Ancient ships on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded
fro
K. Klein Goldewijk, A. Beusen and P. Janssen, "HYDE 3.1: Long-term dynamic modeling of global population and built-up area in a spatially explicit way", from table on p. 2, Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency (MNP), Bilthoven, The Netherlands.

 The
The  Parthia was an Iranian civilisation situated in the northeastern part of modern Iran. Their power was based on a combination of military power based on heavy cavalry with a decentralised governing structure based on a federated system. The Parthian Empire was led by the Arsacid dynasty, which by around 155 BC under Mithradates I had mostly conquered the
Parthia was an Iranian civilisation situated in the northeastern part of modern Iran. Their power was based on a combination of military power based on heavy cavalry with a decentralised governing structure based on a federated system. The Parthian Empire was led by the Arsacid dynasty, which by around 155 BC under Mithradates I had mostly conquered the
 The Hittites first came to Anatolia about 1900 BC and during the period 1600-1500 they expanded into Mesopotamia where they adopted the cuneiform script to their Indo-European language. By 1200 their empire stretched to Phoenicia and eastern Anatolia. They improved two earlier technologies from Mesopotamia and spread these new techniques widely – improved iron working and light
The Hittites first came to Anatolia about 1900 BC and during the period 1600-1500 they expanded into Mesopotamia where they adopted the cuneiform script to their Indo-European language. By 1200 their empire stretched to Phoenicia and eastern Anatolia. They improved two earlier technologies from Mesopotamia and spread these new techniques widely – improved iron working and light
 Israel and Judah were related Iron Age kingdoms of the ancient Levant and had existed during the Iron Ages and the Neo-Babylonian, Persian and Hellenistic periods.
The name Israel first appears in the
Israel and Judah were related Iron Age kingdoms of the ancient Levant and had existed during the Iron Ages and the Neo-Babylonian, Persian and Hellenistic periods.
The name Israel first appears in the
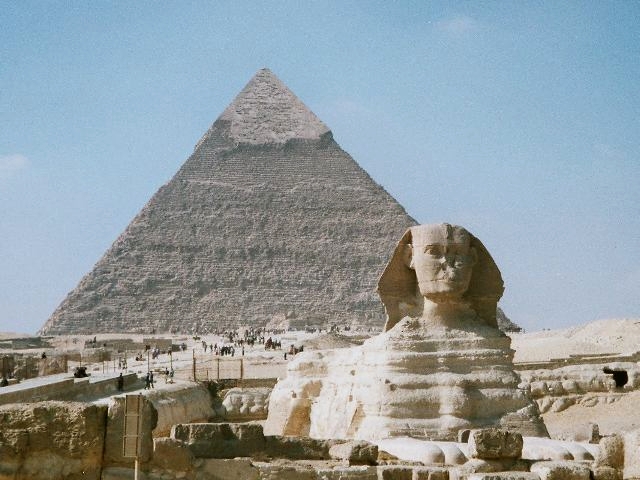 Ancient Egypt was a long-lived civilisation geographically located in north-eastern Africa. It was concentrated along the middle to lower reaches of the Nile River, reaching its greatest extension during the 2nd millennium BC, which is referred to as the New Kingdom period. It reached broadly from the
Ancient Egypt was a long-lived civilisation geographically located in north-eastern Africa. It was concentrated along the middle to lower reaches of the Nile River, reaching its greatest extension during the 2nd millennium BC, which is referred to as the New Kingdom period. It reached broadly from the
 The Ta-Seti kingdom in Nubia to the south of Egypt was conquered by Egyptian rulers around 3100 BC, but by 2500 BC the Nubians had created a new kingdom further south, known as the Kingdom of Kush, centred on the upper Nile with a capital at Kerma. In the Egyptian New Kingdom period, Kush once more was conquered by Egypt, but by 1100 BC a new kingdom of Kush had formed, with a capital at Napata. Nubian rulers conquered Egypt around 760 BC and retained control for about a century.
The Ta-Seti kingdom in Nubia to the south of Egypt was conquered by Egyptian rulers around 3100 BC, but by 2500 BC the Nubians had created a new kingdom further south, known as the Kingdom of Kush, centred on the upper Nile with a capital at Kerma. In the Egyptian New Kingdom period, Kush once more was conquered by Egypt, but by 1100 BC a new kingdom of Kush had formed, with a capital at Napata. Nubian rulers conquered Egypt around 760 BC and retained control for about a century.
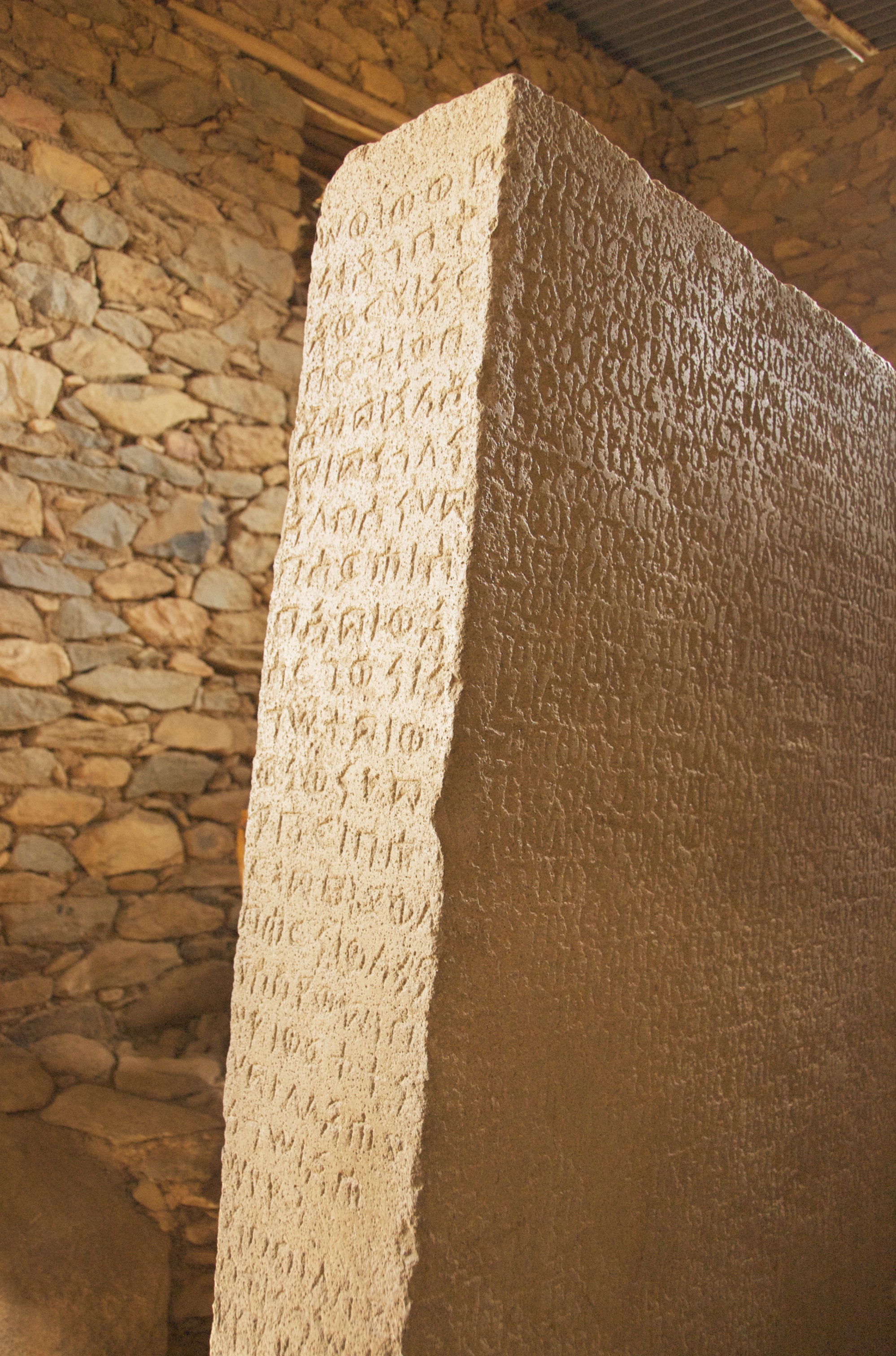 The Axumite Empire was an important trading nation in northeastern Africa centered in present-day
The Axumite Empire was an important trading nation in northeastern Africa centered in present-day
 The Nok culture appeared in Nigeria around 1000 BC and mysteriously vanished around AD 200. The civilisation's social system is thought to have been highly advanced. The Nok civilisation was considered to be the earliest sub-Saharan producer of life-sized Terracotta which have been discovered by archaeologists. The Nok also used iron smelting that may have been independently developed.
