architecture domain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An architecture domain in
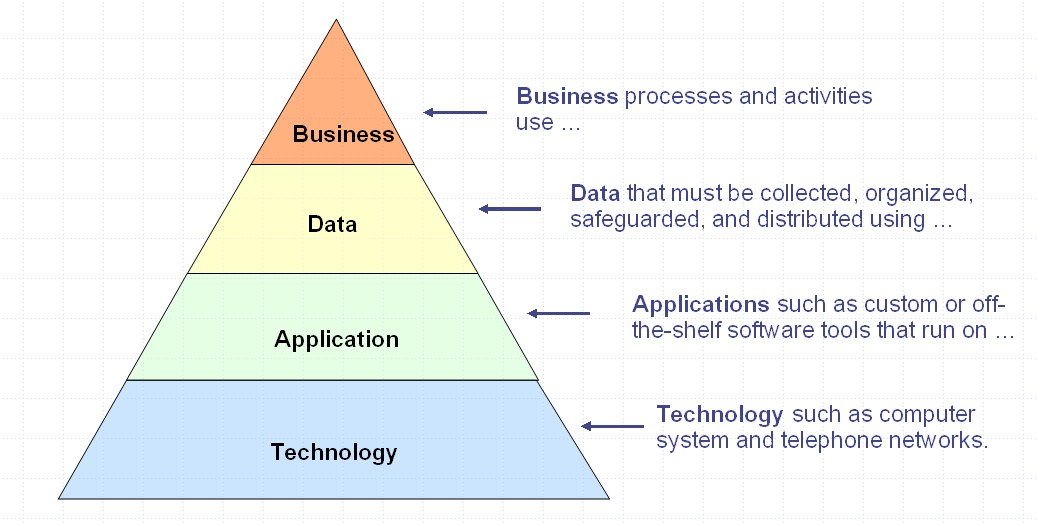
 Since Stephen Spewak's book called enterprise architecture planning (EAP) in 1993, and perhaps before then, it has been normal to recognise four types of architecture domain. The
Since Stephen Spewak's book called enterprise architecture planning (EAP) in 1993, and perhaps before then, it has been normal to recognise four types of architecture domain. The Human activity systems - Systems Thinking, Systems Practice, Peter Checkland, 1981, page 115, 314
/ref>) and above the technology (the platform IT infrastructure). There are many variations on this theme.
enterprise architecture
Enterprise architecture (EA) is a business function concerned with the structures and behaviours of a business, especially business roles and processes that create and use business data. The international definition according to the Federation of ...
is a broad view of an enterprise
Enterprise (or the archaic spelling Enterprize) may refer to:
Business and economics
Brands and enterprises
* Enterprise GP Holdings, an energy holding company
* Enterprise plc, a UK civil engineering and maintenance company
* Enterpris ...
or system. It is a partial representation of a whole system that addresses several concerns of several stakeholders. It is a description that hides other views or facets of the system described. Business
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or Trade, buying and selling Product (business), products (such as goods and Service (economics), services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for ...
, data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
, application and technology
Technology is the application of Conceptual model, conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible too ...
architectures are recognized as the core domains in the most of proposed concepts concerned with the definition of enterprise architecture.
Overview

British Computer Society
image:Maurice Vincent Wilkes 1980 (3).jpg, Sir Maurice Wilkes served as the first President of BCS in 1957.
The British Computer Society (BCS), branded BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT, since 2009, is a professional body and a learned ...
's "Reference Model for Enterprise and Solution Architecture" also follows this subdivision but additionally mentions the (single) application architecture level just below the application''s'' architecture as well as the domains of information architecture, information systems architecture, or security architecture (a cross-cutting concern):
* Business architecture
In the business sector, business architecture is a discipline that "represents holistic, multidimensional business views of: capabilities, end-to-end value delivery, information, and organizational structure; and the relationships among these ...
: The structure and behaviour of a business system (not necessarily related to computers). Covers business goals, business functions or capabilities, business processes and roles etc. Business functions and business processes are often mapped to the applications and data they need.
* Data architecture
Data architecture consist of models, policies, rules, and standards that govern which data is collected and how it is stored, arranged, integrated, and put to use in data systems and in organizations. Data is usually one of several architecture d ...
: The data structures used by a business and/or its applications. Descriptions of data in storage and data in motion. Descriptions of data stores, data groups and data items. Mappings of those data artifacts to data qualities, applications, locations etc.
* Applications architecture
In information systems, applications architecture or application architecture is one of several architecture domains that form the pillars of an enterprise architecture (EA).
Scope
An applications architecture describes the behavior of applica ...
: The structure and behaviour of applications used in a business, focused on how they interact with each other and with users. Focused on the data consumed and produced by applications rather than their internal structure. In application portfolio management, the applications are usually mapped to business functions and to application platform technologies.
*: Application (or Component) architecture: The internal structure, the modularisation of software, within an application. This is software architecture
Software architecture is the set of structures needed to reason about a software system and the discipline of creating such structures and systems. Each structure comprises software elements, relations among them, and properties of both elements a ...
at the lowest level of granularity. It is usually below the level of modularisation that solution architects define. However, ''there is no rigid dividing line''.
* Technology architecture
Technology is the application of conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible tools such as utens ...
or infrastructure architecture: The structure and behaviour of the IT infrastructure
Information technology infrastructure is defined broadly as a set of information technology (IT) components that are the foundation of an IT service; typically physical components (Computer hardware, computer and networking hardware and facilitie ...
. Covers the client and server nodes of the hardware configuration, the infrastructure applications that run on them, the infrastructure services they offer to applications, the protocols and networks that connect applications and nodes.
Note that the applications architecture is about the application portfolio, not the internal architecture of a single application - which is often called the application architecture.
Many EA frameworks combine data and application domains into a single layer, sitting below the business (usually a human activity system; that is a notational system expressing a purposeful human activity in a theoretical way using intellectual constructs and not descriptions of actual real-world activity/ref>) and above the technology (the platform IT infrastructure). There are many variations on this theme.
See also
*Enterprise Architecture framework
An enterprise architecture framework (EA framework) defines how to create and use an enterprise architecture. An architecture framework provides principles and practices for creating and using the architecture description of a system. It structu ...
* Federal Enterprise Architecture
* Solution architecture
Solution architecture is a term used in information technology with various definitions, such as "a description of a discrete and focused business operation or activity and how IS/ IT supports that operation".
Definitions
The Open Group's defin ...
* TOGAF
The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF) is the most used framework for enterprise architecture as of 2020 that provides an approach for designing, planning, implementing, and governing an enterprise information technology architecture. TOG ...
* Architecture Patterns (EA Reference Architecture)
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Architecture Domain Enterprise architecture