Appendix Rupture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Appendicitis is

 Acute appendicitis seems to be the result of a primary obstruction of the appendix. Once this obstruction occurs, the appendix becomes filled with
Acute appendicitis seems to be the result of a primary obstruction of the appendix. Once this obstruction occurs, the appendix becomes filled with
 Diagnosis is based on a medical history (symptoms) and physical examination, which can be supported by an elevation of neutrophilic white blood cells and imaging studies if needed. Histories fall into two categories, typical and atypical.
Typical appendicitis includes several hours of generalized abdominal pain that begins in the region of the umbilicus with associated anorexia, nausea, or vomiting. The pain then "localizes" into the right lower quadrant where the tenderness increases in intensity. It is possible the pain could localize to the left lower quadrant in people with
Diagnosis is based on a medical history (symptoms) and physical examination, which can be supported by an elevation of neutrophilic white blood cells and imaging studies if needed. Histories fall into two categories, typical and atypical.
Typical appendicitis includes several hours of generalized abdominal pain that begins in the region of the umbilicus with associated anorexia, nausea, or vomiting. The pain then "localizes" into the right lower quadrant where the tenderness increases in intensity. It is possible the pain could localize to the left lower quadrant in people with
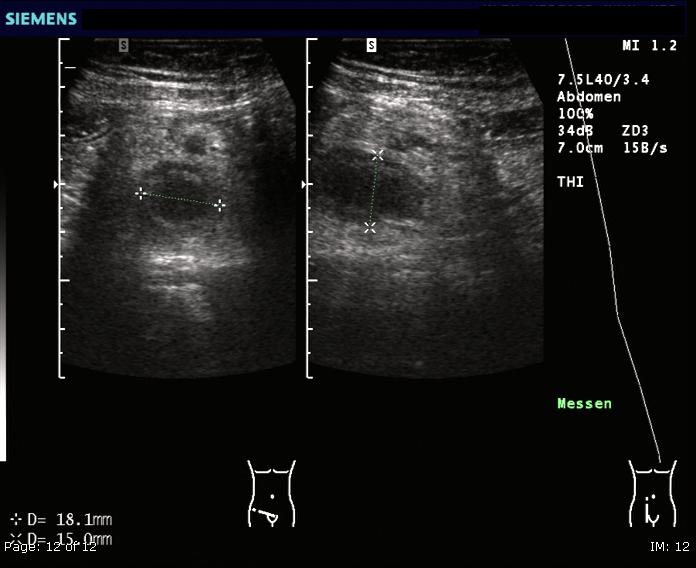 Abdominal ultrasonography, preferably with
Abdominal ultrasonography, preferably with
File:UOTW 45 - Ultrasound of the Week 1.webm, Ultrasound showing appendicitis and an appendicolith
File:UOTW 45 - Ultrasound of the Week 3.jpg, Ultrasound showing appendicitis and an appendicolith
File:Ultrasonography of a normal appendix, annotated.jpg, Ultrasound of a normal appendix for comparison
File:Ultrasonography of a normal appendix without and with compression.jpg, A normal appendix without and with compression. Absence of compressibility indicates appendicitis.

 Where it is readily available,
Where it is readily available,
 In general, plain abdominal radiography (PAR) is not useful in making the diagnosis of appendicitis and should not be routinely obtained from a person being evaluated for appendicitis. Plain abdominal films may be useful for the detection of ureteral calculi,
In general, plain abdominal radiography (PAR) is not useful in making the diagnosis of appendicitis and should not be routinely obtained from a person being evaluated for appendicitis. Plain abdominal films may be useful for the detection of ureteral calculi,
An opaque
File:Appendicitis - low mag.jpg,
 Children:
Children:


 The surgical procedure for the removal of the appendix is called an
The surgical procedure for the removal of the appendix is called an
 The surgeon will explain how long the recovery process should take. Abdomen hair is usually removed to avoid complications that may appear regarding the incision.
In most cases, patients going in for surgery experience nausea or vomiting that require medication before surgery. Antibiotics, along with pain medication, may be administered before appendectomies.
The surgeon will explain how long the recovery process should take. Abdomen hair is usually removed to avoid complications that may appear regarding the incision.
In most cases, patients going in for surgery experience nausea or vomiting that require medication before surgery. Antibiotics, along with pain medication, may be administered before appendectomies.
 Hospital lengths of stay typically range from a few hours to a few days but can be a few weeks if complications occur. The recovery process may vary depending on the severity of the condition: if the appendix had ruptured or not before surgery. Appendix surgery recovery is generally a lot faster if the appendix did not rupture. It is important that people undergoing surgery respect their doctor's advice and limit their physical activity so the tissues can heal faster. Recovery after an appendectomy may not require diet changes or a lifestyle change.
The length of hospital stays for appendicitis varies on the severity of the condition. A study from the United States found that in 2010, the average appendicitis hospital stay was 1.8 days. For stays where the person's appendix had ruptured, the average length of stay was 5.2 days.
After surgery, the patient will be transferred to a
Hospital lengths of stay typically range from a few hours to a few days but can be a few weeks if complications occur. The recovery process may vary depending on the severity of the condition: if the appendix had ruptured or not before surgery. Appendix surgery recovery is generally a lot faster if the appendix did not rupture. It is important that people undergoing surgery respect their doctor's advice and limit their physical activity so the tissues can heal faster. Recovery after an appendectomy may not require diet changes or a lifestyle change.
The length of hospital stays for appendicitis varies on the severity of the condition. A study from the United States found that in 2010, the average appendicitis hospital stay was 1.8 days. For stays where the person's appendix had ruptured, the average length of stay was 5.2 days.
After surgery, the patient will be transferred to a

 Appendicitis is most common between the ages of 5 and 40. In 2013, it resulted in 72,000 deaths globally, down from 88,000 in 1990.
In the United States, there were nearly 293,000 hospitalizations involving appendicitis in 2010. Appendicitis is one of the most frequent diagnoses for emergency department visits resulting in hospitalization among children ages 5–17 years in the United States.
