Antimicrobial Spectrum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The antimicrobial spectrum of an
The antimicrobial spectrum of an
Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee
(HICPAC) recommends the use of narrow-spectrum antibiotics whenever possible.
 The antimicrobial spectrum of an
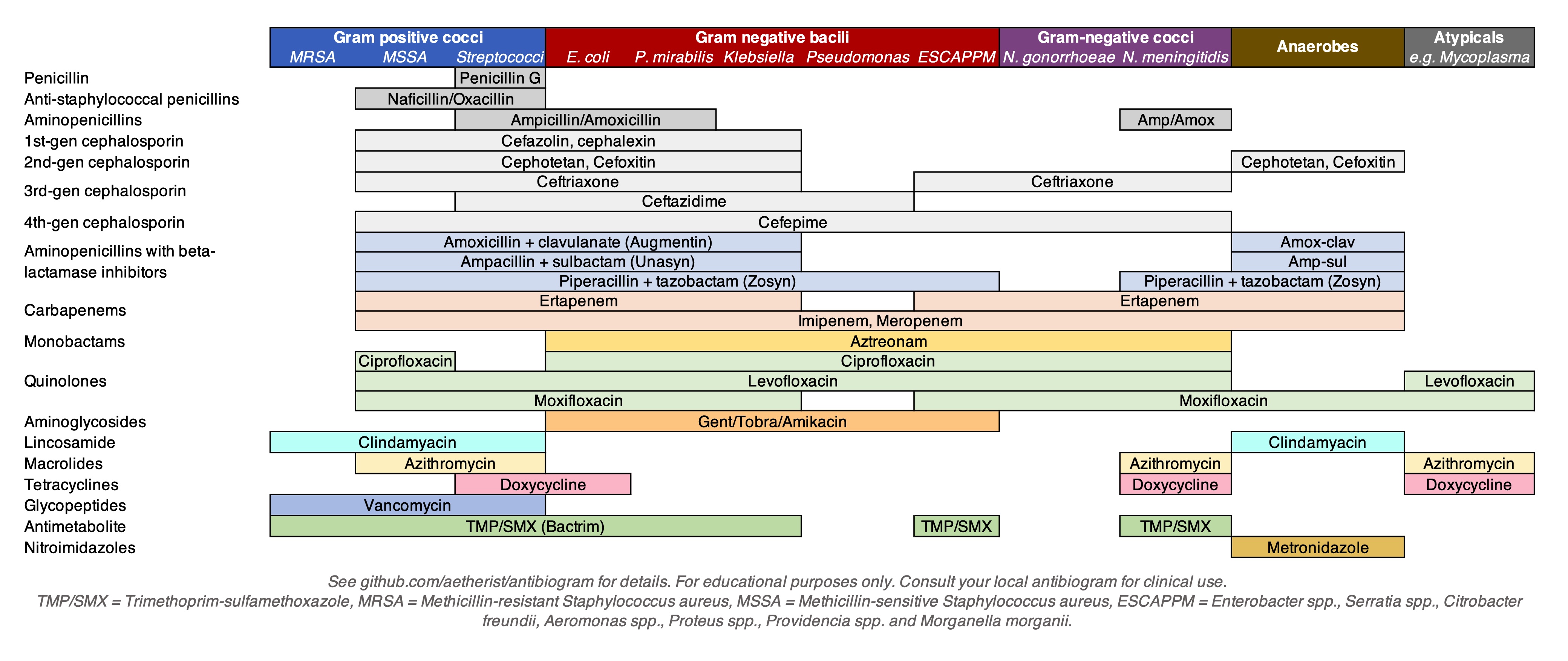
The antimicrobial spectrum of an antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
means the range of microorganisms it can kill or inhibit. Antibiotics can be divided into broad-spectrum antibiotics, extended-spectrum antibiotics and narrow-spectrum antibiotics based on their spectrum of activity. Detailedly, broad-spectrum antibiotics can kill or inhibit a wide range of microorganisms; extended-spectrum antibiotic can kill or inhibit Gram positive bacteria and some Gram negative bacteria; narrow-spectrum antibiotic can only kill or inhibit limited species of bacteria.
Currently no antibiotic's spectrum can completely cover all types of microorganisms.
Determination
The antimicrobial spectrum of an antibiotic can be determined by testing its antimicrobial activity against a wide range of microbes '' in vitro ''. Nonetheless, the range of microorganisms which an antibiotic can kill or inhibit ''in vivo'' may not always be the same as the antimicrobial spectrum based on data collected in vitro.Significance
Narrow-spectrum antibiotics have low propensity to inducebacterial resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. P ...
and are less likely to disrupt the microbiome (normal microflora). On the other hand, indiscriminate use of broad-spectrum antibiotics may not only induce the development of bacterial resistance and promote the emergence of multidrug-resistant
Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are c ...
organisms, but also cause off-target effects due to dysbiosis
Dysbiosis (also called dysbacteriosis) is characterized by a disruption to the microbiome resulting in an imbalance in the microbiota, changes in their functional composition and metabolic activities, or a shift in their local distribution. For ex ...
. They may also have side effects, such as diarrhea or rash. Generally, a broad antibiotic has more clinical indications, and therefore are more widely used. ThHealthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee
(HICPAC) recommends the use of narrow-spectrum antibiotics whenever possible.
Examples
*Broad-spectrum
A broad-spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic that acts on the two major bacterial groups, Gram-positive and Gram-negative, or any antibiotic that acts against a wide range of disease-causing bacteria. These medications are used when a bacterial inf ...
antibiotic: Ciprofloxacin, Doxycycline
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline class antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus, an ...
, Minocycline, Tetracycline, Imipenem, Azithromycine
*Extended-spectrum antibiotic: Ampicillin
* Narrow-spectrum antibiotic: Sarecycline
Sarecycline is a narrow-spectrum tetracycline-derived antibiotic. It is specifically designed for the treatment of acne, and was approved by the FDA in October 2018 for the treatment of inflammatory lesions of non-nodular moderate to severe acn ...
, Vancomycin, Isoniazid
See also
*Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
* Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
References
{{Medicine, state=collapsed Antibiotics Clinical pharmacology