Aragonese Crusade on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Aragonese Crusade or Crusade of Aragon, a part of the larger War of the Sicilian Vespers, was declared by 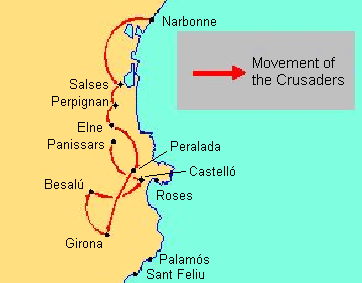 The French soon experienced a reversal, however, at the hands of Peter III's admiral, Roger de Lauria. The French fleet was defeated and destroyed at the Battle of Les Formigues. As well, the French camp was hit hard by an epidemic of
The French soon experienced a reversal, however, at the hands of Peter III's admiral, Roger de Lauria. The French fleet was defeated and destroyed at the Battle of Les Formigues. As well, the French camp was hit hard by an epidemic of
Pope Martin IV
Pope Martin IV ( la, Martinus IV; c. 1210/1220 – 28 March 1285), born Simon de Brion, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 22 February 1281 to his death on 28 March 1285. He was the last French pope to have ...
against King Peter III of Aragon in 1284 and 1285. Because of the recent conquest of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
by Peter, Martin declared a crusade against him and officially deposed him as king, on the grounds that Aragon was a papal fief: Peter's grandfather and namesake, Peter II, had surrendered the kingdom as a fief to the Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of R ...
. Martin bestowed Aragon on Peter's nephew Count Charles of Valois
Charles of Valois (12 March 1270 – 16 December 1325), the fourth son of King Philip III of France and Isabella of Aragon, was a member of the House of Capet and founder of the House of Valois, whose rule over France would start in ...
, son of King Philip III of France
Philip III (1 May 1245 – 5 October 1285), called the Bold (french: le Hardi), was King of France from 1270 until his death in 1285. His father, Louis IX, died in Tunis during the Eighth Crusade. Philip, who was accompanying him, returne ...
.
The crusade soon caused civil war within Aragon, as Peter's brother, King James II of Majorca
James II ( ca, Jaume) (31 May 1243 – 29 May 1311) was King of Majorca and Lord of Montpellier from 1276 until his death. He was the second son of James I of Aragon and his wife, Violant, daughter of Andrew II of Hungary. In 1279, by the T ...
, joined the French. James had also inherited the County of Roussillon
The County of Roussillon ( ca, Comtat de Rosselló, , la, Comitatus Ruscinonensis) was one of the Catalan counties in the Marca Hispanica during the Middle Ages. The rulers of the county were the counts of Roussillon, whose interests lay both n ...
and thus stood between the dominions of the French and Aragonese monarchs. Peter had opposed James' inheritance as a younger son and reaped the consequence of such rivalry in the crusade.
Peter's eldest son, the future Alfonso III, was placed in charge of defending the border with Navarre
Navarre (; es, Navarra ; eu, Nafarroa ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre ( es, Comunidad Foral de Navarra, links=no ; eu, Nafarroako Foru Komunitatea, links=no ), is a foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, ...
, which was ruled by Philip III's son, Philip the Fair
Philip IV (April–June 1268 – 29 November 1314), called Philip the Fair (french: Philippe le Bel), was King of France from 1285 to 1314. By virtue of his marriage with Joan I of Navarre, he was also King of Navarre as Philip I from 1 ...
. Although Peter feared a full-scale invasion from Navarre, there were only some cross-border raids. The Navarrese king joined the main invading army under his father.Antonio Zaldívar, "Emphasizing Royal Orders Using the Romance Languages: An Example of Strategic Codeswitching in the Crown of Aragon's Thirteenth-century Royal Chancery", in Yuen-Gen Liang and Jarbel Rodriguez (eds.), ''Authority and Spectacle in Medieval and Early Modern Europe: Essays in Honor of Teofilo F. Ruiz'' (Routledge, 2017), pp. 73–83, at 76.
