Antioch On The Orontes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Δάφνῃ "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; la, Antiochia ad Orontem; hy, Անտիոք ''Antiokʽ''; syr, ܐܢܛܝܘܟܝܐ ''Anṭiokya''; he, אנטיוכיה, ''Anṭiyokhya''; ar, أنطاكية, ''Anṭākiya''; fa, انطاکیه; tr,
Antakya
Antakya (), historically known as Antioch ( el, Ἀντιόχεια; hy, Անտիոք, Andiok), is the capital of Hatay Province, the southernmost province of Turkey. The city is located in a well-watered and fertile valley on the Orontes Rive ...
. was a Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
, and later, a Biblical Christian city, founded by Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; ; grc-gre, Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ , ) was a Macedonian Greek general who was an officer and successor ( ''diadochus'') of Alexander the Great. Seleucus was the founder of the eponymous Seleucid Empire. In the po ...
in 300 BC. This city served as the capital of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
and later as regional capital to both the Roman and Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. During the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
, Antioch served as the capital of the Principality of Antioch
The Principality of Antioch was one of the crusader states created during the First Crusade which included parts of modern-day Turkey and Syria. The principality was much smaller than the County of Edessa or the Kingdom of Jerusalem. It extende ...
, one of four Crusader states
The Crusader States, also known as Outremer, were four Catholic realms in the Middle East that lasted from 1098 to 1291. These feudal polities were created by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade through conquest and political in ...
that were founded in the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
. Its inhabitants were known as ''Antiochenes''; the city's ruin lies on the Orontes River
The Orontes (; from Ancient Greek , ) or Asi ( ar, العاصي, , ; tr, Asi) is a river with a length of in Western Asia that begins in Lebanon, flowing northwards through Syria before entering the Mediterranean Sea near Samandağ in Turkey.
...
, near Antakya
Antakya (), historically known as Antioch ( el, Ἀντιόχεια; hy, Անտիոք, Andiok), is the capital of Hatay Province, the southernmost province of Turkey. The city is located in a well-watered and fertile valley on the Orontes Rive ...
, the modern city in Hatay Province
Hatay Province ( tr, Hatay ili, ) is the southernmost province of Turkey. It is situated almost entirely outside Anatolia, along the eastern coast of the Levantine Sea. The province borders Syria to its south and east, the Turkish province of A ...
of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
(Türkiye), to which the ancient city lends its name.
Antioch was founded near the end of the fourth century BC by Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; ; grc-gre, Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ , ) was a Macedonian Greek general who was an officer and successor ( ''diadochus'') of Alexander the Great. Seleucus was the founder of the eponymous Seleucid Empire. In the po ...
, one of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
's generals, as one of the four cities of the Seleucis of Syria
Seleucis of Syria ( grc, Σελευκίς τῆς Συρίας ) was a region of the Seleucid Empire located in northern Syria. It was also known as the Syrian Tetrapolis,
The four cities had been founded by Seleucus Nicator;
*Antioch—named af ...
. The city's location offered geographical, military, and economic benefits to its occupants; Antioch was heavily involved in the spice trade and lay within easy reach of the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
and the Royal Road
The Royal Road was an ancient highway reorganized and rebuilt by the Persian king Darius the Great (Darius I) of the first (Achaemenid) Persian Empire in the 5th century BC. Darius built the road to facilitate rapid communication on the western ...
. During the late Hellenistic period and Middle Roman Empire, Antioch's population may have reached a peak of over 500,000 inhabitants (most generally estimate between 200,000–250,000), making the city the third largest in the Empire after Rome and Alexandria and one of the most important cities in the eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to communi ...
. The city was the capital of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
from 240 BC until 63 BC, when the Romans took control, making it capital of the province of Syria
Roman Syria was an early Roman province annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC by Pompey in the Third Mithridatic War following the defeat of King of Armenia Tigranes the Great.
Following the partition of the Herodian Kingdom of Judea into tetr ...
and later of Coele Syria
Coele-Syria (, also spelt Coele Syria, Coelesyria, Celesyria) alternatively Coelo-Syria or Coelosyria (; grc-gre, Κοίλη Συρία, ''Koílē Syría'', 'Hollow Syria'; lat, Cœlē Syria or ), was a region of Syria (region), Syria in cl ...
. From the early fourth century, Antioch was the seat of the Count of the Orient, head of the Diocese of the East
The Diocese of the East ( la, Dioecesis Orientis; el, ) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of the western Middle East, between the Mediterranean Sea and Mesopotamia. During late Antiquity, it was one of the majo ...
. The Romans provided the city with walls that covered almost , of which one quarter was mountain, leaving – about one-fifth the area of Rome within the Aurelian Walls.
It was also the main center of Hellenistic Judaism
Hellenistic Judaism was a form of Judaism in classical antiquity that combined Jewish religious tradition with elements of Greek culture. Until the early Muslim conquests of the eastern Mediterranean, the main centers of Hellenistic Judaism were A ...
at the end of the Second Temple period
The Second Temple period in Jewish history lasted approximately 600 years (516 BCE - 70 CE), during which the Second Temple existed. It started with the return to Zion and the construction of the Second Temple, while it ended with the First Jewis ...
. Antioch was part of the pentarchy
Pentarchy (from the Greek , ''Pentarchía'', from πέντε ''pénte'', "five", and ἄρχειν ''archein'', "to rule") is a model of Church organization formulated in the laws of Emperor Justinian I (527–565) of the Roman Empire. In this ...
and was called "the cradle of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
" as a result of its longevity and the pivotal role that it played in the emergence of early Christianity
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewish ...
. The Christian New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
asserts that the name "Christian" first emerged in Antioch. The city declined to relative insignificance during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
due to warfare, repeated earthquakes, and a change in trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a sing ...
s. The city still lends its name to Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch
The Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch ( el, Ελληνορθόδοξο Πατριαρχείο Αντιοχείας), also known as the Antiochian Orthodox Church and legally as the Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch and All the East ( ar ...
, one of the most important churches of the Levant and eastern Mediterranean.
Geography
Two routes from theMediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
, lying through the Orontes river gorge and the Belen Pass
The Belen Pass ( tr, Belen Geçidi), known in antiquity as the Syrian Gates ( grc-gre, Συρίαι πύλαι, ''Syríai Pýlai''; la, Syriae Portae), is a pass through the Nur Mountains located in the Belen District of Hatay Province in sou ...
, converge in the plain of the Antioch Lake, now called Lake Amik
Lake Amik or the Lake of Antioch ( ar, بحيرة العمق) ( tr, Amik Gölü) was a large freshwater lake in the basin of the Orontes River in Hatay Province, Turkey; it was located north-east of the ancient city of Antioch (modern Antakya). The ...
, and are met there by
#the road from the Amanian Gate
The Amanian Gate ( la, Amani Portae) or Bahçe Pass ( tr, Bahçe Geçidi), also known as the Amanus Pass or Amanides Pylae (Ἀμανίδες or Ἀμανικαί Πύλαι 'Amanus Gates'), is a mountain pass located on the border between Osmaniye ...
(Baghche Pass) and western Kingdom of Commagene
Commagene ( grc-gre, Κομμαγηνή) was an ancient Greco-Iranian kingdom ruled by a Hellenized branch of the Iranian Orontid dynasty that had ruled over Armenia. The kingdom was located in and around the ancient city of Samosata, which ser ...
, which descends the valley of the Karasu
Karasu, Kara-su, Kara su, Qarasu or Gharasu (lit. 'black water/river' in Turkic languages) may refer to:
Rivers
The Balkans
* A former name of the Struma River (Struma Karasu) in Bulgaria and Thrace, northern Greece
* A former name of the Mest ...
to the Afrin River
The Afrin River ( ar, نهر عفرين ''Nahr ʻIfrīn''; ( ku, Çemê Efrînê; northern Syrian vernacular: ''Nahər ʻAfrīn''; tr, Afrin Çayı) is a tributary of the Orontes River in Turkey and Syria. It rises in the Kartal Mountains in ...
#the roads from eastern Commagene and the Euphratean crossings at Samosata (now Samsat
Samsat ( ku, Samîsad), formerly Samosata ( grc, Σαμόσατα) is a small town in the Adıyaman Province of Turkey, situated on the upper Euphrates river. It is the seat of Samsat District.Apamea Zeugma (Birejik), which descend the valleys of the Afrin and the


PDF
/ref> After Alexander's death in 323 BCE, his generals, the
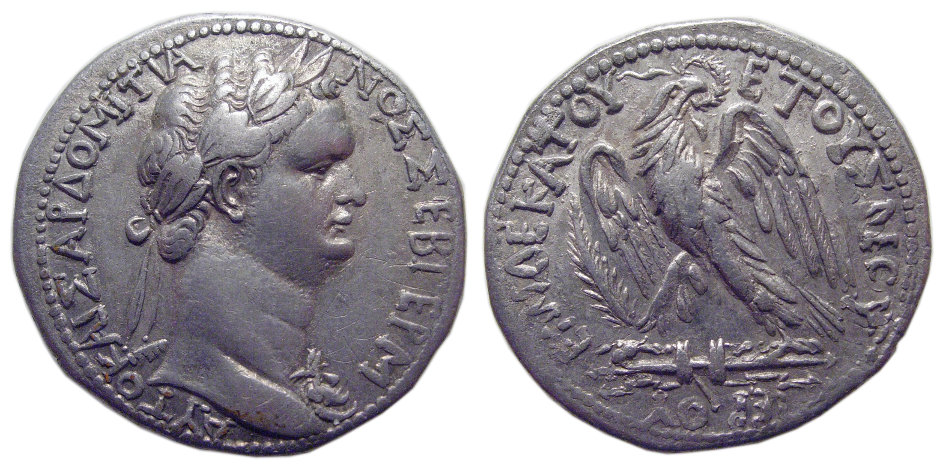


 The Roman emperors favored the city from the first moments, seeing it as a more suitable capital for the eastern part of the empire than Alexandria could be, because of the isolated position of Egypt. To a certain extent they tried to make it an eastern Rome.
