Ardea Cinerea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The grey heron (''Ardea cinerea'') is a long-legged wading bird of the

 Herons are a fairly ancient lineage and first appeared in the fossil record in the
Herons are a fairly ancient lineage and first appeared in the fossil record in the
 The grey heron is a large bird, standing up to tall and measuring long with a wingspan. The body weight can range from . The
The grey heron is a large bird, standing up to tall and measuring long with a wingspan. The body weight can range from . The
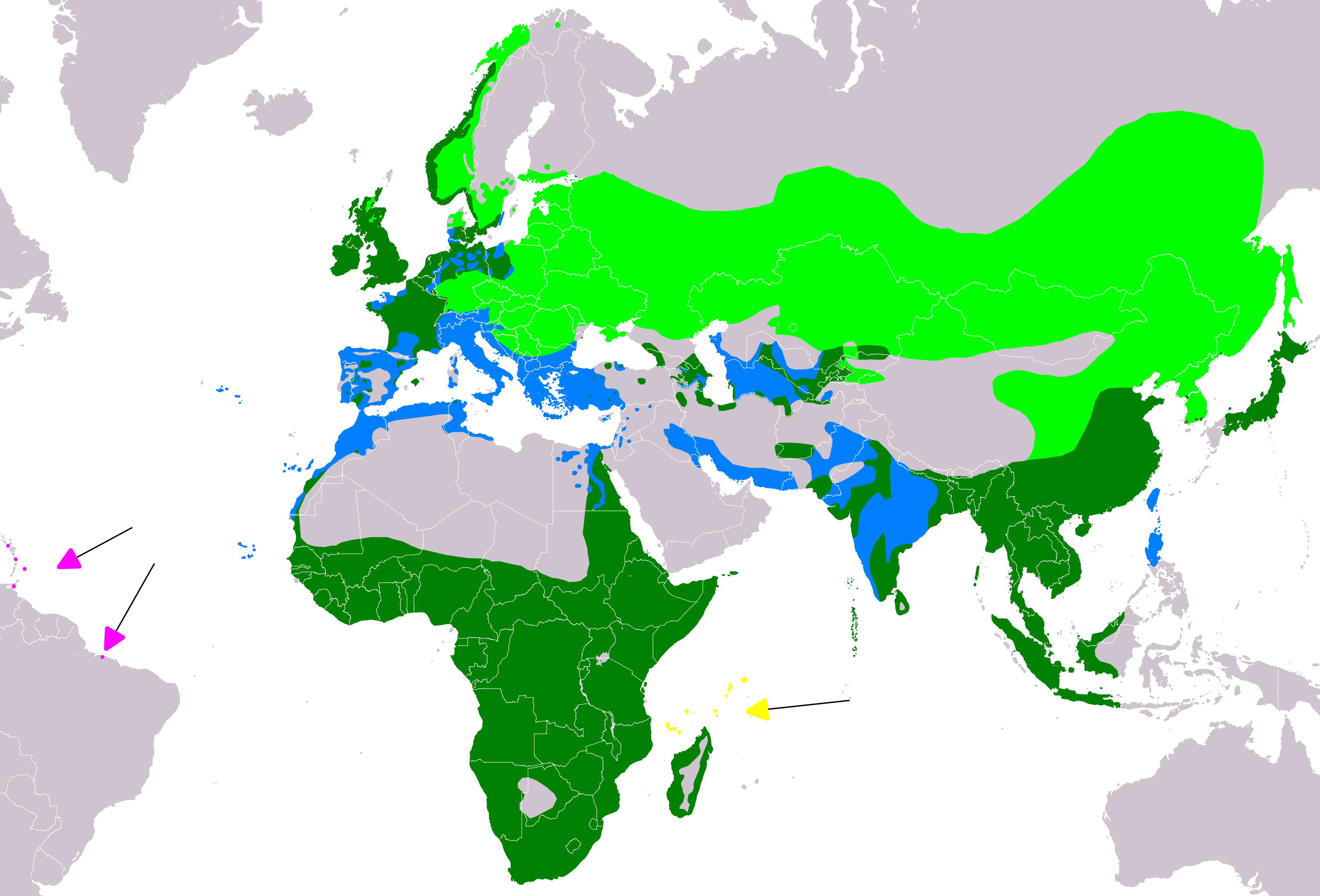 The grey heron has an extensive range throughout most of the Palearctic realm. The range of the nominate subspecies ''A. c. cinerea'' extends to 70° N in Norway and 66°N in Sweden, but otherwise its northerly limit is around 60°N across the rest of Europe and Asia eastwards as far as the Ural Mountains. To the south, its range extends to northern Spain, France, central Italy, the Balkans, the Caucasus, Iraq, Iran, India, The Maldives and Myanmar (Burma). It is also present in Africa south of the Sahara Desert, the
The grey heron has an extensive range throughout most of the Palearctic realm. The range of the nominate subspecies ''A. c. cinerea'' extends to 70° N in Norway and 66°N in Sweden, but otherwise its northerly limit is around 60°N across the rest of Europe and Asia eastwards as far as the Ural Mountains. To the south, its range extends to northern Spain, France, central Italy, the Balkans, the Caucasus, Iraq, Iran, India, The Maldives and Myanmar (Burma). It is also present in Africa south of the Sahara Desert, the
 Grey herons are apex predator in the aquatic ecosystems. Fish,
Grey herons are apex predator in the aquatic ecosystems. Fish,
 This species breeds in colonies known as heronries, usually in high trees close to lakes, the seashore, or other wetlands. Other sites are sometimes chosen, and these include low trees and bushes, bramble patches,
This species breeds in colonies known as heronries, usually in high trees close to lakes, the seashore, or other wetlands. Other sites are sometimes chosen, and these include low trees and bushes, bramble patches,  The
The
 In Ancient Egypt, the bird
In Ancient Egypt, the bird
heron
The herons are long-legged, long-necked, freshwater and coastal birds in the family Ardeidae, with 72 recognised species, some of which are referred to as egrets or bitterns rather than herons. Members of the genera ''Botaurus'' and ''Ixobrychus ...
