)#History, former section of I-540 that extended north of I-40. The state also has the 13th largest List of Arkansas state highways, state highway system in the nation.
 Arkansas is served by of railroad track divided among twenty-six railroad companies including three Class I railroads. Freight railroads are concentrated in southeast Arkansas to serve the industries in the region. The Texas Eagle, an Amtrak passenger train, serves five stations in the state Walnut Ridge (Amtrak station), Walnut Ridge, Little Rock (Amtrak station), Little Rock, Malvern (Amtrak station), Malvern, Arkadelphia (Amtrak station), Arkadelphia, and Texarkana (Amtrak station), Texarkana.
Arkansas also benefits from the use of its rivers for commerce. The
Arkansas is served by of railroad track divided among twenty-six railroad companies including three Class I railroads. Freight railroads are concentrated in southeast Arkansas to serve the industries in the region. The Texas Eagle, an Amtrak passenger train, serves five stations in the state Walnut Ridge (Amtrak station), Walnut Ridge, Little Rock (Amtrak station), Little Rock, Malvern (Amtrak station), Malvern, Arkadelphia (Amtrak station), Arkadelphia, and Texarkana (Amtrak station), Texarkana.
Arkansas also benefits from the use of its rivers for commerce. The Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
and Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in the western United Stat ...
are both major rivers. The United States Army Corps of Engineers maintains the McClellan-Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System, allowing barge traffic up the Arkansas River to the Port of Catoosa in Tulsa, Oklahoma.
There are four airports with commercial service: Clinton National Airport (formerly Little Rock National Airport or Adams Field), Northwest Arkansas Regional Airport, Fort Smith Regional Airport, and Texarkana Regional Airport, with List of airports in Arkansas, dozens of smaller airports in the state.
Public transit and community transport services for the elderly or those with developmental disabilities are provided by agencies such as the Central Arkansas Transit Authority and the Ozark Regional Transit, organizations that are part of the Arkansas Transit Association.
Government
As with the federal government of the United States, political power in Arkansas is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. Each officer's term is four years long. Office holders are term-limited to two full terms plus any partial terms before the first full term. In a 2020 study, Arkansas was ranked as the 9th hardest state for citizens to vote in.Executive
The governor of Arkansas is Asa Hutchinson, a Republican Party (United States), Republican, who was inaugurated on January 13, 2015. The six other elected executive positions in Arkansas are Lieutenant Governor of Arkansas, lieutenant governor, Secretary of State of Arkansas, secretary of state, Arkansas Attorney General, attorney general, Arkansas State Treasurer, treasurer, Arkansas State Auditor, auditor, and Arkansas Land Commissioner, land commissioner. The governor also appoints the leaders of various state boards, committees, and departments. Arkansas governors served two-year terms until a referendum lengthened the term to four years, effective with the 1986 election. In Arkansas, the lieutenant governor is elected separately from the governor and thus can be from a different political party.Legislative
Arkansas General Assembly
The General Assembly of Arkansas is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The legislature is a bicameral body composed of the upper house Arkansas Senate with 35 members, and the lower Arkansas House of Representatives with 100 ...
is the state's bicameral bodies of legislators, composed of the Arkansas Senate, Senate and Arkansas House of Representatives, House of Representatives. The Senate contains 35 members from districts of approximately equal population. These districts are redrawn decennially with each US census, and in election years ending in "2", the entire body is put up for reelection. Following the election, half of the seats are designated as two-year seats and are up for reelection again in two years, these "half-terms" do not count against a legislator's term limits. The remaining half serve a full four-year term. This staggers elections such that half the body is up for reelection every two years and allows for complete body turnover following redistricting. Arkansas voters elected a 21ŌĆō14 Republican majority in the Senate in 2012. Arkansas House members can serve a maximum of three two-year terms. House districts are redistricted by the Arkansas Board of Apportionment. In the 2012 elections, Republicans gained a 51ŌĆō49 majority in the House of Representatives.