The Roman emperors favored the city from the first moments, seeing it as a more suitable capital for the eastern part of the empire than Alexandria could be, because of the isolated position of Egypt. To a certain extent they tried to make it an eastern Rome.  In 256 AD, the town was suddenly raided by the Sasanian Empire, Persians under Shapur I, and many of the people were slain in the theatre. It was recaptured by the Roman emperor Valerian (emperor), Valerian the following year.
In 256 AD, the town was suddenly raided by the Sasanian Empire, Persians under Shapur I, and many of the people were slain in the theatre. It was recaptured by the Roman emperor Valerian (emperor), Valerian the following year.
 John Chrysostom writes that when Ignatius of Antioch was bishop in the city, the ''dêmos,'' probably meaning the number of free adult men and women without counting children and slaves, numbered 200,000. In a letter written in 363, Libanius says the city contains 150,000 ''anthrôpoi,'' a word which would ordinarily mean all human beings of any age, sex, or social status, seemingly indicating a decline in the population since the 1st Century. Chrysostom also says in one of his homilies on the Gospel of Matthew, which were delivered between 386 and 393, that in his own time there were 100,000 Christians in Antioch, a figure which may refer to orthodox Christians who belonged to the Great Church as opposed to members of other groups such as Arians and Apollinarians, or to all Christians of any persuasion.
The Maronite Catholic Church's patriarch is called the Patriarch of Antioch and all the East. He currently resides in Bkerke - Lebanon. The Maronites continue the Antiochene liturgical tradition and the use of the Syrian-Aramaic (Syro-Aramaic or Western Aramaic) language in their liturgies.
One of the canonical Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox churches is still called the Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch, although it moved its headquarters from Antioch to Damascus, Syria, several centuries ago (see list of Patriarchs of Antioch), and its prime bishop retains the title "Patriarch of Antioch", somewhat analogous to the manner in which several Popes, heads of the Roman Catholic Church remained "Bishop of Rome" even while residing in Avignon, in present-day France, in the 14th century.
Syriac Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch and All the East, is an Oriental Orthodox Christian denomination, Church with Autocephaly, autocephalous List of Syriac Orthodox Patriarchs of Antioch, patriarchate founded by Saint Peter and Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul in the Christianity in the 1st century, 1st century, according to its tradition. The Syriac Orthodox Church is part of Oriental Orthodoxy, a distinct Communion (Christian), communion of churches claiming to continue the patristic and Apostolic Christology before the schism following the Council of Chalcedon in 451.
John Chrysostom writes that when Ignatius of Antioch was bishop in the city, the ''dêmos,'' probably meaning the number of free adult men and women without counting children and slaves, numbered 200,000. In a letter written in 363, Libanius says the city contains 150,000 ''anthrôpoi,'' a word which would ordinarily mean all human beings of any age, sex, or social status, seemingly indicating a decline in the population since the 1st Century. Chrysostom also says in one of his homilies on the Gospel of Matthew, which were delivered between 386 and 393, that in his own time there were 100,000 Christians in Antioch, a figure which may refer to orthodox Christians who belonged to the Great Church as opposed to members of other groups such as Arians and Apollinarians, or to all Christians of any persuasion.
The Maronite Catholic Church's patriarch is called the Patriarch of Antioch and all the East. He currently resides in Bkerke - Lebanon. The Maronites continue the Antiochene liturgical tradition and the use of the Syrian-Aramaic (Syro-Aramaic or Western Aramaic) language in their liturgies.
One of the canonical Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox churches is still called the Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch, although it moved its headquarters from Antioch to Damascus, Syria, several centuries ago (see list of Patriarchs of Antioch), and its prime bishop retains the title "Patriarch of Antioch", somewhat analogous to the manner in which several Popes, heads of the Roman Catholic Church remained "Bishop of Rome" even while residing in Avignon, in present-day France, in the 14th century.
Syriac Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch and All the East, is an Oriental Orthodox Christian denomination, Church with Autocephaly, autocephalous List of Syriac Orthodox Patriarchs of Antioch, patriarchate founded by Saint Peter and Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul in the Christianity in the 1st century, 1st century, according to its tradition. The Syriac Orthodox Church is part of Oriental Orthodoxy, a distinct Communion (Christian), communion of churches claiming to continue the patristic and Apostolic Christology before the schism following the Council of Chalcedon in 451.
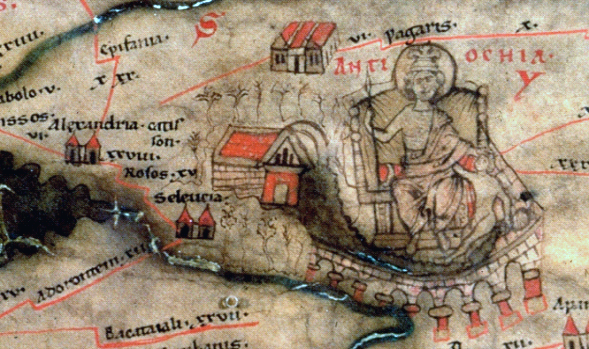 Antioch and its port,
Antioch and its port,
 In 637, during the reign of the Byzantine emperor Heraclius, Antioch was conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate during the Battle of the Iron Bridge. The city became known in Arabic as . Since the Umayyad, Umayyad dynasty was unable to penetrate the Anatolian plateau, Antioch found itself on the frontline of the conflicts between two hostile empires during the next 350 years, so that the city went into a precipitous decline.
In 969, Siege of Antioch (968-969), the city was recovered for the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Emperor Nikephoros II Phokas by Michael Bourtzes and the ''stratopedarches'' Peter (stratopedarches), Peter. It soon became the seat of a ''Dux#Later developments, doux'', the civil governor of the homonymous Theme (Byzantine district), theme, but also the seat of the somewhat more important ''Domestic of the Schools of the Orient'', the supreme military commander of the imperial forces on the eastern frontier. Sometimes both offices were held by the same person, usually military officers such as Nikephoros Ouranos, or Philaretos Brachamios, who managed to retain the integrity of the eastern borderline after the Seljuk conquest of Anatolia. As the empire disintegrated rapidly before the Komnenian restoration, ''Dux of Antioch'' & ''Domestic of the Schools of the East'' Philaretos Brachamios held the city until Suleiman ibn Qutalmish, the Sultanate of Rum, emir of Rum, captured it from him in 1084. Two years later, Suleiman was killed fighting against Tutush I, Tutush, the brother of the Malik-Shah I, Seljuk Sultan, who annexed the city into the Seljuk empire. Yagisiyan was appointed governor and became increasingly independent within the tumtuluous years following Malik-Shah's death in 1092.
In 637, during the reign of the Byzantine emperor Heraclius, Antioch was conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate during the Battle of the Iron Bridge. The city became known in Arabic as . Since the Umayyad, Umayyad dynasty was unable to penetrate the Anatolian plateau, Antioch found itself on the frontline of the conflicts between two hostile empires during the next 350 years, so that the city went into a precipitous decline.
In 969, Siege of Antioch (968-969), the city was recovered for the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Emperor Nikephoros II Phokas by Michael Bourtzes and the ''stratopedarches'' Peter (stratopedarches), Peter. It soon became the seat of a ''Dux#Later developments, doux'', the civil governor of the homonymous Theme (Byzantine district), theme, but also the seat of the somewhat more important ''Domestic of the Schools of the Orient'', the supreme military commander of the imperial forces on the eastern frontier. Sometimes both offices were held by the same person, usually military officers such as Nikephoros Ouranos, or Philaretos Brachamios, who managed to retain the integrity of the eastern borderline after the Seljuk conquest of Anatolia. As the empire disintegrated rapidly before the Komnenian restoration, ''Dux of Antioch'' & ''Domestic of the Schools of the East'' Philaretos Brachamios held the city until Suleiman ibn Qutalmish, the Sultanate of Rum, emir of Rum, captured it from him in 1084. Two years later, Suleiman was killed fighting against Tutush I, Tutush, the brother of the Malik-Shah I, Seljuk Sultan, who annexed the city into the Seljuk empire. Yagisiyan was appointed governor and became increasingly independent within the tumtuluous years following Malik-Shah's death in 1092.
 The Crusaders' Siege of Antioch conquered the city in June 1098 on their way to Jerusalem. At this time, the bulk of far eastern trade traveled through Egypt, but in the second half of the 12th century Nur ad-Din Zangi, Nur ed-Din and later Saladin brought order to Muslim Syria, opening up long-distance trade routes, including to Antioch and on to its new port, Port Saint Symeon, St Symeon, which had replaced Seleucia Pieria. However, the Mongol conquests of the 13th century altered the main trade routes from the far east, as they encouraged merchants to take the overland route through Mongol territory to the Black Sea, reducing the prosperity of Antioch.
In 1100, Tancred, Prince of Galilee, Tancred became the regent of Antioch after his uncle and predecessor Bohemond I of Antioch was taken prisoner for three years (1100–03) by Gazi Gümüshtigin of the Danishmends at the Battle of Melitene. Tancred expanded the territory of Antioch by conquering Cilicia, Byzantine Cilicia, Tarsus, Mersin, Tarsus, and Adana in 1101 and founding the principality, Lattakieh, Byzantine Latakia, in 1103. In 1107 Bohemond enraged by an earlier defeat when he, allianced with Edessa, attacked Aleppo, and Baldwin of Bourcq and Joscelin I of Edessa, Joscelin of Courtenay (Bourcq's most powerful vassal) were briefly captured, as well as the Byzantines recapturing of Cilicia and the harbor and lower town of Lattakieh, he renamed Tancred as the regent of Antioch and sailed for Europe with the intent of gaining support for an attack against the Greeks.
