Aphid Moon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects and members of the

 Most aphids have soft bodies, which may be green, black, brown, pink, or almost colorless. Aphids have antennae with two short, broad basal segments and up to four slender terminal segments. They have a pair of compound eyes, with an ocular tubercle behind and above each eye, made up of three lenses (called triommatidia). They feed on sap using sucking mouthparts called stylets, enclosed in a sheath called a rostrum, which is formed from modifications of the mandible and maxilla of the insect mouthparts.
They have long, thin legs with two-jointed, two-clawed tarsi. The majority of aphids are wingless, but winged forms are produced at certain times of year in many species. Most aphids have a pair of cornicles (siphunculi), abdominal tubes on the dorsal surface of their fifth abdominal segment, through which they exude droplets of a quick-hardening defensive fluid containing
Most aphids have soft bodies, which may be green, black, brown, pink, or almost colorless. Aphids have antennae with two short, broad basal segments and up to four slender terminal segments. They have a pair of compound eyes, with an ocular tubercle behind and above each eye, made up of three lenses (called triommatidia). They feed on sap using sucking mouthparts called stylets, enclosed in a sheath called a rostrum, which is formed from modifications of the mandible and maxilla of the insect mouthparts.
They have long, thin legs with two-jointed, two-clawed tarsi. The majority of aphids are wingless, but winged forms are produced at certain times of year in many species. Most aphids have a pair of cornicles (siphunculi), abdominal tubes on the dorsal surface of their fifth abdominal segment, through which they exude droplets of a quick-hardening defensive fluid containing
 The simplest reproductive strategy is for an aphid to have a single host all year round. On this it may alternate between sexual and asexual generations (holocyclic) or alternatively, all young may be produced by parthenogenesis,
The simplest reproductive strategy is for an aphid to have a single host all year round. On this it may alternate between sexual and asexual generations (holocyclic) or alternatively, all young may be produced by parthenogenesis,  In autumn, aphids reproduce sexually and lay eggs. Environmental factors such as a change in
In autumn, aphids reproduce sexually and lay eggs. Environmental factors such as a change in
Dysaphis plantaginea
') reproduction, but contributes to the development of aphids with wings, which can transmit the virus more easily to new host plants. Additionally, symbiotic bacteria that live inside of the aphids can also alter aphid reproductive strategies based on the exposure to environmental stressors.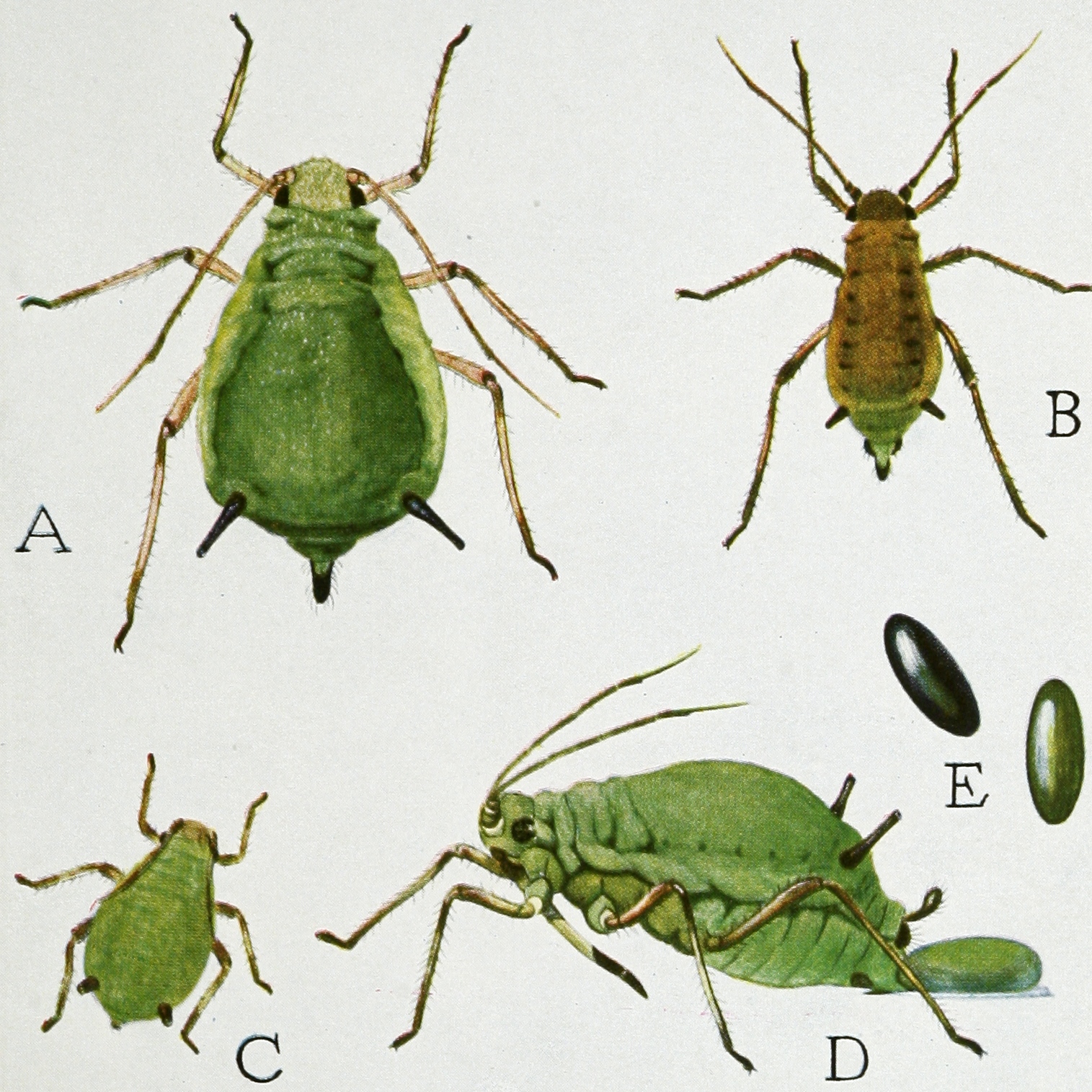 In the autumn, host-alternating (
In the autumn, host-alternating (

 Some species of ants farm aphids, protecting them on the plants where they are feeding, and consuming the honeydew the aphids release from the terminations of their
Some species of ants farm aphids, protecting them on the plants where they are feeding, and consuming the honeydew the aphids release from the terminations of their  An interesting variation in ant–aphid relationships involves lycaenid butterflies and ''
An interesting variation in ant–aphid relationships involves lycaenid butterflies and ''
 Most aphids have little protection from predators. Some species interact with plant tissues forming a
Most aphids have little protection from predators. Some species interact with plant tissues forming a
 Plants mount local and systemic defenses against aphid attack. Young leaves in some plants contain chemicals that discourage attack while the older leaves have lost this resistance, while in other plant species, resistance is acquired by older tissues and the young shoots are vulnerable. Volatile products from interplanted onions have been shown to prevent aphid attack on adjacent potato plants by encouraging the production of terpenoids, a benefit exploited in the traditional practice of companion planting, while plants neighboring infested plants showed increased root growth at the expense of the extension of aerial parts. The wild potato, ''
Plants mount local and systemic defenses against aphid attack. Young leaves in some plants contain chemicals that discourage attack while the older leaves have lost this resistance, while in other plant species, resistance is acquired by older tissues and the young shoots are vulnerable. Volatile products from interplanted onions have been shown to prevent aphid attack on adjacent potato plants by encouraging the production of terpenoids, a benefit exploited in the traditional practice of companion planting, while plants neighboring infested plants showed increased root growth at the expense of the extension of aerial parts. The wild potato, '' The coating of plants with honeydew can contribute to the spread of fungi which can damage plants. Honeydew produced by aphids has been observed to reduce the effectiveness of fungicides as well.
A hypothesis that insect feeding may improve plant fitness was floated in the mid-1970s by Owen and Wiegert. It was felt that the excess honeydew would nourish soil micro-organisms, including nitrogen fixers. In a nitrogen-poor environment, this could provide an advantage to an infested plant over an uninfested plant. However, this does not appear to be supported by observational evidence.
The coating of plants with honeydew can contribute to the spread of fungi which can damage plants. Honeydew produced by aphids has been observed to reduce the effectiveness of fungicides as well.
A hypothesis that insect feeding may improve plant fitness was floated in the mid-1970s by Owen and Wiegert. It was felt that the excess honeydew would nourish soil micro-organisms, including nitrogen fixers. In a nitrogen-poor environment, this could provide an advantage to an infested plant over an uninfested plant. However, this does not appear to be supported by observational evidence.

 Aphid populations can be sampled using yellow-pan or Moericke traps. These are yellow containers with water that attract aphids. Aphids respond positively to green and their attraction to yellow may not be a true colour preference but related to brightness. Their visual receptors peak in sensitivity from 440 to 480 nm and are insensitive in the red region. Moericke found that aphids avoided landing on white coverings placed on soil and were repelled even more by shiny aluminium surfaces. Integrated pest management of various species of aphids can be achieved using biological insecticides based on fungi such as ''Lecanicillium lecanii'', ''Beauveria bassiana'' or '' Isaria fumosorosea''. Fungi are the main pathogens of aphids; Entomophthorales can quickly cut aphid numbers in nature.