The Republican Party majority status in the Arkansas State House of Representatives after the 2012 elections is the party's first since 1874. Arkansas was the last state of the old Confederacy to never have Republicans control either chamber of its house since the American Civil War.
Following the term limits changes, studies have shown that lobbyists have become less influential in state politics. Legislative staff, not subject to term limits, have acquired additional power and influence due to the high rate of elected official turnover.
Judicial
Arkansas's judicial branch has five court systems: Arkansas Supreme Court, Arkansas Court of Appeals, Circuit Courts, District Courts and City Courts. Most cases begin in district court, which is subdivided into state district court and local district court. State district courts exercise district-wide jurisdiction over the districts created by the General Assembly, and local district courts are presided over by part-time judges who may privately practice law. 25 state district court judges preside over 15 districts, with more districts created in 2013 and 2017. There are 28 judicial circuits of Circuit Court, with each contains five subdivisions: criminal, civil, probate, domestic relations, and juvenile court. The jurisdiction of the Arkansas Court of Appeals is determined by the Arkansas Supreme Court, and there is no appeal, right of appeal from the Court of Appeals to the high court. The Arkansas Supreme Court can review Court of Appeals cases upon application by either a party to the litigation, upon request by the Court of Appeals, or if the Arkansas Supreme Court feels the case should have been initially assigned to it. The twelve judges of the Arkansas Court of Appeals are elected from judicial districts to renewable six-year terms. The Arkansas Supreme Court is the court of last resort in the state, composed of seven justices elected to eight-year terms. Established by the Arkansas Constitution in 1836, the court's decisions can be appealed to only the Supreme Court of the United States.Federal
Both Arkansas's U.S. senators, John Boozman and Tom Cotton, are Republicans. The state has four seats in United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives. All four seats are held by Republicans: Rick Crawford (politician), Rick Crawford (Arkansas's 1st congressional district, 1st district), French Hill (politician), French Hill (Arkansas's 2nd congressional district, 2nd district), Steve Womack (Arkansas's 3rd congressional district, 3rd district), and Bruce Westerman (Arkansas's 4th congressional district, 4th district).Politics
Arkansas governorBill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( n├® Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
brought national attention to the state with a long speech at the 1988 Democratic National Convention endorsing Michael Dukakis. Some journalists suggested the speech was a threat to his ambitions; Clinton defined it "a comedy of error, just one of those fluky things". He won the Democratic nomination for president in 1992. Presenting himself as a "New Democrat" and using incumbent George H. W. Bush's Read my lips: no new taxes, broken promise against him, Clinton won the U.S. presidential election, 1992, 1992 presidential election with 43.0% of the vote to Bush's 37.5% and independent billionaire Ross Perot's 18.9%.
Most Republican strength traditionally lay mainly in the northwestern part of the state, particularly Fort Smith, Arkansas, Fort Smith and Bentonville, as well as North Central Arkansas around the Mountain Home, Arkansas, Mountain Home area. In the latter area, Republicans have been known to get 90% or more of the vote, while the rest of the state was more Democratic. After 2010, Republican strength expanded further to the Northeast and Southwest and into the Little Rock suburbs. The Democrats are mostly concentrated to central Little Rock, the Mississippi Delta, the Pine Bluff area, and the areas around the southern border with Louisiana.
Arkansas has elected only three Republicans to the U.S. Senate since Reconstruction era of the United States, Reconstruction: Tim Hutchinson, who was defeated after one term by Mark Pryor; John Boozman, who defeated incumbent Blanche Lincoln; and Tom Cotton, who defeated Pryor in 2014. Before 2013, the General Assembly had not been controlled by the Republican Party since Reconstruction, with the GOP holding a 51-seat majority in the state House and a 21-seat (of 35) in the state Senate following victories in 2012. Arkansas was one of just three states among the states of the former Confederate States of America, Confederacy that sent two Democrats to the U.S. Senate (the others being Florida and Virginia) for any period during the first decade of the 21st century.
