Arched Dam on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An arch-gravity dam or arched dam is a dam with the characteristics of both an arch dam and a
An arch-gravity dam or arched dam is a dam with the characteristics of both an arch dam and a
 Arch-gravity dams are dams that resist the thrust of water by their weight using the force of gravity and the arch action.
An arch-gravity dam incorporates the
Arch-gravity dams are dams that resist the thrust of water by their weight using the force of gravity and the arch action.
An arch-gravity dam incorporates the
 An arch-gravity dam or arched dam is a dam with the characteristics of both an arch dam and a
An arch-gravity dam or arched dam is a dam with the characteristics of both an arch dam and a gravity dam
A gravity dam is a dam constructed from concrete or stone masonry and designed to hold back water by using only the weight of the material and its resistance against the foundation to oppose the horizontal pressure of water pushing against it. ...
. It is a dam that curves upstream in a narrowing curve that directs most of the water pressure against the canyon
A canyon (from ; archaic British English spelling: ''cañon''), or gorge, is a deep cleft between escarpments or cliffs resulting from weathering and the erosion, erosive activity of a river over geologic time scales. Rivers have a natural tenden ...
rock walls, providing the force to compress the dam. It combines the strengths of two common dam forms and is considered a compromise between the two. They are made of conventional concrete, roller-compacted concrete
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) or rolled concrete (rollcrete) is a special blend of concrete that has essentially the same ingredients as conventional concrete but in different ratios, and increasingly with partial substitution of fly ash for Po ...
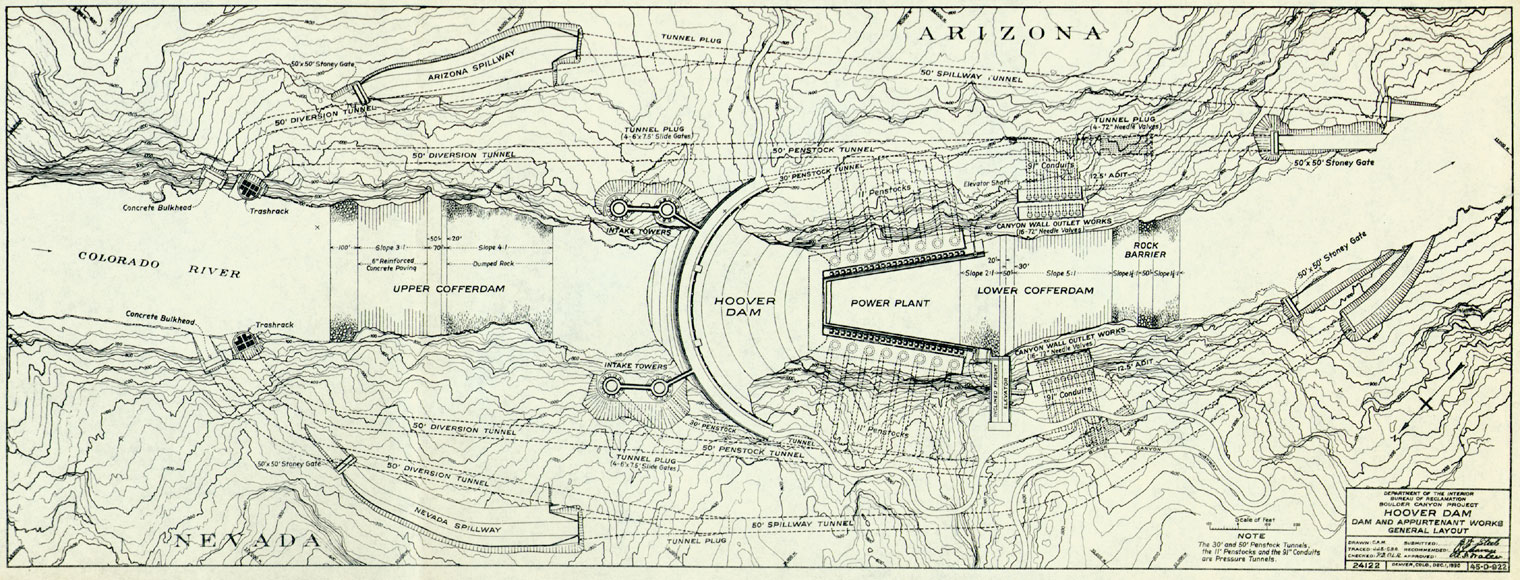
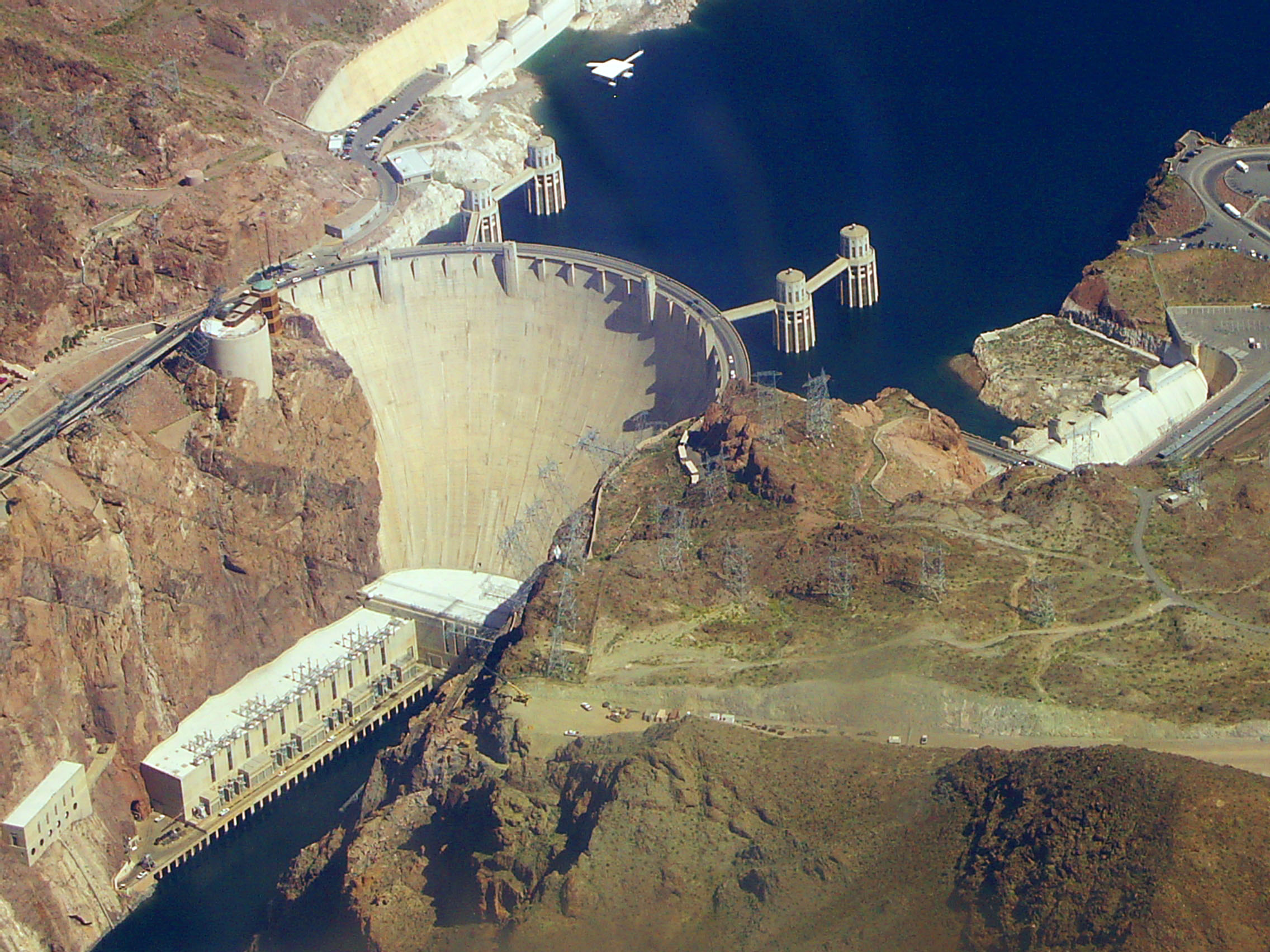
(RCC), or masonry. Arch-gravity dams are not reinforced except at the spillway. A typical example of the conventional concrete dam is the Hoover Dam
Hoover Dam is a concrete arch-gravity dam in the Black Canyon of the Colorado River, on the border between the U.S. states of Nevada and Arizona. It was constructed between 1931 and 1936 during the Great Depression and was dedicated on Se ...
