Antarctic Krill on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Antarctic krill (''Euphausia superba'') is a
 The main spawning season of Antarctic krill is from January to March, both above the continental shelf and also in the upper region of deep sea oceanic areas. In the typical way of all krill, the male attaches a
The main spawning season of Antarctic krill is from January to March, both above the continental shelf and also in the upper region of deep sea oceanic areas. In the typical way of all krill, the male attaches a 
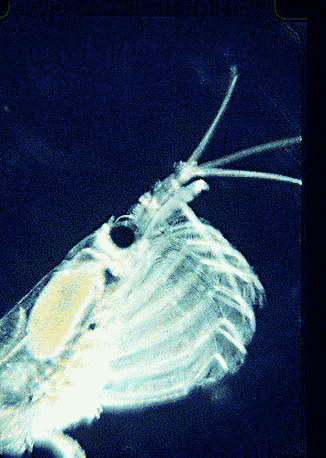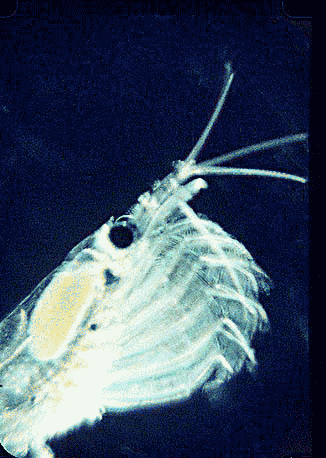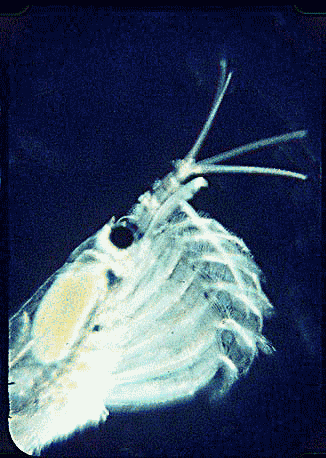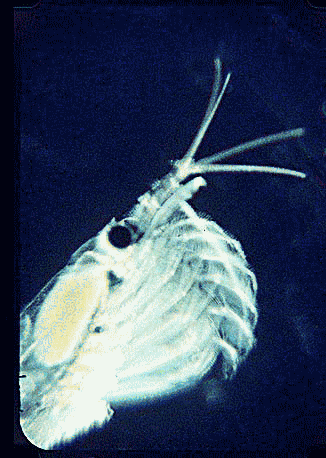

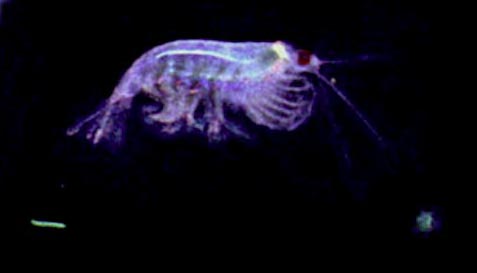 Krill are thought to undergo between one and three vertical migrations from mixed surface waters to depths of 100 m daily. The krill is a very untidy feeder, and it often spits out aggregates of
Krill are thought to undergo between one and three vertical migrations from mixed surface waters to depths of 100 m daily. The krill is a very untidy feeder, and it often spits out aggregates of  If the phytoplankton is consumed by other components of the pelagic ecosystem, most of the carbon remains in the upper layers of the ocean. There is speculation that this process is one of the largest biofeedback mechanisms of the planet, maybe the most sizable of all, driven by a gigantic biomass. Still more research is needed to quantify the Southern Ocean ecosystem.
If the phytoplankton is consumed by other components of the pelagic ecosystem, most of the carbon remains in the upper layers of the ocean. There is speculation that this process is one of the largest biofeedback mechanisms of the planet, maybe the most sizable of all, driven by a gigantic biomass. Still more research is needed to quantify the Southern Ocean ecosystem.
