Arctic S on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the
 The Arctic is characterized by cold winters and cool summers. Its precipitation mostly comes in the form of snow and is low, with most of the area receiving less than . High winds often stir up snow, creating the illusion of continuous snowfall. Average winter temperatures can go as low as , and the coldest recorded temperature is approximately . Coastal Arctic climates are moderated by oceanic influences, having generally warmer temperatures and heavier snowfalls than the colder and drier interior areas. The Arctic is affected by current
The Arctic is characterized by cold winters and cool summers. Its precipitation mostly comes in the form of snow and is low, with most of the area receiving less than . High winds often stir up snow, creating the illusion of continuous snowfall. Average winter temperatures can go as low as , and the coldest recorded temperature is approximately . Coastal Arctic climates are moderated by oceanic influences, having generally warmer temperatures and heavier snowfalls than the colder and drier interior areas. The Arctic is affected by current
 Arctic vegetation is composed of plants such as dwarf shrubs, graminoids, herbs, lichens, and mosses, which all grow relatively close to the ground, forming
Arctic vegetation is composed of plants such as dwarf shrubs, graminoids, herbs, lichens, and mosses, which all grow relatively close to the ground, forming
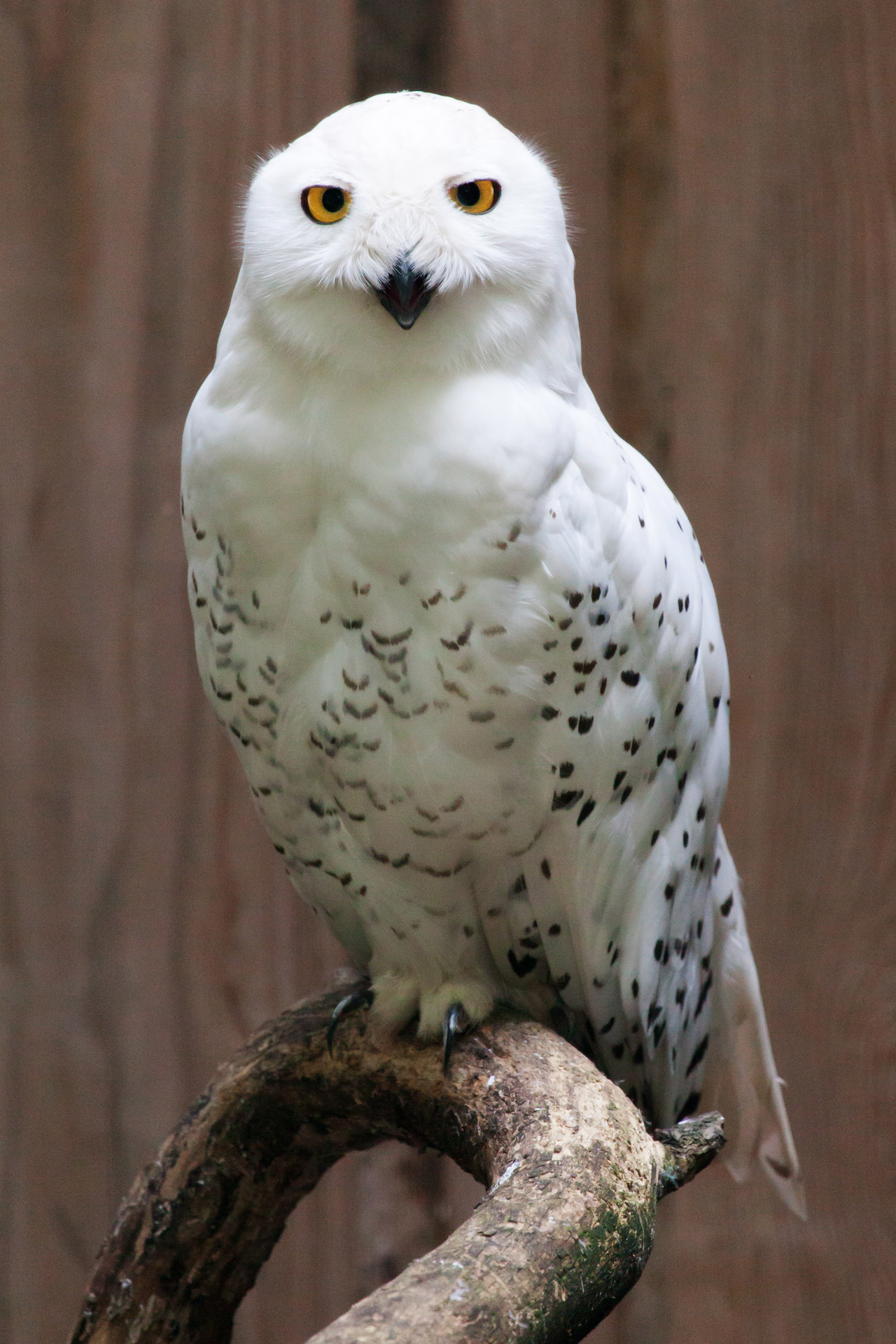
 Herbivores on the tundra include the
Herbivores on the tundra include the
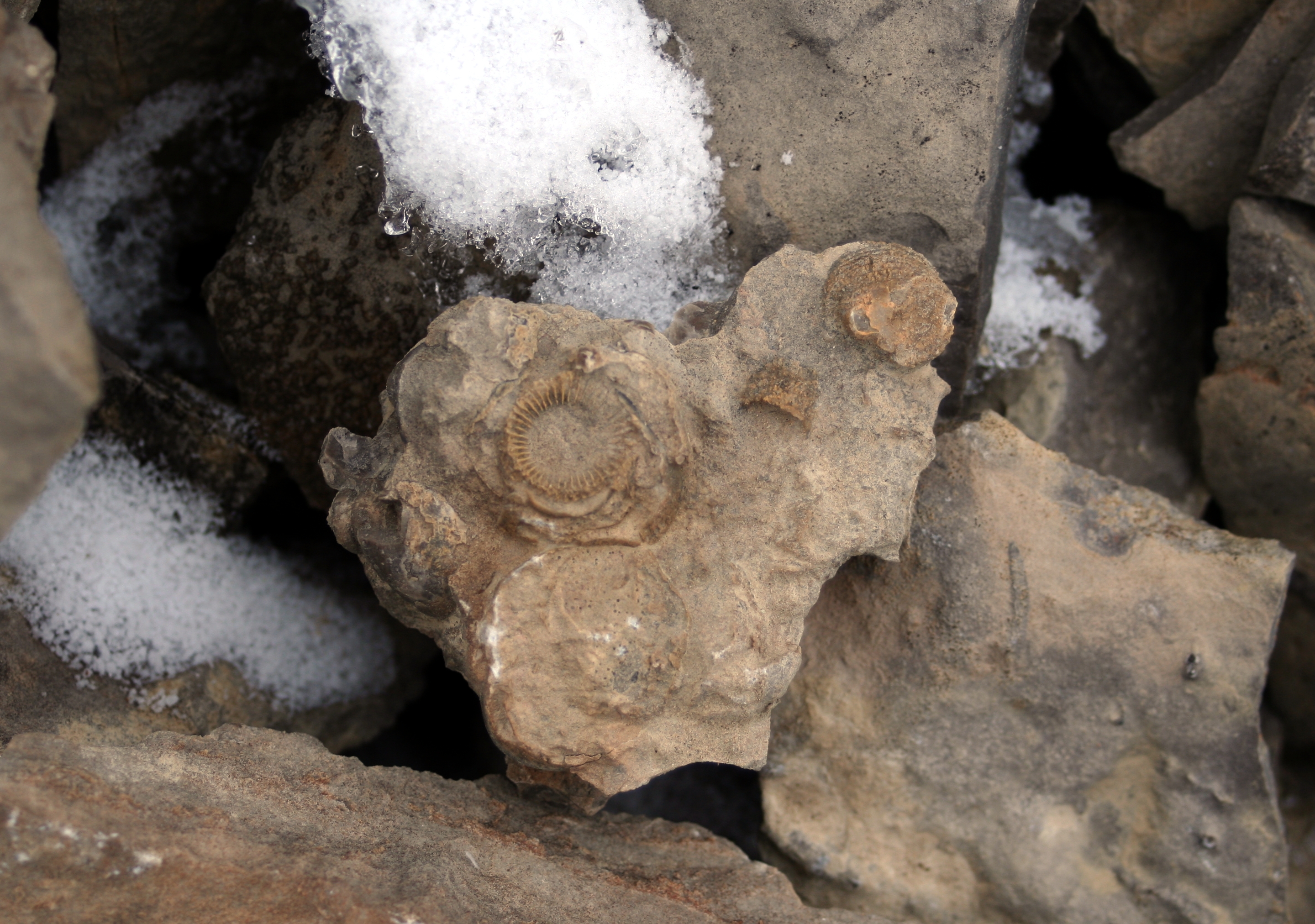 During the Cretaceous time period, the Arctic still had seasonal snows, though only a light dusting and not enough to permanently hinder plant growth. Animals such as the ''
During the Cretaceous time period, the Arctic still had seasonal snows, though only a light dusting and not enough to permanently hinder plant growth. Animals such as the ''
 The earliest inhabitants of North America's central and eastern Arctic are referred to as the
The earliest inhabitants of North America's central and eastern Arctic are referred to as the
 The eight Arctic nations (Canada, Kingdom of Denmark [Greenland & The Faroe Islands], Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Russia, and USA) are all members of the Arctic Council, as are organizations representing six indigenous populations. The council operates on consensus basis, mostly dealing with environmental treaties and not addressing boundary or resource disputes.
Though Arctic cooperation and politics, Arctic policy priorities differ, every Arctic nation is concerned about sovereignty/defense, resource development, shipping routes, and environmental protection. Much work remains on regulatory agreements regarding shipping, tourism, and Arctic resources race, resource development in Arctic waters. Arctic shipping is subject to some regulatory control through the International Code for Ships Operating in Polar Waters, adopted by the International Maritime Organization on 1 January 2017 and applies to all ships in Arctic waters over 500 tonnes.
Research in the Arctic has long been a collaborative international effort, evidenced by the International Polar Year. The International Arctic Science Committee, hundreds of scientists and specialists of the Arctic Council, and the Barents Euro-Arctic Council are more examples of collaborative international Arctic research.