From 1107 to 1108, Bohemond led a 'crusade' against Byzantium, with the Latins crossing the Adriatic in October 1107 and laying siege to the city of Durrës (in modern Albania), which is often regarded as the western gate of the Greek empire. Bohemond was outwitted by Alexius, who deployed his forces to cut the invaders' supply lines whilst avoiding direct confrontation. The Latins were weakened by hunger and proved unable to break the defenses of Durrës. Bohemond capitulated in September 1108 and was forced to accede to a peace accord, the Treaty of Devol. The terms of this agreement stipulated that Bohemond was to hold Antioch for the remainder of his life as the emperor's subject and the Greek patriarch was to be restored to power in the city. However Tancred refused to honor the Treaty of Devol in which Bohemond swore an oath, and it is not until 1158 that it truly became a vassal state of the
The Crusaders' Siege of Antioch conquered the city in June 1098 on their way to Jerusalem. At this time, the bulk of far eastern trade traveled through Egypt, but in the second half of the 12th century Nur ad-Din Zangi, Nur ed-Din and later Saladin brought order to Muslim Syria, opening up long-distance trade routes, including to Antioch and on to its new port, Port Saint Symeon, St Symeon, which had replaced Seleucia Pieria. However, the Mongol conquests of the 13th century altered the main trade routes from the far east, as they encouraged merchants to take the overland route through Mongol territory to the Black Sea, reducing the prosperity of Antioch.
In 1100, Tancred, Prince of Galilee, Tancred became the regent of Antioch after his uncle and predecessor Bohemond I of Antioch was taken prisoner for three years (1100–03) by Gazi Gümüshtigin of the Danishmends at the Battle of Melitene. Tancred expanded the territory of Antioch by conquering Cilicia, Byzantine Cilicia, Tarsus, Mersin, Tarsus, and Adana in 1101 and founding the principality, Lattakieh, Byzantine Latakia, in 1103. In 1107 Bohemond enraged by an earlier defeat when he, allianced with Edessa, attacked Aleppo, and Baldwin of Bourcq and Joscelin I of Edessa, Joscelin of Courtenay (Bourcq's most powerful vassal) were briefly captured, as well as the Byzantines recapturing of Cilicia and the harbor and lower town of Lattakieh, he renamed Tancred as the regent of Antioch and sailed for Europe with the intent of gaining support for an attack against the Greeks.
From 1107 to 1108, Bohemond led a 'crusade' against Byzantium, with the Latins crossing the Adriatic in October 1107 and laying siege to the city of Durrës (in modern Albania), which is often regarded as the western gate of the Greek empire. Bohemond was outwitted by Alexius, who deployed his forces to cut the invaders' supply lines whilst avoiding direct confrontation. The Latins were weakened by hunger and proved unable to break the defenses of Durrës. Bohemond capitulated in September 1108 and was forced to accede to a peace accord, the Treaty of Devol. The terms of this agreement stipulated that Bohemond was to hold Antioch for the remainder of his life as the emperor's subject and the Greek patriarch was to be restored to power in the city. However Tancred refused to honor the Treaty of Devol in which Bohemond swore an oath, and it is not until 1158 that it truly became a vassal state of the
 Few traces of the once great Roman city are visible today aside from the massive fortification walls that snake up the mountains to the east of the modern city, several aqueducts, and the Church of St Peter (St Peter's Cave Church, Cave-Church of St. Peter), said to be a meeting place of an Early Christian community. The majority of the Roman city lies buried beneath deep sediments from the Orontes River, or has been obscured by recent construction.
Between 1932 and 1939, archaeological excavations of Antioch were undertaken under the direction of the "Committee for the Excavation of Antioch and Its Vicinity", which was made up of representatives from the Louvre Museum, the Baltimore Museum of Art, the Worcester Art Museum, Princeton University, Wellesley College, and later (1936) also the Fogg Art Museum at Harvard University and its affiliate Dumbarton Oaks.
The excavation team failed to find the major buildings they hoped to unearth, including Domus Aurea (Antioch), Constantine's Great Octagonal Church or the imperial palace. However, a great accomplishment of the expedition was the discovery of high-quality Roman mosaics from villas and baths in Antioch, Daphne and Seleucia Pieria.
The principal excavations of Mosaics at Antioch led by Princeton University in March 1932 recovered nearly 300 mosaics. Many of these mosaics were originally displayed as floor mosaics in private homes during the 2nd through 6th centuries AD, while others were displayed in baths and other public buildings. The majority of the Antioch mosaics are from the fourth and fifth centuries, Antioch's golden age, though others from earlier times have survived as well
. The mosaics depict a variety of images including animals, plants, and mythological beings, as well as scenes from the daily lives of people living in the area at the time. Each mosaic is bordered by intricate designs and contains bold, vibrant colors.
One mosaic includes a border that depicts a walk from Antioch to Daphne, showing many ancient buildings along the way. The mosaics are now displayed in the Hatay Archaeology Museum in
Few traces of the once great Roman city are visible today aside from the massive fortification walls that snake up the mountains to the east of the modern city, several aqueducts, and the Church of St Peter (St Peter's Cave Church, Cave-Church of St. Peter), said to be a meeting place of an Early Christian community. The majority of the Roman city lies buried beneath deep sediments from the Orontes River, or has been obscured by recent construction.
Between 1932 and 1939, archaeological excavations of Antioch were undertaken under the direction of the "Committee for the Excavation of Antioch and Its Vicinity", which was made up of representatives from the Louvre Museum, the Baltimore Museum of Art, the Worcester Art Museum, Princeton University, Wellesley College, and later (1936) also the Fogg Art Museum at Harvard University and its affiliate Dumbarton Oaks.
The excavation team failed to find the major buildings they hoped to unearth, including Domus Aurea (Antioch), Constantine's Great Octagonal Church or the imperial palace. However, a great accomplishment of the expedition was the discovery of high-quality Roman mosaics from villas and baths in Antioch, Daphne and Seleucia Pieria.
The principal excavations of Mosaics at Antioch led by Princeton University in March 1932 recovered nearly 300 mosaics. Many of these mosaics were originally displayed as floor mosaics in private homes during the 2nd through 6th centuries AD, while others were displayed in baths and other public buildings. The majority of the Antioch mosaics are from the fourth and fifth centuries, Antioch's golden age, though others from earlier times have survived as well
. The mosaics depict a variety of images including animals, plants, and mythological beings, as well as scenes from the daily lives of people living in the area at the time. Each mosaic is bordered by intricate designs and contains bold, vibrant colors.
One mosaic includes a border that depicts a walk from Antioch to Daphne, showing many ancient buildings along the way. The mosaics are now displayed in the Hatay Archaeology Museum in
The Ancient City of Antioch
Map
Richard Stillwell, ed. ''Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites'', 1976:
"Antioch on the Orontes (Antaky), Turkey"
Includes timeline, maps, and photo galleries of Antioch's mosaics and artifacts
Antakya Museum
Many photos of the collection in Antakya's museum, in particular Roman mosaics
Antiochepedia Blog
News and information about ancient Antioch
(mosaics from Antioch) {{Authority control History of Antioch, 01 Ancient Greek cities in Anatolia Roman towns and cities in Turkey Populated places along the Silk Road Former populated places in Turkey Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Archaeological sites in Hatay Province Coloniae (Roman) Crusade places Geography of Hatay Province Holy cities New Testament cities Roman sites in Turkey Seleucid colonies in Anatolia Populated places established in the 4th century BC 290s BC establishments 1268 disestablishments Populated places disestablished in the 13th century
Queiq
The Queiq (Modern Standard Arabic: , ''Quwayq'', ; northern Syrian Arabic: ''ʾWēʾ'', ), with many variant spellings, known in antiquity as the Belus ( grc-gre, Βήλος, ''Bēlos''), Chalos and also known in English as the Aleppo Rive ...
, and
#the road from the Euphratean ford at Thapsacus Thapsacus ( grc, Θάψακος, Thapsakos; he, תִּפְסַח ''Tipsah'') was an ancient town along the western bank of the Euphrates river that would now lie in modern Syria. Thapsacus was the Greek and Roman name for the town. The town was imp ...
, which skirts the fringe of the Syrian steppe. A single route proceeds south in the Orontes valley.
History


Prehistory
The settlement called Meroe pre-dated Antioch. A shrine of the Semitic goddessAnat
Anat (, ), Anatu, classically Anath (; uga, 𐎓𐎐𐎚 ''ʿnt''; he, עֲנָת ''ʿĂnāṯ''; ; el, Αναθ, translit=Anath; Egyptian: '' ꜥntjt'') was a goddess associated with warfare and hunting, best known from the Ugaritic texts. ...
, called by Herodotus the "Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
Artemis
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Artemis (; grc-gre, Ἄρτεμις) is the goddess of the hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, nature, vegetation, childbirth, care of children, and chastity. She was heavily identified wit ...
", was located here. This site was included in the eastern suburbs of Antioch. There was a village on the spur of Mount Silpius named ''Io'', or '' Iopolis''. This name was always adduced as evidence by Antiochenes (''e.g.'' Libanius
Libanius ( grc-gre, Λιβάνιος, Libanios; ) was a teacher of rhetoric of the Sophist school in the Eastern Roman Empire. His prolific writings make him one of the best documented teachers of higher education in the ancient world and a criti ...
) anxious to affiliate themselves to the Attic Ionians
The Ionians (; el, Ἴωνες, ''Íōnes'', singular , ''Íōn'') were one of the four major tribes that the Greeks considered themselves to be divided into during the ancient period; the other three being the Dorians, Aeolians, and Achae ...
—an eagerness which is illustrated by the Athenian types used on the city's coins. Io may have been a small early colony of trading Greeks (Javan
Javan () was the fourth son of Noah's son Japheth according to the "Generations of Noah" (Book of Genesis, chapter 10) in the Hebrew Bible. Josephus states the traditional belief that this individual was the ancestor of the Greeks.
Also servin ...
). John Malalas
John Malalas ( el, , ''Iōánnēs Malálas''; – 578) was a Byzantine chronicler from Antioch (now Antakya, Turkey).
Life
Malalas was of Syrian descent, and he was a native speaker of Syriac who learned how to write in Greek later in ...
also mentions an archaic village, Bottia, in the plain by the river.
