Andhra on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in the south-eastern coastal
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in ...
region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian subcontinent, Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India b ...
to the north-west, Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (, ) is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Prade ...
to the north, Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
to the north-east, Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a States and union territories of India, state in southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of India ...
to the south, Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
to the west and the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
to the east. It has the second longest coastline in India after Gujarat, of about . Andhra State
Andhra State (IAST: ; ) was a Administrative divisions of India#States and union territories, state in India created in 1953 from the Telugu language, Telugu-speaking northern List of districts in India, districts of Madras State. The state was ...
was the first state to be formed on a linguistic basis in India on 1 October 1953. On 1 November 1956, Andhra State was merged with the Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
S ...
-speaking areas (ten districts) of the Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and t ...
to form United Andhra Pradesh
United may refer to:
Places
* United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
Arts and entertainment Films
* United (2003 film), ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film
* United (2011 film) ...
. ln 2014 these merged areas of Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and t ...
are bifurcated from United Andhra Pradesh
United may refer to:
Places
* United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
Arts and entertainment Films
* United (2003 film), ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film
* United (2011 film) ...
to form new state Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian subcontinent, Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India b ...
. Present form of Andhra
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
similar to Andhra state
Andhra State (IAST: ; ) was a Administrative divisions of India#States and union territories, state in India created in 1953 from the Telugu language, Telugu-speaking northern List of districts in India, districts of Madras State. The state was ...
.but some mandalas like Bhadrachalam
Bhadrachalam is a census town in Bhadradri Kothagudem district in the Indian state of Telangana. It is an important Hindu pilgrimage town with the Bhadrachalam Temple of Lord Rama, situated on the banks of Godavari river. It is located east o ...
still with Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian subcontinent, Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India b ...
. Visakhapatnam
, image_alt =
, image_caption = From top, left to right: Visakhapatnam aerial view, Vizag seaport, Simhachalam Temple, Aerial view of Rushikonda Beach, Beach road, Novotel, Novotel Visakhapatnam, INS Kursura (S20), INS ...
, Guntur
Guntur () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Guntur district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. Guntur is spread across 168.49 km square and is the third-largest city in the state. It is situated to the west of the Ba ...
, Kurnool
Kurnool is a city in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India. It formerly served as the capital of Andhra State (1953–1956). The city is often referred to as "The Gateway of Rayalaseema".Kurnool is also known as The City of Gem Stones. It also se ...
is People Capital of Andhra Pradesh.
Andhra Pradesh was once a major Buddhist pilgrimage site in the country and a Buddhist learning center which can be seen in many sites in the state in the form of monastery ruins, chaitya
A chaitya, chaitya hall, chaitya-griha, (Sanskrit:''Caitya''; Pāli: ''Cetiya'') refers to a shrine, sanctuary, temple or prayer hall in Indian religions. The term is most common in Buddhism, where it refers to a space with a stupa and a rounded ...
s and stupa
A stupa ( sa, स्तूप, lit=heap, ) is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics (such as ''śarīra'' – typically the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns) that is used as a place of meditation.
In Buddhism, circumamb ...
s. It is also known for being the land of Koh-i-Noor
The Koh-i-Noor ( ; from ), also spelled Kohinoor and Koh-i-Nur, is one of the largest cut diamonds in the world, weighing . It is part of the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom. The diamond is currently set in the Crown of Queen Elizabeth The ...
and other globally known diamonds from Kollur Mine
Kollur Mine was a series of gravel-clay pits on the south bank of the Krishna River in the Golconda Sultanate of India. It currently falls within the state of Andhra Pradesh. It is thought to have produced many large diamonds, known as Golcond ...
. It is also a major producer of rice known as the "Rice bowl
The breadbasket of a country or of a region is an area which, because of the richness of the soil and/or advantageous climate, produces large quantities of wheat or other grain. Rice bowl is a similar term used to refer to Southeast Asia; and C ...
of India". Its official language is Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
S ...
; one of the classical languages of India
Languages spoken in India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-European languages spoken by 78.05% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians, both families together are sometimes known ...
, the fourth most spoken language in India and the 13th-most spoken language in the world. Andhra Pradesh's second official language is Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
''
''
Early inhabitants were known as the Andhras, tracing their history back to the
 The
The  The Vijayanagara Empire, Vijayanagara Empire originated in the Deccan Plateau region in the early 14th century. It was established in 1336 by Harihara I, Harihara Raya I and his brother Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, Sangama Dynasty.By James Mansel Longworth page 204edited by J C morris page 261 The empire's patronage enabled fine arts and literature to reach new heights in Kannada,
The Vijayanagara Empire, Vijayanagara Empire originated in the Deccan Plateau region in the early 14th century. It was established in 1336 by Harihara I, Harihara Raya I and his brother Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, Sangama Dynasty.By James Mansel Longworth page 204edited by J C morris page 261 The empire's patronage enabled fine arts and literature to reach new heights in Kannada,
 Harihara and Bukka, who served as treasury officers of the Kakatiyas of Warangal, founded the
Harihara and Bukka, who served as treasury officers of the Kakatiyas of Warangal, founded the
 In an effort to gain an independent state based on linguistic identity, and to protect the interests of the Telugu-speaking people of Madras State, Potti Sreeramulu fasted to death in 1952. As Madras became a bone of contention, in 1949 a JVP committee report stated: "Andhra Province could be formed provided the Andhras give up their claim on the city of Madras [now Chennai]". After Potti Sreeramulu's death, the Telugu-speaking area of
In an effort to gain an independent state based on linguistic identity, and to protect the interests of the Telugu-speaking people of Madras State, Potti Sreeramulu fasted to death in 1952. As Madras became a bone of contention, in 1949 a JVP committee report stated: "Andhra Province could be formed provided the Andhras give up their claim on the city of Madras [now Chennai]". After Potti Sreeramulu's death, the Telugu-speaking area of
File:Andhra Pradesh and Telangana Physical.jpeg, Andhra Pradesh topographical map
File:AP map.jpg, Map of Andhra Pradesh
File:Srisailam Dam and River Krishna.jpg, Krishna River at Srisailam
The state has varied topography ranging from the hills of Eastern Ghats and Nallamala Hills to the shores of
 The Andhra Pradesh Forest Department deals with protection, conservation and management of forests. The total forest cover of the state after the bifurcation is left with an area of . The forest in the state can be broadly divided into four major biotic provinces. They are:
# Deccan Plateau
# Central Plateau
# Eastern Highland
# East Coastal Plains
Eastern Ghats region is home to dense tropical forests, while the vegetation becomes sparse as the Ghats give way to the Deccan Plateau, where shrub vegetation is more common. The vegetation found in the state is largely of dry deciduous types with a mixture of teak, ''Terminalia (plant), Terminalia'', ''Dalbergia'', ''Pterocarpus'', ''Anogeissus'', etc.
The state has many List of wildlife sanctuaries of India, sanctuaries, List of national parks of India, national parks and Zoo Park, zoological parks, such as Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary, Coringa, Krishna Wildlife Sanctuary, Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve, Kambalakonda Wildlife Sanctuary, Sri Venkateswara Zoological Park and Indira Gandhi Zoological Park. Kolleru Bird Sanctuary, Atapaka Bird Sanctuary, Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary, Telineelapuram and Telukunchi Bird Sanctuaries and Pulicat Lake Bird Sanctuary attract many migratory birds. The state possesses some rare and endemic plants like ''Cycas beddomei'', ''Pterocarpus santalinus'', ''Terminalia pallida'', ''Syzygium alternifolium'', ''Shorea talura'', ''Shorea tumburgia'', ''Psilotum nudum'', etc. The diversity of fauna includes tigers, panthers, hyenas, Blackbuck, black bucks, Cheetah, cheetals, Sambar deer, sambars, sea turtles and a number of birds and reptiles. The estuaries of the Godavari and Krishna rivers support rich Mangrove, mangrove forests with fishing cats and otters as keystone species.
The Andhra Pradesh Forest Department deals with protection, conservation and management of forests. The total forest cover of the state after the bifurcation is left with an area of . The forest in the state can be broadly divided into four major biotic provinces. They are:
# Deccan Plateau
# Central Plateau
# Eastern Highland
# East Coastal Plains
Eastern Ghats region is home to dense tropical forests, while the vegetation becomes sparse as the Ghats give way to the Deccan Plateau, where shrub vegetation is more common. The vegetation found in the state is largely of dry deciduous types with a mixture of teak, ''Terminalia (plant), Terminalia'', ''Dalbergia'', ''Pterocarpus'', ''Anogeissus'', etc.
The state has many List of wildlife sanctuaries of India, sanctuaries, List of national parks of India, national parks and Zoo Park, zoological parks, such as Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary, Coringa, Krishna Wildlife Sanctuary, Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve, Kambalakonda Wildlife Sanctuary, Sri Venkateswara Zoological Park and Indira Gandhi Zoological Park. Kolleru Bird Sanctuary, Atapaka Bird Sanctuary, Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary, Telineelapuram and Telukunchi Bird Sanctuaries and Pulicat Lake Bird Sanctuary attract many migratory birds. The state possesses some rare and endemic plants like ''Cycas beddomei'', ''Pterocarpus santalinus'', ''Terminalia pallida'', ''Syzygium alternifolium'', ''Shorea talura'', ''Shorea tumburgia'', ''Psilotum nudum'', etc. The diversity of fauna includes tigers, panthers, hyenas, Blackbuck, black bucks, Cheetah, cheetals, Sambar deer, sambars, sea turtles and a number of birds and reptiles. The estuaries of the Godavari and Krishna rivers support rich Mangrove, mangrove forests with fishing cats and otters as keystone species.
 Census of India, the residual state had a population of with a population density of . According to the Polavaram ordinance bill 2014, 7 Tehsil, mandals of Khammam district in Telangana state merged with Andhra Pradesh to facilitate Polavaram Project, Polavaram project, due to which population of added to Andhra Pradesh. Thus the final population of Andhra Pradesh in the year 2014, as per census 2011 is , with a density of .
The total population constitute, 70.4% of rural population with inhabitants and 29.6% of urban population with inhabitants. Children in the age group of 0–6 years are , constituting 10.6% of the total population, among them are boys and are girls. Visakhapatnam district has the largest urban population of 47.5% and Srikakulam district with 83.8%, has the largest rural population, among others districts in the state. The overall population of the state comprises 17.1% of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, Scheduled Caste and 5.3% of Scheduled Tribe population.
There are male and female citizens—a Human sex ratio, sex ratio of 996 females per 1000 males, higher than the national average of 926 per 1000. The Literacy, literacy rate of the state stands at 67.41%. However, post bifurcation from Telangana, the state is expected to reach 91.1% by 2021. West Godavari district has the highest literacy rate of 74.6% and Vizianagaram district has the least with 58.9%.
Andhra Pradesh ranks tenth of all Indian States in the Human Development Index scores with a score of 0.416. The National Council of Applied Economic Research district analysis in 2001 reveals that
Census of India, the residual state had a population of with a population density of . According to the Polavaram ordinance bill 2014, 7 Tehsil, mandals of Khammam district in Telangana state merged with Andhra Pradesh to facilitate Polavaram Project, Polavaram project, due to which population of added to Andhra Pradesh. Thus the final population of Andhra Pradesh in the year 2014, as per census 2011 is , with a density of .
The total population constitute, 70.4% of rural population with inhabitants and 29.6% of urban population with inhabitants. Children in the age group of 0–6 years are , constituting 10.6% of the total population, among them are boys and are girls. Visakhapatnam district has the largest urban population of 47.5% and Srikakulam district with 83.8%, has the largest rural population, among others districts in the state. The overall population of the state comprises 17.1% of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, Scheduled Caste and 5.3% of Scheduled Tribe population.
There are male and female citizens—a Human sex ratio, sex ratio of 996 females per 1000 males, higher than the national average of 926 per 1000. The Literacy, literacy rate of the state stands at 67.41%. However, post bifurcation from Telangana, the state is expected to reach 91.1% by 2021. West Godavari district has the highest literacy rate of 74.6% and Vizianagaram district has the least with 58.9%.
Andhra Pradesh ranks tenth of all Indian States in the Human Development Index scores with a score of 0.416. The National Council of Applied Economic Research district analysis in 2001 reveals that 
Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betw ...
, when they were mentioned in the 8th century BCE Rigvedic
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one S ...
text Aitareya Brahmana The Aitareya Brahmana ( sa, ऐतरेय ब्राह्मण) is the Brahmana of the Shakala Shakha of the Rigveda, an ancient Indian collection of sacred hymns. This work, according to the tradition, is ascribed to Mahidasa Aitareya.
Aut ...
. According to the Aitareya Brahmana, the Andhras left North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central ...
from the banks of the Yamuna river
The Yamuna ( Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Ban ...
and migrated to South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territo ...
. The Assaka
Ashmaka (Sanskrit: ) or Assaka (Pali: ) was a Mahajanapada in ancient India which existed between 700 BCE and 425 or 345 BCE according to the Buddhist texts '' Anguttara Nikaya'' and ''Puranas''. It was located around and between the Godavar ...
Mahajanapada
The Mahājanapadas ( sa, great realm, from ''maha'', "great", and ''janapada'' "foothold of a people") were sixteen kingdoms or oligarchic republics that existed in ancient India from the sixth to fourth centuries BCE during the second urba ...
(700–300 BCE) was an ancient kingdom located between the Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
and Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
rivers in southeastern India. Accounts that people in the region are descended from the Viswamitra
Vishvamitra ( sa, विश्वामित्र, ) is one of the most venerated rishis or sages of ancient India. According to Hindu tradition, he is stated to have written most of the Mandala 3 of the Rigveda, including the Gayatri Mant ...
are found in the ''Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th ...
'', the ''Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kuruk ...
'' and the Puranas
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends an ...
. The region also derives its name from the Satavahanas
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan region. Mos ...
, who are also known as Andhras, the earliest kings of Andhra Pradesh and India.
People of the said era supported local art and culture by building temples and sculptures of the Buddhist monuments in the state. It was ruled by the Mauryan Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
, Satavahana dynasty
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan region. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the late ...
, Salankayanas, Andhra Ikshvaku
The Ikshvaku ( IAST: Ikṣvāku) dynasty ruled in the eastern Krishna River valley of India, from their capital at Vijayapuri (modern Nagarjunakonda in Andhra Pradesh) during approximately 3rd and 4th centuries CE. The Ikshvakus are also kn ...
s, Pallavas
The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of South India, the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The dynasty rose to prominence after the downfall of the Satavahanas, Satavahana dynasty, with whom they ...
, Vishnukundinas
The Vishnukundina dynasty (IAST: Viṣṇukundina) was an Indian dynasty based in Deccan Plateau, Deccan, which ruled modern Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Odisha and parts of South India during the 5th and 6th centuries, carving land out from the V ...
, Eastern Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas
Rashtrakuta (IAST: ') (r. 753-982 CE) was a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the sixth and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing their ...
, Cholas, Kakatiyas, Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also called the Karnata Kingdom, was a Hinduism, Hindu empire based in the region of South India, which consisted the modern states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa and some parts of Telangana an ...
, Gajapati Empire
The Gajapati Empire or the Suryavamsa (IAST: Sūryavaṃśa, "Solar dynasty") dynasty was a medieval dynasty from the Indian subcontinent, it originated in the region of Trikalinga (most of the present-day Odisha and North coastal Andhra) a ...
, Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
, Deccan sultanates, Qutb Shahi dynasty, and Asaf Jahis
The Asaf Jahi was a Muslim dynasty that ruled the Kingdom of Hyderabad. The family came to India in the late 17th century and became employees of the Mughal Empire. They were great patrons of Persian culture, language, and literature, the fami ...
. In the 3rd century BCE, Andhra was a vassal kingdom of Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, ...
, but after his death Andhra became powerful and extended its empire to the whole of Maratha country and beyond.
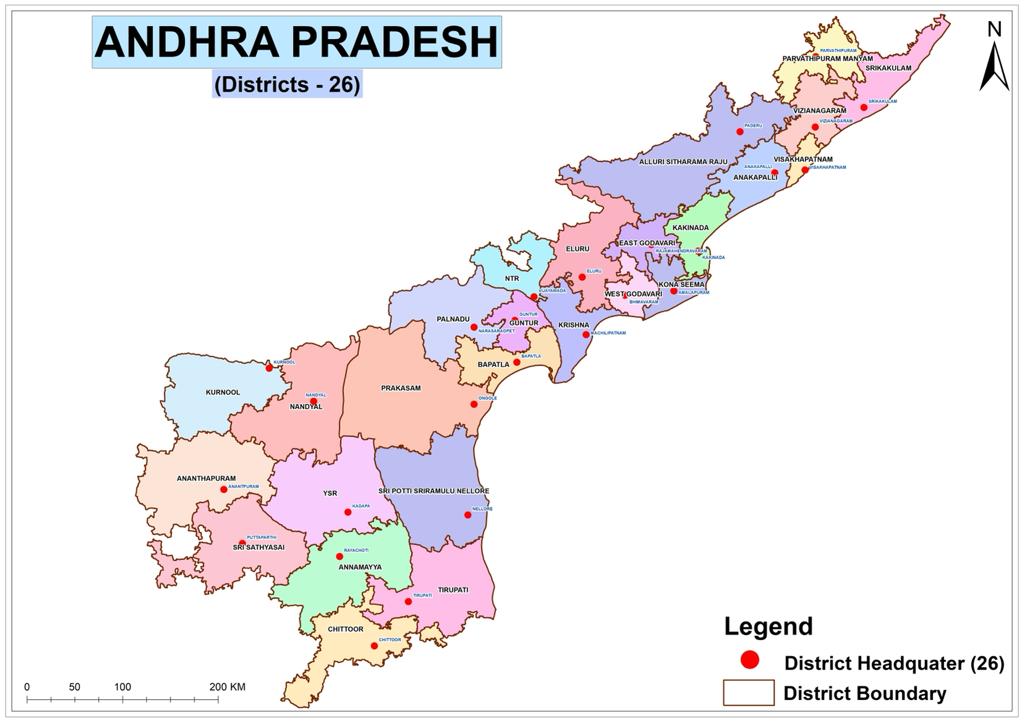
Andhra Pradesh comprises three major regions namely Rayalaseema in the south-west, Coastal Andhra
Coastal Andhra (South costal Andhra) also known as Kostha Andhra is a region in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India. Vijayawada is the largest city in this region. It was part of Madras State before 1953 and Andhra State from 1953 to 1956. ...
bordering the Bay of Bengal in the east and Uttarandhra
Uttarandhra or North coastal Andhra, also known as Kalinga Andhra is a region consisting of six northern districts of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It comprises the districts of Srikakulam, Parvathipuram Manyam, Vizianagaram, Visakhapat ...
at north-east. The state has 26 districts, 6 in Uttarandhra, 12 in Coastal Andhra and 8 in Rayalaseema. The state also borders a union territory, Yanam
Yanam (Telugu: ''యానాం'') is a town located in the Yanam district in Puducherry. It has a population of 35,000 and is entirely surrounded by Andhra Pradesh. It was formerly a French colony for nearly 200 years, and, though united ...
– a district of Puducherry Puducherry or Pondicherry may refer to:
* Puducherry (union territory), a union territory of India
** Pondicherry, capital of the union territory of Puducherry
** Puducherry district, a district of the union territory of Puducherry
** Puducherry t ...
, which lies to the south of Kakinada
Kakinada (List of renamed places in India, formerly called Kakinandiwada, Coringa, and Cocanada; ) is the List of cities in Andhra Pradesh by population, sixth largest city of the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Andhra P ...
in the Godavari delta on the eastern side of the state. The economy of Andhra Pradesh
The GSDP at constant (2011–12) Prices for the year 2018-19 (Advance Estimates) is estimated at 850,000 crores as against 490,134 crores for 2015-16 (First Revised Estimates) indicating a growth of 11.61%. Per Capita Income at current prices i ...
is the 8th largest in India, with a gross state domestic product (GSDP) of and has the country's 17th-highest GSDP per capita of . Andhra Pradesh ranks 27th among Indian states in Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, whi ...
(HDI). It has a jurisdiction over almost of territorial waters.
Andhra Pradesh hosted 121.8 million visitors in 2015, a 30% growth in tourist arrivals over the previous year, making it the third most-visited state in India. The Tirumala Venkateswara Temple
Sri Venkateswara Swami Vaari Temple is a Hindu temple situated in the hill town of Tirumala at Tirupati in Tirupati district of Andhra Pradesh, India. The Temple is dedicated to Venkateswara, a form of Vishnu, who is believed to have appeared ...
in Tirupati
Tirupati () is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Tirupati district. The city is home to the important Hindu shrine of Tirumala Venkateswara Temple and other historic temples and is refe ...
is one of the world's most visited religious sites, with 18.25 million visitors per year. The region is also home to a variety of other pilgrimage centres, such as the Pancharama Kshetras
The Pancharama Kshetras (or the Pancharamas) are five ancient Hindu temples of Shiva in Andhra Pradesh. The Sivalingas at these temples are made from a single Sivalinga.
Legend
As per the legend, a Shiva Lingam was owned by the Rakshasa ki ...
, Mallikarjuna Jyotirlinga
Sri Bhramaramba Mallikarjuna Temple or Srisailam Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to the deities Shiva and Parvati, located at Srisailam in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh.
It is significant to the Hindu sects of both Shaivism and Shakt ...
and Kodanda Rama Temple. The state's natural attractions include the beaches
A beach is a landform alongside a body of water which consists of loose particles. The particles composing a beach are typically made from rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle, pebbles, etc., or biological sources, such as mollusc shel ...
of Visakhapatnam, hill station
A hill station is a town located at a higher elevation than the nearby plain or valley. The term was used mostly in colonial Asia (particularly in India), but also in Africa (albeit rarely), for towns founded by European colonialists as refuges ...
s such as the Araku Valley
Araku Valley is a hill station in Alluri Sitharama Raju district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh, lying 111 km west of Visakhapatnam city. This place is often referred to as ''Ooty of Andhra''. It is a valley in the Eastern Ghats inh ...
and Horsley Hills, and the deltas of Konaseema
Konaseema is a group of islands between the tributaries of the Godavari River and Bay of Bengal located in Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Konaseema district of Andhra Pradesh in southern India. It is nicknamed "Gods Own Creation" due to similarities wit ...
in the Godavari river, and Diviseema
Diviseema is a small and deltaic island in Krishna District of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It comprises three Mandals - Avanigadda, Koduru and Nagayalanka.
Etymology
The word Diviseema translates as the ''abode of the divine''.
Div ...
in the Krishna river.
History
Toponym
A group of people named Andhras was mentioned inSanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
texts such as Aitareya Brahmana The Aitareya Brahmana ( sa, ऐतरेय ब्राह्मण) is the Brahmana of the Shakala Shakha of the Rigveda, an ancient Indian collection of sacred hymns. This work, according to the tradition, is ascribed to Mahidasa Aitareya.
Aut ...
(800–500 BCE
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the or ...
). According to ''Aitareya Brahmana'' of the Rig Veda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Sh ...
, the Andhras left north India from banks of River Yamuna
The Yamuna ( Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Ban ...
and settled in south India. The Satavahanas have been mentioned by the names ''Andhra'', ''Andhrara-jateeya'' and ''Andhrabhrtya
The s (Devanagari:आन्ध्रभृत्य) was an Indian dynasty mentioned in the Puranas. Lists of Andhrabhrtyas have been mentioned in various Puranas. They are mostly identified with Satavahanas which replaced the house of the Maurya ...
'' in the Puranic literature. They did not refer themselves as ''Andhra'' in any of their coins or inscriptions; it is possible that they were termed as Andhras because of their ethnicity or because their territory included the Andhra region.
Early and medieval history
Assaka
Ashmaka (Sanskrit: ) or Assaka (Pali: ) was a Mahajanapada in ancient India which existed between 700 BCE and 425 or 345 BCE according to the Buddhist texts '' Anguttara Nikaya'' and ''Puranas''. It was located around and between the Godavar ...
Mahajanapada, one of the sixteen Vedic Mahajanapadas, included Andhra, Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