Aphids may also be controlled by the release of natural enemies, in particular lady beetles and parasitoid wasps. However, since adult lady beetles tend to fly away within 48 hours after release, without laying eggs, repeated applications of large numbers of lady beetles are needed to be effective. For example, one large, heavily infested rose bush may take two applications of 1500 beetles each.
The ability to produce allomones such as farnesene to repel and disperse aphids and to attract their predators has been experimentally transferred to
Aphid populations can be sampled using yellow-pan or Moericke traps. These are yellow containers with water that attract aphids. Aphids respond positively to green and their attraction to yellow may not be a true colour preference but related to brightness. Their visual receptors peak in sensitivity from 440 to 480 nm and are insensitive in the red region. Moericke found that aphids avoided landing on white coverings placed on soil and were repelled even more by shiny aluminium surfaces. Integrated pest management of various species of aphids can be achieved using biological insecticides based on fungi such as ''Lecanicillium lecanii'', ''Beauveria bassiana'' or '' Isaria fumosorosea''. Fungi are the main pathogens of aphids; Entomophthorales can quickly cut aphid numbers in nature.
Aphids may also be controlled by the release of natural enemies, in particular lady beetles and parasitoid wasps. However, since adult lady beetles tend to fly away within 48 hours after release, without laying eggs, repeated applications of large numbers of lady beetles are needed to be effective. For example, one large, heavily infested rose bush may take two applications of 1500 beetles each.
The ability to produce allomones such as farnesene to repel and disperse aphids and to attract their predators has been experimentally transferred to
Aphids of southeastern U.S. woody ornamentals
''Acyrthosiphon pisum''
MetaPathogen – facts, life cycle, life cycle image
Agricultural Research Service
Insect Olfaction of Plant Odour: Colorado Potato Beetle and Aphid Studies
Center for Invasive Species Research On the University of Florida /
''Aphis gossypii'', melon or cotton aphid
{{Authority control Agricultural pest insects Insect pests of temperate forests Insect pests of ornamental plants Insect vectors of plant pathogens Sternorrhyncha Extant Permian first appearances Insects in culture
superfamily
SUPERFAMILY is a database and search platform of structural and functional annotation for all proteins and genomes. It classifies amino acid sequences into known structural domains, especially into SCOP superfamilies. Domains are functional, str ...
Aphidoidea. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white woolly aphids. A typical life cycle involves flightless females giving live birth to female nymphs—who may also be already pregnant
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
, an adaptation scientists call telescoping generations—without the involvement of males. Maturing rapidly, females breed profusely so that the number of these insects multiplies quickly. Winged females may develop later in the season, allowing the insects to colonize new plants. In temperate regions, a phase of sexual reproduction occurs in the autumn
Autumn, also known as fall in American English and Canadian English, is one of the four temperate seasons on Earth. Outside the tropics, autumn marks the transition from summer to winter, in September ( Northern Hemisphere) or March ( Sou ...
, with the insects often overwintering as eggs.
The life cycle of some species involves an alternation between two species of host plants, for example between an annual crop and a woody plant. Some species feed on only one type of plant, while others are generalists, colonizing many plant groups. About 5,000 species of aphid have been described, all included in the family Aphididae. Around 400 of these are found on food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is inge ...
and fiber crops, and many are serious pests of agriculture and forestry, as well as an annoyance for gardeners. So-called dairying ants have a mutualistic relationship with aphids, tending them for their honeydew, and protecting them from predators.
Aphids are among the most destructive insect pests on cultivated plants in temperate regions. In addition to weakening the plant by sucking sap, they act as vectors for plant viruses and disfigure ornamental plants with deposits of honeydew and the subsequent growth of sooty moulds. Because of their ability to rapidly increase in numbers by asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the fu ...
and telescopic development, they are a highly successful group of organisms from an ecological standpoint.
Control of aphids is not easy. Insecticides do not always produce reliable results, given resistance
Resistance may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Comics
* Either of two similarly named but otherwise unrelated comic book series, both published by Wildstorm:
** ''Resistance'' (comics), based on the video game of the same title
** ''T ...
to several classes of insecticide and the fact that aphids often feed on the undersides of leaves. On a garden scale, water jets and soap sprays are quite effective. Natural enemies include predatory ladybugs, hoverfly larvae, parasitic wasps, aphid midge larvae, crab spider
The Thomisidae are a family of spiders, including about 170 genera and over 2,100 species. The common name crab spider is often linked to species in this family, but is also applied loosely to many other families of spiders. Many members of th ...
s, lacewing
The insect order Neuroptera, or net-winged insects, includes the lacewings, mantidflies, antlions, and their relatives. The order consists of some 6,000 species. Neuroptera can be grouped together with the Megaloptera and Raphidioptera in t ...
larvae, and entomopathogenic fungi. An integrated pest management strategy using biological pest control
Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, such as insects, mites, weeds, and plant diseases, using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism, herbivory, or other natural mechanisms, but typically also invo ...
can work, but is difficult to achieve except in enclosed environments such as greenhouses
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown.These s ...
.
Distribution
Aphids are distributed worldwide, but are most common in temperate zones. In contrast to many taxa, aphid species diversity is much lower in the tropics than in the temperate zones. They can migrate great distances, mainly through passive dispersal by winds. Winged aphids may also rise up in the day as high as 600 m where they are transported by strong winds. For example, the currant-lettuce aphid, ''Nasonovia ribisnigri
''Nasonovia ribisnigri'' is a species of aphid. Their primary hosts are currant plants, including blackcurrants (''Ribes nigrum'') and gooseberries (''Ribes uva-crispa''), while the secondary hosts are a wider range of plants, including members ...
'', is believed to have spread from New Zealand to Tasmania around 2004 through easterly winds. Aphids have also been spread by human transportation of infested plant materials, making some species nearly cosmopolitan
Cosmopolitan may refer to:
Food and drink
* Cosmopolitan (cocktail), also known as a "Cosmo"
History
* Rootless cosmopolitan, a Soviet derogatory epithet during Joseph Stalin's anti-Semitic campaign of 1949–1953
Hotels and resorts
* Cosmopoli ...
in their distribution.
Evolution

Fossil history
Aphids, and the closely related adelgids and phylloxerans, probably evolved from a common ancestor some , in theEarly Permian 01 or '01 may refer to:
* The year 2001, or any year ending with 01
* The month of January
* 1 (number)
Music
* '01 (Richard Müller album), 01'' (Richard Müller album), 2001
* 01 (Son of Dave album), ''01'' (Son of Dave album), 2000
* 01 (Urban ...
period. They probably fed on plants like Cordaitales or Cycadophyta
Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk (botany), trunk with a crown (botany), crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants o ...
. With their soft bodies, aphids do not fossilize well, and the oldest known fossil is of the species '' Triassoaphis cubitus'' from the Triassic. They do however sometimes get stuck in plant exudates which solidify into amber. In 1967, when Professor Ole Heie wrote his monograph ''Studies on Fossil Aphids'', about sixty species have been described from the Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous and mostly the Tertiary periods, with Baltic amber contributing another forty species. The total number of species was small, but increased considerably with the appearance of the angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s , as this allowed aphids to specialise, the speciation of aphids going hand-in-hand with the diversification of flowering plants. The earliest aphids were probably polyphagous
Feeding is the process by which organisms, typically animals, obtain food. Terminology often uses either the suffixes -vore, -vory, or -vorous from Latin ''vorare'', meaning "to devour", or -phage, -phagy, or -phagous from Greek φαγε ...
, with monophagy
Feeding is the process by which organisms, typically animals, obtain food. Terminology often uses either the suffixes -vore, -vory, or -vorous from Latin ''vorare'', meaning "to devour", or -phage, -phagy, or -phagous from Greek φαγε ...
developing later. It has been hypothesized that the ancestors of the Adelgidae
The Adelgidae are a small family of the Hemiptera closely related to the aphids, and often included in the Aphidoidea with the Phylloxeridae or placed within the superfamily Phylloxeroidea as a sister of the Aphidoidea within the infraorder Aphid ...
lived on conifer
Conifers are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single ...
s while those of the Aphididae fed on the sap of Podocarpaceae or Araucariaceae that survived extinctions in the late Cretaceous. Organs like the cornicles did not appear until the Cretaceous period. One study alternatively suggests that ancestral aphids may have lived on angiosperm bark and that feeding on leaves may be a derived trait. The Lachninae
Lachninae is a subfamily of the family Aphididae, containing some of the largest aphids, and they are sometimes referred to as "giant aphids". Members of this subfamily typically have greatly reduced cornicle
The cornicle (or siphuncule) is o ...
have long mouth parts that are suitable for living on bark and it has been suggested that the mid-Cretaceous ancestor fed on the bark of angiosperm trees, switching to leaves of conifer hosts in the late Cretaceous. The Phylloxeridae may well be the oldest family still extant, but their fossil record is limited to the Lower Miocene '' Palaeophylloxera''.