family, Ardeidae, native throughout temperate Europe and Asia and also parts of Africa. It is resident in much of its range, but some populations from the more northern parts migrate
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
southwards in autumn. A bird of wetland areas, it can be seen around lakes, rivers, ponds, marshes and on the sea coast. It feeds mostly on aquatic creatures which it catches after standing stationary beside or in the water or stalking its prey through the shallows.
Standing up to tall, adults weigh from . They have a white head and neck with a broad black stripe that extends from the eye to the black crest. The body and wings are grey above and the underparts are greyish-white, with some black on the flanks. The long, sharply pointed beak is pinkish-yellow and the legs are brown.
The birds breed colonially in spring in "heronries", usually building their nests high in trees. A clutch of usually three to five bluish-green eggs is laid. Both birds incubate the eggs for around 25 days, and then both feed the chicks, which fledge when 7-8 weeks old. Many juveniles do not survive their first winter, but if they do, they can expect to live for about 5 years.
In Ancient Egypt, the deity
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greate ...
Bennu was depicted as a heron in New Kingdom artwork.
In Ancient Rome, the heron was a bird of divination
Divination (from Latin ''divinare'', 'to foresee, to foretell, to predict, to prophesy') is the attempt to gain insight into a question or situation by way of an occultic, standardized process or ritual. Used in various forms throughout histor ...
. Roast heron was once a specially prized dish; when George Neville became Archbishop of York in 1465, 400 herons were served to the guests.
Taxonomy

 Herons are a fairly ancient lineage and first appeared in the fossil record in the
Herons are a fairly ancient lineage and first appeared in the fossil record in the Paleogene
The Paleogene ( ; British English, also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period, geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million yea ...
period; very few fossil herons have been found, though. By seven million years ago (the late Miocene), birds closely resembling modern forms and attributable to modern genera had appeared.
Herons are members of the family Ardeidae, and the majority of extant
Extant is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Extant taxon, a taxon which is not extinct, ...
species are in the subfamily Ardeinae
Ardeinae is a subfamily of herons, which includes the day herons, night herons, and egrets.