In 2010, Republicans captured three of the state's four seats in the U.S. House of Representatives. In 2012, they won election to all four House seats. Arkansas held the distinction of having a U.S. House delegation composed entirely of military veterans (Rick Crawford (politician), Rick Crawford, United States Army, Army; Tim Griffin, United States Army Reserve, Army Reserve; Steve Womack, Army National Guard of the United States, National Guard; Tom Cotton, Army). When Pryor was defeated in 2014, the entire congressional delegation was in GOP hands for the first time since Reconstruction era of the United States, Reconstruction.
Reflecting the state's large evangelical population, Arkansas has a strong Social conservatism, social conservative bent. In the aftermath of the landmark Supreme Court decision ''Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization'', Arkansas became one of nine states where abortion is banned. Under the Arkansas Constitution
The Constitution of Arkansas is the primary organizing law for the U.S. state of Arkansas delineating the duties, powers, structures, and functions of the state government. Arkansas' original constitution was adopted at a constitutional conv ...
, Arkansas is a Right-to-work law, right to work state. Its voters passed a ban on same-sex marriage in 2004, with 75% voting yes, although that ban has been inactive since the Supreme Court protected same-sex marriage in ''Obergefell v. Hodges''.
Military
The Strategic Air Command facility of Little Rock Air Force Base was one of eighteen silos in the command of the 308th Armament Systems Wing#Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles, 308th Strategic Missile Wing (308th SMW), specifically one of the nine silos within its 374th Strategic Missile Squadron (374th SMS). The squadron was responsible for Launch Complex 374ŌĆō7, site of the 1980 Damascus Titan missile explosion, 1980 explosion of a Titan (missile), TitanII Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) in Damascus, Arkansas.Taxation
Taxes are collected by the Arkansas Department of Finance and Administration.Health
Education
Arkansas has 1,064 state-funded kindergartens, elementary, junior and senior high schools. The state supports a network of public university, universities and colleges, including two major university systems: Arkansas State University System and University of Arkansas System. The University of Arkansas, flagship campus of the University of Arkansas System in Fayetteville was ranked #63 among public schools in the nation by ''U.S. News & World Report''. Other public institutions include University of Arkansas at Pine Bluff, Arkansas Tech University, Henderson State University, Southern Arkansas University, and University of Central Arkansas across the state. It is also home to 11 private colleges and universities including Hendrix College, one of the nation's top 100 liberal arts colleges, according to U.S. News & World Report. In the 1920s the state required all children to attend public schools. The school year was set at 131 days, although some areas were unable to meet that requirement. Generally prohibited in the Western world, West at large, school corporal punishment is not unusual in Arkansas, with 20,083 public school students paddle (spanking), paddled at least one time, according to government data for the 2011ŌĆō12 school year. The rate of corporal punishment in public schools is higher only inMississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
.