Taxonomy
Late 20th-century reclassification within the Hemiptera reduced the old taxon "Homoptera" to two suborders: Sternorrhyncha (aphids, whiteflies, scales,psyllids
Psyllidae, the jumping plant lice or psyllids, are a family of small plant-feeding insects that tend to be very host-specific, i.e. each plant-louse species only feeds on one plant species (monophagous) or feeds on a few closely related plants ( ...
, etc.) and Auchenorrhyncha ( cicadas, leafhopper
A leafhopper is the common name for any species from the family Cicadellidae. These minute insects, colloquially known as hoppers, are plant feeders that suck plant sap from grass, shrubs, or trees. Their hind legs are modified for jumping, and a ...
s, treehoppers, planthopper
A planthopper is any insect in the infraorder Fulgoromorpha, in the suborder Auchenorrhyncha, a group exceeding 12,500 described species worldwide. The name comes from their remarkable resemblance to leaves and other plants of their environment ...
s, etc.) with the suborder Heteroptera
The Heteroptera are a group of about 40,000 species of insects in the order Hemiptera. They are sometimes called "true bugs", though that name more commonly refers to the Hemiptera as a whole. "Typical bugs" might be used as a more unequivocal al ...
containing a large group of insects known as the true bugs. The infraorder Aphidomorpha within the Sternorrhyncha varies with circumscription with several fossil groups being especially difficult to place but includes the Adelgoidea, the Aphidoidea and the Phylloxeroidea. Some authors use a single superfamily Aphidoidea within which the Phylloxeridae
Phylloxeridae is a small family of plant-parasitic hemipterans closely related to aphids with only 75 described species. This group comprises two subfamilies (Phylloxerininae and Phylloxerinae) and 11 genera with one that is fossil. The genus ...
and Adelgidae are also included while others have Aphidoidea with a sister superfamily Phylloxeroidea within which the Adelgidae and Phylloxeridae are placed. Early 21st-century reclassifications substantially rearranged the families within Aphidoidea: some old families were reduced to subfamily rank (''e.g.'', Eriosomatidae
Woolly aphids (subfamily: Eriosomatinae) are sap-sucking insects that produce a filamentous waxy white covering which resembles cotton or wool. The adults are winged and move to new locations where they lay egg masses. The nymphs often form la ...
), and many old subfamilies were elevated to family rank. The most recent authoritative classifications have three superfamilies Adelgoidea, Phylloxeroidea and Aphidoidea. The Aphidoidea includes a single large family Aphididae that includes all the ~5000 extant species.
Phylogeny
External
Aphids, adelgids, and phylloxerids are very closely related, and are all within the suborder Sternorrhyncha, the plant-sucking bugs. They are either placed in the insect superfamily Aphidoidea or into the superfamily Phylloxeroidea which contains the family Adelgidae and the family Phylloxeridae. Like aphids, phylloxera feed on the roots, leaves, and shoots of grape plants, but unlike aphids, do not produce honeydew orcornicle
The cornicle (or siphuncule) is one of a pair of small upright backward-pointing tubes found on the dorsal side of the 5th or 6th abdominal segments of aphids. They are sometimes mistaken for cerci. They are no more than pores in some species.
...
secretions. Phylloxera (''Daktulosphaira vitifoliae'') are insects which caused the Great French Wine Blight
The Great French Wine Blight was a severe blight of the mid-19th century that destroyed many of the vineyards in France and laid waste to the wine industry. It was caused by an aphid that originated in North America and was carried across the Atl ...
that devastated European viticulture in the 19th century. Similarly, adelgids or woolly conifer aphids, also feed on plant phloem and are sometimes described as aphids, but are more properly classified as aphid-like insects, because they have no cauda or cornicles.
The treatment of the groups especially concerning fossil groups varies greatly due to difficulties in resolving relationships. Most modern treatments include the three superfamilies, the Adelogidea, the Aphidoidea, and the Phylloxeroidea within the infraorder Aphidomorpha along with several fossil groups but other treatments have the Aphidomorpha containing the Aphidoidea with the families Aphididae, Phylloxeridae and Adelgidae; or the Aphidomorpha with two superfamilies, Aphidoidea and Phylloxeroidea, the latter containing the Phylloxeridae and the Adelgidae.
The phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spec ...
of the Sternorrhyncha is inferred from analysis of small subunit (18S) ribosomal RNA.
Internal
The phylogenetic tree, based on Papasotiropoulos 2013 and Kim 2011, with additions from Ortiz-Rivas and Martinez-Torres 2009, shows the internal phylogeny of the Aphididae. It has been suggested that the phylogeny of the aphid groups might be revealed by examining the phylogeny of their bacterial endosymbionts, especially the obligate endosymbiont '' Buchnera''. The results depend on the assumption that the symbionts are strictly transmitted vertically through the generations. This assumption is well supported by the evidence, and several phylogenetic relationships have been suggested on the basis of endosymbiont studies.Anatomy
 Most aphids have soft bodies, which may be green, black, brown, pink, or almost colorless. Aphids have antennae with two short, broad basal segments and up to four slender terminal segments. They have a pair of compound eyes, with an ocular tubercle behind and above each eye, made up of three lenses (called triommatidia). They feed on sap using sucking mouthparts called stylets, enclosed in a sheath called a rostrum, which is formed from modifications of the mandible and maxilla of the insect mouthparts.
They have long, thin legs with two-jointed, two-clawed tarsi. The majority of aphids are wingless, but winged forms are produced at certain times of year in many species. Most aphids have a pair of cornicles (siphunculi), abdominal tubes on the dorsal surface of their fifth abdominal segment, through which they exude droplets of a quick-hardening defensive fluid containing
Most aphids have soft bodies, which may be green, black, brown, pink, or almost colorless. Aphids have antennae with two short, broad basal segments and up to four slender terminal segments. They have a pair of compound eyes, with an ocular tubercle behind and above each eye, made up of three lenses (called triommatidia). They feed on sap using sucking mouthparts called stylets, enclosed in a sheath called a rostrum, which is formed from modifications of the mandible and maxilla of the insect mouthparts.
They have long, thin legs with two-jointed, two-clawed tarsi. The majority of aphids are wingless, but winged forms are produced at certain times of year in many species. Most aphids have a pair of cornicles (siphunculi), abdominal tubes on the dorsal surface of their fifth abdominal segment, through which they exude droplets of a quick-hardening defensive fluid containing triacylglycerol
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and ''glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as we ...
s, called cornicle wax. Other defensive compounds can also be produced by some species. Aphids have a tail-like protrusion called a cauda above their rectal apertures. They have lost their Malpighian tubules
The Malpighian tubule system is a type of excretory and osmoregulatory system found in some insects, myriapods, arachnids and tardigrades.
The system consists of branching tubules extending from the alimentary canal that absorbs solutes, water, ...
.
When host plant quality becomes poor or conditions become crowded, some aphid species produce winged offspring ( alates) that can disperse to other food sources. The mouthparts or eyes can be small or missing in some species and forms.
Diet
Many aphid species are monophagous (that is, they feed on only one plant species). Others, like the green peach aphid, feed on hundreds of plant species across many families. About 10% of species feed on different plants at different times of the year. A new host plant is chosen by a winged adult by using visual cues, followed by olfaction using the antennae; if the plant smells right, the next action is probing the surface upon landing. The stylus is inserted and saliva secreted, the sap is sampled, the xylem may be tasted and finally, the phloem is tested. Aphid saliva may inhibit phloem-sealing mechanisms and has pectinases that ease penetration. Non-host plants can be rejected at any stage of the probe, but the transfer of viruses occurs early in the investigation process, at the time of the introduction of the saliva, so non-host plants can become infected. Aphids usually feed passively on sap of phloem vessels in plants, as do many of other hemipterans such as scale insects and cicadas. Once a phloem vessel is punctured, the sap, which is under pressure, is forced into the aphid's food canal. Occasionally, aphids also ingest xylem sap, which is a more dilute diet than phloem sap as the concentrations of sugars and amino acids are 1% of those in the phloem. Xylem sap is under negative hydrostatic pressure and requires active sucking, suggesting an important role in aphid physiology. As xylem sap ingestion has been observed following a dehydration period, aphids are thought to consume xylem sap to replenish their water balance; the consumption of the dilute sap of xylem permitting aphids to rehydrate. However, recent data showed aphids consume more xylem sap than expected and they notably do so when they are not dehydrated and when their fecundity decreases. This suggests aphids, and potentially, all the phloem-sap feeding species of the order Hemiptera, consume xylem sap for reasons other than replenishing water balance. Although aphids passively take in phloem sap, which is under pressure, they can also draw fluid at negative or atmospheric pressure using the cibarial-pharyngeal pump mechanism present in their head. Xylem sap consumption may be related to osmoregulation. High osmotic pressure in the stomach, caused by high sucrose concentration, can lead to water transfer from the hemolymph to the stomach, thus resulting in hyperosmotic stress and eventually to the death of the insect. Aphids avoid this fate by osmoregulating through several processes. Sucrose concentration is directly reduced by assimilating sucrose toward metabolism and by synthesizing oligosaccharides from several sucrose molecules, thus reducing the solute concentration and consequently the osmotic pressure. Oligosaccharides are then excreted through honeydew, explaining its high sugar concentrations, which can then be used by other animals such as ants. Furthermore, water is transferred from thehindgut
The hindgut (or epigaster) is the posterior ( caudal) part of the alimentary canal. In mammals, it includes the distal one third of the transverse colon and the splenic flexure, the descending colon, sigmoid colon and up to the ano-rectal juncti ...