 Krill are often referred to as ''light-shrimp'' because they emit light through bioluminescent organs. These organs are located on various parts of the individual krill's body: one pair of organs at the
Krill are often referred to as ''light-shrimp'' because they emit light through bioluminescent organs. These organs are located on various parts of the individual krill's body: one pair of organs at the 
 Antarctic krill has a circumpolar distribution, being found throughout the
Antarctic krill has a circumpolar distribution, being found throughout the
 A possible decline in Antarctic krill biomass may have been caused by the reduction of the pack ice zone due to
A possible decline in Antarctic krill biomass may have been caused by the reduction of the pack ice zone due to
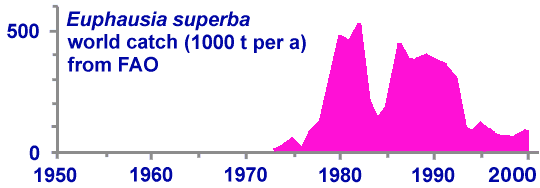 The fishery of Antarctic krill is on the order of 100,000 tonnes per year. The major catching nations are
The fishery of Antarctic krill is on the order of 100,000 tonnes per year. The major catching nations are
Krill Count Project
giving a popular introduction to the Antarctic krill
''Euphausia superba''
from ''MarineBio''
A time to krill
Webcam of krill aquarium
Antarctic Krill fact sheet
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of ...
of krill
Krill are small crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, and are found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian word ', meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish.
Krill are consid ...
found in the Antarctic
The Antarctic ( or , American English also or ; commonly ) is a polar region around Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau and o ...
waters of the Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is regarded as the second-smal ...
. It is a small, swimming crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gro ...
that lives in large schools, called swarms, sometimes reaching densities of 10,000–30,000 individual animals per cubic metre. It feeds directly on minute phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
P ...
, thereby using the primary production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through c ...
energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of hea ...
that the phytoplankton originally derived from the sun in order to sustain their pelagic
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean, and can be further divided into regions by depth (as illustrated on the right). The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or w ...
(open ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
) life cycle
Life cycle, life-cycle, or lifecycle may refer to:
Science and academia
* Biological life cycle, the sequence of life stages that an organism undergoes from birth to reproduction ending with the production of the offspring
* Life-cycle hypothesi ...
. It grows to a length of , weighs up to , and can live for up to six years. It is a key species in the Antarctic ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
and in terms of biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms biom ...
, is one of the most abundant animal species on the planet (approximately 500 million tons, corresponding to 300 to 400 trillion individuals).
Life cycle
 The main spawning season of Antarctic krill is from January to March, both above the continental shelf and also in the upper region of deep sea oceanic areas. In the typical way of all krill, the male attaches a
The main spawning season of Antarctic krill is from January to March, both above the continental shelf and also in the upper region of deep sea oceanic areas. In the typical way of all krill, the male attaches a spermatophore
A spermatophore or sperm ampulla is a capsule or mass containing spermatozoa created by males of various animal species, especially salamanders and arthropods, and transferred in entirety to the female's ovipore during reproduction. Spermatophores ...
to the genital opening of the female. For this purpose, the first pleopods (legs attached to the abdomen) of the male are constructed as mating tools. Females lay 6,000–10,000 eggs at one time. They are fertilised
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Proce ...
as they pass out of the genital opening.
According to the classical hypothesis of Marriosis De' Abrtona, derived from the results of the expedition of the famous British research vessel RRS ''Discovery'', egg development then proceeds as follows: gastrulation
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of cells), or in mammals the blastocyst is reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. ...
(development of egg into embryo) sets in during the descent of the eggs on the shelf at the bottom, in oceanic areas in depths around . The egg hatches as a nauplius larva; once this has moulted into a metanauplius, the young animal starts migrating towards the surface in a migration known as developmental ascent.
The next two larval stages, termed second nauplius and metanauplius, still do not eat but are nourished by the remaining yolk
Among animals which produce eggs, the yolk (; also known as the vitellus) is the nutrient-bearing portion of the egg whose primary function is to supply food for the development of the embryo. Some types of egg contain no yolk, for example bec ...
