Arachosia Oblonga on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Arachosia () is the Hellenized name of an ancient
Arachosia () is the Hellenized name of an ancient
 "Arachosia" is the Latinized form of Greek (''Arach┼Źs├Ł─ü''). "The same region appears in the
"Arachosia" is the Latinized form of Greek (''Arach┼Źs├Ł─ü''). "The same region appears in the
 The region is first referred to in the Achaemenid-era Elamite Persepolis fortification tablets. It appears again in the
The region is first referred to in the Achaemenid-era Elamite Persepolis fortification tablets. It appears again in the  The chronologically next reference to Arachosia comes from the Greeks and Romans, who record that under
The chronologically next reference to Arachosia comes from the Greeks and Romans, who record that under
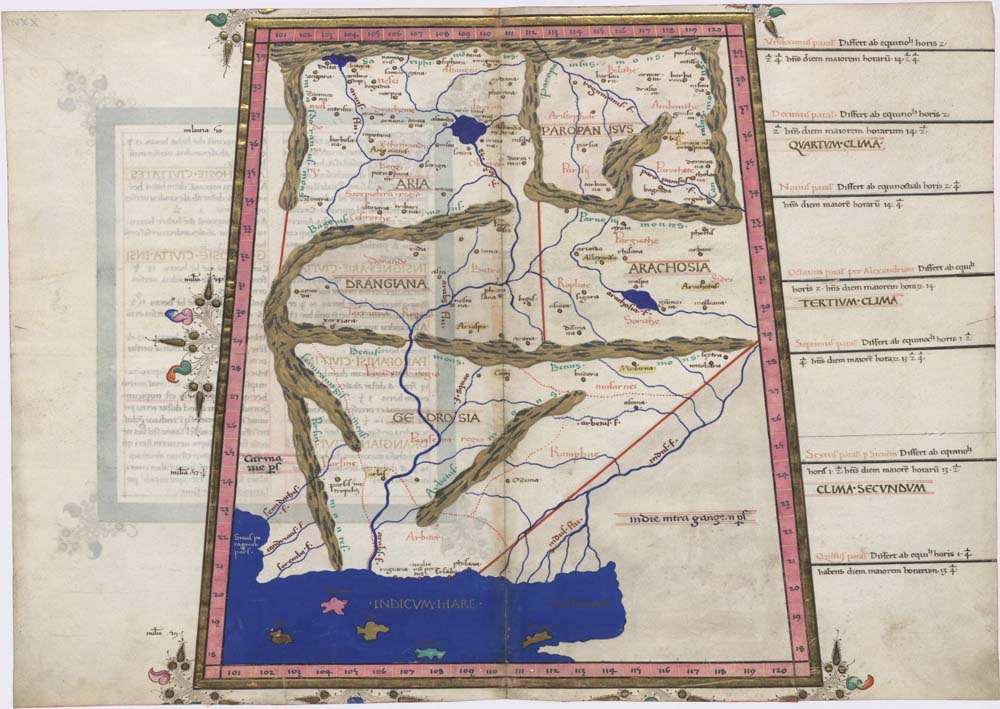 The inhabitants of Arachosia were Iranian peoples, and were referred to as ''Arachosians'' or ''Arachoti''. They were called ''Pactyans'' in reference to their individual ethnicity, and that name may have been in reference to the modern-day ethnic group known as the
The inhabitants of Arachosia were Iranian peoples, and were referred to as ''Arachosians'' or ''Arachoti''. They were called ''Pactyans'' in reference to their individual ethnicity, and that name may have been in reference to the modern-day ethnic group known as the
The Western Regions according to the Hou Hanshu.
' Draft annotated English translation. * Hill, John E. 2004.
' ķŁÅńĢź ''by Yu Huan'' ķŁÜĶ▒ó'': A Third Century Chinese Account Composed between 239 and 265 CE.'' Draft annotated English translation. * Hill, John E. (2009) ''Through the Jade Gate to Rome: A Study of the Silk Routes during the Later Han Dynasty, 1st to 2nd Centuries CE''. BookSurge, Charleston, South Carolina. . * Toynbee, Arnold J. (1961). ''Between Oxus and Jumna''. London. Oxford University Press. * Vogelsang, W. (1985). "Early historical Arachosia in South-east Afghanistan; Meeting-place between East and West." ''Iranica antiqua'', 20 (1985), pp. 55ŌĆō99.