and Telangana. Archaeological evidence from places such as Amaravati
Amaravati () is the capital of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located on the banks of the river Krishna in Guntur district.
The Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone at a ceremonial event in Uddandara ...
, Dharanikota
Dharanikota is a village in Palnadu district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located in Amaravathi mandal of Guntur revenue division. The village forms a part of Andhra Pradesh Capital Region, under the jurisdiction of APCRDA.
H ...
, and Vaddamanu
Vaddamanu is a village in Guntur district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located at a distance of 7km from Krishna River in Thullur mandal of Guntur revenue division. The village is a part of the new capital, Amaravati.
Demogra ...
suggests that the Andhra region was part of the Mauryan Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
. Amaravati
Amaravati () is the capital of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located on the banks of the river Krishna in Guntur district.
The Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone at a ceremonial event in Uddandara ...
might have been a regional centre for the Mauryan rule. After the death of Emperor Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, ...
, Mauryan rule weakened around 200 BCE and was replaced by several smaller kingdoms
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
in the Andhra region.
The Satavahana dynasty
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan region. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the late ...
dominated the Deccan region from the 1st century BCE to the 3rd century CE. The later Satavahanas made Dharanikota and Amaravathi their capital, which according to the Buddhists is the place where Nagarjuna
Nāgārjuna . 150 – c. 250 CE (disputed)was an Indian Mahāyāna Buddhist thinker, scholar-saint and philosopher. He is widely considered one of the most important Buddhist philosophers.Garfield, Jay L. (1995), ''The Fundamental Wisdom of ...
, the philosopher of Mahayana
''Mahāyāna'' (; "Great Vehicle") is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, texts, philosophies, and practices. Mahāyāna Buddhism developed in India (c. 1st century BCE onwards) and is considered one of the three main existing bra ...
lived in the 2nd and 3rd centuries. The Andhra Ikshvaku
The Ikshvaku ( IAST: Ikṣvāku) dynasty ruled in the eastern Krishna River valley of India, from their capital at Vijayapuri (modern Nagarjunakonda in Andhra Pradesh) during approximately 3rd and 4th centuries CE. The Ikshvakus are also kn ...
s, with their capital at Vijayapuri, succeeded the Satavahanas in the Krishna River valley in the latter half of the 2nd century. Pallavas, who were originally executive officers under the Satavahana kings, were not a recognised political power before the 2nd century CE and were swept away by the Western Chalukyan invasion, led by Pulakesin II
Pulakeshin II ( IAST: Pulakeśin, r. c. 610–642 CE) was the most famous ruler of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi (present-day Badami in Karnataka, India). During his reign, the Chalukya kingdom expanded to cover most of the Deccan region in ...
in the first quarter of the 7th century CE. After the downfall of the Ikshvakus, the Vishnukundinas
The Vishnukundina dynasty (IAST: Viṣṇukundina) was an Indian dynasty based in Deccan Plateau, Deccan, which ruled modern Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Odisha and parts of South India during the 5th and 6th centuries, carving land out from the V ...
were the first great dynasty in the 5th and 6th centuries, and held sway over the entire Andhra country, including Kalinga Kalinga may refer to:
Geography, linguistics and/or ethnology
* Kalinga (historical region), a historical region of India
** Kalinga (Mahabharata), an apocryphal kingdom mentioned in classical Indian literature
** Kalinga script, an ancient writ ...
and parts of Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian subcontinent, Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India b ...
. They played an important role in the history of Deccan during the 5th and 6th century CE, with Eluru
Eluru is a city and the district headquarters of Eluru district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the 14 municipal corporations in the state and the mandal headquarters of Eluru mandal in the Eluru revenue division. The city ...
, Amaravathi and Puranisangam.
The Salankayanas were an ancient dynasty that ruled the Andhra region between Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
and Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
with their capital at Vengi (modern Pedavegi
Pedavegi is a village in Eluru district in the state of Andhra Pradesh in India, 10 km north of Eluru. It is administered under Eluru revenue division. Pedavegi also serves as the mandal headquarters of Pedavegi mandal. The nearest railway st ...
) from 300 to 440 CE. The Eastern Chalukyas of Vengi
Vengi (or Venginadu) is a delta region spread over the Krishna and Godavari River, (also called Godavari and Krishna districts), the region is also known as Godavari Delta, that used to house world famous diamond mines in the Medieval period ...
, whose dynasty lasted for around five hundred years from the 7th century until 1130 CE, eventually merged with the Chola dynasty
The Chola dynasty was a Tamils, Tamil thalassocratic Tamil Dynasties, empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated ...
. They continued to rule under the protection of the Chola dynasty until 1189 CE when the kingdom succumbed to the Hoysalas
The Hoysala Empire was a Kannadiga power originating from the Indian subcontinent that ruled most of what is now Karnataka between the 10th and the 14th centuries. The capital of the Hoysalas was initially located at Belur, but was later moved ...
and the Yadava
The Yadava (literally, descended from Yadu) were an ancient Indian people who believed to be descended from Yadu, a legendary king of Chandravamsha lineage. The community was formed of various clans, being the Abhira, Andhaka, Vrishni, and Sat ...
s. The roots of the Telugu language
Telugu (; , ) is a Dravidian language spoken by Telugu people predominantly living in the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, where it is also the official language. It is the most widely spoken member of the Dravidian language fami ...
have been seen on inscriptions found near the Guntur district
Guntur district is one of the twenty six districts in the Coastal Andhra region of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. The administrative seat of the district is located at Guntur, the largest city of the district in terms of area and with a po ...
and from others dating to the rule of Renati Cholas in the fifth century CE.
Kayastha chiefs descended from North Indian Kayasthas ruled over vast swathes of land in Andhra country, and they are recorded in Andhra history dating back to the 13th century CE. Kakatiyas ruled Andhra Pradesh state for nearly two hundred years and constructed several forts. They were succeeded by the Musunuri Nayaks
The Musunuri Nayakas were warrior kings of 14th-century South India who were briefly significant in the region of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh. Musunuri Kapaya Nayaka is said to have taken a leadership role among the Andhra chieftains and driv ...
. Musunuri Nayaks led a confederation of Nayakas to overthrow the rule of the Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
Sultanate in Telugu lands.
The Reddi kingdom
The Reddi kingdom or Kondavidu Reddi kingdom (1325–1448 CE) was established in southern India by Prolaya Vema Reddi. Most of the region that was ruled by the Reddi dynasty is now part of modern-day coastal and central Andhra Pradesh.
Orig ...
(1325–1448 CE) was established by Prolaya Vema Reddi in the early 14th century, who ruled from present day Kondaveedu. Prolaya Vema Reddi was part of the confederation of states that started a movement against the invading Turkic Muslim armies of the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
. They constructed Kondaveedu Fort
Kondaveedu Fort is a historically significant ancient hill fortress located in Kondaveedu, a village in the Chilakaluripet constituency of Palnadu district, Andhra Pradesh, India. The site is located 16 miles west of the city of Guntur. Apart fr ...
, which they ruled between 1328 and 1428, before it was taken over by the Gajpathis of Orissa, and later ravaged by the Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
rulers of the Bahmani kingdom
The Bahmani Sultanate, or Deccan, was a Persianate Sunni Muslim Indian Kingdom located in the Deccan region. It was the first independent Muslim kingdom of the Deccan,
in 1458. The Vijayanagara emperor Krishnadevaraya captured it in 1516. The Qutb Shahi dynasty, Golconda Sultans fought for the fort in 1531, 1536 and 1579, and Sultan Quli Qutb Shah captured it in 1579, renaming it ''Murtuzanagar''. It was reconquered by Vijayanagara who overthrew sultanate rule across the entirety of modern-day Andhra Pradesh (excluding Telangana). After this rebellion, the Bahmani sultans launched no further military campaigns outside their kingdoms, because the Maratha Empire, Maratha empire soon emerged as the strongest power in India. Efforts are in progress to classify Kondaveedu Fort
Kondaveedu Fort is a historically significant ancient hill fortress located in Kondaveedu, a village in the Chilakaluripet constituency of Palnadu district, Andhra Pradesh, India. The site is located 16 miles west of the city of Guntur. Apart fr ...
as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
S ...
, Tamil language, Tamil, and Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
, while Carnatic music evolved into its current form.Historians such as P. B. Desai (''History of Vijayanagar Empire'', 1936), Henry Heras (''The Aravidu Dynasty of Vijayanagara'', 1927), B. A. Saletore (''Social and Political Life in the Vijayanagara Empire'', 1930), G.S. Gai (Archaeological Survey of India), William Coelho (''The Hoysala Vamsa'', 1955) and Kamath (Kamath 2001, pp. 157–160) During the Vijayanagara Empire, the Pemmasani Nayaks controlled parts of Andhra Pradesh and had large mercenary armies that were the vanguard of the Vijayanagara Empire in the sixteenth century. The Lepakshi group of monuments are culturally and archaeologically significant as it is the location of shrines dedicated to Shiva, Vishnu, and Veerabhadra Temple, Lepakshi, Veerabhadra which were built during the Vijayanagara Kings' period (1336–1646). The temples are the location of mural paintings of the Vijayanagara kings, Dravidian art, and inscriptions. Near the temple complex is a large granite Nandi (mythology), Nandi bull. On a hillock known as ''Kurma Saila'' ('tortoise-shaped hill') are other temples to Papanatheswara, Raghunatha, Rama, Srirama, and Durga.
The Government of Andhra Pradesh has taken the initiative for including the "Lepakshi Group of Monuments" among the List of World Heritage Sites in India, UNESCO World Heritage sites in India.
Modern history
 Harihara and Bukka, who served as treasury officers of the Kakatiyas of Warangal, founded the
Harihara and Bukka, who served as treasury officers of the Kakatiyas of Warangal, founded the Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also called the Karnata Kingdom, was a Hinduism, Hindu empire based in the region of South India, which consisted the modern states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa and some parts of Telangana an ...
. In 1347 CE, an independent Muslim state, the Bahmani Sultanate, was established in south India by Ala-ud-Din Bahman Shah in a revolt against the Delhi Sultanate. The Qutb Shahi dynasty held sway over the Andhra country after the resolution of Vijayanagar empire by joint action of Mughals, Bijapur and Golconda sultanates.
In the early nineteenth century, Northern Circars was ceded to the East India Company, British East India Company and became part of the Madras Presidency. Eventually, this region emerged as the Coastal Andhra
Coastal Andhra (South costal Andhra) also known as Kostha Andhra is a region in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India. Vijayawada is the largest city in this region. It was part of Madras State before 1953 and Andhra State from 1953 to 1956. ...
region. Later the Nizam of Hyderabad, Nizam rulers of Hyderabad ceded five territories to the British that eventually became the Rayalaseema region. The Nizams retained control of the interior provinces as the princely state of Hyderabad State, Hyderabad, acknowledging British Raj, British rule in return for local autonomy. However, Komaram Bheem, a tribal leader, started his fight against the erstwhile Asaf Jahi dynasty, Asaf Jahi Dynasty for the liberation of Hyderabad State. Meanwhile, the French colonial empire, French occupied Yanam, in the Godavari delta, and (save for periods of British control) would hold it until 1954. In 1947, Vizianagaram was the largest Hindu princely state in Andhra Pradesh.
In 1839 just before the British Raj, a cyclone struck Coringa, East Godavari district and toppled buildings, as a result 20,000 ships were destroyed and over 300,000 people were killed.
Indian independence movement, India became independent from the British Raj in 1947. The 7th Nizam wanted to retain the independence of the Princely Hyderabad State from India, but the people of the region launched a movement to join the Indian Union. The state of Hyderabad was integrated into the Dominion of India, Indian Union with Annexation of Hyderabad, Operation Polo in 1948.
Post-independence
 In an effort to gain an independent state based on linguistic identity, and to protect the interests of the Telugu-speaking people of Madras State, Potti Sreeramulu fasted to death in 1952. As Madras became a bone of contention, in 1949 a JVP committee report stated: "Andhra Province could be formed provided the Andhras give up their claim on the city of Madras [now Chennai]". After Potti Sreeramulu's death, the Telugu-speaking area of
In an effort to gain an independent state based on linguistic identity, and to protect the interests of the Telugu-speaking people of Madras State, Potti Sreeramulu fasted to death in 1952. As Madras became a bone of contention, in 1949 a JVP committee report stated: "Andhra Province could be formed provided the Andhras give up their claim on the city of Madras [now Chennai]". After Potti Sreeramulu's death, the Telugu-speaking area of Andhra State
Andhra State (IAST: ; ) was a Administrative divisions of India#States and union territories, state in India created in 1953 from the Telugu language, Telugu-speaking northern List of districts in India, districts of Madras State. The state was ...
was carved out of Madras State on 1 October 1953, with Kurnool
Kurnool is a city in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India. It formerly served as the capital of Andhra State (1953–1956). The city is often referred to as "The Gateway of Rayalaseema".Kurnool is also known as The City of Gem Stones. It also se ...
as its capital city. On the basis of the Gentlemen's Agreement of 1956, gentlemen's agreement of 1 November 1956, the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Reorganisation Act formed United Andhra Pradesh (1956-2014), combined Andhra Pradesh by merging the Telugu-speaking areas of the already existing Hyderabad State. Hyderabad was made the capital of the new state. The Marathi-speaking areas of Hyderabad State merged with Bombay State and the Kannada-speaking areas were merged with Mysore State.
In February 2014, the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014, Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act bill was passed by the Parliament of India for the formation of the Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian subcontinent, Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India b ...
state comprising List of districts of Telangana, ten districts. Hyderabad will remain as a joint capital for not exceeding ten years. The new state of Telangana came into existence on 2 June 2014 after approval from the President of India. Number of petitions questioning the validity of Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014 is long pending for the verdict since April 2014 before the Supreme Court of India, Supreme Court constitutional bench.
In 2017, Government of Andhra Pradesh began operating from the newly planned capital city Amaravati
Amaravati () is the capital of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located on the banks of the river Krishna in Guntur district.
The Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone at a ceremonial event in Uddandara ...
. In August 2020, Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly passed Andhra Pradesh Decentralisation and Inclusive Development of All Regions Act, 2020. The decision resulted in widespread 2019–2020 Amaravati protests, protests by the farmers of Amaravati. The act has been challenged in Andhra Pradesh High Court, which ordered to maintain status quo until the court completes its hearing. On 22 November 2021, the Government of Andhra Pradesh, government, led by Y. S. Jagan Mohan Reddy, has withdrawn the Andhra Pradesh Decentralisation and Inclusive Development of All Regions Act, 2020, act. The Chief Minister, however, said his government would bring a better and more complete bill.
Geography
Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
that support varied ecosystems, the rich diversity of flora and fauna. There are two main rivers namely, Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
and Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
, that flow through the state. The Coastline of Andhra Pradesh, coastline of the state extends along the Bay of Bengal from Srikakulam district, Srikakulam to Nellore district with a length of 975 km (606 mi). The plains to the east of Eastern Ghats form the Eastern Coastal Plains, Eastern Coastal plains. The coastal plains are for the most part of delta regions formed by the Godavari, Krishna, and Penna River, Penna rivers. The Eastern Ghats are discontinuous and individual sections have local names. The Eastern Ghats are a major dividing line in the state's geography. The Kadapa Basin formed by two arching branches of the Eastern Ghats is a mineral-rich area. The Ghats become more pronounced towards the south and extreme north of the coast. Most of the coastal plains are put to intense agricultural use. The Rayalaseema region has semi-arid conditions.
Natural vegetation and conservation
 The Andhra Pradesh Forest Department deals with protection, conservation and management of forests. The total forest cover of the state after the bifurcation is left with an area of . The forest in the state can be broadly divided into four major biotic provinces. They are:
# Deccan Plateau
# Central Plateau
# Eastern Highland
# East Coastal Plains
Eastern Ghats region is home to dense tropical forests, while the vegetation becomes sparse as the Ghats give way to the Deccan Plateau, where shrub vegetation is more common. The vegetation found in the state is largely of dry deciduous types with a mixture of teak, ''Terminalia (plant), Terminalia'', ''Dalbergia'', ''Pterocarpus'', ''Anogeissus'', etc.
The state has many List of wildlife sanctuaries of India, sanctuaries, List of national parks of India, national parks and Zoo Park, zoological parks, such as Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary, Coringa, Krishna Wildlife Sanctuary, Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve, Kambalakonda Wildlife Sanctuary, Sri Venkateswara Zoological Park and Indira Gandhi Zoological Park. Kolleru Bird Sanctuary, Atapaka Bird Sanctuary, Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary, Telineelapuram and Telukunchi Bird Sanctuaries and Pulicat Lake Bird Sanctuary attract many migratory birds. The state possesses some rare and endemic plants like ''Cycas beddomei'', ''Pterocarpus santalinus'', ''Terminalia pallida'', ''Syzygium alternifolium'', ''Shorea talura'', ''Shorea tumburgia'', ''Psilotum nudum'', etc. The diversity of fauna includes tigers, panthers, hyenas, Blackbuck, black bucks, Cheetah, cheetals, Sambar deer, sambars, sea turtles and a number of birds and reptiles. The estuaries of the Godavari and Krishna rivers support rich Mangrove, mangrove forests with fishing cats and otters as keystone species.
The Andhra Pradesh Forest Department deals with protection, conservation and management of forests. The total forest cover of the state after the bifurcation is left with an area of . The forest in the state can be broadly divided into four major biotic provinces. They are:
# Deccan Plateau
# Central Plateau
# Eastern Highland
# East Coastal Plains
Eastern Ghats region is home to dense tropical forests, while the vegetation becomes sparse as the Ghats give way to the Deccan Plateau, where shrub vegetation is more common. The vegetation found in the state is largely of dry deciduous types with a mixture of teak, ''Terminalia (plant), Terminalia'', ''Dalbergia'', ''Pterocarpus'', ''Anogeissus'', etc.
The state has many List of wildlife sanctuaries of India, sanctuaries, List of national parks of India, national parks and Zoo Park, zoological parks, such as Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary, Coringa, Krishna Wildlife Sanctuary, Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve, Kambalakonda Wildlife Sanctuary, Sri Venkateswara Zoological Park and Indira Gandhi Zoological Park. Kolleru Bird Sanctuary, Atapaka Bird Sanctuary, Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary, Telineelapuram and Telukunchi Bird Sanctuaries and Pulicat Lake Bird Sanctuary attract many migratory birds. The state possesses some rare and endemic plants like ''Cycas beddomei'', ''Pterocarpus santalinus'', ''Terminalia pallida'', ''Syzygium alternifolium'', ''Shorea talura'', ''Shorea tumburgia'', ''Psilotum nudum'', etc. The diversity of fauna includes tigers, panthers, hyenas, Blackbuck, black bucks, Cheetah, cheetals, Sambar deer, sambars, sea turtles and a number of birds and reptiles. The estuaries of the Godavari and Krishna rivers support rich Mangrove, mangrove forests with fishing cats and otters as keystone species.
Climate
The climate of Andhra Pradesh varies considerably, depending on the geographical region. Summers last from March to June. In the coastal plain, the summer temperatures are generally higher than the rest of the state, with temperature ranging between . July to September is the season for tropical rains. About one-third of the total rainfall is brought by the northeast monsoon. October and November see low-pressure systems and tropical cyclones form in the Bay of Bengal which, along with the northeast monsoon, bring rains to the southern and coastal regions of the state. November, December, January, and February are the winter months in Andhra Pradesh. Since the state has a long coastal belt the winters are not very cold. The range of winter temperature is generally . Lambasingi in Visakhapatnam district is also nicknamed as the "Kashmir of Andhra Pradesh" due to its relatively cool climate as compared to others and the temperature ranges from .Demographics
 Census of India, the residual state had a population of with a population density of . According to the Polavaram ordinance bill 2014, 7 Tehsil, mandals of Khammam district in Telangana state merged with Andhra Pradesh to facilitate Polavaram Project, Polavaram project, due to which population of added to Andhra Pradesh. Thus the final population of Andhra Pradesh in the year 2014, as per census 2011 is , with a density of .
The total population constitute, 70.4% of rural population with inhabitants and 29.6% of urban population with inhabitants. Children in the age group of 0–6 years are , constituting 10.6% of the total population, among them are boys and are girls. Visakhapatnam district has the largest urban population of 47.5% and Srikakulam district with 83.8%, has the largest rural population, among others districts in the state. The overall population of the state comprises 17.1% of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, Scheduled Caste and 5.3% of Scheduled Tribe population.
There are male and female citizens—a Human sex ratio, sex ratio of 996 females per 1000 males, higher than the national average of 926 per 1000. The Literacy, literacy rate of the state stands at 67.41%. However, post bifurcation from Telangana, the state is expected to reach 91.1% by 2021. West Godavari district has the highest literacy rate of 74.6% and Vizianagaram district has the least with 58.9%.
Andhra Pradesh ranks tenth of all Indian States in the Human Development Index scores with a score of 0.416. The National Council of Applied Economic Research district analysis in 2001 reveals that
Census of India, the residual state had a population of with a population density of . According to the Polavaram ordinance bill 2014, 7 Tehsil, mandals of Khammam district in Telangana state merged with Andhra Pradesh to facilitate Polavaram Project, Polavaram project, due to which population of added to Andhra Pradesh. Thus the final population of Andhra Pradesh in the year 2014, as per census 2011 is , with a density of .
The total population constitute, 70.4% of rural population with inhabitants and 29.6% of urban population with inhabitants. Children in the age group of 0–6 years are , constituting 10.6% of the total population, among them are boys and are girls. Visakhapatnam district has the largest urban population of 47.5% and Srikakulam district with 83.8%, has the largest rural population, among others districts in the state. The overall population of the state comprises 17.1% of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, Scheduled Caste and 5.3% of Scheduled Tribe population.
There are male and female citizens—a Human sex ratio, sex ratio of 996 females per 1000 males, higher than the national average of 926 per 1000. The Literacy, literacy rate of the state stands at 67.41%. However, post bifurcation from Telangana, the state is expected to reach 91.1% by 2021. West Godavari district has the highest literacy rate of 74.6% and Vizianagaram district has the least with 58.9%.
Andhra Pradesh ranks tenth of all Indian States in the Human Development Index scores with a score of 0.416. The National Council of Applied Economic Research district analysis in 2001 reveals that Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
, West Godavari and Chittoor district, Chittoor are the three districts in rural AP with the highest Human Development Index scores in ascending order.

