Areas Annexed By Nazi Germany on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

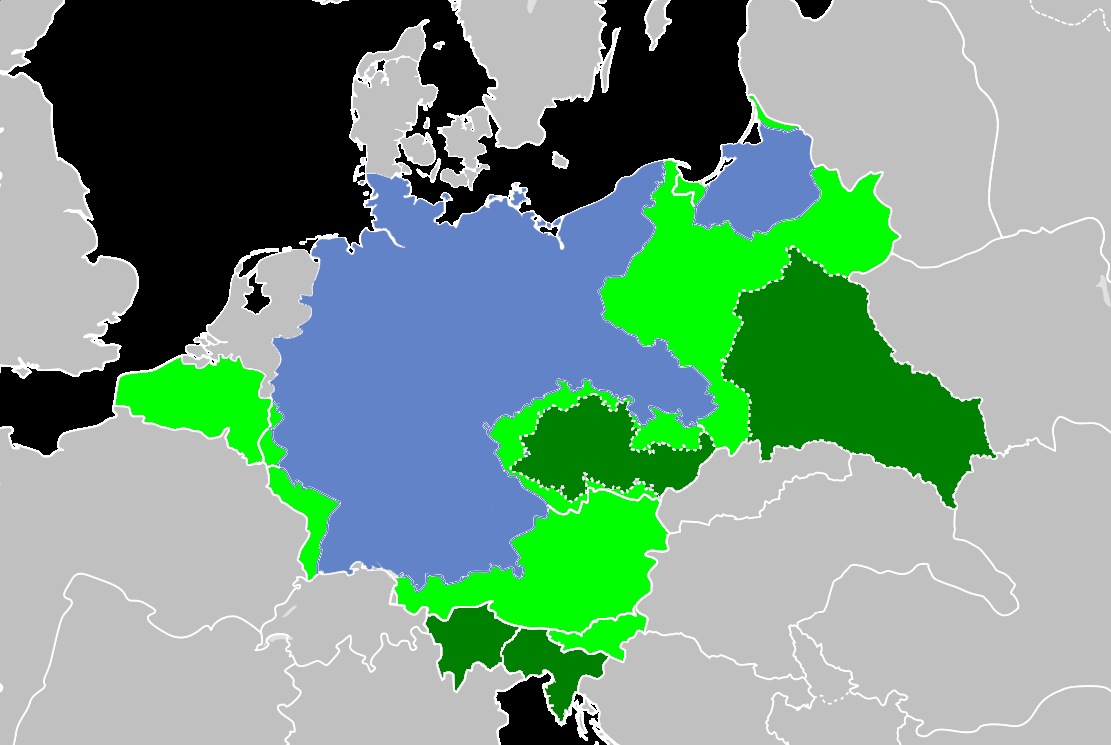 There were many areas annexed by Germany both immediately before and throughout the course of
There were many areas annexed by Germany both immediately before and throughout the course of

 There were many areas annexed by Germany both immediately before and throughout the course of
There were many areas annexed by Germany both immediately before and throughout the course of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. Territories that were part of Germany before the annexations were known as the "Altreich" (Old Reich).
Fully annexed territories
According to theTreaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
, the Territory of the Saar Basin
The Territory of the Saar Basin (german: Saarbeckengebiet, ; french: Territoire du bassin de la Sarre) was a region of Germany occupied and governed by the United Kingdom and France from 1920 to 1935 under a League of Nations mandate. It had its ...
was split from Germany for at least 15 years. In 1935, the Saarland rejoined Germany in a lawful way after a plebiscite.
The territories listed below are those that were fully annexed
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
into Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
proper.
Partially incorporated territories
The territories listed below are those that were partially incorporated into the Greater German Reich.Planned annexations
In the coming Nazi New Order, other lands were considered for annexation sooner or later, for instanceNorth Schleswig
Southern Jutland ( da, Sønderjylland; German: Südjütland) is the name for the region south of the Kongeå in Jutland, Denmark and north of the Eider (river) in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The region north of the Kongeå is called da, Nørr ...
, German-speaking Switzerland
The German-speaking part of Switzerland (german: Deutschschweiz, french: Suisse alémanique, it, Svizzera tedesca, rm, Svizra tudestga) comprises about 65 percent of Switzerland (North Western Switzerland, Eastern Switzerland, Central Switz ...
, and the zone of intended German settlement in north-eastern France, where a Gau or a Reichskommissariat centred on Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The c ...
was intended for creation, and which Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was of the (Protection Squadron; SS), and a leading member of the Nazi Party of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of th ...
wanted to turn into the SS's very own fiefdom The goal was to unite all or as many as possible ethnic Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
and Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
, including non-Germanic speaking ones considered "Aryans", in a Greater Germanic Reich
The Greater Germanic Reich (german: Großgermanisches Reich), fully styled the Greater Germanic Reich of the German Nation (german: Großgermanisches Reich deutscher Nation), was the official state name of the political entity that Nazi Germany ...
.
The eastern Reichskommissariat
''Reichskommissariat'' ( en, Imperial Commissariat) is a German word for a type of administrative entity headed by a government official known as a ''Reichskommissar'' ( en, Imperial Commissioner). Although many offices existed, primarily throug ...
s in the vast stretches of Ukraine and Russia were also intended for future integration into that Reich, with plans for them stretching to the Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the List of rivers of Europe#Rivers of Europe by length, longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Cas ...
or even beyond the Urals
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through European ...
, where the potential westernmost reaches of Imperial Japanese influence would have existed, following an Axis victory in World War II
A hypothetical military victory of the Axis powers over the Allies of World War II (1939–1945) is a common topic in speculative literature. Works of alternative history (fiction) and of counterfactual history (non-fiction), including stories, ...