* {{Authority control Historical regions of Afghanistan Ancient history of Afghanistan Historical regions
 Arachosia () is the Hellenized name of an ancient
Arachosia () is the Hellenized name of an ancient satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with consid ...
y situated in the eastern parts of the Achaemenid empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, ÉĦÉÅüÉÅé, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
. It was centred around the valley of the Arghandab River in modern-day southern Afghanistan, and extended as far east as the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
, in modern-day Pakistan. The Old Persian
Old Persian is one of the two directly attested Old Iranian languages (the other being Avestan language, Avestan) and is the ancestor of Middle Persian (the language of Sasanian Empire). Like other Old Iranian languages, it was known to its native ...
form of its name is ''Harauvati┼Ī'', being the etymological equivalent of Vedic Sanskrit ''S├Īrasvat─½''. The province name is derived after its main river, the modern Arghandab (in Greek called Arach┼Źt├│s), a tributary of the Helmand river. The capital of Arachosia was Alexandria of Arachosia
Alexandria in Arachosia ( el, ß╝ł╬╗╬Ą╬Š╬¼╬Į╬┤Žü╬Ą╬╣╬▒ ß╝łŽü╬▒ŽćŽēŽā╬»╬▒Žé) also known as Alexandropolis (ß╝ł╬╗╬Ą╬Š╬▒╬Į╬┤ŽüŽīŽĆ╬┐╬╗╬╣Žé) was a city in ancient times that is now called Kandahar in Afghanistan. It was one of more than twenty citie ...
, an ancient Greek city that was situated over what is now known as Kandahar.
Etymology
 "Arachosia" is the Latinized form of Greek (''Arach┼Źs├Ł─ü''). "The same region appears in the
"Arachosia" is the Latinized form of Greek (''Arach┼Źs├Ł─ü''). "The same region appears in the Avestan
Avestan (), or historically Zend, is an umbrella term for two Old Iranian languages: Old Avestan (spoken in the 2nd millennium BCE) and Younger Avestan (spoken in the 1st millennium BCE). They are known only from their conjoined use as the scrip ...
'' Vid─ōvd─üt'' (1.12) under the indigenous dialect form ɼĄÉ¼ĆɼŁÉ¼ĆɼōɼĆɼīɼÖɼŹ - (whose ''-axva-'' is typical non-Avestan)." In Old Persian
Old Persian is one of the two directly attested Old Iranian languages (the other being Avestan language, Avestan) and is the ancestor of Middle Persian (the language of Sasanian Empire). Like other Old Iranian languages, it was known to its native ...
inscriptions, the region is referred to as ÉÅāÉÄ╝ÉÄóÉÄ║ÉĽÉÄĪÉÅü, written ''h(a)-r(a)-u-v(a)-t-i''. This form is the "etymological equivalent" of Vedic Sanskrit -, the name of a river literally meaning "rich in waters/lakes" and derived from ''s├Īras-'' "lake, pond." (''cf.'' Aredvi Sura Anahita).
"Arachosia" was named after the name of a river that runs through it, known in ancient Greek as the ''Arach┼Źt├│s'' and today as the Arghandab River, a left-bank tributary of the Helmand River.
Geography
Arachosia bordered on Drangiana to the west, on the Paropamisadae to the north, Hindush to the east, and Gedrosia to the south. Isidore and Ptolemy (6.20.4-5) each provide a list of cities in Arachosia, among them (yet another) Alexandria, which lay on the river Arachotus. This city is frequently misidentified with present-day Kandahar in Afghanistan, the name of which was thought to be derived (via "Iskanderiya") from "Alexandria", reflecting a connection to Alexander the Great's visit to the city on his campaign towards India. But a recent discovery of an inscription on a clay tablet has provided proof that 'Kandahar' was already a city that traded actively with Persia well before Alexander's time. Isidore,Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
(11.8.9) and Pliny (6.61) also refer to the city as "metropolis of Arachosia."
In his list, Ptolemy also refers to a city named Arachotus ( en, Arachote ; el, ) or Arachoti (acc. to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
), which was the earlier capital of the land. Pliny the Elder and Stephen of Byzantium
Stephanus or Stephan of Byzantium ( la, Stephanus Byzantinus; grc-gre, ╬ŻŽä╬ŁŽå╬▒╬Į╬┐Žé ╬ÆŽģ╬Č╬¼╬ĮŽä╬╣╬┐Žé, ''St├®phanos Byz├Īntios''; centuryAD), was a Byzantine grammarian and the author of an important geographical dictionary entitled ''Ethni ...
mention that its original name was Cophen (╬ÜŽēŽå╬«╬Į). Hsuan Tsang
Xuanzang (, ; 602ŌĆō664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
refers to the name as ''Kaofu''. This city is identified today with Arghandab which lies northwest of present-day Kandahar.