The eight Arctic nations (Canada, Kingdom of Denmark [Greenland & The Faroe Islands], Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Russia, and USA) are all members of the Arctic Council, as are organizations representing six indigenous populations. The council operates on consensus basis, mostly dealing with environmental treaties and not addressing boundary or resource disputes.
Though Arctic cooperation and politics, Arctic policy priorities differ, every Arctic nation is concerned about sovereignty/defense, resource development, shipping routes, and environmental protection. Much work remains on regulatory agreements regarding shipping, tourism, and Arctic resources race, resource development in Arctic waters. Arctic shipping is subject to some regulatory control through the International Code for Ships Operating in Polar Waters, adopted by the International Maritime Organization on 1 January 2017 and applies to all ships in Arctic waters over 500 tonnes.
Research in the Arctic has long been a collaborative international effort, evidenced by the International Polar Year. The International Arctic Science Committee, hundreds of scientists and specialists of the Arctic Council, and the Barents Euro-Arctic Council are more examples of collaborative international Arctic research.
 Foreign ministers and other officials representing Canada, the Kingdom of Denmark, Norway, Russia, and the United States met in Ilulissat, Ilulissat, Greenland on 28 May 2008 at the Arctic Ocean Conference and announced the Ilulissat Declaration, blocking any "new comprehensive international legal regime to govern the Arctic Ocean," and pledging "the orderly settlement of any possible overlapping claims."
As of 2012, the Kingdom of Denmark is claiming the continental shelf based on the Lomonosov Ridge between Greenland and over the North Pole to the northern limit of the Russian EEZ.
The Russian Federation is also claiming a large swath of seabed along the Lomonosov Ridge but, unlike Denmark, confined its claim to its side of the Arctic. In August 2015, Russia made a supplementary submission for the expansion of the external borders of its continental shelf in the Arctic Ocean, asserting that the eastern part of the Lomonosov Ridge and the Mendeleyev Ridge are an extension of the Eurasian continent. In August 2016, the UN Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf began to consider Russia's submission.
Canada claims the Northwest Passage as part of its Canadian Internal Waters, internal waters belonging to Canada, while the United States and most maritime nations regards it as an Territorial waters, international strait, which means that foreign vessels have right of transit passage.
Foreign ministers and other officials representing Canada, the Kingdom of Denmark, Norway, Russia, and the United States met in Ilulissat, Ilulissat, Greenland on 28 May 2008 at the Arctic Ocean Conference and announced the Ilulissat Declaration, blocking any "new comprehensive international legal regime to govern the Arctic Ocean," and pledging "the orderly settlement of any possible overlapping claims."
As of 2012, the Kingdom of Denmark is claiming the continental shelf based on the Lomonosov Ridge between Greenland and over the North Pole to the northern limit of the Russian EEZ.
The Russian Federation is also claiming a large swath of seabed along the Lomonosov Ridge but, unlike Denmark, confined its claim to its side of the Arctic. In August 2015, Russia made a supplementary submission for the expansion of the external borders of its continental shelf in the Arctic Ocean, asserting that the eastern part of the Lomonosov Ridge and the Mendeleyev Ridge are an extension of the Eurasian continent. In August 2016, the UN Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf began to consider Russia's submission.