Educational attainment
Arkansas is one of the least educated U.S. states. It ranks near the bottom in terms of percentage of the population with a high school or college degree. The state's educational system has a history of underfunding, low teachers' salaries and political meddling in the curriculum. Educational statistics during the early days are fragmentary and unreliable. Many counties did not submit full reports to the secretary of state, who did double duty as commissioner of common schools. But the percentage of whites over 20 years old who were illiterate was given as: :1840, 21% :1850, 25% :1860, 17% In 2010 Arkansas students earned an average score of 20.3 on the ACT (examination), ACT exam, just below the national average of 21. These results were expected due to the large increase in the number of students taking the exam since the establishment of the Academic Challenge Scholarship. Top high schools receiving recognition from the U.S. News & World Report are spread across the state, including Haas Hall Academy in Fayetteville, KIPP Delta Collegiate High School, KIPP Delta Collegiate in Helena-West Helena, Arkansas, Helena-West Helena, Bentonville High School, Bentonville, Rogers High School (Arkansas), Rogers, Rogers Heritage High School, Rogers Heritage, Valley Springs High School, Valley Springs, Searcy High School (Arkansas), Searcy, and McCrory High School, McCrory. A total of 81 Arkansas high schools were ranked by the U.S. News & World Report in 2012. Arkansas ranks as the 32nd smartest state on the Morgan Quitno Smartest State Award, 44th in percentage of residents with at least a high school diploma, and 48th in percentage of bachelor's degree attainment. Arkansas has been making strides in education reform. ''Education Week'' has praised the state, ranking Arkansas in the top 10 of their Quality Counts Education Rankings every year since 2009 while scoring it in the top5 during 2012 and 2013. Arkansas specifically received an A in Transition and Policy Making for progress in this area consisting of early-childhood education, college readiness, and career readiness. Governor Mike Beebe has made improving education a major issue through his attempts to spend more on education. Through reforms, the state is a leader in requiring curricula designed to prepare students for postsecondary education, rewarding teachers for student achievement, and providing incentives for principals who work in lower-tier schools.
Arkansas ranks as the 32nd smartest state on the Morgan Quitno Smartest State Award, 44th in percentage of residents with at least a high school diploma, and 48th in percentage of bachelor's degree attainment. Arkansas has been making strides in education reform. ''Education Week'' has praised the state, ranking Arkansas in the top 10 of their Quality Counts Education Rankings every year since 2009 while scoring it in the top5 during 2012 and 2013. Arkansas specifically received an A in Transition and Policy Making for progress in this area consisting of early-childhood education, college readiness, and career readiness. Governor Mike Beebe has made improving education a major issue through his attempts to spend more on education. Through reforms, the state is a leader in requiring curricula designed to prepare students for postsecondary education, rewarding teachers for student achievement, and providing incentives for principals who work in lower-tier schools.
Funding
As an organized territory, and later in the early days of statehood, education was funded by the sales of federally controlled public lands. This system was inadequate and prone to local graft. In an 1854 message to the legislature, Governor Elias N. Conway said, "We have a common-school law intended as a system to establish common schools in all part of the state; but for the want of adequate means there are very few in operation under this law." At the time, only about a quarter of children were enrolled in school. By the beginning of the American Civil War, the state had only twenty-five publicly funded common schools. In 1867, the state legislature was still controlled by ex-Confederates. It passed a Common Schools Law that allowed public funded but limited schools to white children. The 1868 legislature banned former Confederates and passed a more wide-ranging law detailing funding and administrative issues and allowing black children to attend school. In furtherance of this, the postwar 1868 state constitution was the first to permit a personal-property tax to fund the lands and buildings for public schools. With the 1868 elections, the first county school commissioners took office. In 2014, the state spent $9,616 per student, compared with a national average of about $11,000 putting Arkansas in nineteenth place.Timeline