Languages
Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
S ...
is the official language of Andhra Pradesh, which is also the mother tongue of nearly 90% of the population. Rajahmundry is the cultural capital of Andhra Pradesh and Telugu language has roots originated from this region. The Minister of Tourism and Culture has declared Telugu a Classical languages of India#Classical, Classical Language. Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
''
''
Tamil Nadu, Tamil, Kannada and Odia language, Odia are also spoken mainly in the border-areas. Lambadi, Koya language, Koya, Sora language, Savara, Konda language (Dravidian), Konda, Ollari language, Gadaba and a number of other languages are spoken by the Scheduled Tribes of the state.
File:Sri Kala Hasti.jpg, Srikalahasti Temple
File:Tirumala 090615.jpg, Venkateswara Temple, Tirumala
File:Rock-cut Lord --Buddha-- Statue at Bojjanakonda near Anakapalle of Visakhapatnam dist in AP.jpg, Rock-cut Buddha statue at Bojjannakonda near Anakapalle,

 When the state was first created, Tanguturi Prakasam Pantulu, became the Chief minister (India), Chief Minister. After the unification with Telangana, Neelam Sanjiva Reddy became the first List of chief ministers of Andhra Pradesh, Chief Minister. He later served as the List of presidents of India, President of India.
The Indian National Congress (INC), the Praja Socialist Party and the Krishi Lok Party were the major parties in the 1950s. Later the Communist Party of India (CPI) became the dominant opposition party. In the 1967 Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, 1967 state assembly elections, all socialist parties were eliminated and the CPI lost opposition party status.
The INC ruled the state from 1956 to 1982. In 1983, the Telugu Desam Party (TDP) won the state elections and N. T. Rama Rao became the Chief Minister of the state for the first time. This broke the long-time single party monopoly enjoyed by the INC. The 1989 Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, 1989 elections ended the rule of Rao, with the INC returning to power with Marri Chenna Reddy at the helm. He was replaced by N. Janardhana Reddy, Janardhan Reddy in 1990, who was replaced by Kotla Vijaya Bhaskara Reddy in 1992.
In 1994 Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, 1994, Andhra Pradesh gave a mandate to the Telugu Desam Party again, and Rao became the Chief Minister again. N. Chandrababu Naidu, Nara Chandrababu Naidu, Rao's son-in-law, came to power in 1995 with the backing of a majority of the Member of the Legislative Assembly (India), MLAs. The Telugu Desam Party won both the 1999 Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, assembly and Lok Sabha 1999 Indian general election, election in 1999 under the leadership of Chandrababu Naidu. Thus Naidu held the record for the longest-serving Chief Minister (1995 to 2004).
In 2004 Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, 2004, Congress returned to power with a new chief ministerial face, Y. S. Rajasekhara Reddy, YS Rajashekara Reddy, better known as YSR. He also won the 2009 Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, 2009 elections, but shortly afterward was killed in a 2009 Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister helicopter crash, helicopter crash in September of that year. He was succeeded by two other Congressmen, namely Konijeti Rosaiah and Nallari Kiran Kumar Reddy, the last resigning over the impending Telangana movement, division of
When the state was first created, Tanguturi Prakasam Pantulu, became the Chief minister (India), Chief Minister. After the unification with Telangana, Neelam Sanjiva Reddy became the first List of chief ministers of Andhra Pradesh, Chief Minister. He later served as the List of presidents of India, President of India.
The Indian National Congress (INC), the Praja Socialist Party and the Krishi Lok Party were the major parties in the 1950s. Later the Communist Party of India (CPI) became the dominant opposition party. In the 1967 Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, 1967 state assembly elections, all socialist parties were eliminated and the CPI lost opposition party status.
The INC ruled the state from 1956 to 1982. In 1983, the Telugu Desam Party (TDP) won the state elections and N. T. Rama Rao became the Chief Minister of the state for the first time. This broke the long-time single party monopoly enjoyed by the INC. The 1989 Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, 1989 elections ended the rule of Rao, with the INC returning to power with Marri Chenna Reddy at the helm. He was replaced by N. Janardhana Reddy, Janardhan Reddy in 1990, who was replaced by Kotla Vijaya Bhaskara Reddy in 1992.
In 1994 Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, 1994, Andhra Pradesh gave a mandate to the Telugu Desam Party again, and Rao became the Chief Minister again. N. Chandrababu Naidu, Nara Chandrababu Naidu, Rao's son-in-law, came to power in 1995 with the backing of a majority of the Member of the Legislative Assembly (India), MLAs. The Telugu Desam Party won both the 1999 Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, assembly and Lok Sabha 1999 Indian general election, election in 1999 under the leadership of Chandrababu Naidu. Thus Naidu held the record for the longest-serving Chief Minister (1995 to 2004).
In 2004 Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, 2004, Congress returned to power with a new chief ministerial face, Y. S. Rajasekhara Reddy, YS Rajashekara Reddy, better known as YSR. He also won the 2009 Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, 2009 elections, but shortly afterward was killed in a 2009 Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister helicopter crash, helicopter crash in September of that year. He was succeeded by two other Congressmen, namely Konijeti Rosaiah and Nallari Kiran Kumar Reddy, the last resigning over the impending Telangana movement, division of

