Anglo-Zulu War Of 1879 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Anglo-Zulu War was fought in 1879 between the
 By 1877, Sir Theophilus Shepstone, the British Secretary for Native Affairs in Natal, annexed the Transvaal Republic for Britain using a special warrant. The Transvaal Boers objected but as long as the Zulu threat remained, found themselves between two threats; they feared that if they took up arms to resist the British annexation, King Cetshwayo and the Zulus would take the opportunity to attack. The successive British annexations and in particular the annexation of West Griqualand caused a climate of simmering unease for the Boer republics.
Shepstone railed against the disruptive effect of allowing Cetshwayo's regime to remain. "Zulu power", he said, "is the root and real strength of all native difficulties in South Africa". In December 1877, he wrote to Carnarvon "Cetshwayo is the secret hope of every petty independent chief hundreds of miles from him who feels a desire that his colour shall prevail, and it will not be until this hope is destroyed that they will make up their minds to submit to the rule of civilisation". Earlier in October 1877, Shepstone had attended a meeting with Zulu leaders near the Blood River to resolve the land dispute between the Zulus and the Boers. He suggested a compromise with the Boers and the meeting broke up without clear resolutions. He turned against the Zulus with vengeance, saying he had come into possession of "the most incontrovertible, overwhelming and clear evidence" never previously disclosed, for supporting the claims of the Boers. He rejected Zulu claims as "characterised by lying and treachery to an extent that I could not have believed even savages are capable of".
Shepstone, in his capacity as British governor of Natal, had expressed concerns about the Zulu army under King Cetshwayo and the potential threat to Natal – especially given the adoption by some of the Zulus of old muskets and other out-of-date firearms. In his new role of Administrator of the Transvaal, he was now responsible for protecting the Transvaal and had direct involvement in the Zulu border dispute from the side of the Transvaal. Persistent Boer representations and
By 1877, Sir Theophilus Shepstone, the British Secretary for Native Affairs in Natal, annexed the Transvaal Republic for Britain using a special warrant. The Transvaal Boers objected but as long as the Zulu threat remained, found themselves between two threats; they feared that if they took up arms to resist the British annexation, King Cetshwayo and the Zulus would take the opportunity to attack. The successive British annexations and in particular the annexation of West Griqualand caused a climate of simmering unease for the Boer republics.
Shepstone railed against the disruptive effect of allowing Cetshwayo's regime to remain. "Zulu power", he said, "is the root and real strength of all native difficulties in South Africa". In December 1877, he wrote to Carnarvon "Cetshwayo is the secret hope of every petty independent chief hundreds of miles from him who feels a desire that his colour shall prevail, and it will not be until this hope is destroyed that they will make up their minds to submit to the rule of civilisation". Earlier in October 1877, Shepstone had attended a meeting with Zulu leaders near the Blood River to resolve the land dispute between the Zulus and the Boers. He suggested a compromise with the Boers and the meeting broke up without clear resolutions. He turned against the Zulus with vengeance, saying he had come into possession of "the most incontrovertible, overwhelming and clear evidence" never previously disclosed, for supporting the claims of the Boers. He rejected Zulu claims as "characterised by lying and treachery to an extent that I could not have believed even savages are capable of".
Shepstone, in his capacity as British governor of Natal, had expressed concerns about the Zulu army under King Cetshwayo and the potential threat to Natal – especially given the adoption by some of the Zulus of old muskets and other out-of-date firearms. In his new role of Administrator of the Transvaal, he was now responsible for protecting the Transvaal and had direct involvement in the Zulu border dispute from the side of the Transvaal. Persistent Boer representations and
 Shaka Zulu, the first Zulu king, had through war and conquest built the small Zulu tribe into the
Shaka Zulu, the first Zulu king, had through war and conquest built the small Zulu tribe into the 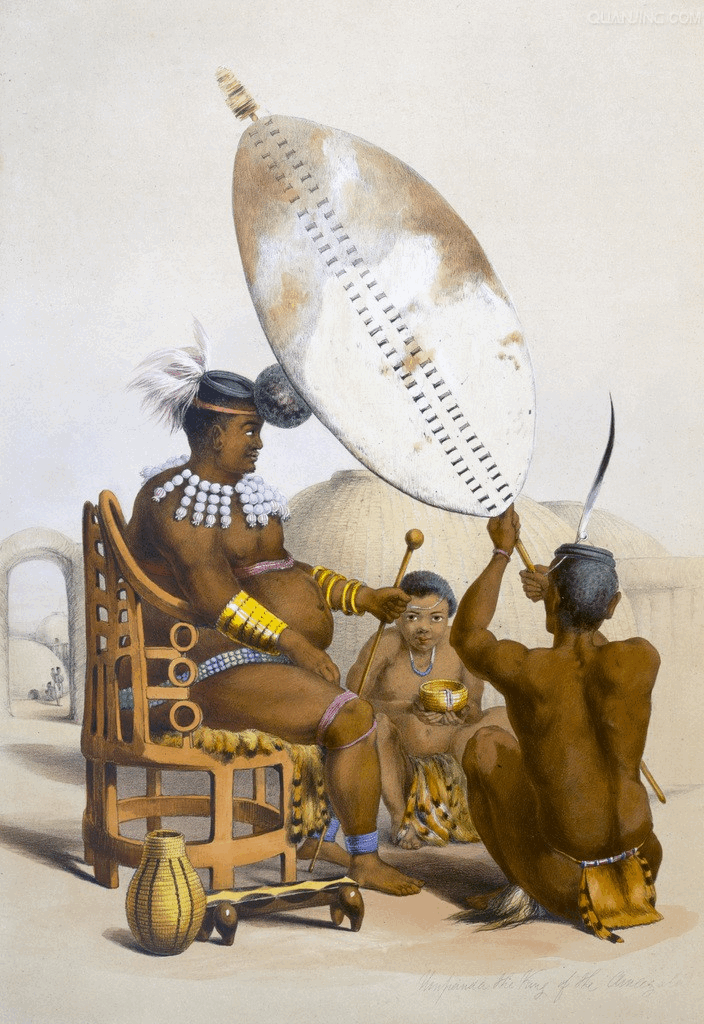 In 1843, Mpande ordered a purge of perceived dissidents within his kingdom. This resulted in numerous deaths, and the fleeing of thousands of refugees into neighbouring areas, including the British-controlled Natal. Many of these refugees fled with cattle, the main measure of the Zulu wealth. Mpande began raiding the surrounding areas, culminating in the invasion of
In 1843, Mpande ordered a purge of perceived dissidents within his kingdom. This resulted in numerous deaths, and the fleeing of thousands of refugees into neighbouring areas, including the British-controlled Natal. Many of these refugees fled with cattle, the main measure of the Zulu wealth. Mpande began raiding the surrounding areas, culminating in the invasion of  The boundary was beaconed in 1864, but when in 1865 Umtonga again fled from Zululand to Natal, Cetshwayo, seeing that he had lost his part of the bargain (for he feared that the still living Umtonga might be used to supplant him, as Mpande had been used to supplant
The boundary was beaconed in 1864, but when in 1865 Umtonga again fled from Zululand to Natal, Cetshwayo, seeing that he had lost his part of the bargain (for he feared that the still living Umtonga might be used to supplant him, as Mpande had been used to supplant
 After considerable discussion and exchanges of views between Sir Bartle Frere and Sir
After considerable discussion and exchanges of views between Sir Bartle Frere and Sir
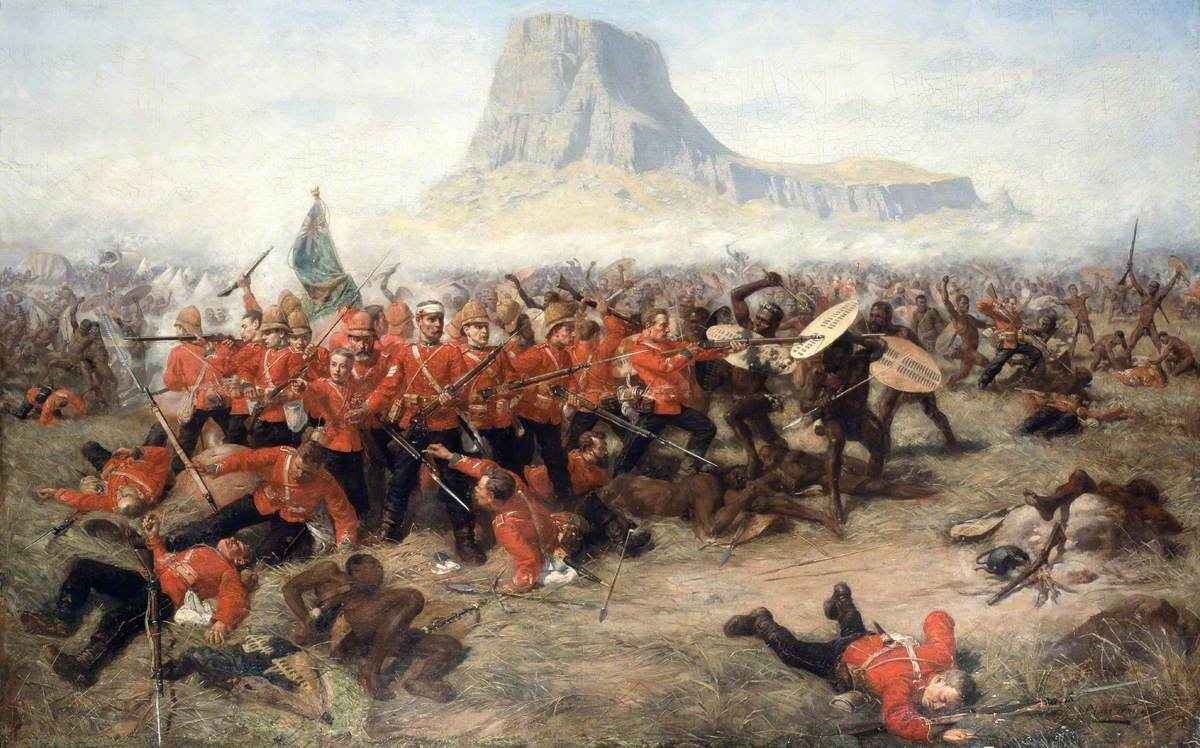

 The pretext for the war had its origins in border disputes between the Zulu leader, Cetshwayo, and the
The pretext for the war had its origins in border disputes between the Zulu leader, Cetshwayo, and the  While the British central column under Chelmsford's command was thus engaged, the right flank column on the coast, under Colonel
While the British central column under Chelmsford's command was thus engaged, the right flank column on the coast, under Colonel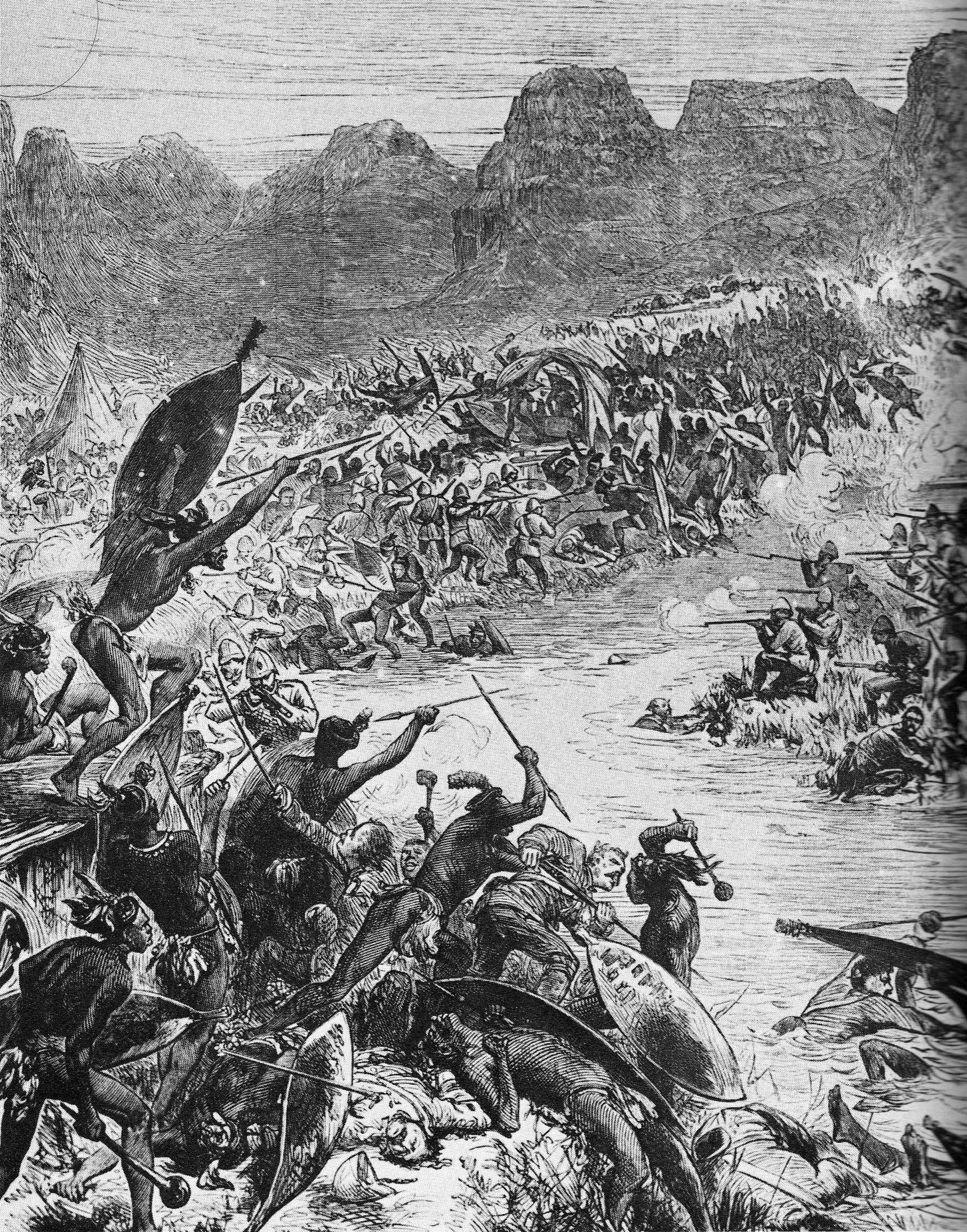  It had never been Cetshwayo's intention to invade Natal, but to simply fight within the boundaries of the Zulu kingdom. Chelmsford used the next two months to regroup and build a fresh invading force with the initial intention of relieving Pearson at Eshowe. The British government rushed seven regiments of reinforcements to Natal, along with two artillery batteries.
On 12 March, an armed escort of stores marching to Luneberg, was defeated by about 500 Zulus at the
It had never been Cetshwayo's intention to invade Natal, but to simply fight within the boundaries of the Zulu kingdom. Chelmsford used the next two months to regroup and build a fresh invading force with the initial intention of relieving Pearson at Eshowe. The British government rushed seven regiments of reinforcements to Natal, along with two artillery batteries.
On 12 March, an armed escort of stores marching to Luneberg, was defeated by about 500 Zulus at the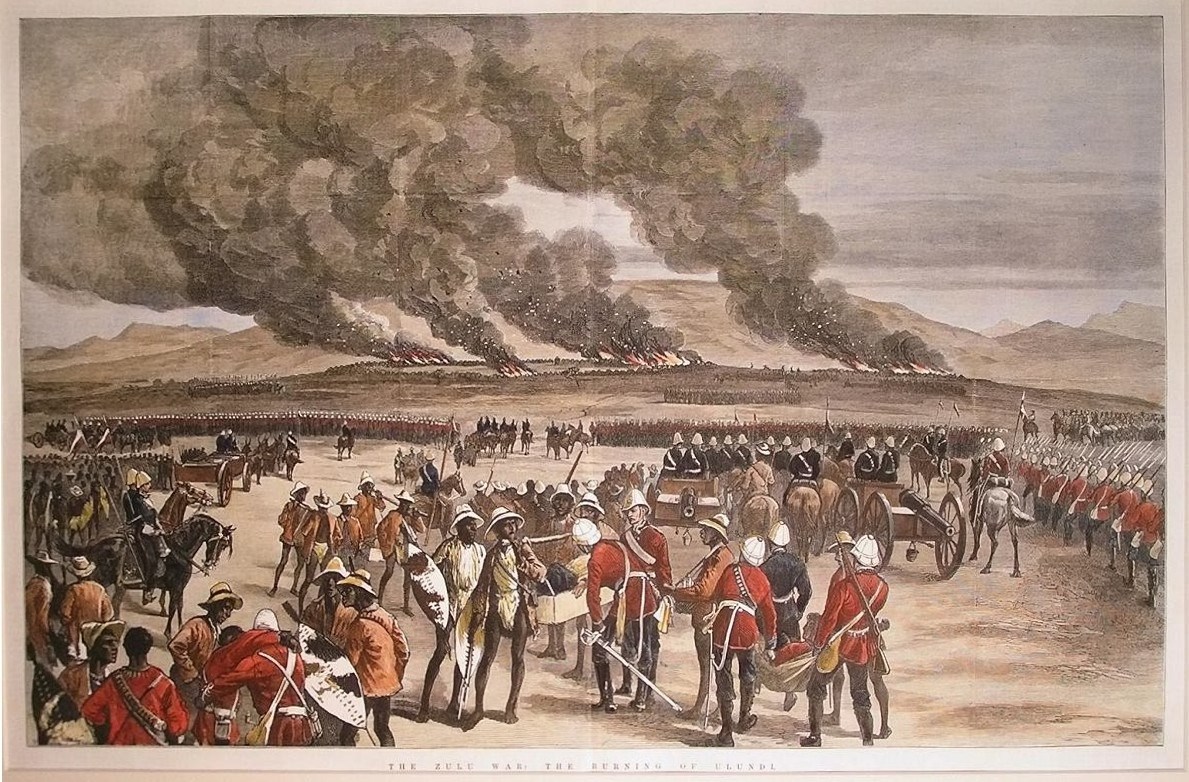  While Woods was thus engaged, Chelmsford's column was marching on Eshowe. On 2 April this force was attacked en route at
While Woods was thus engaged, Chelmsford's column was marching on Eshowe. On 2 April this force was attacked en route at
 The new start of the larger, heavily reinforced second invasion was not promising for the British. Despite their successes at Kambula, Gingindlovu and Eshowe, they were right back where they had started from at the beginning of January. Nevertheless, Chelmsford had a pressing reason to proceed with haste – Sir Garnet Wolseley was being sent to replace him, and he wanted to inflict a decisive defeat on Cetshwayo's forces before then. With yet more reinforcements arriving, soon to total 16,000 British and 7,000 Native troops, Chelmsford reorganised his forces and again advanced into Zululand in June, this time with extreme caution building fortified camps all along the way to prevent any repeat of Isandlwana.
One of the early British casualties was the exiled heir to the French throne, Imperial Prince Napoleon Eugene, who had volunteered to serve in the British army and was killed on 1 June while out with a reconnoitering party.
Cetshwayo, knowing that the newly reinforced British would be a formidable opponent, attempted to negotiate a peace treaty. Chelmsford was not open to negotiations, as he wished to restore his reputation before Wolseley relieved him of command, and he proceeded to the royal kraal of Ulundi, intending to defeat the main Zulu army. On 4 July, the armies clashed at the
The new start of the larger, heavily reinforced second invasion was not promising for the British. Despite their successes at Kambula, Gingindlovu and Eshowe, they were right back where they had started from at the beginning of January. Nevertheless, Chelmsford had a pressing reason to proceed with haste – Sir Garnet Wolseley was being sent to replace him, and he wanted to inflict a decisive defeat on Cetshwayo's forces before then. With yet more reinforcements arriving, soon to total 16,000 British and 7,000 Native troops, Chelmsford reorganised his forces and again advanced into Zululand in June, this time with extreme caution building fortified camps all along the way to prevent any repeat of Isandlwana.
One of the early British casualties was the exiled heir to the French throne, Imperial Prince Napoleon Eugene, who had volunteered to serve in the British army and was killed on 1 June while out with a reconnoitering party.
Cetshwayo, knowing that the newly reinforced British would be a formidable opponent, attempted to negotiate a peace treaty. Chelmsford was not open to negotiations, as he wished to restore his reputation before Wolseley relieved him of command, and he proceeded to the royal kraal of Ulundi, intending to defeat the main Zulu army. On 4 July, the armies clashed at the
Rorke's Drift and the Anglo–Zulu War website
Anglo–Zulu War Historical Society
The Keynsham Light Horse
by Ralph Zuljan {{Authority control 1879 in the British Empire 1879 in the Colony of Natal 1879 in the Zulu Kingdom African resistance to colonialism Battles involving the Zulu History of KwaZulu-Natal Invasions by the United Kingdom Last stands Military history of South Africa Wars involving the states and peoples of Africa Zulu British colonisation in Africa
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
and the Zulu Kingdom
The Zulu Kingdom (, ), sometimes referred to as the Zulu Empire or the Kingdom of Zululand, was a monarchy in Southern Africa. During the 1810s, Shaka established a modern standing army that consolidated rival clans and built a large following ...
. Following the passing of the British North America Act of 1867
The ''Constitution Act, 1867'' (french: Loi constitutionnelle de 1867),''The Constitution Act, 1867'', 30 & 31 Victoria (U.K.), c. 3, http://canlii.ca/t/ldsw retrieved on 2019-03-14. originally enacted as the ''British North America Act, 186 ...
forming a federation in Canada, Lord Carnarvon
Earl of Carnarvon is a title that has been created three times in British history. The current holder is George Herbert, 8th Earl of Carnarvon. The town and county in Wales to which the title refers are historically spelled ''Caernarfon,'' havi ...
thought that a similar political effort, coupled with military campaigns, might succeed with the African Kingdoms, tribal areas and Boer republics in South Africa. In 1874, Sir Bartle Frere was sent to South Africa as High Commissioner for the British Empire to effect such plans. Among the obstacles were the armed independent states of the South African Republic
The South African Republic ( nl, Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek, abbreviated ZAR; af, Suid-Afrikaanse Republiek), also known as the Transvaal Republic, was an independent Boer Republic in Southern Africa which existed from 1852 to 1902, when it ...
and the Kingdom of Zululand.Knight (1992, 2002), p. 8.
Frere, on his own initiative, sent a provocative ultimatum
An ultimatum (; ) is a demand whose fulfillment is requested in a specified period of time and which is backed up by a threat to be followed through in case of noncompliance (open loop). An ultimatum is generally the final demand in a series o ...
on 11 December 1878 to the Zulu king Cetshwayo and upon its rejection sent Lord Chelmsford
Viscount Chelmsford, of Chelmsford in the County of Essex, is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. It was created in 1921 for Frederic Thesiger, 3rd Baron Chelmsford, the former Viceroy of India. The title of Baron Chelmsford, of Chelm ...
to invade Zululand. The war is notable for several particularly bloody battles, including an opening victory of the Zulu at the Battle of Isandlwana
The Battle of Isandlwana (alternative spelling: Isandhlwana) on 22 January 1879 was the first major encounter in the Anglo-Zulu War between the British Empire and the Zulu Kingdom. Eleven days after the British commenced their invasion of Zulul ...
, followed by the defence of Rorke's Drift
The Battle of Rorke's Drift (1879), also known as the Defence of Rorke's Drift, was an engagement in the Anglo-Zulu War. The successful British defence of the mission station of Rorke's Drift, under the command of Lieutenants John Chard of the ...
by a small British force from attack by a large Zulu force. The British eventually won the war, ending Zulu dominance of the region.
Background
British Empire
By the 1850s, theBritish Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
had colonies in southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number of ...
bordering on various Boer settlements, native African kingdoms such as the Zulus and the Basotho and numerous indigenous tribal areas and states. Various interactions with those groups followed an expansionist policy. Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British Empire, British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope, which existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when i ...
was formed after the Anglo–Dutch Treaty of 1814 had permanently ceded the Dutch colony of Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
to Britain, and its territory expanded very substantially in the 19th century. Natal, in south-eastern Africa, was proclaimed a British colony on 4 May 1843, after the British government had annexed the Boer Republic of Natalia. Matters were brought to a head when three sons (led by Mehlokazulu kaSihayo) and a brother of the Zulu inkosi Sihayo organized a raid into Natal and carried off two women who were under British protection.
The discovery of diamonds in 1867 near the Vaal River, some northeast of Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
, ended the isolation of the Boers in the interior and had a significant effect on events. The discovery triggered a diamond rush that attracted people from all over the world, which turned Kimberley
Kimberly or Kimberley may refer to:
Places and historical events
Australia
* Kimberley (Western Australia)
** Roman Catholic Diocese of Kimberley
* Kimberley Warm Springs, Tasmania
* Kimberley, Tasmania a small town
* County of Kimberley, a ...
into a town of 50,000 within five years and drew the attention of British imperial interests. In the 1870s, the British annexed West Griqualand
Griqualand West is an area of central South Africa with an area of 40,000 km2 that now forms part of the Northern Cape Province. It was inhabited by the Griqua people – a semi-nomadic, Afrikaans-speaking nation of mixed-race origin, wh ...
, site of the Kimberley diamond discoveries.
In 1874 Lord Carnarvon
Earl of Carnarvon is a title that has been created three times in British history. The current holder is George Herbert, 8th Earl of Carnarvon. The town and county in Wales to which the title refers are historically spelled ''Caernarfon,'' havi ...
, Secretary of State for the Colonies
The secretary of state for the colonies or colonial secretary was the Cabinet of the United Kingdom, British Cabinet government minister, minister in charge of managing the United Kingdom's various British Empire, colonial dependencies.
Histor ...
, who had brought about federation in Canada in 1867, thought that a similar scheme might work in South Africa. The South African plan called for a ruling white minority over a black majority, which would provide a large pool of cheap labour for the British sugar plantations and mines. Carnarvon, in an attempt to extend British influence in 1875, approached the Boer states of the Orange Free State
The Orange Free State ( nl, Oranje Vrijstaat; af, Oranje-Vrystaat;) was an independent Boer sovereign republic under British suzerainty in Southern Africa during the second half of the 19th century, which ceased to exist after it was defeat ...
and the Transvaal Republic
The South African Republic ( nl, Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek, abbreviated ZAR; af, Suid-Afrikaanse Republiek), also known as the Transvaal Republic, was an independent Boer Republic in Southern Africa which existed from 1852 to 1902, when it ...
and tried to organize a federation of the British and Boer territories but the Boer leaders turned him down.
In 1877, Sir Bartle Frere was made High Commissioner for Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number of ...
by Lord Carnarvon. Carnarvon appointed Frere to the position on the understanding that he would work to enforce Carnarvon's confederation plan and Frere could then become the first British governor of a federated southern African dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 1926 ...
. Frere was sent to South Africa as High Commissioner to bring this plan about. One of the obstacles to such a scheme was the presence of the independent Boer states of the South African Republic
The South African Republic ( nl, Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek, abbreviated ZAR; af, Suid-Afrikaanse Republiek), also known as the Transvaal Republic, was an independent Boer Republic in Southern Africa which existed from 1852 to 1902, when it ...
, informally known as the Transvaal Republic and the Orange Free State, and the Kingdom of Zululand. Bartle Frere wasted no time in putting the scheme forward and manufacturing a casus belli
A (; ) is an act or an event that either provokes or is used to justify a war. A ''casus belli'' involves direct offenses or threats against the nation declaring the war, whereas a ' involves offenses or threats against its ally—usually one b ...
against the Zulu by exaggerating the significance of a number of recent incidents.
 By 1877, Sir Theophilus Shepstone, the British Secretary for Native Affairs in Natal, annexed the Transvaal Republic for Britain using a special warrant. The Transvaal Boers objected but as long as the Zulu threat remained, found themselves between two threats; they feared that if they took up arms to resist the British annexation, King Cetshwayo and the Zulus would take the opportunity to attack. The successive British annexations and in particular the annexation of West Griqualand caused a climate of simmering unease for the Boer republics.
Shepstone railed against the disruptive effect of allowing Cetshwayo's regime to remain. "Zulu power", he said, "is the root and real strength of all native difficulties in South Africa". In December 1877, he wrote to Carnarvon "Cetshwayo is the secret hope of every petty independent chief hundreds of miles from him who feels a desire that his colour shall prevail, and it will not be until this hope is destroyed that they will make up their minds to submit to the rule of civilisation". Earlier in October 1877, Shepstone had attended a meeting with Zulu leaders near the Blood River to resolve the land dispute between the Zulus and the Boers. He suggested a compromise with the Boers and the meeting broke up without clear resolutions. He turned against the Zulus with vengeance, saying he had come into possession of "the most incontrovertible, overwhelming and clear evidence" never previously disclosed, for supporting the claims of the Boers. He rejected Zulu claims as "characterised by lying and treachery to an extent that I could not have believed even savages are capable of".
Shepstone, in his capacity as British governor of Natal, had expressed concerns about the Zulu army under King Cetshwayo and the potential threat to Natal – especially given the adoption by some of the Zulus of old muskets and other out-of-date firearms. In his new role of Administrator of the Transvaal, he was now responsible for protecting the Transvaal and had direct involvement in the Zulu border dispute from the side of the Transvaal. Persistent Boer representations and
By 1877, Sir Theophilus Shepstone, the British Secretary for Native Affairs in Natal, annexed the Transvaal Republic for Britain using a special warrant. The Transvaal Boers objected but as long as the Zulu threat remained, found themselves between two threats; they feared that if they took up arms to resist the British annexation, King Cetshwayo and the Zulus would take the opportunity to attack. The successive British annexations and in particular the annexation of West Griqualand caused a climate of simmering unease for the Boer republics.
Shepstone railed against the disruptive effect of allowing Cetshwayo's regime to remain. "Zulu power", he said, "is the root and real strength of all native difficulties in South Africa". In December 1877, he wrote to Carnarvon "Cetshwayo is the secret hope of every petty independent chief hundreds of miles from him who feels a desire that his colour shall prevail, and it will not be until this hope is destroyed that they will make up their minds to submit to the rule of civilisation". Earlier in October 1877, Shepstone had attended a meeting with Zulu leaders near the Blood River to resolve the land dispute between the Zulus and the Boers. He suggested a compromise with the Boers and the meeting broke up without clear resolutions. He turned against the Zulus with vengeance, saying he had come into possession of "the most incontrovertible, overwhelming and clear evidence" never previously disclosed, for supporting the claims of the Boers. He rejected Zulu claims as "characterised by lying and treachery to an extent that I could not have believed even savages are capable of".
Shepstone, in his capacity as British governor of Natal, had expressed concerns about the Zulu army under King Cetshwayo and the potential threat to Natal – especially given the adoption by some of the Zulus of old muskets and other out-of-date firearms. In his new role of Administrator of the Transvaal, he was now responsible for protecting the Transvaal and had direct involvement in the Zulu border dispute from the side of the Transvaal. Persistent Boer representations and Paul Kruger
Stephanus Johannes Paulus Kruger (; 10 October 1825 – 14 July 1904) was a South African politician. He was one of the dominant political and military figures in 19th-century South Africa, and President of the South African Republic (or ...
's diplomatic manoeuvres added to the pressure. There were incidents involving Zulu paramilitary actions on either side of the Transvaal/Natal border, and Shepstone increasingly began to regard King Cetshwayo, as having permitted such "outrages", and to be in a "defiant mood". King Cetshwayo now found no defender in Natal save the bishop of Natal, John Colenso
John William Colenso (24 January 1814 – 20 June 1883) was a Cornish cleric and mathematician, defender of the Zulu and biblical scholar, who served as the first Bishop of Natal. He was a scholar of the Zulu language. In his role as an Angl ...
.
Colenso advocated for native Africans in Natal and Zululand who had been unjustly treated by the colonial regime in Natal. In 1874 he took up the cause of Langalibalele and the Hlubi and Ngwe tribes in representations to the Colonial Secretary, Lord Carnarvon. Langalibalele had been falsely accused of rebellion in 1873 and, following a charade of a trial, was found guilty and imprisoned on Robben Island
Robben Island ( af, Robbeneiland) is an island in Table Bay, 6.9 kilometres (4.3 mi) west of the coast of Bloubergstrand, north of Cape Town, South Africa. It takes its name from the Dutch word for seals (''robben''), hence the Dutch/Afrik ...
. In taking the side of Langalibalele against the colonial regime in Natal and Theophilus Shepstone, the Secretary for Native Affairs, Colenso found himself even further estranged from colonial society in Natal.
Bishop Colenso's concern about the misleading information that was being provided to the Colonial Secretary in London by Shepstone and the Governor of Natal prompted him to champion the cause of the Zulus against Boer oppression and official encroachments. He was a prominent critic of Frere's efforts to depict the Zulu kingdom as a threat to Natal. Colenso's campaigns revealed the racialist foundation underpinning the colonial regime in Natal and made him enemies among the colonists.
British Prime Minister Benjamin Disraeli
Benjamin Disraeli, 1st Earl of Beaconsfield, (21 December 1804 – 19 April 1881) was a British statesman and Conservative politician who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. He played a central role in the creation o ...
's Tory administration in London did not want a war with the Zulus. "The fact is," wrote Sir Michael Hicks Beach
Michael Edward Hicks Beach, 1st Earl St Aldwyn, (23 October 1837 – 30 April 1916), known as Sir Michael Hicks Beach, Bt, from 1854 to 1906 and subsequently as The Viscount St Aldwyn to 1915, was a British Conservative politician. Known as " ...
, who would replace Carnarvon as Secretary of State for the Colonies, in November 1878, "that matters in Eastern Europe and India ... wore so serious an aspect that we cannot have a Zulu war in addition to other greater and too possible troubles." However, Sir Bartle Frere had already been into the Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British Empire, British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope, which existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when i ...
as governor and High Commissioner since 1877 with the brief of creating a Confederation of South Africa from the various British colonies, Boer Republics and native states and his plans were well advanced. He had concluded that the powerful Zulu kingdom stood in the way of this, and so was receptive to Shepstone's arguments that King Cetshwayo and his Zulu army posed a threat to the peace of the region. Preparations for a British invasion of the Zulu kingdom had been underway for months. In December 1878, notwithstanding the reluctance of the British government to start yet another colonial war, Frere presented Cetshwayo with an ultimatum that the Zulu army be disbanded and the Zulus accept a British resident. This was unacceptable to the Zulus as it effectively meant that Cetshwayo, had he agreed, would have lost his throne.
Zulu Kingdom
 Shaka Zulu, the first Zulu king, had through war and conquest built the small Zulu tribe into the
Shaka Zulu, the first Zulu king, had through war and conquest built the small Zulu tribe into the Zulu Kingdom
The Zulu Kingdom (, ), sometimes referred to as the Zulu Empire or the Kingdom of Zululand, was a monarchy in Southern Africa. During the 1810s, Shaka established a modern standing army that consolidated rival clans and built a large following ...
, which by 1825 encompassed an area of around . In 1828 he was assassinated at Dukuza by one of his inDunas and two of his half-brothers, one of whom, Dinggh kaSenzangakhona, succeeded him as king. By the 1830s migrating Boers came into conflict with the Zulu Kingdom, then ruled by Dingane. Dingane suffered a crushing defeat on 16 December 1838, when he attacked a group of 470 Voortrekker settlers led by Pretorius
Pretorius is a common Afrikaans surname.
Recorded in several forms (including ''Praetor'', ''Praetorius'', ''Pratorius'', ''Pretorius'', (German), and in English ''Preater'', ''Preter'' and ''Pretor''), Pretorius is a surname of Germanic origins, ...
at the Battle of Blood River
The Battle of Blood River (16 December 1838) was fought on the bank of the Ncome River, in what is today KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa between 464 Voortrekkers ("Pioneers"), led by Andries Pretorius, and an estimated 10,000 to 15,000 Zulu. Est ...
. Dingane's half brother, Mpande kaSenzangakhona
Mpande kaSenzangakhona (1798–18 October 1872) was monarch of the Zulu Kingdom from 1840 to 1872. He was a half-brother of Sigujana, Shaka and Dingane, who preceded him as Zulu kings. He came to power after he had overthrown Dingane in 1840.
...
, then defected with some 17,000 followers and allied with the Boers against Dingane. Dingane was assassinated and Mpande became king of the Zulu empire.
In 1839, the Boer Voortrekkers, under Pretorius, formed the Boer Republic of Natalia, south of the Tugela, and west of the British settlement of Port Natal (now Durban). Mpande and Pretorius maintained peaceful relations. However, in 1842, war broke out between the British and the Boers, resulting in the British annexation of Natalia. Mpande shifted his allegiance to the British, and remained on good terms with them.
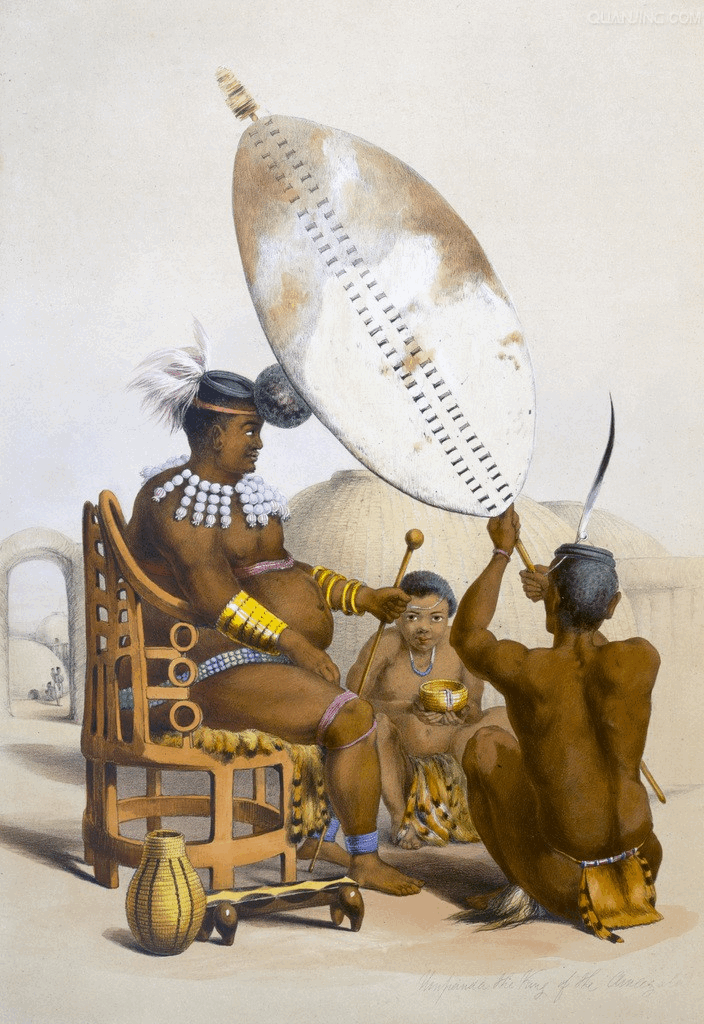 In 1843, Mpande ordered a purge of perceived dissidents within his kingdom. This resulted in numerous deaths, and the fleeing of thousands of refugees into neighbouring areas, including the British-controlled Natal. Many of these refugees fled with cattle, the main measure of the Zulu wealth. Mpande began raiding the surrounding areas, culminating in the invasion of
In 1843, Mpande ordered a purge of perceived dissidents within his kingdom. This resulted in numerous deaths, and the fleeing of thousands of refugees into neighbouring areas, including the British-controlled Natal. Many of these refugees fled with cattle, the main measure of the Zulu wealth. Mpande began raiding the surrounding areas, culminating in the invasion of Swaziland
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
in 1852. However, the British pressured him into withdrawing, which he did shortly afterwards. At this time, a battle for the succession broke out between two of Mpande's sons, Cetshwayo and Mbuyazi. This culminated in 1856 with the Battle of Ndondakusuka, which left Mbuyazi dead. Cetshwayo then set about usurping his father's authority. When Mpande died of old age in 1872, Cetshwayo took over as ruler.
In 1861, Umtonga, another son of Mpande
Mpande kaSenzangakhona (1798–18 October 1872) was monarch of the Zulu Kingdom from 1840 to 1872. He was a half-brother of Sigujana, Shaka and Dingane, who preceded him as Zulu kings. He came to power after he had overthrown Dingane in 1840.
...
, fled to the Utrecht district, prompting Cetshwayo to assemble an army on the nearby frontier. According to claims later brought forward by the Boers, Cetshwayo offered the farmers a strip of land along the border if they would surrender his brother. The Boers complied on the condition that Umtonga's life was spared, and in 1861 Mpande signed a deed transferring this land to the Boers. The south boundary of the land added to Utrecht ran from Rorke's Drift
The Battle of Rorke's Drift (1879), also known as the Defence of Rorke's Drift, was an engagement in the Anglo-Zulu War. The successful British defence of the mission station of Rorke's Drift, under the command of Lieutenants John Chard of the ...
on the Buffalo to a point on the Pongola River.
 The boundary was beaconed in 1864, but when in 1865 Umtonga again fled from Zululand to Natal, Cetshwayo, seeing that he had lost his part of the bargain (for he feared that the still living Umtonga might be used to supplant him, as Mpande had been used to supplant
The boundary was beaconed in 1864, but when in 1865 Umtonga again fled from Zululand to Natal, Cetshwayo, seeing that he had lost his part of the bargain (for he feared that the still living Umtonga might be used to supplant him, as Mpande had been used to supplant Dingane
Dingane ka Senzangakhona Zulu (–29 January 1840), commonly referred to as Dingane or Dingaan, was a Zulu chief who became king of the Zulu Kingdom in 1828, after assassinating his brother Shaka. He set up his royal capital, uMgungundlovu, a ...
), removed the beacon and claimed the land ceded by the Swazis
The Swazi or Swati ( Swati: ''Emaswati'', singular ''Liswati'') are a Bantu ethnic group native to Southern Africa, inhabiting Eswatini, a sovereign kingdom in Southern Africa. EmaSwati are part of the Nguni-language speaking peoples whose or ...
to Lydenburg. The Zulus asserted that the Swazis were their vassals and therefore had no right to part with this territory. For a year, a Boer commando unit, under Paul Kruger
Stephanus Johannes Paulus Kruger (; 10 October 1825 – 14 July 1904) was a South African politician. He was one of the dominant political and military figures in 19th-century South Africa, and President of the South African Republic (or ...
and an army under Cetshwayo were posted to defend the newly acquired Utrecht border. The Zulu forces took back their land north of the Pongola. Questions were also raised as to the validity of the documents signed by the Zulus concerning the Utrecht strip; in 1869 the services of the lieutenant-governor of Natal, then Robert William Keate
Robert William Keate (16 June 1814 – 17 March 1873) was a career British colonial governor, serving as Commissioner of the Seychelles from 1850 to 1852, Governor of Trinidad from 1857 to 1864, Lieutenant-governor of the Colony of Natal from ...
, were accepted by both parties as arbitrator, but the attempt then made to settle disagreements proved unsuccessful.
In spite of his dislike for their activities, Cetshwayo permitted European missionaries in Zululand. Though he did not harm or persecute the missionaries themselves, several converts were killed. The missionaries, for their part, were a source of hostile reports. While numerous Zulus of rival factions fled into Natal and some of the surrounding areas, Cetshwayo continued and maintained the peaceful relations with the Natal colonists that had prevailed for decades. Such was the political background when Cetshwayo became absolute ruler of the Zulus upon his father's death in 1873.
As ruler, Cetshwayo set about reviving the military methods of his uncle Shaka as far as possible. He formed new age-set
In anthropology, an age set is a social category or corporate social group, consisting of people of similar age, who have a common identity, maintain close ties over a prolonged period, and together pass through a series of age-related statuses. T ...
regiments and even succeeded in equipping his regiments with a few antiquated muskets and other outdated firearms. Most Zulu warriors were armed with an ''iklwa
An assegai or assagai (Arabic ''az-zaġāyah'', Berber ''zaġāya'' "spear", Old French ''azagaie'', Spanish ''azagaya'', Italian ''zagaglia'', Middle English ''lancegay'') is a pole weapon used for throwing, usually a light spear or javelin m ...
'' (the Zulu refinement of the ''assegai
An assegai or assagai (Arabic ''az-zaġāyah'', Berber languages, Berber ''zaġāya'' "spear", French language, Old French ''azagaie'', Spanish ''azagaya'', Italian ''zagaglia'', Middle English ''lancegay'') is a pole weapon used for throwing, ...
'' thrusting spear) and a shield made of cowhide. The Zulu army drilled in the personal and tactical use and coordination of this weapons system. While some Zulus also had firearms, their marksmanship training was poor and the quality and supply of their powder and shot was dreadful. The Zulu attitude towards firearms was summarized: "The generality of Zulu warriors, however, would not have firearms – the arms of a coward, as they said, for they enable the poltroon to kill the brave without awaiting his attack."
Boundary Commission and ultimatum
The tension between Cetshwayo and the Transvaal over border disputes continued. Sir Theophilus Shepstone, whom Cetshwayo regarded as his friend, had supported him in the border dispute, but in 1877 he led a small force into the Transvaal and persuaded the Boers to give up their independence. Shepstone became administrator of the Transvaal, and in that role saw the border dispute from the other side. Shepstone claimed to have evidence supporting the Boer position but, ultimately, he failed to provide any. In a meeting with Zulu notables at Blood River in October 1877, Shepstone attempted to placate the Zulu with paternal speeches, however they were unconvinced and accused Shepstone of betraying them. Shepstone's subsequent reports to Carnarvon then began to paint the Zulu as an aggressive threat where he had previously presented Cetshwayo in a most favourable light. In February 1878 a commission was appointed byHenry Bulwer
(William) Henry Lytton Earle Bulwer, 1st Baron Dalling and Bulwer GCB, PC (13 February 180123 May 1872) was a British Liberal politician, diplomat and writer.
Background and education
Bulwer was the second son of General William Bulwer and hi ...
, the lieutenant-governor of Natal since 1875, to report on the boundary question. The commission reported in July and found almost entirely in favour of the contention of the Zulu. However, Sir Henry Bartle Frere
Sir Henry Bartle Edward Frere, 1st Baronet, (29 March 1815 – 29 May 1884) was a Welsh British colonial administrator. He had a successful career in India, rising to become Governor of Bombay (1862–1867). However, as High Commissioner for ...
, then high commissioner and still pressing forward with Carnarvon's federation plan, characterized the award as "one-sided and unfair to the Boers", stipulated that on the land being given to the Zulu, the Boers living on it should be compensated if they left or protected if they remained. In addition, Frere planned to use the meeting on the boundary commission report with the Zulu representatives to also present a surprise ultimatum
An ultimatum (; ) is a demand whose fulfillment is requested in a specified period of time and which is backed up by a threat to be followed through in case of noncompliance (open loop). An ultimatum is generally the final demand in a series o ...
he had devised that would allow British forces under Lord Chelmsford, which he had previously been instructed to use only in defense against a Zulu invasion of Natal, to instead invade Zululand. Three incidents occurred in late July, August and September which Frere seized upon as his ''casus belli
A (; ) is an act or an event that either provokes or is used to justify a war. A ''casus belli'' involves direct offenses or threats against the nation declaring the war, whereas a ' involves offenses or threats against its ally—usually one b ...
'' and were the basis for the ultimatum with which Frere knew Cetshwayo could not comply, giving Frere a pretext to attack the Zulu kingdom.
The first two incidents related to the flight into Natal of two wives of Sihayo kaXongo
Sihayo kaXongo (c. 1824 – 2 July 1883) was a Zulu inKosi (chief). In some contemporary British documents he is referred to as Sirhayo or Sirayo. He was an inDuna (commander) of the iNdabakawombe iButho (social age group and regiment) and supp ...
and their subsequent seizure and execution by his brother and sons and were described thus:
The third incident occurred in September when two men were detained while on a sandbank of the Thukela River
The Tugela River ( zu, Thukela; af, Tugelarivier) is the largest river in KwaZulu-Natal Province
KwaZulu-Natal (, also referred to as KZN and known as "the garden province") is a province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the ...
near the Middle Drift. Sir Bartle Frere described this matter in a despatch to Sir Michael Hicks Beach, who had replaced Carnarvon as Secretary of State for the Colonies:
By themselves, these incidents were flimsy grounds upon which to found an invasion of Zululand. Bulwer did not initially hold Cetshwayo responsible for what was clearly not a political act in the seizure and murder of the two women.
Cetshwayo also treated the complaint rather lightly, responding
The original complaint carried to Cetshwayo from the lieutenant-governor was in the form of a request for the surrender of the culprits. The request was subsequently transformed by Sir Bartle Frere into a "demand". Frere wrote to Hicks Beach, 30 September 1878:
In reply, in at least three dispatches, 17 October, 21 November and 18 December, Hicks Beach emphatically states that war is to be avoided and a British invasion of Zululand prohibited. From 21 November dispatch:
 After considerable discussion and exchanges of views between Sir Bartle Frere and Sir
After considerable discussion and exchanges of views between Sir Bartle Frere and Sir Henry Ernest Gascoyne Bulwer
Sir Henry Ernest Gascoyne Bulwer, (11 December 1836 – 30 September 1914), the nephew of Sir Henry Lytton Bulwer and brother to Edward Earle Gascoyne Bulwer, was a British colonial administrator and diplomat.
Bulwer was educated at Charterh ...
, it was decided to arrange a meeting with representatives of the Zulu king. The ostensible reason for this ''indaba'' was to present the findings of the long-awaited Boundary Commission to the Zulu people. The occasion was also to be used to present the king with an ultimatum.
When the ultimatum was presented, the two infractions by Sihayo’s sons and the roughing up of Smith and Deighton had become only part of the justification that was used, as several matters had arisen in the meantime. One of them was Cetshwayo’s apparent breaking of promises to Mr Theophilus Shepstone at the king’s "coronation" in 1872. That farcical piece of theatre had been agreed to by Cetshwayo simply to satisfy the wishes of Shepstone and meant nothing to the Zulu people. Indeed, his real Zulu installation had taken place several weeks earlier when he had been acclaimed by his izinduna.
A second addition to the ultimatum, which seems almost like an afterthought, required the surrender of Mbelini kaMswati. Mbelini was the son of a Swazi king who unsuccessfully disputed the succession with his brother, resulting in his exile from the kingdom. He took refuge with Cetshwayo and was granted land in the region of the Intombe River
The Battle of Intombe (also Intombi or Intombi River Drift) was an action fought on 12 March 1879, between Zulu troops loyal to Mbilini waMswati and British soldiers and African civilian conductors, drivers and (scouts) defending a convoy of ...
in western Zululand. (It is entirely possible that Cetshwayo regarded him as a useful buffer between him and the Boers of the Transvaal.) Here, he took up residence on the Tafelberg, a flat-topped mountain overlooking the river. Something of a brigand, Mbelini made raids on anyone in his area, Boer and Zulu alike, accruing cattle and prisoners in the process. With the annexation of the Transvaal, Britain had also to deal with Mbelini and because Frere was convinced that the bandit chief was in the pay of the Zulu king, his surrender was included in the ultimatum. The light in which Mbelini was regarded is shown in a paragraph from a memorandum written by Sir Henry Bulwer:
Frere has been accused of chicanery by taking deliberate advantage of the length of time it took for correspondence to pass between South Africa and London to conceal his intentions from his political masters or at least defer giving them the necessary information until it was too late for them to act. The first intimation to the British government of his intention to make 'demands' on the Zulu was in a private letter to Hicks Beach written on 14 October 1878. The letter only arrived in London on 16 November and by then messengers had already been despatched from Natal to the Zulu king to request the presence of a delegation at the Lower Tugela on 11 December for the purpose of receiving the Boundary Commission’s findings. Had Hicks Beach then sent off a telegraph forbidding any action other than the announcement of the boundary award, it might have arrived in South Africa just in time to prevent the ultimatum being presented. No prohibition was sent and could hardly be expected to have been, for Hicks Beach had no means of knowing the urgency of the events that were in train. Nowhere in Frere’s letter was there anything to indicate how soon he intended to act, nor was there anything to suggest how stringent his demands would be.
In January 1879 Hicks Beach wrote to Bartle Frere:
Hicks Beach had earlier admitted his helplessness with regard to the Frere's actions in a telling note to his Prime Minister:
Frere wanted to provoke a conflict with the Zulus and in that goal he succeeded. Cetshwayo rejected the demands of 11 December, by not responding by the end of the year. A concession was granted by Bartle Frere until 11 January 1879, after which Bartle Frere deemed a state of war to exist. The British forces intended for the defense of Natal had already been on the march with the intention to attack the Zulu kingdom. On 10 January they were poised on the border. On 11 January, they crossed the border and invaded Zululand.
Terms
The terms included in the ultimatum were delivered to the representatives of King Cetshwayo on the banks of the Thukela river at the Ultimatum Tree on 11 December 1878. No time was specified for compliance with item 4, twenty days were allowed for compliance with items 1–3, that is, until 31 December inclusive; ten days more were allowed for compliance with the remaining demands, items 4–13. The earlier time limits were subsequently altered so that all expired on 10 January 1879. # Surrender of Sihayo’s three sons and brother to be tried by the Natal courts. # Payment of a fine of 500 head of cattle for the outrages committed by the above and for Cetshwayo’s delay in complying with the request of the Natal Government for the surrender of the offenders. # Payment of 100 head of cattle for the offence committed against Messrs. Smith and Deighton. # Surrender of the Swazi chief Umbilini and others to be named hereafter, to be tried by the Transvaal courts. # Observance of the coronation promises. # That the Zulu army be disbanded and the men allowed to go home. # That the Zulu military system be discontinued and other military regulations adopted, to be decided upon after consultation with the Great Council and British Representatives. # That every man, when he comes to man’s estate, shall be free to marry. # All missionaries and their converts, who until 1877 lived in Zululand, shall be allowed to return and reoccupy their stations. # All such missionaries shall be allowed to teach and any Zulu, if he chooses, shall be free to listen to their teaching. # A British Agent shall be allowed to reside in Zululand, who will see that the above provisions are carried out. # All disputes in which a missionary or European is concerned, shall be heard by the king in public and in presence of the Resident. # No sentence of expulsion from Zululand shall be carried out until it has been approved by the Resident. To ensure that there was no interference from London, Frere delayed informing the Colonial Office about his ultimatum until it was too late for it to be countermanded. The full text of his demands did not reach London until 2 January 1879. By then, Chelmsford had assembled an army of 18,000 men- redcoats, colonial volunteers and Natal African auxiliariesalong the Zululand border ready for the invasion. For his part, Cetshwayo strenuously attempted to avoid war with the British and, should it occur, to limit its scope and effects. He ordered his troops to defend their country only if attacked and not to carry the war beyond its borders. He directed them to avoid killing any of the invaders other than the regular British soldiers in their red coats.First invasion

 The pretext for the war had its origins in border disputes between the Zulu leader, Cetshwayo, and the
The pretext for the war had its origins in border disputes between the Zulu leader, Cetshwayo, and the Boers
Boers ( ; af, Boere ()) are the descendants of the Dutch-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled this area ...
in the Transvaal Transvaal is a historical geographic term associated with land north of (''i.e.'', beyond) the Vaal River in South Africa. A number of states and administrative divisions have carried the name Transvaal.
* South African Republic (1856–1902; af, ...
region. Following a commission inquiry on the border dispute which reported in favour of the Zulu nation in July 1878, Sir Henry Bartle Frere
Sir Henry Bartle Edward Frere, 1st Baronet, (29 March 1815 – 29 May 1884) was a Welsh British colonial administrator. He had a successful career in India, rising to become Governor of Bombay (1862–1867). However, as High Commissioner for ...
, acting on his own, added an ultimatum to the commission meeting, much to the surprise of the Zulu representatives who then relayed it to Cetshwayo. Cetshwayo had not responded by the end of the year, so an extension was granted by Bartle Frere until 11 January 1879. Cetshwayo returned no answer to the demands of Bartle Frere, and in January 1879 a British force under Lieutenant General Frederic Thesiger, 2nd Baron Chelmsford
Frederic Augustus Thesiger, 2nd Baron Chelmsford, (31 May 18279 April 1905) was a British Army officer who rose to prominence during the Anglo-Zulu War, when an expeditionary force under his command suffered a decisive defeat at the hands of a ...
invaded Zululand, without authorization by the British Government. The exact date of the invasion was 11 January 1879. Chelmsford crossed the Buffalo River at Rorke's Drift
The Battle of Rorke's Drift (1879), also known as the Defence of Rorke's Drift, was an engagement in the Anglo-Zulu War. The successful British defence of the mission station of Rorke's Drift, under the command of Lieutenants John Chard of the ...
, an old Irish trader's post that had become a mission station, in command of 4,700 men, which included 1,900 White troops and 2,400 African auxiliaries.
Lord Chelmsford, the Commander-in-Chief of British forces during the war, initially planned a five-pronged invasion of Zululand composed of over 16,500 troops in five columns and designed to encircle the Zulu army and force it to fight as he was concerned that the Zulus would avoid battle. In the event, Chelmsford settled on three invading columns with the main center column, now consisting of some 7,800 men comprising the previously called No. 3 Column and Durnford's No. 2 Column, under his direct command. He moved his troops from Pietermaritzburg
Pietermaritzburg (; Zulu: umGungundlovu) is the capital and second-largest city in the province of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. It was founded in 1838 and is currently governed by the Msunduzi Local Municipality. Its Zulu name umGungundlovu ...
to a forward camp at Helpmekaar, past Greytown. On 9 January 1879 they moved to Rorke's Drift
The Battle of Rorke's Drift (1879), also known as the Defence of Rorke's Drift, was an engagement in the Anglo-Zulu War. The successful British defence of the mission station of Rorke's Drift, under the command of Lieutenants John Chard of the ...
, and early on 11 January commenced crossing the Buffalo River into Zululand. Three columns were to invade Zululand, from the Lower Tugela, Rorke's Drift
The Battle of Rorke's Drift (1879), also known as the Defence of Rorke's Drift, was an engagement in the Anglo-Zulu War. The successful British defence of the mission station of Rorke's Drift, under the command of Lieutenants John Chard of the ...
, and Utrecht respectively, their objective being Ulundi, the royal capital.
While Cetshwayo's army numbered perhaps 35,000 men, it was essentially a militia force which could be called out in time of national danger. It had a very limited logistical capacity and could only stay in the field a few weeks before the troops would be obliged to return to their civilian duties. Zulu warriors were armed primarily with ''Assegai
An assegai or assagai (Arabic ''az-zaġāyah'', Berber languages, Berber ''zaġāya'' "spear", French language, Old French ''azagaie'', Spanish ''azagaya'', Italian ''zagaglia'', Middle English ''lancegay'') is a pole weapon used for throwing, ...
'' thrusting spears, known in Zulu as ''iklwa
An assegai or assagai (Arabic ''az-zaġāyah'', Berber ''zaġāya'' "spear", Old French ''azagaie'', Spanish ''azagaya'', Italian ''zagaglia'', Middle English ''lancegay'') is a pole weapon used for throwing, usually a light spear or javelin m ...
'', clubs, some throwing spears and shields made of cowhide.
The initial entry of all three columns was unopposed. On 22 January the centre column, which had advanced from Rorke's Drift, was encamped near Isandlwana; on the morning of that day Lord Chelmsford split his forces and moved out to support a reconnoitering party, leaving the camp in charge of Colonel Pulleine Pulleine is an English surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Henry Pulleine (1838–1879), English army officer
* John Pulleine
John James Pulleine (10 September 1841, Spennithorne, Yorkshire - 15 April 1913) was an Anglican Suffr ...
. The British were outmanoeuvred by the main Zulu army nearly 20,000 strong led by Ntshingwayo Khoza
Ntshingwayo kaMahole of the Khoza ( 1809 – 21 July 1883) was the commanding general ('' inDuna'') of King Cetshwayo's Zulu Army during the first Anglo-Zulu War.
Anglo-Zulu War
Ntshingwayo was given overall field command of the Zulu impi against ...
. Chelmsford was lured eastward with much of his centre column by a Zulu diversionary force while the main Impi attacked his camp. Chelmsford's decision not to set up the British camp defensively, contrary to established doctrine, and ignoring information that the Zulus were close at hand were decisions that the British were soon to regret. The ensuing Battle of Isandlwana
The Battle of Isandlwana (alternative spelling: Isandhlwana) on 22 January 1879 was the first major encounter in the Anglo-Zulu War between the British Empire and the Zulu Kingdom. Eleven days after the British commenced their invasion of Zulul ...
was the greatest victory that the Zulu kingdom would enjoy during the war. The British centre column was wrecked and its camp annihilated with heavy casualties as well as the loss of all its supplies, ammunition and transport. The defeat left Chelmsford no choice but to hastily retreat out of Zululand. In the battle's aftermath, a party of some 4,000 Zulu reserves mounted an unauthorised raid on the nearby British army border post of Rorke's Drift
The Battle of Rorke's Drift (1879), also known as the Defence of Rorke's Drift, was an engagement in the Anglo-Zulu War. The successful British defence of the mission station of Rorke's Drift, under the command of Lieutenants John Chard of the ...
and were driven off after 10 hours of ferocious fighting.
 While the British central column under Chelmsford's command was thus engaged, the right flank column on the coast, under Colonel
While the British central column under Chelmsford's command was thus engaged, the right flank column on the coast, under Colonel Charles Pearson
Charles Pearson (4 October 1793 – 14 September 1862) was a British lawyer and politician. He was solicitor to the City of London, a reforming campaigner, and – briefly – Member of Parliament for Lambeth. He campaigned against corruption in ...
, crossed the Tugela River, skirmished with a Zulu impi that was attempting to set up an ambush at the Inyezane River, and advanced as far as the deserted missionary station of Eshowe, which he set about fortifying. On learning of the disaster at Isandlwana, Pearson made plans to withdraw back beyond the Tugela River. However, before he had decided whether or not to put these plans into effect, the Zulu army managed to cut off his supply lines, and the Siege of Eshowe
The siege of Eshowe took place during the Anglo-Zulu War of 1879. The siege was part of a three-pronged attack on the Zulu Impis of king Cetshwayo at Ulundi. After an incursion as far as Eshowe (then also known as Fort Ekowe or kwaMondi) Colo ...
had begun.
Meanwhile, the left flank column at Utrecht, under Colonel Evelyn Wood, had originally been charged with occupying the Zulu tribes of north-west Zululand and preventing them from interfering with the British central column's advance on Ulundi. To this end Wood set up camp at Tinta's Kraal, just 10 miles south of Hlobane Mountain
The Battle of Hlobane (28 March 1879) took place at Hlobane, near the modern town of Vryheid in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa during the Anglo-Zulu War.
Background
The British commander Frederic Thesiger (Lord Chelmsford) intended to invade Zu ...
, where a force of 4,000 Zulus had been spotted. He planned to attack them on 24 January, but on learning of the disaster at Isandlwana, he decided to withdraw back to the Kraal. Thus one month after the British invasion, only their left flank column remained militarily effective, and it was too weak to conduct a campaign alone. The first invasion of Zululand had been a failure.
 It had never been Cetshwayo's intention to invade Natal, but to simply fight within the boundaries of the Zulu kingdom. Chelmsford used the next two months to regroup and build a fresh invading force with the initial intention of relieving Pearson at Eshowe. The British government rushed seven regiments of reinforcements to Natal, along with two artillery batteries.
On 12 March, an armed escort of stores marching to Luneberg, was defeated by about 500 Zulus at the
It had never been Cetshwayo's intention to invade Natal, but to simply fight within the boundaries of the Zulu kingdom. Chelmsford used the next two months to regroup and build a fresh invading force with the initial intention of relieving Pearson at Eshowe. The British government rushed seven regiments of reinforcements to Natal, along with two artillery batteries.
On 12 March, an armed escort of stores marching to Luneberg, was defeated by about 500 Zulus at the Battle of Intombe
The Battle of Intombe (also Intombi or Intombi River Drift) was an action fought on 12 March 1879, between Zulu troops loyal to Mbilini waMswati and British soldiers and African civilian conductors, drivers and (scouts) defending a convoy of ...
; the British force suffered 80 killed and all the stores were lost. The first troops arrived at Durban on 7 March. On the 29th a column, under Lord Chelmsford, consisting of 3,400 British and 2,300 African soldiers, marched to the relief of Eshowe, entrenched camps being formed each night.
Chelmsford ordered Sir Evelyn Wood's troops to attack the abaQulusi Zulu stronghold in Hlobane. Lieutenant Colonel Redvers Buller, led the attack on Hlobane on 28 March. However, as the Zulu main army of 20,000 men approached to help their besieged tribesmen, the British force began a retreat which turned into a rout and were pursued by 1,000 Zulus of the abaQulusi who inflicted some 225 casualties on the British force.
The next day 20,000 Zulu warriors attacked Wood's 2,068 men in a well-fortified camp at Kambula, apparently without Cetshwayo's permission. The British held them off in the Battle of Kambula and after five hours of heavy attacks the Zulus withdrew with heavy losses but were pursued by British mounted troops, who killed many more fleeing and wounded warriors. British losses amounted to 83 (28 killed and 55 wounded), while the Zulus lost up to 2,000 killed. The effect of the battle of Kambula on the Zulu army was severe. Their commander Mnyamana Buthelezi tried to get the regiments to return to Ulundi but many demoralised warriors simply went home.
 While Woods was thus engaged, Chelmsford's column was marching on Eshowe. On 2 April this force was attacked en route at
While Woods was thus engaged, Chelmsford's column was marching on Eshowe. On 2 April this force was attacked en route at Gingindlovu
Gingindlovu is a town in Uthungulu District Municipality in the KwaZulu-Natal province of South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of c ...
, the Zulu being repulsed. Their losses were heavy, estimated at 1,200, but the British suffered only two dead and 52 wounded and the next they relieved Pearson's men. They evacuated Eshowe on 5 April after which the Zulu forces burned it down.
Second invasion
 The new start of the larger, heavily reinforced second invasion was not promising for the British. Despite their successes at Kambula, Gingindlovu and Eshowe, they were right back where they had started from at the beginning of January. Nevertheless, Chelmsford had a pressing reason to proceed with haste – Sir Garnet Wolseley was being sent to replace him, and he wanted to inflict a decisive defeat on Cetshwayo's forces before then. With yet more reinforcements arriving, soon to total 16,000 British and 7,000 Native troops, Chelmsford reorganised his forces and again advanced into Zululand in June, this time with extreme caution building fortified camps all along the way to prevent any repeat of Isandlwana.
One of the early British casualties was the exiled heir to the French throne, Imperial Prince Napoleon Eugene, who had volunteered to serve in the British army and was killed on 1 June while out with a reconnoitering party.
Cetshwayo, knowing that the newly reinforced British would be a formidable opponent, attempted to negotiate a peace treaty. Chelmsford was not open to negotiations, as he wished to restore his reputation before Wolseley relieved him of command, and he proceeded to the royal kraal of Ulundi, intending to defeat the main Zulu army. On 4 July, the armies clashed at the
The new start of the larger, heavily reinforced second invasion was not promising for the British. Despite their successes at Kambula, Gingindlovu and Eshowe, they were right back where they had started from at the beginning of January. Nevertheless, Chelmsford had a pressing reason to proceed with haste – Sir Garnet Wolseley was being sent to replace him, and he wanted to inflict a decisive defeat on Cetshwayo's forces before then. With yet more reinforcements arriving, soon to total 16,000 British and 7,000 Native troops, Chelmsford reorganised his forces and again advanced into Zululand in June, this time with extreme caution building fortified camps all along the way to prevent any repeat of Isandlwana.
One of the early British casualties was the exiled heir to the French throne, Imperial Prince Napoleon Eugene, who had volunteered to serve in the British army and was killed on 1 June while out with a reconnoitering party.
Cetshwayo, knowing that the newly reinforced British would be a formidable opponent, attempted to negotiate a peace treaty. Chelmsford was not open to negotiations, as he wished to restore his reputation before Wolseley relieved him of command, and he proceeded to the royal kraal of Ulundi, intending to defeat the main Zulu army. On 4 July, the armies clashed at the Battle of Ulundi
The Battle of Ulundi took place at the Zulu capital of Ulundi (Zulu:''oNdini'') on 4 July 1879 and was the last major battle of the Anglo-Zulu War. The British army broke the military power of the Zulu nation by defeating the main Zulu army ...
, and Cetshwayo's forces were decisively defeated.
Aftermath
After the battle of Ulundi, the Zulu army dispersed, most of the leading chiefs tendered their submission, and Cetshwayo became a fugitive. Wolseley, having relieved Chelmsford after Ulundi, took over the final operations. On 28 August the king was captured and sent toCape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
. It is said that scouts spotted the water-carriers of the king, distinctive because the water was carried above, not upon, their heads. His deposition was formally announced to the Zulu. Wolseley wasted no time in discarding Bartle Frere's confederation scheme and drew up a new scheme which divided Zululand into thirteen chiefdoms headed by compliant chiefs which ensured that the Zulus would no longer unite under a single king and made internal divisions and civil wars inevitable. The dynasty of Shaka was deposed, and the Zulu country portioned among eleven Zulu chiefs, including Zibhebhu, John Robert Dunn
John Robert Dunn (1834 – 5 August 1895) was a South African settler, hunter, and diplomat of British descent. Born in Port Alfred in 1834, he spent his childhood in Port Natal/Durban. He was orphaned as a teenager, and lived in native dress on ...
, a white adventurer, and Hlubi, a Basuto chief allied to the British in the war.
Chelmsford received a Knight Grand Cross of Bath, largely because of Ulundi. However, he was severely criticized by the Horse Guards investigation and would never serve in the field again. Bartle Frere was relegated to a minor post in Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
.
Following the conclusion of the Anglo-Zulu War, Bishop Colenso interceded on behalf of Cetshwayo with the British government and succeeded in getting him released from Robben Island
Robben Island ( af, Robbeneiland) is an island in Table Bay, 6.9 kilometres (4.3 mi) west of the coast of Bloubergstrand, north of Cape Town, South Africa. It takes its name from the Dutch word for seals (''robben''), hence the Dutch/Afrik ...
and returned to Zululand in 1883.
A Resident (Melmoth Osborn Melmoth may refer to:
*Garrison Melmoth, a homebuilt aircraft designed by Peter Garrison
* Garrison Melmoth 2, a follow-up design to the Garrison Melmoth
* ''Melmoth'' (comics), a graphic novel by Dave Sim featuring Cerebus the Aardvark
*''Melmoth ...
) was appointed to be the channel of communication between the chiefs and the British government. This arrangement led to much bloodshed and disturbance, and in 1882 the British government determined to restore Cetshwayo to power. In the meantime, however, blood feuds had been engendered between the chiefs Usibepu
Zibhebhu kaMaphitha Zulu (1841–1904) (also called Usibepu/Ziphewu) was a Zulu chief. After the defeat of the Zulu Kingdom by the British, he attempted to create his own independent kingdom. From 1883 to 1884, he fought the Zulu king Cetshwayo, ...
(Zibebu) and Hamu on the one side and the tribes who supported the ex-king and his family on the other. Cetshwayo's party (who now became known as the Usuthu) suffered severely at the hands of the two chiefs, who were aided by a band of white freebooters.
When Cetshwayo was restored Usibepu was left in possession of his territory, while Dunn's land and that of the Basuto chief (the country between the Tugela River
The Tugela River ( zu, Thukela; af, Tugelarivier) is the largest river in KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa. With a total length of , it is one of the most important rivers of the country.
The river originates in Mont-aux-Sources of the Dra ...
and the Umhlatuzi, i.e., adjoining Natal) was constituted a reserve, in which locations were to be provided for Zulu unwilling to serve the restored king. This new arrangement proved as futile as had Wolseley's. Usibepu, having created a formidable force of well-armed and trained warriors, and being left in independence on the borders of Cetshwayo's territory, viewed with displeasure the re-installation of his former king, and Cetshwayo was desirous of humbling his relative. A collision very soon took place; Usibepu's forces were victorious, and on 22 July 1883, led by a troop of mounted Boer mercenary troops, he made a sudden descent upon Cetshwayo's kraal at Ulundi, which he destroyed, massacring such of the inmates of both sexes as could not save themselves by flight. The king escaped, though wounded, into Nkandla forest. After appeals to Melmoth Osborn Melmoth may refer to:
*Garrison Melmoth, a homebuilt aircraft designed by Peter Garrison
* Garrison Melmoth 2, a follow-up design to the Garrison Melmoth
* ''Melmoth'' (comics), a graphic novel by Dave Sim featuring Cerebus the Aardvark
*''Melmoth ...
he moved to Eshowe, where he died soon after.
Last veterans
* Colour Sergeant (later Lieutenant-Colonel andOBE
The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding contributions to the arts and sciences, work with charitable and welfare organisations,
and public service outside the civil service. It was established o ...
) Frank Bourne
Lieutenant-Colonel Frank Edward Bourne OBE DCM (27 April 1855 – 9 May 1945) was a decorated British soldier who participated in the defence of Rorke's Drift during the 1879 Anglo-Zulu War.
Early life
Born in Balcombe, Sussex, England on ...
, DCM (1854–1945) Last survivor of Rorke's Drift
The Battle of Rorke's Drift (1879), also known as the Defence of Rorke's Drift, was an engagement in the Anglo-Zulu War. The successful British defence of the mission station of Rorke's Drift, under the command of Lieutenants John Chard of the ...
.
* Private Charles Wallace Warden (died 8 March 1953)
* Henry "Harry" Figg R.N. (died 23 May 1953)
Film adaptions
* '' Zulu'' (1964), the Battle at Rorke's Drift. * '' Zulu Dawn'' (1979), the Battle of Isandlwana.See also
* Bambatha Rebellion * Colony of Natal * First Boer War * Military history of South Africa * Shaka Zulu *Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also called the Partition of Africa, or Conquest of Africa, was the invasion, annexation, division, and colonisation of Africa, colonization of most of Africa by seven Western Europe, Western European powers during a ...
*Kingdom of Zululand
The Zulu Kingdom (, ), sometimes referred to as the Zulu Empire or the Kingdom of Zululand, was a monarchy in Southern Africa. During the 1810s, Shaka established a modern standing army that consolidated rival clans and built a large following ...
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * *External links
Rorke's Drift and the Anglo–Zulu War website
Anglo–Zulu War Historical Society
The Keynsham Light Horse
by Ralph Zuljan {{Authority control 1879 in the British Empire 1879 in the Colony of Natal 1879 in the Zulu Kingdom African resistance to colonialism Battles involving the Zulu History of KwaZulu-Natal Invasions by the United Kingdom Last stands Military history of South Africa Wars involving the states and peoples of Africa Zulu British colonisation in Africa