. After three weeks, the young krill has finished the ascent. They can appear in enormous numbers counting 2 per litre in water depth. Growing larger, additional larval stages follow (second and third calyptopis, first to sixth furcilia). They are characterised by increasing development of the additional legs, the compound eyes and the setae (bristles). At , the juvenile krill resembles the habitus of the adults. Krill reach maturity after two to three years. Like all crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gro ...
s, krill must moult
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer ...
in order to grow. Approximately every 13 to 20 days, krill shed their chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
ous exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton ( endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
and leave it behind as exuvia.

Food
The gut of E. superba can often be seen shining green through its transparent skin. This species feeds predominantly onphytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
P ...
—especially very small diatoms (20 μm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Unit ...
), which it filters from the water with a feeding basket. The glass-like shells of the diatoms are cracked in the " gastric mill" and then digested in the hepatopancreas
The hepatopancreas, digestive gland or midgut gland is an organ of the digestive tract of arthropods and molluscs. It provides the functions which in mammals are provided separately by the liver and pancreas, including the production of digesti ...
. The krill can also catch and eat copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthic (living on the ocean floor), a number of species have p ...
s, amphipods and other small zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
. The gut forms a straight tube; its digestive efficiency is not very high and therefore a lot of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes ...
is still present in the feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a rela ...
. Antarctic krill (''E.superba'') primarily has chitinolytic enzymes in the stomach and mid-gut to break down chitinous spines on diatoms, additional enzymes can vary due to its expansive diet.
In aquaria, krill have been observed to eat each other. When they are not fed, they shrink in size after moulting
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer ...
, which is exceptional for animals this size. It is likely that this is an adaptation to the seasonality of their food supply, which is limited in the dark winter months under the ice. However, the animal's compound eyes do not shrink, and so the ratio between eye size and body length has thus been found to be a reliable indicator of starvation. A krill with ample food supply would have eyes proportional to body length, compared to a starving krill that would have eyes that appeared larger than what is normal.

Filter feeding
Antarctic krill directly ingest minutephytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
P ...
cells, which no other animal of krill size can do. This is accomplished through filter feeding, using the krill's highly developed front legs which form an efficient filtering apparatus: the six thoracopods (legs attached to the thorax
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the ...
) create a "feeding basket" used to collect phytoplankton from the open water. In the finest areas the openings in this basket are only 1 μm in diameter. In lower food concentrations, the feeding basket is pushed through the water for over half a metre in an opened position, and then the algae are combed to the mouth opening with special setae
In biology, setae (singular seta ; from the Latin word for " bristle") are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms.
Animal setae
Protostomes
Annelid setae are stiff bristles present on the body. ...
(bristles) on the inner side of the thoracopods.
Ice-algae raking
Antarctic krill can scrape off the green lawn ofice-algae
Ice algae are any of the various types of algal communities found in annual and multi-year sea or terrestrial ice. On sea ice in the polar oceans, ice algae communities play an important role in primary production. The timing of blooms of the alg ...
from the underside of pack ice. Krill have developed special rows of rake-like setae at the tips of their thoracopods, and graze the ice in a zig-zag fashion. One krill can clear an area of a square foot in about 10 minutes (1.5 cm2/s). Recent discoveries have found that the film of ice algae is well developed over vast areas, often containing much more carbon than the whole water column below. Krill find an extensive energy source here, especially in the spring after food sources have been limited during the winter months.
Biological pump and carbon sequestration
 Krill are thought to undergo between one and three vertical migrations from mixed surface waters to depths of 100 m daily. The krill is a very untidy feeder, and it often spits out aggregates of
Krill are thought to undergo between one and three vertical migrations from mixed surface waters to depths of 100 m daily. The krill is a very untidy feeder, and it often spits out aggregates of phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
P ...
(spit balls) containing thousands of cells sticking together. It also produces fecal strings that still contain significant amounts of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes ...
and, glass
Glass is a non-Crystallinity, crystalline, often transparency and translucency, transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most ...
shells of the diatoms. Both are heavy and sink very fast into the abyss. This process is called the biological pump. As the waters around Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest co ...
are very deep (), they act as a carbon dioxide sink
A carbon sink is anything, natural or otherwise, that accumulates and stores some carbon-containing chemical compound for an indefinite period and thereby removes carbon dioxide () from the atmosphere.
Globally, the two most important carbon ...
: this process exports large quantities of carbon (fixed carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
, CO2) from the biosphere and sequesters it for about 1,000 years.
 If the phytoplankton is consumed by other components of the pelagic ecosystem, most of the carbon remains in the upper layers of the ocean. There is speculation that this process is one of the largest biofeedback mechanisms of the planet, maybe the most sizable of all, driven by a gigantic biomass. Still more research is needed to quantify the Southern Ocean ecosystem.
If the phytoplankton is consumed by other components of the pelagic ecosystem, most of the carbon remains in the upper layers of the ocean. There is speculation that this process is one of the largest biofeedback mechanisms of the planet, maybe the most sizable of all, driven by a gigantic biomass. Still more research is needed to quantify the Southern Ocean ecosystem.
Biology
Bioluminescence
 Krill are often referred to as ''light-shrimp'' because they emit light through bioluminescent organs. These organs are located on various parts of the individual krill's body: one pair of organs at the
Krill are often referred to as ''light-shrimp'' because they emit light through bioluminescent organs. These organs are located on various parts of the individual krill's body: one pair of organs at the eyestalk
In anatomy, an eyestalk (sometimes spelled eye stalk and also known as an ommatophore) is a protrusion that extends an eye away from the body, giving the eye a better field of view. It is a common feature in nature and frequently appears in fic ...
(cf. the image of the head above), another pair are on the hips of the second and seventh thoracopods, and singular organs on the four pleonsternite
The sternum (pl. "sterna") is the ventral portion of a segment of an arthropod thorax or abdomen.
In insects, the sterna are usually single, large sclerites, and external. However, they can sometimes be divided in two or more, in which case th ...
s. These light organs emit a yellow-green light periodically, for up to 2–3 s. They are considered so highly developed that they can be compared with a flashlight. There is a concave reflector in the back of the organ and a lens in the front that guide the light produced. The whole organ can be rotated by muscles, which can direct the light to a specific area. The function of these lights is not yet fully understood; some hypotheses have suggested they serve to compensate the krill's shadow so that they are not visible to predators from below; other speculations maintain that they play a significant role in mating
In biology, mating is the pairing of either opposite- sex or hermaphroditic organisms for the purposes of sexual reproduction. ''Fertilization'' is the fusion of two gametes. '' Copulation'' is the union of the sex organs of two sexually rep ...
or schooling at night.
The krill's bioluminescent organs contain several fluorescent substances. The major component has a maximum fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, ...
at an excitation of 355 nm and emission of 510 nm.

Escape reaction
Krill use anescape reaction
Escape response, escape reaction, or escape behavior is a mechanism by which animals avoid potential predation. It consists of a rapid sequence of movements, or lack of movement, that position the animal in such a way that allows it to hide, freeze ...
to evade predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill ...
s, swimming backwards very quickly by flipping their rear ends. This swimming pattern is also known as lobstering. Krill can reach speeds of over . The trigger time to optical stimulus is, despite the low temperatures, only 55 ms.
Geographic distribution
 Antarctic krill has a circumpolar distribution, being found throughout the
Antarctic krill has a circumpolar distribution, being found throughout the Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is regarded as the second-smal ...
, and as far north as the Antarctic Convergence
The Antarctic Convergence or Antarctic Polar Front is a marine belt encircling Antarctica, varying in latitude seasonally, where cold, northward-flowing Antarctic waters meet the relatively warmer waters of the sub-Antarctic. Antarctic waters p ...
. At the Antarctic Convergence, the cold Antarctic surface water submerges below the warmer subantarctic
The sub-Antarctic zone is a region in the Southern Hemisphere, located immediately north of the Antarctic region. This translates roughly to a latitude of between 46° and 60° south of the Equator. The subantarctic region includes many islands ...
waters. This front runs roughly at 55° south; from there to the continent, the Southern Ocean covers 32 million square kilometres. This is 65 times the size of the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
. In the winter season, more than three-quarters of this area become covered by ice, whereas become ice free in summer. The water temperature fluctuates at .
The waters of the Southern Ocean form a system of currents. Whenever there is a West Wind Drift, the surface strata travels around Antarctica in an easterly direction. Near the continent, the East Wind Drift runs counterclockwise. At the front between both, large eddies develop, for example, in the Weddell Sea
The Weddell Sea is part of the Southern Ocean and contains the Weddell Gyre. Its land boundaries are defined by the bay formed from the coasts of Coats Land and the Antarctic Peninsula. The easternmost point is Cape Norvegia at Princess Mar ...
. The krill swarms swim with these water masses, to establish one single stock all around Antarctica, with gene exchange over the whole area. Currently, there is little knowledge of the precise migration patterns since individual krill cannot yet be tagged to track their movements. The largest shoals are visible from space and can be tracked by satellite. One swarm covered an area of of ocean, to a depth of and was estimated to contain over 2 million tons of krill.Hoare, Ben (2009). Animal Migration. London: Natural History Museum. p. 107. Recent research suggests that krill do not simply drift passively in these currents but actually modify them. By moving vertically through the ocean on a 12-hour cycle, the swarms play a major part in mixing deeper, nutrient-rich water with nutrient-poor water at the surface.
Ecology
Antarctic krill is thekeystone species
A keystone species is a species which has a disproportionately large effect on its natural environment relative to its abundance, a concept introduced in 1969 by the zoologist Robert T. Paine. Keystone species play a critical role in maintaini ...
of the Antarctic
The Antarctic ( or , American English also or ; commonly ) is a polar region around Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau and o ...
ecosystem beyond the coastal shelf, and provides an important food source for whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
s, seals (such as leopard seals, fur seals, and crabeater seals), squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting ...
, icefish, penguin
Penguins ( order Sphenisciformes , family Spheniscidae ) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is found north of the Equator. Highly adapt ...
s, albatross
Albatrosses, of the biological family Diomedeidae, are large seabirds related to the procellariids, storm petrels, and diving petrels in the order Procellariiformes (the tubenoses). They range widely in the Southern Ocean and the North P ...
es and many other species of bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s. Crabeater seals have even developed special teeth as an adaptation to catch this abundant food source: its unusual multilobed teeth enable this species to sieve krill from the water. Its dentition looks like a perfect strainer, but how it operates in detail is still unknown. Crabeaters are the most abundant seal in the world; 98% of their diet is made up of '' E. superba''. These seals consume over 63 million tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s of krill each year. Leopard seals have developed similar teeth (45% krill in diet). All seals consume 63–130 million tonnes, all whales 34–43 million tonnes, birds 15–20 million tonnes, squid 30–100 million tonnes, and fish 10–20 million tonnes, adding up to 152–313 million tonnes of krill consumption each year.
The size step between krill and its prey is unusually large: generally it takes three or four steps from the 20 μm small phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
P ...
cells to a krill-sized organism (via small copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthic (living on the ocean floor), a number of species have p ...
s, large copepods, mysids to 5 cm fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% ...
). ''E. superba'' lives only in the Southern Ocean. In the North Atlantic, '' Meganyctiphanes norvegica'' and in the Pacific, '' Euphausia pacifica'' are the dominant species.
Biomass and production
Thebiomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms biom ...
of Antarctic krill was estimated in 2009 to be 0.05 gigatons of carbon (Gt C), similar to the total biomass of humans (0.06 Gt C). The reason Antarctic krill are able to build up such a high biomass and production is that the waters around the icy Antarctic continent harbour one of the largest plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a cr ...
assemblages in the world, possibly ''the'' largest. The ocean is filled with phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
P ...
; as the water rises from the depths to the light-flooded surface, it brings nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excr ...
s from all of the world's oceans back into the photic zone where they are once again available to living organisms.
Thus primary production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through c ...
—the conversion of sunlight into organic biomass, the foundation of the food chain—has an annual carbon fixation of 1–2 g/m2 in the open ocean. Close to the ice it can reach 30–50 g/m2. These values are not outstandingly high, compared to very productive areas like the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
or upwelling
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The nut ...
regions, but the area over which it takes place is enormous, even compared to other large primary producers such as rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfo ...
s. In addition, during the Austral summer there are many hours of daylight to fuel the process. All of these factors make the plankton and the krill a critical part of the planet's ecocycle.
Decline with shrinking pack ice
 A possible decline in Antarctic krill biomass may have been caused by the reduction of the pack ice zone due to
A possible decline in Antarctic krill biomass may have been caused by the reduction of the pack ice zone due to global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in a broader sense also includes ...
. Antarctic krill, especially in the early stages of development, seem to need the pack ice structures in order to have a fair chance of survival. The pack ice provides natural cave-like features which the krill uses to evade their predators. In the years of low pack ice conditions the krill tend to give way to salp
A salp (plural salps, also known colloquially as “sea grape”) or salpa (plural salpae or salpas) is a barrel-shaped, planktic tunicate. It moves by contracting, thereby pumping water through its gelatinous body, one of the most efficient ...
s, a barrel-shaped free-floating filter feeder
Filter feeders are a sub-group of suspension feeding animals that feed by straining suspended matter and food particles from water, typically by passing the water over a specialized filtering structure. Some animals that use this method of feedin ...
that also grazes on plankton.
Ocean acidification
Another challenge for Antarctic krill, as well as many calcifying organisms (corals, bivalve mussels, snails etc.), is the acidification of the oceans caused by increasing levels of carbon dioxide. Krill exoskeleton contains carbonate, which is susceptible to dissolution under low pH conditions. It has already been shown that increased carbon dioxide can disrupt the development of krill eggs and even prevent the juvenile krill from hatching, leading to future geographically widespread decreases in krill hatching success. The further effects of ocean acidification on the krill life cycle however remains unclear but scientists fear that it could significantly impact on its distribution, abundance and survival.Fisheries
 The fishery of Antarctic krill is on the order of 100,000 tonnes per year. The major catching nations are
The fishery of Antarctic krill is on the order of 100,000 tonnes per year. The major catching nations are South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
, Japan and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
. The products are used as animal food and fish bait. Krill fisheries are difficult to operate in two important respects. First, a krill net needs to have very fine meshes, producing a very high drag
Drag or The Drag may refer to:
Places
* Drag, Norway, a village in Tysfjord municipality, Nordland, Norway
* ''Drág'', the Hungarian name for Dragu Commune in Sălaj County, Romania
* Drag (Austin, Texas), the portion of Guadalupe Street adj ...
, which generates a bow wave that deflects the krill to the sides. Second, fine meshes tend to clog very fast.
Yet another problem is bringing the krill catch on board. When the full net is hauled out of the water, the organisms compress each other, resulting in great loss of the krill's liquids. Experiments have been carried out to pump krill, while still in water, through a large tube on board. Special krill nets also are currently under development. The processing of the krill must be very rapid since the catch deteriorates within several hours. Its high protein and vitamin content makes krill quite suitable for both direct human consumption and the animal-feed industry.
Fishing and potentially overfishing krill is an issue of increasing concern. References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* *Krill Count Project
giving a popular introduction to the Antarctic krill
''Euphausia superba''
from ''MarineBio''
A time to krill
Australian Antarctic Division
The Australian Antarctic Division (AAD) is a division of the Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water. The Division undertakes science programs and research projects to contribute to an understanding of Antarctica and th ...
Webcam of krill aquarium
Australian Antarctic Division
The Australian Antarctic Division (AAD) is a division of the Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water. The Division undertakes science programs and research projects to contribute to an understanding of Antarctica and th ...
Antarctic Krill fact sheet
Australian Antarctic Division
The Australian Antarctic Division (AAD) is a division of the Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water. The Division undertakes science programs and research projects to contribute to an understanding of Antarctica and th ...
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Antarctic Krill
Krill
Fauna of Antarctica
Fauna of the Southern Ocean
Crustaceans described in 1850
Taxa named by James Dwight Dana
Spoken articles