Anti-RNP Antibodies on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with
 Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating interaction with the negatively charged nucleic acid chains. The
Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating interaction with the negatively charged nucleic acid chains. The
PRIDB Protein-RNA Interface Database
{{Authority control Proteins
 Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main cl ...
s (either DNA or RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
). Typical nucleoproteins include ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to ...
s, nucleosome
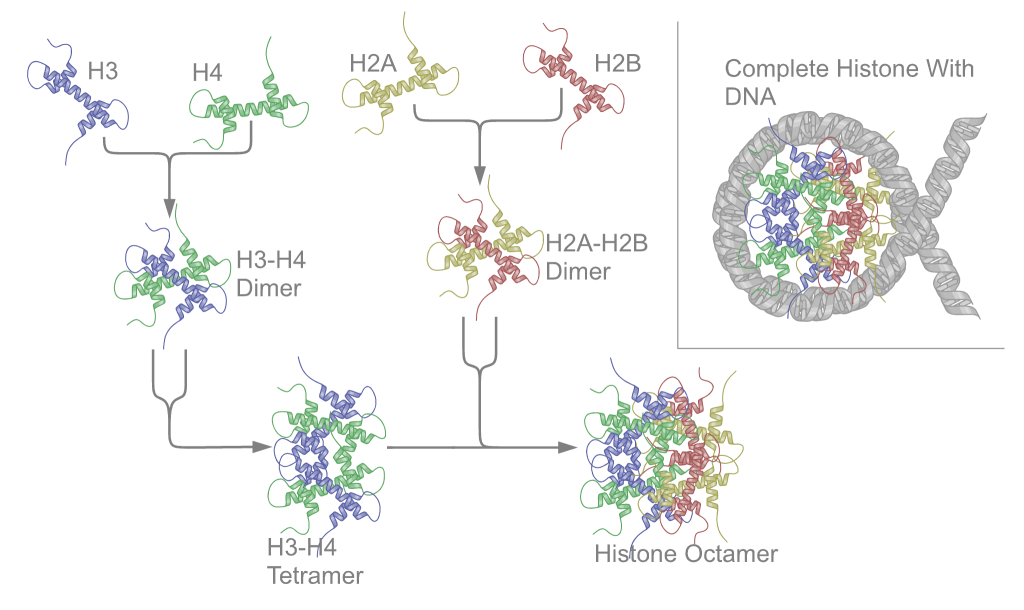
A nucleosome is the basic structural unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes. The structure of a nucleosome consists of a segment of DNA wound around eight histone proteins and resembles thread wrapped around a spool. The nucleosome is the fundamen ...
s and viral nucleocapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may ...
proteins.
Structures
 Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating interaction with the negatively charged nucleic acid chains. The
Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating interaction with the negatively charged nucleic acid chains. The tertiary structures
Biomolecular structure is the intricate folded, three-dimensional shape that is formed by a molecule of protein, DNA, or RNA, and that is important to its function. The structure of these molecules may be considered at any of several length sc ...
and biological functions of many nucleoproteins are understood.Graeme K. Hunter G. K. (2000): Vital Forces. The discovery of the molecular basis of life. Academic Press, London 2000, . Important techniques for determining the structures of nucleoproteins include X-ray diffraction
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
, nuclear magnetic resonance and cryo-electron microscopy.
Viruses
Virus genomes (either DNA orRNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
) are extremely tightly packed into the viral capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or ma ...
. Many viruses are therefore little more than an organised collection of nucleoproteins with their binding sites pointing inwards. Structurally characterised viral nucleoproteins include influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms ...
, rabies, Ebola
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becom ...
, Bunyamwera, Schmallenberg
Schmallenberg ( Westphalian: ''Smalmereg'') is a town and a climatic health resort in the High Sauerland District, Germany. By area, it is the third biggest of all cities and towns of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the second biggest o ...