Foundation by Seleucus I
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
is said to have camped on the site of Antioch and dedicated an altar to Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label=Genitive case, genitive Aeolic Greek, Boeotian Aeolic and Doric Greek#Laconian, Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label=Genitive case, genitive el, Δίας, ''D� ...
Bottiaeus; it lay in the northwest of the future city. This account is found only in the writings of Libanius, a fourth-century orator from Antioch, and may be legend intended to enhance Antioch's status. But the story is not unlikely in itself.Glanville Downey
Robert Emory Glanville Downey (14 June 1908 — 18 December 1991) was an American historian, specializing in history of Late antiquity, primarily in the early Byzantine East and the era of Justinian.
Biography
He was born in Baltimore, Maryland ...
, ''Ancient Antioch'' (Princeton, Princeton University Press
Princeton University Press is an independent publisher with close connections to Princeton University. Its mission is to disseminate scholarship within academia and society at large.
The press was founded by Whitney Darrow, with the financial su ...
, 1963). Available a/ref> After Alexander's death in 323 BCE, his generals, the
Diadochi
The Diadochi (; singular: Diadochus; from grc-gre, Διάδοχοι, Diádochoi, Successors, ) were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The War ...
, divided up the territory he had conquered. After the Battle of Ipsus
The Battle of Ipsus ( grc, Ἱψός) was fought between some of the Diadochi (the successors of Alexander the Great) in 301 BC near the town of Ipsus in Phrygia. Antigonus I Monophthalmus, the Macedonian ruler of large parts of Asia, and his so ...
in 301 BCE, Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; ; grc-gre, Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ , ) was a Macedonian Greek general who was an officer and successor ( ''diadochus'') of Alexander the Great. Seleucus was the founder of the eponymous Seleucid Empire. In the po ...
won the territory of Syria, and he proceeded to found four "sister cities" in northwestern Syria, one of which was Antioch, a city named in honor of his father Antiochus; according to the ''Suda
The ''Suda'' or ''Souda'' (; grc-x-medieval, Σοῦδα, Soûda; la, Suidae Lexicon) is a large 10th-century Byzantine encyclopedia of the ancient Mediterranean world, formerly attributed to an author called Soudas (Σούδας) or Souidas ...
'', it might be named after his son Antiochus. He is reputed to have built sixteen Antiochs.
Seleucus founded Antioch on a site chosen through ritual means. An eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just ...
, the bird of Zeus, had been given a piece of sacrificial meat and the city was founded on the site to which the eagle carried the offering. Seleucus did this on the 22nd day of the month of Artemísios in the twelfth year of his reign, equivalent to May 300 BCE. Antioch soon rose above Seleucia Pieria
Seleucia in Pieria (Greek Σελεύκεια ἐν Πιερίᾳ), also known in English as Seleucia by the Sea, and later named Suedia, was a Hellenistic town, the seaport of Antioch ad Orontes (Syria Prima), the Seleucid capital, modern Antaky ...
to become the Syrian capital.


Hellenistic age
The original city of Seleucus was laid out in imitation of thegrid plan
In urban planning, the grid plan, grid street plan, or gridiron plan is a type of city plan in which streets run at right angles to each other, forming a grid.
Two inherent characteristics of the grid plan, frequent intersections and orthogona ...
of Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria ...
by the architect Xenarius
Xenarius was a Greek architect and urban planner during the 3rd century BC. He is known for his plan for the city of Antioch. The grid layout of the city is believed to be influenced by Dinocrates' plan of Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱ ...
. Libanius describes the first building and arrangement of this city (i. p. 300. 17).
The citadel was on Mount Silpius and the city lay mainly on the low ground to the north, fringing the river. Two great colonnaded streets intersected in the centre. Shortly afterwards a second quarter was laid out, probably on the east and by Antiochus I Soter
Antiochus I Soter ( grc-gre, Ἀντίοχος Σωτήρ, ''Antíochos Sōtér''; "Antiochus the Saviour"; c. 324/32 June 261 BC) was a Greek king of the Seleucid Empire. Antiochus succeeded his father Seleucus I Nicator in 281 BC and reigned du ...
, which, from an expression of Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
, appears to have been the native, as contrasted with the Greek, town. It was enclosed by a wall of its own.
In the Orontes, north of the city, lay a large island, and on this Seleucus II Callinicus
Seleucus II Callinicus Pogon ( el, ; ''Kallinikos'' means "beautifully triumphant"; ''Pogon'' means "the Beard"; July/August 265 BC – December 225 BC),, . was a ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire, who reigned from 246 BC to 225 BC. Faced ...
began a third walled "city", which was finished by Antiochus III the Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the re ...
. A fourth and last quarter was added by Antiochus IV Epiphanes
Antiochus IV Epiphanes (; grc, Ἀντίοχος ὁ Ἐπιφανής, ''Antíochos ho Epiphanḗs'', "God Manifest"; c. 215 BC – November/December 164 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king who ruled the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his deat ...
(175–164 BC); thenceforth Antioch was known as ''Tetrapolis''. From west to east the whole was about in diameter and a little less from north to south. This area included many large gardens.
The new city was populated by a mix of local settlers that Athenians brought from the nearby city of Antigonia, Macedonians, and Jews (who were given full status from the beginning). According to ancient tradition, Antioch was settled by 5,500 Athenians and Macedonians, together with an unknown number of native Syrians. This number probably refers to free adult citizens, so that the total number of free Greek settlers including women and children was probably between 17,000 and 25,000.
About west and beyond the suburb Heraclea lay the paradise of Daphne, a park of woods and waters, in the midst of which rose a great temple to the Pythian Apollo, also founded by Seleucus I and enriched with a cult-statue of the god, as Musagetes, by Bryaxis
Bryaxis ( grc, Βρύαξις or Βρύασσις; fl. 350 BC) was a Greek sculptor. He created the sculptures on the north side of the mausoleum of Maussollos at Halicarnassus which was commissioned by the queen Artemisia II of Caria in memory o ...
. A companion sanctuary of Hecate was constructed underground by Diocletian
Diocletian (; la, Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus, grc, Διοκλητιανός, Diokletianós; c. 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed ''Iovius'', was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Gaius Valerius Diocles ...
. The beauty and the lax morals of Daphne were celebrated all over the ancient world; and indeed Antioch as a whole shared in both these titles to fame.
Antioch became the capital and court-city of the western Seleucid Empire under Antiochus I, its counterpart in the east being Seleucia
Seleucia (; grc-gre, Σελεύκεια), also known as or , was a major Mesopotamian city of the Seleucid empire. It stood on the west bank of the Tigris River, within the present-day Baghdad Governorate in Iraq.
Name
Seleucia ( grc-gre, Σ ...
; but its paramount importance dates from the battle of Ancyra (240 BC), which shifted the Seleucid centre of gravity from Anatolia, and led indirectly to the rise of Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greece, ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a ...
.
The Seleucids reigned from Antioch. We know little of it in the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 3 ...
, apart from Syria, all our information coming from authors of the late Roman time. Among its great Greek buildings we hear only of the theatre, of which substructures still remain on the flank of Silpius, and of the royal palace, probably situated on the island. It enjoyed a reputation for being "a populous city, full of most erudite men and rich in the most liberal studies", but the only names of distinction in these pursuits during the Seleucid period that have come down to us are Apollophanes, the Stoic, and one Phoebus, a writer on dreams. The nicknames which they gave to their later kings were Aramaic; and, except Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
and Daphne
Daphne (; ; el, Δάφνη, , ), a minor figure in Greek mythology, is a naiad, a variety of female nymph associated with fountains, wells, springs, streams, brooks and other bodies of freshwater.
There are several versions of the myth in whi ...
, the great divinities of north Syria seem to have remained essentially native, such as the "Persian Artemis" of Meroe and Atargatis
Atargatis (; grc, Ἀτάργατις, translit=Atárgatis or arc, , translit=ʿtrʿth; syc, ܬܪܥܬܐ, translit=Tarʿaṯā) was the chief goddess of northern Syria in Classical antiquity. Ctesias also used the name Derketo ( grc-koi, Δε� ...
of Hierapolis Bambyce
Manbij ( ar, مَنْبِج, Manbiǧ, ku, مەنبج, Minbic, tr, Münbiç, Menbic, or Menbiç) is a city in the northeast of Aleppo Governorate in northern Syria, 30 kilometers (19 mi) west of the Euphrates. In the 2004 census by the Cent ...
.
The epithet "Golden" suggests that the external appearance of Antioch was impressive, but the city needed constant restoration owing to the seismic disturbances to which the district has always been subjected. The first great earthquake in recorded history was related by the native chronicler John Malalas
John Malalas ( el, , ''Iōánnēs Malálas''; – 578) was a Byzantine chronicler from Antioch (now Antakya, Turkey).
Life
Malalas was of Syrian descent, and he was a native speaker of Syriac who learned how to write in Greek later in ...
. It occurred in 148 BC and did immense damage.
Local politics were turbulent. In the many dissensions of the Seleucid house the population took sides, and frequently rose in rebellion, for example against Alexander Balas
Alexander I Theopator Euergetes, surnamed Balas ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος Βάλας, Alexandros Balas), was the ruler of the Seleucid Empire from 150/Summer 152 – August 145 BC. Picked from obscurity and supported by the neighboring Roman- ...
in 147 BC, and Demetrius II Nicator
Demetrius II ( grc, Δημήτριος Β`, ''Dēmḗtrios B''; died 125 BC), called Nicator ( grc, Νικάτωρ, ''Nikátōr'', "Victor"), was one of the sons of Demetrius I Soter. His mother may have been Laodice V, as was the case with his ...
in 129 BC. The latter, enlisting a body of Jews, punished his capital with fire and sword. In the last struggles of the Seleucid house, Antioch turned against its feeble rulers, invited Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
to occupy the city in 83 BC, tried to unseat Antiochus XIII Asiaticus
Antiochus XIII Philadelphus, (Greek: Ἀντίοχος ΙΓ' Φιλάδελφος) known as Asiaticus, (Ἀσιατικός) was the penultimate ruler of the Seleucid kingdom.