. Changuinola Dam is an example of the RCC arch-gravity dam. A gravity dam requires a large volume of internal fill. An arch-gravity dam can be thinner than the pure gravity dam
A gravity dam is a dam constructed from concrete or stone masonry and designed to hold back water by using only the weight of the material and its resistance against the foundation to oppose the horizontal pressure of water pushing against it. ...
and requires less internal fill.
Overview
 Arch-gravity dams are dams that resist the thrust of water by their weight using the force of gravity and the arch action.
An arch-gravity dam incorporates the
Arch-gravity dams are dams that resist the thrust of water by their weight using the force of gravity and the arch action.
An arch-gravity dam incorporates the arch
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it.
Arches may be synonymous with vaul ...
's curved design which is effective in supporting the water in narrow, rocky locations where the gorge
A canyon (from ; archaic British English spelling: ''cañon''), or gorge, is a deep cleft between escarpments or cliffs resulting from weathering and the erosion, erosive activity of a river over geologic time scales. Rivers have a natural tenden ...
's sides are of hard rock and the water is forced into a narrow channel. Therefore, the span needed for the dam is also relatively narrow, and the dam's curved design effectively holds the water back while using less construction material compared to a pure arch dam or gravity dam.
These dams are more reliable than arch dams. Typically, arch-gravity dams are built in canyon-like terrain, with the surrounding cliffs serving as supporting walls.
Such dams are usually up to hundreds of metres thick at the base, gradually decreasing to 10-30 metres towards the crest. The use of an arch-shaped bank-fill dam reduces the overall mass of the structure and the cost of construction compared to purely gravity dams. For this reason, along with arch dams, arch-gravity dams are most commonly used in hydraulic structures of more than 100 m in height.
See also
* Masonry dam *Embankment dam
An embankment dam is a large artificial dam. It is typically created by the placement and compaction of a complex semi-plastic mound of various compositions of soil or rock. It has a semi-pervious waterproof natural covering for its surface and ...
Footnotes
{{reflist, 25em 01 Dams by type Arches and vaults Concrete buildings and structures Masonry dams