, Hazara
Hazara may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* The Hazaras, a Persian-speaking people of Afghanistan and Pakistan
* Aimaq Hazara, Aimaq's subtribe of Hazara origin
* Hazarawals, a Hindko-speaking people of the Hazara region of northern Pakistan
* Hazar ...
, Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, and Lassa.
Deoxyribonucleoproteins
A deoxyribonucleoprotein (DNP) is a complex of DNA and protein. The prototypical examples arenucleosome
A nucleosome is the basic structural unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes. The structure of a nucleosome consists of a segment of DNA wound around eight histone proteins and resembles thread wrapped around a spool. The nucleosome is the fundamen ...
s, complexes in which genomic DNA is wrapped around clusters of eight histone proteins in eukaryotic cell nuclei to form chromatin. Protamines replace histones during spermatogenesis.
Functions
The most widespread deoxyribonucleoproteins arenucleosome
A nucleosome is the basic structural unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes. The structure of a nucleosome consists of a segment of DNA wound around eight histone proteins and resembles thread wrapped around a spool. The nucleosome is the fundamen ...
s, in which the component is nuclear DNA. The proteins combined with DNA are histones and protamines; the resulting nucleoproteins are located in chromosomes. Thus, the entire chromosome, i.e. chromatin in eukaryotes
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
consists of such nucleoproteins.
In eukaryotic cells, DNA is associated with about an equal mass of histone proteins in a highly condensed nucleoprotein complex called chromatin. Deoxyribonucleoproteins in this kind of complex interact to generate a multiprotein regulatory complex in which the intervening DNA is looped or wound. The deoxyribonucleoproteins participate in regulating DNA replication and transcription.
Deoxyribonucleoproteins are also involved in homologous recombination, a process for repairing DNA that appears to be nearly universal. A central intermediate step in this process is the interaction of multiple copies of a recombinase
Recombinases are genetic recombination enzymes.
Site specific recombinases
DNA recombinases are widely used in multicellular organisms to manipulate the structure of genomes, and to control gene expression. These enzymes, derived from bacteria (b ...
protein with single-stranded DNA to form a DNP filament. Recombinases employed in this process are produced by archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
(RadA recombinase), by bacteria (RecA recombinase) and by eukaryotes from yeast to humans (Rad51
DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1 is a protein encoded by the gene ''RAD51''. The enzyme encoded by this gene is a member of the RAD51 protein family which assists in repair of DNA double strand breaks. RAD51 family members are homologous to th ...
and Dmc1
Meiotic recombination protein DMC1/LIM15 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DMC1'' gene.
Meiotic recombination protein Dmc1 is a homolog of the bacterial strand exchange protein RecA. Dmc1 plays the central role in homologous ...
recombinases).
Ribonucleoproteins
A ribonucleoprotein (RNP) is a complex ofribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
and RNA-binding protein. These complexes play an integral part in a number of important biological functions that include transcription, translation and regulating gene expression and regulating the metabolism of RNA. A few examples of RNPs include the ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to ...
, the enzyme telomerase, vault ribonucleoproteins, RNase P, hnRNP Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) are complexes of RNA and protein present in the cell nucleus during gene transcription and subsequent post-transcriptional modification of the newly synthesized RNA (pre-mRNA). The presence of the pr ...
and small nuclear RNPs ( snRNPs), which have been implicated in pre-mRNA splicing ( spliceosome) and are among the main components of the nucleolus. Some viruses are simple ribonucleoproteins, containing only one molecule of RNA and a number of identical protein molecules. Others are ribonucleoprotein or deoxyribonucleoprotein complexes containing a number of different proteins, and exceptionally more nucleic acid molecules. Currently, over 2000 RNPs can be found in the RCSB Protein Data Bank (PDB). Furthermore, the Protein-RNA Interface Data Base (PRIDB) possesses a collection of information on RNA-protein interfaces based on data drawn from the PDB. Some common features of protein-RNA interfaces were deduced based on known structures. For example, RNP in snRNPs have an RNA-binding motif
Motif may refer to:
General concepts
* Motif (chess composition), an element of a move in the consideration of its purpose
* Motif (folkloristics), a recurring element that creates recognizable patterns in folklore and folk-art traditions
* Moti ...