Appendicitis is most common between the ages of 5 and 40. In 2013, it resulted in 72,000 deaths globally, down from 88,000 in 1990.
In the United States, there were nearly 293,000 hospitalizations involving appendicitis in 2010. Appendicitis is one of the most frequent diagnoses for emergency department visits resulting in hospitalization among children ages 5–17 years in the United States.
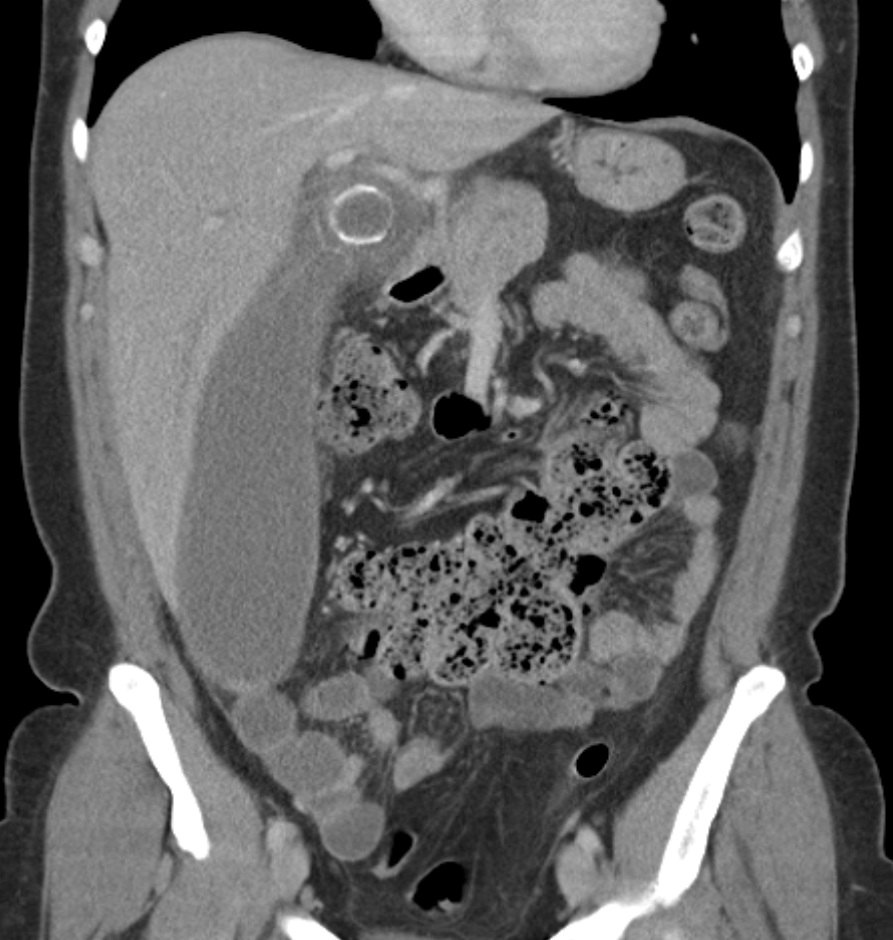
CT of the abdomen showing acute appendicitis
by Surgeons Net Education
from the Merck Manual Professional (content last modified September 2007)
Appendicitis – Symptoms Causes and Treatment
at Health N Surgery {{Authority control Acute pain Diseases of appendix General surgery Inflammations Medical emergencies Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
of the appendix
Appendix, or its plural form appendices, may refer to:
__NOTOC__ In documents
* Addendum, an addition made to a document by its author after its initial printing or publication
* Bibliography, a systematic list of books and other works
* Index (pub ...
. Symptoms commonly include right lower abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than ...
, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the Human nose, nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like Food-poisoning, foo ...
, and decreased appetite
Anorexia is a medical term for a loss of appetite. While the term in non-scientific publications is often used interchangeably with anorexia nervosa, many possible causes exist for a loss of appetite, some of which may be harmless, while others i ...
. However, approximately 40% of people do not have these typical symptoms. Severe complications of a ruptured appendix include widespread, painful inflammation of the inner lining of the abdominal wall and sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
.
Appendicitis is caused by a blockage of the hollow portion of the appendix. This is most commonly due to a calcified "stone" made of feces. Inflamed lymphoid tissue from a viral infection, parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
s, gallstone, or tumors
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
may also cause the blockage. This blockage leads to increased pressures in the appendix, decreased blood flow to the tissues of the appendix, and bacterial growth inside the appendix causing inflammation. The combination of inflammation, reduced blood flow to the appendix and distention of the appendix causes tissue injury and tissue death. If this process is left untreated, the appendix may burst, releasing bacteria into the abdominal cavity, leading to increased complications.
The diagnosis of appendicitis is largely based on the person's signs and symptoms. In cases where the diagnosis is unclear, close observation, medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
, and laboratory tests can be helpful. The two most common imaging tests used are an ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hea ...
and computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
(CT scan). CT scan has been shown to be more accurate than ultrasound in detecting acute appendicitis. However, ultrasound may be preferred as the first imaging test in children and pregnant women because of the risks associated with radiation exposure from CT scans.
The standard treatment for acute appendicitis is surgical removal of the appendix. This may be done by an open incision in the abdomen (laparotomy
A laparotomy is a surgical procedure involving a surgical incision through the abdominal wall to gain access into the abdominal cavity. It is also known as a celiotomy.
Origins and history
The first successful laparotomy was performed without ane ...
) or through a few smaller incisions with the help of cameras ( laparoscopy). Surgery decreases the risk of side effects or death associated with rupture of the appendix. Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s may be equally effective in certain cases of non-ruptured appendicitis. It is one of the most common and significant causes of abdominal pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
that comes on quickly. In 2015 about 11.6 million cases of appendicitis occurred which resulted in about 50,100 deaths. In the United States, appendicitis is one of the most common cause of sudden abdominal pain requiring surgery. Each year in the United States, more than 300,000 people with appendicitis have their appendix surgically removed. Reginald Fitz is credited with being the first person to describe the condition in 1886.