Taxonomy
* Genus ''Zeltornis'' (fossil, Early Miocene of Djebel Zelten, Libya)
* Genus ''Nycticorax'' – typical night herons (two living species, fou ...
and known as true or typical herons. This subfamily includes the herons and egrets, the green herons
The green heron (''Butorides virescens'') is a small heron of North and Central America. ''Butorides'' is from Middle English ''butor'' "bittern" and Ancient Greek ''-oides'', "resembling", and ''virescens'' is Latin for "greenish".
It was long c ...
, the pond heron
Pond herons (''Ardeola'') are herons, typically long with an wingspan. Most breed in the tropical Old World, but the migratory squacco heron occurs in southern Europe and the Middle East and winters in Africa. The scientific name comes fro ...
s, the night herons, and a few other species. The grey heron belongs in this subfamily.
The grey heron was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nomen ...
''. He placed it with the cattle egret and the great egret in the genus '' Ardea'' and coined the binomial name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ...
''Ardea cinerea''. The scientific name comes the Latin ''ardea'' meaning "heron" and ''cinereus'' meaning "ash-grey" or "ash-coloured".
Four subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
are recognised:
* ''A. c. cinerea'' – Linnaeus, 1758
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Swedish biologist Carl Linnaeus (Carl von Linné) publishes in Stockholm the first volume (''Animalia'') of the 10th edition of Systema Naturae, 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'', the sta ...
: nominate, found in Europe, Africa, western Asia
* ''A. c. jouyi'' – Clark, 1907: found in eastern Asia
* ''A. c. firasa'' – Hartert
Ernst Johann Otto Hartert (29 October 1859 – 11 November 1933) was a widely published German ornithologist.
Life and career
Hartert was born in Hamburg, Germany on 29 October 1859. In July 1891, he married the illustrator Claudia Bernadine E ...
, 1917: found in Madagascar
* ''A. c. monicae'' – Jouanin & Roux, 1963: found on islands off Banc d'Arguin
The Banc d'Arguin National Park ( ar, حوض أركين) of Bay of Arguin lies in Western Africa on the west coast of Mauritania between Nouakchott and Nouadhibou and is the former mouth of the Tamanrasset River. The World Heritage Site is a ...
, Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
.
It is closely related and similar to the North American great blue heron
The great blue heron (''Ardea herodias'') is a large wading bird in the heron family Ardeidae, common near the shores of open water and in wetlands over most of North America and Central America, as well as the Caribbean and the Galápagos ...
(''Ardea herodias''), which differs in being larger, and having chestnut-brown flanks and thighs, and to the cocoi heron (''Ardea cocoi'') from South America with which it forms a superspecies. Some authorities believe that the subspecies ''A. c. monicae'' should be considered a separate species. It has been known to hybridise with the great egret (''Ardea alba''), the little egret (''Egretta garzetta''), the great blue heron and the purple heron (''Ardea purpurea''). The Australian white-faced heron is often incorrectly called a grey heron. In Ireland, the grey heron is often colloquially called a "crane".
Description
 The grey heron is a large bird, standing up to tall and measuring long with a wingspan. The body weight can range from . The
The grey heron is a large bird, standing up to tall and measuring long with a wingspan. The body weight can range from . The plumage
Plumage ( "feather") is a layer of feathers that covers a bird and the pattern, colour, and arrangement of those feathers. The pattern and colours of plumage differ between species and subspecies and may vary with age classes. Within species, ...
is largely ashy-grey above, and greyish-white below with some black on the flanks. Adults have the head and neck white with a broad black supercilium
The supercilium is a plumage feature found on the heads of some bird species. It is a stripe which runs from the base of the bird's beak above its eye, finishing somewhere towards the rear of the bird's head.Dunn and Alderfer (2006), p. 10 Also ...
that terminates in the slender, dangling crest, and bluish-black streaks on the front of the neck. The scapular feathers are elongated and the feathers at the base of the neck are also somewhat elongated. Immature birds lack the dark stripe on the head and are generally duller in appearance than adults, with a grey head and neck, and a small, dark grey crest. The pinkish-yellow beak is long, straight and powerful, and is brighter in colour in breeding adults. The iris is yellow and the legs are brown and very long.