* 1829 Territorial legislature permits townships to establish schools * 1868 State law requires racial segregation of schools * 1871 University of Arkansas established * 1873 University of Arkansas at Pine Bluff established as a school to train black teachers * 1877 Philander Smith College established as a school for black students * 1890 Henderson State University established (as a private school, becoming Henderson ''State'' Teachers ''College'' in 1929) * 1885 Arkansas School for the Deaf and Arkansas School for the Blind established * 1909 Arkansas Tech University, Southern Arkansas University, University of Arkansas at Monticello and Arkansas State University established as schools offering high school diplomas and vocational training * Schooling made compulsory * 1925 University of Central Arkansas established (as Arkansas State Normal School) * 1948 University of Arkansas School of Law admits a black student * 1957 Governor Orval Faubus uses National Guard troops to oppose racial integration of Little Rock Central High School * 1958 United States Supreme Court Cooper v. Aaron, overrules the governor * 1983 Arkansas State Supreme Court rules that the state's funding of education is Constitutionally deficientMedia
As of 2010 many Arkansas local newspapers are owned by WEHCO Media, Alabama-based Lancaster Management, Kentucky-based Paxton Media Group, Missouri-based Rust Communications, Nevada-based Stephens Media (newspapers), Stephens Media, and New York-based GateHouse Media.Culture
 The culture of Arkansas includes distinct cuisine, dialect, and traditional festivals. Sports are also very important to the culture, including football, baseball, basketball, hunting, and fishing. Perhaps the best-known aspect of Arkansas's culture is the stereotype that its citizens are shiftless hillbillies. The reputation began when early explorers characterized the state as a savage wilderness full of outlaws and thieves. The most enduring icon of Arkansas's hillbilly reputation is ''Edward Washburn, The Arkansas Traveller'', a painted depiction of a folk tale from the 1840s. Though intended to represent the divide between rich southeastern plantation Arkansas planters and the poor northwestern hill country, the meaning was twisted to represent a Northerner lost in the Ozarks on a white horse asking a backwoods Arkansan for directions. The state also suffers from the racial stigma common to former Confederate states, with historical events such as the
The culture of Arkansas includes distinct cuisine, dialect, and traditional festivals. Sports are also very important to the culture, including football, baseball, basketball, hunting, and fishing. Perhaps the best-known aspect of Arkansas's culture is the stereotype that its citizens are shiftless hillbillies. The reputation began when early explorers characterized the state as a savage wilderness full of outlaws and thieves. The most enduring icon of Arkansas's hillbilly reputation is ''Edward Washburn, The Arkansas Traveller'', a painted depiction of a folk tale from the 1840s. Though intended to represent the divide between rich southeastern plantation Arkansas planters and the poor northwestern hill country, the meaning was twisted to represent a Northerner lost in the Ozarks on a white horse asking a backwoods Arkansan for directions. The state also suffers from the racial stigma common to former Confederate states, with historical events such as the Little Rock Nine
The Little Rock Nine were a group of nine African American students enrolled in Little Rock Central High School in 1957. Their enrollment was followed by the Little Rock Crisis, in which the students were initially prevented from entering ...
adding to Arkansas's enduring image.
Art and history museums display pieces of cultural value for Arkansans and tourists to enjoy. Crystal Bridges Museum of American Art in Bentonville was visited by 604,000 people in 2012, its first year. The museum includes walking trails and educational opportunities in addition to displaying over 450 works covering five centuries of American art. Several historic town sites have been restored as Arkansas List of Arkansas state parks, state parks, including Historic Washington State Park, Powhatan Historic State Park, and Davidsonville Historic State Park.
Arkansas features a variety of native music across the state, ranging from the blues heritage of West Memphis, Arkansas, West Memphis, Pine Bluff, HelenaŌĆōWest Helena, Arkansas, HelenaŌĆōWest Helena to rockabilly, bluegrass music, bluegrass, and folk music from the Ozarks. Festivals such as the King Biscuit Blues Festival and Bikes, Blues, and BBQ pay homage to the history of blues in the state. The Ozark Folk Festival in Mountain View, Arkansas, Mountain View is a celebration of Ozark culture and often features folk and bluegrass musicians. Literature set in Arkansas such as ''I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings'' by Maya Angelou
Maya Angelou ( ; born Marguerite Annie Johnson; April 4, 1928 ŌĆō May 28, 2014) was an American memoirist, popular poet, and civil rights activist. She published seven autobiographies, three books of essays, several books of poetry, and ...
and ''A Painted House'' by John Grisham
John Ray Grisham Jr. (; born February 8, 1955 in Jonesboro, Arkansas) is an American novelist, lawyer and former member of the 7th district of the Mississippi House of Representatives, known for his popular legal thrillers. According to the Am ...
describe the culture at various time periods.