In 1284, the first French armies under Philip and Charles entered Roussillon. They included 16,000 cavalry, 17,000 crossbowmen, and 100,000 infantry, along with 100 ships in south French ports. Though they had James' support, the local populace rose against them. The city of Elne
Elne (; ca, Elna ) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France.
It lies in the former province of Roussillon, of which it was the first capital, being later replaced by Perpignan. Its inhabitants are still called '' ...
was valiantly defended by the so-called ''Bâtard de Roussillon'' (Bastard of Roussillon), the illegitimate son of Nuño Sánchez
Nuño Sánchez ( ca, Nunó, ''Nunyó'', or'' Nunyo Sanç'', french: Nuno Sanche) ( 1185 – 1242) was a nobleman and statesman in the Crown of Aragon.
Nuño was the son of Sancho, Count of Provence, Roussillon, and Cerdagne, and Sancha Núñe ...
, late count of Roussillon (1212–1242). Eventually he was overcome and the cathedral was burned, despite the presence of papal legate
300px, A woodcut showing Henry II of England greeting the pope's legate.
A papal legate or apostolic legate (from the ancient Roman title ''legatus'') is a personal representative of the pope to foreign nations, or to some part of the Catholic ...
s, while the population was massacred, all save the ''Bâtard''. He succeeded in negotiating his surrender and accompanied the advancing royal forces as a prisoner.
In 1285, Philip the Bold entrenched himself before Girona
Girona (officially and in Catalan , Spanish: ''Gerona'' ) is a city in northern Catalonia, Spain, at the confluence of the Ter, Onyar, Galligants, and Güell rivers. The city had an official population of 103,369 in 2020. Girona is the capit ...
in an attempt to besiege it. The resistance was strong, but the city was taken. Charles was crowned there, but without an actual crown. On 28 April, Cardinal Jean Cholet placed his own hat on the count's head. For this, Charles was derisively but not unaffectionately nicknamed ''roi du chapeau'' ("king of the hat").
dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complication ...
. Philip himself was afflicted. The heir to the French throne, Philip of Navarre, opened negotiations with Peter for free passage for the royal family through the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
. But the troops were not offered such passage and were decimated at the Battle of the Col de Panissars. The king of France himself died at Perpignan
Perpignan (, , ; ca, Perpinyà ; es, Perpiñán ; it, Perpignano ) is the prefecture of the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France, in the heart of the plain of Roussillon, at the foot of the Pyrenees a few kilometres from the ...
, the capital of James of Majorca, and was buried in Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in Southern France in the Occitanie region. It lies from Paris in the Aude department, of which it is a sub-prefecture. It is located about from the shores of the M ...
. Peter did not long survive him.
Historian H. J. Chaytor described the Aragonese Crusade as "perhaps the most unjust, unnecessary and calamitous enterprise ever undertaken by the Capetian monarchy." W. C. Jordan has blamed it for the young Philip's opposition to papal interference in French foreign policy upon his succession, which had long-reaching consequences for Europe. The crusade's legacy to France was slight, but Majorca was devastated as an independent polity. Alfonso III annexed Majorca, Ibiza, and Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from la, Insula Minor, , smaller island, later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Majorca. Its capi ...
in the following years. In 1295, the Treaty of Anagni
{{Unreferenced, date=June 2019, bot=noref (GreenC bot)
The Treaty of Anagni was an accord between the Pope Boniface VIII, James II of Aragon, Philip IV of France, Charles II of Naples, and James II of Majorca. It was signed on 20 June 1295 at Ana ...
returned the islands to James and the Treaty of Tarascon of 1291 officially restored Aragon to Alfonso and lifted the ban of the church.
Notes
Sources
* * * * * * * * * {{Use dmy dates, date=May 2017 Conflicts in 1284 Conflicts in 1285 Wars involving the Crown of Aragon 13th-century military history of France 13th century in Catalonia 13th century in Aragon 13th-century crusades Medieval Catalonia War of the Sicilian Vespers 1284 in Europe 1285 in Europe Military history of Catalonia