Signs and symptoms
The presentation of acute appendicitis includes acute abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. As the appendix becomes more swollen and inflamed, it begins to irritate the adjoining abdominal wall. This leads to the localization of the pain to the right lower quadrant. This classic migration of pain may not be seen in children under three years. This pain can be elicited through signs, which can feel sharp. Pain from appendicitis may begin as dull pain around the navel. After several hours, pain will usually transition towards the right lower quadrant, where it becomes localized. Symptoms include localized findings in the right iliac fossa. The abdominal wall becomes very sensitive to gentle pressure ( palpation). There is pain in the sudden release of deep tension in the lower abdomen (Blumberg sign
Blumberg's sign (also referred to as rebound tenderness or Shchetkin–Blumberg's sign) is a clinical sign in which there is pain upon removal of pressure rather than application of pressure to the abdomen. (The latter is referred to simply as '' ...
). If the appendix is retrocecal (localized behind the cecum), even deep pressure in the right lower quadrant may fail to elicit tenderness (silent appendix). This is because the cecum, distended with gas, protects the inflamed appendix from pressure. Similarly, if the appendix lies entirely within the pelvis, there is typically a complete absence of abdominal rigidity. In such cases, a digital rectal examination
Digital rectal examination (DRE; la, palpatio per anum, PPA) is an internal examination of the rectum, performed by a healthcare provider. Prior to a 2018 report from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, the DRE was a common and "dreaded" co ...
elicits tenderness in the rectovesical pouch. Coughing causes point tenderness in this area ( McBurney's point), historically called Dunphy's sign
Dunphy's sign is a medical sign characterized by increased abdominal pain with coughing. It may be an indicator of appendicitis. Named after Osborne Joby Dunphy (1898–1989), a British-American
British American usually refers to Americans ...
.
Causes
 Acute appendicitis seems to be the result of a primary obstruction of the appendix. Once this obstruction occurs, the appendix becomes filled with
Acute appendicitis seems to be the result of a primary obstruction of the appendix. Once this obstruction occurs, the appendix becomes filled with mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is ...
and swells. This continued production of mucus leads to increased pressures within the lumen and the walls of the appendix. The increased pressure results in thrombosis
Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek "clotting") is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thro ...
and occlusion of the small vessels, and stasis of lymphatic flow. At this point, spontaneous recovery rarely occurs. As the occlusion of blood vessels progresses, the appendix becomes ischemic and then necrotic. As bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
begin to leak out through the dying walls, pus
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during bacterial or fungal infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection ...
forms within and around the appendix (suppuration). The result is appendiceal rupture (a 'burst appendix') causing peritonitis, which may lead to sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
and in rare cases, death
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain ...
. These events are responsible for the slowly evolving abdominal pain and other commonly associated symptoms.
The causative agents include bezoar
A bezoar is a mass often found trapped in the gastrointestinal system, though it can occur in other locations. A pseudobezoar is an indigestible object introduced intentionally into the digestive system.
There are several varieties of bezoar, s ...
s, foreign bodies, trauma
Trauma most often refers to:
*Major trauma, in physical medicine, severe physical injury caused by an external source
*Psychological trauma, a type of damage to the psyche that occurs as a result of a severely distressing event
*Traumatic inju ...
, lymphadenitis and, most commonly, calcified fecal deposits that are known as appendicolith
A fecalith is a stone made of feces. It is a hardening of feces into lumps of varying size and may occur anywhere in the intestinal tract but is typically found in the colon. It is also called appendicolith when it occurs in the appendix and is s ...
s or fecalith
A fecalith is a stone made of feces. It is a hardening of feces into lumps of varying size and may occur anywhere in the intestinal tract but is typically found in the colon. It is also called appendicolith when it occurs in the appendix and is ...
s. The occurrence of obstructing fecaliths has attracted attention since their presence in people with appendicitis is higher in developed than in developing countries. In addition an appendiceal fecalith is commonly associated with complicated appendicitis. Fecal stasis and arrest may play a role, as demonstrated by people with acute appendicitis having fewer bowel movements per week compared with healthy controls.
The occurrence of a fecalith in the appendix was thought to be attributed to a right-sided fecal retention reservoir in the colon and a prolonged transit time. However, a prolonged transit time was not observed in subsequent studies. Diverticular disease
Diverticular disease is when problems occur due to diverticulosis, a condition defined by the presence of pouches in the wall of the large intestine (diverticula). This includes diverticula becoming inflamed ( diverticulitis) or bleeding. Colonic ...
and adenomatous polyps
In anatomy, a polyp is an abnormal growth of tissue projecting from a mucous membrane. If it is attached to the surface by a narrow elongated stalk, it is said to be ''pedunculated''; if it is attached without a stalk, it is said to be ''sess ...
was historically unknown and colon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel mo ...
was exceedingly rare in communities where appendicitis itself was rare or absent, such as various African communities. Studies have implicated a transition to a Western diet lower in fibre
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate ...
in rising frequencies of appendicitis as well as the other aforementioned colonic diseases in these communities. And acute appendicitis has been shown to occur antecedent to cancer in the colon and rectum. Several studies offer evidence that a low fiber intake is involved in the pathogenesis of appendicitis. This low intake of dietary fiber is in accordance with the occurrence of a right-sided fecal reservoir and the fact that dietary fiber reduces transit time.
Diagnosis
 Diagnosis is based on a medical history (symptoms) and physical examination, which can be supported by an elevation of neutrophilic white blood cells and imaging studies if needed. Histories fall into two categories, typical and atypical.