, where osmotic pressure has already been reduced, to the stomach to dilute stomach content. Eventually, aphids consume xylem sap to dilute the stomach osmotic pressure. All these processes function synergetically, and enable aphids to feed on high-sucrose-concentration plant sap, as well as to adapt to varying sucrose concentrations.
Plant sap is an unbalanced diet for aphids, as it lacks essential amino acids, which aphids, like all animals, cannot synthesise, and possesses a high osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane.
It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in a pure ...
due to its high sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
concentration. Essential amino acids are provided to aphids by bacterial endosymbionts
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship.
(The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within" ...
, harboured in special cells, bacteriocyte
A bacteriocyte (Greek for ''bacteria cell''), also known as a mycetocyte, is a specialized adipocyte found primarily in certain insect groups such as aphids, tsetse flies, German cockroaches, weevils. These cells contain endosymbiotic organisms su ...
s. These symbionts recycle glutamate, a metabolic waste of their host, into essential amino acids.
Carotenoids and photoheterotrophy
Some species of aphids have acquired the ability to synthesise redcarotenoid
Carotenoids (), also called tetraterpenoids, are yellow, orange, and red organic compound, organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, and Fungus, fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpki ...
s by horizontal gene transfer from fungi. They are the only animals other than two-spotted spider mites
''Tetranychus urticae'' (common names include red spider mite and two-spotted spider mite) is a species of plant-feeding mite generally considered to be a pest (animal), pest. It is the most widely known member of the family Tetranychidae or spi ...
and the oriental hornet
The Oriental hornet (''Vespa orientalis'') is a social insect species of the family Vespidae. It can be found in Southwest Asia, Northeast Africa, the island of Madagascar (but no reports have been made of its presence on the island for many year ...
with this capability. Using their carotenoids, aphids may well be able to absorb solar energy and convert it to a form that their cells can use, ATP
ATP may refer to:
Companies and organizations
* Association of Tennis Professionals, men's professional tennis governing body
* American Technical Publishers, employee-owned publishing company
* ', a Danish pension
* Armenia Tree Project, non ...
. This is the only known example of photoheterotrophy in animals. The carotene
The term carotene (also carotin, from the Latin ''carota'', "carrot") is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but in general cannot be made by animals (with the exc ...
pigments in aphids form a layer close to the surface of the cuticle, ideally placed to absorb sunlight. The excited carotenoids seem to reduce NAD to NADH which is oxidized in the mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosi ...
for energy.
Reproduction
 The simplest reproductive strategy is for an aphid to have a single host all year round. On this it may alternate between sexual and asexual generations (holocyclic) or alternatively, all young may be produced by parthenogenesis,
The simplest reproductive strategy is for an aphid to have a single host all year round. On this it may alternate between sexual and asexual generations (holocyclic) or alternatively, all young may be produced by parthenogenesis, egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the a ...
s never being laid (anholocyclic). Some species can have both holocyclic and anholocyclic populations under different circumstances but no known aphid species reproduce solely by sexual means. The alternation of sexual and asexual generations may have evolved repeatedly.
However, aphid reproduction is often more complex than this and involves migration between different host plants. In about 10% of species, there is an alternation between woody (primary hosts) on which the aphids overwinter and herbaceous
Herbaceous plants are vascular plants that have no persistent woody stems above ground. This broad category of plants includes many perennials, and nearly all annuals and biennials.
Definitions of "herb" and "herbaceous"
The fourth edition of t ...
(secondary) host plants, where they reproduce abundantly in the summer. A few species can produce a soldier caste, other species show extensive polyphenism
A polyphenic trait is a trait for which multiple, discrete phenotypes can arise from a single genotype as a result of differing environmental conditions. It is therefore a special case of phenotypic plasticity.
There are several types of polyphen ...
under different environmental conditions and some can control the sex ratio of their offspring depending on external factors.
When a typical sophisticated reproductive strategy is used, only females are present in the population at the beginning of the seasonal cycle (although a few species of aphids have been found to have both male and female sexes at this time). The overwintering eggs that hatch in the spring result in females, called fundatrices (stem mothers). Reproduction typically does not involve males ( parthenogenesis) and results in a live birth ( viviparity). The live young are produced by pseudoplacental viviparity, which is the development of eggs, deficient in the yolk, the embryos fed by a tissue acting as a placenta. The young emerge from the mother soon after hatching.
Eggs are parthenogenetically produced without meiosis and the offspring are clonal to their mother, so they are all female ( thelytoky). The embryos develop within the mothers' ovarioles
An ovariole is a tubular component of the insect ovary, and the basic unit of egg production. Each ovariole is composed of a germarium (the germline stem cell niche) at the anterior tip, a set of developing oocytes contained within follicles, and ...
, which then give birth to live (already hatched) first- instar female nymphs. As the eggs begin to develop immediately after ovulation, an adult female can house developing female nymphs which already have parthenogenetically developing embryos inside them (i.e. they are born pregnant). This telescoping of generations enables aphids to increase in number with great rapidity. The offspring resemble their parent in every way except size. Thus, a female's diet can affect the body size and birth rate of more than two generations (daughters and granddaughters).
This process repeats itself throughout the summer, producing multiple generations that typically live 20 to 40 days. For example, some species of cabbage aphids (like ''Brevicoryne brassicae
''Brevicoryne brassicae'', commonly known as the cabbage aphid or cabbage aphis, is a destructive aphid (plant louse) native to Europe that is now found in many other areas of the world. The aphids feed on many varieties of produce, including ca ...
'') can produce up to 41 generations of females in a season. Thus, one female hatched in spring can theoretically produce billions of descendants, were they all to survive.
 In autumn, aphids reproduce sexually and lay eggs. Environmental factors such as a change in
In autumn, aphids reproduce sexually and lay eggs. Environmental factors such as a change in photoperiod
Photoperiodism is the physiological reaction of organisms to the length of night or a dark period. It occurs in plants and animals. Plant photoperiodism can also be defined as the developmental responses of plants to the relative lengths of light a ...
and temperature, or perhaps a lower food quantity or quality, causes females to parthenogenetically produce sexual females and males. The males are genetically identical to their mothers except that, with the aphids' X0 sex-determination system, they have one fewer sex chromosome. These sexual aphids may lack wings or even mouthparts. Sexual females and males mate, and females lay eggs that develop outside the mother. The eggs survive the winter and hatch into winged (alate) or wingless females the following spring. This occurs in, for example, the life cycle of the rose aphid
''Macrosiphum rosae'', the rose aphid, is a species of sap-sucking aphids in the subfamily Aphidinae. They have a world-wide distribution and infest rosebushes as the main host in spring and early summer, congregating on the tips of shoots and a ...
(''Macrosiphum rosae''), which may be considered typical of the family. However, in warm environments, such as in the tropics or a greenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of Transparent ceramics, transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic condit ...
, aphids may go on reproducing asexually for many years.
Aphids reproducing asexually by parthenogenesis can have genetically identical winged and non-winged female progeny. Control is complex; some aphids alternate during their life-cycles between genetic control (polymorphism
Polymorphism, polymorphic, polymorph, polymorphous, or polymorphy may refer to:
Computing
* Polymorphism (computer science), the ability in programming to present the same programming interface for differing underlying forms
* Ad hoc polymorphis ...
) and environmental control (polyphenism
A polyphenic trait is a trait for which multiple, discrete phenotypes can arise from a single genotype as a result of differing environmental conditions. It is therefore a special case of phenotypic plasticity.
There are several types of polyphen ...
) of production of winged or wingless forms. Winged progeny tend to be produced more abundantly under unfavorable or stressful conditions. Some species produce winged progeny in response to low food quality or quantity. e.g. when a host plant is starting to senesce
Senescence () or biological aging is the gradual deterioration of functional characteristics in living organisms. The word ''senescence'' can refer to either cellular senescence or to senescence of the whole organism. Organismal senescence invol ...
. The winged females migrate to start new colonies on a new host plant. For example, the apple aphid
''Aphis pomi'', commonly known as the apple aphid (the literal meaning of its binomial name), or the green apple aphid, is a true bug in the family Aphididae. It is found on young growth of apple trees and on other members of the rose family wh ...
(''Aphis pomi''), after producing many generations of wingless females gives rise to winged forms that fly to other branches or trees of its typical food plant. Aphids that are attacked by ladybugs, lacewings
The insect order Neuroptera, or net-winged insects, includes the lacewings, mantidflies, antlions, and their relatives. The order consists of some 6,000 species. Neuroptera can be grouped together with the Megaloptera and Raphidioptera in the ...