The Nok culture appeared in Nigeria around 1000 BC and mysteriously vanished around AD 200. The civilisation's social system is thought to have been highly advanced. The Nok civilisation was considered to be the earliest sub-Saharan producer of life-sized Terracotta which have been discovered by archaeologists. The Nok also used iron smelting that may have been independently developed.
 Paleolithic tools have been discovered in India dating to 200,000 years ago, and neolithic sites are known from near the
Paleolithic tools have been discovered in India dating to 200,000 years ago, and neolithic sites are known from near the 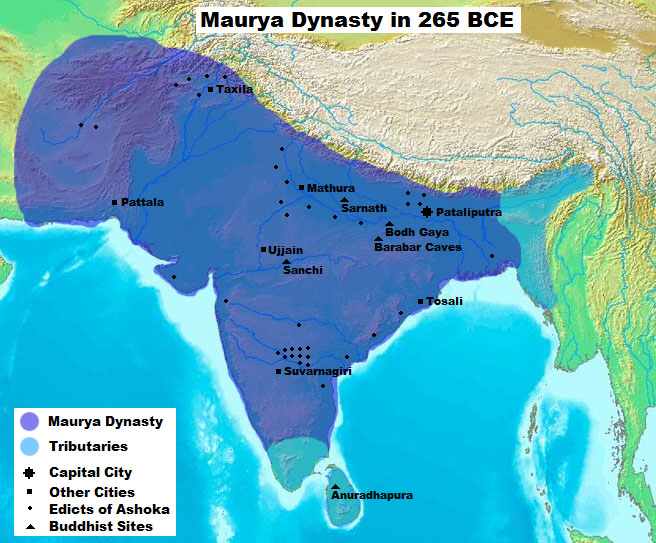 The Indus Valley civilization developed around 3000 BC in the
The Indus Valley civilization developed around 3000 BC in the
 The Chinese civilisation that emerged within the Yellow River valley is one of earliest civilisations in the world. Prior to the formation of civilisation, neolithic cultures such as the Longshan and Yangshao dating to 5000 BC produced sophisticated pottery, cultivated millet, and likely produced clothes woven from
The Chinese civilisation that emerged within the Yellow River valley is one of earliest civilisations in the world. Prior to the formation of civilisation, neolithic cultures such as the Longshan and Yangshao dating to 5000 BC produced sophisticated pottery, cultivated millet, and likely produced clothes woven from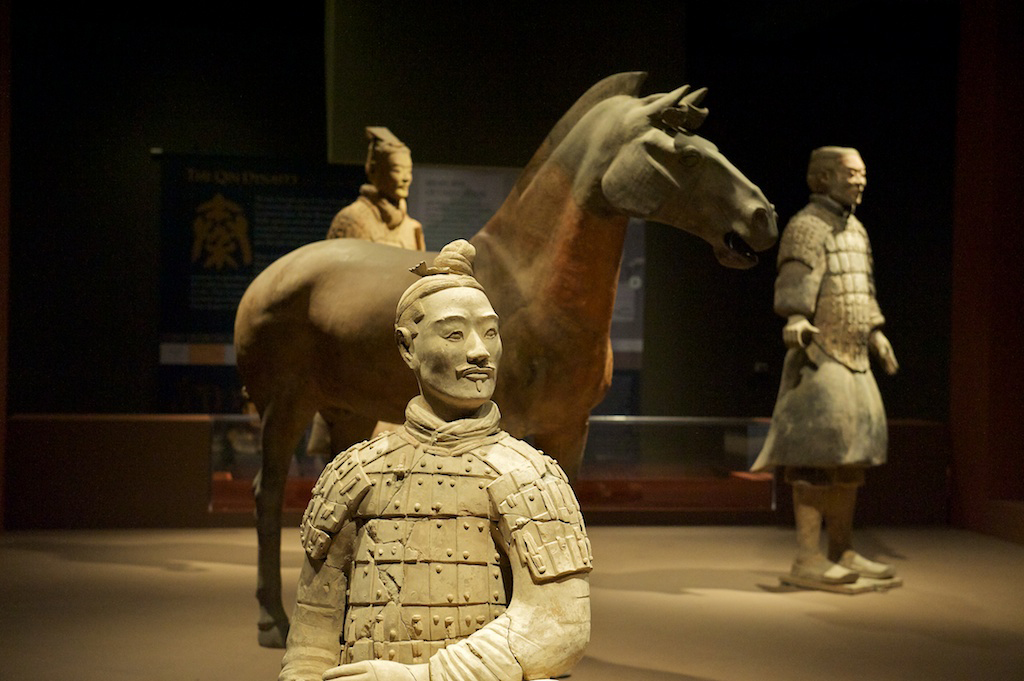  In the 8th century BC, power became decentralized during the
In the 8th century BC, power became decentralized during the 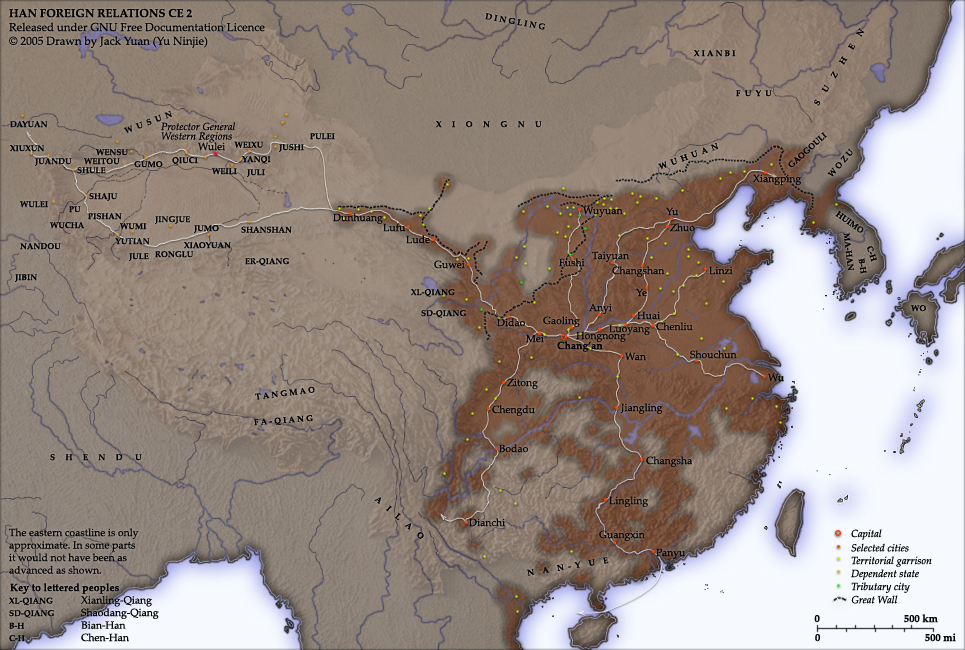 Qin Shi Huangdi ruled the unified China directly with absolute power. In contrast to the decentralized and feudal rule of earlier dynasties the Qin ruled directly. Nationwide the philosophy of legalism was enforced and publications promoting rival ideas such as Confucianism were prohibited. In his reign unified China created the first continuous Great Wall with the use of forced labour. Invasions were launched southward to annex Vietnam. The Qin period also saw the standardization of the Chinese writing system and the government unified the legal systems as well as setting standardized units of measurement throughout the empire. After the emperor's death rebellions began and the Han dynasty took power and ruled China for over four centuries with a brief interruption from AD 9 to 23. The Han dynasty promoted the spread of iron agricultural tools, which helped create a food surplus that led to a large growth of population during the Han period. Silk production also increased and the manufacture of paper was invented. Though the Han enjoyed great military and economic success, it was strained by the rise of aristocrats who disobeyed the central government. Public frustration provoked the
Qin Shi Huangdi ruled the unified China directly with absolute power. In contrast to the decentralized and feudal rule of earlier dynasties the Qin ruled directly. Nationwide the philosophy of legalism was enforced and publications promoting rival ideas such as Confucianism were prohibited. In his reign unified China created the first continuous Great Wall with the use of forced labour. Invasions were launched southward to annex Vietnam. The Qin period also saw the standardization of the Chinese writing system and the government unified the legal systems as well as setting standardized units of measurement throughout the empire. After the emperor's death rebellions began and the Han dynasty took power and ruled China for over four centuries with a brief interruption from AD 9 to 23. The Han dynasty promoted the spread of iron agricultural tools, which helped create a food surplus that led to a large growth of population during the Han period. Silk production also increased and the manufacture of paper was invented. Though the Han enjoyed great military and economic success, it was strained by the rise of aristocrats who disobeyed the central government. Public frustration provoked the
 The East Asian nations adjacent to China were all profoundly influenced by their interactions with Chinese civilisation. Korea and Vietnam were brought under Han rule by Han Wudi in the second century BC, and this rule led to cultural influences on both areas for many centuries to come. Wudi also faced a threat from the
The East Asian nations adjacent to China were all profoundly influenced by their interactions with Chinese civilisation. Korea and Vietnam were brought under Han rule by Han Wudi in the second century BC, and this rule led to cultural influences on both areas for many centuries to come. Wudi also faced a threat from the
 Agricultural cultivation began around 8000 BC in Mesoamerica, where avocados, beans, chili peppers, gourds, and squashes were grown from about 7000 BC. Around 4000 BC maize began to be grown, and soon after this tomatoes. Settlements appeared around 3000 BC and by 2000 BC most of Mesoamerica was practicing agriculture. Although some animals were domesticated — notably turkeys and dogs — the lack of suitable large animals precluded the development of animals used for transportation or labour.