Typical appendicitis includes several hours of generalized abdominal pain that begins in the region of the umbilicus with associated anorexia, nausea, or vomiting. The pain then "localizes" into the right lower quadrant where the tenderness increases in intensity. It is possible the pain could localize to the left lower quadrant in people with
Diagnosis is based on a medical history (symptoms) and physical examination, which can be supported by an elevation of neutrophilic white blood cells and imaging studies if needed. Histories fall into two categories, typical and atypical.
Typical appendicitis includes several hours of generalized abdominal pain that begins in the region of the umbilicus with associated anorexia, nausea, or vomiting. The pain then "localizes" into the right lower quadrant where the tenderness increases in intensity. It is possible the pain could localize to the left lower quadrant in people with situs inversus totalis
Situs inversus (also called situs transversus or oppositus) is a congenital condition in which the major visceral organs are reversed or mirrored from their normal positions. The normal arrangement of internal organs is known as situs solitus. Al ...
. The combination of pain, anorexia, leukocytosis, and fever is classic.
Atypical histories lack this typical progression and may include pain in the right lower quadrant as an initial symptom. Irritation of the peritoneum (inside lining of the abdominal wall) can lead to increased pain on movement, or jolting, for example going over speed bumps. Atypical histories often require imaging with ultrasound or CT scanning.
Clinical
*Aure-Rozanova's sign
Aure-Rozanova's sign is a medical sign
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowere ...
: Increased pain on palpation with finger in right Petit triangle
The lumbar triangle can refer to either the inferior lumbar (Petit) triangle, which lies superficially, or the superior lumbar (Grynfeltt) triangle, which is deep and superior to the inferior triangle. Of the two, the superior triangle is the more ...
(can be a positive Shchetkin-Bloomberg's).
* Bartomier-Michelson's sign
Bartomier-Michelson's sign is a medical sign characterized by increased pain on palpation at the right iliac region as the person being examined lies on their left side compared to when they lie on their back.
It helps in detection of appendicit ...
: Increased pain on palpation at the right iliac region as the person being examined lies on their left side compared to when they lie on their back.
* Dunphy's sign
Dunphy's sign is a medical sign characterized by increased abdominal pain with coughing. It may be an indicator of appendicitis. Named after Osborne Joby Dunphy (1898–1989), a British-American
British American usually refers to Americans ...
: Increased pain in the right lower quadrant with coughing.
* Hamburger sign The hamburger sign is used in the diagnosis of appendicitis. The sign is used to rule out that disease, with the physician inquiring if the patient would like to consume his/her favourite food. If a patient wants to eat, consider a diagnosis other t ...
: The patient refuses to eat ( anorexia is 80% sensitive for appendicitis)
* Kocher's (Kosher's) sign: From the person's medical history, the start of pain in the umbilical region with a subsequent shift to the right iliac region.
* Massouh sign Massouh's sign is a clinical sign for acute localised appendicitis, named after General Surgeon Farouk Massouh from Frimley Park Hospital in Frimley ( Surrey, the United Kingdom).
The sign describes a firm swish of the examiner’s index and middl ...
: Developed in and popular in southwest England, the examiner performs a firm swish with his or her index and middle finger across the abdomen from the xiphoid process to the left and the right iliac fossa.
* Obturator sign
The obturator sign, also called Cope's obturator test, is an indicator of irritation to the obturator internus muscle.
The technique for detecting the obturator sign, called the ''obturator test'', is carried out on each leg in succession. The pa ...
: The person being evaluated lies on her or his back with the hip and knee both flexed at ninety degrees. The examiner holds the person's ankle with one hand and knee with the other hand. The examiner rotates the hip by moving the person's ankle away from his or her body while allowing the knee to move only inward. A positive test is pain with internal rotation of the hip.
* Psoas sign, also known as "Obraztsova's sign", is right lower-quadrant pain that is produced with either the passive extension of the right hip or by the active flexion of the person's right hip while supine. The pain that is elicited is due to inflammation of the peritoneum overlying the iliopsoas muscles and inflammation of the psoas muscles themselves. Straightening out the leg causes pain because it stretches these muscles, while flexing the hip activates the iliopsoas and causes pain.
* Rovsing's sign
Rovsing's sign, named after the Danish surgeon Niels Thorkild Rovsing (1862–1927), is a sign of appendicitis. If palpation of the left lower quadrant of a person's abdomen increases the pain felt in the right lower quadrant, the patient is said ...
: Pain in the lower right abdominal quadrant with continuous deep palpation starting from the left iliac fossa upwards (counterclockwise along the colon). The thought is there will be increased pressure around the appendix by pushing bowel contents and air toward the ileocaecal valve
The ileocecal valve (ileal papilla, ileocaecal valve, Tulp's valve, Tulpius valve, Bauhin's valve, ileocecal eminence, valve of Varolius or colic valve) is a sphincter muscle valve that separates the small intestine and the large intestine. Its cr ...
provoking right-sided abdominal pain.
* Sitkovskiy (Rosenstein)'s sign: Increased pain in the right iliac region as the person is being examined lies on their left side.
*Perman's sign: In acute appendicitis palpation in the left iliac fossa may produce pain in the right iliac fossa.
Blood and urine test
While there is no laboratory test specific for appendicitis, acomplete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cell ...
(CBC) is done to check for signs of infection. Although 70–90 percent of people with appendicitis may have an elevated white blood cell (WBC) count, there are many other abdominal and pelvic conditions that can cause the WBC count to be elevated. Due to its low sensitivity and specificity, on its own, WBC is not seen as a good indicator of appendicitis.
A urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and microscopic examination. Macroscopic e ...
generally does not show infection, but it is important for determining pregnancy status, especially the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these symptoms. ...
in women of childbearing age. The urinalysis is also important for ruling out a urinary tract infection as the cause of abdominal pain. The presence of more than 20 WBC per high-power field in the urine is more suggestive of a urinary tract disorder.