 Andhra Pradesh was ranked eighth among other Indian states in terms of Gross regional domestic product, GSDP for the financial year 2014–2015. The GSDP at current prices was and at constant prices was . The domestic product of agriculture sector accounts for and industrial sector for . The service sector of the state accounts more percentage of the GSDP with a total of . In the 2010 list by ''Forbes'' magazine, several people from Andhra Pradesh were among the top List of Indian people by net worth, 100 richest Indians.
Andhra Pradesh was ranked eighth among other Indian states in terms of Gross regional domestic product, GSDP for the financial year 2014–2015. The GSDP at current prices was and at constant prices was . The domestic product of agriculture sector accounts for and industrial sector for . The service sector of the state accounts more percentage of the GSDP with a total of . In the 2010 list by ''Forbes'' magazine, several people from Andhra Pradesh were among the top List of Indian people by net worth, 100 richest Indians.
File:Konaseema greenery 1.JPG, Lush green farms in
Andhra Pradesh's economy is mainly based on agriculture and livestock. Four important rivers of India, the


 The industrial sector of the state includes some of the key sectors like Pharmaceutical industry in India, pharmaceutical, Automotive industry in India, automobile, Textile industry in India, textiles etc. Sri City, Sricity located in Chittoor district is an integrated business city which is home to firms including PepsiCo, Isuzu Motors India, Isuzu Motors, Cadbury, Cadbury India, Kellogg's, Colgate-Palmolive, Kobe Steel, Kobelco etc. The PepsiCo firm has its largest plant in India at Sri City. The state is also emerging as destination for the automobile industry which already hosts companies including Ashok Leyland in Krishna district, Hero Motors in Chittoor district, Kia Motors India, Kia Motors in Anantapur district.
The industrial sector of the state includes some of the key sectors like Pharmaceutical industry in India, pharmaceutical, Automotive industry in India, automobile, Textile industry in India, textiles etc. Sri City, Sricity located in Chittoor district is an integrated business city which is home to firms including PepsiCo, Isuzu Motors India, Isuzu Motors, Cadbury, Cadbury India, Kellogg's, Colgate-Palmolive, Kobe Steel, Kobelco etc. The PepsiCo firm has its largest plant in India at Sri City. The state is also emerging as destination for the automobile industry which already hosts companies including Ashok Leyland in Krishna district, Hero Motors in Chittoor district, Kia Motors India, Kia Motors in Anantapur district.
 The state is also emerging in Information technology in India, information technology and Biotechnology in India, biotechnology. The IT/ITES revenues of Visakhapatnam is at in 2012–2013. The development of IT in Tier-II and Tier-III cities like Vijayawada,
The state is also emerging in Information technology in India, information technology and Biotechnology in India, biotechnology. The IT/ITES revenues of Visakhapatnam is at in 2012–2013. The development of IT in Tier-II and Tier-III cities like Vijayawada, 