Canada claims the Northwest Passage as part of its Canadian Internal Waters, internal waters belonging to Canada, while the United States and most maritime nations regards it as an Territorial waters, international strait, which means that foreign vessels have right of transit passage.
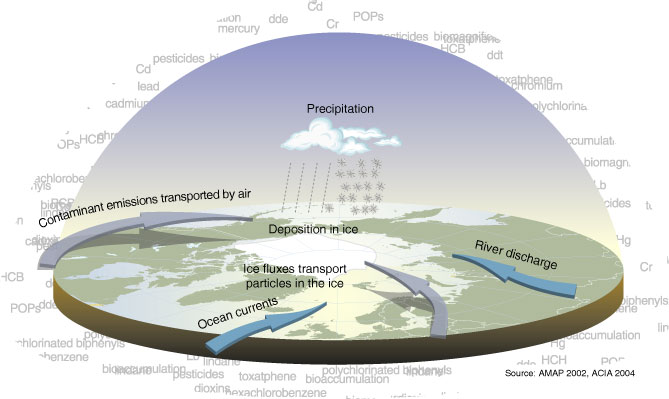 The Arctic is comparatively clean, although there are certain ecologically difficult localized pollution problems that present a serious threat to people's health living around these pollution sources. Due to the prevailing worldwide sea and air currents, the Arctic area is the fallout region for long-range transport pollutants, and in some places the concentrations exceed the levels of densely populated urban areas. An example of this is the phenomenon of Arctic haze, which is commonly blamed on long-range pollutants. Another example is with the bioaccumulation of PCB's (polychlorinated biphenyls) in Arctic wildlife and people.
The Arctic is comparatively clean, although there are certain ecologically difficult localized pollution problems that present a serious threat to people's health living around these pollution sources. Due to the prevailing worldwide sea and air currents, the Arctic area is the fallout region for long-range transport pollutants, and in some places the concentrations exceed the levels of densely populated urban areas. An example of this is the phenomenon of Arctic haze, which is commonly blamed on long-range pollutants. Another example is with the bioaccumulation of PCB's (polychlorinated biphenyls) in Arctic wildlife and people.
 The effects of global warming in the Arctic include rising temperatures, loss of sea ice, and melting of the Greenland ice sheet. Potential Arctic methane release, methane release from the region, especially through the thawing of permafrost and methane clathrates, is also a concern. Because of the Polar amplification, amplified response of the Arctic to global warming, it is often seen as a leading indicator of
The effects of global warming in the Arctic include rising temperatures, loss of sea ice, and melting of the Greenland ice sheet. Potential Arctic methane release, methane release from the region, especially through the thawing of permafrost and methane clathrates, is also a concern. Because of the Polar amplification, amplified response of the Arctic to global warming, it is often seen as a leading indicator of  Climate change is also predicted to have a large impact on tundra vegetation, causing an increase of shrubs, and having a negative impact on bryophytes and lichens.
Apart from concerns regarding the detrimental effects of warming in the Arctic, some potential opportunities have gained attention. The melting of the ice is making the Northwest Passage, the shipping routes through the northernmost latitudes, more navigable, raising the possibility that the Arctic region will become a prime trade route. One harbinger of the opening navigability of the Arctic took place in the summer of 2016 when the Crystal Serenity successfully navigated the Northwest Passage, a first for a large cruise ship.
In addition, it is believed that the Arctic seabed may contain substantial oil fields which may become accessible if the ice covering them melts. These factors have led to recent international debates as to which nations can claim sovereignty or ownership over the waters of the Arctic.Shaw, Rob
Climate change is also predicted to have a large impact on tundra vegetation, causing an increase of shrubs, and having a negative impact on bryophytes and lichens.
Apart from concerns regarding the detrimental effects of warming in the Arctic, some potential opportunities have gained attention. The melting of the ice is making the Northwest Passage, the shipping routes through the northernmost latitudes, more navigable, raising the possibility that the Arctic region will become a prime trade route. One harbinger of the opening navigability of the Arctic took place in the summer of 2016 when the Crystal Serenity successfully navigated the Northwest Passage, a first for a large cruise ship.
In addition, it is believed that the Arctic seabed may contain substantial oil fields which may become accessible if the ice covering them melts. These factors have led to recent international debates as to which nations can claim sovereignty or ownership over the waters of the Arctic.Shaw, Rob
"New patrol ships will reassert northern sovereignty: PM".
Victoria Times Colonist. 9 July 2007.



"Global Security, Climate Change, and the Arctic"
– 24-page special journal issue (Fall 2009), ''Swords and Ploughshares'', Program in Arms Control, Disarmament, and International Security (ACDIS), University of Illinois
GLOBIO Human Impact maps
''Report on human impacts on the Arctic'' * Krupnik, Igor, Michael A. Lang, and Scott E. Miller, eds
''Smithsonian at the Poles: Contributions to International Polar Year Science.''
Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Scholarly Press, 2009.
Konyshev, Valery & Sergunin, Alexander: The Arctic at the Crossroads of Geopolitical Interests
Russian Politics and Law, 2012, Vol.50, No.2, pp. 34–54
Käpylä, Juha & Mikkola, Harri: The Global Arctic: The Growing Arctic Interests of Russia, China, the United States and the European Union
FIIA Briefing Paper 133, August 2013
The Finnish Institute of International Affairs
Konyshev, Valery & Sergunin, Alexander. The Arctic at the crossroads of geopolitical interests // Russian Politics and Law, 2012. Vol. 50, No. 2. p. 34–54
Konyshev, Valery & Sergunin, Alexander: Is Russia a revisionist military power in the Arctic?
Defense & Security Analysis, September 2014.
Konyshev, Valery & Sergunin, Alexander. Russia in search of its Arctic strategy: between hard and soft power?
Polar Journal, April 2014. * McCannon, John. ''A History of the Arctic: Nature, Exploration and Exploitation''. Reaktion Books and University of Chicago Press, 2012. * *
Arctic Report Card
Blossoming Arctic
International Arctic Research Center
{{Authority control Arctic, Geography of Eastern Europe Geography of North America North Asia Geography of Northeast Asia Geography of Northern Europe Geography of Siberia Polar regions of the Earth
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm
The Danish Realm ( da, Danmarks Rige; fo, Danmarkar Ríki; kl, Danmarkip Naalagaaffik), officially the Kingdom of Denmark (; ; ), is a sovereign state located in Northern Europe and Northern North America. It consists of metropolitan Denma ...