, parasitoid wasps, or other predators can change the dynamics of their progeny production. When aphids are attacked by these predators, alarm pheromones, in particular beta-farnesene, are released from the cornicle
The cornicle (or siphuncule) is one of a pair of small upright backward-pointing tubes found on the dorsal side of the 5th or 6th abdominal segments of aphids. They are sometimes mistaken for cerci. They are no more than pores in some species.
...
s. These alarm pheromones cause several behavioral modifications that, depending on the aphid species, can include walking away and dropping off the host plant. Additionally, alarm pheromone perception can induce the aphids to produce winged progeny that can leave the host plant in search of a safer feeding site. Viral infections, which can be extremely harmful to aphids, can also lead to the production of winged offspring. For example, '' Densovirus'' infection has a negative impact on rosy apple aphid (Dysaphis plantaginea
') reproduction, but contributes to the development of aphids with wings, which can transmit the virus more easily to new host plants. Additionally, symbiotic bacteria that live inside of the aphids can also alter aphid reproductive strategies based on the exposure to environmental stressors.
 In the autumn, host-alternating (
In the autumn, host-alternating (heteroecious
A heteroecious parasite is one that requires at least two hosts. The ''primary host'' is the host in which the parasite spends its adult life; the other is the ''secondary host''. Both hosts are required for the parasite to complete its life cycle ...
) aphid species produce a special winged generation that flies to different host plants for the sexual part of the life cycle. Flightless female and male sexual forms are produced and lay eggs. Some species such as ''Aphis fabae
The black bean aphid (''Aphis fabae'') is a small black insect in the genus ''Aphis'', with a broad, soft body, a member of the order Hemiptera. Other common names include blackfly, bean aphid, and beet leaf aphid. In the warmer months of the ye ...
'' (black bean aphid), ''Metopolophium dirhodum
''Metopolophium dirhodum'', the rose-grain aphid or rose-grass aphid, is a species of sap-sucking insect in the family Aphididae found worldwide. Its primary host is rose, and its secondary host is a grass, including cereals such as wheat, barley ...
'' (rose-grain aphid), '' Myzus persicae'' (peach-potato aphid), and ''Rhopalosiphum padi
Bird cherry-oat aphid (''Rhopalosiphum padi'') is an aphid in the superfamily Aphidoidea in the order Hemiptera. It is a true bug and sucks sap from plants. It is considered a major pest in cereal crops, especially in temperate regions, as well ...
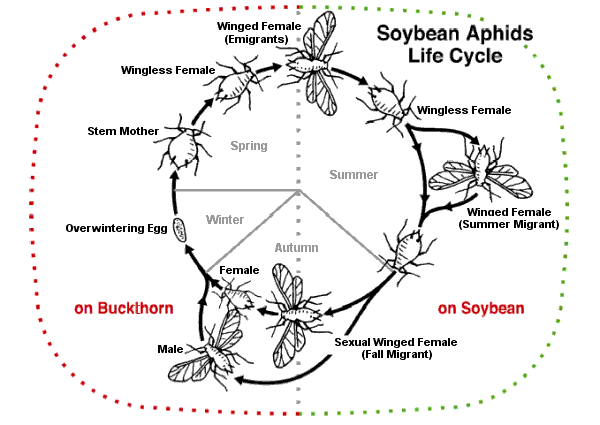
'' (bird cherry-oat aphid) are serious pests. They overwinter on primary hosts on trees or bushes; in summer, they migrate to their secondary host on a herbaceous plant, often a crop, then the gynoparae return to the tree in autumn. Another example is the soybean aphid (''Aphis glycines''). As fall approaches, the soybean plants begin to senesce from the bottom upwards. The aphids are forced upwards and start to produce winged forms, first females and later males, which fly off to the primary host, buckthorn
''Rhamnus'' is a genus of about 110 accepted species of shrubs or small trees, commonly known as buckthorns, in the family Rhamnaceae. Its species range from tall (rarely to ) and are native mainly in east Asia and North America, but found thr ...
. Here they mate and overwinter as eggs.
Ecology
Ant mutualism

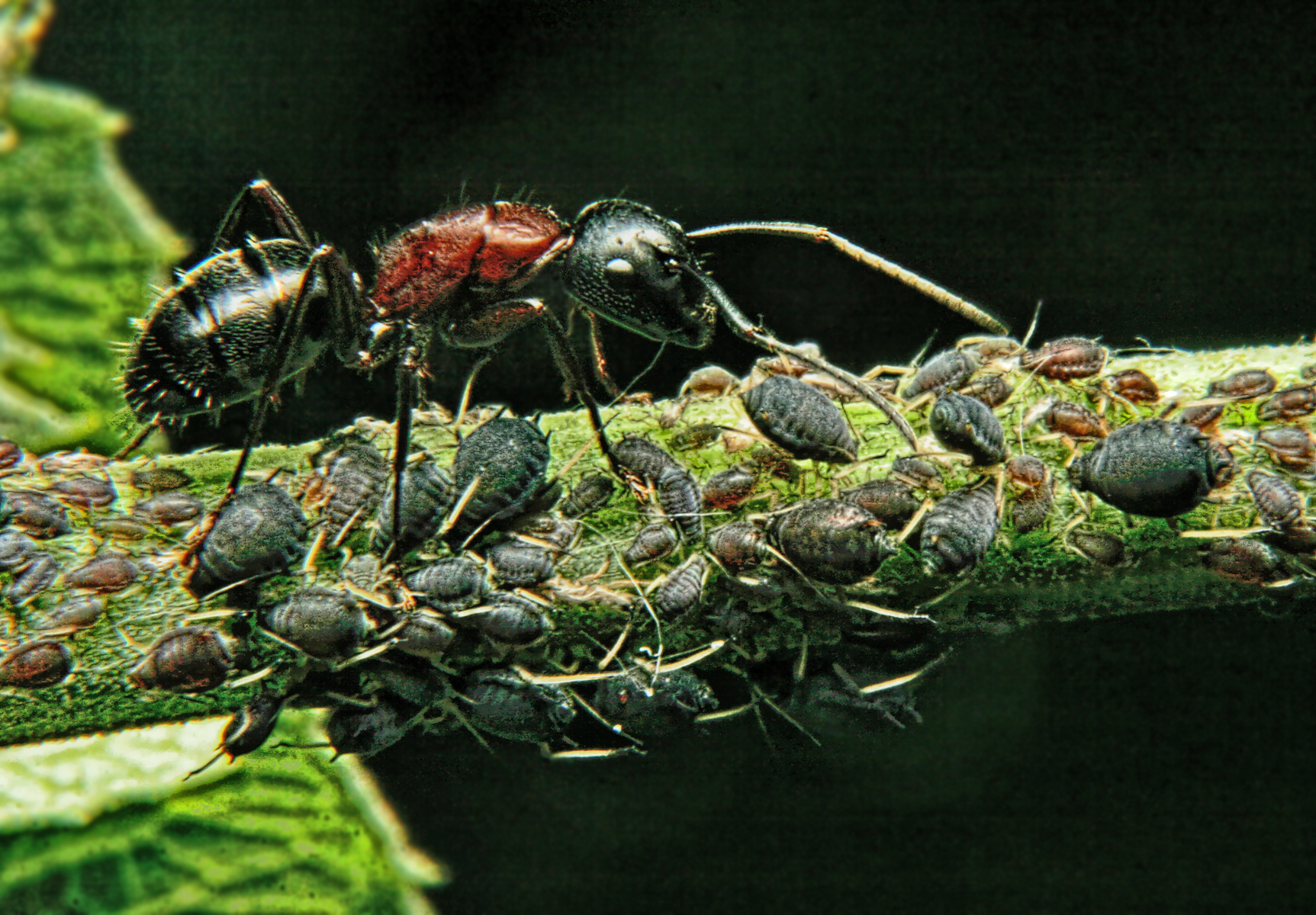
 Some species of ants farm aphids, protecting them on the plants where they are feeding, and consuming the honeydew the aphids release from the terminations of their
Some species of ants farm aphids, protecting them on the plants where they are feeding, and consuming the honeydew the aphids release from the terminations of their alimentary canals
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
. This is a mutualistic relationship, with these dairying ants milking the aphids by stroking them with their antennae. Although mutualistic, the feeding behaviour of aphids is altered by ant attendance. Aphids attended by ants tend to increase the production of honeydew in smaller drops with a greater concentration of amino acids.
Some farming ant species gather and store the aphid eggs in their nests over the winter. In the spring, the ants carry the newly hatched aphids back to the plants. Some species of dairying ants (such as the European yellow meadow ant
The yellow meadow ant (''Lasius flavus''), also known as the yellow hill ant, is a species of ant occurring in Europe (where it is one of the most common ants), Asia, and North Africa. Populations in North America are now considered a different, ...