Around 1200 BC the first Olmec center of
Agricultural cultivation began around 8000 BC in Mesoamerica, where avocados, beans, chili peppers, gourds, and squashes were grown from about 7000 BC. Around 4000 BC maize began to be grown, and soon after this tomatoes. Settlements appeared around 3000 BC and by 2000 BC most of Mesoamerica was practicing agriculture. Although some animals were domesticated — notably turkeys and dogs — the lack of suitable large animals precluded the development of animals used for transportation or labour.
Around 1200 BC the first Olmec center of
 The Classical Greek world was dominated throughout the 5th century BC by the major powers of Athens and Sparta. Through the
The Classical Greek world was dominated throughout the 5th century BC by the major powers of Athens and Sparta. Through the
human history
Human history, also called world history, is the narrative of humanity's past. It is understood and studied through anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and linguistics. Since the invention of writing, human history has been studied throug ...
to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian
Sumerian or Sumerians may refer to:
*Sumer, an ancient civilization
**Sumerian language
**Sumerian art
**Sumerian architecture
**Sumerian literature
**Cuneiform script, used in Sumerian writing
*Sumerian Records, an American record label based in ...
cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with t ...
, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others.
During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incre ...
, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood at 2 million, it rose to 45 million by 3,000 BC. By the Iron Age in 1000 BC, the population had risen to 72 million. By the end of the ancient period in AD 500, the world population is thought to have stood at 209 million. In 10,500 years, the world population increased by 100 times.Datafro
K. Klein Goldewijk, A. Beusen and P. Janssen, "HYDE 3.1: Long-term dynamic modeling of global population and built-up area in a spatially explicit way", from table on p. 2, Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency (MNP), Bilthoven, The Netherlands.
Study
History is the study of the past using sources such as archaeology and written records. Historians divide source texts into two general types – primary sources andsecondary source
In Scholarly method, scholarship, a secondary sourcePrimary, secondary and tertiary ...
s. Primary sources are usually considered to be those recorded near to the event or events being narrated. Historians consider texts recorded after an event to be secondary sources, and they usually draw on primary sources directly. Historians use archaeological evidence to help round out the written record or when there is no written record at all. Archaeology is the excavation and study of artifacts in an effort to interpret and reconstruct past human behavior.
A fundamental difficulty of studying ancient history is that recorded histories cannot document the entirety of human events, and only a fraction of those documents have survived into the present day.Gardner, P. (1892). New chapters in Greek history, historical results of recent excavations in Greece and Asia Minor. New York: G.P. Putnam's Sons. pp. 1–. Furthermore, the reliability of the information obtained from these surviving records must be considered. Few people were capable of writing histories, as literacy was not widespread in almost any culture until long after the end of ancient history.
Prehistory
Prehistory is the period before written history. Most of our knowledge of that period comes from the work of archaeologists. Prehistory is often known as theStone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with t ...
, and is divided into the Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
(earliest), Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
, and Neolithic.
The early human migrations in the Lower Paleolithic
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears in ...
saw ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor' ...
'' spread across Eurasia 1.8 million years ago. Evidence for the use of fire has been dated as early as 1.8 million years ago, a date which is contested, with generally accepted evidence for the controlled use of fire dating to 780,000 years ago. Actual use of hearths first appears 400,000 years ago. Dates for the emergence of '' Homo sapiens'' (modern humans) range from 250,000 to 160,000 years ago, with the varying dates being based on DNA studies and fossils respectively. Some 50,000 years ago, ''Homo sapiens'' migrated out of Africa. They reached Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
about 45,000 years ago, southwestern Europe about the same time, southeastern Europe and Siberia around 40,000 years ago, and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
about 30,000 years ago. Humans migrated to the Americas about 15,000 years ago.
Evidence for agriculture emerges in about 9000 BC in what is now eastern Turkey and spread through the Fertile Crescent. Settlement at Göbekli Tepe began around 9500 BC and may have the world's oldest temple. The Nile River Valley
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest rive ...
has evidence of sorghum
''Sorghum'' () is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family (Poaceae). Some of these species are grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species is grown for grain, while many othe ...
and millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets al ...
cultivation starting around 8000 BC and agricultural use of yam
Yam or YAM may refer to:
Plants and foods
*Yam (vegetable), common name for members of ''Dioscorea''
* Taro, known in Malaysia and Singapore as yam
* Sweet potato, specifically its orange-fleshed cultivars, often referred to as yams in North Amer ...
s in Western Africa perhaps dates to the same time period. Cultivation of millet, rice, and legume
A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock f ...
s began around 7000 BC in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. Taro cultivation in New Guinea dates to about 7000 BC also with squash cultivation in Mesoamerica perhaps sharing that date. Animal domestication
The domestication of animals is the mutual relationship between non-human animals and the humans who have influence on their care and reproduction.
Charles Darwin recognized a small number of traits that made domesticated species different from t ...
began with the domestication of dogs, which dates to at least 15,000 years ago, and perhaps even earlier. Sheep and goats were domesticated around 9000 BC in the Fertile Crescent, alongside the first evidence for agriculture. Other animals, such as pigs and poultry, were later domesticated and used as food sources. Cattle and water buffalo were domesticated around 7000 BC and horses
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million yea ...
, donkey
The domestic donkey is a hoofed mammal in the family Equidae, the same family as the horse. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a ...
s, and camel
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. C ...
s were domesticated by about 4000 BC. All of these animals were used not only for food, but to carry and pull people and loads, greatly increasing human ability to do work. The invention of the simple plough
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or ...
by 6000 BC further increased agricultural efficiency.
Metal use in the form of hammered copper items predates the discovery of smelting of copper ores, which happened around 6000 BC in western Asia and independently in eastern Asia before 2000 BC. Gold and silver use dates to between 6000 and 5000 BC. How to make metal alloys began with bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
in about 3500 BC in Mesopotamia and was developed independently in China by 2000 BC. Pottery developed independently throughout the world, with fired pots appearing first among the Jomon of Japan and in West Africa at Mali. Sometime between 5000 and 4000 BC the potter's wheel was invented. By 3000 BC, the pottery wheel was adapted into wheeled vehicles which could be used to carry loads further and easier than with human or animal power alone.
Writing developed separately in five different locations in human history: Mesopotamia, Egypt, India, China, and Mesoamerica. By 3400 BC, "proto-literate" cuneiform spread in the Middle East. Egypt developed its own system of hieroglyphs by about 3200 BC. By 2800 BC the Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
had developed its Indus script, which remains undeciphered. Writing in China was developed in the Shang Dynasty dating to the period 1600 to 1100 BC. Writing in Mesoamerica dates to 600 BC with the Zapotec civilization.
History by region
Southwest Asia (Near East)
The ancient Near East is considered the cradle of civilisation. It was the first to practice intensive year-round agriculture; created one of the first coherent writing systems, invented the potter's wheel and then the vehicularwheel
A wheel is a circular component that is intended to rotate on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction wi ...