Biography
He was son of king Antiochus X Eusebes and the Ptolemaic ...
in 65 BC, and petitioned Rome against his restoration in the following year. Antioch's wish prevailed, and it passed with Syria to the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kin ...
in 64 BC, but remained a ''civitas libera''.
Roman period


 The Roman emperors favored the city from the first moments, seeing it as a more suitable capital for the eastern part of the empire than Alexandria could be, because of the isolated position of Egypt. To a certain extent they tried to make it an eastern Rome.
The Roman emperors favored the city from the first moments, seeing it as a more suitable capital for the eastern part of the empire than Alexandria could be, because of the isolated position of Egypt. To a certain extent they tried to make it an eastern Rome. Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
visited it in 47 BC, and confirmed its freedom. A great temple to Jupiter Capitolinus rose on Silpius, probably at the insistence of Octavian
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
, whose cause the city had espoused. A forum
Forum or The Forum (plural forums or fora) may refer to:
Common uses
* Forum (legal), designated space for public expression in the United States
*Forum (Roman), open public space within a Roman city
**Roman Forum, most famous example
*Internet ...
of Roman type was laid out. Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
built two long colonnades on the south towards Silpius.
Strabo, writing in the reign of Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
and the first years of Tiberius, states that Antioch is not much smaller than Seleucia and Alexandria; Alexandria had been said by Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
in the mid-1st Century BC to have 300,000 free inhabitants, which would mean that Antioch was about this size in Strabo's time.
Agrippa Agrippa may refer to:
People Antiquity
* Agrippa (mythology), semi-mythological king of Alba Longa
* Agrippa (astronomer), Greek astronomer from the late 1st century
* Agrippa the Skeptic, Skeptic philosopher at the end of the 1st century
* Agri ...
and Tiberius enlarged the theatre, and Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
finished their work. Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius (Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 – 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty.
Born into a senatoria ...
paved the great east to west artery with granite. A circus, other colonnades and great numbers of baths were built, and new aqueducts
Aqueduct may refer to:
Structures
*Aqueduct (bridge), a bridge to convey water over an obstacle, such as a ravine or valley
*Navigable aqueduct, or water bridge, a structure to carry navigable waterway canals over other rivers, valleys, railw ...
to supply them bore the names of Caesars, the finest being the work of Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania B ...
. The Roman client, King Herod (most likely the great builder Herod the Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a Roman Jewish client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renov ...
), erected a long ''stoa
A stoa (; plural, stoas,"stoa", ''Oxford English Dictionary'', 2nd Ed., 1989 stoai, or stoae ), in ancient Greek architecture, is a covered walkway or portico, commonly for public use. Early stoas were open at the entrance with columns, usually ...
'' on the east, and Agrippa (–12 BC) encouraged the growth of a new suburb south of this.
One of the most famous urban additions to Antioch, done by the Romans probably under Augustus when the city had more than half a million inhabitants, was the Circus of Antioch: it was a Roman hippodrome
The hippodrome ( el, ἱππόδρομος) was an ancient Greek stadium for horse racing and chariot racing. The name is derived from the Greek words ''hippos'' (ἵππος; "horse") and ''dromos'' (δρόμος; "course"). The term is used i ...
. Used for chariot racing
Chariot racing ( grc-gre, ἁρματοδρομία, harmatodromia, la, ludi circenses) was one of the most popular ancient Greek, Roman, and Byzantine sports. In Greece, chariot racing played an essential role in aristocratic funeral games from ...
, it was modelled on the Circus Maximus
The Circus Maximus (Latin for "largest circus"; Italian: ''Circo Massimo'') is an ancient Roman chariot-racing stadium and mass entertainment venue in Rome, Italy. In the valley between the Aventine and Palatine hills, it was the first and lar ...
in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and other circus buildings throughout the empire. Measuring more than in length and of width, the Circus could house up to 80,000 spectators.
Zarmanochegas
Zarmanochegas ( el, Ζαρμανοχηγάς; according to Strabo) or Zarmarus (according to Dio Cassius) was a gymnosophist (naked philosopher), a monk of the Sramana tradition (possibly, but not necessarily a Buddhist) who, according to ancient ...
(Zarmarus) a monk of the Sramana tradition of India, according to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
and Dio Cassius, met Nicholas of Damascus in Antioch around 13 AD as part of a Mission to Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
. At Antioch Germanicus died in 19 AD, and his body was burnt in the forum.
An earthquake that shook Antioch in AD 37 caused the emperor Caligula to send two senators to report on the condition of the city. Another quake followed in the next reign.
Titus set up the Cherubim, captured from the Second Temple, Jewish temple, over one of the gates.
In 115 AD, during Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
's travel there during his war against Parthia, the whole site was 115 Antioch earthquake, convulsed by a huge earthquake. The landscape altered, and the emperor himself was forced to take shelter in the circus for several days. He and his successor restored the city, but the population was reduced to less than 400,000 inhabitants and many sections of the city were abandoned.
Commodus (r. 177–192 AD) had Olympic games celebrated at Antioch.
 In 256 AD, the town was suddenly raided by the Sasanian Empire, Persians under Shapur I, and many of the people were slain in the theatre. It was recaptured by the Roman emperor Valerian (emperor), Valerian the following year.
In 256 AD, the town was suddenly raided by the Sasanian Empire, Persians under Shapur I, and many of the people were slain in the theatre. It was recaptured by the Roman emperor Valerian (emperor), Valerian the following year.
Age of Julian and Valens
When Julian the Apostate, the emperor Julian visited in 362 on a detour to Persia, he had high hopes for Antioch, regarding it as a rival to the imperial capital of Constantinople. Antioch had a mixed pagan and Christian population, which Ammianus Marcellinus implies lived quite harmoniously together. However Julian's visit began ominously as it coincided with a lament for Adonis, the doomed lover of Aphrodite. Thus, Ammianus wrote, the emperor and his soldiers entered the city not to the sound of cheers but to wailing and screaming. After being advised that the bones of 3rd-century martyred bishop Babylas of Antioch, Babylas were suppressing the oracle of Apollo at Daphne, he made a public-relations mistake in ordering the removal of the bones from the vicinity of the temple. The result was a massive Christian procession. Shortly after that, when the temple was destroyed by fire, Julian suspected the Christians and ordered stricter investigations than usual. He also shut up the chief Christian church of the city, before the investigations proved that the fire was the result of an accident. Julian found much else about which to criticize the Antiochene; Julian had wanted the empire's cities to be more self-managing, as they had been some Antonines, 200 years before. However Antioch's Decurion (administrative), city councilmen showed themselves unwilling to shore up Antioch's food shortage with their own resources, so dependent were they on the emperor. Ammianus wrote that the councilmen shirked their duties by bribing unwitting men in the marketplace to do the job for them. The city's impiety to the old religion was clear to Julian when he attended the city's annual feast of Apollo. To his surprise and dismay the only Antiochene present was an old priest clutching a goose. The Antiochenes in turn hated Julian for worsening the food shortage with the burden of his billeted troops, wrote Ammianus. The soldiers were often to be found gorged on sacrificial meat, making a drunken nuisance of themselves on the streets while Antioch's hungry citizens looked on in disgust. The Christian Antiochenes and Julian's pagan Gauls, Gallic soldiers also never quite saw eye to eye. Julian's piety was distasteful to the Antiochenes, even to those who kept the old religion. Julian's brand of paganism was very much unique to himself, with little support outside the most educated Neo Platonism, Neoplatonist circles. The irony of Julian's enthusiasm for large scale animal sacrifice could not have escaped the hungry Antiochenes. Julian gained no admiration for his personal involvement in the sacrifices, only the nickname ''axeman'', wrote Ammianus. The emperor's high-handed, severe methods and his rigid administration prompted Antiochene parody, lampoons about, among other things, Julian's unfashionably goatee, pointed beard. Julian's successor, Valens, who endowed Antioch with a new forum, including a statue of Valentinian on a central column, reopened the great church of Constantine, which stood until the Persian sack in 538, by Khosrau I, Chosroes.Christianity
Early centers of Christianity#Antioch, Antioch was a chief center of early Christianity during Roman times. The city had a large population of Jewish origin in a quarter called the Kerateion, and so attracted the earliest missionaries. Evangelized, among others, by Saint Peter, Peter himself, according to the tradition upon which the Patriarch of Antioch still rests its claim for primacy, and certainly later by Barnabas and Paul of Tarsus, Paul. Its converts were the first to be called ''Christians.'' This is not to be confused with Antioch, Pisidia, Antioch in Pisidia, to which Barnabas and Paul of Tarsus, Paul later travelled. Surrounding the city were a number of Greek, Syrian, Armenian, and Latin monasteries. Between 252 and 300 AD, ten assemblies of the church were held at Antioch and it became the seat of one of the five original patriarchates, along with Constantinople, Jerusalem,Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria ...
, and Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
(see Pentarchy).
 John Chrysostom writes that when Ignatius of Antioch was bishop in the city, the ''dêmos,'' probably meaning the number of free adult men and women without counting children and slaves, numbered 200,000. In a letter written in 363, Libanius says the city contains 150,000 ''anthrôpoi,'' a word which would ordinarily mean all human beings of any age, sex, or social status, seemingly indicating a decline in the population since the 1st Century. Chrysostom also says in one of his homilies on the Gospel of Matthew, which were delivered between 386 and 393, that in his own time there were 100,000 Christians in Antioch, a figure which may refer to orthodox Christians who belonged to the Great Church as opposed to members of other groups such as Arians and Apollinarians, or to all Christians of any persuasion.
The Maronite Catholic Church's patriarch is called the Patriarch of Antioch and all the East. He currently resides in Bkerke - Lebanon. The Maronites continue the Antiochene liturgical tradition and the use of the Syrian-Aramaic (Syro-Aramaic or Western Aramaic) language in their liturgies.