. They were deemed of vital interest for the survival of the German nation, as it was a core tenet of Nazism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Na ...
that Germany needed "living space" (''Lebensraum
(, ''living space'') is a German concept of settler colonialism, the philosophy and policies of which were common to German politics from the 1890s to the 1940s. First popularized around 1901, '' lso in:' became a geopolitical goal of Imperi ...
''), creating a "pull towards the East" (''Drang nach Osten
(; 'Drive to the East',Ulrich Best''Transgression as a Rule: German–Polish cross-border cooperation, border discourse and EU-enlargement'' 2008, p. 58, , Edmund Jan Osmańczyk, Anthony Mango, ''Encyclopedia of the United Nations and Interna ...
'') where that could be found and colonized
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When ...
.
North-East Italy
In European elections, North-East Italy is a constituency of the European Parliament. It consists of the regions of Emilia-Romagna, Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol and Veneto
Veneto (, ; vec, Vèneto ) or Venetia is ...
was also eventually to be annexed, including both the Operational Zone of the Adriatic Littoral
The Operational Zone of the Adriatic Littoral (german: Operationszone Adriatisches Küstenland, OZAK; or colloquially: ''Operationszone Adria''; it, Zona d'operazioni del Litorale adriatico; hr, Operativna zona Jadransko primorje; sl, Operacijs ...
and the Operational Zone of the Alpine Foothills
The Operational Zone of the Alpine Foothills (german: Operationszone Alpenvorland (OZAV); it, Zona d'operazione delle Prealpi) was a Nazi German occupation zone in the sub-Alpine area in Italy during World War II.
Origin and geography
OZAV was ...
, but also the Venice region. Goebbels went as far as to suggest taking control of Lombardy
Lombardy ( it, Lombardia, Lombard language, Lombard: ''Lombardia'' or ''Lumbardia' '') is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in the northern-central part of the country and has a population of about 10 ...
as well:
The annexation of the entire North Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative regions ...
was also suggested in the long run.Kersten 1947, p. 186.
See also
*''Alldeutscher Verband
The Pan-German League (german: Alldeutscher Verband) was a Pan-German nationalist organization which was officially founded in 1891, a year after the Zanzibar Treaty was signed.
Primarily dedicated to the German Question of the time, it held pos ...
''
*''Blut und Boden
Atrocity is a German heavy metal band from Ludwigsburg that formed in 1985.
History
First started in 1985 as Instigators and playing grindcore, Atrocity arose as a death metal band with their debut EP, ''Blue Blood'', in 1989, followed soon b ...
''
*Former eastern territories of Germany
The former eastern territories of Germany (german: Ehemalige deutsche Ostgebiete) refer in present-day Germany to those territories east of the current eastern border of Germany i.e. Oder–Neisse line which historically had been considered Ger ...
*''Generalplan Ost
The ''Generalplan Ost'' (; en, Master Plan for the East), abbreviated GPO, was the Nazi German government's plan for the genocide and ethnic cleansing on a vast scale, and colonization of Central and Eastern Europe by Germans. It was to be un ...
''
*German Question
The "German question" was a debate in the 19th century, especially during the Revolutions of 1848, over the best way to achieve a unification of Germany, unification of all or most lands inhabited by Germans. From 1815 to 1866, about 37 independ ...
*''Heim ins Reich
The ''Heim ins Reich'' (; meaning "back home to the Reich") was a foreign policy pursued by Adolf Hitler before and during World War II, beginning in 1938. The aim of Hitler's initiative was to convince all ''Volksdeutsche'' (ethnic Germans) wh ...
''
*''Ostsiedlung
(, literally "East-settling") is the term for the Early Medieval and High Medieval migration-period when ethnic Germans moved into the territories in the eastern part of Francia, East Francia, and the Holy Roman Empire (that Germans had al ...
''
*Pan-Germanism
Pan-Germanism (german: Pangermanismus or '), also occasionally known as Pan-Germanicism, is a pan-nationalist political idea. Pan-Germanists originally sought to unify all the German-speaking people – and possibly also Germanic-speaking ...
*Recovered Territories
The Recovered Territories or Regained Lands ( pl, Ziemie Odzyskane), also known as Western Borderlands ( pl, Kresy Zachodnie), and previously as Western and Northern Territories ( pl, Ziemie Zachodnie i Północne), Postulated Territories ( pl, Z ...
*Territorial evolution of Germany
The territorial evolution of Germany include all of changes on the territorial borders of Germany. Modern Germany was formed in 1871 when Kingdom of Prussia unified most of the German states, with the notable exception of Austria, into the Ger ...
*''Volk ohne Raum
"" (; "people without space") was a political slogan used in the Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany. The term was coined by the nationalist writer Hans Grimm with his novel ''Volk ohne Raum'' (1926). The novel immediately attracted much attention an ...
''
*''Volksdeutsche
In Nazi German terminology, ''Volksdeutsche'' () were "people whose language and culture had German origins but who did not hold German citizenship". The term is the nominalised plural of '' volksdeutsch'', with ''Volksdeutsche'' denoting a sin ...
''
*''Wehrbauer
''Wehrbauer'' (, ''defensive peasant''), plural ''Wehrbauern'', is a German term for settlers living on the marches of a realm, who were tasked with holding back foreign invaders until the arrival of proper military reinforcements. In turn, they w ...
''
Notes
{{Authority control Aftermath of World War I in Germany Borders of Germany Foreign relations of Nazi Germany German colonial empire German diaspora in Europe Pan-GermanismGermany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
German irredentism
Axis powers