 Reliance Industries struck nine trillion cubic feet of gas reserves in the Krishna Godavari Basin, KG basin, off the Andhra Pradesh coast near
Reliance Industries struck nine trillion cubic feet of gas reserves in the Krishna Godavari Basin, KG basin, off the Andhra Pradesh coast near
 The state is a pioneer nationwide in Solar power in India, solar power generation. Andhra Pradesh Power Generation Corporation, APGENCO is the power generating company owned by the state. The state has become power surplus with excess power generation being exported to other states. The state is abundantly endowed with solar power and high head Pumped-storage hydroelectricity, PHES sites to convert the solar power available during the day time in to round the clock power supply. PHES projects also has synergy with the lift irrigation projects in storing water available during the monsoon season and supplying to the uplands throughout the year. Ultimate water and energy requirements of the state can be fully met by the combination of cheap solar power, PHES and irrigation projects economically harnessing Renewable energy in India, renewable energy without much damage to the environment.
The state is a pioneer nationwide in Solar power in India, solar power generation. Andhra Pradesh Power Generation Corporation, APGENCO is the power generating company owned by the state. The state has become power surplus with excess power generation being exported to other states. The state is abundantly endowed with solar power and high head Pumped-storage hydroelectricity, PHES sites to convert the solar power available during the day time in to round the clock power supply. PHES projects also has synergy with the lift irrigation projects in storing water available during the monsoon season and supplying to the uplands throughout the year. Ultimate water and energy requirements of the state can be fully met by the combination of cheap solar power, PHES and irrigation projects economically harnessing Renewable energy in India, renewable energy without much damage to the environment.
 Thermal power station, Thermal (Gas-fired power plant, natural gas and Coal-fired power station, coal based) and Renewable energy, renewable power plants totaling to 21,000 MW were installed in the state by 2015. Local power plants of 9,600 Watt, MW capacity only are supplying electricity in the state, which includes Simhadri Super Thermal Power Station (2000 MW) of NTPC Limited, NTPC, Vizag Thermal Power Station (1040 MW), Rayalaseema Thermal Power Station (1650 MW), Sri Damodaram Sanjeevaiah Thermal Power Station (2400 MW), and Dr Narla Tata Rao Thermal Power Station, Narla Tata Rao Thermal Power Plant (1760 MW). Hydel power plants have a capacity of 1671 MW.
Thermal power station, Thermal (Gas-fired power plant, natural gas and Coal-fired power station, coal based) and Renewable energy, renewable power plants totaling to 21,000 MW were installed in the state by 2015. Local power plants of 9,600 Watt, MW capacity only are supplying electricity in the state, which includes Simhadri Super Thermal Power Station (2000 MW) of NTPC Limited, NTPC, Vizag Thermal Power Station (1040 MW), Rayalaseema Thermal Power Station (1650 MW), Sri Damodaram Sanjeevaiah Thermal Power Station (2400 MW), and Dr Narla Tata Rao Thermal Power Station, Narla Tata Rao Thermal Power Plant (1760 MW). Hydel power plants have a capacity of 1671 MW.
 Machilipatnam and Srikalahasti Kalamkari are the two unique textile art forms practised in India. There are also other notable handicrafts present in the state, like the soft limestone Cult image, idol carvings of Durgi. Etikoppaka in Visakhapatnam district is notable for its lac industry, producing lacquered wooden.
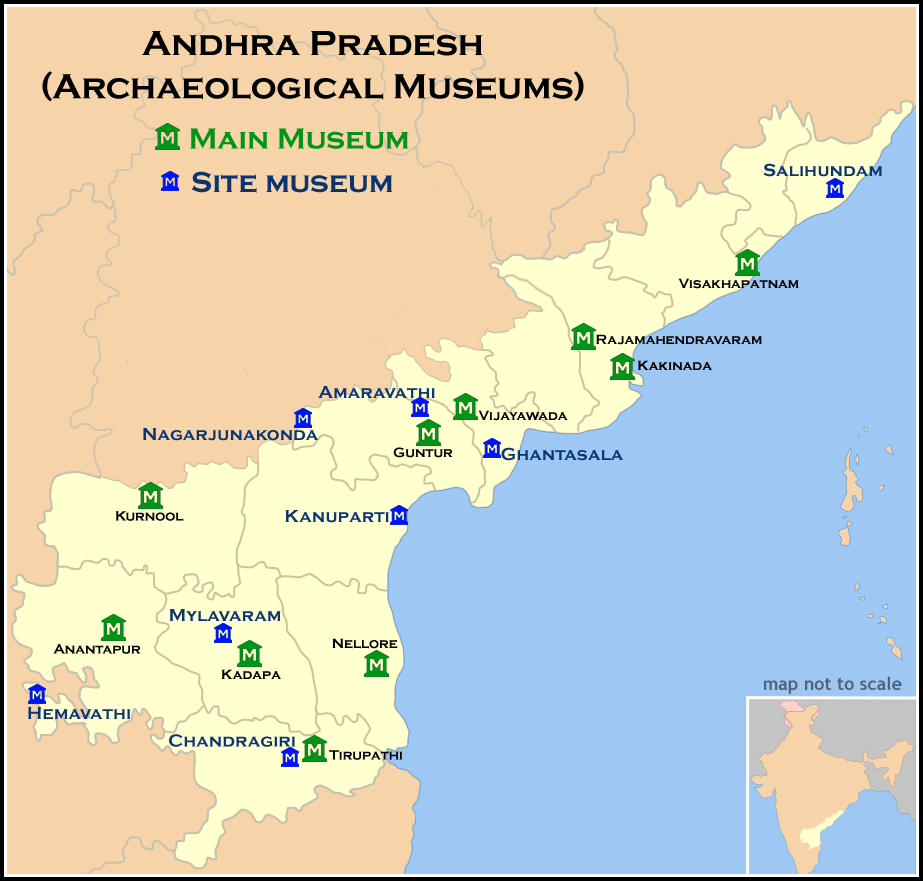
The state has many museums, which features a varied collection of ancient sculptures, paintings, idols, weapons, cutlery, and inscriptions, and religious artifacts such as the Archaeological Museum, Amaravati, Amaravati Archaeological Museum, Visakha Museum and Culture of Andhra Pradesh, Telugu Cultural Museum in Visakhapatnam displays the history of the pre-independence and the Bapu Museum, Vijayawada, Victoria Jubilee Museum in Vijayawada with a large collection of artifacts.
Machilipatnam and Srikalahasti Kalamkari are the two unique textile art forms practised in India. There are also other notable handicrafts present in the state, like the soft limestone Cult image, idol carvings of Durgi. Etikoppaka in Visakhapatnam district is notable for its lac industry, producing lacquered wooden.
The state has many museums, which features a varied collection of ancient sculptures, paintings, idols, weapons, cutlery, and inscriptions, and religious artifacts such as the Archaeological Museum, Amaravati, Amaravati Archaeological Museum, Visakha Museum and Culture of Andhra Pradesh, Telugu Cultural Museum in Visakhapatnam displays the history of the pre-independence and the Bapu Museum, Vijayawada, Victoria Jubilee Museum in Vijayawada with a large collection of artifacts.
 Many composers of Carnatic music like Annamacharya, Kshetrayya, Tyagaraja, and Bhadrachala Ramadasu, Bhadrachala Ramadas were of Telugu descent. Modern Carnatic music composers and singers like Ghantasala (musician), Ghantasala and M. Balamuralikrishna are also of Telugu descent. The Telugu film industry hosts many music composers and playback singers such as S. P. Balasubrahmanyam, P. Susheela, S. Janaki and P. B. Sreenivas. Folk songs are very important and popular in the many rural areas of the state. Forms such as the ''Burra katha'' and ''Poli'' are still performed today. ''Harikathaa Kalakshepam (or Harikatha)'' involves the narration of a story, intermingled with various songs relating to the story. Harikatha was originated in Andhra. ''Burra katha'' is an oral storytelling technique with the topic be either a Hinduism, Hindu mythological story or a contemporary social issue. ''Rangasthalam'' is an Theatre of India, Indian theatre in the
Many composers of Carnatic music like Annamacharya, Kshetrayya, Tyagaraja, and Bhadrachala Ramadasu, Bhadrachala Ramadas were of Telugu descent. Modern Carnatic music composers and singers like Ghantasala (musician), Ghantasala and M. Balamuralikrishna are also of Telugu descent. The Telugu film industry hosts many music composers and playback singers such as S. P. Balasubrahmanyam, P. Susheela, S. Janaki and P. B. Sreenivas. Folk songs are very important and popular in the many rural areas of the state. Forms such as the ''Burra katha'' and ''Poli'' are still performed today. ''Harikathaa Kalakshepam (or Harikatha)'' involves the narration of a story, intermingled with various songs relating to the story. Harikatha was originated in Andhra. ''Burra katha'' is an oral storytelling technique with the topic be either a Hinduism, Hindu mythological story or a contemporary social issue. ''Rangasthalam'' is an Theatre of India, Indian theatre in the
 Telugu people's traditional sweet Pootharekulu originated from Atreyapuram village of East Godavari district.
Telugu people's traditional sweet Pootharekulu originated from Atreyapuram village of East Godavari district.
 The state has several beaches in its coastal districts such as Rushikonda, Mypadu, Suryalanka Beach, Suryalanka etc.; caves such as, Borra Caves, Indian rock-cut architecture depicting Undavalli Caves and the country's second longest caves- the Belum Caves. The valleys and hills include,
The state has several beaches in its coastal districts such as Rushikonda, Mypadu, Suryalanka Beach, Suryalanka etc.; caves such as, Borra Caves, Indian rock-cut architecture depicting Undavalli Caves and the country's second longest caves- the Belum Caves. The valleys and hills include,
 The state has a total road network of , of which of National highways of India, National highways, of State highways in India, state highways and of district roads. National Highway 16 (India), NH 16, with a highway network of around in the state, is a part of Golden Quadrilateral, Golden Quadrilateral Project undertaken by National Highways Development Project. It also forms part of AH45, AH 45 which comes under the Asian Highway Network.
The state has a total road network of , of which of National highways of India, National highways, of State highways in India, state highways and of district roads. National Highway 16 (India), NH 16, with a highway network of around in the state, is a part of Golden Quadrilateral, Golden Quadrilateral Project undertaken by National Highways Development Project. It also forms part of AH45, AH 45 which comes under the Asian Highway Network.
 The state government owned Andhra Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (APSRTC) is the major public bus transport, which runs thousands of buses connecting different parts of the state. Pandit Nehru bus station, Pandit Nehru Bus Station (PNBS) in Vijayawada is one of the largest bus terminals in Asia. From 30 January 2019, all the vehicles in the state are registered as List of Regional Transport Office districts in India, AP–39, followed by an alphabet and four digits.
The state government owned Andhra Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (APSRTC) is the major public bus transport, which runs thousands of buses connecting different parts of the state. Pandit Nehru bus station, Pandit Nehru Bus Station (PNBS) in Vijayawada is one of the largest bus terminals in Asia. From 30 January 2019, all the vehicles in the state are registered as List of Regional Transport Office districts in India, AP–39, followed by an alphabet and four digits.
 Andhra Pradesh has a total broad-gauge railway route of and has no metre-gauge railway. The rail density of the state is 16.59 per , compared to an all India average of 20. The Howrah–Chennai main line which runs through the state is proposed to be upgraded into a High-speed rail in India, high-speed rail corridor through the Diamond Quadrilateral project of the Indian Railways.
The railway network spans two Zones and divisions of Indian Railways, zones, further subdivided into divisions – Vijayawada railway division, Vijayawada, Guntur railway division, Guntur and Guntakal railway division, Guntakal railway divisions of South Central Railway zone, and Waltair railway division of East Coast Railway zone. There is a demand for creating a unified zone for the state based out of Visakhapatnam.
There are three A1 and twenty-three A-category railway stations in the state. has been declared the cleanest railway station in the country. The railway station of Shimiliguda was the first highest broad gauge railway station in the country.
As on date the Railways lines in Andhra Pradesh are under the following Railway zones/Divisions
* South Central Railway-Secunderabad railway division, Secunderabad Division
* South Central Railway-Hyderabad railway division, Hyderabad Division
* South Central Railway-Vijayawada railway division, Vijayawada Division
* South Central Railway-Guntakal railway division, Guntakal Division
* South Central Railway-Guntur railway division, Guntur Division
* East Coast Railway- Waltair railway division, Waltair Division
* East Coast Railway- Khurda Road railway division, Khurda Road Division
A new railway zone South Coast Railway Zone (SCoR) has been announced as the newest Zones and divisions of Indian Railways, railway zone of the Indian Railways and is headquartered at
Andhra Pradesh has a total broad-gauge railway route of and has no metre-gauge railway. The rail density of the state is 16.59 per , compared to an all India average of 20. The Howrah–Chennai main line which runs through the state is proposed to be upgraded into a High-speed rail in India, high-speed rail corridor through the Diamond Quadrilateral project of the Indian Railways.
The railway network spans two Zones and divisions of Indian Railways, zones, further subdivided into divisions – Vijayawada railway division, Vijayawada, Guntur railway division, Guntur and Guntakal railway division, Guntakal railway divisions of South Central Railway zone, and Waltair railway division of East Coast Railway zone. There is a demand for creating a unified zone for the state based out of Visakhapatnam.
There are three A1 and twenty-three A-category railway stations in the state. has been declared the cleanest railway station in the country. The railway station of Shimiliguda was the first highest broad gauge railway station in the country.
As on date the Railways lines in Andhra Pradesh are under the following Railway zones/Divisions
* South Central Railway-Secunderabad railway division, Secunderabad Division
* South Central Railway-Hyderabad railway division, Hyderabad Division
* South Central Railway-Vijayawada railway division, Vijayawada Division
* South Central Railway-Guntakal railway division, Guntakal Division
* South Central Railway-Guntur railway division, Guntur Division
* East Coast Railway- Waltair railway division, Waltair Division
* East Coast Railway- Khurda Road railway division, Khurda Road Division
A new railway zone South Coast Railway Zone (SCoR) has been announced as the newest Zones and divisions of Indian Railways, railway zone of the Indian Railways and is headquartered at


 Visakhapatnam Airport is the only airport in the state with operating international flights while Vijayawada Airport at Gannavaram has launched an international flight to Singapore, recently. The state has four other domestic airports, Rajahmundry Airport, Kadapa Airport, Kurnool Airport a privately owned, public use airport at Sri Sathya Sai Airport, Puttaparthi, and Tirupati Airport located in the city of
Visakhapatnam Airport is the only airport in the state with operating international flights while Vijayawada Airport at Gannavaram has launched an international flight to Singapore, recently. The state has four other domestic airports, Rajahmundry Airport, Kadapa Airport, Kurnool Airport a privately owned, public use airport at Sri Sathya Sai Airport, Puttaparthi, and Tirupati Airport located in the city of
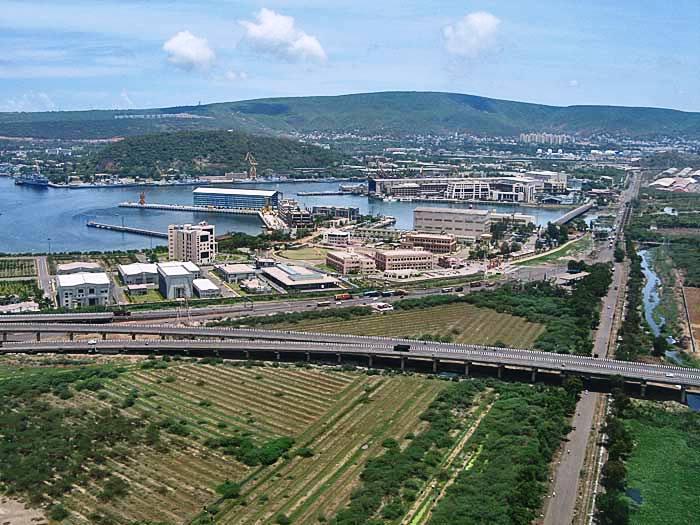



 Andhra Pradesh has an overall Literacy, literacy rate of 67.41% as per the 2011 Indian census. The primary and secondary school education is imparted by State school, government, aided and private schools, managed and regulated by the School Education Department of the state. There are urban, rural and Gurukula Patasala, residential schools. As per the child info and school information report (2018–19), there were a total of students, enrolled in schools respectively. The Directorate of Government Examinations of the state administers and conduct the Secondary School Certificate (SSC) examination. More than students have appeared for the 2019 SSC exam and recorded an overall pass percentage of 94.88% with a 100% pass percentage in 5,464 schools. The mediums of instruction are primarily
Andhra Pradesh has an overall Literacy, literacy rate of 67.41% as per the 2011 Indian census. The primary and secondary school education is imparted by State school, government, aided and private schools, managed and regulated by the School Education Department of the state. There are urban, rural and Gurukula Patasala, residential schools. As per the child info and school information report (2018–19), there were a total of students, enrolled in schools respectively. The Directorate of Government Examinations of the state administers and conduct the Secondary School Certificate (SSC) examination. More than students have appeared for the 2019 SSC exam and recorded an overall pass percentage of 94.88% with a 100% pass percentage in 5,464 schools. The mediums of instruction are primarily
Religion
The majority of the people in Andhra Pradesh are Hindus while Muslims constitute a sizeable minority. According to the 2011 census, the major religious groups in the state are Hindus (90.87%), Muslims (7.32%) and Christians (1.38%). Buddhists, Sikhs, Jains and the people who declined to state their religion make up the remaining portion of population.Visakhapatnam
, image_alt =
, image_caption = From top, left to right: Visakhapatnam aerial view, Vizag seaport, Simhachalam Temple, Aerial view of Rushikonda Beach, Beach road, Novotel, Novotel Visakhapatnam, INS Kursura (S20), INS ...
.
Hinduism
Venkateswara Temple, Tirumala, Venkateswara Temple atTirupati
Tirupati () is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Tirupati district. The city is home to the important Hindu shrine of Tirumala Venkateswara Temple and other historic temples and is refe ...
is the world's second-richest Hindu temple, temple and is visited by millions of devotees throughout the year. Andhra Pradesh is home to Shankaracharya of Pushpagiri Peetham. Other Hindu saints include Sadasiva Brahmendra, Kannappa, Bhaktha Kannappa, Vemana, Yogi Vemana and Potuluri Veerabrahmam, Pothuluru Veerabrahmendra.
Mahayana Buddhism
Buddhism spread to Andhra Pradesh early in its history. The Krishna river valley was "a site of extraordinary Buddhist activity for almost a thousand years." The ancient Buddhist sites in the lower Krishna valley, including Amaravati, Nagarjunakonda and Jaggayyapeta "can be traced to at least the third century BCE, if not earlier." The region played a central role in the development of Mahayana, Mahayana Buddhism, along with the Magadha-area in northeastern India. A. K. Warder holds that "the Mahāyāna originated in the south of India and almost certainly in the Andhra country." According to Xing, "Several scholars have suggested that the Prajnaparamita probably developed among the Mahasamghikas in Southern India probably in the Andhra country, on the Krishna River." The Prajnaparamita, Prajñāpāramitā Sutras belong to the earliest Mahayana sutras, Mahayana Sutras.Administrative divisions
Regions
Andhra Pradesh comprises three regions:Uttarandhra
Uttarandhra or North coastal Andhra, also known as Kalinga Andhra is a region consisting of six northern districts of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It comprises the districts of Srikakulam, Parvathipuram Manyam, Vizianagaram, Visakhapat ...
, Coastal Andhra
Coastal Andhra (South costal Andhra) also known as Kostha Andhra is a region in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India. Vijayawada is the largest city in this region. It was part of Madras State before 1953 and Andhra State from 1953 to 1956. ...
and Rayalaseema.
Districts
It has a total of 26 districts, twelve in Coastal Andhra region, six in Uttarandhra and eight in the Rayalaseema region.Uttarandhra
Uttarandhra or North coastal Andhra, also known as Kalinga Andhra is a region consisting of six northern districts of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It comprises the districts of Srikakulam, Parvathipuram Manyam, Vizianagaram, Visakhapat ...
region :
# Alluri Sitharama Raju district, Alluri Sitharama Raju
# Anakapalli district, Anakapalli
# Parvathipuram Manyam district, Parvathipuram Manyam
# Srikakulam district, Srikakulam
# Visakhapatnam district, Visakhapatnam
# Vizianagaram district, Vizianagaram
Coastal Andhra
Coastal Andhra (South costal Andhra) also known as Kostha Andhra is a region in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India. Vijayawada is the largest city in this region. It was part of Madras State before 1953 and Andhra State from 1953 to 1956. ...
region :
# Bapatla district, Bapatla
# Konaseema district, Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Konaseema
# East Godavari district, East Godavari District with Rajahmundry Headquarters
# Eluru district, Eluru
# Guntur district, Guntur
# Kakinada district, Kakinada
# Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
# NTR district, NTR
# Palnadu district, Palnadu
# Prakasam district, Prakasam
# Nellore district, Sri Potti Sriramulu Nellore
# West Godavari district, West Godavari
Rayalaseema region :
# Anantapur district, Anantapur
# Annamayya district, Annamayya
# Chittoor district, Chittoor
# Kadapa district, YSR
# Kurnool district, Kurnool
# Nandyal district, Nandyal
# Sri Sathya Sai district, Sri Sathya Sai
# Tirupati district, Tirupati
Revenue divisions
These 26 districts are further divided into 77 revenue divisions.Mandals
The 77 revenue divisions are in turn divided into 679 Tehsil, mandals.Cities
There are a total of List of urban agglomerations in Andhra Pradesh, 31 cities which include, List of municipal corporations in India, 16 municipal corporations and List of cities in Andhra Pradesh, 14 municipalities. There are two cities with List of cities in India by population, more than one million inhabitants, namelyVisakhapatnam
, image_alt =
, image_caption = From top, left to right: Visakhapatnam aerial view, Vizag seaport, Simhachalam Temple, Aerial view of Rushikonda Beach, Beach road, Novotel, Novotel Visakhapatnam, INS Kursura (S20), INS ...
and Vijayawada.
Government and politics


Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian subcontinent, Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India b ...
.
In the last elections held in the unified state in 2014 Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, 2014, the TDP got a mandate in their favour in the residuary (new) state. After Telangana became a separate state, N. Chandrababu Naidu , the chief of the TDP became the Chief Minister on 8 June 2014, for the new state of Andhra Pradesh.
As of 2014, the Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly, Legislative Assembly of Andhra Pradesh is the lower house of the state with 175 members and the Andhra Pradesh Legislative Council, Legislative Council is the upper house with 58 members. In the Parliament of India, Andhra Pradesh has 11 seats in the Rajya Sabha, and 25 seats in the Lok Sabha. There are a total of 175 List of constituencies of the Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly, Assembly constituencies in the state. East Godavari, East Godavari district has the highest number of constituencies with 19 and Vizianagaram district has the least with 9 assembly seats. Whereas, the legislative council of the state has 58 seats, which is one-third of total assembly seats.
In the 2019 Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, 2019 elections, YSR's son Y. S. Jaganmohan Reddy of the YSR Congress Party (founded in 2011) became the Chief Minister with a resounding mandate by winning 151 out of 175 seats.
Economy

Agriculture
Konaseema
Konaseema is a group of islands between the tributaries of the Godavari River and Bay of Bengal located in Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Konaseema district of Andhra Pradesh in southern India. It is nicknamed "Gods Own Creation" due to similarities wit ...
, East Godavari district, East Godavari
File:Map of Sugar industries in Andhra Pradesh.png, Map of Sugar industries in Andhra Pradesh
Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
, Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
, Penner River, Penna, and Tungabhadra River, Tungabhadra flow through the state and provide irrigation. 60 percent of the population is engaged in agriculture and related activities. Rice is the major food crop and staple food of the state. It is an exporter of many agricultural products and is also known as "Rice Bowl of India". The state has three Agricultural Economic Zones in Chittoor district for mango pulp and vegetables, Krishna district for mangoes, Guntur district for chilies.
Besides rice, farmers also grow Sorghum bicolor, jowar, Pearl millet, bajra, maize, minor millet, coarse grain, many varieties of Legume, pulses, Vegetable oil, oil seeds, sugarcane, cotton, chili pepper, mango nuts and tobacco. Crops used for vegetable oil production such as Helianthus, sunflower and peanuts are popular. There are many multi-state irrigation projects under development, including Godavari River Basin Irrigation Projects and Nagarjuna Sagar Dam.
Livestock and Poultry farming, poultry is also another profitable business, which involves rearing cattle in enclosed areas for commercial purposes. The state is also a largest producer of Egg as food, eggs in the country and hence, it is nicknamed as "Egg Bowl of Asia".
Fishery, Fisheries contribute 10% of total fish and over 70% of the Shrimp and prawn as food, shrimp production of India. The geographical location of the state allows marine fishing as well as inland fish production. The most exported marine exports include ''Whiteleg shrimp, Vannamei shrimp''
Infrastructure
Andhra Pradesh is investing in building infrastructure in the state such as highways and making every service of the government digital. National Highway 16 (India), National Highway 16 passes through Andhra Pradesh. The List of state highways in Andhra Pradesh, highways in the state are also being widened. Andhra Pradesh State FiberNet Limited, APSFL is an initiative of the government of Andhra Pradesh to set up an optical fiber network throughout the thirteen districts of Andhra Pradesh. This network provides internet connectivity, telephony and Internet Protocol television, IPTV with fiber to private and corporate users of Andhra Pradesh. The state also has seaports such as Visakhapatnam Port, Kakinada Port, Krishnapatnam Port for import and export and a shipyard for building ships at Visakhapatnam. Major airports in the state are Visakhapatnam, Rajahmundry, Vijayawada, with Visakhapatnam Airport, Visakhapatnam, Tirupati Airport, Tirupati and Vijayawada Airport, Vijayawada being international airports.
Industrial sector

 The industrial sector of the state includes some of the key sectors like Pharmaceutical industry in India, pharmaceutical, Automotive industry in India, automobile, Textile industry in India, textiles etc. Sri City, Sricity located in Chittoor district is an integrated business city which is home to firms including PepsiCo, Isuzu Motors India, Isuzu Motors, Cadbury, Cadbury India, Kellogg's, Colgate-Palmolive, Kobe Steel, Kobelco etc. The PepsiCo firm has its largest plant in India at Sri City. The state is also emerging as destination for the automobile industry which already hosts companies including Ashok Leyland in Krishna district, Hero Motors in Chittoor district, Kia Motors India, Kia Motors in Anantapur district.
The industrial sector of the state includes some of the key sectors like Pharmaceutical industry in India, pharmaceutical, Automotive industry in India, automobile, Textile industry in India, textiles etc. Sri City, Sricity located in Chittoor district is an integrated business city which is home to firms including PepsiCo, Isuzu Motors India, Isuzu Motors, Cadbury, Cadbury India, Kellogg's, Colgate-Palmolive, Kobe Steel, Kobelco etc. The PepsiCo firm has its largest plant in India at Sri City. The state is also emerging as destination for the automobile industry which already hosts companies including Ashok Leyland in Krishna district, Hero Motors in Chittoor district, Kia Motors India, Kia Motors in Anantapur district.
 The state is also emerging in Information technology in India, information technology and Biotechnology in India, biotechnology. The IT/ITES revenues of Visakhapatnam is at in 2012–2013. The development of IT in Tier-II and Tier-III cities like Vijayawada,
The state is also emerging in Information technology in India, information technology and Biotechnology in India, biotechnology. The IT/ITES revenues of Visakhapatnam is at in 2012–2013. The development of IT in Tier-II and Tier-III cities like Vijayawada, Kakinada
Kakinada (List of renamed places in India, formerly called Kakinandiwada, Coringa, and Cocanada; ) is the List of cities in Andhra Pradesh by population, sixth largest city of the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Andhra P ...
and Tirupati
Tirupati () is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Tirupati district. The city is home to the important Hindu shrine of Tirumala Venkateswara Temple and other historic temples and is refe ...
is also improving. In the fiscal year 2012–2013, Vijayawada's IT/ITeS revenues were . Tirupati with and Kakinada with stand next. For the benefit of state, that is, after separating Telangana from Andhra, people of Andhra protested for special status during January in 2017.