in its RNA-binding protein. Aromatic amino acid residues in this motif result in stacking interactions with RNA. Lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −C ...
residues in the helical portion of RNA-binding proteins help to stabilize interactions with nucleic acids. This nucleic acid binding is strengthened by electrostatic attraction between the positive lysine side chains and the negative nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main cl ...
phosphate backbones. Additionally, it is possible to model RNPs computationally. Although computational methods of deducing RNP structures are less accurate than experimental methods, they provide a rough model of the structure which allows for predictions of the identity of significant amino acids and nucleotide residues. Such information helps in understanding the overall function the RNP.'RNP' can also refer to ribonucleoprotein particles. Ribonucleoprotein particles are distinct intracellular foci for post-transcriptional regulation. These particles play an important role in influenza A virus
''Influenza A virus'' (''IAV'') causes influenza in birds and some mammals, and is the only species of the genus ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' of the virus family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. Strain (biology)#Microbiology or virology, Strains of all subtypes ...
replication
Replication may refer to:
Science
* Replication (scientific method), one of the main principles of the scientific method, a.k.a. reproducibility
** Replication (statistics), the repetition of a test or complete experiment
** Replication crisi ...
. The influenza viral genome is composed of eight ribonucleoprotein particles formed by a complex of negative-sense RNA bound to a viral nucleoprotein. Each RNP carries with it an RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the ...
complex. When the nucleoprotein binds to the viral
Viral means "relating to viruses" (small infectious agents).
Viral may also refer to:
Viral behavior, or virality
Memetic behavior likened that of a virus, for example:
* Viral marketing, the use of existing social networks to spread a marke ...
RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
, it is able to expose the nucleotide bases which allow the viral polymerase to transcribe RNA. At this point, once the virus enters a host cell it will be prepared to begin the process of replication.
Anti-RNP antibodies
Anti-RNP antibodies areautoantibodies
An autoantibody is an antibody (a type of protein) produced by the immune system that is directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins. Many autoimmune diseases (notably lupus erythematosus) are associated with such antibodies.
Pr ...
associated with '' mixed connective tissue disease'' and are also detected in nearly 40% of Lupus erythematosus patients. Two types of anti-RNP antibodies are closely related to Sjögren's syndrome: SS-A
Anti-SSA autoantibodies (anti–Sjögren's-syndrome-related antigen A autoantibodies, also called anti-Ro, or similar names including anti-SSA/Ro, anti-Ro/SSA, anti–SS-A/Ro, and anti-Ro/SS-A) are a type of anti-nuclear autoantibodies that are a ...
(Ro) and SS-B
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human prote ...
(La). Autoantibodies
An autoantibody is an antibody (a type of protein) produced by the immune system that is directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins. Many autoimmune diseases (notably lupus erythematosus) are associated with such antibodies.
Pr ...
against snRNP are called Anti-Smith antibodies and are specific for SLE. The presence of a significant level of anti-U1-RNP also serves a possible indicator of MCTD when detected in conjunction with several other factors.
Functions
The ribonucleoproteins play a role of protection. mRNAs never occur as free RNA molecules in the cell. They always associate with ribonucleoproteins and function as ribonucleoprotein complexes. In the same way, the genomes of negative-strand RNA viruses never exist as free RNA molecule. The ribonucleoproteins protect their genomes from RNase. Nucleoproteins are often the major antigens for viruses because they have strain-specific and group-specificantigenic determinant
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The epitope is the specific piece of the antigen to which an antibody binds. The p ...
s.
See also
* DNA-binding protein * RNA-binding proteinReferences
External links
PRIDB Protein-RNA Interface Database
{{Authority control Proteins