(Greenland
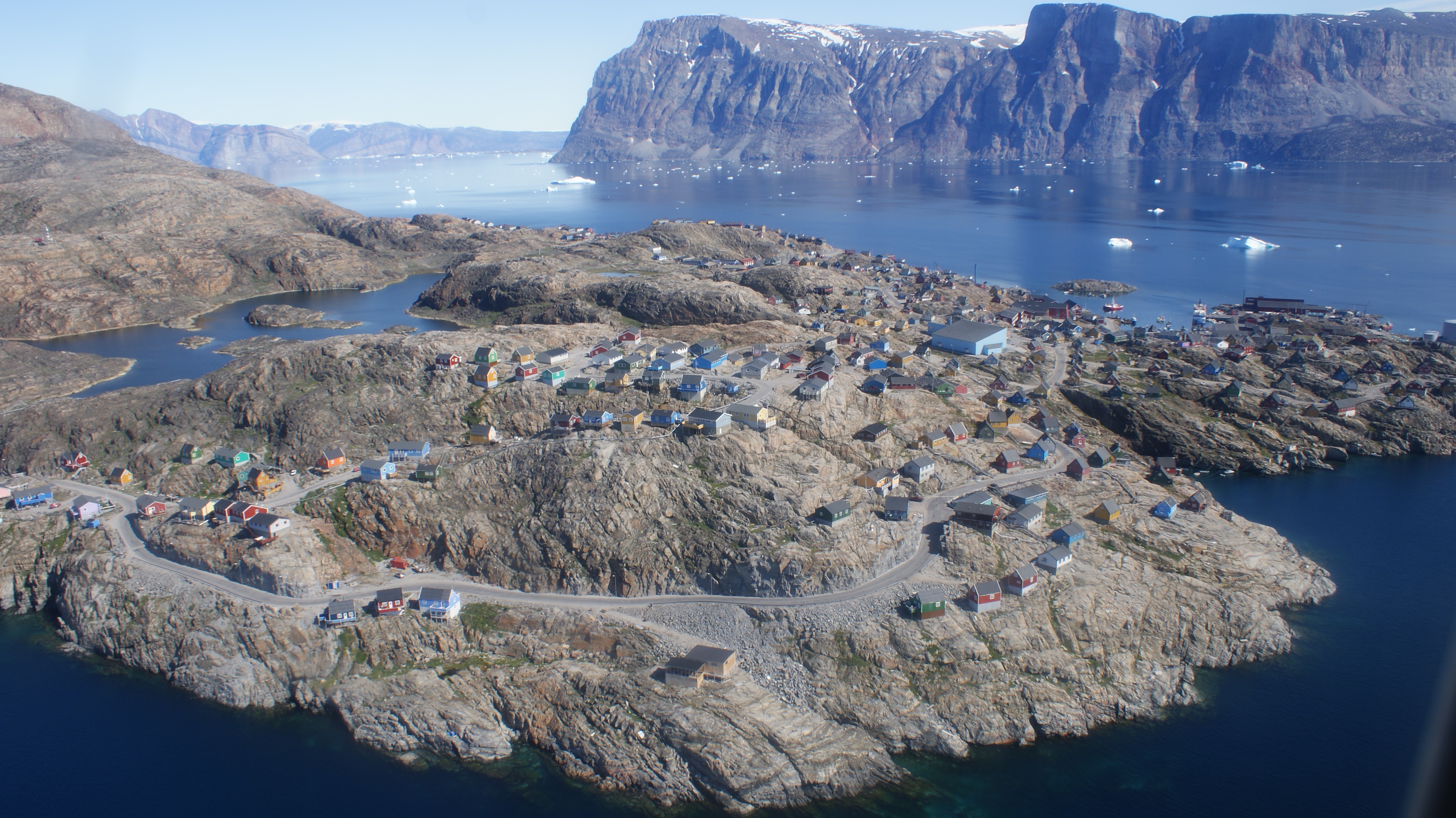
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland i ...
), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia (Murmansk
Murmansk (Russian: ''Мурманск'' lit. "Norwegian coast"; Finnish: ''Murmansk'', sometimes ''Muurmanski'', previously ''Muurmanni''; Norwegian: ''Norskekysten;'' Northern Sámi: ''Murmánska;'' Kildin Sámi: ''Мурман ланнҍ'') ...
, Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
, Nenets Okrug Nenets may refer to:
*Nenets Autonomous Okrug, a federal subject of Russia
*Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, a federal subject of Russia
* Nenets people, a Samoyedic people
*Nenets languages, a small language family of two closely related Samoyedic l ...
, Novaya Zemlya), Sweden and the United States (Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
). Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying snow and ice cover
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less density, dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the wo ...
, with predominantly treeless permafrost (permanently frozen underground ice) containing tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mou ...
. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places.
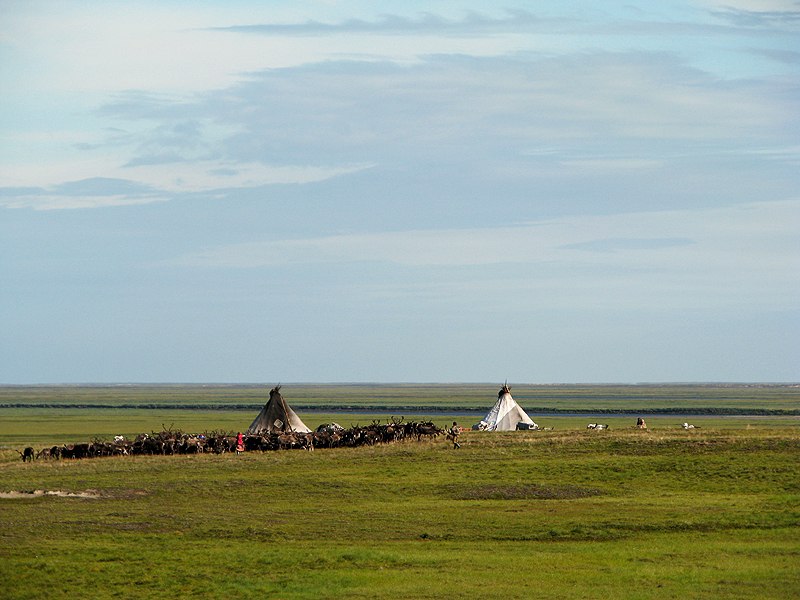
The Arctic region is a unique area among Earth's ecosystems. The cultures in the region and the Arctic indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
have adapted to its cold and extreme conditions. Life in the Arctic includes zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
and phytoplankton, fish and marine mammal
Marine mammals are aquatic mammals that rely on the ocean and other marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as seals, whales, manatees, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their ...
s, birds, land animals, plants and human societies. Arctic land is bordered by the subarctic.
Definition and etymology
The word Arctic comes from theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
word (''arktikos''), "near the Bear, northern" and from the word (''arktos''), meaning bear. The name refers either to the constellation Ursa Major
Ursa Major (; also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear," referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa ...
, the "Great Bear", which is prominent in the northern portion of the celestial sphere, or to the constellation Ursa Minor
Ursa Minor (Latin: 'Lesser Bear', contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation located in the far northern sky. As with the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, ...