One of the canonical Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox churches is still called the Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch, although it moved its headquarters from Antioch to Damascus, Syria, several centuries ago (see list of Patriarchs of Antioch), and its prime bishop retains the title "Patriarch of Antioch", somewhat analogous to the manner in which several Popes, heads of the Roman Catholic Church remained "Bishop of Rome" even while residing in Avignon, in present-day France, in the 14th century.
Syriac Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch and All the East, is an Oriental Orthodox Christian denomination, Church with Autocephaly, autocephalous List of Syriac Orthodox Patriarchs of Antioch, patriarchate founded by Saint Peter and Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul in the Christianity in the 1st century, 1st century, according to its tradition. The Syriac Orthodox Church is part of Oriental Orthodoxy, a distinct Communion (Christian), communion of churches claiming to continue the patristic and Apostolic Christology before the schism following the Council of Chalcedon in 451.
John Chrysostom writes that when Ignatius of Antioch was bishop in the city, the ''dêmos,'' probably meaning the number of free adult men and women without counting children and slaves, numbered 200,000. In a letter written in 363, Libanius says the city contains 150,000 ''anthrôpoi,'' a word which would ordinarily mean all human beings of any age, sex, or social status, seemingly indicating a decline in the population since the 1st Century. Chrysostom also says in one of his homilies on the Gospel of Matthew, which were delivered between 386 and 393, that in his own time there were 100,000 Christians in Antioch, a figure which may refer to orthodox Christians who belonged to the Great Church as opposed to members of other groups such as Arians and Apollinarians, or to all Christians of any persuasion.
The Maronite Catholic Church's patriarch is called the Patriarch of Antioch and all the East. He currently resides in Bkerke - Lebanon. The Maronites continue the Antiochene liturgical tradition and the use of the Syrian-Aramaic (Syro-Aramaic or Western Aramaic) language in their liturgies.
One of the canonical Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox churches is still called the Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch, although it moved its headquarters from Antioch to Damascus, Syria, several centuries ago (see list of Patriarchs of Antioch), and its prime bishop retains the title "Patriarch of Antioch", somewhat analogous to the manner in which several Popes, heads of the Roman Catholic Church remained "Bishop of Rome" even while residing in Avignon, in present-day France, in the 14th century.
Syriac Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch and All the East, is an Oriental Orthodox Christian denomination, Church with Autocephaly, autocephalous List of Syriac Orthodox Patriarchs of Antioch, patriarchate founded by Saint Peter and Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul in the Christianity in the 1st century, 1st century, according to its tradition. The Syriac Orthodox Church is part of Oriental Orthodoxy, a distinct Communion (Christian), communion of churches claiming to continue the patristic and Apostolic Christology before the schism following the Council of Chalcedon in 451.
Theodosius and after
In 387 AD, there was a great sedition caused by a new tax levied by order of Theodosius I, and the city was punished by the loss of its metropolitan status. He divided the Roman Empire, and since then Antioch was under Constantinople's rule. Antioch and its port,
Antioch and its port, Seleucia Pieria
Seleucia in Pieria (Greek Σελεύκεια ἐν Πιερίᾳ), also known in English as Seleucia by the Sea, and later named Suedia, was a Hellenistic town, the seaport of Antioch ad Orontes (Syria Prima), the Seleucid capital, modern Antaky ...
, were severely damaged by the 526 Antioch earthquake, great earthquake of 526. Seleucia Pieria, which was already fighting a losing battle against continual silting, never recovered. Justinian I renamed Antioch Theopolis ("City of God") and restored many of its public buildings, but the destructive work was completed by the Persian king, Khosrau I, twelve years later, who deported the population to a newly built city in Persian Mesopotamia, Weh Antiok Khosrow. Antioch lost as many as 300,000 people. Justinian I made an effort to revive it, and Procopius describes his repairing of the walls; but its glory was past.
During the Byzantine–Sassanid War of 602–628 the Emperor Heraclius confronted the invading Persian army of Khosrow II outside Antioch in 613. The Byzantines were defeated by forces under the generals Shahrbaraz and Shahin Vahmanzadegan at the Battle of Antioch (613), Battle of Antioch, after which the city fell to the Sassanians, together with much of Syria and eastern Anatolia.
Antioch gave its name to a School of Antioch, certain school of Christian thought, distinguished by literal interpretation of the Scriptures and insistence on the human limitations of Jesus. Diodorus of Tarsus and Theodore of Mopsuestia were the leaders of this school. The principal local saint was Simeon Stylites, who lived an extremely ascetic life atop a pillar for 40 years some east of Antioch. His body was brought to the city and buried in a building erected under the emperor Leo II (emperor), Leo. During the Byzantine era great Bath House, bathhouses were built in Byzantine Empire, Byzantine centers such as Constantinople and Antioch.
Arab conquest and Byzantine reconquest

 In 637, during the reign of the Byzantine emperor Heraclius, Antioch was conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate during the Battle of the Iron Bridge. The city became known in Arabic as . Since the Umayyad, Umayyad dynasty was unable to penetrate the Anatolian plateau, Antioch found itself on the frontline of the conflicts between two hostile empires during the next 350 years, so that the city went into a precipitous decline.
In 969, Siege of Antioch (968-969), the city was recovered for the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Emperor Nikephoros II Phokas by Michael Bourtzes and the ''stratopedarches'' Peter (stratopedarches), Peter. It soon became the seat of a ''Dux#Later developments, doux'', the civil governor of the homonymous Theme (Byzantine district), theme, but also the seat of the somewhat more important ''Domestic of the Schools of the Orient'', the supreme military commander of the imperial forces on the eastern frontier. Sometimes both offices were held by the same person, usually military officers such as Nikephoros Ouranos, or Philaretos Brachamios, who managed to retain the integrity of the eastern borderline after the Seljuk conquest of Anatolia. As the empire disintegrated rapidly before the Komnenian restoration, ''Dux of Antioch'' & ''Domestic of the Schools of the East'' Philaretos Brachamios held the city until Suleiman ibn Qutalmish, the Sultanate of Rum, emir of Rum, captured it from him in 1084. Two years later, Suleiman was killed fighting against Tutush I, Tutush, the brother of the Malik-Shah I, Seljuk Sultan, who annexed the city into the Seljuk empire. Yagisiyan was appointed governor and became increasingly independent within the tumtuluous years following Malik-Shah's death in 1092.
In 637, during the reign of the Byzantine emperor Heraclius, Antioch was conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate during the Battle of the Iron Bridge. The city became known in Arabic as . Since the Umayyad, Umayyad dynasty was unable to penetrate the Anatolian plateau, Antioch found itself on the frontline of the conflicts between two hostile empires during the next 350 years, so that the city went into a precipitous decline.
In 969, Siege of Antioch (968-969), the city was recovered for the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Emperor Nikephoros II Phokas by Michael Bourtzes and the ''stratopedarches'' Peter (stratopedarches), Peter. It soon became the seat of a ''Dux#Later developments, doux'', the civil governor of the homonymous Theme (Byzantine district), theme, but also the seat of the somewhat more important ''Domestic of the Schools of the Orient'', the supreme military commander of the imperial forces on the eastern frontier. Sometimes both offices were held by the same person, usually military officers such as Nikephoros Ouranos, or Philaretos Brachamios, who managed to retain the integrity of the eastern borderline after the Seljuk conquest of Anatolia. As the empire disintegrated rapidly before the Komnenian restoration, ''Dux of Antioch'' & ''Domestic of the Schools of the East'' Philaretos Brachamios held the city until Suleiman ibn Qutalmish, the Sultanate of Rum, emir of Rum, captured it from him in 1084. Two years later, Suleiman was killed fighting against Tutush I, Tutush, the brother of the Malik-Shah I, Seljuk Sultan, who annexed the city into the Seljuk empire. Yagisiyan was appointed governor and became increasingly independent within the tumtuluous years following Malik-Shah's death in 1092.
Crusader era
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. Six months after the Treaty of Devol Bohemond died, and Tancred remained regent of Antioch until his death during a typhoid epidemic in 1112.
After the death of Tancred, the principality passed to Roger of Salerno, who helped rebuild Antioch after an earthquake destroyed its foundations in 1114. With the defeat of Roger's crusading army and his death at the Battle of Ager Sanguinis in 1119 the role of regent was assumed by Baldwin II of Jerusalem, lasting until 1126, with the exception from 1123 to 1124 when he was briefly captured by the Artuqids and held captive alongside Joscelin I of Edessa, Joscelin of Courtenay. In 1126 Bohemond II of Antioch, Bohemond II arrived from Apulia in order to gain regency over Antioch. In February 1130 Bohemond was lured into an ambush by Leo I, Prince of Armenia who allied with the Danishmend Gazi Gümüshtigin, and was killed in the subsequent battle, his head was then embalmed, placed in a silver box, and sent as a gift to the Abbasid caliph in Baghdad.
Antioch was again ruled by a regency, firstly being Baldwin II, after his daughter and Bohemond II's wife, Alice of Antioch attempted to block Baldwin from entering Antioch, but failed when Antiochene nobles such as Fulk of Jerusalem (Alice's brother-in-law) opened up the gates for representatives of Baldwin II. Alice was then expelled from Antioch. With the death of Balwin in 1131, Alice briefly took control of Antioch and allied herself with Pons of Tripoli and Joscelin II of Edessa in an attempt to prevent Fulk, King of Jerusalem from marching north in 1132, however this attempt failed and Fulk and Pons fought a brief battle before peace was made and Alice was exiled again. In 1133 the king chose Raymond of Poitiers as a groom for Constance of Antioch, daughter of Bohemund II of Antioch and Alice of Antioch, Alice, kingdom of Jerusalem, princess of Jerusalem. The marriage took place in 1136 between the 21-year-old Raymond and the 9-year-old Constance.