, created the first centralized governments, law codes and empires, as well as displaying social stratification
Social stratification refers to a society's categorization of its people into groups based on socioeconomic factors like wealth, income, race, education, ethnicity, gender, occupation, social status, or derived power (social and political). As ...
, slavery, and organized warfare. It began the study of the stars and the sciences of astronomy and mathematics.

Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is the site of some of the earliest known civilisations in the world. Agricultural communities emerged in the area with the Halaf culture around 8000 BC and continued to expand through the Ubaid period around 6000 BC. Cities began in the Uruk period (4000–3100 BC) and expanded during theJemdet Nasr
Jemdet Nasr ( ar, جمدة نصر) is a tell or settlement mound in Babil Governorate (Iraq) that is best known as the eponymous type site for the Jemdet Nasr period (3100–2900 BC), and was one of the oldest Sumerian cities. The site was first ...
(3100–2900 BC) and Early Dynastic (2900–2350 BC) periods. The surplus of storable foodstuffs created by this economy allowed the population to settle in one place instead of migrating after crops and herds. It also allowed for a much greater population density, and in turn required an extensive labour force and division of labour. This organization led to the necessity of record keeping and the development of writing.
Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
was an Amorite state in lower Mesopotamia (modern southern Iraq), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged when Hammurabi created an empire out of the territories of the former kingdoms of Sumer and Akkad Akkad may refer to:
*Akkad (city), the capital of the Akkadian Empire
*Akkadian Empire, the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia
*Akkad SC, Iraqi football club
People with the name
*Abbas el-Akkad, Egyptian writer
*Abdulrahman Akkad, Syrian LGBT act ...
.
The Neo-Babylonian Empire, or Chaldea
Chaldea () was a small country that existed between the late 10th or early 9th and mid-6th centuries BCE, after which the country and its people were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia. Semitic-speaking, it was ...
, was Babylonia from the 7th and 6th centuries BC. Under the reign of Nebuchadnezzar II
Nebuchadnezzar II (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-kudurri-uṣur'', meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir"; Biblical Hebrew: ''Nəḇūḵaḏneʾṣṣar''), also spelled Nebuchadrezzar II, was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling ...
, it conquered Jerusalem. This empire also created the Hanging Gardens of Babylon
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon were one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World listed by Hellenic culture. They were described as a remarkable feat of engineering with an ascending series of tiered gardens containing a wide variety of tre ...
and the still-surviving Ishtar Gate as architectural embellishments of its capital at Babylon.
Akkad Akkad may refer to:
*Akkad (city), the capital of the Akkadian Empire
*Akkadian Empire, the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia
*Akkad SC, Iraqi football club
People with the name
*Abbas el-Akkad, Egyptian writer
*Abdulrahman Akkad, Syrian LGBT act ...
was a city and its surrounding region near Babylon. Akkad also became the capital of the Akkadian Empire. Despite an extensive search, the precise site has never been found. Akkad reached the height of its power between about 2330 and 2150 BC, following the conquests of King Sargon of Akkad
Sargon of Akkad (; akk, ''Šarrugi''), also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC.The date of the reign of Sargon is highl ...
. Through the spread of Sargon's empire, the language of Akkad, known as Akkadian from the city, spread and replaced the Sumerian language in Mesopotamia and eventually by 1450 BC was the main language of diplomacy in the Near East.
Assyria was originally a region on the Upper Tigris, where a small state was created in the 19th century BC. The capital was at Assur, which gave the state its name. Later, as a nation and empire that came to control all of the Fertile Crescent, Egypt and much of Anatolia, the term "Assyria proper" referred to roughly the northern half of Mesopotamia (the southern half being Babylonia), with Nineveh
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul in northern Iraq. It is located on the eastern ban ...
as its capital. The Assyrian kings controlled a large kingdom at three different times in history. These are called the ''Old'' (20th to 18th centuries BC), ''Middle'' (14th to 11th centuries BC), and '' Neo-Assyrian'' (9th to 7th centuries BC) kingdoms, or periods.
Mitanni was a Hurrian empire in northern Mesopotamia founded around 1500 BC. The Mitanians conquered and controlled Assyria until the 14th century BC while contending with Egypt for control of parts of modern Syria. Its capital was Washukanni, whose precise location has not been determined by archaeologists.
Iranian people
The Medes and Persians were peoples who had appeared in the Iranian plateau around 1500 BC. Both peoples spoke Indo-European languages and were mostly pastoralists with a tradition of horse archery. The Medes established their ownMedian Empire
The Medes (Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, the ...
by the 6th century BC, having defeated the Neo-Assyrian Empire with the Chaldea
Chaldea () was a small country that existed between the late 10th or early 9th and mid-6th centuries BCE, after which the country and its people were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia. Semitic-speaking, it was ...
ns in 614 BC.
 The
The Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
was founded by Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia (; peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first Persian empire. Schmitt Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Under his rule, the empire embraced ...
, who first became king of the Persians, then conquered the Medes, Lydia
Lydia (Lydian language, Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the mod ...
, and Babylon by 539 BC. The empire built on earlier Mesopotamian systems of government to govern their large empire. By building roads, they improved both the ability to send governmental instructions throughout their lands as well as improving the ability of their military forces to be deployed rapidly. Increased trade and upgraded farming techniques increased wealth, but also exacerbated inequalities between social classes. The empire's location at the centre of trading networks spread its intellectual and philosophical ideas throughout a wide area, and its religion, while not itself spreading far, had an impact on later religions such as Christianity, Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, and Judaism. Cyrus' son Cambyses II
Cambyses II ( peo, 𐎣𐎲𐎢𐎪𐎡𐎹 ''Kabūjiya'') was the second King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 530 to 522 BC. He was the son and successor of Cyrus the Great () and his mother was Cassandane.
Before his accession, Cambyses ...
conquered Egypt, while a later emperor, Darius the Great
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his d ...
, expanded the empire to the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
, creating the largest empire in the world to that date. But Darius and his son Xerxes I failed to expand into Greece, with expeditions in 490 and 480 BC eventually failing. The Achaemenid dynasty and empire fell to Alexander the Great by 330 BC, and after Alexander's death, much of the area previously ruled by the Cyrus and his successors was ruled by the Seleucid dynasty
The Seleucid dynasty or the Seleucidae (from el, Σελευκίδαι, ') was a Macedonian Greeks (ancient), Macedonian Greek royal family, founded by Seleucus I Nicator, which ruled the Seleucid Empire centered in the Near East and regions o ...
.
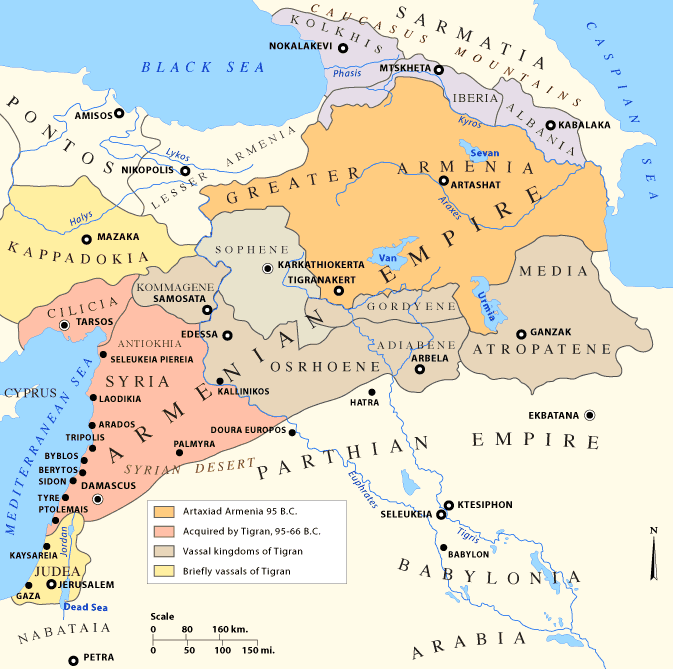
 Parthia was an Iranian civilisation situated in the northeastern part of modern Iran. Their power was based on a combination of military power based on heavy cavalry with a decentralised governing structure based on a federated system. The Parthian Empire was led by the Arsacid dynasty, which by around 155 BC under Mithradates I had mostly conquered the
Parthia was an Iranian civilisation situated in the northeastern part of modern Iran. Their power was based on a combination of military power based on heavy cavalry with a decentralised governing structure based on a federated system. The Parthian Empire was led by the Arsacid dynasty, which by around 155 BC under Mithradates I had mostly conquered the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
. Parthia had many wars with the Romans, but it was rebellions within the empire that ended it in the 3rd century AD.
