Anti-Soviet Factions In The Soviet–Afghan War on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


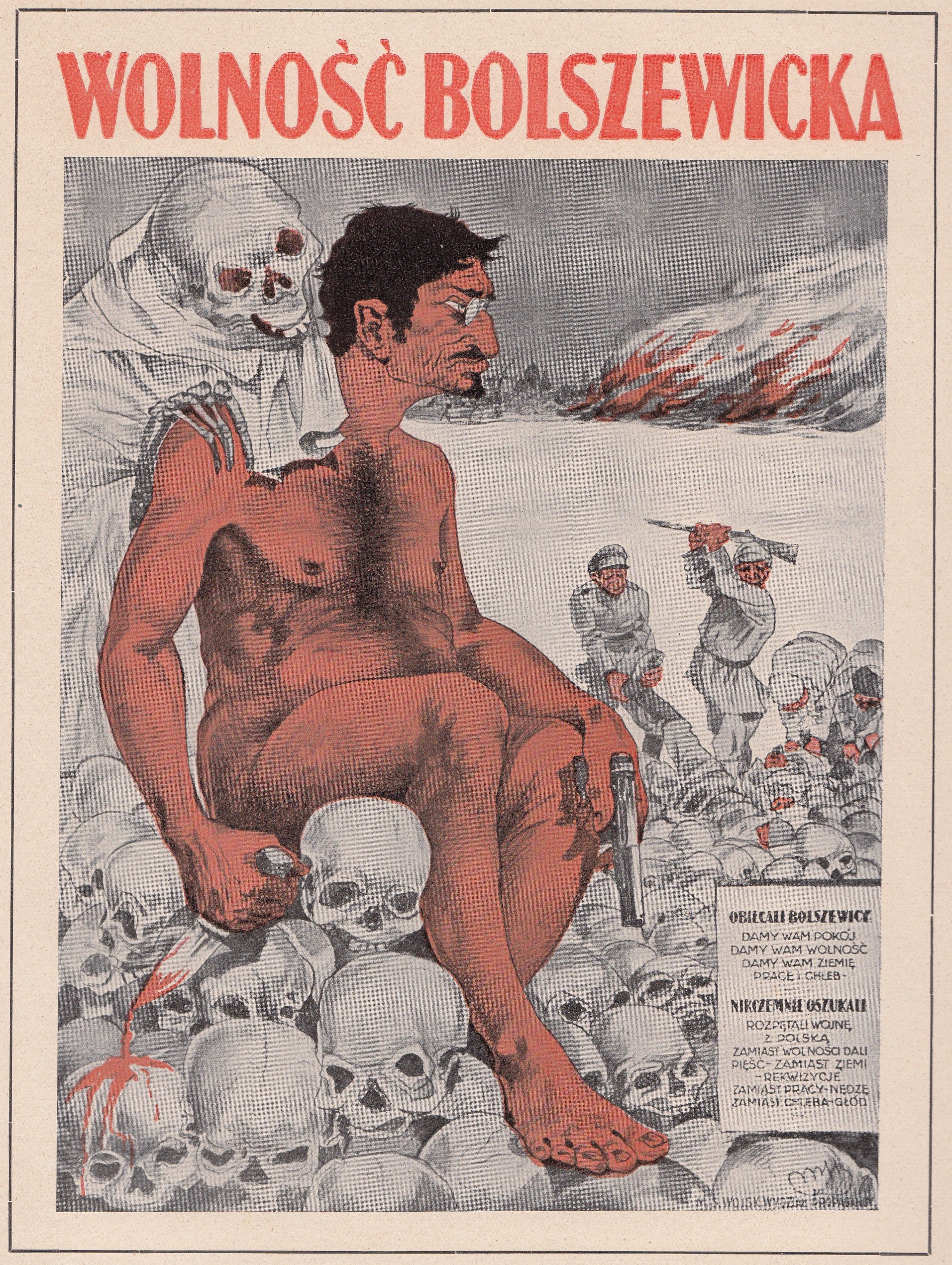 Anti-Sovietism or anti-Soviet sentiment are activities that were actually or allegedly aimed against the
Anti-Sovietism or anti-Soviet sentiment are activities that were actually or allegedly aimed against the


 Anti-Sovietism or anti-Soviet sentiment are activities that were actually or allegedly aimed against the
Anti-Sovietism or anti-Soviet sentiment are activities that were actually or allegedly aimed against the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
or government power within the Soviet Union.