Imaging
In children the clinical examination is important to determine which children with abdominal pain should receive immediate surgical consultation and which should receive diagnostic imaging. Because of the health risks of exposing children to radiation, ultrasound is the preferred first choice with CT scan being a legitimate follow-up if the ultrasound is inconclusive. CT scan is more accurate than ultrasound for the diagnosis of appendicitis in adults and adolescents. CT scan has a sensitivity of 94%, specificity of 95%. Ultrasonography had an overall sensitivity of 86%, a specificity of 81%.Ultrasound
doppler sonography
Doppler ultrasonography is medical ultrasonography that employs the Doppler effect to perform imaging of the movement of tissues and body fluids (usually blood), and their relative velocity to the probe. By calculating the frequency shift of ...
, is useful to detect appendicitis, especially in children. Ultrasound can show the free fluid collection in the right iliac fossa, along with a visible appendix with increased blood flow when using color Doppler, and noncompressibility of the appendix, as it is essentially walled-off abscess. Other secondary sonographic signs of acute appendicitis include the presence of echogenic mesenteric fat surrounding the appendix and the acoustic shadowing of an appendicolith. In some cases (approximately 5%), ultrasonography of the iliac fossa does not reveal any abnormalities despite the presence of appendicitis. This false-negative finding is especially true of early appendicitis before the appendix has become significantly distended. Also, false-negative findings are more common in adults where larger amounts of fat and bowel gas make visualizing the appendix technically difficult. Despite these limitations, sonographic imaging with experienced hands can often distinguish between appendicitis and other diseases with similar symptoms. Some of these conditions include inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
of lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
near the appendix or pain originating from other pelvic organs such as the ovaries or Fallopian tubes. Ultrasounds may be either done by the radiology department or by the emergency physician.
Computed tomography

 Where it is readily available,
Where it is readily available, computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
(CT) has become frequently used, especially in people whose diagnosis is not obvious on history and physical examination. Although some concerns about interpretation are identified, a 2019 Cochrane review found that sensitivity and specificity of CT for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in adults was high. Concerns about radiation tend to limit use of CT in pregnant women and children, especially with the increasingly widespread usage of MRI.
The accurate diagnosis of appendicitis is multi-tiered, with the size of the appendix having the strongest positive predictive value
The positive and negative predictive values (PPV and NPV respectively) are the proportions of positive and negative results in statistics and diagnostic tests that are true positive and true negative results, respectively. The PPV and NPV descr ...
, while indirect features can either increase or decrease sensitivity and specificity. A size of over 6 mm is both 95% sensitive and specific for appendicitis.
However, because the appendix can be filled with fecal material, causing intraluminal distention, this criterion has shown limited utility in more recent meta-analyses. This is as opposed to ultrasound, in which the wall of the appendix can be more easily distinguished from intraluminal feces. In such scenarios, ancillary features such as increased wall enhancement as compared to adjacent bowel and inflammation of the surrounding fat, or fat stranding, can be supportive of the diagnosis. However, their absence does not preclude it. In severe cases with perforation, an adjacent phlegmon
A phlegmon is a localized area of acute inflammation of the soft tissues. It is a descriptive term which may be used for inflammation related to a bacterial infection or non-infectious causes (e.g. pancreatitis). Most commonly, it is used in con ...
or abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends b ...
can be seen. Dense fluid layering in the pelvis can also result, related to either pus
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during bacterial or fungal infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection ...
or enteric spillage. When patients are thin or younger, the relative absence of fat can make the appendix and surrounding fat stranding difficult to see.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(MRI) use has become increasingly common for diagnosis of appendicitis in children and pregnant patients due to the radiation dosage that, while of nearly negligible risk in healthy adults, can be harmful to children or the developing baby. In pregnancy, it is more useful during the second and third trimester, particularly as the enlargening uterus displaces the appendix, making it difficult to find by ultrasound. The periappendiceal stranding that is reflected on CT by fat stranding on MRI appears as an increased fluid signal on T2 weighted sequences. First trimester pregnancies are usually not candidates for MRI, as the fetus is still undergoing organogenesis, and there are no long-term studies to date regarding its potential risks or side effects.
X-ray
 In general, plain abdominal radiography (PAR) is not useful in making the diagnosis of appendicitis and should not be routinely obtained from a person being evaluated for appendicitis. Plain abdominal films may be useful for the detection of ureteral calculi,
In general, plain abdominal radiography (PAR) is not useful in making the diagnosis of appendicitis and should not be routinely obtained from a person being evaluated for appendicitis. Plain abdominal films may be useful for the detection of ureteral calculi, small bowel obstruction
Bowel obstruction, also known as intestinal obstruction, is a mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines which prevents the normal movement of the products of digestion. Either the small bowel or large bowel may be affected. Signs an ...
, or perforated ulcer, but these conditions are rarely confused with appendicitis.APPENDICITIS from Townsend: Sabiston Textbook of Surgery on MD ConsultAn opaque
fecalith
A fecalith is a stone made of feces. It is a hardening of feces into lumps of varying size and may occur anywhere in the intestinal tract but is typically found in the colon. It is also called appendicolith when it occurs in the appendix and is ...
can be identified in the right lower quadrant in fewer than 5% of people being evaluated for appendicitis. A barium enema has proven to be a poor diagnostic tool for appendicitis. While failure of the appendix to fill during a barium enema has been associated with appendicitis, up to 20% of normal appendices do not fill.
Scoring systems
Several scoring systems have been developed to try to identify people who are likely to have appendicitis. The performance of scores such as theAlvarado score
The Alvarado score is a clinical scoring system used in the diagnosis of appendicitis. Alvarado scoring has largely been superseded as a clinical prediction tool by the Appendicitis Inflammatory Response score.
Also known by the mnemonic MANTREL ...
and the Pediatric Appendicitis Score, however, are variable.
The Alvarado score is the most known scoring system. A score below 5 suggests against a diagnosis of appendicitis, whereas a score of 7 or more is predictive of acute appendicitis. In a person with an equivocal score of 5 or 6, a CT scan or ultrasound exam may be used to reduce the rate of negative appendectomy.
