Argo (NASA Spacecraft) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 ''Argo'' was a 2009 spacecraft mission concept by
''Argo'' was a 2009 spacecraft mission concept by White Paper: Argo Mission to Neptune, Triton, and a KBO
''Future Planetary Exploration'', 30 August 2009. The concept included flybys of
Future Planetary Exploration - ''Argo''
Proposed NASA space probes Missions to Neptune Triton (moon) {{spacecraft-stub
 ''Argo'' was a 2009 spacecraft mission concept by
''Argo'' was a 2009 spacecraft mission concept by NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
to the outer planets
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
and beyond.''Future Planetary Exploration'', 30 August 2009. The concept included flybys of
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but ...
, Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
, Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times ...
, and a Kuiper belt object
The Kuiper belt () is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times ...
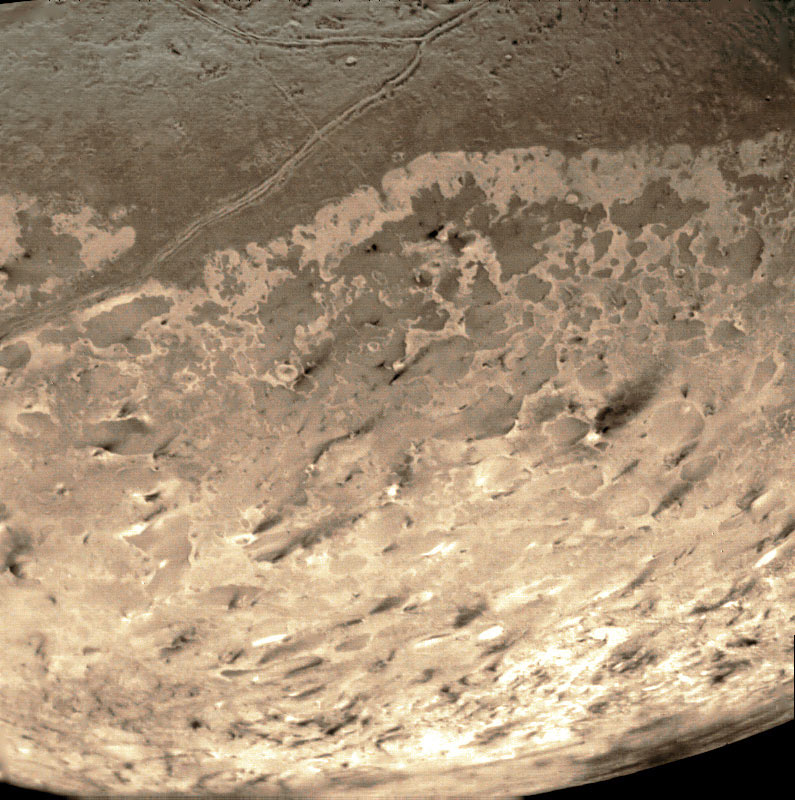
. A focus on Neptune and its largest moon Triton
Triton commonly refers to:
* Triton (mythology), a Greek god
* Triton (moon), a satellite of Neptune
Triton may also refer to:
Biology
* Triton cockatoo, a parrot
* Triton (gastropod), a group of sea snails
* ''Triton'', a synonym of ''Triturus' ...
would have helped answer some of the questions generated by ''Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, ''Voyager 1'', on a ...
'' flyby in 1989, and would have provided clues to ice giant
An ice giant is a giant planet composed mainly of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, such as oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. There are two ice giants in the Solar System: Uranus and Neptune.
In astrophysics and planetary science t ...
formation and evolution.
Mission
The ''Argo'' mission was meant to compete for the New Frontiers mission 4 (~$650M). One of the reasons ''Argo'' was not formally proposed was the shortage ofplutonium-238
Plutonium-238 (238Pu or Pu-238) is a fissile, radioactive isotope of plutonium that has a half-life of 87.7 years.
Plutonium-238 is a very powerful alpha emitter; as alpha particles are easily blocked, this makes the plutonium-238 isotope suitab ...
for the required radioisotope thermoelectric generator
A radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG, RITEG), sometimes referred to as a radioisotope power system (RPS), is a type of nuclear battery that uses an array of thermocouples to convert the heat released by the decay of a suitable radioacti ...
(RTG) for electric power. The current launch window for this mission had been particularly favorable. It opened in 2015 and lasted through the end of 2019, so future missions would need to be redesigned for the relevant planetary alignments.
It was noted that although it offered a Neptune mission at the price of New Frontier's budget, it would be flyby only, limiting the amount of time at Neptune and Triton compared to an orbiter. However, the advantage would be access to a wide variety of Kuiper belt objects by using a gravity assist
In orbital mechanics and aerospace engineering, a gravitational slingshot, gravity assist maneuver, or swing-by is the use of the relative movement (e.g. orbit around the Sun) and gravity of a planet or other astronomical object to alter the p ...
at Neptune, which would allow a wide range of objects to potentially be targeted. In addition, with a flyby of Jupiter and Saturn, the Planetary Society compared the mission to ''Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, ''Voyager 1'', on a ...
''.
Itinerary
During its flybys of the giant planets, there would have been potentially well over 100 other moons that could have been studied, and beyond Neptune, the possibility of visiting Kuiper belt objects.See also
*''New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research ...
'' probe, performed a Pluto flyby in 2015
*''New Horizons 2
''New Horizons 2'' (also ''New Horizons II'', NHII, or NH2) was a proposed mission to the trans-Neptunian objects by NASA. It was conceived as a planetary flyby mission in 2002, based on the ''New Horizons'' spacecraft, which was in development ...
''
References
External links
Future Planetary Exploration - ''Argo''
Proposed NASA space probes Missions to Neptune Triton (moon) {{spacecraft-stub