Three common uses of the term include the following:
* Anti-Sovietism in international politics, such as the Western opposition to the Soviet Union during the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
as part of broader anti-communism
Anti-communism is Political movement, political and Ideology, ideological opposition to communism, communist beliefs, groups, and individuals. Organized anti-communism developed after the 1917 October Revolution in Russia, and it reached global ...
.
* Anti-Soviet opponents of the Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
s shortly after the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution, social change in Russian Empire, Russia, starting in 1917. This period saw Russia Dissolution of the Russian Empire, abolish its mona ...
and during the Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
.
* Soviet citizens (allegedly or actually) involved in anti-government activities.
History
In the Soviet Union
During theRussian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
that followed the October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two r ...
of 1917, the anti-Soviet side was the White movement
The White movement,. The old spelling was retained by the Whites to differentiate from the Reds. also known as the Whites, was one of the main factions of the Russian Civil War of 1917–1922. It was led mainly by the Right-wing politics, right- ...
. During the Interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) – from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II ( ...
, some resistance movements, particularly in the 1920s, were cultivated by Polish intelligence in the form of the Promethean project. After Germany's attack on the Soviet Union in 1941, anti-Soviet forces were created and led primarily by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
(see Russian Liberation Movement). During the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
, the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
led the anti-Soviet and anti-communist Western Bloc
The Western Bloc, also known as the Capitalist Bloc, the Freedom Bloc, the Free Bloc, and the American Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of countries that were officially allied with the United States during the Cold War (1947–1991). While ...
.
During the Russian Civil War, whole classes of people, such as the clergy, kulak
Kulak ( ; rus, кула́к, r=kulák, p=kʊˈɫak, a=Ru-кулак.ogg; plural: кулаки́, ''kulakí'', 'fist' or 'tight-fisted'), also kurkul () or golchomag (, plural: ), was the term which was used to describe peasants who owned over ...
s and former Imperial Russia
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor/empress, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* ...
n officers, were automatically considered anti-Soviet. More categories are listed in the article "Enemy of the People
The terms enemy of the people and enemy of the nation are designations for the political opponents and the social class, social-class opponents of the Power (social and political), power group within a larger social unit, who, thus identified, ...
". Those who were deemed anti-Soviet in this way, because of their former social status, were often presumed guilty whenever tried for a crime. Yevgenia Albats and Catherine A. Fitzpatrick. ''The State Within a State: The KGB and Its Hold on Russia - Past, Present, and Future'', 1994. .
The Soviet Union made extensive use of the term "enemy of the people" (). The term was first used in a speech by Felix Dzerzhinsky, the first chairman of the Cheka
The All-Russian Extraordinary Commission ( rus, Всероссийская чрезвычайная комиссия, r=Vserossiyskaya chrezvychaynaya komissiya, p=fsʲɪrɐˈsʲijskəjə tɕrʲɪzvɨˈtɕæjnəjə kɐˈmʲisʲɪjə, links=yes), ...
, after the October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two r ...
. The Petrograd Military Revolutionary Committee printed lists of "enemies of the people", and Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 until Death and state funeral of ...
invoked it in his decree of 28 November 1917:
Other similar terms were in use as well:
*''enemy of the labourers'' ()
*''enemy of the proletariat'' ()
*''class enemy'' (), etc.
In particular, the term "enemy of the workers" was formalized in the Article 58 (RSFSR Penal Code)
Article 58 of the Russian SFSR Penal Code was put in force on 25 February 1927 to prosecute those suspected of counter-revolutionary activities. It was revised several times. In particular, its Article 58-1 was updated by the listed sub-articles ...
, and similar articles in the codes of the other Soviet Republics.
At various times these terms were applied, in particular, to Tsar Nicholas II and the Imperial family
A royal family is the immediate family of monarch, monarchs and sometimes their extended family.
The term imperial family appropriately describes the family of an emperor or emperor, empress, and the term papal family describes the family of ...
, aristocrat
The aristocracy (''from Greek'' ''ἀριστοκρατία'' ''aristokratía'', "rule of the best"; ''Latin: aristocratia'') is historically associated with a "hereditary" or a "ruling" social class. In many states, the aristocracy included the ...
s, the bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie ( , ) are a class of business owners, merchants and wealthy people, in general, which emerged in the Late Middle Ages, originally as a "middle class" between the peasantry and aristocracy. They are traditionally contrasted wi ...
, cleric
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
s, business entrepreneurs, anarchists
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or hierarchy, primarily targeting the state and capitalism. Anarchism advocates for the replacement of the state w ...