, the "Little Bear", which contains the celestial north pole (currently very near Polaris, the current north Pole Star, or North Star).
There are a number of definitions of what area is contained within the Arctic. The area can be defined as north of the Arctic Circle (about 66° 34'N), the approximate southern limit of the midnight sun
The midnight sun is a natural phenomenon that occurs in the summer months in places north of the Arctic Circle or south of the Antarctic Circle, when the Sun remains visible at the local midnight. When the midnight sun is seen in the Arctic, ...
and the polar night
The polar night is a phenomenon where the nighttime lasts for more than 24 hours that occurs in the northernmost and southernmost regions of Earth. This occurs only inside the polar circles. The opposite phenomenon, the polar day, or midni ...
. Another definition of the Arctic, which is popular with ecologists
This is a list of notable ecologists.
A-D
* John Aber (USA)
* Aziz Ab'Saber (Brazil)
* Charles Christopher Adams (USA)
* Warder Clyde Allee (USA)
* Herbert G. Andrewartha ( Australia)
* Sarah Martha Baker ( UK)
* Fakhri A. Bazzaz (USA) ...
, is the region in the Northern Hemisphere where the average temperature for the warmest month (July) is below ; the northernmost tree line
The tree line is the edge of the habitat at which trees are capable of growing. It is found at high elevations and high latitudes. Beyond the tree line, trees cannot tolerate the environmental conditions (usually cold temperatures, extreme snow ...
roughly follows the isotherm at the boundary of this region.
Climate
 The Arctic is characterized by cold winters and cool summers. Its precipitation mostly comes in the form of snow and is low, with most of the area receiving less than . High winds often stir up snow, creating the illusion of continuous snowfall. Average winter temperatures can go as low as , and the coldest recorded temperature is approximately . Coastal Arctic climates are moderated by oceanic influences, having generally warmer temperatures and heavier snowfalls than the colder and drier interior areas. The Arctic is affected by current
The Arctic is characterized by cold winters and cool summers. Its precipitation mostly comes in the form of snow and is low, with most of the area receiving less than . High winds often stir up snow, creating the illusion of continuous snowfall. Average winter temperatures can go as low as , and the coldest recorded temperature is approximately . Coastal Arctic climates are moderated by oceanic influences, having generally warmer temperatures and heavier snowfalls than the colder and drier interior areas. The Arctic is affected by current global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
, leading to Arctic sea ice shrinkage, diminished ice in the Greenland ice sheet, and Arctic methane release
Arctic methane release is the release of methane from seas and soils in permafrost regions of the Arctic. While it is a long-term natural process, methane release is exacerbated by global warming. This results in a positive feedback cycle, as ...
as the permafrost thaws. The melting of Greenland's ice sheet is linked to polar amplification.
Due to the poleward migration of the planet's isotherms (about per decade during the past 30 years as a consequence of global warming), the Arctic region (as defined by tree line
The tree line is the edge of the habitat at which trees are capable of growing. It is found at high elevations and high latitudes. Beyond the tree line, trees cannot tolerate the environmental conditions (usually cold temperatures, extreme snow ...
and temperature) is currently shrinking. Perhaps the most alarming result of this is Arctic sea ice shrinkage. There is a large variance in predictions of Arctic sea ice loss, with models showing near-complete to complete loss in September from 2035 to some time around 2067.
Flora and fauna
Arctic life is characterized by adaptation to short growing seasons with long periods of sunlight, and cold, dark, snow-covered winter conditions.Plants
 Arctic vegetation is composed of plants such as dwarf shrubs, graminoids, herbs, lichens, and mosses, which all grow relatively close to the ground, forming
Arctic vegetation is composed of plants such as dwarf shrubs, graminoids, herbs, lichens, and mosses, which all grow relatively close to the ground, forming tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mou ...
. An example of a dwarf shrub is the bearberry
Bearberries ( indigenous kinnickinnick) are three species of dwarf shrubs in the genus ''Arctostaphylos''. Unlike the other species of ''Arctostaphylos'' (see manzanita), they are adapted to Arctic and Subarctic climates, and have a circumpolar ...
. As one moves northward, the amount of warmth available for plant growth decreases considerably. In the northernmost areas, plants are at their metabolic limits, and small differences in the total amount of summer warmth make large differences in the amount of energy available for maintenance, growth and reproduction. Colder summer temperatures cause the size, abundance, productivity and variety of plants to decrease. Trees cannot grow in the Arctic, but in its warmest parts, shrubs are common and can reach in height; sedges
The Cyperaceae are a family of graminoid (grass-like), monocotyledonous flowering plants known as sedges. The family is large, with some 5,500 known species described in about 90 genera, the largest being the "true sedges" genus ''Carex'' wit ...
, mosses and lichens can form thick layers. In the coldest parts of the Arctic, much of the ground is bare; non-vascular plant
Non-vascular plants are plants without a vascular system consisting of xylem and phloem. Instead, they may possess simpler tissues that have specialized functions for the internal transport of water.
Non-vascular plants include two distantly rel ...
s such as lichens and mosses predominate, along with a few scattered grasses and forb
A forb or phorb is an herbaceous flowering plant that is not a graminoid (grass, sedge, or rush). The term is used in biology and in vegetation ecology, especially in relation to grasslands and understory. Typically these are dicots without woo ...
s (like the Arctic poppy).
Animals

 Herbivores on the tundra include the
Herbivores on the tundra include the Arctic hare
The Arctic hare (''Lepus arcticus'') is a species of hare highly adapted to living in the Arctic tundra and other icy biomes. The Arctic hare survives with shortened ears and limbs, a small nose, fat that makes up close to 20% of its body, and a ...
, lemming
A lemming is a small rodent, usually found in or near the Arctic in tundra biomes. Lemmings form the subfamily Arvicolinae (also known as Microtinae) together with voles and muskrats, which form part of the superfamily Muroidea, which also includ ...
, muskox
The muskox (''Ovibos moschatus'', in Latin "musky sheep-ox"), also spelled musk ox and musk-ox, plural muskoxen or musk oxen (in iu, ᐅᒥᖕᒪᒃ, umingmak; in Woods Cree: ), is a hoofed mammal of the family Bovidae. Native to the Arctic, ...
, and caribou. They are preyed on by the snowy owl
The snowy owl (''Bubo scandiacus''), also known as the polar owl, the white owl and the Arctic owl, is a large, white owl of the true owl family. Snowy owls are native to the Arctic regions of both North America and the Palearctic, breeding m ...
, Arctic fox
The Arctic fox (''Vulpes lagopus''), also known as the white fox, polar fox, or snow fox, is a small fox native to the Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and common throughout the Arctic tundra biome. It is well adapted to living in ...