History
 The region is first referred to in the Achaemenid-era Elamite Persepolis fortification tablets. It appears again in the
The region is first referred to in the Achaemenid-era Elamite Persepolis fortification tablets. It appears again in the Old Persian
Old Persian is one of the two directly attested Old Iranian languages (the other being Avestan language, Avestan) and is the ancestor of Middle Persian (the language of Sasanian Empire). Like other Old Iranian languages, it was known to its native ...
, Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform, early writing system
* Akkadian myt ...
and Aramaic inscriptions of Darius I
Darius I ( peo, ÉÄŁÉÄĀÉÄ╝ÉÄ╣ÉÄ║ÉÄóÉÅü ; grc-gre, ╬ö╬▒Žü╬Ąß┐¢╬┐Žé ; ŌĆō 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his ...
and Xerxes I among lists of subject peoples and countries. It is subsequently also identified as the source of the ivory used in Darius' palace at Susa. In the Behistun inscription (DB 3.54-76), the King recounts that a Persian was thrice defeated by the Achaemenid governor of Arachosia, Vivana, who so ensured that the province remained under Darius' control. It has been suggested that this "strategically unintelligible engagement" was ventured by the rebel because "there were close relations between Persia and Arachosia concerning the Zoroastrian faith."
 The chronologically next reference to Arachosia comes from the Greeks and Romans, who record that under
The chronologically next reference to Arachosia comes from the Greeks and Romans, who record that under Darius III
Darius III ( peo, ÉÄŁÉÄĀÉÄ╝ÉÄ╣ÉÄ║ÉÄóÉÅü ; grc-gre, ╬ö╬▒Žü╬Ąß┐¢╬┐Žé ; c. 380 ŌĆō 330 BC) was the last Achaemenid King of Kings of Persia, reigning from 336 BC to his death in 330 BC.
Contrary to his predecessor Artaxerxes IV Arses, Dar ...
the Arachosians and Drangians were under the command of a governor who, together with the army of the Bactrian governor, contrived a plot of the Arachosians against Alexander ( Curtius Rufus 8.13.3). Following Alexander's conquest of the Achaemenids, the Macedonian appointed his generals as governors (Arrian 3.28.1, 5.6.2; Curtius Rufus 7.3.5; Plutarch, Eumenes 19.3; Polyaenus 4.6.15; Diodorus 18.3.3; Orosius 3.23.1 3; Justin 13.4.22).
In 316 BCE Antigonus I Monophthalmus
Antigonus I Monophthalmus ( grc-gre, ß╝ł╬ĮŽä╬»╬│╬┐╬Į╬┐Žé ╬£╬┐╬ĮŽīŽå╬Ė╬▒╬╗╬╝╬┐Žé , 'the One-Eyed'; 382 ŌĆō 301 BC), son of Philip from Elimeia, was a Macedonian Greek nobleman, general, satrap, and king. During the first half of his life he serv ...
sent most of the elite Argyraspides, a veteran Macedonian corps with over forty years experience, to Arachosia to protect the Eastern frontier with India. However they were sent with the order to Sibyrtius, the Macedonian satrap of Arachosia, to dispatch them by small groups of two or three to dangerous missions so that their numbers would rapidly dwindle and remove them as a military threat to his power.
Following the Wars of the Diadochi, the region became part of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, ╬Æ╬▒Žā╬╣╬╗╬Ą╬»╬▒ Žäß┐Č╬Į ╬Ż╬Ą╬╗╬ĄŽģ╬║╬╣╬┤ß┐Č╬Į, ''Basile├Ła t┼Źn Seleukid┼Źn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
, which traded it to the Mauryan Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
in 305 BCE as part of an alliance. The Shunga dynasty
The Shunga Empire (IAST: ') was an ancient Indian dynasty from Magadha that controlled areas of the most of the northern Indian subcontinent from around 185 to 73 BCE. The dynasty was established by Pushyamitra, after taking the throne of the ...
overthrew the Mauryans in 185 BC, but shortly afterwards lost Arachosia to the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Hellenistic Greece, Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Helleni ...
. It then became part of the break-away Indo-Greek Kingdom in the mid 2nd century BCE. Indo-Scythians expelled the Indo-Greeks by the mid 1st century BCE, but lost the region to the Arsacids and Indo-Parthians. At what time (and in what form) Parthian rule over Arachosia was reestablished cannot be determined with any authenticity. From Isidore 19 it is certain that a part (perhaps only a little) of the region was under Arsacid rule in the 1st century CE, and that the Parthians called it ''Indik─ō Leuk─ō'', "White India."