Pathology
Even for clinically certain appendicitis, routinehistopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Spe ...
examination of appendectomy specimens is of value for identifying unsuspected pathologies requiring further postoperative management. Notably, appendix cancer
Appendix cancer are very rare cancers of the vermiform appendix.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors are rare tumors with malignant potential. Primary lymphomas can occur in the appendix. Breast cancer, colon cancer, and tumors of the female genital t ...
is found incidentally in about 1% of appendectomy specimens.
Pathology diagnosis of appendicitis can be made by detecting a neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in ...
ic infiltrate of the muscularis propria
The muscular layer (muscular coat, muscular fibers, muscularis propria, muscularis externa) is a region of muscle in many organs in the vertebrate body, adjacent to the submucosa. It is responsible for gut movement such as peristalsis. The Latin, ...
.
Periappendicitis, inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
of tissues around the appendix, is often found in conjunction with other abdominal pathology.
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a mic ...
of appendicitis and periappendicitis. H&E stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnos ...
.
File:Acute appendicitis High Power.jpg, Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a mic ...
of appendicitis showing neutrophils in the muscularis propria. H&E stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnos ...
.
File:Acute suppurative appendicitis with perforation.jpg, Acute suppurative appendicitis with perforation (at right). H&E stain.
Differential diagnosis
 Children:
Children: Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea and gastro, is an inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of energy, and dehydra ...
, mesenteric adenitis
Adenitis is a general term for an inflammation of a gland. Often it is used to refer to lymphadenitis which is the inflammation of a lymph node.
Classification
Lymph node adenitis
''Lymph adenitis'' or ''lymph node adenitis'' is caused by infe ...
, Meckel's diverticulitis, intussusception Intussusception may refer to:
* Intussusception (medical disorder)
Intussusception is a medical condition in which a part of the intestine folds into the section immediately ahead of it. It typically involves the small bowel and less commonly t ...
, Henoch–Schönlein purpura
Henoch–Schönlein purpura (HSP), also known as IgA vasculitis, is a disease of the skin, mucous membranes, and sometimes other organs that most commonly affects children. In the skin, the disease causes palpable purpura (small, raised areas of bl ...
, lobar pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ...
, urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney ...
(abdominal pain in the absence of other symptoms can occur in children with UTI), new-onset Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distension ...
or ulcerative colitis, pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large organ behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and a number of hormones. There are two main types: acute pancreatitis, and chronic pancr ...
, and abdominal trauma from child abuse
Child abuse (also called child endangerment or child maltreatment) is physical, sexual, and/or psychological maltreatment or neglect of a child or children, especially by a parent or a caregiver. Child abuse may include any act or failure to a ...
; distal intestinal obstruction syndrome
Distal intestinal obstruction syndrome (DIOS) involves obstruction of the distal part of the small intestines by thickened intestinal content and occurs in about 20% of mainly adult individuals with cystic fibrosis. DIOS was previously known as ...
in children with cystic fibrosis; typhlitis in children with leukemia.
Women: A pregnancy test is important for all women of childbearing age since an ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these symptoms. ...
can have signs and symptoms similar to those of appendicitis. Other obstetrical/ gynecological causes of similar abdominal pain in women include pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease, also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder (PID), is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, namely the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no ...
, ovarian torsion, menarche
Menarche ( ; ) is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fertility.
Gir ...
, dysmenorrhea, endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease of the female reproductive system in which cells similar to those in the endometrium, the layer of tissue that normally covers the inside of the uterus, grow outside the uterus. Most often this is on the ovaries, f ...
, and Mittelschmerz
''Mittelschmerz'' (German: "middle pain") is a colloquial term for "ovulation pain" or "midcycle pain". About 20% of women experience mittelschmerz, some every cycle, some intermittently.
Signs and symptoms
Mittelschmerz is characterized by lo ...
(the passing of an egg in the ovaries approximately two weeks before menstruation).
Men: testicular torsion
Adults: new-onset Crohn disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distension ...
, ulcerative colitis, regional enteritis, cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. Symptoms include right upper abdominal pain, pain in the right shoulder, nausea, vomiting, and occasionally fever. Often gallbladder attacks (biliary colic) precede acute cholecystitis. The pain l ...
, renal colic, perforated peptic ulcer, pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large organ behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and a number of hormones. There are two main types: acute pancreatitis, and chronic pancr ...
, rectus sheath hematoma
A rectus sheath hematoma is an accumulation of blood in the sheath of the rectus abdominis muscle. It causes abdominal pain with or without a mass.
The hematoma may be caused by either rupture of the Inferior epigastric artery, epigastric artery ...
and epiploic appendagitis
Epiploic appendagitis (EA) is an uncommon, benign, self-limiting inflammatory process of the epiploic appendices. Other, older terms for the process include appendicitis epiploica and appendagitis, but these terms are used less now in order to avo ...
.
Elderly: diverticulitis
Diverticulitis, specifically colonic diverticulitis, is a gastrointestinal disease characterized by inflammation of abnormal pouches—diverticula—which can develop in the wall of the large intestine. Symptoms typically include lower abdominal ...
, intestinal obstruction, colonic carcinoma, mesenteric ischemia
Intestinal ischemia is a medical condition in which injury to the large or small intestine occurs due to not enough blood supply. It can come on suddenly, known as acute intestinal ischemia, or gradually, known as chronic intestinal ischemia. The ...
, leaking aortic aneurysm
An aortic aneurysm is an enlargement (dilatation) of the aorta to greater than 1.5 times normal size. They usually cause no symptoms except when ruptured. Occasionally, there may be abdominal, back, or leg pain. The prevalence of abdominal aortic ...
.
The term "" is used to describe a condition mimicking appendicitis. It can be associated with ''Yersinia enterocolitica
''Yersinia enterocolitica'' is a Gram-negative, bacillus-shaped bacterium, belonging to the family Yersiniaceae. It is motile at temperatures of 22–29° C (72–84 °F), but becomes nonmotile at normal human body temperature. ''Y. enterocolitic ...