, ''Lasius flavus'') manage large herds of aphids that feed on roots of plants in the ant colony. Queens leaving to start a new colony take an aphid egg to found a new herd of underground aphids in the new colony. These farming ants protect the aphids by fighting off aphid predators. Some bee
Bees are winged insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their roles in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western honey bee, for producing honey. Bees are a monophyly, monophyletic lineage within the ...
s in coniferous forests collect aphid honeydew to make forest honey.
Myrmica
''Myrmica'' is a genus of ants within the subfamily Myrmicinae. It is widespread throughout the temperate regions of the Holarctic and high mountains in Southeast Asia.
The genus consists of around 200 known species and additional subspecies, ...
'' ants. For example, ''Niphanda fusca
''Niphanda fusca'' is a parasitic butterfly primarily found in East Asian countries such as Japan and Korea. It is a "cuckoo-type" parasite of the ant '' Camponotus japonicus''. It utilizes chemical mimicry to trick the host worker ants into ad ...
'' butterflies lay eggs on plants where ants tend herds of aphids. The eggs hatch as caterpillar
Caterpillars ( ) are the larval stage of members of the order Lepidoptera (the insect order comprising butterflies and moths).
As with most common names, the application of the word is arbitrary, since the larvae of sawflies (suborder Sym ...
s which feed on the aphids. The ants do not defend the aphids from the caterpillars, since the caterpillars produce a pheromone which deceives the ants into treating them like ants, and carrying the caterpillars into their nest. Once there, the ants feed the caterpillars, which in return produce honeydew for the ants. When the caterpillars reach full size, they crawl to the colony entrance and form cocoons. After two weeks, the adult butterflies emerge and take flight. At this point, the ants attack the butterflies, but the butterflies have a sticky wool-like substance on their wings that disables the ants' jaws, allowing the butterflies to fly away without being harmed.
Another ant-mimicking gall aphid, ''Paracletus cimiciformis
''Paracletus cimiciformis'' is a species of aphid with a complex life cycle. Its primary host plant is ''Pistacia'' and its secondary host is a grass, where it is present on the roots. Here it is associated with an ant and part of its life cycle ...
'' (Eriosomatinae), has evolved a complex double strategy involving two morphs of the same clone and '' Tetramorium'' ants. Aphids of the round morph cause the ants to farm them, as with many other aphids. The flat morph aphids are aggressive mimics
Aggressive mimicry is a form of mimicry in which predators, parasites, or parasitoids share similar signals, using a harmless model, allowing them to avoid being correctly identified by their prey or host. Zoologists have repeatedly compared ...
with a " wolf in sheep's clothing" strategy: they have hydrocarbons in their cuticle that mimic those of the ants, and the ants carry them into the brood chamber of the ants' nest and raise them like ant larvae. Once there, the flat morph aphids behave like predators, drinking the body fluids of ant larvae.
Bacterial endosymbiosis
Endosymbiosis with micro-organisms is common in insects, with more than 10% of insect species relying on intracellular bacteria for their development and survival. Aphids harbour a vertically transmitted (from parent to its offspring) obligatesymbiosis
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasit ...
with '' Buchnera aphidicola'', the primary symbiont, inside specialized cells, the bacteriocytes
A bacteriocyte (Greek for ''bacteria cell''), also known as a mycetocyte, is a specialized adipocyte found primarily in certain insect groups such as aphids, tsetse flies, German cockroaches, weevils. These cells contain endosymbiotic organisms su ...
. Five of the bacteria genes have been transferred to the aphid nucleus. The original association may is estimated to have occurred in a common ancestor and enabled aphids to exploit a new ecological niche, feeding on phloem-sap of vascular plants. ''B. aphidicola'' provides its host with essential amino acids, which are present in low concentrations in plant sap. The metabolites from endosymbionts are also excreted in honeydew. The stable intracellular conditions, as well as the bottleneck effect experienced during the transmission of a few bacteria from the mother to each nymph, increase the probability of transmission of mutations and gene deletions. As a result, the size of the ''B. aphidicola'' genome is greatly reduced, compared to its putative ancestor. Despite the apparent loss of transcription factors in the reduced genome, gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. The ...
is highly regulated, as shown by the ten-fold variation in expression levels between different genes under normal conditions. ''Buchnera aphidicola'' gene transcription, although not well understood, is thought to be regulated by a small number of global transcriptional regulators and/or through nutrient supplies from the aphid host.
Some aphid colonies also harbour secondary or facultative (optional extra) bacterial symbionts. These are vertically transmitted, and sometimes also horizontally (from one lineage to another and possibly from one species to another). So far, the role of only some of the secondary symbionts has been described; ''Regiella insecticola
''Regiella insecticola'' is a species of bacteria, that lives as a symbiont of aphids. It shows a relationship with ''Photorhabdus'' species, together with ''Hamiltonella defensa''. Together with other endosymbionts, it provides aphids protection ...
'' plays a role in defining the host-plant range, ''Hamiltonella defensa
''Hamiltonella defensa'' (''H. defensa'') is a species of bacteria. It is maternally or sexually transmitted and lives as an endosymbiont of whiteflies and aphids, meaning that it lives within a host, protecting its host from attack. It does this ...
'' provides resistance to parasitoids but only when it is in turn infected by the bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteri ...
APSE, and '' Serratia symbiotica'' prevents the deleterious effects of heat.
Predators
Aphids are eaten by many bird and insect predators. In a study on a farm in North Carolina, six species of passerine bird consumed nearly a million aphids per day between them, the top predators being the American goldfinch, with aphids forming 83% of its diet, and the vesper sparrow. Insects that attack aphids include the adults and larvae of predatory ladybirds, hoverfly larvae, parasitic wasps,aphid midge
''Aphidoletes aphidimyza'', commonly referred to as the aphid midge, is a midge whose larvae feed on over 70 aphid species, including the green peach aphid.
Description
The adults are small (less than long), black, delicate flies (similar ...
larvae, "aphid lions" (the larvae of green lacewings
Green lacewings are insects in the large family Chrysopidae of the order Neuroptera. There are about 85 genera and (differing between sources) 1,300–2,000 species in this widespread group. Members of the genera ''Chrysopa'' and ''Chrysoperla'' ...
), and arachnids such as spiders. Among ladybirds, ''Myzia oblongoguttata
''Myzia oblongoguttata'', commonly known as the striped ladybird, is a species of beetle in family Coccinellidae. It is found in the Palearctic (Europe, North Africa, Asia Minor, European Russia, Caucasus, Siberia, Russian Far East, Belarus, Uk ...
'' is a dietary specialist which only feeds on conifer aphids, whereas '' Adalia bipunctata'' and '' Coccinella septempunctata'' are generalists, feeding on large numbers of species. The eggs are laid in batches, each female laying several hundred. Female hoverflies lay several thousand eggs. The adults feed on pollen and nectar but the larvae feed voraciously on aphids; ''Eupeodes corollae
''Eupeodes corollae'' is a very common European species of hoverfly. Adults are in body length. Males and females have different marking on the abdomen; males have square commas on tergites 3 and 4, whereas females have narrow commas. Larvae fee ...
'' adjusts the number of eggs laid to the size of the aphid colony.
Aphids are often infected by bacteria, viruses, and fungi. They are affected by the weather, such as precipitation, temperature and wind. Fungi that attack aphids include '' Neozygites fresenii'', ''Entomophthora
''Entomophthora'' is a fungal genus in the family Entomophthoraceae. Species in this genus are parasitic on flies and other two-winged insects. The genus was circumscribed by German physician Johann Baptist Georg Wolfgang Fresenius (1808-1866) ...
'', ''Beauveria bassiana
''Beauveria bassiana'' is a fungus that grows naturally in soils throughout the world and acts as a parasite on various arthropod species, causing white muscardine disease; it thus belongs to the entomopathogenic fungi. It is used as a biological ...
'', '' Metarhizium anisopliae'', and entomopathogenic fungi such as '' Lecanicillium lecanii''. Aphids brush against the microscopic spores. These stick to the aphid, germinate, and penetrate the aphid's skin. The fungus grows in the aphid's hemolymph. After about three days, the aphid dies and the fungus releases more spores into the air. Infected aphids are covered with a woolly mass that progressively grows thicker until the aphid is obscured. Often, the visible fungus is not the one that killed the aphid, but a secondary infection.
Aphids can be easily killed by unfavourable weather, such as late spring freezes. Excessive heat kills the symbiotic bacteria that some aphids depend on, which makes the aphids infertile. Rain prevents winged aphids from dispersing, and knocks aphids off plants and thus kills them from the impact or by starvation, but cannot be relied on for aphid control.
Anti-predator defences
 Most aphids have little protection from predators. Some species interact with plant tissues forming a
Most aphids have little protection from predators. Some species interact with plant tissues forming a gall
Galls (from the Latin , 'oak-apple') or ''cecidia'' (from the Greek , anything gushing out) are a kind of swelling growth on the external tissues of plants, fungi, or animals. Plant galls are abnormal outgrowths of plant tissues, similar to be ...