The Sassanid Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
began when the Parthian Empire ended in AD 224. Their rulers claimed the Achaemenids as ancestors and set up their capital at Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; Middle Persian: 𐭲𐭩𐭮𐭯𐭥𐭭 ''tyspwn'' or ''tysfwn''; fa, تیسفون; grc-gre, Κτησιφῶν, ; syr, ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢThomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modi ...
in Mesopotamia. Their period of greatest military expansion occurred under Shapur I, who by the time of his death in AD 272 had defeated Roman imperial armies and set up buffer states between the Sassanid and Roman Empires. After Shapur, the Sassanids were under more pressure from the Kushans to their east as well as the Roman then Byzantine empire to its west. But the Sassanids rebuild and founded numerous cities and their merchants traveled widely and introduced crops such as sugar, rice, and cotton into the Iranian plateau. But in AD 651, the last Sassanid emperor was killed by the expanding Islamic Arabs.
Hittites
 The Hittites first came to Anatolia about 1900 BC and during the period 1600-1500 they expanded into Mesopotamia where they adopted the cuneiform script to their Indo-European language. By 1200 their empire stretched to Phoenicia and eastern Anatolia. They improved two earlier technologies from Mesopotamia and spread these new techniques widely – improved iron working and light
The Hittites first came to Anatolia about 1900 BC and during the period 1600-1500 they expanded into Mesopotamia where they adopted the cuneiform script to their Indo-European language. By 1200 their empire stretched to Phoenicia and eastern Anatolia. They improved two earlier technologies from Mesopotamia and spread these new techniques widely – improved iron working and light chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000&nbs ...
s with spoked wheel
A spoke is one of some number of rods radiating from the center of a wheel (the Bicycle hub, hub where the axle connects), connecting the hub with the round traction surface.
The term originally referred to portions of a log that had been ri ...
s in warfare. The Hittites introduced the casting of iron with molds and then hammering it which enabled weapons and tools to be made stronger and also cheaper. Although chariots had been used previously, the use of spoked wheels allowed the chariots to be much lighter and more maneuverable. In 1274 BC the Hittites clashed with the Egyptians at the Battle of Kadesh, where both sides claimed victory. But in 1207 the Hittite capital of Hattusa was sacked, ending the Hittite Empire.
Israel
stele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), whe ...
of the Egyptian pharaoh Merneptah around 1209 BC. This "Israel" was a cultural and probably political entity of the central highlands, well enough established to be perceived by the Egyptians as a possible challenge to their hegemony, but an ethnic group rather than an organised state.
Israel had emerged by the middle of the 9th century BC, when the Assyrian King Shalmaneser III names " Ahab the Israelite" among his enemies at the battle of Qarqar (853). Judah emerged somewhat later than Israel, probably during the 9th century BC, but the subject is one of considerable controversy. Israel came into conflict with the Assyrians, who conquered Israel in 722 BC. The Neo-Babylonian Empire did the same to Judah in 586. After both conquests, the conquering forces deported many of the inhabitants to other regions of their respective empires.
Following the fall of Babylon to the Persian Empire, Cyrus the Great allowed the rebuilding of the temple at Jerusalem, and some of the exiles from Judah returned to Judea, where they remained under Persian rule until the Maccabean revolt led to independence during Hellenistic period until Roman conquest.
Phoenicia
Phoenicia was an ancient civilisation centered in the north of ancient Canaan, with its heartland along the coastal regions of modern-day Lebanon, Syria and Israel. Phoenician civilisation was an enterprising maritime trading culture that spread across the Mediterranean between the period of 1550 to 300 BC. One Phoenician colony, Carthage, ruled an empire in the Western Mediterranean until being defeated by Rome in thePunic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146BC fought between Roman Republic, Rome and Ancient Carthage, Carthage. Three conflicts between these states took place on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region and i ...
. The Phoenicians invented the Phoenician alphabet, the forerunner of the modern alphabet still in use today.
Arabia
The history of Pre-Islamic Arabia before the rise ofIslam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
in the AD 630s is not known in great detail. Archaeological exploration in the Arabian peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
has been sparse; indigenous written sources are limited to the many inscriptions and coins from southern Arabia. Existing material consists primarily of written sources from other traditions (such as Egyptians, Greeks, Persians, Romans, etc.) and oral traditions later recorded by Islamic scholars. A number of small kingdoms existed in Arabia from around AD 100 to perhaps about AD 400.
Afro-Asiatic Africa
Carthage
Carthage was founded around 814 BC by Phoenician settlers. Ancient Carthage was a city-state that ruled an empire through alliances and trade influence that stretched throughout North Africa and modern Spain. At the height of the city's influence, its empire included most of the western Mediterranean. The empire was in a constant state of struggle with the Roman Republic, which led to a series of conflicts known as thePunic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146BC fought between Roman Republic, Rome and Ancient Carthage, Carthage. Three conflicts between these states took place on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region and i ...
. After the third and final Punic War, Carthage was destroyed then occupied by Roman forces. Nearly all of the territory held by Carthage fell into Roman hands.
Egypt
 Ancient Egypt was a long-lived civilisation geographically located in north-eastern Africa. It was concentrated along the middle to lower reaches of the Nile River, reaching its greatest extension during the 2nd millennium BC, which is referred to as the New Kingdom period. It reached broadly from the
Ancient Egypt was a long-lived civilisation geographically located in north-eastern Africa. It was concentrated along the middle to lower reaches of the Nile River, reaching its greatest extension during the 2nd millennium BC, which is referred to as the New Kingdom period. It reached broadly from the Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Po ...
in the north, as far south as Jebel Barkal at the Fourth Cataract of the Nile. Extensions to the geographical range of ancient Egyptian civilisation included, at different times, areas of the southern Levant, the Eastern Desert and the Red Sea coastline, the Sinai Peninsula, and the Western Desert (focused on the several oases
In ecology, an oasis (; ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environment'ksar''with its surrounding feeding source, the palm grove, within a relational and circulatory nomadic system.”
The location of oases has been of critical imp ...
).
Ancient Egypt developed over at least three and a half millennia. It began with the incipient unification of Nile Valley polities around 3100 BC, traditionally under Menes. The civilisation of ancient Egypt was characterised primarily by intensive agricultural use of the fertile Nile Valley; the use of the Nile itself for transportation; the development of writing systems – first hieroglyphs and then later hieratic
Hieratic (; grc, ἱερατικά, hieratiká, priestly) is the name given to a cursive writing system used for Ancient Egyptian and the principal script used to write that language from its development in the third millennium BC until the ris ...
and other derived scripts – and literature; the organisation of collective projects such as the pyramids
A pyramid (from el, πυραμίς ') is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrilate ...
; trade with surrounding regions; and a polytheistic religious tradition that included elaborate funeral customs including mummification. Overseeing these activities were a socio-political and economic elite
In political and sociological theory, the elite (french: élite, from la, eligere, to select or to sort out) are a small group of powerful people who hold a disproportionate amount of wealth, privilege, political power, or skill in a group. D ...
under the figure of a (semi)-divine ruler from a succession of ruling dynasties.
Ancient Egyptian history is divided across various periods, beginning with the Old Kingdom, which saw pyramid building on a large scale. After 2100 BC, the Old Kingdom dissolved into smaller states during the First Intermediate Period
The First Intermediate Period, described as a 'dark period' in ancient Egyptian history, spanned approximately 125 years, c. 2181–2055 BC, after the end of the Old Kingdom. It comprises the Seventh (although this is mostly considered spurious ...
, which lasted about 100 years. The Middle Kingdom began around 2000 BC with the reunification of Egypt under pharoes ruling from Thebes. The Middle Kingdom ended with the conquest of northern Egypt by the Hyksos around 1650 BC. The Hyksos were expelled from Egypt and the land was reunited in the New Kingdom
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, ...
around 1550 BC. This period lasted until about 1000 BC, and saw Egypt expand its borders into Palestine and Syria. The Third Intermediate Period was marked by the rule of priests as well as the conquest of Egypt by Nubian kings and then later Assyria, Persia, and Macedonians.
Nubia
 The Ta-Seti kingdom in Nubia to the south of Egypt was conquered by Egyptian rulers around 3100 BC, but by 2500 BC the Nubians had created a new kingdom further south, known as the Kingdom of Kush, centred on the upper Nile with a capital at Kerma. In the Egyptian New Kingdom period, Kush once more was conquered by Egypt, but by 1100 BC a new kingdom of Kush had formed, with a capital at Napata. Nubian rulers conquered Egypt around 760 BC and retained control for about a century.