''.
Management
Acute appendicitis is typically managed bysurgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
. While antibiotics are safe and effective for treating uncomplicated appendicitis, 26% of people had a recurrence within a year and required an eventual appendectomy. Antibiotics are less effective if an appendicolith
A fecalith is a stone made of feces. It is a hardening of feces into lumps of varying size and may occur anywhere in the intestinal tract but is typically found in the colon. It is also called appendicolith when it occurs in the appendix and is s ...
is present. Surgery is the standard management approach for acute appendicitis, however, the 2011 Cochrane review comparing appendectomy with antibiotics treatments has not been updated and has been withdrawn. The cost effectiveness of surgery versus antibiotics is unclear.
Using antibiotics to prevent potential postoperative complications in emergency appendectomy procedures is recommended, and the antibiotics are effective when given to a person before, during, or after surgery.
Pain
Pain medications (such asmorphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a analgesic, pain medication, and is also commonly used recreational drug, recreationally, or to make ...
) do not appear to affect the accuracy of the clinical diagnosis of appendicitis and therefore should be given early in the patient's care. Historically there were concerns among some general surgeons that analgesics would affect the clinical exam in children, and some recommended that they not be given until the surgeon was able to examine the person.
Surgery


 The surgical procedure for the removal of the appendix is called an
The surgical procedure for the removal of the appendix is called an appendectomy
An appendectomy, also termed appendicectomy, is a Surgery, surgical operation in which the vermiform appendix (a portion of the intestine) is removed. Appendectomy is normally performed as an urgent or emergency procedure to treat complicated acu ...
. Appendectomy can be performed through open or laparoscopic surgery. Laparoscopic appendectomy has several advantages over open appendectomy as an intervention for acute appendicitis.
Open appendectomy
For over a century, laparotomy (open appendectomy) was the standard treatment for acute appendicitis. This procedure consists of the removal of the infected appendix through a single large incision in the lower right area of the abdomen. The incision in a laparotomy is usually long. During an open appendectomy, the person with suspected appendicitis is placed under generalanesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), ...
to keep the muscles completely relaxed and to keep the person unconscious. The incision is two to three inches (76 mm) long, and it is made in the right lower abdomen, several inches above the hip bone. Once the incision opens the abdomen cavity, and the appendix is identified, the surgeon
In modern medicine, a surgeon is a medical professional who performs surgery. Although there are different traditions in different times and places, a modern surgeon usually is also a licensed physician or received the same medical training as ...
removes the infected tissue and cuts the appendix from the surrounding tissue. After careful and close inspection of the infected area, and ensuring there are no signs that surrounding tissues are damaged or infected. In case of complicated appendicitis managed by an emergency open appendectomy, abdominal drainage (a temporary tube from the abdomen to the outside to avoid abscess formation) may be inserted, but this may increase the hospital stay. The surgeon will start closing the incision. This means sewing the muscles and using surgical staple
Surgical staples are specialized staples used in surgery in place of sutures to close skin wounds or connect or remove parts of the bowels or lungs. The use of staples over sutures reduces the local inflammatory response, width of the wound, a ...
s or stitches to close the skin up. To prevent infections, the incision is covered with a sterile bandage or surgical adhesive.
Laparoscopic appendectomy
Laparoscopic appendectomy was introduced in 1983 and has become an increasingly prevalent intervention for acute appendicitis. This surgical procedure consists of making three to four incisions in the abdomen, each long. This type of appendectomy is made by inserting a special surgical tool called a laparoscope into one of the incisions. The laparoscope is connected to a monitor outside the person's body, and it is designed to help the surgeon to inspect the infected area in the abdomen. The other two incisions are made for the specific removal of the appendix by using surgical instruments. Laparoscopic surgery requiresgeneral anesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is a medically induced loss of consciousness that renders the patient unarousable even with painful stimuli. This effect is achieved by administering either intravenous or inhalational general ...
, and it can last up to two hours. Laparoscopic appendectomy has several advantages over open appendectomy, including a shorter post-operative recovery, less post-operative pain, and lower superficial surgical site infection rate. However, the occurrence of an intra-abdominal abscess is almost three times more prevalent in laparoscopic appendectomy than open appendectomy.
Laparoscopic-assisted transumbilical appendectomy
In pediatric patients, the high mobility of the cecum allows externalization of the appendix through the umbilicus, and the entire procedure can be performed with a single incision. Laparoscopic-assisted transumbilical appendectomy is a relatively recent technique but with long published series and very good surgical and aesthetic results.Pre-surgery
The treatment begins by keeping the person who will be having surgery from eating or drinking for a given period, usually overnight. An intravenous drip is used to hydrate the person who will be having surgery.Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s given intravenously such as cefuroxime and metronidazole
Metronidazole, sold under the brand name Flagyl among others, is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. It is used either alone or with other antibiotics to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, endocarditis, and bacterial vaginosis. It is ef ...
may be administered early to help kill bacteria and thus reduce the spread of infection in the abdomen and postoperative complications in the abdomen or wound. Equivocal cases may become more difficult to assess with antibiotic treatment and benefit from serial examinations. If the stomach is empty (no food in the past six hours), general anaesthesia is usually used. Otherwise, spinal anaesthesia
Spinal anaesthesia (or spinal anesthesia), also called spinal block, subarachnoid block, intradural block and intrathecal block, is a form of neuraxial regional anaesthesia involving the injection of a local anaesthetic or opioid into the subarac ...
may be used.