, an abnormal swelling of plant tissue. Aphids can live inside the gall, which provides protection from predators and the elements. A number of galling aphid species are known to produce specialised "soldier" forms, sterile nymphs with defensive features which defend the gall from invasion. For example, Alexander's horned aphids are a type of soldier aphid that has a hard exoskeleton and pincer-like mouthparts. A woolly aphid, ''Colophina clematis
''Colophina clematis'' is a species of aphid in the woolly aphid subfamily, Eriosomatinae, native to Japan. This woolly aphid has the distinction of being the first species of aphid to have been identified as having a "soldier" caste. First insta ...
'', has first instar "soldier" larvae that protect the aphid colony, killing larvae of ladybirds, hoverflies and the flower bug '' Anthocoris nemoralis'' by climbing on them and inserting their stylets.
Although aphids cannot fly for most of their life cycle, they can escape predators and accidental ingestion by herbivores by dropping off the plant onto the ground. Others species use the soil as a permanent protection, feeding on the vascular systems of roots and remaining underground all their lives. They are often attended by ants, for the honeydew they produce and are carried from plant to plant by the ants through their tunnels.
Some species of aphid, known as "woolly aphids" (Eriosomatinae
Woolly aphids (subfamily: Eriosomatinae) are sap-sucking insects that produce a filamentous waxy white covering which resembles cotton or wool. The adults are winged and move to new locations where they lay egg masses. The nymphs often form la ...
), excrete a "fluffy wax coating" for protection. The cabbage aphid, ''Brevicoryne brassicae
''Brevicoryne brassicae'', commonly known as the cabbage aphid or cabbage aphis, is a destructive aphid (plant louse) native to Europe that is now found in many other areas of the world. The aphids feed on many varieties of produce, including ca ...
'', sequesters secondary metabolites from its host, stores them and releases chemicals that produce a violent chemical reaction and strong mustard oil smell to repel predators. Peptides produced by aphids, Thaumatins, are thought to provide them with resistance to some fungi.
It was common at one time to suggest that the cornicles were the source of the honeydew, and this was even included in the '' Shorter Oxford English Dictionary'' and the 2008 edition of the '' World Book Encyclopedia''. In fact, honeydew secretions are produced from the anus of the aphid, while cornicles mostly produce defensive chemicals such as waxes. There also is evidence of cornicle wax attracting aphid predators in some cases.
Some clones of ''Aphis craccivora
''Aphis craccivora'', variously known as the cowpea aphid, groundnut aphid or black legume aphid, is a true bug in the family ''Aphididae''. Originally of probable Palearctic origin, it is now an invasive species of cosmopolitan distribution. ...
'' are sufficiently toxic to the invasive and dominant predatory ladybird '' Harmonia axyridis'' to suppress it locally, favouring other ladybird species; the toxicity is in this case narrowly specific to the dominant predator species.
Parasitoids
Aphids are abundant and widespread, and serve as hosts to a large number ofparasitoid
In evolutionary ecology, a parasitoid is an organism that lives in close association with its host (biology), host at the host's expense, eventually resulting in the death of the host. Parasitoidism is one of six major evolutionarily stable str ...
s, many of them being very small (c. long) parasitoid wasps.
One species, ''Aphis ruborum
''Aphis'' is a genus of insects in the family Aphididae containing at least 600 species of aphids. It includes many notorious agricultural pests, such as the soybean aphid ''Aphis glycines''. Many species of ''Aphis'', such as '' A. coreopsidis ...
'', for example, is host to at least 12 species of parasitoid wasps. Parasitoids have been investigated intensively as biological control agents, and many are used commercially for this purpose.
Plant-aphid interactions
 Plants mount local and systemic defenses against aphid attack. Young leaves in some plants contain chemicals that discourage attack while the older leaves have lost this resistance, while in other plant species, resistance is acquired by older tissues and the young shoots are vulnerable. Volatile products from interplanted onions have been shown to prevent aphid attack on adjacent potato plants by encouraging the production of terpenoids, a benefit exploited in the traditional practice of companion planting, while plants neighboring infested plants showed increased root growth at the expense of the extension of aerial parts. The wild potato, ''
Plants mount local and systemic defenses against aphid attack. Young leaves in some plants contain chemicals that discourage attack while the older leaves have lost this resistance, while in other plant species, resistance is acquired by older tissues and the young shoots are vulnerable. Volatile products from interplanted onions have been shown to prevent aphid attack on adjacent potato plants by encouraging the production of terpenoids, a benefit exploited in the traditional practice of companion planting, while plants neighboring infested plants showed increased root growth at the expense of the extension of aerial parts. The wild potato, ''Solanum berthaultii
''Solanum berthaultii'' (syn. ''Solanum tarijense'') is a species of wild potato in the family Solanaceae, native to Bolivia and northwestern Argentina. It is being extensively studied for its resistance to ''Phytophthora infestans'', the late ...
'', produces an aphid alarm pheromone, (E)-β- farnesene, as an allomone, a pheromone to ward off attack; it effectively repels the aphid '' Myzus persicae'' at a range of up to 3 millimetres. ''S. berthaultii'' and other wild potato species have a further anti-aphid defence in the form of glandular hairs which, when broken by aphids, discharge a sticky liquid that can immobilise some 30% of the aphids infesting a plant.
Plants exhibiting aphid damage can have a variety of symptoms, such as decreased growth rates, mottled leaves, yellowing, stunted growth, curled leaves, browning, wilting, low yields, and death. The removal of sap creates a lack of vigor in the plant, and aphid saliva is toxic to plants. Aphids frequently transmit plant viruses to their hosts, such as to potatoes, cereal
A cereal is any Poaceae, grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, Cereal germ, germ, and bran. Cereal Grain, grain crops are grown in greater quantit ...
s, sugarbeets, and citrus plants. The green peach aphid, '' Myzus persicae'', is a vector for more than 110 plant viruses. Cotton aphids (''Aphis gossypii'') often infect sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
, papaya
The papaya (, ), papaw, () or pawpaw () is the plant species ''Carica papaya'', one of the 21 accepted species in the genus ''Carica'' of the family Caricaceae. It was first domesticated in Mesoamerica, within modern-day southern Mexico and ...
and peanuts with viruses. In plants which produce the phytoestrogen coumestrol
Coumestrol is a natural organic compound in the class of phytochemicals known as coumestans. Coumestrol was first identified as a compound with estrogenic properties by E. M. Bickoff in ladino clover and alfalfa in 1957. It has garnered research ...
, such as alfalfa, damage by aphids is linked with higher concentrations of coumestrol.
 The coating of plants with honeydew can contribute to the spread of fungi which can damage plants. Honeydew produced by aphids has been observed to reduce the effectiveness of fungicides as well.
A hypothesis that insect feeding may improve plant fitness was floated in the mid-1970s by Owen and Wiegert. It was felt that the excess honeydew would nourish soil micro-organisms, including nitrogen fixers. In a nitrogen-poor environment, this could provide an advantage to an infested plant over an uninfested plant. However, this does not appear to be supported by observational evidence.
The coating of plants with honeydew can contribute to the spread of fungi which can damage plants. Honeydew produced by aphids has been observed to reduce the effectiveness of fungicides as well.
A hypothesis that insect feeding may improve plant fitness was floated in the mid-1970s by Owen and Wiegert. It was felt that the excess honeydew would nourish soil micro-organisms, including nitrogen fixers. In a nitrogen-poor environment, this could provide an advantage to an infested plant over an uninfested plant. However, this does not appear to be supported by observational evidence.
Sociality
Some aphids show some of the traits of eusociality, joining insects such as ants, bees, and termites. However, there are differences between these sexual social insects and the clonal aphids, which are all descended from a single female parthenogenetically and share an identical genome. About fifty species of aphid, scattered among the closely related, host-alternating lineagesEriosomatinae
Woolly aphids (subfamily: Eriosomatinae) are sap-sucking insects that produce a filamentous waxy white covering which resembles cotton or wool. The adults are winged and move to new locations where they lay egg masses. The nymphs often form la ...
and Hormaphidinae
Hormaphidinae is a subfamily of the family Aphididae.
Genera
Tribe: Cerataphidini
''Aleurodaphis'' -
''Astegopteryx'' -
''Cerataphis'' -
''Ceratoglyphina'' -
''Ceratovacuna'' -
''Chaitoregma'' -
''Glyphinaphis'' -
''Ktenopteryx'' -
''Pseudoregm ...
, have some type of defensive morph. These are gall-creating species, with the colony living and feeding inside a gall that they form in the host's tissues. Among the clonal population of these aphids, there may be several distinct morphs and this lays the foundation for a possible specialization of function, in this case, a defensive caste. The soldier morphs are mostly first and second instars with the third instar being involved in ''Eriosoma moriokense'' and only in ''Smythurodes betae'' are adult soldiers known. The hind legs of soldiers are clawed, heavily sclerotized and the stylets are robust making it possible to rupture and crush small predators. The larval soldiers are altruistic individuals, unable to advance to breeding adults but acting permanently in the interests of the colony. Another requirement for the development of sociality is provided by the gall, a colonial home to be defended by the soldiers.
The soldiers of gall-forming aphids also carry out the job of cleaning the gall. The honeydew secreted by the aphids is coated in a powdery wax to form " liquid marbles" that the soldiers roll out of the gall through small orifices. Aphids that form closed galls use the plant's vascular system for their plumbing: the inner surfaces of the galls are highly absorbent and wastes are absorbed and carried away by the plant.