The Kushans captured Arachosia from the Indo-Parthians and ruled the region until around 230 CE, when they were defeated by the Sassanids, the second Persian Empire, after which the Kushans were replaced by Sassanid vassals known as the Kushanshas or Indo-Sassanids. In 420 CE the Kushanshas were driven out of present Afghanistan by the Chionites, who established the Kidarite Kingdom. The Kidarites
The Kidarites, or Kidara Huns, were a dynasty that ruled Bactria and adjoining parts of Central Asia and South Asia in the 4th and 5th centuries. The Kidarites belonged to a complex of peoples known collectively in India as the Huna, and in Euro ...
were replaced in the 460s CE by the Hephthalites, who were defeated in 565 CE by a coalition of Persian and Turkish armies. Arachosia became part of the surviving Kushano-Hephthalite
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ╬Ę╬▓╬┐╬┤╬▒╬╗╬┐, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian languages, Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Cen ...
Kingdoms of Kapisa, then Kabul, before coming under attack from the Moslem Arabs. These kingdoms were at first vassals of Sassanids. Around 870 CE the Kushano-Hephthalites (aka Turkshahi Dynasty) was replaced by the Saffarids, then the Samanid Empire and Muslim Turkish Ghaznavids
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( fa, ž║ž▓┘å┘ł█īž¦┘å ''─Āaznaviy─ün'') was a culturally Persianate, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic ''mamluk'' origin, ruling, at its greatest extent, large parts of Persia, Khorasan, much of Transoxiana and the northwest ...
in the early 11th century CE.
Arab geographers referred to the region (or parts of it) as 'Arokhaj', 'Rokhaj', 'Rohkaj' or simply 'Roh'.
Inhabitants
 The inhabitants of Arachosia were Iranian peoples, and were referred to as ''Arachosians'' or ''Arachoti''. They were called ''Pactyans'' in reference to their individual ethnicity, and that name may have been in reference to the modern-day ethnic group known as the
The inhabitants of Arachosia were Iranian peoples, and were referred to as ''Arachosians'' or ''Arachoti''. They were called ''Pactyans'' in reference to their individual ethnicity, and that name may have been in reference to the modern-day ethnic group known as the Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, ┘Š┌Üž¬ž¦┘å┘ć, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically re ...
.
Isidore of Charax, in his 1st-century CE "Parthian stations" itinerary, described an "Alexandropolis, the metropolis of Arachosia", which he said was still Greek even at such a late time:
Theory of Croatian origin from the Iranian peoples
One theory of Croatian origin traces the origin of the Croats to the area of Arachosia. This connection was at first drawn due to the similarity of Croatian ( Croatia -Croatian
Croatian may refer to:
* Croatia
*Croatian language
*Croatian people
*Croatians (demonym)
See also
*
*
* Croatan (disambiguation)
* Croatia (disambiguation)
* Croatoan (disambiguation)
* Hrvatski (disambiguation)
* Hrvatsko (disambiguation)
* S ...
: Hrvatska, Croats - Croatian: Hrvati / ─īakavian dialect
Chakavian or ─īakavian (, , , sh-Latn, ─Źakavski proper name: or own name: ''─Źokovski, ─Źakavski, ─Źekavski'') is a South Slavic regiolect or language spoken primarily by Croats along the Adriatic coast, in the historical regions of Dalmat ...
: Harvati / Kajkavian dialect: Horvati) and Arachosian name, but other researches indicate that there are also linguistic, cultural, agrobiological and genetic ties. Since Croatia became an independent state in 1991, the Iranian theory gained more popularity, and many scientific papers and books have been published.Vernadsky 1952: "Der sarmatische Hintergrund der germanischen Voelkerwanderung," (Sarmatian background of the Germanic Migrations), G. Vernadsky, Saeculum, II (1952), 340-347.
See also
* History of Afghanistan * Kandahar province * Old KandaharNotes
References
* Frye, Richard N. (1963). ''The Heritage of Persia''. World Publishing company, Cleveland, Ohio. Mentor Book edition, 1966. * Hill, John E. 2004.The Western Regions according to the Hou Hanshu.
' Draft annotated English translation. * Hill, John E. 2004.
' ķŁÅńĢź ''by Yu Huan'' ķŁÜĶ▒ó'': A Third Century Chinese Account Composed between 239 and 265 CE.'' Draft annotated English translation. * Hill, John E. (2009) ''Through the Jade Gate to Rome: A Study of the Silk Routes during the Later Han Dynasty, 1st to 2nd Centuries CE''. BookSurge, Charleston, South Carolina. . * Toynbee, Arnold J. (1961). ''Between Oxus and Jumna''. London. Oxford University Press. * Vogelsang, W. (1985). "Early historical Arachosia in South-east Afghanistan; Meeting-place between East and West." ''Iranica antiqua'', 20 (1985), pp. 55ŌĆō99.
External links
* {{Authority control Historical regions of Afghanistan Ancient history of Afghanistan Historical regions