The Ta-Seti kingdom in Nubia to the south of Egypt was conquered by Egyptian rulers around 3100 BC, but by 2500 BC the Nubians had created a new kingdom further south, known as the Kingdom of Kush, centred on the upper Nile with a capital at Kerma. In the Egyptian New Kingdom period, Kush once more was conquered by Egypt, but by 1100 BC a new kingdom of Kush had formed, with a capital at Napata. Nubian rulers conquered Egypt around 760 BC and retained control for about a century.
Axum and Ancient Ethiopia
 The Axumite Empire was an important trading nation in northeastern Africa centered in present-day
The Axumite Empire was an important trading nation in northeastern Africa centered in present-day Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
and northern Ethiopia, it existed from approximately AD 100 to 940, growing from the Iron Age proto-Aksumite period around the 4th century BC to achieve prominence by the 1st century AD. The Empire of Aksum at its height at its climax by the early 6th-century AD extended through much of modern Ethiopia and across the Red Sea to Arabia. The capital city of the empire was Aksum, now in northern Ethiopia.
Niger-Congo Africa
Nok culture
 The Nok culture appeared in Nigeria around 1000 BC and mysteriously vanished around AD 200. The civilisation's social system is thought to have been highly advanced. The Nok civilisation was considered to be the earliest sub-Saharan producer of life-sized Terracotta which have been discovered by archaeologists. The Nok also used iron smelting that may have been independently developed.
The Nok culture appeared in Nigeria around 1000 BC and mysteriously vanished around AD 200. The civilisation's social system is thought to have been highly advanced. The Nok civilisation was considered to be the earliest sub-Saharan producer of life-sized Terracotta which have been discovered by archaeologists. The Nok also used iron smelting that may have been independently developed.
The Sahel
Djenné-Djenno
The civilisation of Djenné-Djenno was located in the Niger River Valley in the country of Mali and is considered to be among the oldest urbanized centers and the best-known archaeology site in Sub-Saharan Africa. This archaeological site is located about 3 kilometers (1.9 mi) away from the modern town and is believed to have been involved in long-distance trade and possibly the domestication of African rice. The site is believed to exceed 33 hectares (82 acres); however, this is yet to be confirmed with extensive survey work. With the help of archaeological excavations mainly by Susan and Roderick McIntosh, the site is known to have been occupied from 250 BC to AD 900. The city is believed to have been abandoned and moved where the current city is located due to the spread of Islam and the building of the Great Mosque of Djenné. Previously, it was assumed that advanced trade networks and complex societies did not exist in the region until the arrival of traders from Southwest Asia. However, sites such as Djenné-Djenno disprove this, as these traditions in West Africa flourished long before. Towns similar to that at Djenne-Jeno also developed at the site of Dia, also in Mali along the Niger River, from around 900 BC.Dhar Tichitt and Oulata
Dhar Tichitt and Oualata were prominent among the early urban centres, dated to 2000 BC, in present-day Mauritania. About 500 stone settlements littered the region in the former savannah of the Sahara. Its inhabitants fished and grew millet. It has been found that the Soninke of the Mandé peoples were responsible for constructing such settlements. Around 300 BC, the region became more desiccated and the settlements began to decline, most likely relocating to Koumbi Saleh. From the type of architecture and pottery, it is believed that Tichit was related to the subsequent Ghana Empire. Old Jenne (Djenne) began to be settled around 300 BC, producing iron and with sizeable population, evidenced in crowded cemeteries. The inhabitants and creators of these settlements during these periods thought to have been ancestors of the Soninke people.Bantu expansion
Peoples speaking precursors to the modern-dayBantu languages
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀) are a large family of languages spoken by the Bantu people of Central, Southern, Eastern africa and Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages.
The t ...
began to spread throughout southern Africa, and by 2000 BC they were expanding past the Congo River and into the Great Lakes area. By AD 1000 these groups had spread throughout all of southern Africa south of the equator. Iron metallurgy and agriculture spread along with these peoples, with the cultivation of millet, oil palms, sorghum, and yams as well as the use of domesticated cattle, pigs, and sheep. These technologies helped increase population, and settled communities became common in sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
except in deserts or heavy forests.
South Asia
 Paleolithic tools have been discovered in India dating to 200,000 years ago, and neolithic sites are known from near the
Paleolithic tools have been discovered in India dating to 200,000 years ago, and neolithic sites are known from near the Indus Valley
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
dating to around 8000 BC. Agriculture began in the Indus Valley around 7000 BC, and to the Ganges Valley by 3000 BC. Barley, cotton, and wheat were grown and the population had domesticated cattle, goats, and sheep.
 The Indus Valley civilization developed around 3000 BC in the
The Indus Valley civilization developed around 3000 BC in the Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
and Ghaggar-Hakra
The Ghaggar-Hakra River is an intermittent river in India and Pakistan that flows only during the monsoon season. The river is known as Ghaggar in India, before the Ottu barrage, and as the Hakra in Pakistan, downstream of the barrage, ending i ...
river valleys of eastern Afghanistan, Pakistan, and western India. Another name for this civilisation is Harappan, after the first of its cities to be excavated, Harappa
Harappa (; Urdu/ pnb, ) is an archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan, about west of Sahiwal. The Bronze Age Harappan civilisation, now more often called the Indus Valley Civilisation, is named after the site, which takes its name from a mode ...
in the Pakistani province of Punjab. Harappan civilization grew out of the earlier agricultural communities as they evolved into cities. These communities created and traded jewelry, figurines, and seals that appear widely scattered throughout Mesopotamia, Afghanistan, and Iran. Chickens were domesticated in addition to the earlier crops and animals. They developed their own writing system, the Indus Valley script, which is still mostly undeciphered. The exact structure of society and the way the cities were governed is not known. By about 1600 BC, the Indus Valley culture had abandoned many of their cities, including Mohenjo-Daro. The exact reason for this decline is not known.
Indo-European speaking peoples began to spread into India about 1500 BC. The '' Rigveda'', in Sanskrit, dates to this period and begins a period often known as the Vedic period. Between 1500 and 500 BC these peoples spread throughout most of India and had begun to found small cities. Vedic society was characterized by the ''varna
Varna may refer to:
Places Europe
*Varna, Bulgaria, a city in Bulgaria
**Varna Province
**Varna Municipality
** Gulf of Varna
**Lake Varna
**Varna Necropolis
*Vahrn, or Varna, a municipality in Italy
*Varniai, a city in Lithuania
* Varna (Šaba ...
'' system which divided society into four broad castes, which were later elaborated. By the end of the Vedic period, this way of organizing society had become central to Indian society. Religion in the late Vedic period was evolving into Hinduism, which spread throughout Southeast Asia. Siddhartha Gautama, born around 560 BC in northern India, went on to found a new religion based on his ascetic life – Buddhism. This faith also spread throughout Eastern and Southeastern Asia after his death. This period also saw the composition of the epics '' Ramayana'' and '' Mahabharata''.
The kingdom of Magadha rose to prominence under a number of dynasties that peaked in power under the reign of Ashoka Maurya, one of India's most legendary and famous emperors. During the reign of Ashoka, the four dynasties of Chola
The Chola dynasty was a Tamils, Tamil thalassocratic Tamil Dynasties, empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated ...
, Chera, and Pandya were ruling in the South, while Devanampiya Tissa (250–210 BC) controlled Anuradhapura (now Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
). These kingdoms, while not part of Ashoka's empire, were in friendly terms with the Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
. An alliance existed between Devanampiya Tissa and Ashoka of India, who sent Buddhist missionaries to Sri Lanka.
Most of North India was reunited under the Gupta Empire beginning under Chandragupta I around AD 320. Under his successors the empire spread to include much of India except for the Deccan Plateau and the very south of the peninsula. This was a period of relative peace, and the Gupta rulers generally left administration in local rulers. The Gupta Empire was weakened and ultimately ruined by the raids of Hunas (a branch of the Hephthalite
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during th ...
s emanating from Central Asia), and the empire broke up into smaller regional kingdoms by the end of the fifth century AD. India would remain fragmented into smaller states until the rise of the Mughal Empire in the 1500s.