Immediately after assuming control, Raymond was involved in conflicts with the Byzantine Emperor John II Comnenus who had come south to recover Cilicia from Leo I, Prince of Armenia, Leo of Armenia, and to reassert his rights over Antioch. The engagement lasted until 1137 when emperor John II arrived with an army before the walls of Antioch. Although the basileus did not enter the city, his banner was raised atop the citadel and Raymond was compelled to do homage. Raymond agreed with the emperor that if he was capable of capturing Aleppo, Shaizar, and Homs, he would exchange Antioch for them.''Annales Herbipolenses'', s.a. 1147: A Hostile View of the Crusade
John went on to attack Aleppo with the aid of Antioch and Edessa, and failed to capture it, with the Franks withdrawing their support when he moved on to capture Shaizar. John returned to Antioch ahead of his army and entered Antioch, only to be forced to leave when Joscelin II, Count of Edessa rallied the citizens to oust him. In 1142 John then returned but Raymond refused to submit and John was forced to return to Cilicia again due to the coming winter, to plan an attack the following season. However the emperor died on April 8, 1143.
Second Crusade
The following year after the death of John II Comnenus, Imad ad-Din Zengi lay Siege of Edessa (1144), siege to Edessa, the crusader capital, and with the death of Imad ad-Din Zengi in 1146, he was succeeded by his son, Nur ad-Din Zangi. Zangi attacked Antioch in both 1147 and 1148 and succeeded during the second venture in occupying most of the territory east of the Orontes river, Orontes including Artah, Kafr Latah, Kafar Latha, Basarfut, and Balat, but failing to capture Antioch itself. With the Second Crusades army previously nearly entirely defeated by the Turks and by sickness, Louis VII of France arrived in Antioch on March 19, 1148, after being delayed by storms. Louis was welcomed by the uncle of his spouse Eleanor of Aquitaine, Raymond of Poitiers. Louis refused to help Antioch defend against the Turks and to lead an expedition against Aleppo, and instead decided to finish his pilgrimage to Jerusalem rather than focus on the military aspect of the Crusades. With Louis quickly leaving Antioch again and the Crusades returning home in 1149, Nur ad-Din launched an offensive against the territories which were dominated by the Castle of Harim, situated on the eastern bank of the Orontes, after which Nur besieged the castle of Inab. Raymond of Poitiers quickly came to the aid of the citadel, where he was defeated and killed at the Battle of Inab, Raymond's head was then cut off and sent to Nur, who sent it to the caliph in Baghdad. However, Nur ad-Din did not attack Antioch itself and was content with capturing all of Antiochene territory that lay east of the Orontes.After the Second Crusade
With Raymond dead and Bohemond III only five years of age, the principality came under the control of Raymond's widow Constance of Antioch, however real control lay with Aimery of Limoges. In 1152 Baldwin III of Jerusalem came of age, but from 1150 he had proposed three different but respectable suitors for Constance's hand in marriage, all of whom she rejected. In 1153 however, she chose Raynald of Châtillon and married him in secret without consulting her first cousin and liege lord, Baldwin III, and neither Baldwin nor Aimery of Limoges approved of her choice. In 1156 Raynald claimed that the Byzantine emperor Manuel I Comnenus had reneged on his promises to pay Raynald a sum of money, and vowed to attack the island of Cyprus in revenge. However Aimery refused to finance Raynald's expedition, so in turn Raynald had the Patriarch seized, beaten, stripped naked, covered in honey, and had him left in the burning sun on top of the citadel to be attacked by insects. When the Patriarch was released, he collapsed in exhaustion and agreed to finance Raynald's expedition. In the meantime, Raynald had allied himself with the Armenian prince, Thoros II, Prince of Armenia, Thoros II. In 1156 Raynald's forces attacked Cyprus, ravaging the island over a three-week period, with Wiktionary:rapine, rapine, killing, and plundering its citizens. After which, Manuel I Comnenus raised an army and began their march towards Syria, as a result Raynald threw himself to the mercy of the emperor who insisted on the installation of a Greek Patriarch and the surrender of the citadel in Antioch. The following spring, Manuel made a triumphant entry into the city and established himself as the unquestioned suzerain of Antioch. In 1160 Raynald was captured by Muslims during a plundering raid against the Syrian and Armenian peasants of the neighborhood of Marash. He was held captive for sixteen years, and as the stepfather of the Empress Maria, he was ransomed by Manuel for 120,000 gold dinars in 1176 (about 500 kg of gold, worth approximately £16 million or US$26 million ). With Raynald disposed of for a long time, the patriarch Aimery became the new regent, chosen by Baldwin III. To further consolidate his own claim over Antioch, Manuel chose Maria of Antioch as his bride, daughter of Constance of Antioch and Raymond of Poitiers. But the government of Antioch remained in crisis up until 1163, when Constance asked the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia to help maintain her rule, as a result the citizens of Antioch exiled her and installed her son Bohemond III and now brother-in-law to the emperor, as regent. One year later, Nur ad-Din Zangi captured Bohemond III when he defeated a joint Antiochene-Tripolitan army. Bohemond III was soon released, however Harem, Syria which Raynald had recaptured in 1158, was lost again and the frontier of Antioch was permanently placed west of the Orontes. Byzantine influence remained in Antioch and in 1165, Bohemond III married a niece of the emperor, Maria of Antioch, and installed a Greek patriarch in the city, Athanasius II, Patriarch of Antioch, who remained in his position until he died in an earthquake five years later.Third Crusade
On October 29, 1187, Pope Gregory VIII issued the papal bull ''Audita tremendi'', his call for the Third Crusade. Frederick I Barbarossa, Richard I of England, and Philip II of France answered the summons. With Richard and Philip deciding to take a sea route, Frederick lacked the necessary ships and took a land route where he pushed on through Anatolia, defeating the Turks in the Battle of Iconium (1190), Battle of Iconium, however upon reaching Christian territory in Lesser Armenia (Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia) the emperor drowned in the river Saleph. The emperor was buried at Antioch and the Germans became an insignificant contingent during the crusade. Throughout the Third Crusade Antioch remained neutral, however with the end of the Third Crusade (1192), they were included in the Treaty of Ramla between Richard and Saladin.Battles for sovereignty
With no heir after the death of Raymond III, Count of Tripoli in the Battle of Hattin he left his godson, Raymond IV, Count of Tripoli, the eldest son of Bohemond III. However Bohemond installed his younger, the future prince Bohemond IV of Antioch, as count of Tripoli. Shortly after the end of the Third Crusade, Raymond IV, Count of Tripoli married Alice of Armenia, the niece of Leo II, or Leo I, King of Armenia, and a vassal to Antioch. Alice bore Raymond IV a son in 1199, Raymond-Roupen, after which Raymond IV died in the coming months. In 1194 Leo II tricked Bohemond III making him believe that the new born prince had been captured by the Roupenians. Leo made a failed attempt at capturing Antioch believing the city would be weakened with the absence of Bohemond. Henry II, Count of Champagne nephew to both Richard I and Philip II, travelled to Lesser Armenia and managed to persuade Leo that in exchange for Antioch, renouncing its overlordship to Lesser Armenia and to release Bohemond, who in 1201 died. With the death of Bohemond III there followed a 15-year struggle for power of Antioch, between Tripoli and Lesser Armenia. According to the rules of primogeniture Leo's great nephew Raymond-Roupen was the rightful heir of Antioch, and Leo's position was supported by the pope. However, on the other hand, the city commune of Antioch supported Bohemond IV of Antioch, on the grounds that he was the closest blood relative to the last ruling prince, Bohemond III. In 1207 Bohemond IV installed a Greek patriarch in Antioch, despite the East-West Schism, under the help of Aleppo, Bohemond IV drove Leo out of Antioch.Fifth Crusade and afterwards
In 1213 Pope Innocent III's papal bull ''Quia maior'' called for all of Christendom to lead a new (Fifth) crusade. This strengthened the support of sultan al-Adil I, an Ayyubid-Egyptian general who supported Raymond-Roupen's claims in Antioch. In 1216 Leo installed Raymond-Roupen as prince of Antioch, and ending all military aspect of the struggle between Tripoli and Lesser Armenia, but the citizens again revolted against Raymond-Roupen in and Bohemond of Tripoli was recognised as the fourth prince of that name. Bohemond IV and his son Bohemond V remained neutral in the struggles of the Ghibellines, Guelphs and Ghibellines to the south which arose when Frederich II married Isabella II, and in 1233 Bohemond IV died. From 1233 onwards Antioch declined and appeared rarely in records for 30 years, and in 1254 the altercations of the past between Antioch and Armenia were laid to rest when Bohemond VI of Antioch married the then 17‑year‑old Sibylla of Armenia, and Bohemond VI became a vassal of the Armenian kingdom. Effectively, the Armenian kings ruled Antioch while the prince of Antioch resided in Tripoli. The Armenians drew up a treaty with the Mongols, who were now ravaging Muslim lands, and under protection they extended their territory into the lands of the Seljuq dynasty in the north and the Aleppo territory to the south. Antioch was part of this Armeno-Mongol alliance. Bohemond VI managed to retake Lattakieh and reestablished the land bridge between Antioch and Tripoli, while the Mongols insisted he install the Greek patriarch there rather than a Latin one, due to the Mongols attempting to strengthen ties with theByzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. This earned Bohemond the enmity of the Latins of Acre, and Bohemond was excommunicated by the Patriarch of Jerusalem, Pope Urban IV, which was later suspended.