, kulak
Kulak ( ; rus, кула́к, r=kulák, p=kʊˈɫak, a=Ru-кулак.ogg; plural: кулаки́, ''kulakí'', 'fist' or 'tight-fisted'), also kurkul () or golchomag (, plural: ), was the term which was used to describe peasants who owned over ...
s, monarchists
Monarchism is the advocacy of the system of monarchy or monarchical rule. A monarchist is an individual who supports this form of government independently of any specific monarch, whereas one who supports a particular monarch is a royalist. C ...
, Mensheviks
The Mensheviks ('the Minority') were a faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with Vladimir Lenin's Bolshevik faction at the Second Party Congress in 1903. Mensheviks held more moderate and reformist ...
, Esers, Bundists, Trotskyists
Trotskyism (, ) is the political ideology and branch of Marxism developed by Russian revolutionary and intellectual Leon Trotsky along with some other members of the Left Opposition and the Fourth International. Trotsky described himself as a ...
, Bukharinists, the " old Bolsheviks", the army and police, emigrant
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
s, saboteurs, wreckers (вредители, "vrediteli"), " social parasites" (тунеядцы, "tuneyadtsy"), ''Kavezhedists'' (people who administered and serviced the KVZhD (China Far East Railway), particularly the Russian population of Harbin
Harbin, ; zh, , s=哈尔滨, t=哈爾濱, p=Hā'ěrbīn; IPA: . is the capital of Heilongjiang, China. It is the largest city of Heilongjiang, as well as being the city with the second-largest urban area, urban population (after Shenyang, Lia ...
, China), and those considered bourgeois nationalists (notably Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
, Lithuanian, Latvian, Estonian nationalists
Estonian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Estonia, a country in the Baltic region in northern Europe
* Estonians, people from Estonia, or of Estonian descent
* Estonian language
* Estonian cuisine
* Estonian culture
See also
*
...
, Zionists, Basmachi).
Since 1927, Article 20 of the Common Part of the penal code that listed possible "measures of social defence" had the following item 20a: "declaration to be an enemy of the workers with deprivation of the union republic citizenship and hence of the USSR citizenship, with obligatory expulsion from its territory". Nevertheless, most "enemies of the people" suffered labor camps, rather than expulsion.
Later in the Soviet Union, being anti-Soviet was a criminal offense, known as " Anti-Soviet agitation". The epithet
An epithet (, ), also a byname, is a descriptive term (word or phrase) commonly accompanying or occurring in place of the name of a real or fictitious person, place, or thing. It is usually literally descriptive, as in Alfred the Great, Suleima ...
"antisoviet" was synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means precisely or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are a ...
ous with " counter-revolutionary". The noun "antisovietism" was rarely used and the noun "antisovietist" () was used in a derogatory sense. Anti-Soviet agitation and activities were political crimes handled by the Article 58 and later Article 70 of the RSFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
penal code and similar articles in other Soviet republics. In February 1930, there was an anti-Soviet insurgency
An insurgency is a violent, armed rebellion by small, lightly armed bands who practice guerrilla warfare against a larger authority. The key descriptive feature of insurgency is its asymmetric warfare, asymmetric nature: small irregular forces ...
in the Kazak Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic
The Kazakh Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic (; ), abbreviated as Kazak ASSR (; ) and simply Kazakhstan (; ), was an Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics, autonomous republic of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR) within ...
village of Sozak.
After the end of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, there were Eastern European anti-Communist insurgencies against the Soviet Union.
In Post-Soviet countries
Estonia
In August 2022Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
began removing Soviet monuments, beginning with a T-34
The T-34 is a Soviet medium tank from World War II. When introduced, its 76.2 mm (3 in) tank gun was more powerful than many of its contemporaries, and its 60-degree sloped armour provided good protection against Anti-tank warfare, ...
tank in Narva, claiming it was necessary for "public order" and "internal security".
Latvia
On 6 May 2022, following theRussian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
, Latvian Prime Minister Krišjānis Kariņš
Arturs Krišjānis Kariņš (; born 13 December 1964) is a Latvian American politician who served as the prime minister of Latvia from 2019 until 2023. A linguist and businessman by profession, he previously served as Latvia's minister of Economic ...
announced that the removal of the controversial monument
A monument is a type of structure that was explicitly created to commemorate a person or event, or which has become relevant to a social group as a part of their remembrance of historic times or cultural heritage, due to its artistic, historical ...
to the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
was inevitable. Five days later a public fundraising campaign was launched and more than 39,000 euros had been donated by 12 May when the Saeima
The Saeima () is the parliament of the Latvia, Republic of Latvia. It is a unicameral parliament consisting of 100 members who are elected by proportional representation, with seats allocated to political parties which gain at least 5% of the p ...
voted to suspend the functioning of a section regarding the preservation of memorial structures in an agreement between Latvia and Russia. By 13 May, the total amount of donations had almost reached 200,000 euros.