East Asia
China
 The Chinese civilisation that emerged within the Yellow River valley is one of earliest civilisations in the world. Prior to the formation of civilisation, neolithic cultures such as the Longshan and Yangshao dating to 5000 BC produced sophisticated pottery, cultivated millet, and likely produced clothes woven from
The Chinese civilisation that emerged within the Yellow River valley is one of earliest civilisations in the world. Prior to the formation of civilisation, neolithic cultures such as the Longshan and Yangshao dating to 5000 BC produced sophisticated pottery, cultivated millet, and likely produced clothes woven from hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a botanical class of ''Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial or medicinal use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest growing plants o ...
and silk. Rice was also farmed and pigs and water buffalo were kept for food. Longshan potters may have used the pottery wheel to produce their wares. Ancient Chinese traditions described three ancient dynasties that predated the unification under the Qin Qin may refer to:
Dynasties and states
* Qin (state) (秦), a major state during the Zhou Dynasty of ancient China
* Qin dynasty (秦), founded by the Qin state in 221 BC and ended in 206 BC
* Daqin (大秦), ancient Chinese name for the Roman Emp ...
and Han dynasties. These were the Xia, the Shang
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and f ...
, and the Zhou. It wasn't until the later 20th century that many historians considered the Shang or Xia to be anything other than legendary. Little is yet known about the Xia, which appears to have begun around 2200 BC, and may have controlled parts of the Yangtze River valley.
The Shang dynasty traditionally is dated to 1766 to 1122 BC. Bronze was central to Shang culture and technology, with chariots and bronze weapons helping to expand Shang control over northern China. The cities at Ao and Yinxu, near Anyang
Anyang (; ) is a prefecture-level city in Henan province, China. The northernmost city in Henan, Anyang borders Puyang to the east, Hebi and Xinxiang to the south, and the provinces of Shanxi and Hebei to its west and north respectively.
It had a ...
, have been excavated and city walls, royal palaces, and archives as well as tombs and workshops were found. A system of writing developed, beginning with oracle bones, of which over 100,000 are still extant.
Towards the end of the 2nd millennium BC, the Shang were overrun by the Zhou dynasty from the Wei River valley to the west. The Zhou rulers at this time invoked the concept of the Mandate of Heaven
The Mandate of Heaven () is a Chinese political philosophy that was used in ancient and imperial China to legitimize the rule of the King or Emperor of China. According to this doctrine, heaven (天, ''Tian'') – which embodies the natural ...
to legitimize their rule, a concept that would be influential for almost every successive dynasty. The Zhou initially established their capital in the west near modern Xi'an, near the Yellow River, but they would preside over a series of expansions into the Yangtze River valley. Zhou administration was decentralised, with local elites responsible for collecting tribute and providing military support to the Zhou rulers.
 In the 8th century BC, power became decentralized during the
In the 8th century BC, power became decentralized during the Spring and Autumn period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives fr ...
, named after the influential '' Spring and Autumn Annals''. In this period, local military leaders used by the Zhou began to assert their power and vie for hegemony. The situation was aggravated by the invasion of other peoples, forcing the Zhou to move their capital east to Luoyang. In each of the hundreds of states that eventually arose, local strongmen held most of the political power and continued their subservience to the Zhou kings in name only. The Hundred Schools of Thought of Chinese philosophy blossomed during this period, and such influential intellectual movements as Confucianism, Taoism, Legalism and Mohism
Mohism or Moism (, ) was an ancient Chinese philosophy of ethics and logic, rational thought, and science developed by the academic scholars who studied under the ancient Chinese philosopher Mozi (c. 470 BC – c. 391 BC), embodied in an epony ...
were founded, partly in response to the changing political world.
After further political consolidation, seven prominent states remained by the end of the 5th century BC, and the years in which these few states battled each other is known as the Warring States period. Though there remained a nominal Zhou king until 256 BC, he was largely a figurehead and held little power. As neighboring territories of these warring states, including areas of modern Sichuan and Liaoning
Liaoning () is a coastal province in Northeast China that is the smallest, southernmost, and most populous province in the region. With its capital at Shenyang, it is located on the northern shore of the Yellow Sea, and is the northernmost ...
, were annexed by the growing power of the rulers of Qin Qin may refer to:
Dynasties and states
* Qin (state) (秦), a major state during the Zhou Dynasty of ancient China
* Qin dynasty (秦), founded by the Qin state in 221 BC and ended in 206 BC
* Daqin (大秦), ancient Chinese name for the Roman Emp ...
, they were governed under the new local administrative system of commandery. The final expansion in this period began during the reign of Ying Zheng, the king of Qin. His unification of the other six powers, and further annexations to the south and southeast by 213 BC enabled him to proclaim himself the First Emperor (Qin Shi Huangdi).
 Qin Shi Huangdi ruled the unified China directly with absolute power. In contrast to the decentralized and feudal rule of earlier dynasties the Qin ruled directly. Nationwide the philosophy of legalism was enforced and publications promoting rival ideas such as Confucianism were prohibited. In his reign unified China created the first continuous Great Wall with the use of forced labour. Invasions were launched southward to annex Vietnam. The Qin period also saw the standardization of the Chinese writing system and the government unified the legal systems as well as setting standardized units of measurement throughout the empire. After the emperor's death rebellions began and the Han dynasty took power and ruled China for over four centuries with a brief interruption from AD 9 to 23. The Han dynasty promoted the spread of iron agricultural tools, which helped create a food surplus that led to a large growth of population during the Han period. Silk production also increased and the manufacture of paper was invented. Though the Han enjoyed great military and economic success, it was strained by the rise of aristocrats who disobeyed the central government. Public frustration provoked the
Qin Shi Huangdi ruled the unified China directly with absolute power. In contrast to the decentralized and feudal rule of earlier dynasties the Qin ruled directly. Nationwide the philosophy of legalism was enforced and publications promoting rival ideas such as Confucianism were prohibited. In his reign unified China created the first continuous Great Wall with the use of forced labour. Invasions were launched southward to annex Vietnam. The Qin period also saw the standardization of the Chinese writing system and the government unified the legal systems as well as setting standardized units of measurement throughout the empire. After the emperor's death rebellions began and the Han dynasty took power and ruled China for over four centuries with a brief interruption from AD 9 to 23. The Han dynasty promoted the spread of iron agricultural tools, which helped create a food surplus that led to a large growth of population during the Han period. Silk production also increased and the manufacture of paper was invented. Though the Han enjoyed great military and economic success, it was strained by the rise of aristocrats who disobeyed the central government. Public frustration provoked the Yellow Turban Rebellion
The Yellow Turban Rebellion, alternatively translated as the Yellow Scarves Rebellion, was a List of peasant revolts, peasant revolt in China against the Eastern Han dynasty. The uprising broke out in 184 CE during the reign of Emperor Ling of ...
; though a failure it nonetheless accelerated the empire's downfall. After AD 208, the Han dynasty broke up into rival kingdoms. China would remain divided for almost the next 400 years.
Neighbors of China
 The East Asian nations adjacent to China were all profoundly influenced by their interactions with Chinese civilisation. Korea and Vietnam were brought under Han rule by Han Wudi in the second century BC, and this rule led to cultural influences on both areas for many centuries to come. Wudi also faced a threat from the
The East Asian nations adjacent to China were all profoundly influenced by their interactions with Chinese civilisation. Korea and Vietnam were brought under Han rule by Han Wudi in the second century BC, and this rule led to cultural influences on both areas for many centuries to come. Wudi also faced a threat from the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 ...
, a nomadic people from the Central Asian steppes. Wudi's invasions ended the Xiongnu state.
In 108 BC, the Han dynasty of China conquered much of Korea but when Han China began its decline, three kingdoms in Korea – those of Baekje, Goguryeo and Silla – emerged and expelled the Chinese. Goguryeo and Baekje were eventually destroyed by a Tang dynasty and Silla alliance. Silla then drove out the Tang dynasty in 676 to control most of the Korean peninsula undisputed.
Jomon culture formed in Japan before 500 BC and under Chinese influence became the Yayoi culture which built large tombs by AD 200. In the 300s, a kingdom formed in the Yamato plain, perhaps influenced by Korean refugees.