Fall of Antioch
In 1259 the Mongol Empire, Mongols captured the Syrian city of Damascus, and eventually in 1260, Aleppo. The Mamluk sultan Saif ad-Din Qutuz looked to ally with the Franks, who declined. In September 1260, the Mamluks defeated the Mongols at the Battle of Ain Jalut, shortly after Qutuz was assassinated at El Salheya, Al-Salihiyya, and according to various sources his successor Baibars was involved in his murder. (Baibars "came to power with [the] regicide [of Qutuz] on his conscience" according to Tschanz.) Despite this, Baibars was named sultan, and in 1263 sacked Nazareth, threatened Antioch with invasion, and appeared before the walls of Acre. In January 1265 Baibars launched an offensive against the Latins, starting with Acre, the capital of the remnant of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, but was unable to take it, but defeated the Crusaders in many other battles in Arsuf, Athlith, Haifa, etc. And in 1268 Baibars besieged Antioch, capturing the city on May 18. Baibars promised to spare the lives of the inhabitants, but broke his promise and razed the city, killing or enslaving nearly the entire population upon their surrender. Antioch's ruler, Bohemond VI of Antioch, Prince Bohemond VI was then left with no territories except the County of Tripoli. Without any southern fortifications and with Antioch isolated it could not withstand the onslaught of resurgent Muslim forces, and with the fall of the city, the remainder of northern Syria eventually capitulated, ending the Latin presence in Syria. The Mamluk armies killed or enslaved every Christian in Antioch. In 1355 it still had a considerable population, but by 1432 there were only about 300 inhabited houses within its walls, mostly occupied by Oghuz Turks#Turcoman and Turkmen, Turcomans.Ottoman Period
Antioch was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire with the conquest of Syria in 1516. It formed a sub-province (''sancak'') or tax collectorship (''muhassıllık'') of the province of Aleppo (Aleppo Eyalet). Beginning in the mid-18th century, the district witnessed an influx of Alawite settlers coming from the Latakia area. The famous Barker family of British consuls had a summer home in Suwaydiyya (today's Samandağ), at the mouth of theOrontes River
The Orontes (; from Ancient Greek , ) or Asi ( ar, العاصي, , ; tr, Asi) is a river with a length of in Western Asia that begins in Lebanon, flowing northwards through Syria before entering the Mediterranean Sea near Samandağ in Turkey.
...
, in the 19th century. Between 1831 and 1840, Antioch was the military headquarters of Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt during the Egyptian occupation of Syria, and served as a model site for the modernizing reforms he wished to institute.
Archaeology
 Few traces of the once great Roman city are visible today aside from the massive fortification walls that snake up the mountains to the east of the modern city, several aqueducts, and the Church of St Peter (St Peter's Cave Church, Cave-Church of St. Peter), said to be a meeting place of an Early Christian community. The majority of the Roman city lies buried beneath deep sediments from the Orontes River, or has been obscured by recent construction.
Between 1932 and 1939, archaeological excavations of Antioch were undertaken under the direction of the "Committee for the Excavation of Antioch and Its Vicinity", which was made up of representatives from the Louvre Museum, the Baltimore Museum of Art, the Worcester Art Museum, Princeton University, Wellesley College, and later (1936) also the Fogg Art Museum at Harvard University and its affiliate Dumbarton Oaks.
The excavation team failed to find the major buildings they hoped to unearth, including Domus Aurea (Antioch), Constantine's Great Octagonal Church or the imperial palace. However, a great accomplishment of the expedition was the discovery of high-quality Roman mosaics from villas and baths in Antioch, Daphne and Seleucia Pieria.
The principal excavations of Mosaics at Antioch led by Princeton University in March 1932 recovered nearly 300 mosaics. Many of these mosaics were originally displayed as floor mosaics in private homes during the 2nd through 6th centuries AD, while others were displayed in baths and other public buildings. The majority of the Antioch mosaics are from the fourth and fifth centuries, Antioch's golden age, though others from earlier times have survived as well
. The mosaics depict a variety of images including animals, plants, and mythological beings, as well as scenes from the daily lives of people living in the area at the time. Each mosaic is bordered by intricate designs and contains bold, vibrant colors.
One mosaic includes a border that depicts a walk from Antioch to Daphne, showing many ancient buildings along the way. The mosaics are now displayed in the Hatay Archaeology Museum in
Few traces of the once great Roman city are visible today aside from the massive fortification walls that snake up the mountains to the east of the modern city, several aqueducts, and the Church of St Peter (St Peter's Cave Church, Cave-Church of St. Peter), said to be a meeting place of an Early Christian community. The majority of the Roman city lies buried beneath deep sediments from the Orontes River, or has been obscured by recent construction.
Between 1932 and 1939, archaeological excavations of Antioch were undertaken under the direction of the "Committee for the Excavation of Antioch and Its Vicinity", which was made up of representatives from the Louvre Museum, the Baltimore Museum of Art, the Worcester Art Museum, Princeton University, Wellesley College, and later (1936) also the Fogg Art Museum at Harvard University and its affiliate Dumbarton Oaks.
The excavation team failed to find the major buildings they hoped to unearth, including Domus Aurea (Antioch), Constantine's Great Octagonal Church or the imperial palace. However, a great accomplishment of the expedition was the discovery of high-quality Roman mosaics from villas and baths in Antioch, Daphne and Seleucia Pieria.
The principal excavations of Mosaics at Antioch led by Princeton University in March 1932 recovered nearly 300 mosaics. Many of these mosaics were originally displayed as floor mosaics in private homes during the 2nd through 6th centuries AD, while others were displayed in baths and other public buildings. The majority of the Antioch mosaics are from the fourth and fifth centuries, Antioch's golden age, though others from earlier times have survived as well
. The mosaics depict a variety of images including animals, plants, and mythological beings, as well as scenes from the daily lives of people living in the area at the time. Each mosaic is bordered by intricate designs and contains bold, vibrant colors.
One mosaic includes a border that depicts a walk from Antioch to Daphne, showing many ancient buildings along the way. The mosaics are now displayed in the Hatay Archaeology Museum in Antakya
Antakya (), historically known as Antioch ( el, Ἀντιόχεια; hy, Անտիոք, Andiok), is the capital of Hatay Province, the southernmost province of Turkey. The city is located in a well-watered and fertile valley on the Orontes Rive ...
. A collection of mosaics on both secular and sacred subjects which were once in churches, private homes, and other public spaces now hang in the Princeton University Art Museum and museums of other sponsoring institutions. The non-Islamic coins from the excavations were published by Dorothy B. Waage.
A statue in the Apostolic Palace, Vatican and a number of figurines and statuettes perpetuate the type of its great patron goddess and civic symbol, the Tyche (Fortune) of Antioch – a majestic seated figure, crowned with the Defensive wall, ramparts of Antioch's walls and holding wheat stalks in her right hand, with the river Orontes as a youth swimming under her feet. According to William Robertson Smith the Tyche of Antioch was originally a young virgin sacrificed at the time of the founding of the city to ensure its continued prosperity and good fortune.
The northern edge of Antakya has been growing rapidly over recent years, and this construction has begun to expose large portions of the ancient city, which are frequently bulldozed and rarely protected by the local museum.
In April 2016, archaeologists discovered a Greek mosaic showing a skeleton lying down with a wine pitcher and loaf of bread alongside a text that reads: "Be cheerful, enjoy your life", it is reportedly from the 3rd century BC. Described as the "reckless skeleton" or "skeleton mosaic", the mosaic is once thought to have belonged in the dining room of an upper-class home.
Notable people
*Abba Judan, philantropist *Arcadius of Antioch, Greek grammarian *Asclepiades of Antioch, Patriarch of Antioch *Saint Barnabas, one of the prominent Disciple (Christianity), Christian disciples in Jerusalem *Saint Domnius, Bishop of Salona and patron saint of Split (city), Split *George of Antioch, the first to hold the office of ammiratus ammiratorum *Ignatius of Antioch, Patriarch of Antioch *John Malalas
John Malalas ( el, , ''Iōánnēs Malálas''; – 578) was a Byzantine chronicler from Antioch (now Antakya, Turkey).
Life
Malalas was of Syrian descent, and he was a native speaker of Syriac who learned how to write in Greek later in ...
, a Greek chronicler
*John Chrysostom, (349–407) Patriarch of Constantinople
*Libanius
Libanius ( grc-gre, Λιβάνιος, Libanios; ) was a teacher of rhetoric of the Sophist school in the Eastern Roman Empire. His prolific writings make him one of the best documented teachers of higher education in the ancient world and a criti ...
, 4th century AD, pagan sophist and confidant of Emperor Julian
*Saint Luke, 1st century AD, Christian evangelist and author of the Gospel of St. Luke and Acts of the Apostles
*Severus of Antioch, was the Patriarch of Antioch, and the head of the Syriac Orthodox Church
*Aulus Licinius Archias, Greek poet
*Tiberius Claudius Pompeianus, Roman politician and general
*Maron, Saint Maron, Patriarch of the Maronite Church
See also
*Antiochene Rite *''Holy Hand Grenade of Antioch'' from Monty Python *List of Greek place names *''The Martyr of Antioch'' *Theophilus of AntiochReferences and sources
Notes
References
Sources
* * *Karl Otfried Müller, Müller, Karl Otfried (1839). ''Antiquitates Antiochenae'' *Freund, Albin (1882). ''Beiträge zur antiochenischen und zur konstantinopolitanischen Stadtchronik'' *R. Forster (1897). in ''Jahrbuch'' of Berlin Arch. Institute, xii. *Wickert, Ulrich (1999). "Antioch." In ''The Encyclopedia of Christianity'', edited by Erwin Fahlbusch and Geoffrey William Bromiley, 81–82. Vol. 1. Grand Rapids: Wm. B. Eerdmans, *External links
The Ancient City of Antioch
Map
Richard Stillwell, ed. ''Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites'', 1976:
"Antioch on the Orontes (Antaky), Turkey"
Includes timeline, maps, and photo galleries of Antioch's mosaics and artifacts
Antakya Museum
Many photos of the collection in Antakya's museum, in particular Roman mosaics
Antiochepedia Blog
News and information about ancient Antioch
(mosaics from Antioch) {{Authority control History of Antioch, 01 Ancient Greek cities in Anatolia Roman towns and cities in Turkey Populated places along the Silk Road Former populated places in Turkey Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Archaeological sites in Hatay Province Coloniae (Roman) Crusade places Geography of Hatay Province Holy cities New Testament cities Roman sites in Turkey Seleucid colonies in Anatolia Populated places established in the 4th century BC 290s BC establishments 1268 disestablishments Populated places disestablished in the 13th century