Sports and recreation
 Sports have become an integral part of the culture of Arkansas, and her residents enjoy participating in and spectating various events throughout the year.
Team sports and especially collegiate football are important to Arkansans. College football in Arkansas began from humble beginnings, when the University of Arkansas first fielded a team in 1894 Arkansas Cardinals football team, 1894. Over the years, many Arkansans have looked to Arkansas Razorbacks football as the public image of the state. Although the University of Arkansas is based in Fayetteville, Arkansas, Fayetteville, the Razorbacks have always played at least one game per season at War Memorial Stadium (Arkansas), War Memorial Stadium in
Sports have become an integral part of the culture of Arkansas, and her residents enjoy participating in and spectating various events throughout the year.
Team sports and especially collegiate football are important to Arkansans. College football in Arkansas began from humble beginnings, when the University of Arkansas first fielded a team in 1894 Arkansas Cardinals football team, 1894. Over the years, many Arkansans have looked to Arkansas Razorbacks football as the public image of the state. Although the University of Arkansas is based in Fayetteville, Arkansas, Fayetteville, the Razorbacks have always played at least one game per season at War Memorial Stadium (Arkansas), War Memorial Stadium in Little Rock
( The "Little Rock")
, government_type = Council-manager
, leader_title = Mayor
, leader_name = Frank Scott Jr.
, leader_party = D
, leader_title2 = Council
, leader_name2 ...
in an effort to keep fan support in central and south Arkansas.
Arkansas State University became the second NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) (then known as Division I-A) team in the state in 1992 after playing in lower divisions for nearly two decades. The two schools have never played each other, due to the University of Arkansas's policy of not playing intrastate games. Two other campuses of the University of Arkansas System are Division I members. The University of Arkansas at Pine Bluff is a member of the Southwestern Athletic Conference, a league whose members all play football in the second-level Football Championship Subdivision (FCS). The University of Arkansas at Little Rock, known for sports purposes as Little Rock, joined the Ohio Valley Conference in 2022 after playing in the Sun Belt Conference; unlike many other OVC members, it does not field List of NCAA Division I non-football programs, a football program. The state's other DivisionI member is the University of Central Arkansas (UCA), which joined the ASUN Conference in 2021 after leaving the FCS Southland Conference. Because the ASUN does not plan to start FCS football competition until at least 2022, UCA football is competing in the Western Athletic Conference as part of a formal football partnership between the two leagues. Seven of Arkansas's smaller colleges play in NCAA Division II, with six in the Great American Conference and one in the Lone Star Conference. Two other small Arkansas colleges compete in NCAA Division III, in which athletic scholarships are prohibited. High school football also began to grow in Arkansas in the early 20th century.
Baseball runs deep in Arkansas and was popular before the state hosted Major League Baseball (MLB) spring training in Hot Springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
from 1886 to the 1920s. Two Minor League Baseball, minor league teams are based in the state. The Arkansas Travelers play at DickeyŌĆōStephens Park in North Little Rock, Arkansas, North Little Rock, and the Northwest Arkansas Naturals play in Arvest Ballpark in Springdale, Arkansas, Springdale. Both teams compete in Double-A Central.
Hunting continues in the state. The state created the Arkansas Game and Fish Commission in 1915 to regulate hunting. Today a significant portion of Arkansas's population participates in hunting duck in the Mississippi flyway and deer across the state.Sutherlin 1996, p. 164. Ducks Unlimited has called Stuttgart, Arkansas, "the epicenter of the duck universe". Millions of acres of public land are available for both bow and modern gun hunters.
Fishing has always been popular in Arkansas, and the sport and the state have benefited from the creation of reservoirs across the state. Following the completion of Norfork Dam, the Norfork Tailwater and the White River (Arkansas), White River have become a destination for trout fishers. Several smaller retirement communities such as Bull Shoals, Arkansas, Bull Shoals, Hot Springs Village, Arkansas, Hot Springs Village, and Fairfield Bay, Arkansas, Fairfield Bay have flourished due to their position on a fishing lake. The National Park Service has preserved the Buffalo National River in its natural state and fly fishers visit it annually.