A rally "Getting Rid of Soviet Heritage" taking place on March 20 was attended by approximately 5,000 people, while a counter rally by Latvian Russian Union was prevented from taking place by security forces, claiming threat to "public security".
A list of 93 street names still glorifying the Soviet regime (such as 13 streets named after the Pioneer movement
A pioneer movement is an youth organization, organization for children operated by a communist party. Typically children enter into the organization in elementary school and continue until adolescence. The adolescents then typically join the Yo ...
), as well as 48 street names given during the Russification
Russification (), Russianisation or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians adopt Russian culture and Russian language either voluntarily or as a result of a deliberate state policy.
Russification was at times ...
at the end of the 19th century (like streets named after Alexander Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin () was a Russian poet, playwright, and novelist of the Romantic era.Basker, Michael. Pushkin and Romanticism. In Ferber, Michael, ed., ''A Companion to European Romanticism''. Oxford: Blackwell, 2005. He is consid ...
), has been compiled by historians of the Public Memory Center and sent to the corresponding municipalities who were recommended to change them.
See also
*Anti-communism
Anti-communism is Political movement, political and Ideology, ideological opposition to communism, communist beliefs, groups, and individuals. Organized anti-communism developed after the 1917 October Revolution in Russia, and it reached global ...
** Anti-Soviet partisans
** Criticisms of communist party rule
** Eastern European anti-Communist insurgencies
** White movement
The White movement,. The old spelling was retained by the Whites to differentiate from the Reds. also known as the Whites, was one of the main factions of the Russian Civil War of 1917–1922. It was led mainly by the Right-wing politics, right- ...
** Anti-People's Republic of China
Anti-People's Republic of China ( zh, t=反中華人民共和國), simply anti-PRC ( zh, t=反中, l=anti-China)C Wu (2020)Nationalism and Social Order in Public"Two keywords highlight attacks to the Chinese nation: anti-PRC (反中) and anti-C ...
, distinguished from anti-Chinese sentiment
* Anti-Russian sentiment
Anti-Russian sentiment or Russophobia is the dislike or fear of Russia, Russians, Russian people, or Culture of Russia, Russian culture. The opposite of Russophobia is Russophilia.
Historically, Russophobia has included state-sponsored and gr ...
* Anti-Stalinist left
The anti-Stalinist left encompasses various kinds of Left-wing politics, left-wing political movements that oppose Joseph Stalin, Stalinism, neo-Stalinism and the History of the Soviet Union (1927–1953), system of governance that Stalin impleme ...
* Decommunization
** Decommunization in Russia
** Decommunization in Ukraine
** List of monuments and memorials removed following the Russian invasion of Ukraine
* Enemy of the people
The terms enemy of the people and enemy of the nation are designations for the political opponents and the social class, social-class opponents of the Power (social and political), power group within a larger social unit, who, thus identified, ...
* German atrocities committed against Soviet prisoners of war
* Persecution of Christians in the Soviet Union
** Catacomb Church
* Predictions of the collapse of the Soviet Union
* Political repression in the Soviet Union
Throughout the history of the Soviet Union, tens of millions of people suffered political repression, which was an instrument of the state since the October Revolution. It culminated during the History of the Soviet Union (1927–1953), Stalin er ...
** Refusenik
** Soviet dissidents
* Red Scare and Red Terror
The Red Terror () was a campaign of political repression and Mass killing, executions in Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Soviet Russia which was carried out by the Bolsheviks, chiefly through the Cheka, the Bolshevik secret police ...
* Russian war crimes in the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
* Soviet Empire
* Timeline of events in the Cold War
This is a timeline of the main events of the Cold War, a state of political and military tension after World War II between powers in the Western Bloc (the United States, its NATO allies and others) and powers in the Eastern Bloc (the Soviet Un ...
* White émigré
White Russian émigrés were Russians who emigrated from the territory of the former Russian Empire in the wake of the Russian Revolution (1917) and Russian Civil War (1917–1923), and who were in opposition to the revolutionary Bolshevik com ...
Notes
References
{{Soviet Union topics Political repression in the Soviet Union Foreign relations of the Soviet Union Anti-Soviet resistance