Interactions with humans
Pest status
About 5000 species of aphid have been described and of these, some 450 species have colonized food and fiber crops. As direct feeders on plant sap, they damage crops and reduce yields, but they have a greater impact by being vectors of plant viruses. The transmission of these viruses depends on the movements of aphids between different parts of a plant, between nearby plants, and further afield. In this respect, the probing behavior of an aphid tasting a host is more damaging than lengthy aphid feeding and reproduction by stay-put individuals. The movement of aphids influences the timing of virus epidemics. They are major pests ofgreenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of Transparent ceramics, transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic condit ...
crops and species often encountered in greenhouses include: green peach aphid ('' Myzus persicae''), cotton or melon aphid (''Aphis gossypii
''Aphis gossypii'' is a tiny insect, an aphid ("greenfly") in the superfamily Aphidoidea in the order Hemiptera. It is a true bug and sucks sap from plants. It is a widely distributed pest of a variety of agricultural crops in the families Cucu ...
''), potato aphid (''Macrosiphum euphorbiae
''Macrosiphum euphorbiae'', the potato aphid, is a sap-sucking pest insect in the family Aphididae. It infests potatoes and a number of other commercially important crops.
Distribution
''Macrosiphum euphorbiae'' originated in North America but ...
''), foxglove aphid (''Aulacorthum solani
The foxglove aphid, (''Aulacorthum solani''), also known as glasshouse-potato aphid, is an aphid in the superfamily Aphidoidea in the order Hemiptera. It is a true bug and sucks sap from plants.
Host
It has one of the broadest host ranges of a ...
'') and chrysanthemum aphid (''Macrosiphoniella sanborni
The Chrysanthemum Aphid, (''Macrosiphoniella sanborni''), is an aphid in the superfamily Aphidoidea in the order Hemiptera. It is a true bug and sucks sap from plants.
Host plants
This species of aphid is only known to live on ''Chrysanthemum'' ...
'') and others, which cause leaf yellowing, distorted leaves, and plant stunting; the excreted honeydew is a growing medium for a number of fungal pathogens including black sooty molds from the genera ''Capnodium
''Capnodium'' is a genus of sooty molds in the family Capnodiaceae. It was circumscribed in 1849 by French mycologist Camille Montagne with '' Capnodium salicinum'' as the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typic ...
'', '' Fumago'', and '' Scorias'' which then infect leaves and inhibit growth by reducing photosynthesis.
Aphids, especially during large outbreaks, have been known to trigger allergic inhalant reactions in sensitive humans.
Dispersal can be by walking or flight, appetitive dispersal, or by migration. Winged aphids are weak fliers, lose their wings after a few days and only fly by day. Dispersal by flight is affected by the impact, air currents, gravity, precipitation, and other factors, or dispersal may be accidental, caused by the movement of plant materials, animals, farm machinery, vehicles, or aircraft.
Control

Insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to b ...
control of aphids is difficult, as they breed rapidly, so even small areas missed may enable the population to recover promptly. Aphids may occupy the undersides of leaves where spray misses them, while systemic insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to b ...
s do not move satisfactorily into flower petals. Finally, some aphid species are resistant to common insecticide classes including carbamate
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally o ...
s, organophosphate
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered a ...
s, and pyrethroids.
For small backyard infestations, spraying plants thoroughly with a strong water jet every few days may be sufficient protection. An insecticidal soap Insecticidal soap is used to control many plant insect pests. Soap has been used for more than 200 years as an insect control. Because insecticidal soap works on direct contact with pests via the disruption of cell membranes when the insect is pen ...
solution can be an effective household remedy to control aphids, but it only kills aphids on contact and has no residual effect. Soap spray may damage plants, especially at higher concentrations or at temperatures above ; some plant species are sensitive to soap sprays.
 Aphid populations can be sampled using yellow-pan or Moericke traps. These are yellow containers with water that attract aphids. Aphids respond positively to green and their attraction to yellow may not be a true colour preference but related to brightness. Their visual receptors peak in sensitivity from 440 to 480 nm and are insensitive in the red region. Moericke found that aphids avoided landing on white coverings placed on soil and were repelled even more by shiny aluminium surfaces. Integrated pest management of various species of aphids can be achieved using biological insecticides based on fungi such as ''Lecanicillium lecanii'', ''Beauveria bassiana'' or '' Isaria fumosorosea''. Fungi are the main pathogens of aphids; Entomophthorales can quickly cut aphid numbers in nature.
Aphids may also be controlled by the release of natural enemies, in particular lady beetles and parasitoid wasps. However, since adult lady beetles tend to fly away within 48 hours after release, without laying eggs, repeated applications of large numbers of lady beetles are needed to be effective. For example, one large, heavily infested rose bush may take two applications of 1500 beetles each.
The ability to produce allomones such as farnesene to repel and disperse aphids and to attract their predators has been experimentally transferred to
Aphid populations can be sampled using yellow-pan or Moericke traps. These are yellow containers with water that attract aphids. Aphids respond positively to green and their attraction to yellow may not be a true colour preference but related to brightness. Their visual receptors peak in sensitivity from 440 to 480 nm and are insensitive in the red region. Moericke found that aphids avoided landing on white coverings placed on soil and were repelled even more by shiny aluminium surfaces. Integrated pest management of various species of aphids can be achieved using biological insecticides based on fungi such as ''Lecanicillium lecanii'', ''Beauveria bassiana'' or '' Isaria fumosorosea''. Fungi are the main pathogens of aphids; Entomophthorales can quickly cut aphid numbers in nature.
Aphids may also be controlled by the release of natural enemies, in particular lady beetles and parasitoid wasps. However, since adult lady beetles tend to fly away within 48 hours after release, without laying eggs, repeated applications of large numbers of lady beetles are needed to be effective. For example, one large, heavily infested rose bush may take two applications of 1500 beetles each.
The ability to produce allomones such as farnesene to repel and disperse aphids and to attract their predators has been experimentally transferred to transgenic
A transgene is a gene that has been transferred naturally, or by any of a number of genetic engineering techniques, from one organism to another. The introduction of a transgene, in a process known as transgenesis, has the potential to change the ...
''Arabidopsis thaliana
''Arabidopsis thaliana'', the thale cress, mouse-ear cress or arabidopsis, is a small flowering plant native to Eurasia and Africa. ''A. thaliana'' is considered a weed; it is found along the shoulders of roads and in disturbed land.
A winter a ...
'' plants using an Eβf synthase gene in the hope that the approach could protect transgenic crops. Eβ farnesene has however found to be ineffective in crop situations although stabler synthetic forms help improve the effectiveness of control using fungal spores and insecticides through increased uptake caused by movements of aphids.
In human culture
Aphids are familiar to farmers and gardeners, mainly as pests.Peter Marren
Peter Marren (born 1950) is a British writer, journalist, and naturalist. He has written over 20 books about British nature, including ''Chasing the Ghost: My Search for all the Wild Flowers of Britain'' (2018), an account of a year-long quest ...
and Richard Mabey
Richard Thomas Mabey (born 20 February 1941) is a writer and broadcaster, chiefly on the relations between nature and culture.
Education
Mabey was educated at three independent schools, all in Berkhamsted, Hertfordshire. The first was at Roth ...
record that Gilbert White described an invading "army" of black aphids that arrived in his village of Selborne
Selborne is a village in Hampshire, England, south of Alton, Hampshire, Alton, and just within the northern boundary of the South Downs National Park. The village receives visitors because of its links with the naturalist Revd. Gilbert White, a ...
, Hampshire, England, in August 1774 in "great clouds", covering every plant, while in the unusually hot summer of 1783, White found that honeydew was so abundant as to "deface and destroy the beauties of my garden", though he thought the aphids were consuming rather than producing it.
Infestation of the Chinese sumac ('' Rhus chinensis'') by Chinese sumac aphids ('' Schlechtendalia chinensis'') can create "Chinese galls" which are valued as a commercial product. As "Galla Chinensis", they are used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat coughs, diarrhea, night sweats, dysentery and to stop intestinal and uterine bleeding. Chinese galls are also an important source of tannins.
See also
* Aeroplankton * Economic entomology * Pineapple gallNotes
References
External links
Aphids of southeastern U.S. woody ornamentals
''Acyrthosiphon pisum''
MetaPathogen – facts, life cycle, life cycle image
Agricultural Research Service
Insect Olfaction of Plant Odour: Colorado Potato Beetle and Aphid Studies
Center for Invasive Species Research On the University of Florida /
Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences
The University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (UF/IFAS) is a teaching, research and Extension scientific organization focused on agriculture and natural resources. It is a partnership of federal, state, and county governmen ...
''Featured Creatures'' website:
''Aphis gossypii'', melon or cotton aphid
{{Authority control Agricultural pest insects Insect pests of temperate forests Insect pests of ornamental plants Insect vectors of plant pathogens Sternorrhyncha Extant Permian first appearances Insects in culture