Attractions
 Arkansas is home to many areas protected by the National Park System. These include:
* Arkansas Post National Memorial at Gillett, Arkansas, Gillett
* Blanchard Springs Caverns
* Buffalo National River
* Fort Smith National Historic Site
* Hot Springs National Park
* Little Rock Central High School National Historic Site
* Pea Ridge National Military Park
* President William Jefferson Clinton Birthplace Home National Historic Site
* Arkansas State Capitol Building
* List of Arkansas state parks
Arkansas is home to many areas protected by the National Park System. These include:
* Arkansas Post National Memorial at Gillett, Arkansas, Gillett
* Blanchard Springs Caverns
* Buffalo National River
* Fort Smith National Historic Site
* Hot Springs National Park
* Little Rock Central High School National Historic Site
* Pea Ridge National Military Park
* President William Jefferson Clinton Birthplace Home National Historic Site
* Arkansas State Capitol Building
* List of Arkansas state parks
See also
* Index of Arkansas-related articles * Outline of Arkansas * Spanish Empire * History of Louisiana * '''' * ''''Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Blair, Diane D. & Jay Barth ''Arkansas Politics & Government: Do the People Rule?'' (2005) * Deblack, Thomas A. ''With Fire and Sword: Arkansas, 1861ŌĆō1874'' (2003) * Donovan, Timothy P. and Willard B. Gatewood Jr., eds. ''The Governors of Arkansas'' (1981) * Dougan, Michael B. ''Confederate Arkansas'' (1982), * Duvall, Leland. ed., ''Arkansas: Colony and State'' (1973)Hamilton, Peter Joseph. ''The Reconstruction Period''
(1906), full length history of era; Dunning School approach; 570 pp; ch 13 on Arkansas * Hanson, Gerald T. and Carl H. Moneyhon. ''Historical Atlas of Arkansas'' (1992) * Key, V. O. ''Southern Politics'' (1949) * Kirk, John A., ''Redefining the Color Line: Black Activism in Little Rock, Arkansas, 1940ŌĆō1970'' (2002). * McMath, Sidney S. ''Promises Kept'' (2003) * Moore, Waddy W. ed., ''Arkansas in the Gilded Age, 1874ŌĆō1900'' (1976). * Peirce, Neal R. ''The Deep South States of America: People, Politics, and Power in the Seven Deep South States'' (1974). * Thompson, Brock. ''The Un-Natural State: Arkansas and the Queer South'' (2010) * Thompson, George H. ''Arkansas and Reconstruction'' (1976) * Whayne, Jeannie M. ''Arkansas Biography: A Collection of Notable Lives'' (2000) * White, Lonnie J. ''Politics on the Southwestern Frontier: Arkansas Territory, 1819ŌĆō1836'' (1964) * Williams, C. Fred. ed. ''A Documentary History Of Arkansas'' (2005)
External links
Arkansas.gov
ĆöOfficial State Website
Arkansas State Facts from USDA
Official State tourism website
''Encyclopedia of Arkansas''
Energy & Environmental Data for Arkansas
2000 Census of Population and Housing for Arkansas
U.S. Census Bureau
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Arkansas
Arkansas Summer Camps
Arkansas Shakespeare Theatre
* * *
Arkansas State Code (the state statutes of Arkansas)
Arkansas State Databases
ĆöAnnotated list of searchable databases produced by Arkansas state agencies and compiled by the Government Documents Roundtable of the American Library Association. {{coord, 35, -92, dim:300000_region:US-AR_type:adm1st, name=State of Arkansas, display=title Arkansas, 1836 establishments in the United States South Central United States Southern United States States and territories established in 1836 States of the Confederate States of America States of the United States Contiguous United States