, Grizzly bear, and Arctic wolf
The Arctic wolf (''Canis lupus arctos''), also known as the white wolf or polar wolf, is a subspecies of grey wolf native to the High Arctic tundra of Canada's Queen Elizabeth Islands, from Melville Island to Ellesmere Island.https://ecoreg ...
. The polar bear is also a predator, though it prefers to hunt for marine life from the ice. There are also many birds and marine species endemic to the colder regions. Other terrestrial animals include wolverine
The wolverine (), (''Gulo gulo''; ''Gulo'' is Latin for " glutton"), also referred to as the glutton, carcajou, or quickhatch (from East Cree, ''kwiihkwahaacheew''), is the largest land-dwelling species of the family Mustelidae. It is a muscul ...
s, moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult ma ...
, Dall sheep, ermines, and Arctic ground squirrels. Marine mammals include seals, walrus
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the fami ...
, and several species of cetacean— baleen whales and also narwhals, orca
The orca or killer whale (''Orcinus orca'') is a toothed whale belonging to the oceanic dolphin family, of which it is the largest member. It is the only extant species in the genus '' Orcinus'' and is recognizable by its black-and-white ...
s, and belugas. An excellent and famous example of a ring species
In biology, a ring species is a connected series of neighbouring populations, each of which interbreeds with closely sited related populations, but for which there exist at least two "end" populations in the series, which are too distantly relate ...
exists and has been described around the Arctic Circle in the form of the ''Larus
''Larus'' is a large genus of gulls with worldwide distribution (by far the greatest species diversity is in the Northern Hemisphere).
Many of its species are abundant and well-known birds in their ranges. Until about 2005–2007, most gulls ...
'' gulls.
Natural resources
The Arctic includes copiousnatural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. ...
s (oil, gas, minerals, fresh water, fish and, if the subarctic is included, forest) to which modern technology and the economic opening up of Russia have given significant new opportunities. The interest of the tourism industry is also on the increase.
The Arctic contains some of the last and most extensive continuous wilderness areas in the world, and its significance in preserving biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
and genotypes is considerable. The increasing presence of humans fragments vital habitats. The Arctic is particularly susceptible to the abrasion of groundcover and to the disturbance of the rare breeding grounds of the animals that are characteristic to the region. The Arctic also holds 1/5 of the Earth's water supply.
Paleontology
 During the Cretaceous time period, the Arctic still had seasonal snows, though only a light dusting and not enough to permanently hinder plant growth. Animals such as the ''
During the Cretaceous time period, the Arctic still had seasonal snows, though only a light dusting and not enough to permanently hinder plant growth. Animals such as the ''Chasmosaurus
''Chasmosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of ceratopsid dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period of North America. Its name means 'opening lizard', referring to the large openings ( fenestrae) in its frill (Greek ''chasma'' meaning 'opening' or 'hollow' ...
'', ''Hypacrosaurus
''Hypacrosaurus'' (meaning "near the highest lizard" reek υπο-, ''hypo-'' = less + ακρος, ''akros'', high because it was almost but not quite as large as ''Tyrannosaurus'') was a genus of duckbill dinosaur similar in appearance to ''Co ...
'', ''Troodon
''Troodon'' ( ; ''Troödon'' in older sources) is a wastebasket taxon and a dubious genus of relatively small, bird-like dinosaurs known definitively from the Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous period (about 77 mya). It includes at leas ...
'', and '' Edmontosaurus'' may have all migrated north to take advantage of the summer growing season, and migrated south to warmer climes when winter came. A similar situation may also have been found amongst dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s that lived in Antarctic regions, such as the ''Muttaburrasaurus
''Muttaburrasaurus'' was a genus of herbivorous iguanodontian ornithopod dinosaur, which lived in what is now northeastern Australia sometime between 110 and 103 million years agoHoltz, Thomas R. Jr. (2012) ''Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to ...
'' of Australia.
However, others claim that dinosaurs lived year-round at very high latitudes, such as near the Colville River, which is now at about 70° N but at the time (70 million years ago) was 10° further north.
Indigenous population
 The earliest inhabitants of North America's central and eastern Arctic are referred to as the
The earliest inhabitants of North America's central and eastern Arctic are referred to as the Arctic small tool tradition The Arctic Small Tool tradition (ASTt) was a broad cultural entity that developed along the Alaska Peninsula, around Bristol Bay, and on the eastern shores of the Bering Strait around 2500 BC. ASTt groups were the first human occupants of Arctic Ca ...
(AST) and existed c. 2500 BCE. AST consisted of several Paleo-Eskimo
The Paleo-Eskimo (also pre-Thule or pre-Inuit) were the peoples who inhabited the Arctic region from Chukotka (e.g., Chertov Ovrag) in present-day Russia across North America to Greenland prior to the arrival of the modern Inuit (Eskimo) and rel ...
cultures, including the Independence cultures and Pre-Dorset
The Pre-Dorset is a loosely defined term for a Paleo-Eskimo culture or group of cultures that existed in the Eastern Canadian Arctic from c. 3200 to 850 cal BC, and preceded the Dorset culture.
Due to its vast geographical expanse and to history ...
culture.Gibbon, pp. 28–31 The Dorset culture
The Dorset was a Paleo-Eskimo culture, lasting from to between and , that followed the Pre-Dorset and preceded the Thule people (proto-Inuit) in the North American Arctic. The culture and people are named after Cape Dorset (now Kinngait) in ...
( Inuktitut: ''Tuniit'' or ''Tunit'') refers to the next inhabitants of central and eastern Arctic. The Dorset culture evolved because of technological and economic changes during the period of 1050–550 BCE. With the exception of the Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
/Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
peninsula, the Dorset culture vanished around 1500 CE. Supported by genetic testing, evidence shows that descendants of the Dorset culture, known as the Sadlermiut
The Sadlermiut (also called Sagdlirmiut, or Sallirmiut in modern Inuktitut spelling, from ''Sadlerk'' now ''Salliq'', the Inuktitut name for the settlement of Coral Harbour, Nunavut) were an Inuit group living in near isolation mainly on and aro ...
, survived in Aivilik, Southampton
Southampton () is a port city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also covers Po ...
and Coats Island
Coats Island ( Inuktitut: ᐊᑉᐸᑑᕐᔪᐊᖅ, Appatuurjuaq) lies at the northern end of Hudson Bay in the Kivalliq Region of Nunavut. At in size, it is the 107th largest island in the world, and Canada's 24th largest island.
The island ...
s, until the beginning of the 20th century.
The Dorset/Thule culture
The Thule (, , ) or proto-Inuit were the ancestors of all modern Inuit. They developed in coastal Alaska by the year 1000 and expanded eastward across northern Canada, reaching Greenland by the 13th century. In the process, they replaced people o ...
transition dates around the ninth–10th centuries CE. Scientists theorize that there may have been cross-contact of the two cultures with sharing of technology, such as fashioning harpoon heads, or the Thule may have found Dorset remnants and adapted their ways with the predecessor culture. Others believe the Thule displaced the Dorset.