Resources
Andhra Pradesh is one of the storehouses of mineral resources in India. Andhra Pradesh with varied geological formations, contain rich and variety of industrial minerals and building stones. Andhra Pradesh is listed at the top in the deposit and production of mica in India. Minerals found in the state include limestone, reserves of Oil reserves, oil and natural gas, manganese, asbestos, iron ore, ball clay, fire clay, gold diamonds, graphite, Dolomite (mineral), dolomite, quartz, tungsten, steatitic, feldspar, silica sand. It has about one-third of India's limestone reserves and is known for large exclusive deposits of barytes and Granite, galaxy granite in the international market.Mining
Mining is identified as one of the growth engines for the overall development of industry and infrastructure. The Tummalapalle uranium mine, Tummalapalle Uranium mine in Andhra has confirmed of ore and there are indications that it could hold reserves totaling three times its current size. of metal grade Bauxite deposits in proximity to Visakhapatnam Port. Reliance Industries struck nine trillion cubic feet of gas reserves in the Krishna Godavari Basin, KG basin, off the Andhra Pradesh coast near
Reliance Industries struck nine trillion cubic feet of gas reserves in the Krishna Godavari Basin, KG basin, off the Andhra Pradesh coast near Kakinada
Kakinada (List of renamed places in India, formerly called Kakinandiwada, Coringa, and Cocanada; ) is the List of cities in Andhra Pradesh by population, sixth largest city of the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Andhra P ...
. Discovery of a large quantity of natural gas in KG Basin is expected to provide rapid economic growth. During 2016, nearly of Methane clathrate, methane hydrate deposits were explored in KG basin whose extraction was adequate to impart energy security for many decades to India.
Power plants
 The state is a pioneer nationwide in Solar power in India, solar power generation. Andhra Pradesh Power Generation Corporation, APGENCO is the power generating company owned by the state. The state has become power surplus with excess power generation being exported to other states. The state is abundantly endowed with solar power and high head Pumped-storage hydroelectricity, PHES sites to convert the solar power available during the day time in to round the clock power supply. PHES projects also has synergy with the lift irrigation projects in storing water available during the monsoon season and supplying to the uplands throughout the year. Ultimate water and energy requirements of the state can be fully met by the combination of cheap solar power, PHES and irrigation projects economically harnessing Renewable energy in India, renewable energy without much damage to the environment.
The state is a pioneer nationwide in Solar power in India, solar power generation. Andhra Pradesh Power Generation Corporation, APGENCO is the power generating company owned by the state. The state has become power surplus with excess power generation being exported to other states. The state is abundantly endowed with solar power and high head Pumped-storage hydroelectricity, PHES sites to convert the solar power available during the day time in to round the clock power supply. PHES projects also has synergy with the lift irrigation projects in storing water available during the monsoon season and supplying to the uplands throughout the year. Ultimate water and energy requirements of the state can be fully met by the combination of cheap solar power, PHES and irrigation projects economically harnessing Renewable energy in India, renewable energy without much damage to the environment.
 Thermal power station, Thermal (Gas-fired power plant, natural gas and Coal-fired power station, coal based) and Renewable energy, renewable power plants totaling to 21,000 MW were installed in the state by 2015. Local power plants of 9,600 Watt, MW capacity only are supplying electricity in the state, which includes Simhadri Super Thermal Power Station (2000 MW) of NTPC Limited, NTPC, Vizag Thermal Power Station (1040 MW), Rayalaseema Thermal Power Station (1650 MW), Sri Damodaram Sanjeevaiah Thermal Power Station (2400 MW), and Dr Narla Tata Rao Thermal Power Station, Narla Tata Rao Thermal Power Plant (1760 MW). Hydel power plants have a capacity of 1671 MW.
Thermal power station, Thermal (Gas-fired power plant, natural gas and Coal-fired power station, coal based) and Renewable energy, renewable power plants totaling to 21,000 MW were installed in the state by 2015. Local power plants of 9,600 Watt, MW capacity only are supplying electricity in the state, which includes Simhadri Super Thermal Power Station (2000 MW) of NTPC Limited, NTPC, Vizag Thermal Power Station (1040 MW), Rayalaseema Thermal Power Station (1650 MW), Sri Damodaram Sanjeevaiah Thermal Power Station (2400 MW), and Dr Narla Tata Rao Thermal Power Station, Narla Tata Rao Thermal Power Plant (1760 MW). Hydel power plants have a capacity of 1671 MW.
Culture
Andhra Pradesh has rich culture and heritage. Kuchipudi, the cultural dance recognized as the official dance form of the state of Andhra Pradesh, originated in the village of Kuchipudi, Krishna district, Kuchipudi in Krishna district. It entered the Guinness World Records for performing ''Mahabrinda Natyam'' with a total of 6,117 dancers in Vijayawada. Andhra Pradesh has thirteen geographical indications in categories of agricultural handicrafts, foodstuff and textiles as per ''Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999''. It increased to fifteen with the addition of Benishan (mango), Banaganapalle Mangoes and Bandar laddu. The other GI tagged goods are, Bobbili Veena, Budithi Bell and Brass Craft, Dharmavaram handloom pattu sarees and paavadas, Dharmavaram Handloom Pattu Sarees and Paavadas, Guntur Sannam, Kondapalli Toys, Pedana Kalamkari, Machilipatnam Kalamkari, Mangalagiri Sarees and Fabrics, Srikalahasti Kalamkari, Tirupati Laddu, Uppada Jamdani Sari and Venkatagiri Sari.Arts, crafts and artifacts
 Machilipatnam and Srikalahasti Kalamkari are the two unique textile art forms practised in India. There are also other notable handicrafts present in the state, like the soft limestone Cult image, idol carvings of Durgi. Etikoppaka in Visakhapatnam district is notable for its lac industry, producing lacquered wooden.
The state has many museums, which features a varied collection of ancient sculptures, paintings, idols, weapons, cutlery, and inscriptions, and religious artifacts such as the Archaeological Museum, Amaravati, Amaravati Archaeological Museum, Visakha Museum and Culture of Andhra Pradesh, Telugu Cultural Museum in Visakhapatnam displays the history of the pre-independence and the Bapu Museum, Vijayawada, Victoria Jubilee Museum in Vijayawada with a large collection of artifacts.
Machilipatnam and Srikalahasti Kalamkari are the two unique textile art forms practised in India. There are also other notable handicrafts present in the state, like the soft limestone Cult image, idol carvings of Durgi. Etikoppaka in Visakhapatnam district is notable for its lac industry, producing lacquered wooden.
The state has many museums, which features a varied collection of ancient sculptures, paintings, idols, weapons, cutlery, and inscriptions, and religious artifacts such as the Archaeological Museum, Amaravati, Amaravati Archaeological Museum, Visakha Museum and Culture of Andhra Pradesh, Telugu Cultural Museum in Visakhapatnam displays the history of the pre-independence and the Bapu Museum, Vijayawada, Victoria Jubilee Museum in Vijayawada with a large collection of artifacts.
Literature
Nannayya, Tikkana and Yerrapragada form the trinity who translated theSanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
epic ''Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kuruk ...
'' into Telugu language
Telugu (; , ) is a Dravidian language spoken by Telugu people predominantly living in the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, where it is also the official language. It is the most widely spoken member of the Dravidian language fami ...
. Nannayya wrote the first treatise on Telugu grammar called ''Andhra Shabda Chintamani'' in Sanskrit, as there was no grammatical work in Telugu prior to that. Pothana is the poet who composed the classic ''Srimad Maha Bhagavatamu'', a Telugu translation of ''Bhagavata Purana, Sri Bhagavatam''. Vemana is notable for his philosophical poems. The Vijayanagara emperor Krishnadevaraya wrote Amuktamalyada. Telugu literature after Kandukuri Veeresalingam is termed as Adhunika Telugu Sahityam (Modern Telugu literature). He is known as ''Gadya Tikkana'' and was the author of Telugu social novel, ''Satyavati Charitam''. Jnanpith Award holders from the state include Viswanatha Satyanarayana. The Andhra Pradesh native and revolutionary poet Sri Sri (writer), Sri Sri brought new forms of expressionism into Telugu literature.
Media
The print media in the state consists mainly of Telugu and English newspapers. ''Eenadu'', ''Sakshi (newspaper), Sakshi'', ''Andhra Jyothi'', and Tel.J.D.Patrika Vaartha all these are Telugu newspapers. English newspapers include Deccan Chronicle and The Hans India.Art and cinema
 Many composers of Carnatic music like Annamacharya, Kshetrayya, Tyagaraja, and Bhadrachala Ramadasu, Bhadrachala Ramadas were of Telugu descent. Modern Carnatic music composers and singers like Ghantasala (musician), Ghantasala and M. Balamuralikrishna are also of Telugu descent. The Telugu film industry hosts many music composers and playback singers such as S. P. Balasubrahmanyam, P. Susheela, S. Janaki and P. B. Sreenivas. Folk songs are very important and popular in the many rural areas of the state. Forms such as the ''Burra katha'' and ''Poli'' are still performed today. ''Harikathaa Kalakshepam (or Harikatha)'' involves the narration of a story, intermingled with various songs relating to the story. Harikatha was originated in Andhra. ''Burra katha'' is an oral storytelling technique with the topic be either a Hinduism, Hindu mythological story or a contemporary social issue. ''Rangasthalam'' is an Theatre of India, Indian theatre in the
Many composers of Carnatic music like Annamacharya, Kshetrayya, Tyagaraja, and Bhadrachala Ramadasu, Bhadrachala Ramadas were of Telugu descent. Modern Carnatic music composers and singers like Ghantasala (musician), Ghantasala and M. Balamuralikrishna are also of Telugu descent. The Telugu film industry hosts many music composers and playback singers such as S. P. Balasubrahmanyam, P. Susheela, S. Janaki and P. B. Sreenivas. Folk songs are very important and popular in the many rural areas of the state. Forms such as the ''Burra katha'' and ''Poli'' are still performed today. ''Harikathaa Kalakshepam (or Harikatha)'' involves the narration of a story, intermingled with various songs relating to the story. Harikatha was originated in Andhra. ''Burra katha'' is an oral storytelling technique with the topic be either a Hinduism, Hindu mythological story or a contemporary social issue. ''Rangasthalam'' is an Theatre of India, Indian theatre in the Telugu language
Telugu (; , ) is a Dravidian language spoken by Telugu people predominantly living in the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, where it is also the official language. It is the most widely spoken member of the Dravidian language fami ...
, based predominantly in Andhra Pradesh. Gurajada Apparao wrote the play ''Kanyasulkam'' in 1892, often considered the greatest play in the Telugu language.20th Century Telugu Luminaries, Potti Sriramulu Telugu University, Hyderabad, 2005 C. Pullaiah is cited as the father of Telugu theatre movement.
The Telugu film industry is largely based in Hyderabad and Visakhapatnam. The Telugu film culture (also known as "Telugu cinema, Tollywood") is the second-largest film industry in India next to the Bollywood film industry. Film producer D. Ramanaidu holds a Guinness World Records, Guinness Record for the most films produced by a person. In the years 2005, 2006 and 2008, the Telugu film industry produced the largest number of films in India, exceeding the number of films produced in Bollywood. The industry holds the Guinness World Record for the largest film production facility in the world.
Cuisine
 Telugu people's traditional sweet Pootharekulu originated from Atreyapuram village of East Godavari district.
Telugu people's traditional sweet Pootharekulu originated from Atreyapuram village of East Godavari district.
Tourism
 The state has several beaches in its coastal districts such as Rushikonda, Mypadu, Suryalanka Beach, Suryalanka etc.; caves such as, Borra Caves, Indian rock-cut architecture depicting Undavalli Caves and the country's second longest caves- the Belum Caves. The valleys and hills include,
The state has several beaches in its coastal districts such as Rushikonda, Mypadu, Suryalanka Beach, Suryalanka etc.; caves such as, Borra Caves, Indian rock-cut architecture depicting Undavalli Caves and the country's second longest caves- the Belum Caves. The valleys and hills include, Araku Valley
Araku Valley is a hill station in Alluri Sitharama Raju district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh, lying 111 km west of Visakhapatnam city. This place is often referred to as ''Ooty of Andhra''. It is a valley in the Eastern Ghats inh ...
, Horsley Hills, Papikonda National Park, Papi Hills etc. Arma Konda peak located in Visakhapatnam district is the highest peak in Eastern Ghats.
The state is home to various religious pilgrim destinations such as Venkateswara Temple, Tirumala, Tirumala Temple, Varaha Lakshmi Narasimha temple, Simhachalam, Simhachalam Temple, Annavaram Satyanarayana Temple, Annavaram temple, Mallikarjuna Temple, Srisailam, Srisailam temple, Kanaka Durga Temple, Amararama, Amaravati, Srikalahasti, Shahi Jamia Mosque, Shahi Jamia Masjid in Adoni, St. Mary's Church, Vijayawada, Gunadala Church in Vijayawada, Buddhist centres at Amaravati
Amaravati () is the capital of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located on the banks of the river Krishna in Guntur district.
The Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone at a ceremonial event in Uddandara ...
, and Nagarjunakonda, Nagarjuna Konda, Khadri Lakshmi Narasimha Swamy Temple, Kadiri.
Transport
The state is well connected to other states through road and rail networks. It is also connected to other countries by means of airways and seaports as well. With a long seacoast along theBay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
, it also has many ports for sea trade. The state has one of the List of railway junction stations in India, largest railway junctions at Vijayawada and one of the List of ports in India, largest seaports at Visakhapatnam.
Roads
 The state has a total road network of , of which of National highways of India, National highways, of State highways in India, state highways and of district roads. National Highway 16 (India), NH 16, with a highway network of around in the state, is a part of Golden Quadrilateral, Golden Quadrilateral Project undertaken by National Highways Development Project. It also forms part of AH45, AH 45 which comes under the Asian Highway Network.
The state has a total road network of , of which of National highways of India, National highways, of State highways in India, state highways and of district roads. National Highway 16 (India), NH 16, with a highway network of around in the state, is a part of Golden Quadrilateral, Golden Quadrilateral Project undertaken by National Highways Development Project. It also forms part of AH45, AH 45 which comes under the Asian Highway Network.
 The state government owned Andhra Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (APSRTC) is the major public bus transport, which runs thousands of buses connecting different parts of the state. Pandit Nehru bus station, Pandit Nehru Bus Station (PNBS) in Vijayawada is one of the largest bus terminals in Asia. From 30 January 2019, all the vehicles in the state are registered as List of Regional Transport Office districts in India, AP–39, followed by an alphabet and four digits.
The state government owned Andhra Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (APSRTC) is the major public bus transport, which runs thousands of buses connecting different parts of the state. Pandit Nehru bus station, Pandit Nehru Bus Station (PNBS) in Vijayawada is one of the largest bus terminals in Asia. From 30 January 2019, all the vehicles in the state are registered as List of Regional Transport Office districts in India, AP–39, followed by an alphabet and four digits.
Railways
 Andhra Pradesh has a total broad-gauge railway route of and has no metre-gauge railway. The rail density of the state is 16.59 per , compared to an all India average of 20. The Howrah–Chennai main line which runs through the state is proposed to be upgraded into a High-speed rail in India, high-speed rail corridor through the Diamond Quadrilateral project of the Indian Railways.
The railway network spans two Zones and divisions of Indian Railways, zones, further subdivided into divisions – Vijayawada railway division, Vijayawada, Guntur railway division, Guntur and Guntakal railway division, Guntakal railway divisions of South Central Railway zone, and Waltair railway division of East Coast Railway zone. There is a demand for creating a unified zone for the state based out of Visakhapatnam.
There are three A1 and twenty-three A-category railway stations in the state. has been declared the cleanest railway station in the country. The railway station of Shimiliguda was the first highest broad gauge railway station in the country.
As on date the Railways lines in Andhra Pradesh are under the following Railway zones/Divisions
* South Central Railway-Secunderabad railway division, Secunderabad Division
* South Central Railway-Hyderabad railway division, Hyderabad Division
* South Central Railway-Vijayawada railway division, Vijayawada Division
* South Central Railway-Guntakal railway division, Guntakal Division
* South Central Railway-Guntur railway division, Guntur Division
* East Coast Railway- Waltair railway division, Waltair Division
* East Coast Railway- Khurda Road railway division, Khurda Road Division
A new railway zone South Coast Railway Zone (SCoR) has been announced as the newest Zones and divisions of Indian Railways, railway zone of the Indian Railways and is headquartered at
Andhra Pradesh has a total broad-gauge railway route of and has no metre-gauge railway. The rail density of the state is 16.59 per , compared to an all India average of 20. The Howrah–Chennai main line which runs through the state is proposed to be upgraded into a High-speed rail in India, high-speed rail corridor through the Diamond Quadrilateral project of the Indian Railways.
The railway network spans two Zones and divisions of Indian Railways, zones, further subdivided into divisions – Vijayawada railway division, Vijayawada, Guntur railway division, Guntur and Guntakal railway division, Guntakal railway divisions of South Central Railway zone, and Waltair railway division of East Coast Railway zone. There is a demand for creating a unified zone for the state based out of Visakhapatnam.
There are three A1 and twenty-three A-category railway stations in the state. has been declared the cleanest railway station in the country. The railway station of Shimiliguda was the first highest broad gauge railway station in the country.
As on date the Railways lines in Andhra Pradesh are under the following Railway zones/Divisions
* South Central Railway-Secunderabad railway division, Secunderabad Division
* South Central Railway-Hyderabad railway division, Hyderabad Division
* South Central Railway-Vijayawada railway division, Vijayawada Division
* South Central Railway-Guntakal railway division, Guntakal Division
* South Central Railway-Guntur railway division, Guntur Division
* East Coast Railway- Waltair railway division, Waltair Division
* East Coast Railway- Khurda Road railway division, Khurda Road Division
A new railway zone South Coast Railway Zone (SCoR) has been announced as the newest Zones and divisions of Indian Railways, railway zone of the Indian Railways and is headquartered at Visakhapatnam
, image_alt =
, image_caption = From top, left to right: Visakhapatnam aerial view, Vizag seaport, Simhachalam Temple, Aerial view of Rushikonda Beach, Beach road, Novotel, Novotel Visakhapatnam, INS Kursura (S20), INS ...
, Andhra Pradesh. The formal notification for operationalization of this Zone is yet to be issued. When created it will include Waltair railway division, Waltair Division of East Coast Railway zone and Vijayawada railway division, Vijayawada Division,
Guntakal railway division, Guntakal Division & Guntur railway division, Guntur Division of South Central Railway zone.
Airports


 Visakhapatnam Airport is the only airport in the state with operating international flights while Vijayawada Airport at Gannavaram has launched an international flight to Singapore, recently. The state has four other domestic airports, Rajahmundry Airport, Kadapa Airport, Kurnool Airport a privately owned, public use airport at Sri Sathya Sai Airport, Puttaparthi, and Tirupati Airport located in the city of
Visakhapatnam Airport is the only airport in the state with operating international flights while Vijayawada Airport at Gannavaram has launched an international flight to Singapore, recently. The state has four other domestic airports, Rajahmundry Airport, Kadapa Airport, Kurnool Airport a privately owned, public use airport at Sri Sathya Sai Airport, Puttaparthi, and Tirupati Airport located in the city of Tirupati
Tirupati () is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Tirupati district. The city is home to the important Hindu shrine of Tirumala Venkateswara Temple and other historic temples and is refe ...
. There are also 16 small airstrips located in the state.
Sea ports
Andhra Pradesh has one of the country's largest port at Visakhapatnam Port, Visakhapatnam in terms of cargo handling. The other famous ports are Krishnapatnam Port (Nellore district, Nellore), Gangavaram Port and Kakinada Port. Gangavaram Port is a deep seaport which can accommodate ocean liners up to 200,000–250,000 Deadweight tonnage, DWT. There are 14 notified non-major ports at Bheemunipatnam, S.Yanam, Machilipatnam, Nizampatnam, and Vadarevu.