The main call is a loud croaking "fraaank", but a variety of guttural and raucous noises is heard at the breeding colony. The male uses an advertisement call to encourage a female to join him at the nest, and both sexes use various greeting calls after a pair bond has been established. A loud, harsh "schaah" is used by the male in driving other birds from the vicinity of the nest and a soft "gogogo" expresses anxiety, as when a predator is nearby or a human walks past the colony. The chicks utter loud chattering or ticking noises.
Distribution and habitat
 The grey heron has an extensive range throughout most of the Palearctic realm. The range of the nominate subspecies ''A. c. cinerea'' extends to 70° N in Norway and 66°N in Sweden, but otherwise its northerly limit is around 60°N across the rest of Europe and Asia eastwards as far as the Ural Mountains. To the south, its range extends to northern Spain, France, central Italy, the Balkans, the Caucasus, Iraq, Iran, India, The Maldives and Myanmar (Burma). It is also present in Africa south of the Sahara Desert, the
The grey heron has an extensive range throughout most of the Palearctic realm. The range of the nominate subspecies ''A. c. cinerea'' extends to 70° N in Norway and 66°N in Sweden, but otherwise its northerly limit is around 60°N across the rest of Europe and Asia eastwards as far as the Ural Mountains. To the south, its range extends to northern Spain, France, central Italy, the Balkans, the Caucasus, Iraq, Iran, India, The Maldives and Myanmar (Burma). It is also present in Africa south of the Sahara Desert, the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
, Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, and many of the Mediterranean Islands. It is replaced by ''A. c. jouyi'' in eastern Siberia, Mongolia, eastern China, Hainan, Japan, and Taiwan. In Madagascar and the Aldabra Islands
The Aldabra Group are part of the Outer Islands of the Seychelles, lying in the southwest of the island nation, around from the capital, Victoria, on Mahé Island.
Population and area
The group contains four islands and atolls. The largest in ...
, the subspecies ''A. c. firasa'' is found, while the subspecies ''A. c. monicae'' is restricted to Mauritania and offshore islands.
Over much of its range, the grey heron is resident, but birds from the more northerly parts of Europe migrate southwards, some remaining in Central and Southern Europe, others travelling on to Africa south of the Sahara Desert.
The grey heron is also known to be vagrant
Vagrancy is the condition of homelessness without regular employment or income. Vagrants (also known as bums, vagabonds, rogues, tramps or drifters) usually live in poverty and support themselves by begging, scavenging, petty theft, temporar ...
in the Caribbean, Bermuda, Iceland, Greenland, the Aleutian Islands, and Newfoundland, with a few confirmed sightings in other parts of North America including Nova Scotia and Nantucket.
Within its range, the grey heron can be found anywhere with suitable watery habitat that can supply its food. The water body needs to be either shallow enough, or have a shelving margin in it, which it can wade. Although most common in the lowlands, it also occurs in mountain tarns, lakes, reservoirs, large and small rivers, marshes, ponds, ditches, flooded areas, coastal lagoons, estuaries, and the sea shore. It sometimes forages away from water in pasture, and it has been recorded in desert areas, hunting for beetles and lizards. Breeding colonies are usually near feeding areas, but exceptionally may be up to away, and birds sometimes forage as much as from the nesting site.
Behaviour
The grey heron has a slow flight, with its long neck retracted (S-shaped). This is characteristic of herons and bitterns, and distinguishes them fromstork
Storks are large, long-legged, long-necked wading birds with long, stout bills. They belong to the family called Ciconiidae, and make up the order Ciconiiformes . Ciconiiformes previously included a number of other families, such as herons an ...
s, crane
Crane or cranes may refer to:
Common meanings
* Crane (bird), a large, long-necked bird
* Crane (machine), industrial machinery for lifting
** Crane (rail), a crane suited for use on railroads
People and fictional characters
* Crane (surname) ...
s, and spoonbill
Spoonbills are a genus, ''Platalea'', of large, long-legged wading birds. The spoonbills have a global distribution, being found on every continent except Antarctica. The genus name ''Platalea'' derives from Ancient Greek and means "broad", refe ...
s, which extend their necks. It flies with slow wing-beats and sometimes glides for short distances. It sometimes soars, circling to considerable heights, but not as often as the stork. In spring, and occasionally in autumn, birds may soar high above the heronry and chase each other, undertake aerial manoeuvres or swoop down towards the ground. The birds often perch in trees, but spend much time on the ground, striding about or standing still for long periods with an upright stance, often on a single leg.Diet and feeding
 Grey herons are apex predator in the aquatic ecosystems. Fish,
Grey herons are apex predator in the aquatic ecosystems. Fish, amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
s, small mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s, crustaceans, and insects are taken in shallow water with the heron's long bill. It has also been observed catching and killing juvenile birds such as ducklings, and occasionally takes birds up to the size of a water rail and white-throated rail. It may stand motionless in the shallows, or on a rock or sandbank beside the water, waiting for prey to come within striking distance. Alternatively, it moves slowly and stealthily through the water with its body less upright than when at rest and its neck curved in an "S". It is able to straighten its neck and strike with its bill very quickly.
Small fish are swallowed head first, and larger prey and eels are carried to the shore where they are subdued by being beaten on the ground or stabbed by the bill. They are then swallowed, or have hunks of flesh torn off. For prey such as small mammals and birds or ducklings, the prey is held by the neck and either drowned, suffocated, having its neck snapped with the heron's beak or by being bludgeoned against the ground or a nearby rock, before being swallowed whole. The bird regurgitates pellets of indigestible material such as fur, bones and the chitinous remains of insects. The main periods of hunting are around dawn and dusk, but it is also active at other times of day. At night it roosts in trees or on cliffs, where it tends to be gregarious.
Breeding
 This species breeds in colonies known as heronries, usually in high trees close to lakes, the seashore, or other wetlands. Other sites are sometimes chosen, and these include low trees and bushes, bramble patches,
This species breeds in colonies known as heronries, usually in high trees close to lakes, the seashore, or other wetlands. Other sites are sometimes chosen, and these include low trees and bushes, bramble patches, reed bed
A reedbed or reed bed is a natural habitat found in floodplains, waterlogged depressions and
estuaries. Reedbeds are part of a succession from young reeds colonising open water or wet ground through a gradation of increasingly dry ground. As ...
s, heather clumps and cliff ledges. The same nest is used year after year until blown down; it starts as a small platform of sticks but expands into a bulky nest as more material is added in subsequent years. It may be lined with smaller twigs, strands of root or dead grasses, and in reed beds, it is built from dead reeds. The male usually collects the material, while the female constructs the nest. Breeding activities take place between February and June. When a bird arrives at the nest, a greeting ceremony occurs in which each partner raises and lowers its wings and plumes. In continental Europe, and elsewhere, nesting colonies sometimes include nests of the purple heron and other heron species.
Courtship involves the male calling from his chosen nesting site. On the arrival of the female, both birds participate in a stretching ceremony, in which each bird extends its neck vertically before bringing it backwards and downwards with the bill remaining vertical, simultaneously flexing its legs, before returning to its normal stance. The snapping ceremony is another behaviour where the neck is extended forward, the head is lowered to the level of the feet, and the mandibles are vigorously snapped together. This may be repeated 20-40 times. When the pairing is settled, the birds may caress each other by attending to the other bird's plumage. The male may then offer the female a stick, which she incorporates into the nest. At this, the male becomes excited, further preening the female and copulation takes place.
 The
The clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission, especially from a drive shaft to a driven shaft. In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts). ...
of eggs usually numbers three to five, though as few as two and as many as seven eggs have been recorded. The eggs have a matt surface and are greenish-blue, averaging . The eggs are normally laid at two-day intervals and incubation usually starts after the first or second egg has been laid. Both birds take part in incubation and the period lasts about 25 days. Both parents bring food for the young. At first, the chicks seize the adult's bill from the side and extract regurgitated food from it. Later, the adult disgorges the food at the nest and the chicks squabble for possession. They fledge
Fledging is the stage in a flying animal's life between hatching or birth and becoming capable of flight.
This term is most frequently applied to birds, but is also used for bats. For altricial birds, those that spend more time in vulnerable c ...
at 7-8 weeks. Usually, a single brood is raised each year, but two broods have been recorded.
The oldest recorded bird lived for 23 years, but the average life expectancy in the wild is about 5 years. Only about a third of juveniles survive into their second year, many falling victim to predation.
City life
Grey herons have the ability to live in cities where habitats and nesting space are available. In the Netherlands, it has established itself over the past decades in great numbers in urban environments. In cities such as Amsterdam, they are ever present and well adapted to modern city life. They hunt as usual, but also visit street markets and snackbars. Some individuals make use of people feeding them at their homes or share the catch of recreational fishermen. Similar behaviour on a smaller scale has been reported in Ireland. Garden ponds stocked with ornamental fish are attractive to herons, and may provide young birds with a learning opportunity on how to catch easy prey. Herons have been observed visiting water enclosures in zoos, such as spaces forpenguin
Penguins (order (biology), order List of Sphenisciformes by population, Sphenisciformes , family (biology), family Spheniscidae ) are a group of Water bird, aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: on ...
s, otter
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine, with diets based on fish and invertebrates. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which also includes wea ...
s, pelican
Pelicans (genus ''Pelecanus'') are a genus of large water birds that make up the family Pelecanidae. They are characterized by a long beak and a large throat pouch used for catching prey and draining water from the scooped-up contents before s ...
s, and seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
, and taking food meant for the animals on display.
Predators and parasites
Being large birds with powerful beaks, grey herons have few predators as adults, but the eggs and young are more vulnerable. The adult birds do not usually leave the nest unattended, but may be lured away by marauding crows or kites. A dead grey heron found in the Pyrenees is thought to have been killed by anotter
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine, with diets based on fish and invertebrates. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which also includes wea ...
. The bird may have been weakened by harsh winter weather causing scarcity of its prey.
A study suggested that Central European grey herons host 29 species of parasitic worms. The dominant species consisted of ''Apharyngostrigea cornu'' (67% prevalence), ''Posthodiplostomum cuticola'' (41% prevalence), ''Echinochasmus beleocephalus'' (39% prevalence), ''Uroproctepisthmium bursicola'' (36% prevalence), ''Neogryporhynchus cheilancristrotus'' (31% prevalence), ''Desmidocercella numidica'' (29% prevalence), and ''Bilharziella polonica'' (5% prevalence). Juvenile grey herons were shown to host fewer species, but the intensity of infection was higher in the juveniles than in the adult herons. Of the digenean flatworms found in Central European grey herons, 52% of the species likely infected their definitive hosts outside Central Europe itself, in the premigratory, migratory, or wintering quarters, despite the fact that a substantial proportion of grey herons does not migrate to the south.
In human culture
 In Ancient Egypt, the bird
In Ancient Egypt, the bird deity
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greate ...
Bennu, associated with the sun, creation, and rebirth, was depicted as a heron in New Kingdom artwork.
In Ancient Rome, the heron was a bird of divination
Divination (from Latin ''divinare'', 'to foresee, to foretell, to predict, to prophesy') is the attempt to gain insight into a question or situation by way of an occultic, standardized process or ritual. Used in various forms throughout histor ...
that gave an augury
Augury is the practice from ancient Roman religion of interpreting omens from the observed behavior of birds. When the individual, known as the augur, interpreted these signs, it is referred to as "taking the auspices". "Auspices" (Latin ''aus ...
(sign of a coming event) by its call, like the raven, stork, and owl.
Roast heron was once a specially prized dish in Britain for special occasions such as state banquets. For the appointment of George Neville as Archbishop of York in 1465, 400 herons were served to the guests. Young birds were still being shot and eaten in Romney Marsh in 1896. Two grey herons feature in a stained-glass
Stained glass is coloured glass as a material or works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although tradition ...
window of the church in Selborne, Hampshire.
The English surname
In some cultures, a surname, family name, or last name is the portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family, tribe or community.
Practices vary by culture. The family name may be placed at either the start of a person's full name ...
s Earnshaw, Hernshaw, Herne, and Heron all derive from the heron, the suffix -shaw meaning a wood, referring to a place where herons nested.
References
External links
* * {{Authority control grey heron grey heron Birds of Africa Birds of Eurasia grey heron grey heron Articles containing video clips Birds of Nepal ga:Corr réisc