By 1300 CE, the Inuit, present-day Arctic inhabitants and descendants of Thule culture, had settled in west Greenland, and moved into east Greenland over the following century (Inughuit, Kalaallit and Tunumiit are modern Greenlandic Inuit groups descended from Thule). Over time, the Inuit have migrated throughout the Arctic regions of Eastern Russia, the United States, Canada, and Greenland.
Other Circumpolar North indigenous peoples include the Chukchi people, Chukchi, Evenks, Inupiat people, Iñupiat, Khanty people, Khanty, Koryaks, Nenets people, Nenets, Sami people, Sami, Yukaghir people, Yukaghir, Gwich'in, and Yupik peoples, Yupik.
International cooperation and politics
 The eight Arctic nations (Canada, Kingdom of Denmark [Greenland & The Faroe Islands], Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Russia, and USA) are all members of the Arctic Council, as are organizations representing six indigenous populations. The council operates on consensus basis, mostly dealing with environmental treaties and not addressing boundary or resource disputes.
Though Arctic cooperation and politics, Arctic policy priorities differ, every Arctic nation is concerned about sovereignty/defense, resource development, shipping routes, and environmental protection. Much work remains on regulatory agreements regarding shipping, tourism, and Arctic resources race, resource development in Arctic waters. Arctic shipping is subject to some regulatory control through the International Code for Ships Operating in Polar Waters, adopted by the International Maritime Organization on 1 January 2017 and applies to all ships in Arctic waters over 500 tonnes.
Research in the Arctic has long been a collaborative international effort, evidenced by the International Polar Year. The International Arctic Science Committee, hundreds of scientists and specialists of the Arctic Council, and the Barents Euro-Arctic Council are more examples of collaborative international Arctic research.
The eight Arctic nations (Canada, Kingdom of Denmark [Greenland & The Faroe Islands], Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Russia, and USA) are all members of the Arctic Council, as are organizations representing six indigenous populations. The council operates on consensus basis, mostly dealing with environmental treaties and not addressing boundary or resource disputes.
Though Arctic cooperation and politics, Arctic policy priorities differ, every Arctic nation is concerned about sovereignty/defense, resource development, shipping routes, and environmental protection. Much work remains on regulatory agreements regarding shipping, tourism, and Arctic resources race, resource development in Arctic waters. Arctic shipping is subject to some regulatory control through the International Code for Ships Operating in Polar Waters, adopted by the International Maritime Organization on 1 January 2017 and applies to all ships in Arctic waters over 500 tonnes.
Research in the Arctic has long been a collaborative international effort, evidenced by the International Polar Year. The International Arctic Science Committee, hundreds of scientists and specialists of the Arctic Council, and the Barents Euro-Arctic Council are more examples of collaborative international Arctic research.
Territorial claims
No country owns the geographic North Pole or the region of the Arctic Ocean surrounding it. The surrounding six Arctic states that border the Arctic Ocean—Canada, Kingdom of Denmark (with Greenland), Iceland, Norway, Russia, and the United States—are limited to a exclusive economic zone (EEZ) off their coasts. Two Arctic states (Finland and Sweden) do not have direct access to the Arctic Ocean. Upon ratification of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, a country has ten years to make claims to an extended continental shelf beyond its Exclusive Economic Zone, 200 nautical mile zone. Due to this, Norway (which ratified the convention in 1996), Russia (ratified in 1997), Canada (ratified in 2003) and the Kingdom of Denmark (ratified in 2004) launched projects to establish claims that certain sectors of the Arctic seabed should belong to their territories. On 2 August 2007, two Russian bathyscaphes, MIR (submersible), MIR-1 and MIR-2, for the first time in history descended to the Arctic seabed beneath the North Pole and placed there a flag of Russia, Russian flag made of rust-proof titanium alloy. The flag-placing during Arktika 2007 generated commentary on and concern for a race for control of the Arctic's vast hydrocarbon resources. Foreign ministers and other officials representing Canada, the Kingdom of Denmark, Norway, Russia, and the United States met in Ilulissat, Ilulissat, Greenland on 28 May 2008 at the Arctic Ocean Conference and announced the Ilulissat Declaration, blocking any "new comprehensive international legal regime to govern the Arctic Ocean," and pledging "the orderly settlement of any possible overlapping claims."
As of 2012, the Kingdom of Denmark is claiming the continental shelf based on the Lomonosov Ridge between Greenland and over the North Pole to the northern limit of the Russian EEZ.
The Russian Federation is also claiming a large swath of seabed along the Lomonosov Ridge but, unlike Denmark, confined its claim to its side of the Arctic. In August 2015, Russia made a supplementary submission for the expansion of the external borders of its continental shelf in the Arctic Ocean, asserting that the eastern part of the Lomonosov Ridge and the Mendeleyev Ridge are an extension of the Eurasian continent. In August 2016, the UN Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf began to consider Russia's submission.
Canada claims the Northwest Passage as part of its Canadian Internal Waters, internal waters belonging to Canada, while the United States and most maritime nations regards it as an Territorial waters, international strait, which means that foreign vessels have right of transit passage.
Foreign ministers and other officials representing Canada, the Kingdom of Denmark, Norway, Russia, and the United States met in Ilulissat, Ilulissat, Greenland on 28 May 2008 at the Arctic Ocean Conference and announced the Ilulissat Declaration, blocking any "new comprehensive international legal regime to govern the Arctic Ocean," and pledging "the orderly settlement of any possible overlapping claims."
As of 2012, the Kingdom of Denmark is claiming the continental shelf based on the Lomonosov Ridge between Greenland and over the North Pole to the northern limit of the Russian EEZ.
The Russian Federation is also claiming a large swath of seabed along the Lomonosov Ridge but, unlike Denmark, confined its claim to its side of the Arctic. In August 2015, Russia made a supplementary submission for the expansion of the external borders of its continental shelf in the Arctic Ocean, asserting that the eastern part of the Lomonosov Ridge and the Mendeleyev Ridge are an extension of the Eurasian continent. In August 2016, the UN Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf began to consider Russia's submission.
Canada claims the Northwest Passage as part of its Canadian Internal Waters, internal waters belonging to Canada, while the United States and most maritime nations regards it as an Territorial waters, international strait, which means that foreign vessels have right of transit passage.
Exploration
Since 1937, the larger portion of the Asian-side Arctic region has been extensively explored by Soviet and Russian crewed drifting ice stations. Between 1937 and 1991, 88 international polar crews established and occupied scientific settlements on the drift ice and were carried thousands of kilometres by the ice flow.Pollution
 The Arctic is comparatively clean, although there are certain ecologically difficult localized pollution problems that present a serious threat to people's health living around these pollution sources. Due to the prevailing worldwide sea and air currents, the Arctic area is the fallout region for long-range transport pollutants, and in some places the concentrations exceed the levels of densely populated urban areas. An example of this is the phenomenon of Arctic haze, which is commonly blamed on long-range pollutants. Another example is with the bioaccumulation of PCB's (polychlorinated biphenyls) in Arctic wildlife and people.