Education and research

 Andhra Pradesh has an overall Literacy, literacy rate of 67.41% as per the 2011 Indian census. The primary and secondary school education is imparted by State school, government, aided and private schools, managed and regulated by the School Education Department of the state. There are urban, rural and Gurukula Patasala, residential schools. As per the child info and school information report (2018–19), there were a total of students, enrolled in schools respectively. The Directorate of Government Examinations of the state administers and conduct the Secondary School Certificate (SSC) examination. More than students have appeared for the 2019 SSC exam and recorded an overall pass percentage of 94.88% with a 100% pass percentage in 5,464 schools. The mediums of instruction are primarily
Andhra Pradesh has an overall Literacy, literacy rate of 67.41% as per the 2011 Indian census. The primary and secondary school education is imparted by State school, government, aided and private schools, managed and regulated by the School Education Department of the state. There are urban, rural and Gurukula Patasala, residential schools. As per the child info and school information report (2018–19), there were a total of students, enrolled in schools respectively. The Directorate of Government Examinations of the state administers and conduct the Secondary School Certificate (SSC) examination. More than students have appeared for the 2019 SSC exam and recorded an overall pass percentage of 94.88% with a 100% pass percentage in 5,464 schools. The mediums of instruction are primarily Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
S ...
and English with a very few opting for Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
''


 Higher education in the state is administered by the Department of Higher Education. The central universities are All India Institutes of Medical Sciences, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Indian Institute of Management Visakhapatnam, IIM Visakhapatnam, IIT Tirupati, National Institute of Technology, Andhra Pradesh, NIT Tadepalligudem, Indian Institute of Information Technology, Design and Manufacturing, Kurnool, IIITDM Kurnool, Indian Institute of Petroleum and Energy, National Institute of Design, Andhra Pradesh, NIDV, Central University of Andhra Pradesh, Indian Institute of Information Technology, Sri City, IIIT Sri City, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Tirupati, IISER Tirupati, Agriculture University, Guntur and Indian Institute of Foreign Trade, IIFT Kakinada. The Government of Andhra Pradesh established Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies (RGUKT) in 2008 to cater to the education needs of the rural youth of Andhra Pradesh. As per the University Grants Commission (India), University Grants Commission, Sri Sathya Sai Institute of Higher Learning, Gandhi Institute of Technology and Management, GITAM, KL University and Vignan's Foundation for Science, Technology & Research, Vignan University, MBU University are the Deemed university, Deemed Universities in the state. There are 18 state universities in the districts providing higher education in horticulture, law, medical, technology, Vedas, Vedic and Veterinary education, veterinary. Andhra University is the oldest of the universities in the state, established in 1926.
Higher education in the state is administered by the Department of Higher Education. The central universities are All India Institutes of Medical Sciences, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Indian Institute of Management Visakhapatnam, IIM Visakhapatnam, IIT Tirupati, National Institute of Technology, Andhra Pradesh, NIT Tadepalligudem, Indian Institute of Information Technology, Design and Manufacturing, Kurnool, IIITDM Kurnool, Indian Institute of Petroleum and Energy, National Institute of Design, Andhra Pradesh, NIDV, Central University of Andhra Pradesh, Indian Institute of Information Technology, Sri City, IIIT Sri City, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Tirupati, IISER Tirupati, Agriculture University, Guntur and Indian Institute of Foreign Trade, IIFT Kakinada. The Government of Andhra Pradesh established Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies (RGUKT) in 2008 to cater to the education needs of the rural youth of Andhra Pradesh. As per the University Grants Commission (India), University Grants Commission, Sri Sathya Sai Institute of Higher Learning, Gandhi Institute of Technology and Management, GITAM, KL University and Vignan's Foundation for Science, Technology & Research, Vignan University, MBU University are the Deemed university, Deemed Universities in the state. There are 18 state universities in the districts providing higher education in horticulture, law, medical, technology, Vedas, Vedic and Veterinary education, veterinary. Andhra University is the oldest of the universities in the state, established in 1926.
 Research institutes have been set up by the central state government. Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL), National Institute of Oceanography, India, National Institute of Oceanography, Visakhapatnam (NIO), School of Planning and Architecture, Vijayawada, School of Planning and Architecture at Vijayawada is an autonomous research institute under Ministry of Education (India), Ministry of Human Resource Development of Government of India, National Atmospheric Research Laboratory carry out fundamental and applied research in atmospheric and space sciences, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Tirupati, Society for Applied Microwave Electronics Engineering and Research, Visakhapatnam Central Tobacco Research Institute, Rajahmundry under control of ICAR (Indian Council of Agriculture Research) conducts fundamental and applied research on tobacco for the benefit of the farming community, Indian Institute of Oil Palm Research (IIOPR) at
Research institutes have been set up by the central state government. Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL), National Institute of Oceanography, India, National Institute of Oceanography, Visakhapatnam (NIO), School of Planning and Architecture, Vijayawada, School of Planning and Architecture at Vijayawada is an autonomous research institute under Ministry of Education (India), Ministry of Human Resource Development of Government of India, National Atmospheric Research Laboratory carry out fundamental and applied research in atmospheric and space sciences, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Tirupati, Society for Applied Microwave Electronics Engineering and Research, Visakhapatnam Central Tobacco Research Institute, Rajahmundry under control of ICAR (Indian Council of Agriculture Research) conducts fundamental and applied research on tobacco for the benefit of the farming community, Indian Institute of Oil Palm Research (IIOPR) at
 Satish Dhawan Space Centre, also known as Sriharikota Range (SHAR), at barrier island of Sriharikota in Tirupati district is a satellite launching station operated by Indian Space Research Organisation. It is India's primary orbital launch site. India's lunar orbiter Chandrayaan-1 was launched from the centre at 6:22 Ante meridiem, AM Indian Standard Time, IST on 22 October 2008.
Satish Dhawan Space Centre, also known as Sriharikota Range (SHAR), at barrier island of Sriharikota in Tirupati district is a satellite launching station operated by Indian Space Research Organisation. It is India's primary orbital launch site. India's lunar orbiter Chandrayaan-1 was launched from the centre at 6:22 Ante meridiem, AM Indian Standard Time, IST on 22 October 2008.
 The Sports Authority of Andhra Pradesh is the governing body which looks after the infrastructure development in cricket, field hockey, association football, roller skating, skating, Olympic weightlifting, chess, List of water sports, water sports, tennis, badminton, table tennis, cycle sport, cycling, etc.
Cricket is one of the most popular sports in the state. The Dr. Y. S. Rajasekhara Reddy ACA–VDCA Cricket Stadium, ACA-VDCA Stadium in
The Sports Authority of Andhra Pradesh is the governing body which looks after the infrastructure development in cricket, field hockey, association football, roller skating, skating, Olympic weightlifting, chess, List of water sports, water sports, tennis, badminton, table tennis, cycle sport, cycling, etc.
Cricket is one of the most popular sports in the state. The Dr. Y. S. Rajasekhara Reddy ACA–VDCA Cricket Stadium, ACA-VDCA Stadium in
Andhra Pradesh Government Website
Department of Tourism
''


 Higher education in the state is administered by the Department of Higher Education. The central universities are All India Institutes of Medical Sciences, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Indian Institute of Management Visakhapatnam, IIM Visakhapatnam, IIT Tirupati, National Institute of Technology, Andhra Pradesh, NIT Tadepalligudem, Indian Institute of Information Technology, Design and Manufacturing, Kurnool, IIITDM Kurnool, Indian Institute of Petroleum and Energy, National Institute of Design, Andhra Pradesh, NIDV, Central University of Andhra Pradesh, Indian Institute of Information Technology, Sri City, IIIT Sri City, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Tirupati, IISER Tirupati, Agriculture University, Guntur and Indian Institute of Foreign Trade, IIFT Kakinada. The Government of Andhra Pradesh established Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies (RGUKT) in 2008 to cater to the education needs of the rural youth of Andhra Pradesh. As per the University Grants Commission (India), University Grants Commission, Sri Sathya Sai Institute of Higher Learning, Gandhi Institute of Technology and Management, GITAM, KL University and Vignan's Foundation for Science, Technology & Research, Vignan University, MBU University are the Deemed university, Deemed Universities in the state. There are 18 state universities in the districts providing higher education in horticulture, law, medical, technology, Vedas, Vedic and Veterinary education, veterinary. Andhra University is the oldest of the universities in the state, established in 1926.
Higher education in the state is administered by the Department of Higher Education. The central universities are All India Institutes of Medical Sciences, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Indian Institute of Management Visakhapatnam, IIM Visakhapatnam, IIT Tirupati, National Institute of Technology, Andhra Pradesh, NIT Tadepalligudem, Indian Institute of Information Technology, Design and Manufacturing, Kurnool, IIITDM Kurnool, Indian Institute of Petroleum and Energy, National Institute of Design, Andhra Pradesh, NIDV, Central University of Andhra Pradesh, Indian Institute of Information Technology, Sri City, IIIT Sri City, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Tirupati, IISER Tirupati, Agriculture University, Guntur and Indian Institute of Foreign Trade, IIFT Kakinada. The Government of Andhra Pradesh established Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies (RGUKT) in 2008 to cater to the education needs of the rural youth of Andhra Pradesh. As per the University Grants Commission (India), University Grants Commission, Sri Sathya Sai Institute of Higher Learning, Gandhi Institute of Technology and Management, GITAM, KL University and Vignan's Foundation for Science, Technology & Research, Vignan University, MBU University are the Deemed university, Deemed Universities in the state. There are 18 state universities in the districts providing higher education in horticulture, law, medical, technology, Vedas, Vedic and Veterinary education, veterinary. Andhra University is the oldest of the universities in the state, established in 1926.
Research
 Research institutes have been set up by the central state government. Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL), National Institute of Oceanography, India, National Institute of Oceanography, Visakhapatnam (NIO), School of Planning and Architecture, Vijayawada, School of Planning and Architecture at Vijayawada is an autonomous research institute under Ministry of Education (India), Ministry of Human Resource Development of Government of India, National Atmospheric Research Laboratory carry out fundamental and applied research in atmospheric and space sciences, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Tirupati, Society for Applied Microwave Electronics Engineering and Research, Visakhapatnam Central Tobacco Research Institute, Rajahmundry under control of ICAR (Indian Council of Agriculture Research) conducts fundamental and applied research on tobacco for the benefit of the farming community, Indian Institute of Oil Palm Research (IIOPR) at
Research institutes have been set up by the central state government. Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL), National Institute of Oceanography, India, National Institute of Oceanography, Visakhapatnam (NIO), School of Planning and Architecture, Vijayawada, School of Planning and Architecture at Vijayawada is an autonomous research institute under Ministry of Education (India), Ministry of Human Resource Development of Government of India, National Atmospheric Research Laboratory carry out fundamental and applied research in atmospheric and space sciences, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Tirupati, Society for Applied Microwave Electronics Engineering and Research, Visakhapatnam Central Tobacco Research Institute, Rajahmundry under control of ICAR (Indian Council of Agriculture Research) conducts fundamental and applied research on tobacco for the benefit of the farming community, Indian Institute of Oil Palm Research (IIOPR) at Pedavegi
Pedavegi is a village in Eluru district in the state of Andhra Pradesh in India, 10 km north of Eluru. It is administered under Eluru revenue division. Pedavegi also serves as the mandal headquarters of Pedavegi mandal. The nearest railway st ...
near Eluru
Eluru is a city and the district headquarters of Eluru district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the 14 municipal corporations in the state and the mandal headquarters of Eluru mandal in the Eluru revenue division. The city ...
in West Godavari district serves as a centre for conducting and co-ordinating research on all aspects of Elaeis, oil palm conservation, improvement, production, protection, post-harvest technology and transfer of technology, CCRH Regional Research Institute at Gudivada, Clinical Research Institute at Tirupati
Tirupati () is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Tirupati district. The city is home to the important Hindu shrine of Tirumala Venkateswara Temple and other historic temples and is refe ...
and National Institute of Oceanography at Visakhapatnam are some of them. Agriculture Research Institute (Acharya NG Ranga Agriculture University) Kadiri, KADIRI.
Space research organisation
 Satish Dhawan Space Centre, also known as Sriharikota Range (SHAR), at barrier island of Sriharikota in Tirupati district is a satellite launching station operated by Indian Space Research Organisation. It is India's primary orbital launch site. India's lunar orbiter Chandrayaan-1 was launched from the centre at 6:22 Ante meridiem, AM Indian Standard Time, IST on 22 October 2008.
Satish Dhawan Space Centre, also known as Sriharikota Range (SHAR), at barrier island of Sriharikota in Tirupati district is a satellite launching station operated by Indian Space Research Organisation. It is India's primary orbital launch site. India's lunar orbiter Chandrayaan-1 was launched from the centre at 6:22 Ante meridiem, AM Indian Standard Time, IST on 22 October 2008.
Sports
 The Sports Authority of Andhra Pradesh is the governing body which looks after the infrastructure development in cricket, field hockey, association football, roller skating, skating, Olympic weightlifting, chess, List of water sports, water sports, tennis, badminton, table tennis, cycle sport, cycling, etc.
Cricket is one of the most popular sports in the state. The Dr. Y. S. Rajasekhara Reddy ACA–VDCA Cricket Stadium, ACA-VDCA Stadium in
The Sports Authority of Andhra Pradesh is the governing body which looks after the infrastructure development in cricket, field hockey, association football, roller skating, skating, Olympic weightlifting, chess, List of water sports, water sports, tennis, badminton, table tennis, cycle sport, cycling, etc.
Cricket is one of the most popular sports in the state. The Dr. Y. S. Rajasekhara Reddy ACA–VDCA Cricket Stadium, ACA-VDCA Stadium in Visakhapatnam
, image_alt =
, image_caption = From top, left to right: Visakhapatnam aerial view, Vizag seaport, Simhachalam Temple, Aerial view of Rushikonda Beach, Beach road, Novotel, Novotel Visakhapatnam, INS Kursura (S20), INS ...
is the home to Andhra cricket team, Andhra Pradesh cricket team. The venue regularly hosts international as well as domestic matches. Notable cricketers from Andhra Pradesh include former Indian captain Mohammad Azharuddin, Maharajkumar of Vizianagram, M. V. Narasimha Rao, M. S. K. Prasad, VVS Laxman, Tirumalasetti Suman, Arshad Ayub, Ambati Rayudu, Venkatapathy Raju, Sravanthi Naidu, Venugopal Rao (cricketer), Yalaka Venugopal Rao, Hanuma Vihari and Srikar Bharat.
Koneru Humpy, Humpy Koneru, from Gudivada in Krishna district, is an Indian chess Grandmaster (chess), Grandmaster.
Dandamudi Rajagopal Rao, the first 12 times National heavy weight lifting Champion, hails from krishna district.
Karnam Malleswari, the first female Indian to win an Olympic medal, hails from Srikakulam district. She won the bronze medal on 19 September 2000, in the category with a lift of .
Krishnam Raju Gadiraju of Bhimavaram, is a four-time world record holder. He is a speedcubing, speedsolver and unicycle, unicyclist.
Pullela Gopichand is a former Indian badminton player. He won the All England Open Badminton Championships in 2001, becoming the second Indian to win after Prakash Padukone.
Srikanth Kidambi, a badminton player, is the first ever Indian to reach the World Championships final in 2021 in the men's singles and win a silver medal.
Cherukuri Lenin (1985 or 198624 October 2010) was an Indian archer and coach who won a silver medal at the Asian Grand Prix in Malaysia and was a national archery coach.
See also
* List of people from Andhra Pradesh *Outline of Andhra Pradesh * Middle kingdoms of India * Part I of the Constitution of India, Part One of the Constitution of IndiaNotes
References
External links
Government
Andhra Pradesh Government Website
Department of Tourism
General information
* * {{Authority control Andhra Pradesh, South India, . States and union territories of India States and territories established in 1956 1956 establishments in India