Once the decision to perform an appendectomy
An appendectomy, also termed appendicectomy, is a Surgery, surgical operation in which the vermiform appendix (a portion of the intestine) is removed. Appendectomy is normally performed as an urgent or emergency procedure to treat complicated acu ...
has been made, the preparation procedure takes approximately one to two hours. Meanwhile, the surgeon will explain the surgery procedure and will present the risks that must be considered when performing an appendectomy. (With all surgeries there are risks that must be evaluated before performing the procedures.) The risks are different depending on the state of the appendix. If the appendix has not ruptured, the complication rate is only about 3% but if the appendix has ruptured, the complication rate rises to almost 59%. The most usual complications that can occur are pneumonia, hernia
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ (anatomy), organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. Various types of hernias can occur, most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the gr ...
of the incision, thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is a phlebitis (inflammation of a vein) related to a thrombus (blood clot). When it occurs repeatedly in different locations, it is known as thrombophlebitis migrans (migratory thrombophlebitis).
Signs and symptoms
The following s ...
, bleeding and adhesions. Evidence indicates that a delay in obtaining surgery after admission results in no measurable difference in outcomes to the person with appendicitis.
 The surgeon will explain how long the recovery process should take. Abdomen hair is usually removed to avoid complications that may appear regarding the incision.
In most cases, patients going in for surgery experience nausea or vomiting that require medication before surgery. Antibiotics, along with pain medication, may be administered before appendectomies.
The surgeon will explain how long the recovery process should take. Abdomen hair is usually removed to avoid complications that may appear regarding the incision.
In most cases, patients going in for surgery experience nausea or vomiting that require medication before surgery. Antibiotics, along with pain medication, may be administered before appendectomies.
After surgery
 Hospital lengths of stay typically range from a few hours to a few days but can be a few weeks if complications occur. The recovery process may vary depending on the severity of the condition: if the appendix had ruptured or not before surgery. Appendix surgery recovery is generally a lot faster if the appendix did not rupture. It is important that people undergoing surgery respect their doctor's advice and limit their physical activity so the tissues can heal faster. Recovery after an appendectomy may not require diet changes or a lifestyle change.
The length of hospital stays for appendicitis varies on the severity of the condition. A study from the United States found that in 2010, the average appendicitis hospital stay was 1.8 days. For stays where the person's appendix had ruptured, the average length of stay was 5.2 days.
After surgery, the patient will be transferred to a
Hospital lengths of stay typically range from a few hours to a few days but can be a few weeks if complications occur. The recovery process may vary depending on the severity of the condition: if the appendix had ruptured or not before surgery. Appendix surgery recovery is generally a lot faster if the appendix did not rupture. It is important that people undergoing surgery respect their doctor's advice and limit their physical activity so the tissues can heal faster. Recovery after an appendectomy may not require diet changes or a lifestyle change.
The length of hospital stays for appendicitis varies on the severity of the condition. A study from the United States found that in 2010, the average appendicitis hospital stay was 1.8 days. For stays where the person's appendix had ruptured, the average length of stay was 5.2 days.
After surgery, the patient will be transferred to a postanesthesia care unit
A post-anesthesia care unit, often abbreviated PACU and sometimes referred to as post-anesthesia recovery or PAR, or simply Recovery, is a vital part of hospitals, ambulatory care centers, and other medical facilities. Patients who received gener ...
, so his or her vital signs can be closely monitored to detect anesthesia- or surgery-related complications. Pain medication may be administered if necessary. After patients are completely awake, they are moved to a hospital room to recover. Most individuals will be offered clear liquids the day after the surgery, then progress to a regular diet when the intestines start to function correctly. Patients are recommended to sit upon the edge of the bed and walk short distances several times a day. Moving is mandatory, and pain medication may be given if necessary. Full recovery from appendectomies takes about four to six weeks but can be prolonged to up to eight weeks if the appendix had ruptured.
Prognosis
Most people with appendicitis recover quickly after surgical treatment, but complications can occur if treatment is delayed or if peritonitis occurs. Recovery time depends on age, condition, complications, and other circumstances, including the amount of alcohol consumption, but usually is between 10 and 28 days. For young children (around ten years old), the recovery takes three weeks. The possibility of peritonitis is the reason why acute appendicitis warrants rapid evaluation and treatment. People with suspected appendicitis may have to undergo amedical evacuation
Medical evacuation, often shortened to medevac or medivac, is the timely and efficient movement and en route care provided by medical personnel to wounded being evacuated from a battlefield, to injured patients being evacuated from the scene of a ...
. Appendectomies have occasionally been performed in emergency conditions (i.e., not in a proper hospital) when a timely medical evacuation was impossible.
Typical acute appendicitis responds quickly to appendectomy and occasionally will resolve spontaneously. If appendicitis resolves spontaneously, it remains controversial whether an elective interval appendectomy should be performed to prevent a recurrent episode of appendicitis. Atypical appendicitis (associated with suppurative appendicitis) is more challenging to diagnose and is more apt to be complicated even when operated early. In either condition, prompt diagnosis and appendectomy yield the best results with full recovery in two to four weeks usually. Mortality and severe complications are unusual but do occur, especially if peritonitis persists and is untreated.
Another entity known as the appendicular lump is talked about. It happens when the appendix is not removed early during infection, and omentum and intestine adhere to it, forming a palpable lump. During this period, surgery is risky unless there is pus formation evident by fever and toxicity or by USG. Medical management treats the condition.
An unusual complication of an appendectomy is "stump appendicitis": inflammation occurs in the remnant appendiceal stump left after a prior incomplete appendectomy. Stump appendicitis can occur months to years after initial appendectomy and can be identified with imaging modalities such as ultrasound.
Epidemiology
See also
*Deaths from appendicitis
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain ...
* Evan O'Neill Kane
Evan O'Neill Kane (April 6, 1861 – April 1, 1932) was an American physician and surgeon from the 1880s to the early 1930s who served as chief of surgery at Kane Summit Hospital in Kane, Pennsylvania. He was a significant contributor in his da ...
* Leonid Rogozov
References
External links
*CT of the abdomen showing acute appendicitis
by Surgeons Net Education
from the Merck Manual Professional (content last modified September 2007)
Appendicitis – Symptoms Causes and Treatment
at Health N Surgery {{Authority control Acute pain Diseases of appendix General surgery Inflammations Medical emergencies Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate