Annie Farmer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Jack the Ripper was an unidentified serial killer active in and around the impoverished Whitechapel district of London, England, in the autumn of 1888. In both criminal case files and the contemporaneous journalistic accounts, the killer was called the Whitechapel Murderer and Leather Apron.
Attacks ascribed to Jack the Ripper typically involved female prostitutes who lived and worked in the slums of the
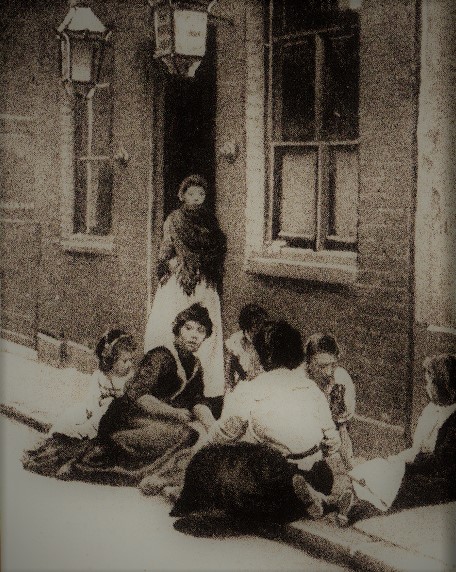 In the mid-19th century, England experienced an influx of Irish immigrants who swelled the populations of the major cities, including the
In the mid-19th century, England experienced an influx of Irish immigrants who swelled the populations of the major cities, including the
 The large number of attacks against women in the East End during this time adds uncertainty to how many victims were murdered by the same individual. Eleven separate murders, stretching from 1888 to 1891, were included in a Metropolitan Police investigation and were known collectively in the police docket as the "Whitechapel murders". Opinions vary as to whether these murders should be linked to the same culprit, but five of the eleven Whitechapel murders, known as the "canonical five", are widely believed to be the work of the Ripper. Most experts point to deep slash wounds to the throat, followed by extensive abdominal and genital-area mutilation, the removal of internal organs, and progressive facial mutilations as the distinctive features of the Ripper's ''
The large number of attacks against women in the East End during this time adds uncertainty to how many victims were murdered by the same individual. Eleven separate murders, stretching from 1888 to 1891, were included in a Metropolitan Police investigation and were known collectively in the police docket as the "Whitechapel murders". Opinions vary as to whether these murders should be linked to the same culprit, but five of the eleven Whitechapel murders, known as the "canonical five", are widely believed to be the work of the Ripper. Most experts point to deep slash wounds to the throat, followed by extensive abdominal and genital-area mutilation, the removal of internal organs, and progressive facial mutilations as the distinctive features of the Ripper's ''
 One week later, on Saturday 1888, the body of Annie Chapman was discovered at approximately near the steps to the doorway of the back yard of 29 Hanbury Street, Spitalfields. As in the case of Nichols, the throat was severed by two deep cuts. Her abdomen had been cut entirely open, with a section of the flesh from her stomach being placed upon her left shoulder and another section of skin and flesh—plus her
One week later, on Saturday 1888, the body of Annie Chapman was discovered at approximately near the steps to the doorway of the back yard of 29 Hanbury Street, Spitalfields. As in the case of Nichols, the throat was severed by two deep cuts. Her abdomen had been cut entirely open, with a section of the flesh from her stomach being placed upon her left shoulder and another section of skin and flesh—plus her  Eddowes's body was found in a corner of Mitre Square in the City of London, three-quarters of an hour after the discovery of the body of Elizabeth Stride. Her throat was severed from ear to ear and her abdomen ripped open by a long, deep and jagged wound before her intestines had been placed over her right shoulder, with a section of intestine being completely detached and placed between her body and left arm.
The left kidney and the major part of Eddowes's uterus had been removed, and her face had been disfigured, with her nose severed, her cheek slashed, and cuts measuring a quarter of an inch and a half an inch respectively vertically incised through each of her eyelids. A triangular incision—the apex of which pointed towards Eddowes's eye—had also been carved upon each of her cheeks, and a section of the auricle and
Eddowes's body was found in a corner of Mitre Square in the City of London, three-quarters of an hour after the discovery of the body of Elizabeth Stride. Her throat was severed from ear to ear and her abdomen ripped open by a long, deep and jagged wound before her intestines had been placed over her right shoulder, with a section of intestine being completely detached and placed between her body and left arm.
The left kidney and the major part of Eddowes's uterus had been removed, and her face had been disfigured, with her nose severed, her cheek slashed, and cuts measuring a quarter of an inch and a half an inch respectively vertically incised through each of her eyelids. A triangular incision—the apex of which pointed towards Eddowes's eye—had also been carved upon each of her cheeks, and a section of the auricle and 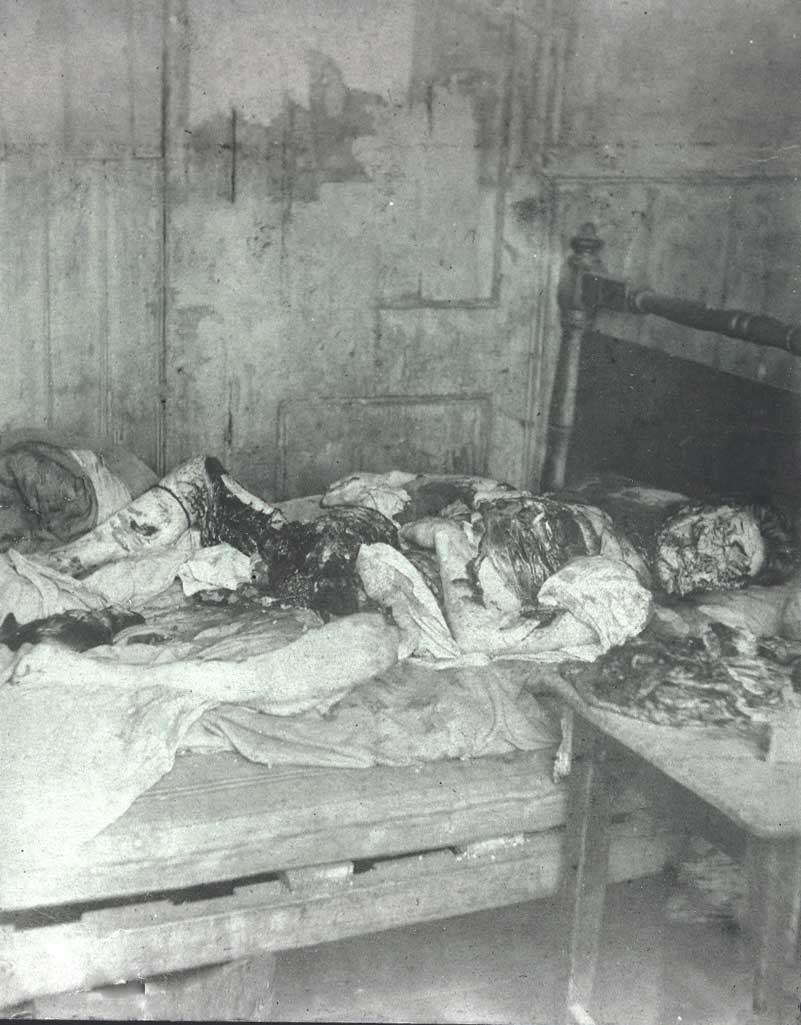 Each of the canonical five murders was perpetrated at night, on or close to a weekend, either at the end of a month or a week (or so) after. The mutilations became increasingly severe as the series of murders proceeded, except for that of Stride, whose attacker may have been interrupted. Nichols was not missing any organs; Chapman's uterus and sections of her bladder and vagina were taken; Eddowes had her uterus and left kidney removed and her face mutilated; and Kelly's body was extensively eviscerated, with her face "gashed in all directions" and the tissue of her neck being severed to the bone, although the heart was the sole body organ missing from this crime scene.
Historically, the belief these five canonical murders were committed by the same perpetrator is derived from contemporaneous documents which link them together to the exclusion of others. In 1894, Sir Melville Macnaghten, Assistant Chief Constable of the
Each of the canonical five murders was perpetrated at night, on or close to a weekend, either at the end of a month or a week (or so) after. The mutilations became increasingly severe as the series of murders proceeded, except for that of Stride, whose attacker may have been interrupted. Nichols was not missing any organs; Chapman's uterus and sections of her bladder and vagina were taken; Eddowes had her uterus and left kidney removed and her face mutilated; and Kelly's body was extensively eviscerated, with her face "gashed in all directions" and the tissue of her neck being severed to the bone, although the heart was the sole body organ missing from this crime scene.
Historically, the belief these five canonical murders were committed by the same perpetrator is derived from contemporaneous documents which link them together to the exclusion of others. In 1894, Sir Melville Macnaghten, Assistant Chief Constable of the
 At on 13 February 1891, PC Ernest Thompson discovered a 25-year-old prostitute named Frances Coles lying beneath a railway arch at Swallow Gardens, Whitechapel. Her throat had been deeply cut but her body was not mutilated, leading some to believe Thompson had disturbed her assailant. Coles was still alive, although she died before medical help could arrive. A 53-year-old stoker, James Thomas Sadler, had earlier been seen drinking with Coles, and the two are known to have argued approximately three hours before her death. Sadler was arrested by the police and charged with her murder. He was briefly thought to be the Ripper, but was later discharged from court for lack of evidence on 1891.Evans and Rumbelow, pp. 218–222; Evans and Skinner, ''The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook'', pp. 551–568
At on 13 February 1891, PC Ernest Thompson discovered a 25-year-old prostitute named Frances Coles lying beneath a railway arch at Swallow Gardens, Whitechapel. Her throat had been deeply cut but her body was not mutilated, leading some to believe Thompson had disturbed her assailant. Coles was still alive, although she died before medical help could arrive. A 53-year-old stoker, James Thomas Sadler, had earlier been seen drinking with Coles, and the two are known to have argued approximately three hours before her death. Sadler was arrested by the police and charged with her murder. He was briefly thought to be the Ripper, but was later discharged from court for lack of evidence on 1891.Evans and Rumbelow, pp. 218–222; Evans and Skinner, ''The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook'', pp. 551–568
 Both the Whitehall Mystery and the Pinchin Street case may have been part of a series of murders known as the " Thames Mysteries", committed by a single serial killer dubbed the "Torso killer". It is debatable whether Jack the Ripper and the "Torso killer" were the same person or separate serial killers active in the same area.Gordon, R. Michael (2002), ''The Thames Torso Murders of Victorian London'', Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland & Company, The ''modus operandi'' of the Torso killer differed from that of the Ripper, and police at the time discounted any connection between the two. Only one of the four victims linked to the Torso killer, Elizabeth Jackson, was ever identified. Jackson was a 24-year-old prostitute from Chelsea whose various body parts were collected from the River Thames over a three-week period between 31 May and 25 June 1889.
On 1888, the body of a seven-year-old boy named John Gill was found in a stable block in
Both the Whitehall Mystery and the Pinchin Street case may have been part of a series of murders known as the " Thames Mysteries", committed by a single serial killer dubbed the "Torso killer". It is debatable whether Jack the Ripper and the "Torso killer" were the same person or separate serial killers active in the same area.Gordon, R. Michael (2002), ''The Thames Torso Murders of Victorian London'', Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland & Company, The ''modus operandi'' of the Torso killer differed from that of the Ripper, and police at the time discounted any connection between the two. Only one of the four victims linked to the Torso killer, Elizabeth Jackson, was ever identified. Jackson was a 24-year-old prostitute from Chelsea whose various body parts were collected from the River Thames over a three-week period between 31 May and 25 June 1889.
On 1888, the body of a seven-year-old boy named John Gill was found in a stable block in
 The vast majority of the
The vast majority of the 
 The concentration of the killings around weekends and public holidays and within a short distance of each other has indicated to many that the Ripper was in regular employment and lived locally. Others have opined that the killer was an educated upper-class man, possibly a doctor or an
The concentration of the killings around weekends and public holidays and within a short distance of each other has indicated to many that the Ripper was in regular employment and lived locally. Others have opined that the killer was an educated upper-class man, possibly a doctor or an
 The "Saucy Jacky" postcard was postmarked 1888 and was received the same day by the Central News Agency. The handwriting was similar to the "Dear Boss" letter, and mentioned the canonical murders committed on 30 September, which the author refers to by writing "double event this time". It has been argued that the postcard was posted before the murders were publicised, making it unlikely that a
The "Saucy Jacky" postcard was postmarked 1888 and was received the same day by the Central News Agency. The handwriting was similar to the "Dear Boss" letter, and mentioned the canonical murders committed on 30 September, which the author refers to by writing "double event this time". It has been argued that the postcard was posted before the murders were publicised, making it unlikely that a
 The Ripper murders mark an important watershed in the treatment of crime by journalists. Jack the Ripper was not the first serial killer, but his case was the first to create a worldwide media frenzy. Davenport-Hines, Richard (2004)
The Ripper murders mark an important watershed in the treatment of crime by journalists. Jack the Ripper was not the first serial killer, but his case was the first to create a worldwide media frenzy. Davenport-Hines, Richard (2004)
"Jack the Ripper (fl. 1888)"
, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography''. Oxford University Press. Subscription required for online version.Woods and Baddeley, pp. 20, 52 The Elementary Education Act 1880 (which had extended upon a previous Act) made school attendance compulsory regardless of
 The nature of the Ripper murders and the impoverished lifestyle of the victims drew attention to the poor living conditions in the East End and galvanised public opinion against the overcrowded, insanitary slums. In the two decades after the murders, the worst of the slums were cleared and demolished, but the streets and some buildings survive, and the legend of the Ripper is still promoted by various guided tours of the murder sites and other locations pertaining to the case. For many years, the Ten Bells public house in Commercial Street (which had been frequented by at least one of the canonical Ripper victims) was the focus of such tours.
In the immediate aftermath of the murders and later, "Jack the Ripper became the children's bogey man." Depictions were often phantasmic or monstrous. In the 1920s and 1930s, he was depicted in film dressed in everyday clothes as a man with a hidden secret, preying on his unsuspecting victims; atmosphere and evil were suggested through lighting effects and shadowplay. By the 1960s, the Ripper had become "the symbol of a predatory aristocracy",Bloom, Clive, "Jack the Ripper – A Legacy in Pictures", in Werner, p. 251 and was more often portrayed in a top hat dressed as a gentleman. The Establishment as a whole became the villain, with the Ripper acting as a manifestation of upper-class exploitation. The image of the Ripper merged with or borrowed symbols from horror stories, such as
The nature of the Ripper murders and the impoverished lifestyle of the victims drew attention to the poor living conditions in the East End and galvanised public opinion against the overcrowded, insanitary slums. In the two decades after the murders, the worst of the slums were cleared and demolished, but the streets and some buildings survive, and the legend of the Ripper is still promoted by various guided tours of the murder sites and other locations pertaining to the case. For many years, the Ten Bells public house in Commercial Street (which had been frequented by at least one of the canonical Ripper victims) was the focus of such tours.
In the immediate aftermath of the murders and later, "Jack the Ripper became the children's bogey man." Depictions were often phantasmic or monstrous. In the 1920s and 1930s, he was depicted in film dressed in everyday clothes as a man with a hidden secret, preying on his unsuspecting victims; atmosphere and evil were suggested through lighting effects and shadowplay. By the 1960s, the Ripper had become "the symbol of a predatory aristocracy",Bloom, Clive, "Jack the Ripper – A Legacy in Pictures", in Werner, p. 251 and was more often portrayed in a top hat dressed as a gentleman. The Establishment as a whole became the villain, with the Ripper acting as a manifestation of upper-class exploitation. The image of the Ripper merged with or borrowed symbols from horror stories, such as
Jack the Ripper
at casebook.org
Home page
of jack-the-ripper.org
Jack the Ripper: The 1888 Autumn of Terror
at whitechapeljack.com
Contemporaneous news article
pertaining to the murders committed by Jack the Ripper * 198
centennial investigation
into the murders committed by Jack the Ripper compiled by the
news article
focusing upon modern geographic profiling techniques used to discover the most likely location Jack the Ripper lived
Letters claiming to be from Jack the Ripper
at nationalarchives.gov.uk
Jack the Ripper
at the '' Encyclopædia Britannica'' * Articl
focusing upon the murders committed by Jack the Ripper
published by the Texas State University {{DEFAULTSORT:Jack the Ripper 1888 in London 19th-century English criminals Date of birth unknown Date of death unknown English serial killers History of the City of London History of the City of London Police History of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets History of the Metropolitan Police Murder in London Nicknames in crime People of the Victorian era Unidentified serial killers Unsolved murders in England Violence against sex workers in the United Kingdom Whitechapel
East End of London
The East End of London, often referred to within the London area simply as the East End, is the historic core of wider East London, east of the Roman and medieval walls of the City of London and north of the River Thames. It does not have uni ...
. Their throats were cut prior to abdominal mutilations. The removal of internal organs from at least three of the victims led to speculation that their killer had some anatomical or surgical knowledge. Rumours that the murders were connected intensified in September and October 1888, and numerous letters were received by media outlets and Scotland Yard
Scotland Yard (officially New Scotland Yard) is the headquarters of the Metropolitan Police, the territorial police force responsible for policing Greater London's 32 boroughs, but not the City of London, the square mile that forms London's ...
from individuals purporting to be the murderer.
The name "Jack the Ripper" originated in the "Dear Boss letter
The "Dear Boss" letter was a message allegedly written by the notorious unidentified Victorian serial killer known as Jack the Ripper. Addressed to the Central News Agency of London and dated 25 September 1888, the letter was postmarked and rec ...
" written by an individual claiming to be the murderer, which was disseminated in the press. The letter is widely believed to have been a hoax and may have been written by journalists to heighten interest in the story and increase their newspapers' circulation. The " From Hell letter" received by George Lusk
George Akin Lusk (1839–1919) was a British builder and decorator who specialised in music hall restoration, and was the chairman of the Whitechapel Vigilance Committee during the Whitechapel murders, including the killings ascribed to Jack th ...
of the Whitechapel Vigilance Committee came with half of a preserved human kidney, purportedly taken from one of the victims. The public came increasingly to believe in the existence of a single serial killer known as Jack the Ripper, mainly because of both the extraordinarily brutal nature of the murders and media coverage of the crimes.
Extensive newspaper coverage bestowed widespread and enduring international notoriety on the Ripper, and the legend solidified. A police investigation into a series of eleven brutal murders committed in Whitechapel and Spitalfields
Spitalfields is a district in the East End of London and within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The area is formed around Commercial Street (on the A1202 London Inner Ring Road) and includes the locale around Brick Lane, Christ Church, ...
between 1888 and 1891 was unable to connect all the killings conclusively to the murders of 1888. Five victims—Mary Ann Nichols
Mary Ann Nichols, known as Polly Nichols (née Walker; 26 August 184531 August 1888), was the first canonical victim of the unidentified serial killer known as Jack the Ripper, who is believed to have murdered and mutilated at least five women i ...
, Annie Chapman
Annie Chapman (born Eliza Ann Smith; 25 September 1840 – 8 September 1888) was the second Jack the Ripper#Canonical five, canonical victim of the notorious unidentified serial killer Jack the Ripper, who killed and mutilation, mutilated a min ...
, Elizabeth Stride
Elizabeth "Long Liz" Stride ( Gustafsdotter; 27 November 1843 – 30 September 1888) is believed to have been the third victim of the unidentified serial killer known as Jack the Ripper, who killed and mutilated at least five women in the Whitecha ...
, Catherine Eddowes
Catherine Eddowes (14 April 1842 – 30 September 1888) was the fourth of the canonical five victims of the notorious unidentified serial killer known as Jack the Ripper, who is believed to have killed and mutilated a minimum of five women in ...
, and Mary Jane Kelly—are known as the "canonical five" and their murders between 31 August and 9 November 1888 are often considered the most likely to be linked. The murders were never solved, and the legends surrounding these crimes became a combination of historical research, folklore, and pseudohistory, capturing public imagination to the present day.
Background
 In the mid-19th century, England experienced an influx of Irish immigrants who swelled the populations of the major cities, including the
In the mid-19th century, England experienced an influx of Irish immigrants who swelled the populations of the major cities, including the East End of London
The East End of London, often referred to within the London area simply as the East End, is the historic core of wider East London, east of the Roman and medieval walls of the City of London and north of the River Thames. It does not have uni ...
. From 1882, Jewish refugees fleeing pogroms in Tsarist Russia Tsarist Russia may refer to:
* Grand Duchy of Moscow (1480–1547)
*Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721)
*Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of ...
and other areas of Eastern Europe emigrated into the same area. The parish of Whitechapel in the East End became increasingly overcrowded, with the population increasing to approximately 80,000 inhabitants by 1888.Honeycombe, ''The Murders of the Black Museum: 1870-1970'', p. 54 Work and housing conditions worsened, and a significant economic underclass developed. Fifty-five percent of children born in the East End died before they were five years old. Robbery, violence, and alcohol dependency were commonplace, and the endemic poverty drove many women to prostitution
Prostitution is the business or practice of engaging in Sex work, sexual activity in exchange for payment. The definition of "sexual activity" varies, and is often defined as an activity requiring physical contact (e.g., sexual intercourse, n ...
to survive on a daily basis.
In October 1888, London's Metropolitan Police Service
The Metropolitan Police Service (MPS), formerly and still commonly known as the Metropolitan Police (and informally as the Met Police, the Met, Scotland Yard, or the Yard), is the territorial police force responsible for law enforcement and ...
estimated that there were 62 brothel
A brothel, bordello, ranch, or whorehouse is a place where people engage in sexual activity with prostitutes. However, for legal or cultural reasons, establishments often describe themselves as massage parlors, bars, strip clubs, body rub par ...
s and 1,200 women working as prostitutes in Whitechapel,Evans and Skinner, ''Jack the Ripper: Letters from Hell'', p. 1; Police report dated 25 October 1888, MEPO 3/141 ff. 158–163, quoted in Evans and Skinner, ''The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook'', p. 283; Fido, p. 82; Rumbelow, p. 12 with approximately 8,500 people residing in the 233 common lodging-houses within Whitechapel every night, with the nightly price for a single bed being fourpence and the cost of sleeping upon a "lean-to" (" hang-over") rope stretched across the dormitory being two pence per person.
The economic problems in Whitechapel were accompanied by a steady rise in social tensions. Between 1886 and 1889, frequent demonstrations led to police intervention and public unrest, such as Bloody Sunday (1887)
Bloody Sunday took place in London on 13 November 1887, when marchers protesting about unemployment and coercion in Ireland, as well as demanding the release of MP William O'Brien, clashed with the Metropolitan Police and the British Army. T ...
. Anti-semitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
, crime, nativism, racism, social disturbance, and severe deprivation influenced public perceptions that Whitechapel was a notorious den of immorality. Such perceptions were strengthened in the autumn of 1888 when the series of vicious and grotesque murders attributed to "Jack the Ripper" received unprecedented coverage in the media.
Murders
modus operandi
A ''modus operandi'' (often shortened to M.O.) is someone's habits of working, particularly in the context of business or criminal investigations, but also more generally. It is a Latin phrase, approximately translated as "mode (or manner) of op ...
''. The first two cases in the Whitechapel murders file, those of Emma Elizabeth Smith
Emma Elizabeth Smith ( 1843 – 4 April 1888) was a prostitute and murder victim of mysterious origins in late-19th century London. Her killing was the first of the Whitechapel murders, and it is possible she was a victim of the serial killer kno ...
and Martha Tabram
Martha Tabram (née White; 10 May 1849 – 7 August 1888) was an English woman killed in a spate of violent murders in and around the Whitechapel district of East London between 1888 and 1891. She may have been the first victim of the still-uni ...
, are not included in the canonical five.
Smith was robbed and sexually assaulted
Sexual assault is an act in which one intentionally sexually touches another person without that person's consent, or coerces or physically forces a person to engage in a sexual act against their will. It is a form of sexual violence, which ...
in Osborn Street, Whitechapel, at approximately on 1888. She had been bludgeoned about the face and received a cut to her ear. A blunt object was also inserted into her vagina, rupturing her peritoneum. She developed peritonitis and died the following day at London Hospital. Smith stated that she had been attacked by two or three men, one of whom she described as a teenager. This attack was linked to the later murders by the press, but most authors attribute Smith's murder to general East End gang violence
A gang is a group or society of associates, friends or members of a family with a defined leadership and internal organization that identifies with or claims control over territory in a community and engages, either individually or collectivel ...
unrelated to the Ripper case.
Tabram was murdered on a staircase landing in George Yard, Whitechapel, on 7 August 1888;Begg, ''Jack the Ripper: The Facts'', p. 35 she had suffered 39 stab wounds to her throat, lungs, heart, liver, spleen, stomach, and abdomen, with additional knife wounds inflicted to her breasts and vagina. All but one of Tabram's wounds had been inflicted with a bladed instrument such as a penknife
Penknife, or pen knife, is a British English term for a small folding knife. Today the word ''penknife'' is the common British English term for both a pocketknife, which can have single or multiple blades, and for multi-tools, with additional too ...
, and with one possible exception, all the wounds had been inflicted by a right-handed individual. Tabram had not been raped.
The savagery of the Tabram murder, the lack of an obvious motive, and the closeness of the location and date to the later canonical Ripper murders led police to link this murder to those later committed by Jack the Ripper. However, this murder differs from the later canonical murders because although Tabram had been repeatedly stabbed, she had not suffered any slash wounds to her throat or abdomen. Many experts do not connect Tabram's murder with the later murders because of this difference in the wound pattern.
Canonical five
The canonical five Ripper victims areMary Ann Nichols
Mary Ann Nichols, known as Polly Nichols (née Walker; 26 August 184531 August 1888), was the first canonical victim of the unidentified serial killer known as Jack the Ripper, who is believed to have murdered and mutilated at least five women i ...
, Annie Chapman
Annie Chapman (born Eliza Ann Smith; 25 September 1840 – 8 September 1888) was the second Jack the Ripper#Canonical five, canonical victim of the notorious unidentified serial killer Jack the Ripper, who killed and mutilation, mutilated a min ...
, Elizabeth Stride
Elizabeth "Long Liz" Stride ( Gustafsdotter; 27 November 1843 – 30 September 1888) is believed to have been the third victim of the unidentified serial killer known as Jack the Ripper, who killed and mutilated at least five women in the Whitecha ...
, Catherine Eddowes
Catherine Eddowes (14 April 1842 – 30 September 1888) was the fourth of the canonical five victims of the notorious unidentified serial killer known as Jack the Ripper, who is believed to have killed and mutilated a minimum of five women in ...
, and Mary Jane Kelly.
The body of Mary Ann Nichols was discovered at about on Friday 1888 in Buck's Row (now Durward Street), Whitechapel. Nichols had last been seen alive approximately one hour before the discovery of her body by a Mrs Emily Holland, with whom she had previously shared a bed at a common lodging-house in Thrawl Street, Spitalfields, walking in the direction of Whitechapel Road. Her throat was severed by two deep cuts, one of which completely severed all the tissue down to the vertebrae. Her vagina had been stabbed twice, and the lower part of her abdomen was partly ripped open by a deep, jagged wound, causing her bowels to protrude. Several other incisions inflicted to both sides of her abdomen had also been caused by the same knife; each of these wounds had been inflicted in a downward thrusting manner.
 One week later, on Saturday 1888, the body of Annie Chapman was discovered at approximately near the steps to the doorway of the back yard of 29 Hanbury Street, Spitalfields. As in the case of Nichols, the throat was severed by two deep cuts. Her abdomen had been cut entirely open, with a section of the flesh from her stomach being placed upon her left shoulder and another section of skin and flesh—plus her
One week later, on Saturday 1888, the body of Annie Chapman was discovered at approximately near the steps to the doorway of the back yard of 29 Hanbury Street, Spitalfields. As in the case of Nichols, the throat was severed by two deep cuts. Her abdomen had been cut entirely open, with a section of the flesh from her stomach being placed upon her left shoulder and another section of skin and flesh—plus her small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
s—being removed and placed above her right shoulder. Chapman's autopsy also revealed that her uterus and sections of her bladder and vagina had been removed.
At the inquest
An inquest is a judicial inquiry in common law jurisdictions, particularly one held to determine the cause of a person's death. Conducted by a judge, jury, or government official, an inquest may or may not require an autopsy carried out by a coro ...
into Chapman's murder, Elizabeth Long described having seen Chapman standing outside 29 Hanbury Street at about in the company of a dark-haired man wearing a brown deer-stalker hat and dark overcoat, and of a "shabby- genteel" appearance. According to this eyewitness, the man had asked Chapman the question, "Will you?" to which Chapman had replied, "Yes."
Elizabeth Stride and Catherine Eddowes were both killed in the early morning hours of Sunday 1888. Stride's body was discovered at approximately in Dutfield's Yard, off Berner Street (now Henriques Street
The Whitechapel murders were committed in or near the largely impoverished Whitechapel district in the East End of London between 3 April 1888 and 13 February 1891. At various points some or all of these eleven unsolved murders of women have b ...
) in Whitechapel. The cause of death was a single clear-cut incision, measuring six inches across her neck which had severed her left carotid artery Carotid artery may refer to:
* Common carotid artery, often "carotids" or "carotid", an artery on each side of the neck which divides into the external carotid artery and internal carotid artery
* External carotid artery, an artery on each side of t ...
and her trachea before terminating beneath her right jaw. The absence of any further mutilations to her body has led to uncertainty as to whether Stride's murder was committed by the Ripper, or whether he was interrupted during the attack. Several witnesses later informed police they had seen Stride in the company of a man in or close to Berner Street on the evening of 29 September and in the early hours of 30 September, but each gave differing descriptions: some said that her companion was fair, others dark; some said that he was shabbily dressed, others well-dressed.
 Eddowes's body was found in a corner of Mitre Square in the City of London, three-quarters of an hour after the discovery of the body of Elizabeth Stride. Her throat was severed from ear to ear and her abdomen ripped open by a long, deep and jagged wound before her intestines had been placed over her right shoulder, with a section of intestine being completely detached and placed between her body and left arm.
The left kidney and the major part of Eddowes's uterus had been removed, and her face had been disfigured, with her nose severed, her cheek slashed, and cuts measuring a quarter of an inch and a half an inch respectively vertically incised through each of her eyelids. A triangular incision—the apex of which pointed towards Eddowes's eye—had also been carved upon each of her cheeks, and a section of the auricle and
Eddowes's body was found in a corner of Mitre Square in the City of London, three-quarters of an hour after the discovery of the body of Elizabeth Stride. Her throat was severed from ear to ear and her abdomen ripped open by a long, deep and jagged wound before her intestines had been placed over her right shoulder, with a section of intestine being completely detached and placed between her body and left arm.
The left kidney and the major part of Eddowes's uterus had been removed, and her face had been disfigured, with her nose severed, her cheek slashed, and cuts measuring a quarter of an inch and a half an inch respectively vertically incised through each of her eyelids. A triangular incision—the apex of which pointed towards Eddowes's eye—had also been carved upon each of her cheeks, and a section of the auricle and lobe
Lobe may refer to:
People with the name
* Lobe (surname)
Science and healthcare
* Lobe (anatomy)
* Lobe, a large-scale structure of a radio galaxy
* Glacial lobe, a lobe-shaped glacier
* Lobation, a characteristic of the nucleus of certain biolo ...
of her right ear was later recovered from her clothing. The police surgeon who conducted the post mortem upon Eddowes's body stated his opinion these mutilations would have taken "at least five minutes" to complete.
A local cigarette salesman named Joseph Lawende
Joseph Lawende (9 February 1847 – 9 January 1925) was a Polish-born British cigarette salesman, who is, with Israel Schwartz, among the most discussed of witnesses in the series of murders committed by Jack the Ripper in and around the Whitecha ...
had passed through the square with two friends shortly before the murder, and he described seeing a fair-haired man of shabby appearance with a woman who may have been Eddowes. Lawende's companions were unable to confirm his description.Begg, ''Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History'', pp. 193–194; Chief Inspector Swanson's report, 1888, HO 144/221/A49301C, quoted in Evans and Skinner, pp. 185–188 The murders of Stride and Eddowes ultimately became known as the "double event".
A section of Eddowes's bloodied apron was found at the entrance to a tenement in Goulston Street, Whitechapel, at A chalk inscription upon the wall directly above this piece of apron read: "The Juwes are The men That Will not be Blamed for nothing." This graffito became known as the Goulston Street graffito
The Goulston Street graffito was a sentence written on a wall beside a clue in the 1888 Whitechapel murders investigation. It has been transcribed as variations on the sentence "The Juwes are the men that will not be blamed for nothing". The mean ...
. The message appeared to imply that a Jew or Jews in general were responsible for the series of murders, but it is unclear whether the graffito was written by the murderer on dropping the section of apron, or was merely incidental and nothing to do with the case. Such graffiti were commonplace in Whitechapel. Police Commissioner Charles Warren feared that the graffito might spark anti-semitic riots and ordered the writing washed away before dawn.
The extensively mutilated and disembowelled body of Mary Jane Kelly was discovered lying on the bed in the single room where she lived at 13 Miller's Court, off Dorset Street, Spitalfields, at on Friday 1888. Her face had been "hacked beyond all recognition", with her throat severed down to the spine, and the abdomen almost emptied of its organs. Her uterus, kidneys and one breast had been placed beneath her head, and other viscera from her body placed beside her foot, about the bed and sections of her abdomen and thighs upon a bedside table. The heart was missing from the crime scene.
Multiple ashes found within the fireplace at 13 Miller's Court suggested Kelly's murderer had burned several combustible items to illuminate the single room as he mutilated her body. A recent fire had been severe enough to melt the solder between a kettle and its spout, which had fallen into the grate of the fireplace.
 Each of the canonical five murders was perpetrated at night, on or close to a weekend, either at the end of a month or a week (or so) after. The mutilations became increasingly severe as the series of murders proceeded, except for that of Stride, whose attacker may have been interrupted. Nichols was not missing any organs; Chapman's uterus and sections of her bladder and vagina were taken; Eddowes had her uterus and left kidney removed and her face mutilated; and Kelly's body was extensively eviscerated, with her face "gashed in all directions" and the tissue of her neck being severed to the bone, although the heart was the sole body organ missing from this crime scene.
Historically, the belief these five canonical murders were committed by the same perpetrator is derived from contemporaneous documents which link them together to the exclusion of others. In 1894, Sir Melville Macnaghten, Assistant Chief Constable of the
Each of the canonical five murders was perpetrated at night, on or close to a weekend, either at the end of a month or a week (or so) after. The mutilations became increasingly severe as the series of murders proceeded, except for that of Stride, whose attacker may have been interrupted. Nichols was not missing any organs; Chapman's uterus and sections of her bladder and vagina were taken; Eddowes had her uterus and left kidney removed and her face mutilated; and Kelly's body was extensively eviscerated, with her face "gashed in all directions" and the tissue of her neck being severed to the bone, although the heart was the sole body organ missing from this crime scene.
Historically, the belief these five canonical murders were committed by the same perpetrator is derived from contemporaneous documents which link them together to the exclusion of others. In 1894, Sir Melville Macnaghten, Assistant Chief Constable of the Metropolitan Police Service
The Metropolitan Police Service (MPS), formerly and still commonly known as the Metropolitan Police (and informally as the Met Police, the Met, Scotland Yard, or the Yard), is the territorial police force responsible for law enforcement and ...
and Head of the Criminal Investigation Department (CID), wrote a report that stated: "the Whitechapel murderer had 5 victims—& 5 victims only". Similarly, the canonical five victims were linked together in a letter written by police surgeon Thomas Bond to Robert Anderson, head of the London CID, on 1888.
Some researchers have posited that some of the murders were undoubtedly the work of a single killer, but an unknown larger number of killers acting independently were responsible for the other crimes. Authors Stewart P. Evans and Donald Rumbelow argue that the canonical five is a "Ripper myth" and that three cases (Nichols, Chapman, and Eddowes) can be definitely linked to the same perpetrator, but that less certainty exists as to whether Stride and Kelly were also murdered by the same individual. Conversely, others suppose that the six murders between Tabram and Kelly were the work of a single killer. Dr Percy Clark, assistant to the examining pathologist George Bagster Phillips
George Bagster Phillips (February 1835 in Camberwell, Surrey – 27 October 1897 in London) was, from 1865, the Police Surgeon for the Metropolitan Police's 'H' Division, which covered London's Whitechapel district. He came to prominence d ...
, linked only three of the murders and thought that the others were perpetrated by "weak-minded individual nbsp;... induced to emulate the crime". Macnaghten did not join the police force until the year after the murders, and his memorandum contains serious factual errors about possible suspects.
Later Whitechapel murders
Mary Jane Kelly is generally considered to be the Ripper's final victim, and it is assumed that the crimes ended because of the culprit's death, imprisonment, institutionalisation, or emigration. The Whitechapel murders file details another four murders that occurred after the canonical five: those of Rose Mylett, Alice McKenzie, the Pinchin Street torso, and Frances Coles. Thestrangled
Strangling is compression of the neck that may lead to unconsciousness or death by causing an increasingly hypoxic state in the brain. Fatal strangling typically occurs in cases of violence, accidents, and is one of two main ways that hanging ...
body of 26-year-old Rose Mylett was found in Clarke's Yard, High Street, Poplar on 1888. There was no sign of a struggle, and the police believed that she had either accidentally hanged herself with her collar while in a drunken stupor or committed suicide. However, faint markings left by a cord on one side of her neck suggested Mylett had been strangled. At the inquest into Mylett's death, the jury returned a verdict of murder.Evans and Rumbelow, pp. 245–246; Evans and Skinner, ''The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook'', pp. 422–439
Alice McKenzie was murdered shortly after midnight on 17 July 1889 in Castle Alley, Whitechapel. She had suffered two stab wounds to her neck, and her left carotid artery Carotid artery may refer to:
* Common carotid artery, often "carotids" or "carotid", an artery on each side of the neck which divides into the external carotid artery and internal carotid artery
* External carotid artery, an artery on each side of t ...
had been severed. Several minor bruises and cuts were found on her body, which also bore a seven-inch long superficial wound extending from her left breast to her navel. One of the examining pathologists, Thomas Bond, believed this to be a Ripper murder, though his colleague George Bagster Phillips, who had examined the bodies of three previous victims, disagreed. Opinions among writers are also divided between those who suspect McKenzie's murderer copied the ''modus operandi'' of Jack the Ripper to deflect suspicion from himself, and those who ascribe this murder to Jack the Ripper.
"The Pinchin Street torso" was a decomposing headless and legless torso of an unidentified woman aged between 30 and 40 discovered beneath a railway arch in Pinchin Street, Whitechapel, on 1889. Bruising about the victim's back, hip, and arm indicated the decedent had been extensively beaten shortly before her death. The victim's abdomen was also extensively mutilated, although her genitals had not been wounded. She appeared to have been killed approximately one day prior to the discovery of her torso. The dismembered sections of the body are believed to have been transported to the railway arch, hidden under an old chemise.
 At on 13 February 1891, PC Ernest Thompson discovered a 25-year-old prostitute named Frances Coles lying beneath a railway arch at Swallow Gardens, Whitechapel. Her throat had been deeply cut but her body was not mutilated, leading some to believe Thompson had disturbed her assailant. Coles was still alive, although she died before medical help could arrive. A 53-year-old stoker, James Thomas Sadler, had earlier been seen drinking with Coles, and the two are known to have argued approximately three hours before her death. Sadler was arrested by the police and charged with her murder. He was briefly thought to be the Ripper, but was later discharged from court for lack of evidence on 1891.Evans and Rumbelow, pp. 218–222; Evans and Skinner, ''The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook'', pp. 551–568
At on 13 February 1891, PC Ernest Thompson discovered a 25-year-old prostitute named Frances Coles lying beneath a railway arch at Swallow Gardens, Whitechapel. Her throat had been deeply cut but her body was not mutilated, leading some to believe Thompson had disturbed her assailant. Coles was still alive, although she died before medical help could arrive. A 53-year-old stoker, James Thomas Sadler, had earlier been seen drinking with Coles, and the two are known to have argued approximately three hours before her death. Sadler was arrested by the police and charged with her murder. He was briefly thought to be the Ripper, but was later discharged from court for lack of evidence on 1891.Evans and Rumbelow, pp. 218–222; Evans and Skinner, ''The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook'', pp. 551–568
Other alleged victims
In addition to the eleven Whitechapel murders, commentators have linked other attacks to the Ripper. In the case of "Fairy Fay", it is unclear whether this attack was real or fabricated as a part of Ripper lore.Evans, Stewart P.; Connell, Nicholas (2000). ''The Man Who Hunted Jack the Ripper''. "Fairy Fay" was a nickname given to an unidentified woman whose body was allegedly found in a doorway close to Commercial Road on 1887 "after a stake had been thrust through her abdomen", but there were no recorded murders in Whitechapel at or around Christmas 1887. "Fairy Fay" seems to have been created through a confused press report of the murder of Emma Elizabeth Smith, who had a stick or other blunt object shoved into her vagina. Most authors agree that the victim "Fairy Fay" never existed.Begg, ''Jack the Ripper: The Facts'', pp. 21–25 A 38-year-old widow named Annie Millwood was admitted to the Whitechapel Workhouse Infirmary with numerous stab wounds to her legs and lower torso on 1888, informing staff she had been attacked with a clasp knife by an unknown man. She was later discharged, but died from apparently natural causes on . Millwood was later postulated to be the Ripper's first victim, although this attack cannot be definitively linked to the perpetrator. Another suspected precanonical victim was a young dressmaker named Ada Wilson, who reportedly survived being stabbed twice in the neck with a clasp knife upon the doorstep of her home in Bow on 1888. A further possible victim, 40-year-old Annie Farmer, resided at the same lodging house as Martha Tabram and reported an attack on 1888. She had received a superficial cut to her throat. Although an unknown man with blood on his mouth and hands had run out of this lodging house, shouting, "Look at what she has done!" before two eyewitnesses heard Farmer scream, her wound was light, and possiblyself-inflicted
Self-Inflicted is the 8th album by Leæther Strip
Leæther Strip is a Danish musical project founded on 13 January 1988 by Claus Larsen. Its influence has been most felt in the electronic body music and electro-industrial genres. Leæther St ...
.
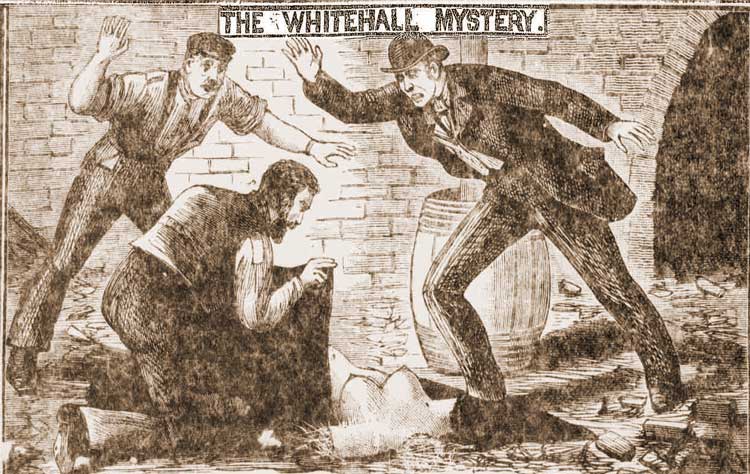
"The Whitehall Mystery
The Whitehall Mystery is an unsolved murder that took place in London in 1888. The dismembered remains of a woman were discovered at three sites in the centre of the city, including the construction site of Scotland Yard, the police headquarters ...
" was a term coined for the discovery of a headless torso of a woman on 1888 in the basement of the new Metropolitan Police headquarters being built in Whitehall. An arm and shoulder belonging to the body were previously discovered floating in the River Thames near Pimlico
Pimlico () is an area of Central London in the City of Westminster, built as a southern extension to neighbouring Belgravia. It is known for its garden squares and distinctive Regency architecture. Pimlico is demarcated to the north by London V ...
on 11 September, and the left leg was subsequently discovered buried near where the torso was found on 17 October. The other limbs and head were never recovered and the body was never identified. The mutilations were similar to those in the Pinchin Street torso case, where the legs and head were severed but not the arms.
 Both the Whitehall Mystery and the Pinchin Street case may have been part of a series of murders known as the " Thames Mysteries", committed by a single serial killer dubbed the "Torso killer". It is debatable whether Jack the Ripper and the "Torso killer" were the same person or separate serial killers active in the same area.Gordon, R. Michael (2002), ''The Thames Torso Murders of Victorian London'', Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland & Company, The ''modus operandi'' of the Torso killer differed from that of the Ripper, and police at the time discounted any connection between the two. Only one of the four victims linked to the Torso killer, Elizabeth Jackson, was ever identified. Jackson was a 24-year-old prostitute from Chelsea whose various body parts were collected from the River Thames over a three-week period between 31 May and 25 June 1889.
On 1888, the body of a seven-year-old boy named John Gill was found in a stable block in
Both the Whitehall Mystery and the Pinchin Street case may have been part of a series of murders known as the " Thames Mysteries", committed by a single serial killer dubbed the "Torso killer". It is debatable whether Jack the Ripper and the "Torso killer" were the same person or separate serial killers active in the same area.Gordon, R. Michael (2002), ''The Thames Torso Murders of Victorian London'', Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland & Company, The ''modus operandi'' of the Torso killer differed from that of the Ripper, and police at the time discounted any connection between the two. Only one of the four victims linked to the Torso killer, Elizabeth Jackson, was ever identified. Jackson was a 24-year-old prostitute from Chelsea whose various body parts were collected from the River Thames over a three-week period between 31 May and 25 June 1889.
On 1888, the body of a seven-year-old boy named John Gill was found in a stable block in Manningham, Bradford
Manningham is an historically industrial workers area as well as a council ward of Bradford, West Yorkshire, England.
The population of the 2011 Census for the Manningham Ward was 19,983.
History
Manningham holds a wealth of industrial hi ...
. Gill had been missing since 27 December. His legs had been severed, his abdomen opened, his intestines partly drawn out, and his heart and one ear removed. Similarities with the Ripper murders led to press speculation that the Ripper had killed him. The boy's employer, 23-year-old milkman William Barrett, was twice arrested for the murder but was released due to insufficient evidence
In a legal dispute, one party has the burden of proof to show that they are correct, while the other party had no such burden and is presumed to be correct. The burden of proof requires a party to produce evidence to establish the truth of facts ...
. No-one was ever prosecuted.Evans and Skinner, ''Jack the Ripper: Letters from Hell'', p. 136
Carrie Brown (nicknamed " Shakespeare", reportedly for her habit of quoting Shakespeare's sonnets) was strangled with clothing and then mutilated with a knife on 1891 in New York City. Her body was found with a large tear through her groin area and superficial cuts on her legs and back. No organs were removed from the scene, though an ovary was found upon the bed, either purposely removed or unintentionally dislodged. At the time, the murder was compared to those in Whitechapel, though the Metropolitan Police eventually ruled out any connection.Vanderlinden, Wolf (2003–04). "The New York Affair", in ''Ripper Notes'' part one No. 16 (July 2003); part two No. 17 (January 2004), part three No. 19 (July 2004 )
Investigation
 The vast majority of the
The vast majority of the City of London Police
The City of London Police is the territorial police force responsible for law enforcement within the City of London, including the Middle and Inner Temples. The force responsible for law enforcement within the remainder of the London region, ou ...
files relating to their investigation into the Whitechapel murders were destroyed in the Blitz. The surviving Metropolitan Police
The Metropolitan Police Service (MPS), formerly and still commonly known as the Metropolitan Police (and informally as the Met Police, the Met, Scotland Yard, or the Yard), is the territorial police force responsible for law enforcement and ...
files allow a detailed view of investigative procedures in the Victorian era. A large team of policemen conducted house-to-house inquiries throughout Whitechapel. Forensic material was collected and examined. Suspects were identified, traced, and either examined more closely or eliminated from the inquiry. Modern police work follows the same pattern. More than 2,000 people were interviewed, "upwards of 300" people were investigated, and 80 people were detained. Following the murders of Stride and Eddowes, the Commissioner of the City Police, Sir James Fraser, offered a reward of £500 for the arrest of the Ripper.
The investigation was initially conducted by the Metropolitan Police Whitechapel (H) Division Criminal Investigation Department (CID) headed by Detective Inspector Edmund Reid
Detective Inspector Edmund John James Reid (21 March 1846 – 5 December 1917) was the head of the CID in the Metropolitan Police's H Division at the time of the Whitechapel murders of Jack the Ripper in 1888. He was also an early aeronaut.' ...
. After the murder of Nichols, Detective Inspectors Frederick Abberline
Frederick George Abberline (8 January 1843 – 10 December 1929) was a British chief inspector for the London Metropolitan Police. He is best known for being a prominent police figure in the investigation into the Jack the Ripper serial killer ...
, Henry Moore
Henry Spencer Moore (30 July 1898 – 31 August 1986) was an English artist. He is best known for his semi- abstract monumental bronze sculptures which are located around the world as public works of art. As well as sculpture, Moore produced ...
, and Walter Andrews were sent from Central Office at Scotland Yard
Scotland Yard (officially New Scotland Yard) is the headquarters of the Metropolitan Police, the territorial police force responsible for policing Greater London's 32 boroughs, but not the City of London, the square mile that forms London's ...
to assist. The City of London Police were involved under Detective Inspector James McWilliam after the Eddowes murder, which occurred within the City of London. The overall direction of the murder enquiries was hampered by the fact that the newly appointed head of the CID Robert Anderson was on leave in Switzerland between and , during the time when Chapman, Stride, and Eddowes were killed. This prompted Metropolitan Police Commissioner Sir Charles Warren to appoint Chief Inspector Donald Swanson
Chief Inspector Donald Sutherland Swanson (12 August 1848 - 24 November 1924) was born at Geise, where his father operated a distillery, before the family moved in 1851 to Thurso, and was a senior police officer in the Metropolitan Police in Lond ...
to coordinate the enquiry from Scotland Yard.
Butchers, slaughterers, surgeons, and physicians were suspected because of the manner of the mutilations. A surviving note from Major Henry Smith, Acting Commissioner of the City Police
Municipal police, city police, or local police are Law enforcement agency, law enforcement agencies that are under the control of local government. This includes the Municipality, municipal government, where it is the smallest Administrat ...
, indicates that the alibis of local butchers and slaughterers were investigated, with the result that they were eliminated from the inquiry. A report from Inspector Swanson to the Home Office confirms that 76 butchers and slaughterers were visited, and that the inquiry encompassed all their employees for the previous six months. Some contemporaneous figures, including Queen Victoria, thought the pattern of the murders indicated that the culprit was a butcher or cattle drover on one of the cattle boats that plied between London and mainland Europe. Whitechapel was close to the London Docks, and usually such boats docked on Thursday or Friday and departed on Saturday or Sunday. The cattle boats were examined but the dates of the murders did not coincide with a single boat's movements and the transfer of a crewman between boats was also ruled out.

Whitechapel Vigilance Committee
In September 1888, a group of volunteer citizens inLondon's East End
The East End of London, often referred to within the London area simply as the East End, is the historic core of wider East London, east of the Roman and medieval walls of the City of London and north of the River Thames. It does not have uni ...
formed the Whitechapel Vigilance Committee. They patrolled the streets looking for suspicious characters, partly because of dissatisfaction with the failure of police to apprehend the perpetrator, and also because some members were concerned that the murders were affecting businesses in the area. The Committee petitioned the government to raise a reward for information leading to the arrest of the killer, offered their own reward of £50 (then a substantial sum) for information leading to his capture, and hired private detectives to question witnesses independently.
Criminal profiling
At the end of October, Robert Anderson asked police surgeon Thomas Bond to give his opinion on the extent of the murderer's surgical skill and knowledge. The opinion offered by Bond on the character of the "Whitechapel murderer" is the earliest surviving offender profile.Canter, pp. 5–6 Bond's assessment was based on his own examination of the most extensively mutilated victim and the post mortem notes from the four previous canonical murders.Letter from Thomas Bond to Robert Anderson, 1888, HO 144/221/A49301C, quoted in Evans and Skinner, ''The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook'', pp. 360–362 and Rumbelow, pp. 145–147 He wrote: Bond was strongly opposed to the idea that the murderer possessed any kind of scientific or anatomical knowledge, or even "the technical knowledge of a butcher or horse slaughterer". In his opinion, the killer must have been a man of solitary habits, subject to "periodical attacks of homicidal and eroticmania
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a mental and behavioral disorder defined as a state of abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level, or "a state of heightened overall activation with enhanced affective expression together wit ...
", with the character of the mutilations possibly indicating "satyriasis
Hypersexuality is extremely frequent or suddenly increased libido. It is controversial whether it should be included as a clinical diagnosis used by mental healthcare professionals. Nymphomania and satyriasis were terms previously used for the c ...
". Bond also stated that "the homicidal impulse may have developed from a revengeful or brooding condition of the mind, or that religious mania may have been the original disease but I do not think either hypothesis is likely".
There is no evidence the perpetrator engaged in sexual activity with any of the victims, yet psychologist
A psychologist is a professional who practices psychology and studies mental states, perceptual, cognitive, emotional, and social processes and behavior. Their work often involves the experimentation, observation, and interpretation of how indi ...
s suppose that the penetration of the victims with a knife and "leaving them on display in sexually degrading positions with the wounds exposed" indicates that the perpetrator derived sexual pleasure from the attacks. This view is challenged by others, who dismiss such hypotheses as insupportable supposition.
In addition to the contradictions and unreliability of contemporaneous accounts, attempts to identify the murderer are hampered by the lack of any surviving forensic evidence. DNA analysis
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
on extant letters is inconclusive; the available material has been handled many times and is too contaminated to provide meaningful results. There have been mutually incompatible claims that DNA evidence points conclusively to two different suspects, and the methodology of both has also been criticised.
Suspects
 The concentration of the killings around weekends and public holidays and within a short distance of each other has indicated to many that the Ripper was in regular employment and lived locally. Others have opined that the killer was an educated upper-class man, possibly a doctor or an
The concentration of the killings around weekends and public holidays and within a short distance of each other has indicated to many that the Ripper was in regular employment and lived locally. Others have opined that the killer was an educated upper-class man, possibly a doctor or an aristocrat
The aristocracy is historically associated with "hereditary" or "ruling" social class. In many states, the aristocracy included the upper class of people (aristocrats) with hereditary rank and titles. In some, such as ancient Greece, ancient Ro ...
who ventured into Whitechapel from a more well-to-do area. Such theories draw on cultural perceptions such as fear of the medical profession, a mistrust of modern science, or the exploitation of the poor by the rich. The term "Ripperology" was coined to describe the study and analysis of the Ripper case in an effort to determine his identity, and the murders have inspired numerous works of fiction.
Suspects proposed years after the murders include virtually anyone remotely connected to the case by contemporaneous documents, as well as many famous names who were never considered in the police investigation, including Prince Albert Victor
Prince Albert Victor, Duke of Clarence and Avondale (Albert Victor Christian Edward; 8 January 1864 – 14 January 1892) was the eldest child of the Prince and Princess of Wales (later King Edward VII and Queen Alexandra) and grandson of the re ...
, artist Walter Sickert, and author Lewis Carroll. Everyone alive at the time is now long dead, and modern authors are free to accuse anyone "without any need for any supporting historical evidence". Suspects named in contemporaneous police documents include three in Sir Melville Macnaghten's 1894 memorandum, but the evidence against each of these individuals is, at best, circumstantial.
There are many, varied theories about the actual identity and profession of Jack the Ripper, but authorities are not agreed upon any of them, and the number of named suspects reaches over one hundred.Whiteway, Ken (2004). "A Guide to the Literature of Jack the Ripper", ''Canadian Law Library Review'', vol. 29 pp. 219–229 Despite continued interest in the case, the Ripper's identity remains unknown.
Letters
Over the course of the Whitechapel murders, the police, newspapers, and other individuals received hundreds of letters regarding the case. Some letters were well-intentioned offers of advice as to how to catch the killer, but the vast majority were either hoaxes or generally useless. Hundreds of letters claimed to have been written by the killer himself, and three of these in particular are prominent: the "Dear Boss" letter, the"Saucy Jacky" postcard
The "Saucy Jacky" postcard is the name given to a postcard received by the Central News Agency of London and postmarked 1 October 1888. The author of the postcard claims to have been the unidentified serial killer known as Jack the Ripper.
Beca ...
and the "From Hell" letter.
The "Dear Boss" letter, dated and postmarked 1888, was received that day by the Central News Agency, and was forwarded to Scotland Yard
Scotland Yard (officially New Scotland Yard) is the headquarters of the Metropolitan Police, the territorial police force responsible for policing Greater London's 32 boroughs, but not the City of London, the square mile that forms London's ...
on . Initially, it was considered a hoax, but when Eddowes was found three days after the letter's postmark with a section of one ear obliquely cut from her body, the promise of the author to "clip the ladys ( sic) ears off" gained attention. Eddowes's ear appears to have been nicked by the killer incidentally during his attack, and the letter writer's threat to send the ears to the police was never carried out. The name "Jack the Ripper" was first used in this letter by the signatory and gained worldwide notoriety after its publication. Most of the letters that followed copied this letter's tone, with some authors adopting pseudonyms such as "George of the High Rip Gang" and "Jack Sheridan, the Ripper." Some sources claim that another letter dated 1888 was the first to use the name "Jack the Ripper", but most experts believe that this was a fake inserted into police records in the 20th century.
 The "Saucy Jacky" postcard was postmarked 1888 and was received the same day by the Central News Agency. The handwriting was similar to the "Dear Boss" letter, and mentioned the canonical murders committed on 30 September, which the author refers to by writing "double event this time". It has been argued that the postcard was posted before the murders were publicised, making it unlikely that a
The "Saucy Jacky" postcard was postmarked 1888 and was received the same day by the Central News Agency. The handwriting was similar to the "Dear Boss" letter, and mentioned the canonical murders committed on 30 September, which the author refers to by writing "double event this time". It has been argued that the postcard was posted before the murders were publicised, making it unlikely that a crank
Crank may refer to:
Mechanisms
* Crank (mechanism), in mechanical engineering, a bent portion of an axle or shaft, or an arm keyed at right angles to the end of a shaft, by which motion is imparted to or received from it
* Crankset, the compone ...
would hold such knowledge of the crime. However, it was postmarked more than 24 hours after the killings occurred, long after details of the murders were known and publicised by journalists, and had become general community gossip by the residents of Whitechapel.Cook, pp. 79–80; Fido, pp. 8–9; Marriott, Trevor, pp. 219–222; Rumbelow, p. 123
The "From Hell" letter was received by George Lusk
George Akin Lusk (1839–1919) was a British builder and decorator who specialised in music hall restoration, and was the chairman of the Whitechapel Vigilance Committee during the Whitechapel murders, including the killings ascribed to Jack th ...
, leader of the Whitechapel Vigilance Committee, on 1888. The handwriting and style is unlike that of the "Dear Boss" letter and "Saucy Jacky" postcard. The letter came with a small box in which Lusk discovered half of a human kidney, preserved in "spirits of wine" ( ethanol).Evans and Rumbelow, p. 170; Fido, pp. 78–80 Eddowes's left kidney had been removed by the killer. The writer claimed that he "fried and ate" the missing kidney half. There is disagreement over the kidney; some contend that it belonged to Eddowes, while others argue that it was a macabre practical joke. The kidney was examined by Dr Thomas Openshaw
Thomas Horrocks Openshaw (17 March 1856 – 17 November 1929) was an English Victorian and Edwardian era surgeon perhaps best known for his brief involvement in the notorious Jack the Ripper murders of 1888.
Early life and medical career
'To ...
of the London Hospital, who determined that it was human and from the left side, but (contrary to false newspaper reports) he could not determine any other biological characteristics. Openshaw subsequently also received a letter signed "Jack the Ripper".
Scotland Yard published facsimiles of the "Dear Boss" letter and the postcard on , in the ultimately vain hope that a member of the public would recognise the handwriting. Charles Warren explained in a letter to Godfrey Lushington, Permanent Under-Secretary of State for the Home Department: "I think the whole thing a hoax but of course we are bound to try & ascertain the writer in any case." On 1888, George R. Sims in the Sunday newspaper ''Referee
A referee is an official, in a variety of sports and competition, responsible for enforcing the rules of the sport, including sportsmanship decisions such as ejection. The official tasked with this job may be known by a variety of other titl ...
'' implied scathingly that the letter was written by a journalist "to hurl the circulation of a newspaper sky high". Police officials later claimed to have identified a specific journalist as the author of both the "Dear Boss" letter and the postcard. The journalist was identified as Tom Bullen in a letter from Chief Inspector John Littlechild
Detective Chief Inspector John George Littlechild (21 December 1848 – 2 January 1923) was the first commander of the London Metropolitan Police Special Irish Branch, renamed Special Branch in 1888.
Littlechild was born in Royston, Her ...
to George R. Sims dated 1913. A journalist named Fred Best reportedly confessed in 1931 that he and a colleague at ''The Star
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the m ...
'' had written the letters signed "Jack the Ripper" to heighten interest in the murders and "keep the business alive".
Media
 The Ripper murders mark an important watershed in the treatment of crime by journalists. Jack the Ripper was not the first serial killer, but his case was the first to create a worldwide media frenzy. Davenport-Hines, Richard (2004)
The Ripper murders mark an important watershed in the treatment of crime by journalists. Jack the Ripper was not the first serial killer, but his case was the first to create a worldwide media frenzy. Davenport-Hines, Richard (2004)"Jack the Ripper (fl. 1888)"
, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography''. Oxford University Press. Subscription required for online version.Woods and Baddeley, pp. 20, 52 The Elementary Education Act 1880 (which had extended upon a previous Act) made school attendance compulsory regardless of
class
Class or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used differentl ...
. As such, by 1888, more working-class
The working class (or labouring class) comprises those engaged in manual-labour occupations or industrial work, who are remunerated via waged or salaried contracts. Working-class occupations (see also " Designation of workers by collar colou ...
people in England and Wales were literate.
Tax reforms in the 1850s had enabled the publication of inexpensive newspapers with a wider circulation. These mushroomed in the later Victorian era to include mass-circulation newspapers costing as little as a halfpenny, along with popular magazines such as ''The Illustrated Police News
''The Illustrated Police News'' was a weekly illustrated newspaper which was one of the earliest British tabloids. It featured sensational and melodramatic reports and illustrations of murders and hangings and was a direct descendant of the exec ...
'' which made the Ripper the beneficiary of previously unparalleled publicity. Consequently, at the height of the investigation, over one million copies of newspapers with extensive coverage devoted to the Whitechapel murders were sold each day. However, many of the articles were sensationalistic
In journalism and mass media, sensationalism is a type of editorial tactic. Events and topics in news stories are selected and worded to excite the greatest number of readers and viewers. This style of news reporting encourages biased or emotion ...
and speculative, and false information was regularly printed as fact. In addition, several articles speculating as to the identity of the Ripper alluded to local xenophobic rumours that the perpetrator was either Jewish or foreign.
In early September, six days after the murder of Mary Ann Nichols, '' The Manchester Guardian'' reported: "Whatever information may be in the possession of the police they deem it necessary to keep secret ... It is believed their attention is particularly directed to ... a notorious character known as 'Leather Apron'." Journalists were frustrated by the unwillingness of the CID to reveal details of their investigation to the public, and so resorted to writing reports of questionable veracity. Imaginative descriptions of "Leather Apron" appeared in the press, but rival journalists dismissed these as "a mythical outgrowth of the reporter's fancy". John Pizer
A series of murders that took place in the East End of London from August to November 1888 was blamed on an unidentified assailant who was nicknamed Jack the Ripper. Since that time, the identity of the killer or killers has been widely debated, ...
, a local Jew who made footwear from leather, was known by the name "Leather Apron"e.g. Marriott, Trevor, p. 251; Rumbelow, p. 49 and was arrested, even though the investigating inspector reported that "at present there is no evidence whatsoever against him". He was soon released after the confirmation of his alibis.
After the publication of the "Dear Boss" letter, "Jack the Ripper" supplanted "Leather Apron" as the name adopted by the press and public to describe the killer. The name "Jack" was already used to describe another fabled London attacker: " Spring-heeled Jack", who supposedly leapt over walls to strike at his victims and escape as quickly as he came. The invention and adoption of a nickname for a particular killer became standard media practice with examples such as the Axeman of New Orleans, the Boston Strangler
The Boston Strangler is the name given to the murderer of 13 women in the Boston, Massachusetts, area during the early 1960s. The crimes were attributed to Albert DeSalvo based on his confession, details revealed in court during a separate case, ...
, and the Beltway Sniper
The D.C. sniper attacks (also known as the Beltway sniper attacks) were a series of coordinated shootings that occurred during three weeks in October 2002 throughout the Washington metropolitan area, consisting of the District of Columbia, Mary ...
. Examples derived from Jack the Ripper include the French Ripper, the Düsseldorf Ripper, the Camden Ripper, the Blackout Ripper
Gordon Frederick Cummins (18 February 1914 – 25 June 1942) was a British serial killer known as the Blackout Killer, the Blackout Ripper and the Wartime Ripper, who murdered four women and attempted to murder two others over a six-day period in ...
, Jack the Stripper
The Hammersmith nude murders is the name of a series of six murders in West London, England, in 1964 and 1965. The victims, all prostitutes, were found undressed in or near the River Thames, leading the press to nickname the killer Jack the Stri ...
, the Yorkshire Ripper, and the Rostov Ripper. Sensational press reports combined with the fact that no one was ever convicted of the murders have confused scholarly analysis and created a legend that casts a shadow over later serial killers.
Legacy
 The nature of the Ripper murders and the impoverished lifestyle of the victims drew attention to the poor living conditions in the East End and galvanised public opinion against the overcrowded, insanitary slums. In the two decades after the murders, the worst of the slums were cleared and demolished, but the streets and some buildings survive, and the legend of the Ripper is still promoted by various guided tours of the murder sites and other locations pertaining to the case. For many years, the Ten Bells public house in Commercial Street (which had been frequented by at least one of the canonical Ripper victims) was the focus of such tours.
In the immediate aftermath of the murders and later, "Jack the Ripper became the children's bogey man." Depictions were often phantasmic or monstrous. In the 1920s and 1930s, he was depicted in film dressed in everyday clothes as a man with a hidden secret, preying on his unsuspecting victims; atmosphere and evil were suggested through lighting effects and shadowplay. By the 1960s, the Ripper had become "the symbol of a predatory aristocracy",Bloom, Clive, "Jack the Ripper – A Legacy in Pictures", in Werner, p. 251 and was more often portrayed in a top hat dressed as a gentleman. The Establishment as a whole became the villain, with the Ripper acting as a manifestation of upper-class exploitation. The image of the Ripper merged with or borrowed symbols from horror stories, such as
The nature of the Ripper murders and the impoverished lifestyle of the victims drew attention to the poor living conditions in the East End and galvanised public opinion against the overcrowded, insanitary slums. In the two decades after the murders, the worst of the slums were cleared and demolished, but the streets and some buildings survive, and the legend of the Ripper is still promoted by various guided tours of the murder sites and other locations pertaining to the case. For many years, the Ten Bells public house in Commercial Street (which had been frequented by at least one of the canonical Ripper victims) was the focus of such tours.
In the immediate aftermath of the murders and later, "Jack the Ripper became the children's bogey man." Depictions were often phantasmic or monstrous. In the 1920s and 1930s, he was depicted in film dressed in everyday clothes as a man with a hidden secret, preying on his unsuspecting victims; atmosphere and evil were suggested through lighting effects and shadowplay. By the 1960s, the Ripper had become "the symbol of a predatory aristocracy",Bloom, Clive, "Jack the Ripper – A Legacy in Pictures", in Werner, p. 251 and was more often portrayed in a top hat dressed as a gentleman. The Establishment as a whole became the villain, with the Ripper acting as a manifestation of upper-class exploitation. The image of the Ripper merged with or borrowed symbols from horror stories, such as Dracula
''Dracula'' is a novel by Bram Stoker, published in 1897. As an epistolary novel, the narrative is related through letters, diary entries, and newspaper articles. It has no single protagonist, but opens with solicitor Jonathan Harker taking ...
's cloak or Victor Frankenstein's organ harvest. The fictional world of the Ripper can fuse with multiple genres, ranging from Sherlock Holmes
Sherlock Holmes () is a fictional detective created by British author Arthur Conan Doyle. Referring to himself as a " consulting detective" in the stories, Holmes is known for his proficiency with observation, deduction, forensic science and ...
to Japanese erotic horror.
Jack the Ripper features in hundreds of works of fiction and works which straddle the boundaries between fact and fiction, including the Ripper letters and a hoax diary: '' The Diary of Jack the Ripper''. The Ripper appears in novels, short stories, poems, comic books, games, songs, plays, operas, television programmes, and films. More than 100 non-fiction works deal exclusively with the Jack the Ripper murders, making this case one of the most written-about in the true-crime genre. The term "ripperology" was coined by Colin Wilson in the 1970s to describe the study of the case by professionals and amateurs. The periodicals ''Ripperana'', ''Ripperologist'', and ''Ripper Notes'' publish their research.
In 2006, a ''BBC History'' magazine poll selected Jack the Ripper as the worst Briton in history.
In 2015, the Jack the Ripper Museum
The Jack the Ripper Museum is a museum and tourist attraction that opened in August 2015 in Cable Street, London. It recreates the East end of London setting in which the unsolved Jack the Ripper murders took place in 1888, and exhibits some ori ...
opened in east London. It attracted criticism from both Tower Hamlets mayor John Biggs and protestors. Similar protests occurred in 2021 when the second of two "Jack The Chipper" fish and chip shops opened in Greenwich, with some patrons threatening to boycott the premises.
See also
*Jack the Ripper in fiction
Jack the Ripper, the notorious serial killer who terrorized Whitechapel in 1888, features in works of fiction ranging from gothic novels published at the time of the murders to modern motion pictures, televised dramas and video games.
Important ...
* List of fugitives from justice who disappeared
This is a list of fugitives from justice, notable people who disappeared or evaded capture while being sought by law enforcement agencies in connection with a crime, and who are currently sought or were sought for the duration of their presume ...
* List of murderers by number of victims
*''For serial killers see:'' List of serial killers by number of victims
*''For mass murderers and spree killers see:'' List of rampage killers
A rampage killer has been defined as follows:
This list should contain, for each category, the ...
* List of serial killers before 1900
References
Sources
* Begg, Paul (2003). ''Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History''. London: Pearson Education. * Begg, Paul (2004). ''Jack the Ripper: The Facts''. Barnes & Noble Books. * Bell, Neil R. A. (2016). ''Capturing Jack the Ripper: In the Boots of a Bobby in Victorian England''. Stroud: Amberley Publishing. * Cook, Andrew (2009). ''Jack the Ripper''. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Amberley Publishing. * Curtis, Lewis Perry (2001). ''Jack The Ripper & The London Press''. Yale University Press. * Eddleston, John J. (2002). ''Jack the Ripper: An Encyclopedia''. London: Metro Books. * Evans, Stewart P.; Rumbelow, Donald (2006). ''Jack the Ripper: Scotland Yard Investigates''. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Sutton Publishing. * Evans, Stewart P.; Skinner, Keith (2000). ''The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook: An Illustrated Encyclopedia''. London: Constable and Robinson. * Evans, Stewart P.; Skinner, Keith (2001). ''Jack the Ripper: Letters from Hell''. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Sutton Publishing. * Fido, Martin (1987), ''The Crimes, Detection and Death of Jack the Ripper'', London: Weidenfeld and Nicolson, * Gordon, R. Michael (2000). ''Alias Jack the Ripper: Beyond the Usual Whitechapel Suspects''. North Carolina: McFarland Publishing. * Holmes, Ronald M.; Holmes, Stephen T. (2002). ''Profiling Violent Crimes: An Investigative Tool''. Thousand Oaks, California: Sage Publications, Inc. * Honeycombe, Gordon (1982), ''The Murders of the Black Museum: 1870–1970'', London: Bloomsbury Books, * Lynch, Terry; Davies, David (2008). ''Jack the Ripper: The Whitechapel Murderer''. Hertfordshire: Wordsworth Editions. * Marriott, Trevor (2005). ''Jack the Ripper: The 21st Century Investigation''. London: John Blake. * Meikle, Denis (2002). ''Jack the Ripper: The Murders and the Movies''. Richmond, Surrey: Reynolds and Hearn Ltd. * Rivett, Miriam; Whitehead, Mark (2006). ''Jack the Ripper''. Harpenden, Hertfordshire: Pocket Essentials. * Rumbelow, Donald (1990). ''Jack the Ripper. The Complete Casebook''. New York City: Berkley Publishing Group. * Rumbelow, Donald (2004). ''The Complete Jack the Ripper. Fully Revised and Updated''. London: Penguin Books. * Sugden, Philip (2002). ''The Complete History of Jack the Ripper''. New York: Carroll & Graf Publishers. * Thurgood, Peter (2013). ''Abberline: The Man Who Hunted Jack the Ripper''. Cheltenham: The History Press Ltd. * Waddell, Bill (1993). ''The Black Museum: New Scotland Yard''. London: Little, Brown and Company. * Werner, Alex (editor, 2008). ''Jack the Ripper and the East End''. London: Chatto & Windus. * Whittington-Egan, Richard; Whittington-Egan, Molly (1992). ''The Murder Almanac''. Glasgow: Neil Wilson Publishing. * Whittington-Egan, Richard (2013). ''Jack the Ripper: The Definitive Casebook''. Stroud: Amberley Publishing. * Wilson, Colin; Odell, Robin; Gaute, J. H. H. (1988). ''Jack the Ripper: Summing up and Verdict''. London: Corgi Publishing. * Woods, Paul; Baddeley, Gavin (2009). ''Saucy Jack: The Elusive Ripper''. Hersham, Surrey: Ian Allan Publishing.External links
* * *Jack the Ripper
at casebook.org
Home page
of jack-the-ripper.org
Jack the Ripper: The 1888 Autumn of Terror
at whitechapeljack.com
Contemporaneous news article
pertaining to the murders committed by Jack the Ripper * 198
centennial investigation
into the murders committed by Jack the Ripper compiled by the
Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, t ...
* 201news article
focusing upon modern geographic profiling techniques used to discover the most likely location Jack the Ripper lived
Letters claiming to be from Jack the Ripper
at nationalarchives.gov.uk
Jack the Ripper
at the '' Encyclopædia Britannica'' * Articl
focusing upon the murders committed by Jack the Ripper
published by the Texas State University {{DEFAULTSORT:Jack the Ripper 1888 in London 19th-century English criminals Date of birth unknown Date of death unknown English serial killers History of the City of London History of the City of London Police History of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets History of the Metropolitan Police Murder in London Nicknames in crime People of the Victorian era Unidentified serial killers Unsolved murders in England Violence against sex workers in the United Kingdom Whitechapel