The Americas
In pre-Columbian times, several large, centralized ancient civilisations developed in the Western Hemisphere, both in Mesoamerica and western South America. Beyond these areas, the use of agriculture expanded East of the Andes Mountains in South America particularly with the Marajoara culture, and in the continental United States.Andean civilisations
Ancient Andean civilisation began with the rise of organized fishing communities from 3500 BC onwards. Along with a sophisticated maritime society came the construction of large monuments, which likely existed as community centers. The peoples of this area grew beans, cotton, peanuts, and sweet potatoes, fished in the ocean, and by about 2000 BC had added the potato to their crops. The Chavin culture, based around theChavin cult
Chavin may refer to:
Places
* Chavín de Huantar, an archaeological site in Peru built by the Chavín culture
* Chavín District, Chincha, Peru
* Chavín de Huantar District, Huari, Peru
* Chavín de Pariarca District, Huamalies, Peru
* Chavin, I ...
, emerged around 1000 BC and led to large temples and artworks as well sophisticated textiles. Gold, silver, and copper were worked for jewelry and occasionally for small copper tools.
After the decline of Chavin culture, a number of cities formed after about 200 BC. The cities at Huari, Pucara, and Tiahuanaco were all likely over 10,000 residents. From about AD 300, the Mochica culture
The Moche civilization (; alternatively, the Mochica culture or the Early, Pre- or Proto-Chimú) flourished in northern Peru with its capital near present-day Moche, Trujillo, Peru from about 100 to 700 AD during the Regional Development Epoch. ...
arose along the Moche River. These people left painted pottery depicting their society and culture with a wide range of varied subjects. Besides the Mochica, there were a number of other large states in the Andes after about AD 100. Included amongst these are the Nazca culture, who were mainly village-dwelling but left behind a large ceremonial centre at Cahuachi
Cahuachi, in Peru, was a major ceremonial center of the Nazca culture, based from 1 AD to about 500 AD in the coastal area of the Central Andes. It overlooked some of the Nazca lines. The Italian archaeologist Giuseppe Orefici has been excavat ...
as well as the Nazca lines, a large number of huge designs set into the desert floor.
Mesoamerica
 Agricultural cultivation began around 8000 BC in Mesoamerica, where avocados, beans, chili peppers, gourds, and squashes were grown from about 7000 BC. Around 4000 BC maize began to be grown, and soon after this tomatoes. Settlements appeared around 3000 BC and by 2000 BC most of Mesoamerica was practicing agriculture. Although some animals were domesticated — notably turkeys and dogs — the lack of suitable large animals precluded the development of animals used for transportation or labour.
Around 1200 BC the first Olmec center of
Agricultural cultivation began around 8000 BC in Mesoamerica, where avocados, beans, chili peppers, gourds, and squashes were grown from about 7000 BC. Around 4000 BC maize began to be grown, and soon after this tomatoes. Settlements appeared around 3000 BC and by 2000 BC most of Mesoamerica was practicing agriculture. Although some animals were domesticated — notably turkeys and dogs — the lack of suitable large animals precluded the development of animals used for transportation or labour.
Around 1200 BC the first Olmec center of San Lorenzo
San Lorenzo is the Italian and Spanish name for Lawrence of Rome, Saint Lawrence, the 3rd-century Christian martyr, and may refer to:
Places Argentina
* San Lorenzo, Santa Fe
* San Lorenzo Department, Chaco
* Monte San Lorenzo, a mountain on t ...
was founded, which remained the centre of Olmec civilisation until around 800 BC when La Venta took over before losing primacy to Tres Zapotes around 400 BC. These and other Olmec centres were groups of tombs, temples, and other ceremonial sites built of stone. Their construction testifies to the complexity of Olmec society, although the exact nature of how they were governed is not known. They also erected large stone sculptures of human heads and other subjects. Jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole group of ...
jewelry and other Olmec objects are found throughout Mesoamerica, likely having travelled via trade networks. The Olmec writing system was mainly used for recording their calendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a physi ...
, both of which influenced later Mesoamericam cultures.
After the decline of the Olmecs, other civilisations in Mesoamerica either arose or emerged from the Olmec shadow - the Mayans, the Zapotecs, and Teotihuacan. The Zapotecs began around 500 BC in the Oaxaca Valley at the site of Monte Alban
Monte may refer to:
Places Argentina
* Argentine Monte, an ecoregion
* Monte Desert
* Monte Partido, a ''partido'' in Buenos Aires Province
Italy
* Monte Bregagno
* Monte Cassino
* Montecorvino (disambiguation)
* Montefalcione
Portugal
* Monte ...
. Monte Alban grew to around 25,000 residents in the period around AD 200, with the city having large stone temples and an expansive stone plaza. Like thei Olmecs, they had a writing system and calendar. But by AD 900 Monte Alban was deserted, for unknown reasons. Teotihuacan developed around AD 200 and centred on the city of Teotihuacan, which grew to perhaps as many as 200,000 inhabitants at its height. Teotihuacan lasted until around AD 700, when it was burned and vandalized.
Maya culture began to emerge around AD 300 in the Yucatan Peninsula and modern-day Guatemala. During the 600 years of the Classical Maya
Classical may refer to:
European antiquity
*Classical antiquity, a period of history from roughly the 7th or 8th century B.C.E. to the 5th century C.E. centered on the Mediterranean Sea
*Classical architecture, architecture derived from Greek and ...
period, more than 80 Mayan sites were built, with temples, pyramids, and palaces the focal point of each centre. The most influential was Tikal, but Mayan civilisation was based on city-states which often were at war with each other. This seems not to have restricted trade, which went on between the cities. A priestly elite kept astronomical and calendrical knowledge, recording it with a writing system based the Olmec system of glyphs. History, poetry, and other records were recorded in books, most of which did not survive the Spanish conquest of Mesoamerica. Mathematics was also studied, and they used the concept of zero in their calculations. The Mayan civilisation began to decline about AD 800, and most of its cities were deserted soon afterwards.
Northern America
Organized societies, in the ancient United States or Canada, were often mound builder civilisations. One of the most significant of these was the Poverty Point culture that existed in the U.S. state of Louisiana, and was responsible for the creation of over 100 mound sites. The Mississippi River was a core area in the development of long-distance trade and culture. Following Poverty Point, successive complex cultures such as the Hopewell emerged in the Southeastern United States in the Early Woodland period. Before AD 500 many mound builder societies retained a hunter gatherer form of subsistence.Oceania
Humans spread toAustralia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
and New Guinea by about 60,000 years ago, with agriculture beginning in New Guinea about 3000 BC. Aboriginal Australians retained a hunter-gatherer society, exploiting the varied plant and animal resources available to them. The peoples of New Guinea began to develop an extensive maritime culture where they sailed across the ocean with large outrigger canoes. They cultivated taro and yams and used chickens and pigs as food animals.
Europe
Greece, Etruria, and Rome
Minoan civilisation emerged around 3000 BC on the island of Crete, where towns emerged on the coast. Trade was important in Minoan civilisation, with artifacts from the Minoans discovered in Egypt, Syria, Cyprus, and Greece. Large palaces grew up on Crete, decorated with painted frescoes. A Minoan writing system is known - Linear A, but it remains mostly undeciphered. An eruption of a volcano on the island of Thera around 1500 BC may have contributed to the decline of Minoan civilisation, with many of the Cretan cities being destroyed around 1450 BC by Mycenaean from mainland Greece. Unlike Linear A, the Mycenaean writing system -Linear B
Linear B was a syllabic script used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest attested form of Greek. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries. The oldest Mycenaean writing dates to about 1400 BC. It is descended from ...
- has been deciphered. Mycenaean culture flourished until around 1200 BC, when it too declined and many of its centres were destroyed.
The Archaic Period in Greece is generally considered to have lasted from around the 8th century BC to the invasion by Xerxes in 480 BC. This period saw the expansion of the Greek world around the Mediterranean, with the founding of Greek city-states as far afield as Sicily in the west and the Black Sea in the east. Politically, the Archaic period in Greece saw the collapse of the power of the old aristocracies, with democratic reforms in Athens and the development of Sparta's unique constitution. The end of the Archaic period also saw the rise of Athens, which would come to be a dominant power in the Classical Period, after the reforms of Solon and the tyranny of Pisistratus
Pisistratus or Peisistratus ( grc-gre, Πεισίστρατος ; 600 – 527 BC) was a politician in ancient Athens, ruling as tyrant in the late 560s, the early 550s and from 546 BC until his death. His unification of Attica, the triangular ...
.
 The Classical Greek world was dominated throughout the 5th century BC by the major powers of Athens and Sparta. Through the
The Classical Greek world was dominated throughout the 5th century BC by the major powers of Athens and Sparta. Through the Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pl ...
, Athens was able to convert pan-hellenist sentiment and fear of the Persian threat into a powerful empire, and this, along with the conflict between Sparta and Athens culminating in the