The Arctic is comparatively clean, although there are certain ecologically difficult localized pollution problems that present a serious threat to people's health living around these pollution sources. Due to the prevailing worldwide sea and air currents, the Arctic area is the fallout region for long-range transport pollutants, and in some places the concentrations exceed the levels of densely populated urban areas. An example of this is the phenomenon of Arctic haze, which is commonly blamed on long-range pollutants. Another example is with the bioaccumulation of PCB's (polychlorinated biphenyls) in Arctic wildlife and people.
Preservation
There have been many proposals to preserve the Arctic over the years. Most recently a group of stars at the Rio Earth Summit, on 21 June 2012, proposed protecting the Arctic, similar to the Antarctic Treaty System, Antarctic protection. The initial focus of the campaign will be a UN resolution creating a global sanctuary around the pole, and a ban on oil drilling and unsustainable fishing in the Arctic. The Arctic has climate change rates that are amongst the highest in the world. Due to the major impacts to the region from climate change the near climate future of the region will be extremely different under all scenarios of warming.Global warming
 The effects of global warming in the Arctic include rising temperatures, loss of sea ice, and melting of the Greenland ice sheet. Potential Arctic methane release, methane release from the region, especially through the thawing of permafrost and methane clathrates, is also a concern. Because of the Polar amplification, amplified response of the Arctic to global warming, it is often seen as a leading indicator of
The effects of global warming in the Arctic include rising temperatures, loss of sea ice, and melting of the Greenland ice sheet. Potential Arctic methane release, methane release from the region, especially through the thawing of permafrost and methane clathrates, is also a concern. Because of the Polar amplification, amplified response of the Arctic to global warming, it is often seen as a leading indicator of global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
. The melting of Greenland's ice sheet is linked to polar amplification.
The Arctic is especially vulnerable to the effects of any climate change, as has become apparent with the reduction of sea ice in recent years. Climate models predict much greater warming in the Arctic than the global average, resulting in significant international attention to the region. In particular, there are concerns that Arctic shrinkage, a consequence of melting glaciers and other ice in Greenland, could soon contribute to a substantial rise in sea levels worldwide.
The current Arctic warming is leading to ancient carbon being released from thawing permafrost, leading to methane and carbon dioxide production by micro-organisms. Release of methane and carbon dioxide stored in permafrost could cause abrupt and severe global warming, as they are potent greenhouse gases.
 Climate change is also predicted to have a large impact on tundra vegetation, causing an increase of shrubs, and having a negative impact on bryophytes and lichens.
Apart from concerns regarding the detrimental effects of warming in the Arctic, some potential opportunities have gained attention. The melting of the ice is making the Northwest Passage, the shipping routes through the northernmost latitudes, more navigable, raising the possibility that the Arctic region will become a prime trade route. One harbinger of the opening navigability of the Arctic took place in the summer of 2016 when the Crystal Serenity successfully navigated the Northwest Passage, a first for a large cruise ship.
In addition, it is believed that the Arctic seabed may contain substantial oil fields which may become accessible if the ice covering them melts. These factors have led to recent international debates as to which nations can claim sovereignty or ownership over the waters of the Arctic.Shaw, Rob
Climate change is also predicted to have a large impact on tundra vegetation, causing an increase of shrubs, and having a negative impact on bryophytes and lichens.
Apart from concerns regarding the detrimental effects of warming in the Arctic, some potential opportunities have gained attention. The melting of the ice is making the Northwest Passage, the shipping routes through the northernmost latitudes, more navigable, raising the possibility that the Arctic region will become a prime trade route. One harbinger of the opening navigability of the Arctic took place in the summer of 2016 when the Crystal Serenity successfully navigated the Northwest Passage, a first for a large cruise ship.
In addition, it is believed that the Arctic seabed may contain substantial oil fields which may become accessible if the ice covering them melts. These factors have led to recent international debates as to which nations can claim sovereignty or ownership over the waters of the Arctic.Shaw, Rob"New patrol ships will reassert northern sovereignty: PM".
Victoria Times Colonist. 9 July 2007.
Arctic waters
*Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
* Baffin Bay
* Beaufort Sea
* Barents Sea
* Bering Sea
* Bering Strait
* Chukchi Sea
* Davis Strait
* Denmark Strait
* East Siberian Sea
* Greenland Sea
* Hudson Bay
* Kara Sea
* Laptev Sea
* Nares Strait
* Norwegian Sea
Arctic lands



See also
* Arctic Search and Rescue Agreement * List of countries by northernmost point * Arctic sanctuary * Poverty in the Arctic * Arctic Winter Games * Winter CityNotes
References
Bibliography
*Further reading
* Brian W. Coad, James D. Reist. (2017). ''Marine Fishes of Arctic Canada''. University of Toronto Press."Global Security, Climate Change, and the Arctic"
– 24-page special journal issue (Fall 2009), ''Swords and Ploughshares'', Program in Arms Control, Disarmament, and International Security (ACDIS), University of Illinois
GLOBIO Human Impact maps
''Report on human impacts on the Arctic'' * Krupnik, Igor, Michael A. Lang, and Scott E. Miller, eds
''Smithsonian at the Poles: Contributions to International Polar Year Science.''
Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Scholarly Press, 2009.
Konyshev, Valery & Sergunin, Alexander: The Arctic at the Crossroads of Geopolitical Interests
Russian Politics and Law, 2012, Vol.50, No.2, pp. 34–54
Käpylä, Juha & Mikkola, Harri: The Global Arctic: The Growing Arctic Interests of Russia, China, the United States and the European Union
FIIA Briefing Paper 133, August 2013
The Finnish Institute of International Affairs
Konyshev, Valery & Sergunin, Alexander. The Arctic at the crossroads of geopolitical interests // Russian Politics and Law, 2012. Vol. 50, No. 2. p. 34–54
Konyshev, Valery & Sergunin, Alexander: Is Russia a revisionist military power in the Arctic?
Defense & Security Analysis, September 2014.
Konyshev, Valery & Sergunin, Alexander. Russia in search of its Arctic strategy: between hard and soft power?
Polar Journal, April 2014. * McCannon, John. ''A History of the Arctic: Nature, Exploration and Exploitation''. Reaktion Books and University of Chicago Press, 2012. * *
External links
Arctic Report Card
Blossoming Arctic
International Arctic Research Center
{{Authority control Arctic, Geography of Eastern Europe Geography of North America North Asia Geography of Northeast Asia Geography of Northern Europe Geography of Siberia Polar regions of the Earth